NMR Reveals the Conformational Changes of Cytochrome C upon Interaction with Cardiolipin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. NMR Experiments
2.3. CD, Fluorescence, and –Visible Absorption Spectra Experiments
3. Results
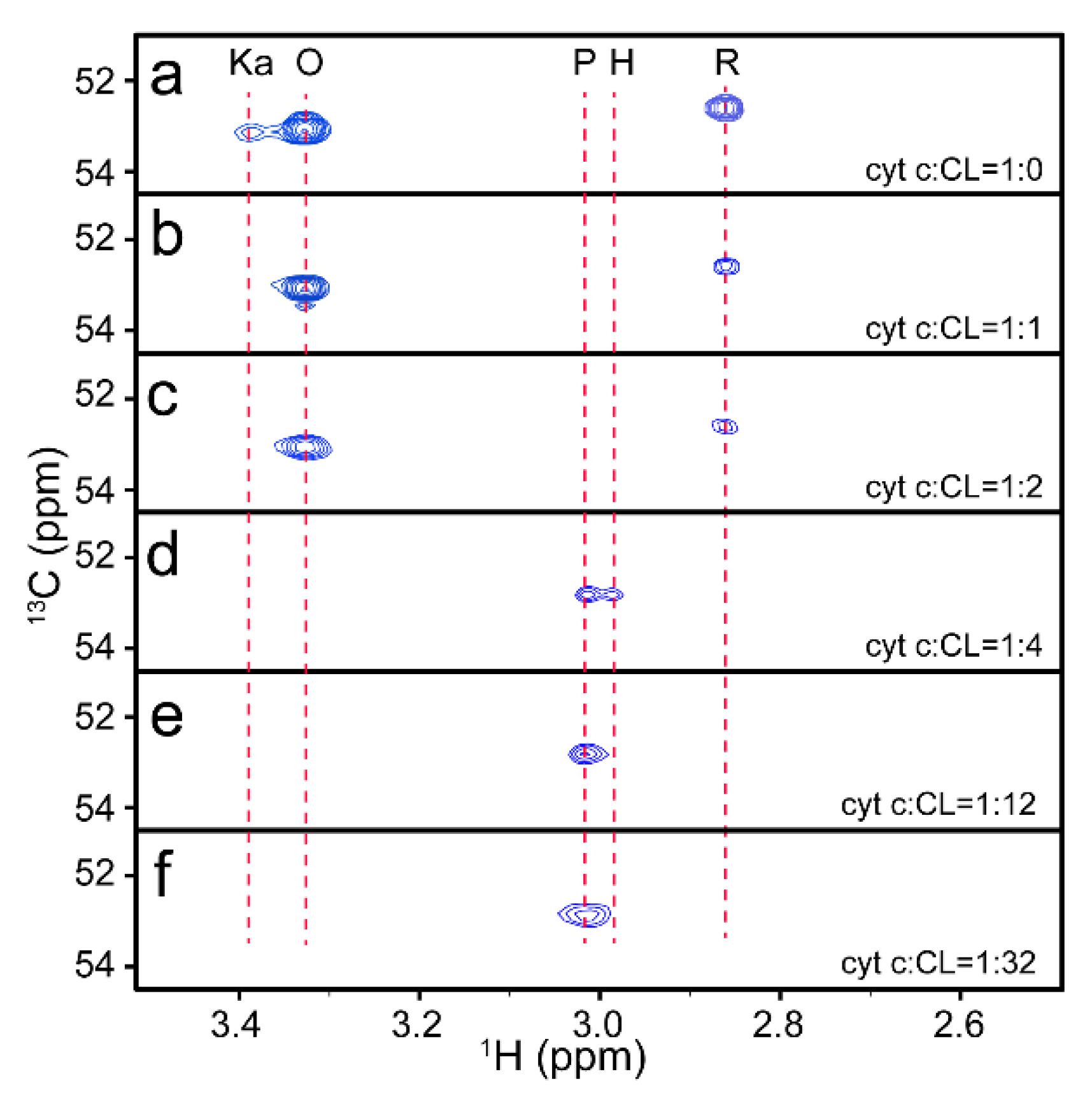
3.1. Identification of Different Conformations of Cyt C at a Natural Isotopic Abundance
3.2. Trace of Conformational Changes of Cyt C upon Interaction with CL
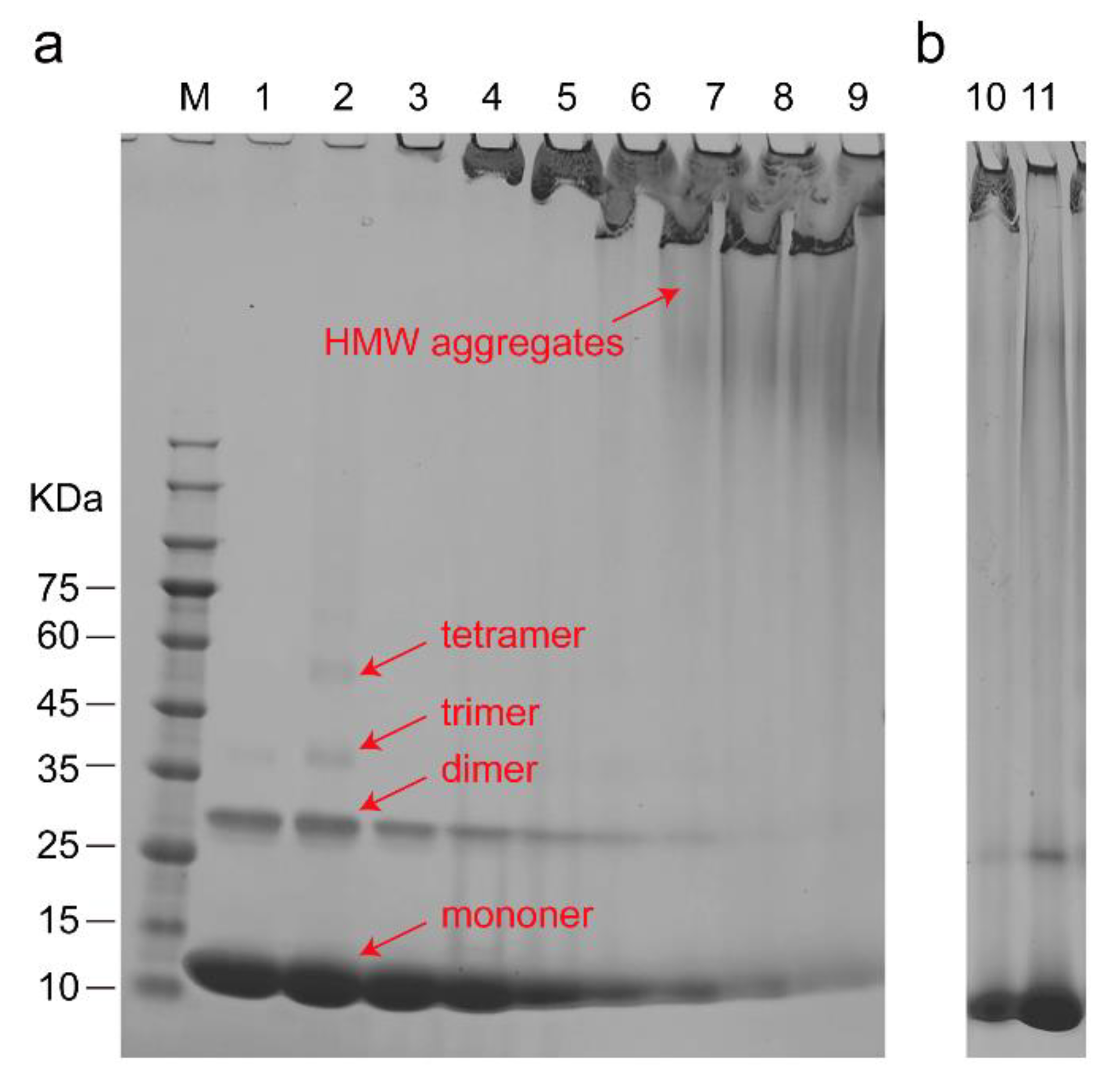
3.3. The Structure of Cyt C Becomes Expanded upon Interaction with CL
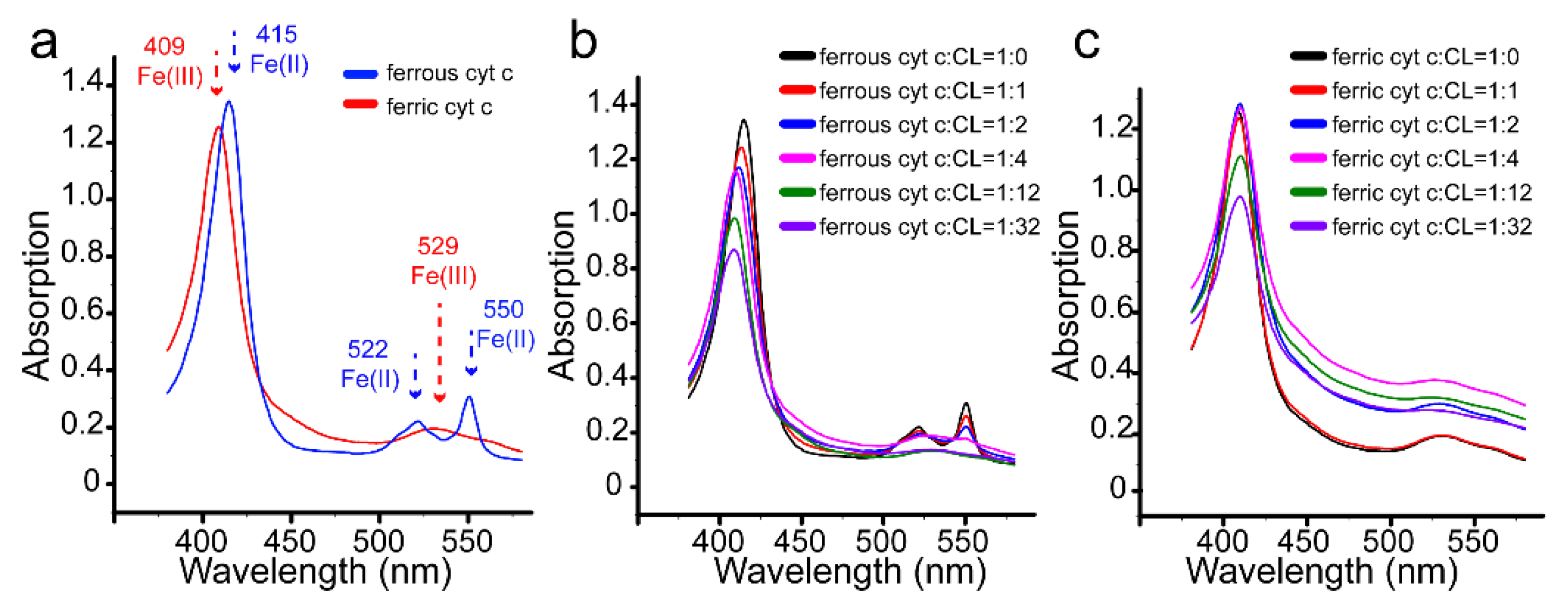
3.4. Redox Conversion of Cyt C
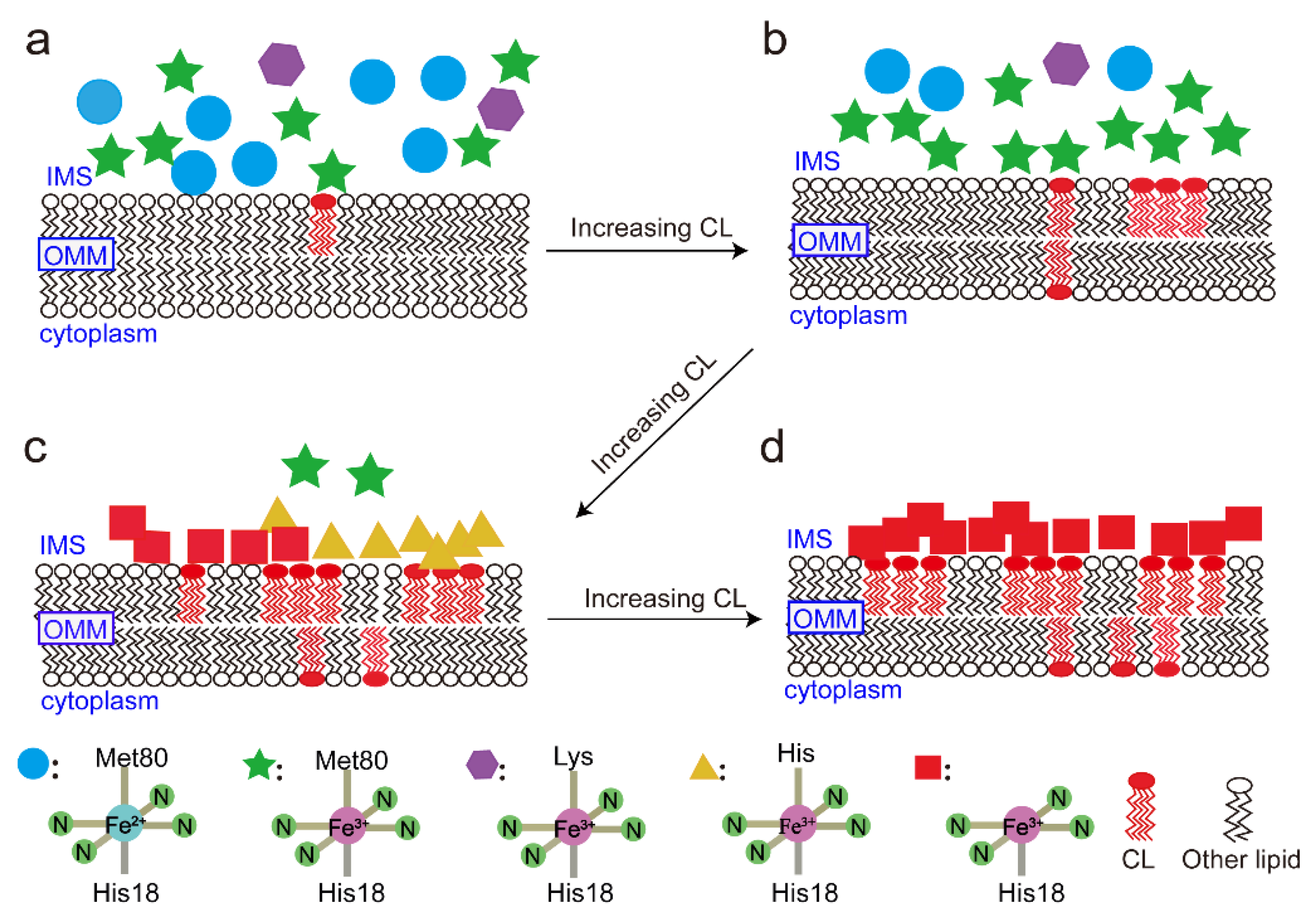
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ow, Y.P.; Green, D.R.; Hao, Z.; Mak, T.W. Cytochrome c: Functions beyond respiration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrenius, S.; Zhivotovsky, B. Cardiolipin oxidation sets cytochrome c free. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, V.E.; Bayir, H.A.; Belikova, N.A.; Kapralov, O.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.A.; Jiang, J.; Stoyanovsky, D.A.; Wipf, P.; Kochanek, P.M.; et al. Cytochrome c/cardiolipin relations in mitochondria: A kiss of death. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 1439–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pointer, C.B.; Klegeris, A. Cardiolipin in Central Nervous System Physiology and Pathology. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.; McElhaney, R.N. The physicochemical properties of cardiolipin bilayers and cardiolipin–containing lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta–Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinibaldi, F.; Howes, B.D.; Droghetti, E.; Polticelli, F.; Piro, M.C.; Di Pierro, D.; Fiorucci, L.; Coletta, M.; Smulevich, G.; Santucci, R. Role of Lysines in Cytochrome c–Cardiolipin Interaction. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 4578–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinibaldi, F.; Milazzo, L.; Howes, B.D.; Piro, M.C.; Fiorucci, L.; Polticelli, F.; Ascenzi, P.; Coletta, M.; Smulevich, G.; Santucci, R. The key role played by charge in the interaction of cytochrome c with cardiolipin. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 22, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kostrzewa, A.; Pali, T.; Froncisz, W.; Marsh, D. Membrane location of spin–labeled cytochrome c determined by paramagnetic relaxation agents. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 6066–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytomaa, M.; Kinnunen, P.K.J. Evidence for 2 distinct acidic phospholipid–binding sites in Cytochrome–c. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, C.; Prado, F.M.; Nunes, G.L.C.; Di Mascio, P.; Carmona–Ribeiro, A.M.; Nantes, I.L. pH–dependent interaction of cytochrome c with mitochondrial mimetic membranes—The role of an array of positively charged amino acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 34709–34717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, E.S.; Nucci, N.V.; Fuglestad, B.; Tommos, C.; Wand, A.J. Defining the Apoptotic Trigger: The interaction of cytochrome c and cardiolipin. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 30879–30887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muenzner, J.; Toffey, J.R.; Hong, Y.N.; Pletneva, E.V. Becoming a Peroxidase: Cardiolipin–Induced Unfolding of Cytochrome c. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 12878–12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basova, L.V.; Kurnikov, I.V.; Wang, L.; Ritov, V.B.; Belikova, N.A.; Vlasova, I.I.; Pacheco, A.A.; Winnica, D.E.; Peterson, J.; Bayir, H.; et al. Cardiolipin switch in mitochondria: Shutting off the reduction of cytochrome c and turning on the peroxidase activity. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 3423–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, W.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Yang, Z.Z.; Ying, T.L.; Zhang, X.; Tan, X.S.; Liu, M.L.; Cao, C.Y.; Huang, Z.X. Structural Basis for Cytochrome c Y67H Mutant to Function as a Peroxidase. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szynakowicz, L.; Lento, C.; Wilson, D.J. Impact of Cardiolipin and Phosphatidylcholine Interactions on the Conformational Ensemble of Cytochrome c. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 3617–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capdevila, D.A.; Rouco, S.O.; Tomasina, F.; Tortora, V.; Demicheli, V.; Radi, R.; Murgida, D.H. Active Site Structure and Peroxidase Activity of Oxidatively Modified Cytochrome c Species in Complexes with Cardiolipin. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 7491–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, J.M.; Silkstone, G.; Wilson, M.T.; Cheesman, M.R.; Butt, J.N. Probing a Complex of Cytochrome c and Cardiolipin by Magnetic Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy: Implications for the Initial Events in Apoptosis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19676–19679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milazzo, L.; Tognaccini, L.; Howes, B.D.; Sinibaldi, F.; Piro, M.C.; Fittipaldi, M.; Baratto, M.C.; Pogni, R.; Santucci, R.; Smulevich, G. Unravelling the Non–Native Low–Spin State of the Cytochrome c–Cardiolipin Complex: Evidence of the Formation of a His–Ligated Species Only. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandiscia, L.A.; Schweitzer–Stenner, R. Coexistence of Native–Like and Non–Native Cytochrome c on Anionic Liposomes with Different Cardiolipin Content. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 12846–12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenzner, J.; Pletneva, E.V. Structural transformations of cytochrome c upon interaction with cardiolipin. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2014, 179, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, H.; Nagao, S.; Hirota, S. Characterization of the Cytochrom c Membrane–Binding Site Using Cardiolipin–Containing Bicelles with NMR. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 128, 14225–14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadyani, D.; Yanamala, N.; Samhan–Arias, A.K.; Kapralov, A.A.; Stepanov, G.; Nuar, N.; Planas–Iglesias, J.; Sanghera, N.; Kagan, V.E.; Klein–Seetharaman, J. Structural characterization of cardiolipin–driven activation of cytochrome c into a peroxidase and membrane perturbation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta–Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Muenzner, J.; Grimm, S.K.; Pletneva, E.V. Origin of the Conformational Heterogeneity of Cardiolipin–bound Cytochrome c. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, S.S.; Sil, P.; Haldar, S.; Mitra, S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Subtle Change in the Charge Distribution of Surface Residues May Affect the Secondary Functions of Cytochrome c. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14476–14490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClelland, L.J.; Mou, T.-C.; Jeakins–Cooley, M.E.; Sprang, S.R.; Bowler, B.E. Structure of a mitochondrial cytochrome c conformer competent for peroxidase activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6648–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherney, M.M.; Junior, C.C.; Bowler, B.E. Mutation of Trimethyllysine 72 to Alanine Enhances His79–Heme–Mediated Dynamics of Iso–1–cytochrome c. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, T.; Buettner, S.; Kroemer, G.; Madeo, F. The mitochondrial pathway in yeast apoptosis. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeo, F.; Herker, E.; Wissing, S.; Jungwirth, H.; Eisenberg, T.; Frohlich, K.U. Apoptosis in yeast. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannattasio, S.; Atlante, A.; Antonacci, L.; Guaragnella, N.; Lattanzio, P.; Passarella, S.; Marra, E. Cytochrome c is released from coupled mitochondria of yeast en route to acetic acid–induced programmed cell death and can work as an electron donor and a ROS scavenger. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madeo, F.; Frohlich, E.; Ligr, M.; Grey, M.; Sigrist, S.J.; Wolf, D.H.; Frohlich, K.U. Oxygen stress: A regulator of apoptosis in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 145, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonis, P.; Kersulis, S.; Stankevich, V.; Kaseta, V.; Lastauskiene, E.; Stirke, A. Caspase dependent apoptosis induced in yeast cells by nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Bioelectrochemistry 2017, 115, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluck, R.M.; Ellerby, L.M.; Ellerby, H.M.; Naiem, S.; Yaffe, M.P.; Margoliash, E.; Bredesen, D.; Mauk, A.G.; Sherman, F.; Newmeyer, D.D. Determinants of cytochrome c pro–apoptotic activity—The role of lysine 72 trimethylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 16127–16133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerfah, R.; Plevin, M.J.; Sounier, R.; Gans, P.; Boisbouvier, J. Methyl–specific isotopic labeling: A molecular tool box for solution NMR studies of large proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 32, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, A.; Saso, A.; Zhao, Q.; Kubo, S.; Nishida, N.; Shimada, I. Balanced Regulation of Redox Status of Intracellular Thioredoxin Revealed by in–Cell NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3784–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zach, S.; Wesley, S.; Lorenzo, C.; Nomura, A.M.; Nobuhisa, S.; Craik, C.S.; Paul, O.D.M.; Volker, D.T. Methyl groups as probes for proteins and complexes in in–cell NMR experiments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7119–7125. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Wang, Q.W.; Yuan, B.; Zhu, Q.J.; Jiang, B.; Li, C.G.; Lan, W.X.; Cao, C.Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.L. Monitoring alkaline transitions of yeast iso–1 cytochrome c at natural isotopic abundance using trimethyllysine as a native NMR probe. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 12630–12633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Farrant, R.D.; Sweatman, B.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Observation of Separate J–Resolved H–1–NMR Spectra from CH, CH2, AND CH3 Groups Using a Maximum–Quantum Filter. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. A 1995, 113, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Sanderson, P.N.; Tranter, G.E. Comparison of maximum quantum filtered NMR spectroscopy (MAXY NMR) and other two–dimensional NMR approaches for resonance assignment of peptides. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1996, 34, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Mao, X.A.; Ye, C.H.; Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Three–dimensional maximum–quantum correlation HMQC NMR spectroscopy (3D MAXY–HMQC). J. Magn. Reson. 1997, 129, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.; Hassan, M.I.; Islam, A.; Ahmad, F. The role of key residues in structure, function, and stability of cytochrome–c. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, K.H.; Moody, P.C.E.; Brown, K.A.; Raven, E.L. Crystal structure of the ascorbate peroxidase–salicylhydroxamic acid complex. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 8644–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, W.B.R.; Rosell, F.I.; Twitchett, M.B.; Dumont, M.E.; Mauk, A.G. Bacterial expression of a mitochondrial cytochrome c. Trimethylation of Lys72 in yeast iso–1–cytochrome c and the alkaline conformational transition. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 6124–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milorey, B.; Malyshka, D.; Schweitzer–Stenner, R. pH Dependence of Ferricytochrome c Conformational Transitions during Binding to Cardiolipin Membranes: Evidence for Histidine as the Distal Ligand at Neutral pH. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Jiang, M.W.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H.J.; Cheng, W.N.; Li, J.B.; Cai, L.J.; Han, X.X.; Zhao, B. Redox–State–Mediated Regulation of Cytochrome c Release in Apoptosis Revealed by Surface–Enhanced Raman Scattering on Nickel Substrates. Angew. Chem. –Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16499–16503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baistrocchi, P.; Banci, L.; Bertini, I.; Turano, P.; Bren, K.L.; Gray, H.B. Three–dimensional solution structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae reduced iso–1–cytochrome c. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 13788–13796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.J.; Bowler, B.E. pH dependence of formation of a partially unfolded state of a lys 73 → his variant of iso–1–cytochrome c: Implications for the alkaline conformational transition of cytochrome c. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 13584–13594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, F.I.; Ferrer, J.C.; Mauk, A.G. Proton–linked protein conformational switching: Definition of the alkaline conformational transition of yeast iso–1–ferricytochrome c. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 11234–11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Shin, D.-W.; Pletneva, E.V. Remote Perturbations in Tertiary Contacts Trigger Ligation of Lysine to the Heme Iron in Cytochrome c. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 2950–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, V.; Shaw, G.S.; Konermann, L. Cytochrome c as a Peroxidase: Activation of the Precatalytic Native State by H2O2–Induced Covalent Modifications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15701–15709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraheni, A.D.; Ren, C.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nagao, S.; Yamanaka, M.; Hirota, S. Oxidative modification of methionine80 in cytochrome c by reaction with peroxides. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 182, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, V.; Mian, S.H.; Konermann, L. Lysine carbonylation is a previously unrecognized contributor to peroxidase activation of cytochrome c by chloramine–T. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 2349–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colon, W.; Wakem, L.P.; Sherman, F.; Roder, H. Identification of the predominant non–native histidine ligand in unfolded cytochrome c. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 12535–12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milorey, B.; Schweitzer–Stenner, R.; Kurbaj, R.; Malyshka, D. pH–Induced Switch between Different Modes of Cytochrome c Binding to Cardiolipin–Containing Liposomes. Acs Omega 2019, 4, 1386–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancalana, M.; Koide, S. Molecular mechanism of Thioflavin–T binding to amyloid fibrils. Biochim. Biophys. Acta–Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinto, I.F.D.; Chaves–Filho, A.D.B.; Cunha, D.D.; Miyamoto, S. Cytochrome c modification and oligomerization induced by cardiolipin hydroperoxides in a membrane mimetic model. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 693, 108568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, S.; Hattori, Y.; Nagao, S.; Taketa, M.; Komori, H.; Kamikubo, H.; Wang, Z.H.; Takahashi, I.; Negi, S.; Sugiura, Y.; et al. Cytochrome c polymerization by successive domain swapping at the C–terminal helix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12854–12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.H.; Matsuo, T.; Nagao, S.; Hirota, S. Peroxidase activity enhancement of horse cytochrome c by dimerization. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4766–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macchioni, L.; Corazzi, T.; Davidescu, M.; Francescangeli, E.; Roberti, R.; Corazzi, L. Cytochrome c redox state influences the binding and release of cytochrome c in model membranes and in brain mitochondria. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 341, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-q.; Li, X.; Wang, M.-q.; Qian, J.; Zheng, K.; Bian, H.-w.; Han, N.; Wang, J.-h.; Pan, J.-w.; Zhu, M.-y. Protective effects of ETC complex III and cytochrome c against hydrogen peroxide–induced apoptosis in yeast. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, J.; Zhang, G.; Chai, X.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, P.; Jiang, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M. NMR Reveals the Conformational Changes of Cytochrome C upon Interaction with Cardiolipin. Life 2021, 11, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11101031
Zhan J, Zhang G, Chai X, Zhu Q, Sun P, Jiang B, Zhou X, Zhang X, Liu M. NMR Reveals the Conformational Changes of Cytochrome C upon Interaction with Cardiolipin. Life. 2021; 11(10):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11101031
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Jianhua, Guangqing Zhang, Xin Chai, Qinjun Zhu, Peng Sun, Bin Jiang, Xin Zhou, Xu Zhang, and Maili Liu. 2021. "NMR Reveals the Conformational Changes of Cytochrome C upon Interaction with Cardiolipin" Life 11, no. 10: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11101031
APA StyleZhan, J., Zhang, G., Chai, X., Zhu, Q., Sun, P., Jiang, B., Zhou, X., Zhang, X., & Liu, M. (2021). NMR Reveals the Conformational Changes of Cytochrome C upon Interaction with Cardiolipin. Life, 11(10), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11101031





