Giant Vesicles Produced with Phosphatidylcholines (PCs) and Phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) by Water-in-Oil Inverted Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lipids, Calcein, Organic Solvents, and Other Reagents
2.2. Solubilized Lipids, Inner and Bottom Aqueous Solutions Preparation
2.3. Preparation of Calcein-Stained Vesicles by the Inverted Emulsion Method
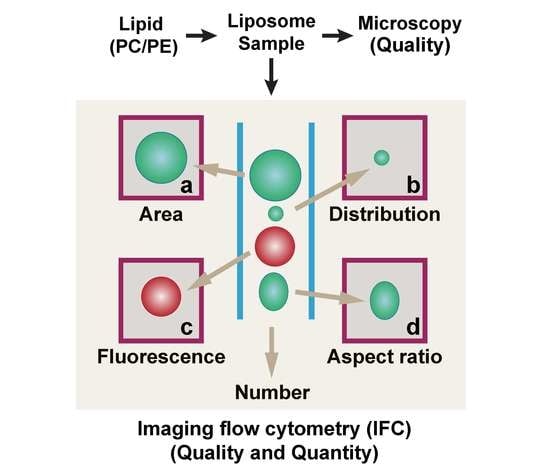
2.4. GV Analysis by Imaging Flow Cytometry (IFC)
2.5. Confocal Microscopy Observation
2.6. Stability Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Using IFC to Analyze GVs Produced by the w/o Emulsion Transfer Method
3.2. Comparing GVs Prepared with Different PC, PE, and PC:DLPE Mixture
3.3. Size Distribution-Based Stability Analysis of GVs via IFC
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luisi, P.L.; Walde, P. Giant Vesicles; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Morigaki, K.; Tanimoto, Y. Evolution and development of model membranes for physicochemical and functional studies of the membrane lateral heterogeneity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 2012–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rideau, E.; Dimova, R.; Schwille, P.; Wurm, F.R.; Landfester, K. Liposomes and polymersomes: A comparative review towards cell mimicking. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8572–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siontorou, C.G.; Nikoleli, G.P.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Karapetis, S.K. Artificial lipid membranes: Past, present, and future. Membranes 2017, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stano, P. Is research on “synthetic cells” moving to the next level? Life 2018, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walde, P.; Cosentino, K.; Engel, H.; Stano, P. Giant vesicles: Preparations and applications. ChemBioChem 2010, 11, 848–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnard, P.A.; Deamer, D.W. Membrane self-assembly processes: Steps toward the first cellular life. Anat. Rec. 2002, 268, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuma, Y.; Imai, M. From vesicles to protocells: The roles of amphiphilic molecules. Life 2015, 5, 651–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostak, J.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Luisi, P.L. Synthesizing life. Nature 2001, 409, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, J.P.; Dowben, R.M. Formation and properties of thin-walled phospholipid vesicles. J. Cell Physiol. 1969, 73, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, A.; Tsai, F.C.; Koenderink, G.H.; Schmidt, T.F.; Itri, R.; Meier, W.; Schmatko, T.; Schroder, A.; Marques, C. Gel-assisted formation of giant unilamellar vesicles. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kresse, K.M.; Xu, M.; Pazzi, J.; Garcia-Ojeda, M.; Subramaniam, A.B. Novel application of cellulose paper as a platform for the macromolecular self-assembly of biomimetic giant liposomes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32102–32107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, M.I.; Dimitrov, D.S. Liposome electroformation. Faraday Discuss. Chem. Soc. 1986, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, M.I.; Soléau, S.; Méléard, P.; Faucon, F.; Bothorel, P. Preparation of giant vesicles by external AC electric fields. Kinetics and applications. In In Trends in Colloid and Interface Science VI; Helm, C., Lösche, M., Möhwald, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1992; pp. 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita-Ishiodori, Y.; Hanczyc, M.M.; Wang, A.; Szostak, J.W.; Yomo, T. Using imaging flow cytometry to quantify and optimize giant vesicle production by water-in-oil emulsion transfer methods. Langmuir 2019, 35, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moga, A.; Yandrapalli, N.; Dimova, R.; Robinson, T. Optimization of the inverted emulsion method for high-yield production of biomimetic giant unilamellar vesicles. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 2674–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pautot, S.; Frisken, B.J.; Weitz, D.A. Production of unilamellar vesicles using an inverted emulsion. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2870–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.; Dekker, C. On-chip microfluidic production of cell-sized liposomes. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 856–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamdad, K.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M.; Brooks, N.J.; Ces, O. Preparation and mechanical characterisation of giant unilamellar vesicles by a microfluidic method. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trantidou, T.; Friddin, M.S.; Salehi-Reyhani, A.; Ces, O.; Elani, Y. Droplet microfluidics for the construction of compartmentalised model membranes. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2488–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Swaay, D.; deMello, A. Microfluidic methods for forming liposomes. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, N.N.; Yelleswarapu, M.; Huck, W.T. Monodisperse uni- and multicompartment liposomes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7584–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, K.; Suzuki, H.; Toyota, T.; Yomo, T. Size control of giant unilamellar vesicles prepared from inverted emulsion droplets. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 376, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.; Kuhn, P.; Eyer, K.; Dittrich, P.S. Microfluidic trapping of giant unilamellar vesicles to study transport through a membrane pore. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 44105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szoka, F., Jr.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Comparative properties and methods of preparation of lipid vesicles (liposomes). Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 1980, 9, 467–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richens, J.L.; Lane, J.S.; Mather, M.L.; O’Shea, P. The interactions of squalene, alkanes and other mineral oils with model membranes; effects on membrane heterogeneity and function. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 457, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamdad, K.; Hindley, J.W.; Bolognesi, G.; Friddin, M.S.; Law, R.V.; Brooks, N.J.; Ces, O.; Elani, Y. Engineering thermoresponsive phase separated vesicles formed via emulsion phase transfer as a content-release platform. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 4851–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsumoto, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Tabata, J.; Tomita, M. A reverse-phase method revisited: Rapid high-yield preparation of giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) using emulsification followed by centrifugation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 546, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, P.F. Static and dynamic lipid asymmetry in cell membranes. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Agellon, L.B.; Allen, T.M.; Umeda, M.; Jewell, L.; Mason, A.; Vance, D.E. The ratio of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine influences membrane integrity and steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akashi, K.; Miyata, H.; Itoh, H.; Kinosita, J.K. Preparation of giant liposomes in physiological conditions and their characterization under an optical microscope. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 3242–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, N.; Pincet, F.; Cribier, S. Giant vesicles formed by gentle hydration and electroformation: A comparison by fluorescence microscopy. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2005, 42, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quemeneur, F.; Rammal, A.; Rinaudo, M.; Pépin-Donat, B. Large and giant vesicles “decorated” with chitosan: Effects of pH, salt or glucose stress, and surface adhesion. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2512–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagatolli, L.A.; Gratton, E. Two-photon fluorescence microscopy observation of shape changes at the phase transition in phospholipid giant unilamellar vesicles. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estes, D.J.; Mayer, M. Giant liposomes in physiological buffer using electroformation in a flow chamber. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2005, 1712, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, A.; Berre, M.L.; Yoshikawa, K.; Baigl, D. Spontaneous generation of giant liposomes from an oil/water interface. ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, A.; Yamanaka, T.; Hamada, T.; Hase, M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Baigl, D. Spontaneous transfer of phospholipid-coated oil-in-oil and water-in-oil micro-droplets through an oil/water interface. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9824–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hupfeld, S.; Holsæter, A.M.; Skar, M.; Frantzen, C.B.; Brandl, M. Liposome size analysis by dynamic/static light scattering upon size exclusion-/field flow-fractionation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2006, 6, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominical, V.; Samsel, L.; Mccoy, J.P. Masks in imaging flow cytometry. Methods 2017, 112, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, A.C.; Lo, Y.H. Review: Imaging technologies for flow cytometry. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 4639–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowhan, W.; Bogdanov, M.; Mileykovskaya, E. Functional roles of lipids in membranes. In Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes, 5th ed.; Vance, D.E., Vance, J.E., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Noireaux, V.; Maeda, Y.T.; Libchaber, A. Development of an artificial cell, from self-organization to computation and self-reproduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3473–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsumotoa, K.; Matsuob, H.; Tomitaa, M.; Yoshimurab, T. Efficient formation of giant liposomes through the gentle hydration of phosphatidylcholine films doped with sugar. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 68, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horger, K.S.; Estes, D.J.; Capone, R.; Mayer, M. Films of agarose enable rapid formation of giant liposomes in solutions of physiologic ionic strength. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimanouchi, T.; Umakoshi, H.; Kuboi, R. Kinetic study on giant vesicle formation with electroformation method. Langmuir 2009, 25, 4835–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.C.; Hettiarachchi, K.; Siu, M.; Pan, Y.R.; Lee, A.P. Controlled microfluidic encapsulation of cells, proteins, and microbeads in lipid vesicles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5656–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.; Oka, M.; Tanaka, T.; Yamazaki, M. A new method for the preparation of giant liposomes in high salt concentrations and growth of protein microcrystals in them. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1561, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chernomordik, L.V.; Kozlov, M.M. Mechanics of membrane fusion. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Lipids | CAS No. | Formula | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| DHPC (1,2-diheptanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | 39036-04-9 | C22H44NO8P |  |
| DLPC (1,2-dilauroyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | 18194-25-7 | C32H64NO8P |  |
| DMPC (1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) | 18194-24-6 | C36H72NO8P |  |
| DPPC (1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) | 63-89-8 | C40H80NO8P |  |
| DPHPC (1,2-diphytanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) | 207131-40-6 | C48H96NO8P |  |
| DSPC(1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) | 816-94-4 | C44H88NO8P |  |
| DOPC (1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) | 4235-95-4 | C44H84NO8P |  |
| POPC (1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) | 26853-31-6 | C42H82NO8P |  |
| DLPE (1,2-dilauroyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine) | 59752-57-7 | C29H58NO8P |  |
| DMPE (1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine) | 998-07-2 | C33H66NO8P |  |
| DPPE (1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-ethanolamine | 923-61-5 | C37H74NO8P |  |
| DSPE (1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine) | 1069-79-0 | C41H82NO8P |  |
| DOPE (1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine) | 4004-05-1 | C41H78NO8P |  |
| POPE (1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine) | 26662-94-2 | C39H76NO8P |  |
| Lipids | Oil | Sonication Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| DHPC | hMO 1 | sonication on ice, equilibration on ice |
| DLPC | hMO | sonication on ice, equilibration on ice |
| DMPC | MO 2 | sonication at RT, equilibration at RT |
| DPPC | hMO | sonication on ice, equilibration at RT |
| DPHPC | hMO | sonication on ice, equilibration on ice |
| DSPC | MO | sonication at RT, equilibration at RT |
| DOPC | hMO | sonication on ice, equilibration at RT |
| POPC | MO | sonication on ice, equilibration on ice |
| DLPE | MO | sonication on ice, equilibration at RT |
| DMPE | hMO | sonication on ice, equilibration at RT |
| DPPE | hMO | sonication on ice, equilibration at RT |
| DSPE | MO | sonication on ice, equilibration at RT |
| DOPE | hMO | sonication on ice, equilibration on ice |
| POPE | hMO | sonication on ice, equilibration at RT |
| POPC: DLPE | MO | sonication on ice, equilibration on ice |
| DOPC: DLPE | hMO | sonication on ice, equilibration at RT |
| DMPC: DLPE | MO | sonication at RT, equilibration at RT |
| GVs | Purity (%) | Concentration (Objects/mL) | Mean Diameter (µm) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POPC | 92.45 ± 0.30 | 5.14 ± 0.22 ×109 | 4.08 ± 0.15 | 91.07 ± 0.15 |
| DOPC | 96.85 ± 0.13 | 6.54 ± 0.17 ×109 | 4.09 ± 0.05 | 94.12 ± 0.30 |
| DMPC | 93.33 ± 0.21 | 2.94 ± 0.13 ×109 | 4.69 ± 0.06 | 89.24 ± 0.35 |
| DLPE | 97.01 ± 0.71 | 7.02 ± 0.90 ×109 | 3.66 ± 0.29 | 91.61 ± 0.35 |
| POPC: DLPE_6:4 | 97.64 ± 0.09 | 6.68 ± 0.78 ×109 | 3.75 ± 0.06 | 93.07 ± 0.04 |
| DOPC: DLPE_7:3 | 93.10 ± 0.32 | 6.94 ± 0.60 ×109 | 3.76 ± 0.10 | 94.21 ± 0.37 |
| DMPC: DLPE_6:4 | 91.61 ± 0.32 | 5.68 ± 0.14 ×109 | 3.44 ± 0.02 | 96.03 ± 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, B.; Ding, J.; Xu, J.; Yomo, T. Giant Vesicles Produced with Phosphatidylcholines (PCs) and Phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) by Water-in-Oil Inverted Emulsions. Life 2021, 11, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030223
Xu B, Ding J, Xu J, Yomo T. Giant Vesicles Produced with Phosphatidylcholines (PCs) and Phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) by Water-in-Oil Inverted Emulsions. Life. 2021; 11(3):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030223
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Boying, Jinquan Ding, Jian Xu, and Tetsuya Yomo. 2021. "Giant Vesicles Produced with Phosphatidylcholines (PCs) and Phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) by Water-in-Oil Inverted Emulsions" Life 11, no. 3: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030223
APA StyleXu, B., Ding, J., Xu, J., & Yomo, T. (2021). Giant Vesicles Produced with Phosphatidylcholines (PCs) and Phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) by Water-in-Oil Inverted Emulsions. Life, 11(3), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030223