The Role of Tumor-Derived Exosomes in the Abscopal Effect and Immunotherapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Tumor-Derived Exosomes (TEXs)
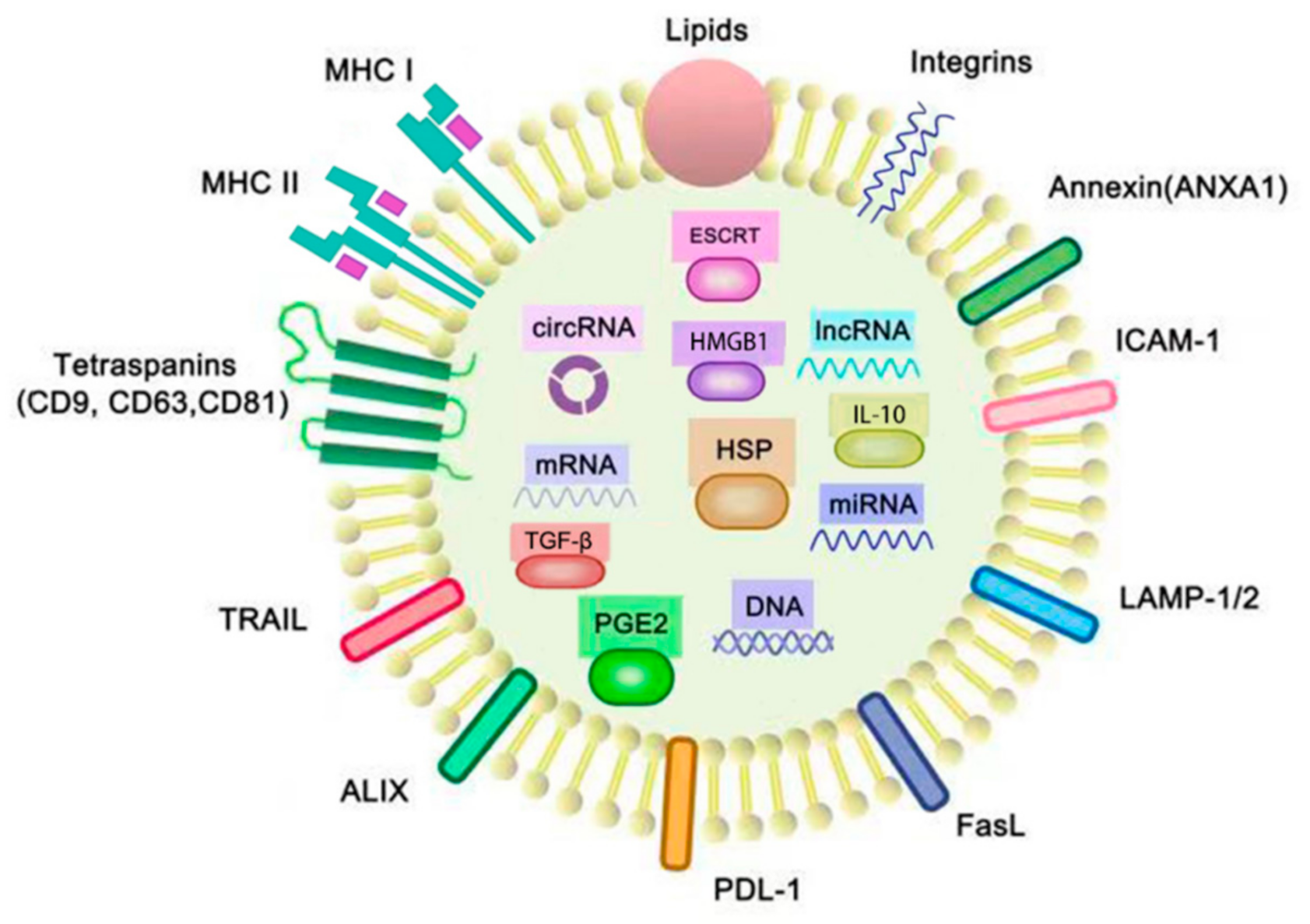
2.1. Exosomes
2.2. Tumor-Derived Exosomes (TEXs)
2.3. Isolation of TEXs from Cancer Patients
3. TEX-Containing Genetic Materials That Are Associated with Cancer Progression and Prognosis
3.1. microRNA (miRNA)
3.2. Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA)
3.3. Circular RNA (circRNA)
3.4. DNA
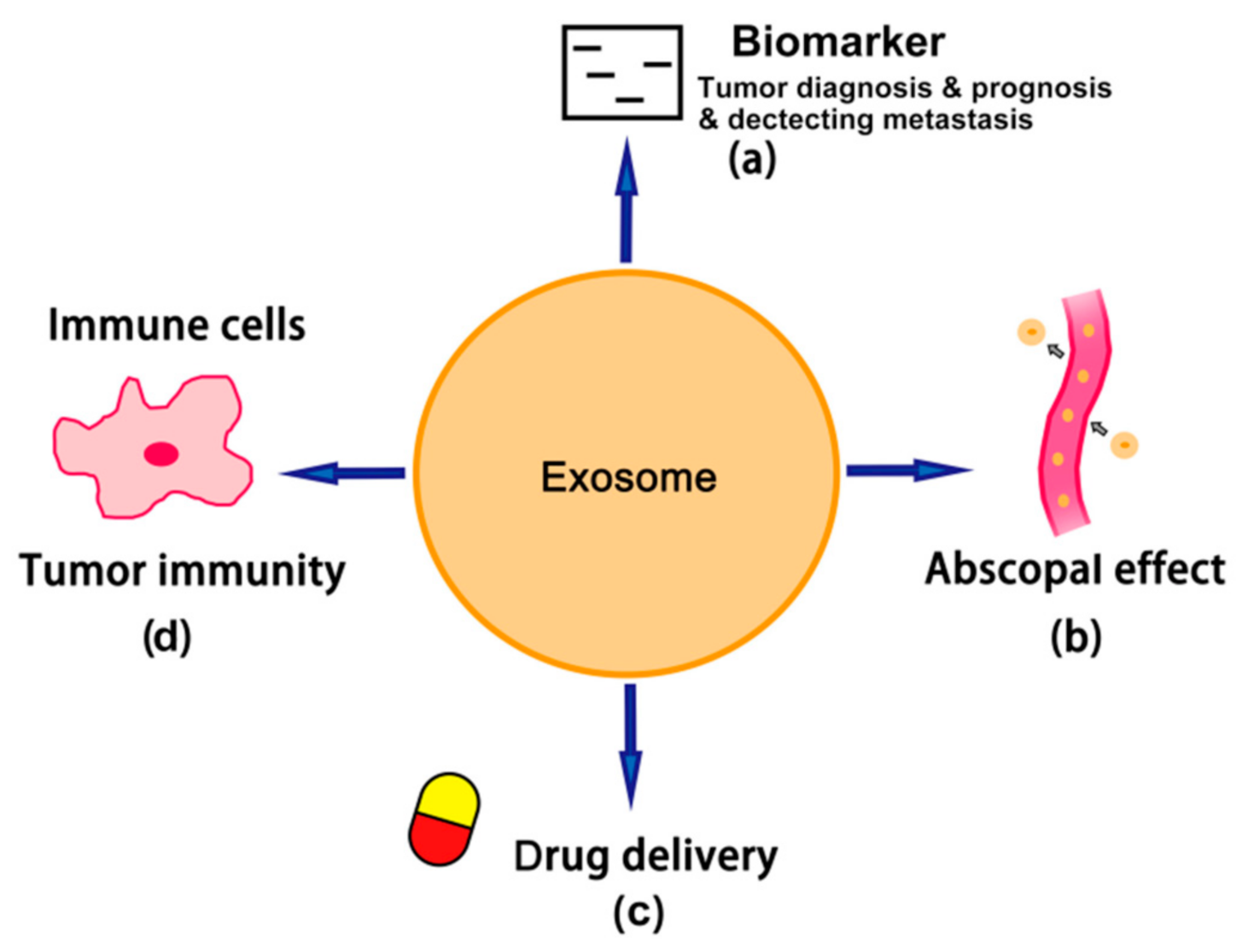
4. TEX-Mediated Abscopal Effect and Immunomodulation
4.1. TEX-Mediated Immunostimulatory Activities
4.2. TEX-Mediated Abscopal Effect and Immunomodulation
5. Tumor-Derived Exosomes as Biomarkers
| Biomarkers | Sources | Tumor Type | Significance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NY-ESO-1, PLAP | EV microarray | NSCLC | Strong association with survival | [86,87] |
| CD91, CD317 | Multivariate extracellular vesicle array | NSCLC | Diagnosis | [87] |
| EGFR | EV microarray, Western blotting and ELISA | NSCLC, prostate cancer, gastric cancer | Diagnosis and potential indicator of tumor progression | [87,94,95] |
| LRG1 | Proteomic mass spectrometry | NSCLC | Diagnosis | [88] |
| CD171, CD151, tetra-spanin 8 | EV microarray | NSCLC | Potential biomarkers for diagnosis | [86,87] |
| ECM1, alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein | Western blotting | NSCLC | Diagnosis | [89] |
| GPC-1 | Ultracentrifugation | Pancreatic cancer | Early diagnosis | [90] |
| Migration inhibitory factor | Ultracentrifugation | Pancreatic cancer | Migration potential monitoring and prognosis | [91] |
| Vimentin | Ultracentrifugation | Pancreatic cancer | Diagnosis and prognosis | [92] |
| PCA3, TMPRSS2: ERG | PCR analysis | Prostate cancer | Diagnosis | [93] |
| TRIM3 | RT-PCR | Gastric cancer | Potential diagnosis biomarker | [96] |
| HGS | Proteomics analysis | Colorectal cancer | Poor prognosis | [97] |
| CD147 | Western blotting, RT-PCR | Colorectal cancer | Diagnosis and poor prognosis | [98,99] |
6. Role of Tumor-Derived Exosomes in Cancer Therapy
6.1. TEX-Targeted Cancer Therapy
6.2. TEX-Based Drug Delivery for Cancer Chemotherapy
6.3. TEX-Based Cancer Vaccine and Immunotherapy
7. Conclusions
TEXs—A Double-Edged Sword
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wani, S.Q.; Dar, I.A.; Khan, T.; Lone, M.M.; Afroz, F. Radiation Therapy and its Effects Beyond the Primary Target: An Abscopal Effect. Cureus 2019, 11, e4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suek, N.; Campesato, L.F.; Merghoub, T.; Khalil, D.N. Targeted APC Activation in Cancer Immunotherapy to Enhance the Abscopal Effect. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grass, G.D.; Krishna, N.; Kim, S. The immune mechanisms of abscopal effect in radiation therapy. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2016, 40, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.I.; McArthur, H.L.; Ho, A.Y. The Abscopal Effect of Radiation Therapy: What Is It and How Can We Use It in Breast Cancer? Curr. Breast Cancer Rep. 2017, 9, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiteside, T.L. Exosomes and tumor-mediated immune suppression. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiteside, T.L. The effect of tumor-derived exosomes on immune regulation and cancer immunotherapy. Future Oncol. 2017, 13, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ochiya, T. The Functional Role of Exosomes in Cancer Biology and Their Potential as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets of Cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 2015, 42, 647–655. [Google Scholar]
- Gluszko, A.; Szczepanski, M.J.; Ludwig, N.; Mirza, S.M.; Olejarz, W. Exosomes in Cancer: Circulating Immune-Related Biomarkers. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1628029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Gu, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, J. Exosomes: Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Delivery Vehicles for Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 3333–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Carpenter, E.; Issadore, D. Detection and isolation of circulating exosomes and microvesicles for cancer monitoring and diagnostics using micro-/nano-based devices. Analyst 2016, 141, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiteside, T.L. The potential of tumor-derived exosomes for noninvasive cancer monitoring: An update. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 18, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.N.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B. Tumor-derived exosomes in oncogenic reprogramming and cancer progression. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abak, A.; Abhari, A.; Rahimzadeh, S. Exosomes in cancer: Small vesicular transporters for cancer progression and metastasis, biomarkers in cancer therapeutics. Peer J. 2018, 6, e4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safaei, R.; Larson, B.J.; Cheng, T.C.; Gibson, M.A.; Otani, S.; Naerdemann, W.; Howell, S.B. Abnormal lysosomal trafficking and enhanced exosomal export of cisplatin in drug-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corcoran, C.; Rani, S.; O’Brien, K.; O’Neill, A.; Prencipe, M.; Sheikh, R.; Webb, G.; McDermott, R.; Watson, W.; Crown, J.; et al. Docetaxel-resistance in prostate cancer: Evaluating associated phenotypic changes and potential for resistance transfer via exosomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, J.L.; Tian, L. Exosomes in tumor microenvironment: Novel transporters and biomarkers. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizutani, K.; Terazawa, R.; Kameyama, K.; Kato, T.; Horie, K.; Tsuchiya, T.; Seike, K.; Ehara, H.; Fujita, Y.; Kawakami, K.; et al. Isolation of prostate cancer-related exosomes. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 3419–3423. [Google Scholar]
- Tauro, B.J.; Greening, D.W.; Mathias, R.A.; Ji, H.; Mathivanan, S.; Scott, A.M.; Simpson, R.J. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods 2012, 56, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrie, A.; Colombo, M.; Krumeich, S.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Diverse subpopulations of vesicles secreted by different intracellular mechanisms are present in exosome preparations obtained by differential ultracentrifugation. J. Extracell Vesicles 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, R.; Shtam, T.; Burdakov, V.; Glotov, A.; Tsyrlina, E.; Berstein, L.; Nosov, A.; Evtushenko, V.; Filatov, M.; Malek, A. Lectin-induced agglutination method of urinary exosomes isolation followed by mi-RNA analysis: Application for prostate cancer diagnostic. Prostate 2016, 76, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jella, K.K.; Nasti, T.H.; Li, Z.; Malla, S.R.; Buchwald, Z.S.; Khan, M.K. Exosomes, Their Biogenesis and Role in Inter-Cellular Communication, Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Immunotherapy. Vaccines 2018, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Shang, L.R.; Luo, Y.W.; Lin, Y.F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S.M. Hepatoma cell-secreted exosomal microRNA-103 increases vascular permeability and promotes metastasis by targeting junction proteins. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1459–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, M.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.G.; Lu, X.J. Decreased levels of serum exosomal miR-638 predict poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 4711–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata-Kawata, H.; Izumiya, M.; Kurioka, D.; Honma, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Furuta, K.; Gunji, T.; Ohta, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sonoda, H.; et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, T.; Sugimachi, K.; Iinuma, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Kurashige, J.; Sawada, G.; Ueda, M.; Uchi, R.; Ueo, H.; Takano, Y.; et al. Exosomal microRNA in serum is a novel biomarker of recurrence in human colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejima, H.; Iinuma, H.; Kanaoka, R.; Matsutani, N.; Kawamura, M. Exosomal microRNA in plasma as a non-invasive biomarker for the recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reclusa, P.; Sirera, R.; Araujo, A.; Giallombardo, M.; Valentino, A.; Sorber, L.; Bazo, I.G.; Pauwels, P.; Rolfo, C. Exosomes genetic cargo in lung cancer: A truly Pandora’s box. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alipoor, S.D.; Adcock, I.M.; Garssen, J.; Mortaz, E.; Varahram, M.; Mirsaeidi, M.; Velayati, A. The roles of miRNAs as potential biomarkers in lung diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 791, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, T.; Tomofuji, T.; Maruyama, T.; Yoneda, T.; Ekuni, D.; Azuma, T.; Miyai, H.; Mizuno, H.; Kato, H.; Tsutsumi, K.; et al. miR1246 and miR4644 in salivary exosome as potential biomarkers for pancreatobiliary tract cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2375–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, P.; Li, J.; Peng, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gan, L.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal lnc-Sox2ot promotes EMT and stemness by acting as a ceRNA in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3822–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Exosomal long noncoding RNA HOTTIP as potential novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker test for gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Ding, J.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z.J.; Liu, B.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, F.; Sun, W.; Li, X.F.; et al. Exosome-Transmitted lncARSR Promotes Sunitinib Resistance in Renal Cancer by Acting as a Competing Endogenous RNA. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Chen, W.; Xiang, A.; Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Pan, J.; Pang, H.; An, H.; Wang, X.; Hou, H.; et al. Hypoxic exosomes facilitate bladder tumor growth and development through transferring long non-coding RNA-UCA1. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Yan, K.; Duan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Expression signatures of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in urine serve as novel non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis and recurrence prediction of bladder cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Liang, W.; Fu, M.; Huang, Z.H.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, P.; Qian, H.; Jiang, P.C.; Xu, W.R.; et al. Exosomes-mediated transfer of long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 promotes gastric cancer progression. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zheng, K.; Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zou, T.; Liu, D. Overexpression of serum exosomal HOTAIR is correlated with poor survival and poor response to chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Jeppesen, D.K.; Weaver, A.M.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.; Coffey, R.J.; Patton, J.G.; et al. Circular RNAs are down-regulated in KRAS mutant colon cancer cells and can be transferred to exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, P.; Peng, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, K.; Liu, H.; Bi, H.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Circular RNA IARS (circ-IARS) secreted by pancreatic cancer cells and located within exosomes regulates endothelial monolayer permeability to promote tumor metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krug, A.K.; Enderle, D.; Karlovich, C.; Priewasser, T.; Bentink, S.; Spiel, A.; Brinkmann, K.; Emenegger, J.; Grimm, D.G.; Castellanos-Rizaldos, E.; et al. Improved EGFR mutation detection using combined exosomal RNA and circulating tumor DNA in NSCLC patient plasma. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahlert, C.; Melo, S.A.; Protopopov, A.; Tang, J.; Seth, S.; Koch, M.; Zhang, J.; Weitz, J.; Chin, L.; Futreal, A.; et al. Identification of double-stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3869–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, V.; Kim, D.U.; San Lucas, F.A.; Castillo, J.; Allenson, K.; Mulu, F.C.; Stephens, B.M.; Huang, J.; Semaan, A.; Guerrero, P.A.; et al. Circulating Nucleic Acids Are Associated With Outcomes of Patients With Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 108–118.e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fricke, F.; Lee, J.; Michalak, M.; Warnken, U.; Hausser, I.; Suarez-Carmona, M.; Halama, N.; Schnolzer, M.; Kopitz, J.; Gebert, J. TGFBR2-dependent alterations of exosomal cargo and functions in DNA mismatch repair-deficient HCT116 colorectal cancer cells. Cell Commun. Signal 2017, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazaro-Ibanez, E.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Visakorpi, T.; Escobedo-Lucea, C.; Siljander, P.; Ayuso-Sacido, A.; Yliperttula, M. Different gDNA content in the subpopulations of prostate cancer extracellular vesicles: Apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, and exosomes. Prostate 2014, 74, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Becker, A.; Matei, I.; Huang, Y.; Costa-Silva, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Brazier, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: A novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chennakrishnaiah, S.; Meehan, B.; D’Asti, E.; Montermini, L.; Lee, T.H.; Karatzas, N.; Buchanan, M.; Tawil, N.; Choi, D.; Divangahi, M.; et al. Leukocytes as a reservoir of circulating oncogenic DNA and regulatory targets of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Thromb. Haemost 2018, 16, 1800–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoller, M. Exosomes in Cancer Disease. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1381, 111–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Johnson, A. Exosome DNA: Critical regulator of tumor immunity and a diagnostic biomarker. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 1921–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, D.P.; Kerin, M.J.; Dwyer, R.M. Exosome-encapsulated microRNAs as circulating biomarkers for breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, S.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Guo, T.; Sheng, H.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Long RNA Sequencing Reveals Abundant mRNA, circRNA, and lncRNA in Human Blood as Potential Biomarkers for Cancer Diagnosis. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greening, D.W.; Gopal, S.K.; Xu, R.; Simpson, R.J.; Chen, W. Exosomes and their roles in immune regulation and cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobiasova, Z.; Pospisilova, D.; Miller, A.M.; Minarik, I.; Sochorova, K.; Spisek, R.; Rob, L.; Bartunkova, J. In vitro assessment of dendritic cells pulsed with apoptotic tumor cells as a vaccine for ovarian cancer patients. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 122, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graner, M.W.; Cumming, R.I.; Bigner, D.D. The heat shock response and chaperones/heat shock proteins in brain tumors: Surface expression, release, and possible immune consequences. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 11214–11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucci, M.; Mannavola, F.; Passarelli, A.; Stucci, L.S.; Cives, M.; Silvestris, F. Exosomes in melanoma: A role in tumor progression, metastasis and impaired immune system activity. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20826–20837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.B.; Zhang, Z.R.; Schluesener, H.J.; Xu, S.Q. Role of exosomes in immune regulation. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2006, 10, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, L.; Wei, W.; Deng, X.; Ma, L.; Hao, S. Tumor cell-derived exosome-targeted dendritic cells stimulate stronger CD8+ CTL responses and antitumor immunities. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 436, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedaeinia, R.; Manian, M.; Jazayeri, M.H.; Ranjbar, M.; Salehi, R.; Sharifi, M.; Mohaghegh, F.; Goli, M.; Jahednia, S.H.; Avan, A.; et al. Circulating exosomes and exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers in gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncay Cagatay, S.; Mayah, A.; Mancuso, M.; Giardullo, P.; Pazzaglia, S.; Saran, A.; Daniel, A.; Traynor, D.; Meade, A.D.; Lyng, F.; et al. Phenotypic and Functional Characteristics of Exosomes Derived from Irradiated Mouse Organs and Their Role in the Mechanisms Driving Non-Targeted Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; MacManus, M.P.; Martin, R.F.; Martin, O.A. Abscopal effects of radiation therapy: A clinical review for the radiobiologist. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Lin, H.W.; Chiang, Y.C.; Chang, C.F.; Hsieh, S.F.; Chen, C.A.; Sun, W.Z.; Cheng, W.F. Irradiation Enhances Abscopal Anti-tumor Effects of Antigen-Specific Immunotherapy through Regulating Tumor Microenvironment. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, U.; Wang, H.; Palmblad, K.; Aveberger, A.C.; Bloom, O.; Erlandsson-Harris, H.; Janson, A.; Kokkola, R.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; et al. High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1) stimulates proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in human monocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshak-Rothstein, A. Toll-like receptors in systemic autoimmune disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richez, C.; Blanco, P.; Rifkin, I.; Moreau, J.F.; Schaeverbeke, T. Role for toll-like receptors in autoimmune disease: The example of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Bone Spine 2011, 78, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Liang, H.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Burnette, B.; Arina, A.; Li, X.D.; Mauceri, H.; Beckett, M.; Darga, T.; et al. STING-Dependent Cytosolic DNA Sensing Promotes Radiation-Induced Type I Interferon-Dependent Antitumor Immunity in Immunogenic Tumors. Immunity 2014, 41, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lugade, A.A.; Sorensen, E.W.; Gerber, S.A.; Moran, J.P.; Frelinger, J.G.; Lord, E.M. Radiation-induced IFN-gamma production within the tumor microenvironment influences antitumor immunity. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3132–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Kong, L.; Shi, F.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J. Abscopal effect of radiotherapy combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poggio, M.; Hu, T.; Pai, C.C.; Chu, B.; Belair, C.D.; Chang, A.; Montabana, E.; Lang, U.E.; Fu, Q.; Fong, L.; et al. Suppression of Exosomal PD-L1 Induces Systemic Anti-tumor Immunity and Memory. Cell 2019, 177, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koller, K.M.; Mackley, H.B.; Liu, J.; Wagner, H.; Talamo, G.; Schell, T.D.; Pameijer, C.; Neves, R.I.; Anderson, B.; Kokolus, K.M.; et al. Improved survival and complete response rates in patients with advanced melanoma treated with concurrent ipilimumab and radiotherapy versus ipilimumab alone. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Rodriguez, I.; Garasa, S.; Barbes, B.; Solorzano, J.L.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Labiano, S.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Azpilikueta, A.; Bolanos, E.; et al. Abscopal Effects of Radiotherapy Are Enhanced by Combined Immunostimulatory mAbs and Are Dependent on CD8 T Cells and Crosspriming. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5994–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farias, V.A.; Tovar, I.; Del Moral, R.; O’Valle, F.; Exposito, J.; Oliver, F.J.; Ruiz de Almodovar, J.M. Enhancing the Bystander and Abscopal Effects to Improve Radiotherapy Outcomes. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhee, K.J.; Lee, J.I.; Eom, Y.W. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Effects of Tumor Support or Suppression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 30015–30033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalapour, S.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer: An eternal fight between good and evil. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3347–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alessandri, A.L.; Sousa, L.P.; Lucas, C.D.; Rossi, A.G.; Pinho, V.; Teixeira, M.M. Resolution of inflammation: Mechanisms and opportunity for drug development. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 139, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tubin, S.; Khan, M.K.; Gupta, S.; Jeremic, B. Biology of NSCLC: Interplay between Cancer Cells, Radiation and Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Cancers 2021, 13, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, K.; Nomura, M.; Ohashi, S.; Hiratsuka, T.; Nakai, Y.; Saito, T.; Kondo, Y.; Fukuyama, K.; Kikuchi, O.; Yamada, A.; et al. Experimental model for the irradiation-mediated abscopal effect and factors influencing this effect. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daguenet, E.; Louati, S.; Wozny, A.S.; Vial, N.; Gras, M.; Guy, J.B.; Vallard, A.; Rodriguez-Lafrasse, C.; Magne, N. Radiation-induced bystander and abscopal effects: Important lessons from preclinical models. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.; Yasmin-Karim, S.; Mueller, R.; Viswanathan, A.N.; Ngwa, W. Single Radiotherapy Fraction with Local Anti-CD40 Therapy Generates Effective Abscopal Responses in Mouse Models of Cervical Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kazandjian, D.; Dew, A.; Hill, E.; Ramirez, E.G.; Morrison, C.; Mena, E.; Lindenberg, L.; Yuan, C.; Maric, I.; Wang, H.W.; et al. Avelumab, a PD-L1 Inhibitor, in Combination with Hypofractionated Radiotherapy and the Abscopal Effect in Relapsed Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Oncologist 2021, 26, 288–e541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiwert, T.Y.; Kiess, A.P. Time to Debunk an Urban Myth? The "Abscopal Effect" With Radiation and Anti-PD-1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.; Bevelacqua, J.J.; Dobrzyński, L.; Mortazavi, S.A.R. Abscopal Effect Following Radiation Therapy in Cancer Patients: A New Look from the Immunological Point of View. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2020, 10, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubin, S.; Yan, W.; Mourad, W.F.; Fossati, P.; Khan, M.K. The future of radiation-induced abscopal response: Beyond conventional radiotherapy approaches. Future Oncol. 2020, 16, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberson, C.D.; Atay, S.; Gercel-Taylor, C.; Taylor, D.D. Tumor-derived exosomes as mediators of disease and potential diagnostic biomarkers. Cancer Biomark 2010, 8, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, S.D.; Mortaz, E.; Varahram, M.; Movassaghi, M.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Garssen, J.; Adcock, I.M. The Potential Biomarkers and Immunological Effects of Tumor-Derived Exosomes in Lung Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soung, Y.H.; Ford, S.; Zhang, V.; Chung, J. Exosomes in Cancer Diagnostics. Cancers 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Salomon, C. Techniques Associated with Exosome Isolation for Biomarker Development: Liquid Biopsies for Ovarian Cancer Detection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2055, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzoli, R.; Buttitta, F.; Di Nicola, M.; Malatesta, S.; Marchetti, A.; Rom, W.N.; Pass, H.I. microRNAs derived from circulating exosomes as noninvasive biomarkers for screening and diagnosing lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reclusa, P.; Taverna, S.; Pucci, M.; Durendez, E.; Calabuig, S.; Manca, P.; Serrano, M.J.; Sober, L.; Pauwels, P.; Russo, A.; et al. Exosomes as diagnostic and predictive biomarkers in lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, S1373–S1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakobsen, K.R.; Paulsen, B.S.; Baek, R.; Varming, K.; Sorensen, B.S.; Jorgensen, M.M. Exosomal proteins as potential diagnostic markers in advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma. J. Extracell Vesicles 2015, 4, 26659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, F.; Qiu, Z. Proteomic identification of exosomal LRG1: A potential urinary biomarker for detecting NSCLC. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Song, X.; Wang, N.; Xue, L.; Song, X.; Xie, L. Tumor-derived exosomal proteins as diagnostic biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.; Deng, C.X. Current Progresses of Exosomes as Cancer Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, M.; Lohse, I.; Tan, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wu, J.; Kurapati, H.; Morgan, M.A.; Lawrence, T.S.; Cuneo, K.C.; Lubman, D.M. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Serum Exosomes from Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Undergoing Chemoradiotherapy. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, J.; Skog, J.; Nordstrand, A.; Baranov, V.; Mincheva-Nilsson, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Widmark, A. Prostate cancer-derived urine exosomes: A novel approach to biomarkers for prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharmate, G.; Hosseini-Beheshti, E.; Caradec, J.; Chin, M.Y.; Tomlinson Guns, E.S. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Prostate Cancer Derived Exosomes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, T.; Liu, R.; Bai, M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; et al. Exosome-delivered EGFR regulates liver microenvironment to promote gastric cancer liver metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Mao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, B.; Sun, Z.; Qian, H.; et al. Exosomal TRIM3 is a novel marker and therapy target for gastric cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Clinical and biological significance of circulating tumor cells, circulating tumor DNA, and exosomes as biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55632–55645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucchetti, D.; Colella, F.; Perelli, L.; Ricciardi-Tenore, C.; Calapa, F.; Fiori, M.E.; Carbone, F.; De Maria, R.; Sgambato, A. CD147 Promotes Cell Small Extracellular Vesicles Release during Colon Cancer Stem Cells Differentiation and Triggers Cellular Changes in Recipient Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landras, A.; Reger de Moura, C.; Jouenne, F.; Lebbe, C.; Menashi, S.; Mourah, S. CD147 Is a Promising Target of Tumor Progression and a Prognostic Biomarker. Cancers 2019, 11, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logozzi, M.; De Milito, A.; Lugini, L.; Borghi, M.; Calabro, L.; Spada, M.; Perdicchio, M.; Marino, M.L.; Federici, C.; Iessi, E.; et al. High levels of exosomes expressing CD63 and caveolin-1 in plasma of melanoma patients. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gamperl, H.; Plattfaut, C.; Freund, A.; Quecke, T.; Theophil, F.; Gieseler, F. Extracellular vesicles from malignant effusions induce tumor cell migration: Inhibitory effect of LMWH tinzaparin. Cell Biol. Int. 2016, 40, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Song, J.; Ji, T.; Zhu, M.; Anderson, G.J.; Wei, J.; Nie, G. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.; Sapp, M.; Feldman, M.; Subklewe, M.; Bhardwaj, N. A monocyte conditioned medium is more effective than defined cytokines in mediating the terminal maturation of human dendritic cells. Blood 1997, 90, 3640–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Peng, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; Chang, X.; Yu, X.; et al. Dendritic cells loaded with tumor derived exosomes for cancer immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 2887–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Erb, U.; Buchler, M.W.; Zoller, M. Improved vaccine efficacy of tumor exosome compared to tumor lysate loaded dendritic cells in mice. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E74–E84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benites, B.D.; Alvarez, M.C.; Saad, S.T.O. Small Particles, Big Effects: The Interplay Between Exosomes and Dendritic Cells in Antitumor Immunity and Immunotherapy. Cells 2019, 8, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, C.S.; Sharma, P.; Yerneni, S.S.; Simms, P.; Jackson, E.K.; Whiteside, T.L.; Boyiadzis, M. Circulating exosomes carrying an immunosuppressive cargo interfere with cellular immunotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samuel, M.; Gabrielsson, S. Personalized medicine and back-allogeneic exosomes for cancer immunotherapy. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 289, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Battke, C.; Ruiss, R.; Welsch, U.; Wimberger, P.; Lang, S.; Jochum, S.; Zeidler, R. Tumour exosomes inhibit binding of tumour-reactive antibodies to tumour cells and reduce ADCC. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Genetic Material | Contents and Functions | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| miRNA | miR-103: Biomarkers for metastasis of Hepatocellular carcinoma. miR-638: Recurrence of Hepatocellular carcinoma. miR-1229, miR-1246, miR-150, miR-223, miR-23a: Diagnosis of colorectal cancer. miR-17-92a, miR-19a: Recurrence of colorectal cancer. miR-217, miR-4257: Recurrence of lung cancer. miR-51, miR-373: Poor diagnosis of lung cancer. miR-208a, miR-1246: Biomarkers of therapeutic effect of lung cancer. miR-4644, miR-1246: Poor diagnosis of pancreatobiliary tract cancer. KRAS mutation: Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer and colorectal cancer. | [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] |
| lncRNA | lnc-sox2ot, lnc-h19, lncRNA-ARSR: Prognosis and survival rate of hepatocellular carcinoma. lncRNA-UCA1: Diagnosis and tumor progression monitoring of bladder cancer. HOTTIP: Diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. lncRNAs-ZFAS1: Biomarkers for metastasis of gastric cancer. HOTAIR: Prognosis of breast cancer. | [22,30,31,32,33,35,36] |
| circRNA | circ-IARS: Biomarkers for tumor progression, invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. | [9,37,38] |
| DNA | EGFR mutation: Prognosis and diagnosis of NSCLC. KRAS mutation: Diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer; regulation of circRNA as diagnostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. TGFBR2 mutation: Diagnosis of colorectal cancer. P53 mutation, MLH1 mutation, PTEN mutation: Diagnosis of prostate cancer. BRAF mutation: Diagnosis of melanoma cancer. HRAS mutation, HER2 mutation: Diagnosis of breast cancer. | [9,36,37,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Min, W. The Role of Tumor-Derived Exosomes in the Abscopal Effect and Immunotherapy. Life 2021, 11, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11050381
Shan Z, Wang H, Zhang Y, Min W. The Role of Tumor-Derived Exosomes in the Abscopal Effect and Immunotherapy. Life. 2021; 11(5):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11050381
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Zechen, Hongmei Wang, Yujuan Zhang, and Weiping Min. 2021. "The Role of Tumor-Derived Exosomes in the Abscopal Effect and Immunotherapy" Life 11, no. 5: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11050381






