Organic Farming Practices and Shade Trees Reduce Pest Infestations in Robusta Coffee Systems in Amazonia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Pest and Disease Sampling
2.4. Shade Estimates and Solar Radiation Measurements
2.5. Determination of Colletotrichum spp. Severity by Image Processing
2.6. Data Processing
2.6.1. Data Quality Control
2.6.2. Calculations
2.6.3. Determination of Shade Percentage
2.7. Statistical Analysis
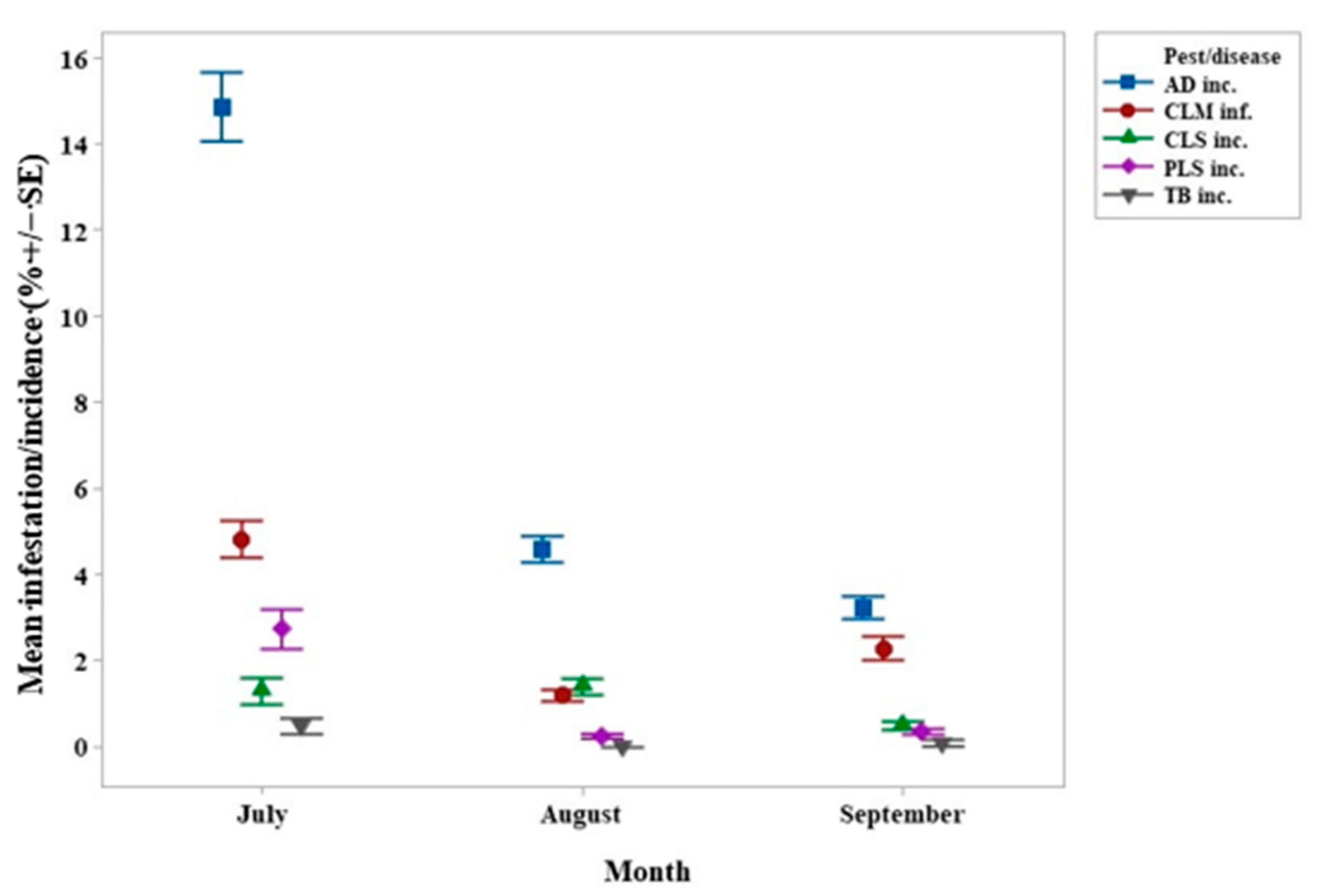
3. Results
4. Discussion
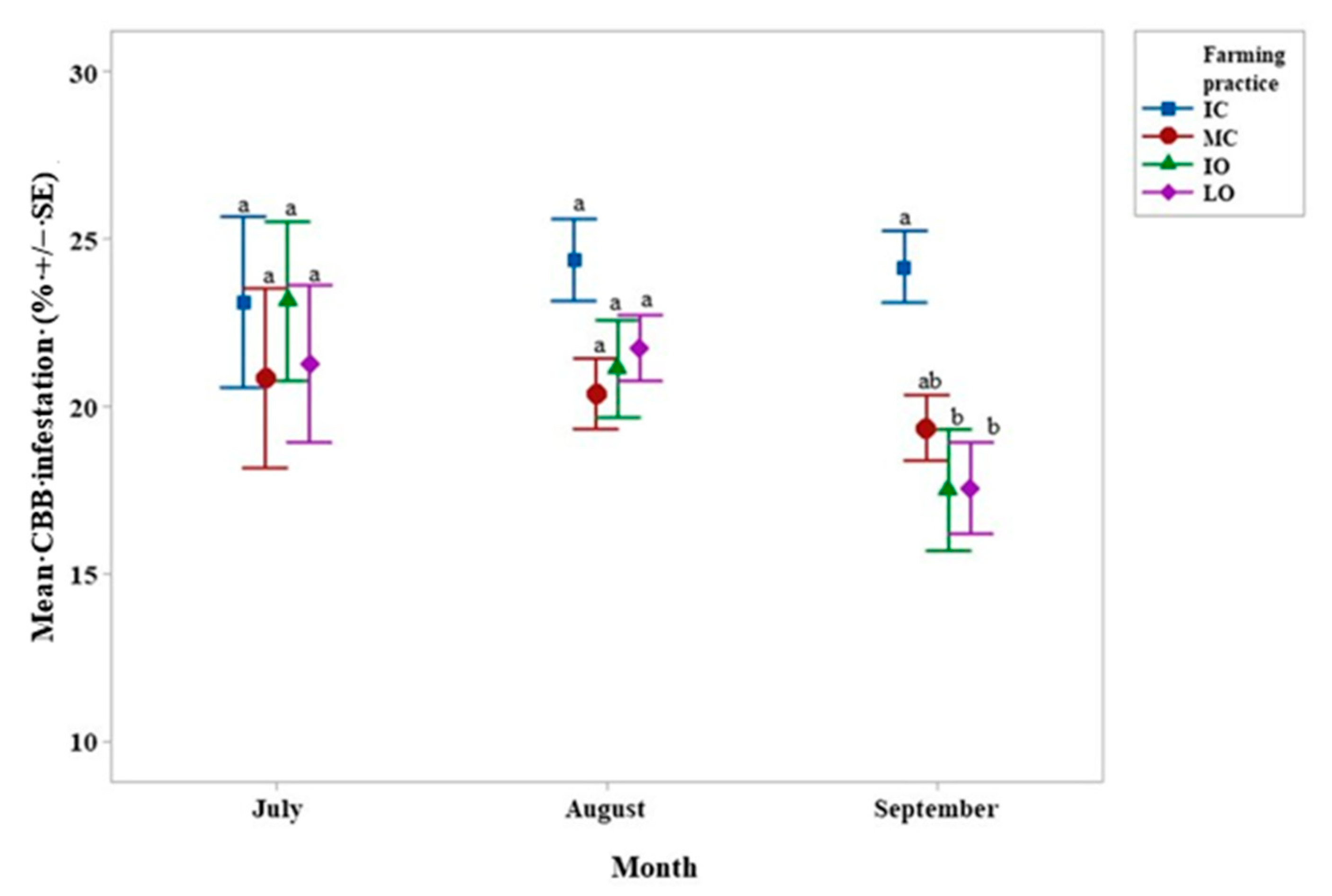
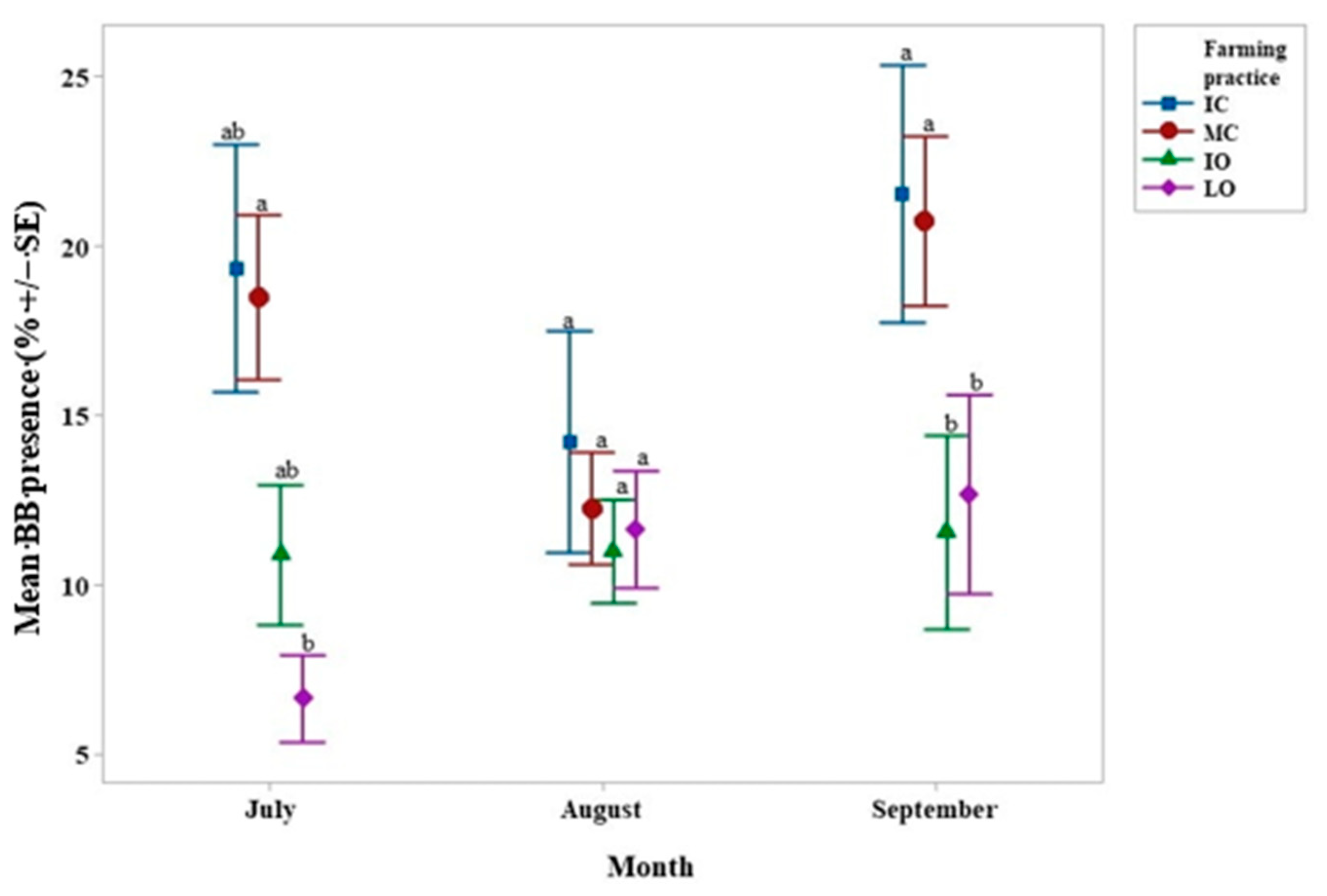
4.1. Hypothenemus Hampei Infestation–Beauveria Bassiana Presence
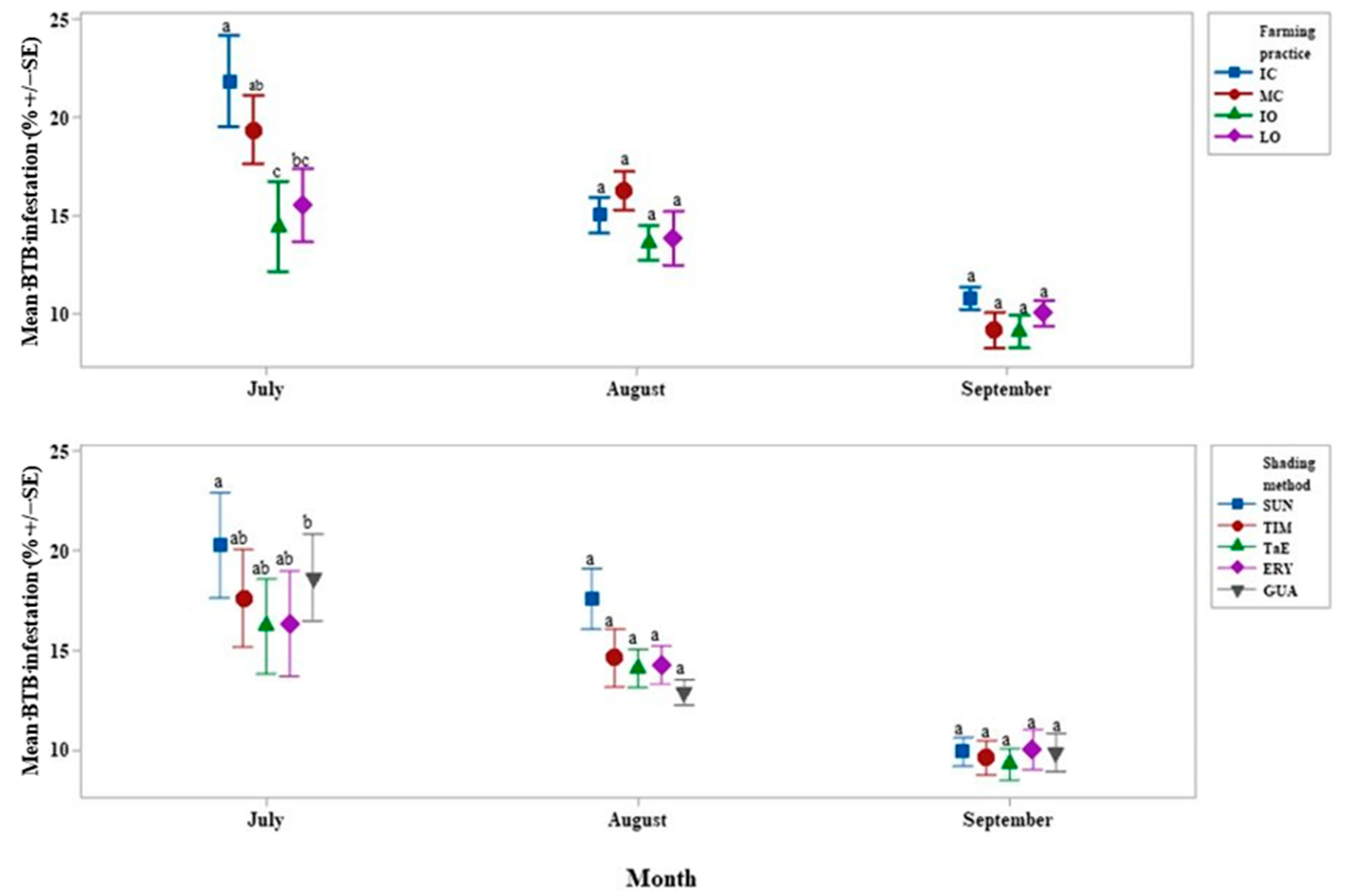
4.2. Xylosandrus Morigerus Infestation
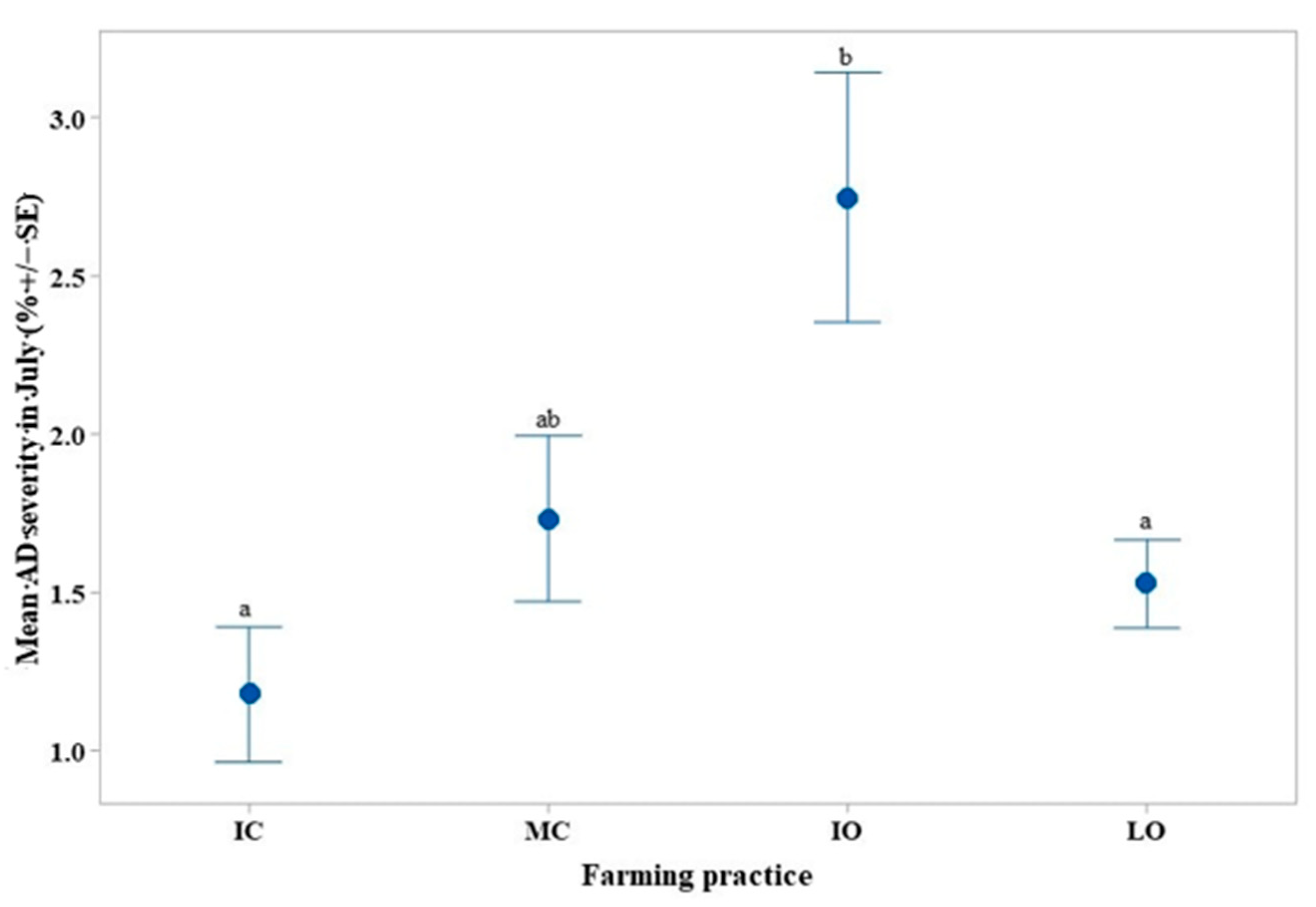
4.3. Colletotrichum spp. (AD) Incidence and Severity
4.4. Shade Percentages
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bunn, C.; Läderach, P.; Ovalle Rivera, O.; Kirschke, D. A bitter cup: Climate change profile of global production of Arabica and Robusta coffee. Clim. Chang. 2015, 129, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaMatta, F.M.; Ramalho, J.D.C. Impacts of drought and temperature stress on coffee physiology and production: A review. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 18, 55–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalle-Rivera, O.; Läderach, P.; Bunn, C.; Obersteiner, M.; Schroth, G. Projected shifts in Coffea arabica suitability among major global producing regions due to climate change. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, M.; Bratescu, A.; Martínez, J.O.; Oviedo, J.A.; Acosta, A. Centroamérica: El Impacto de la Caída de los Precios del Café; Naciones Unidas Comisión Económica para América Latina y el Caribe (CEPAL): Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2002; ISBN 92-1-322015-4. [Google Scholar]
- ICO. Sustainability of the coffee sector in Africa. In 114th International Coffee Council: London, 2–6 March 2015; International Coffee Organization (ICO): London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jácome, A.R.; Garrido, A. A Real Option Analysis applied to the production of Arabica and Robusta Coffee in Ecuador. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 15, e0104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, J.; Muchugu, E.; Vega, F.E.; Davis, A.; Borgemeister, C.; Chabi-Olaye, A. Some like it hot: The influence and implications of climate change on coffee berry borer (Hypothenemus hampei) and coffee production in East Africa. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, J.M.; Bigger, M.; Hillocks, R.J. Coffee Pests, Diseases and Their Management; CABI Pub: Wallingford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-1-84593-129-2. [Google Scholar]
- Staver, C.; Guharay, F.; Monterroso, D.; Muschler, R.G. Designing pest-suppressive multistrata perennial crop systems: Shade-grown coffee in Central America. Agrofor. Syst. 2001, 53, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, J. Advantages, disadvantages and desirable characteristics of shade trees for coffee, cacao and tea. Agrofor. Syst. 1987, 5, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscharntke, T.; Clough, Y.; Bhagwat, S.A.; Buchori, D.; Faust, H.; Hertel, D.; Hölscher, D.; Juhrbandt, J.; Kessler, M.; Perfecto, I.; et al. Multifunctional shade-tree management in tropical agroforestry landscapes—A review. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.; Goulart, F.F.; Jacobson, T.K.B.; Filho, R.J.d.M.; Ribas, C.E.D.C. Shade’s Benefit: Coffee Production under Shade and Full Sun. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 8, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutman, F.J. Studies of the Physiology of Coffea arabica: I. Photosynthesis of Coffee Leaves under Natural Conditions. Ann. Bot. 1937, 1, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutman, F.J. Studies of the Physiology of Coffea arabica: II. Stomatal Movements in Relation to Photosynthesis under Natural Conditions. Ann. Bot. 1937, 1, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedimo, J.A.M.; Dufour, B.P.; Cilas, C.; Avelino, J. Effets des arbres d’ombrage sur les bioagresseurs de Coffea arabica. Cah. Agric. 2012, 21, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroth, G.; Krauss, U.; Gasparotto, L.; Duarte Aguilar, J.A.; Vohland, K. Pests and diseases in agroforestry systems of the humid tropics. Agrofor. Syst. 2000, 50, 199–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas, V.L.; Fanjul, L. Microclimatic chacterization of shaded and open-grown coffee (Coffea arabica L.) plantations in Mexico. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1986, 38, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, J.; Muschler, R.; Kass, D.; Somarriba, E. Shade management in coffee and cacao plantations. Agrofor. Syst. 1998, 38, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piato, K.; Lefort, F.; Subía, C.; Caicedo, C.; Calderón, D.; Pico, J.; Norgrove, L. Effects of shade trees on robusta coffee growth, yield and quality. A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Govaerts, R.; Bridson, D.M.; Stoffelen, P. An annotated taxonomic conspectus of the genus Coffea (Rubiaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 152, 465–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeck, J.; Lambot, C. Crop maintenance. In Coffee: Growing, Processing, Sustainable Production; Wintgens, J.N., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; pp. 251–327. ISBN 9783527619627. [Google Scholar]
- Cerda, R.; Allinne, C.; Gary, C.; Tixier, P.; Harvey, C.A.; Krolczyk, L.; Mathiot, C.; Clément, E.; Aubertot, J.-N.; Avelino, J. Effects of shade, altitude and management on multiple ecosystem services in coffee agroecosystems. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 82, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.; Raphael, I.A.; Ekbom, B.; Kyamanywa, S.; Karungi, J. Contrasting effects of shade level and altitude on two important coffee pests. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesper, M.; Kueffer, C.; Krishnan, S.; Kushalappa, C.G.; Ghazoul, J. Shade tree diversity enhances coffee production and quality in agroforestry systems in the Western Ghats. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukomeko, H.; Jassogne, L.; Kagezi, G.H.; Mukasa, D.; Vaast, P. Influence of shaded systems on Xylosandrus compactus infestation in Robusta coffee along a rainfall gradient in Uganda. Agric. For. Entomol. 2018, 20, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño, Y.A.; Vega, V.J.; García, J.M.; Verle Rodrigues, J.C.; García, N.M.; Bayman, P. The Coffee Berry Borer (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Puerto Rico: Distribution, Infestation, and Population per Fruit. J. Insect Sci. 2017, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.G.; Pozza, E.A.; Vasco, G.B.; Freitas, A.S.; Chaves, E.; Paula, P.V.A.A.; Dornelas, G.A.; Alves, M.C.; Silva, M.L.O.; Pozza, A.A.A. Geostatistical analysis of coffee leaf rust in irrigated crops and its relation to plant nutrition and soil fertility. Phytoparasitica 2019, 47, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelino, J.; Willocquet, L.; Savary, S. Effects of crop management patterns on coffee rust epidemics. Plant Pathol. 2004, 53, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, S.S.; Gómez, M.I.; Jaramillo, J. A Bioeconomic Model of Ecosystem Services Provision: Coffee Berry Borer and Shade-grown Coffee in Colombia. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 144, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICO. Domestic Consumption by All Exporting Countries. Available online: http://www.ico.org/historical/1990%20onwards/PDF/1b-domestic-consumption.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Nieto, C.; Caicedo, C.E.V. Sistemas de Producción Agropecuarios de la Región Amazónica Ecuatoriana RAE: Análisis Reflexivo y Propositivo Sobre las Potencialidades. In Agroforestería Sostenible en la Amazonía Ecuatoriana; de Melo, E.V.F., Caicedo, C.E.V., Astorga, C.D., Eds.; CATIE (Centro Agronómico Tropical de Investigación y Enseñanza): Turrialba, Costa Rica, 2014; pp. 25–34. ISBN 978-9977-57-623-7. [Google Scholar]
- Barrance, A.; Beer, J.; Boshier, D.H.; Chamberlain, J.; Cordero, J.; Detlefsen, G.; Finegan, B.; Galloway, G.; Gómez, M.; Gordon, J.; et al. Inga edulis Mart. In Árboles de Centroamérica: Un Manual Para Extensionistas; Cordero, J., Ed.; CATIE: Turrialba, Costa Rica, 2003; pp. 605–606. ISBN 0850741610. [Google Scholar]
- Stamps, W.T.; Linit, M.J. Plant diversity and arthropod communities: Implications for temperate agroforestry. Agrofor. Syst. 1997, 39, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augspurger, C.K. Seedling Survival of Tropical Tree Species: Interactions of Dispersal Distance, Light-Gaps, and Pathogens. Ecology 1984, 65, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, Â.L.B.; Lewis, G.P.; de Freitas Mansano, V.; de Azevedo Tozzi, A.M. A revision of the genus Myroxylon (Leguminosae: Papilionoideae). Kew Bull. 2015, 70, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, R.; Balslev, H.; Paz, Y.; Miño, C.G. High tree alpha-diversity in Amazonian Ecuador. Biodivers. Conserv. 1994, 3, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; de Souza, E.B.; Fontenelle, R.O.d.S.; de Vasconcelos, M.A.; Santos, H.S.d.; Teixeira, E.H. Diversidade estrutural e potencial biológico dos metabólitos secundários de espécies do gênero Myroxylon L.f. (Fabaceae): Uma revisão da literatura. Hoehnea 2019, 46, e582017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, D.L. Erythrina species: Pantropical multipurpose tree legumes. In Forage Tree Legumes in Tropical Agriculture; Gutteridge, R.C., Shelton, H.M., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1994; pp. 84–96. ISBN 0851988687. [Google Scholar]
- Boreux, V.; Vaast, P.; Madappa, L.P.; Cheppudira, K.G.; Garcia, C.; Ghazoul, J. Agroforestry coffee production increased by native shade trees, irrigation, and liming. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INAMHI. Mapa de Precipitación Media Multianual: Serie 1965–1999. Available online: http://www.serviciometeorologico.gob.ec/docum_institucion/MapasBiblioteca/5%20PrecipitacionA0.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- INAMHI. Mapa de Temperatura Media Multianual: Serie 1965–1999. Available online: http://www.serviciometeorologico.gob.ec/docum_institucion/MapasBiblioteca/6%20TemperaturaA0.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 12th ed.; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS): Washington, DC, USA, 2014; ISBN 9780359573240.
- Holdridge, L.R.; Tosi, J.A. Life Zone Ecology; Tropical Science Center: San Jose, CA, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- INAMHI. Datos Meteorológicos de la EECA en Joya de los Sachas; EECA; Instituto Nacional de Meteorología e Hidrología (INAMHI): Quito, Ecuador, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- World Weather Online. La Joya De Los Sachas Monthly Climate Averages. Available online: https://www.worldweatheronline.com/la-joya-de-los-sachas-weather-averages/orellana/ec.aspx (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Compendium of Coffee Diseases and Pests; Gaitán, A.L., Ed.; APS Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2016; ISBN 0890544727. [Google Scholar]
- Avelino, J.; Muller, R.A.; Cilas, C.; Velasco, H.P. Développement et comportement de la rouille orangée du caféier (Hemileia vastatrix Berk. et Br.) dans des plantations en cours de modernisation, plantées de variétés naines, dans le sud-est du Mexique (Francés traducido integralmente al Español)—Desarrollo y comportamiento de la roya anaranjada del cafeto (Hemileia vastatrix Berk. y Br.) en plantaciones en proceso de modernización, cultivadas con variedades de porte bajo en el Sureste de México. Cafe Cacao The 1991, 35, 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Van Long, N.; Ngoc, N.Q.; Dung, N.N.; Kristiansen, P.; Yunusa, I.; Fyfe, C. The Effects of Shade Tree Types on Light Variation and Robusta Coffee Production in Vietnam. Engineering 2015, 7, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne Rasband. ImageJ; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018.
- Minitab, L.L. Minitab® 18 Statistical Software; Minitab L.L.: State College, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bagny Beilhe, L.; Roudine, S.; Quintero Perez, J.A.; Allinne, C.; Daout, D.; Mauxion, R.; Carval, D. Pest-regulating networks of the coffee berry borer (Hypothenemus hampei) in agroforestry systems. Crop. Prot. 2020, 131, 105036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.M.; Tapias, J.; Ortiz, A.; Benavides, P.; Góngora, C.E. Identification of attractant and repellent plants to coffee berry borer, Hypothenemus Hampei. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2017, 164, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, S.M.; Armbrecht, I. Biodiversity in tropical agroforests and the ecological role of ants and ant diversity in predatory function. Ecol. Entomol. 2006, 31, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbrecht, I.; Gallego, M.C. Testing ant predation on the coffee berry borer in shaded and sun coffee plantations in Colombia. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2007, 124, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo, A.E.; Cárdenas, R.; Posada, F. Natural Enemies and Competitors of Hypothenemus hampei (Ferrari) (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) in Colombia. Neotrop. Entomol. 2002, 31, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.D.; Jiménez-Soto, E.; Philpott, S.M.; Perfecto, I. Ant-mediated (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) biological control of the coffee berry borer: Diversity, ecological complexity, and conservation biocontrol. Myrmecol. News 2018, 26, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Perfecto, I.; Vandermeer, J.H. Coffee Agroecology: A New Approach to Understanding Agricultural Biodiversity, Ecosystem Services and Sustainable Development; Routledge, Eartscan: Abingdon, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-415-82681-5. [Google Scholar]
- De La Rosa, W.; Alatorre, R.; Barrera, J.F.; Toreillo, C. Effect of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae (Deuteromycetes) upon the coffee berry borer (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) under field conditions. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruck, D.J.; Lewis, L.C. Rainfall and crop residue effects on soil dispersion and Beauveria bassiana spread to corn. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2002, 20, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, D.J. Dynamics of the fungus Beauveria bassiana. In Retrospective Theses and Dissertations; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlan, H.A.J.; Janssens, M.J.; Eversbusch, B.G. Impact of Canavalia Cover Crop Management in Coffea arabica L. on Plant-Invertebrate Associations. Open Agric. J. 2008, 2, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soares, F.B.; Monteiro, A.C.; Babosa, J.C.; Mochi, D.A. Population density of Beauveria bassiana in soil under the action of fungicides and native microbial populations. Acta Sci. Agron. 2017, 39, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Quesada-Moraga, E.; Navas-Cortés, J.A.; Maranhao, E.A.A.; Ortiz-Urquiza, A.; Santiago-Alvarez, C. Factors affecting the occurrence and distribution of entomopathogenic fungi in natural and cultivated soils. Mycol. Res. 2007, 111, 947–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, L.M.; Gil, Z.N.; Montoya, E.C.; Benavides, P. Coffee Berry Borer (Hypothenemus hampei) Emergence from Ground Fruits Across Varying Altitudes and Climate Cycles, and the Effect on Coffee Tree Infestation. Neotrop. Entomol. 2021. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, E.B.; Wright, M.G. Ecology, Biology, and Management of Xylosandrus compactus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae) with Emphasis on Coffee in Hawaii. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2015, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, M.G.; Benavides, P.; Constantino, L. Conozca al Pasador de las Ramas del Café Xylosandrus Morigerus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae); Avances Técnicos No. 460; Centro Nacional de Investigationes de Café – Cenicafé: Manizales, Caldas, Colombia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ogogol, R.; Egonyu, J.P.; Bwogi, G.; Kyamanywa, S.; Erbaugh, M. Interaction of the predatory ant Pheidole megacephala (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with the polyphagus pest Xylosandrus compactus (Coleoptera: Curculionidea). Biol. Control. 2017, 104, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, M.G. El Xyleborus morigerus Blandford en Colombia. Cenicafe 1961, 12, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, J.C.; Estrada, A.B.; Matcham, J.; Jeffries, P.; Jeger, M.J. The effect of climatic factors on Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, causal agent of mango anthracnose, in the Philippines. Plant Pathol. 1991, 40, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubballi, M.; Nakkeeran, S.; Raguchander, T.; Anand, T.; Renukadevi, P. Physiological characterisation of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, the incitant of anthracnose disease of noni in India. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Protect. 2011, 44, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, P.; Dodd, J.; Jeger, M.; Plumbley, R. The biology and control of Colletotrichum species on tropical fruit crops. Plant Pathol. 1990, 39, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Month | Mean Max Temp. (°C) | Mean Min Temp. (°C) | Total Rainfall (mm) | Mean RH at 7 am (%) | Mean RH at 1 pm (%) | Mean RH at 7 pm (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| April 18 | 30.1 | 20.8 | 299.0 | 95 | 80 | 85 |
| May 18 | 30.2 | 22.0 | 358.9 | 90 | 80 | 90 |
| June 18 | 29.5 | 21.8 | 193.5 | 95 | 80 | 85 |
| July 18 | 30.3 | 21.4 | 212.9 | 90 | 80 | 85 |
| August 18 | 30.7 | 21.7 | 150.7 | 90 | 75 | 80 |
| September 18 | 32.1 | 22.2 | 114.6 | 90 | 70 | 80 |
| Response Variables (%) | Variables | Meaning | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBB inf. 1 | n’ | Number of cherries where CBB was present | (n’/N’) ×100 |
| N’ | Total number of cherries assessed | ||
| AD inc. 2 | N | Number of infected leaves | (n/N) × 100 |
| PLS inc. | |||
| CLS inc. | N | Total number of leaves | |
| TB inc. | |||
| BTB inf. | R | Number of branches where BTB was present | (r/R) × 100 |
| CLM inf. | R | Total number of branches assessed | |
| AD sev. 3 | S | Total necrotic area of leaves | (s/S) × 100 |
| S | Total area of leaves | ||
| BB pres. 4 | B | Number of cherries perforated by CBB with BB | (b/B) × 100 |
| B | Total number of cherries perforated by CBB |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piato, K.; Subía, C.; Pico, J.; Calderón, D.; Norgrove, L.; Lefort, F. Organic Farming Practices and Shade Trees Reduce Pest Infestations in Robusta Coffee Systems in Amazonia. Life 2021, 11, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11050413
Piato K, Subía C, Pico J, Calderón D, Norgrove L, Lefort F. Organic Farming Practices and Shade Trees Reduce Pest Infestations in Robusta Coffee Systems in Amazonia. Life. 2021; 11(5):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11050413
Chicago/Turabian StylePiato, Kevin, Cristian Subía, Jimmy Pico, Darío Calderón, Lindsey Norgrove, and François Lefort. 2021. "Organic Farming Practices and Shade Trees Reduce Pest Infestations in Robusta Coffee Systems in Amazonia" Life 11, no. 5: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11050413
APA StylePiato, K., Subía, C., Pico, J., Calderón, D., Norgrove, L., & Lefort, F. (2021). Organic Farming Practices and Shade Trees Reduce Pest Infestations in Robusta Coffee Systems in Amazonia. Life, 11(5), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11050413






