OCT Based Interpretation of the Optic Nerve Head Anatomy and Prevalence of Optic Disc Drusen in Patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
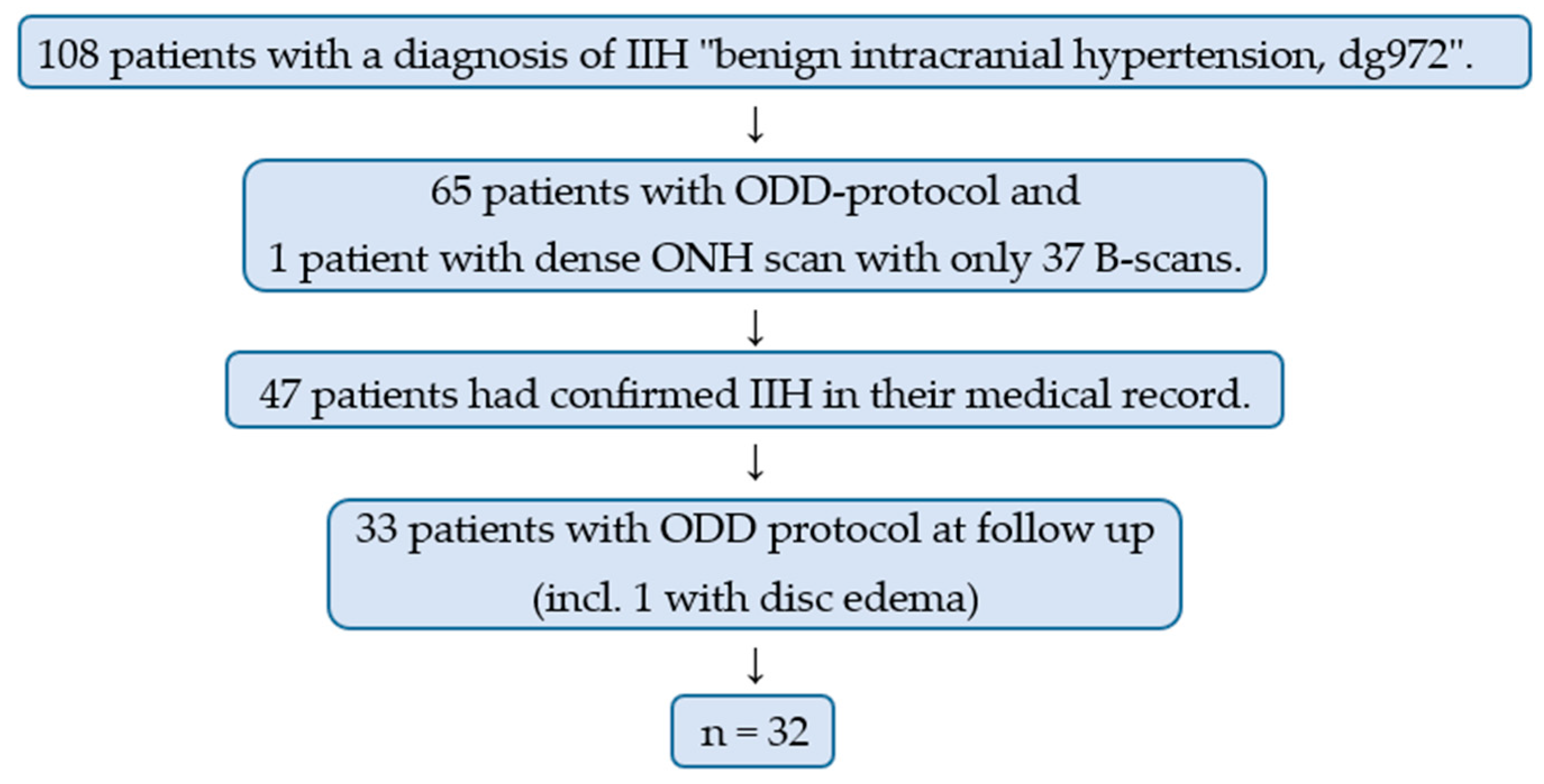
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Age and Gender
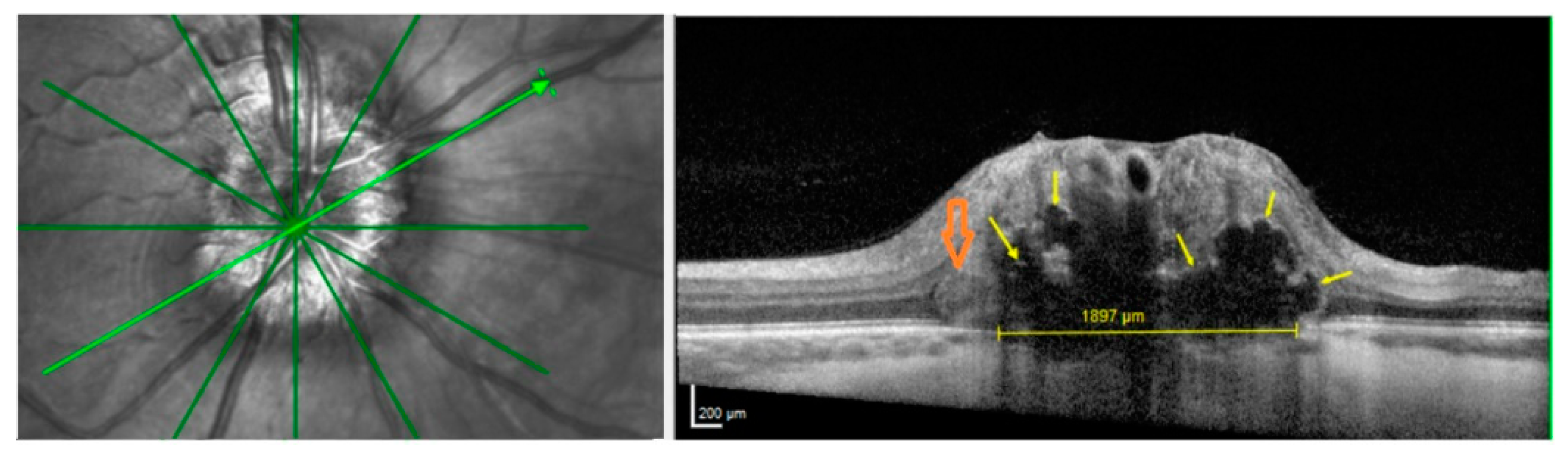
3.2. ODD, HL and PHOMS
3.3. Peripapillary RNFL and Macular GCL
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thurtell, M.J.; Wall, M. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (Pseudotumor Cerebri): Recognition, Treatment, and Ongoing Management. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2013, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004, 24 (Suppl. 1), 9–160. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta, G.M.; Cestari, D.M. An update of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 29, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollan, S.P.; Aguiar, M.; Evison, F.; Frew, E.; Sinclair, A.J. The expanding burden of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Eye 2019, 33, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCluskey, G.; Doherty-Allan, R.; McCarron, P.; Loftus, A.M.; McCarron, L.V.; Mulholland, D.; McVerry, F.; McCarron, M.O. Meta-analysis and systematic review of population-based epidemiological studies in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari-Rafi, A.; Mehdizadeh, R.; Ko, A.W.K.; Ghaffari-Rafi, S.; Leon-Rojas, J.E. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in the United States: Demographic and Socioeconomic Disparities. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilgore, K.P.; Lee, M.S.; Leavitt, J.A.; Mokri, B.; Hodge, D.O.; Frank, R.D.; Chen, J.J. Re-evaluating the Incidence of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension in an Era of Increasing Obesity. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goudie, C.; Shah, P.; McKee, J.; Foot, B.; Kousha, O.; Blaikie, A. The incidence of idiopathic intracranial hypertension in Scotland: A SOSU study. Eye 2019, 33, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durcan, F.J.; Corbett, J.J.; Wall, M. The incidence of pseudotumor cerebri. Population studies in Iowa and Louisiana. Arch. Neurol. 1988, 45, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yri, H.M.; Wegener, M.; Sander, B.; Jensen, R. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is not benign: A long-term outcome study. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johanson, C.E.; Duncan, J.A.; Klinge, P.M.; Brinker, T.; Stopa, E.G.; Silverberg, G.D. Multiplicity of cerebrospinal fluid functions: New challenges in health and disease. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res. 2008, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ljubisavljevic, S.; Trajkovic, J.Z.; Sternic, N.C.; Spasic, M.; Kostic, V.S. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension from the perspective of headache center. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2013, 113, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D′amico, D.; Curone, M.; Ciasca, P.; Cammarata, G.; Melzi, L.; Bussone, G.; Marzoli, S.B. Headache prevalence and clinical features in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH). Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frisén, L. Swelling of the optic nerve head: A staging scheme. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1982, 45, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, W.S.; Wall, M.; McDermott, M.P.; Kupersmith, M.J.; Feldon, S.E. Photographic Reading Center of the Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Treatment Trial (IIHTT): Methods and Baseline Results. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 3292–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Yin, L.-R. The Application of Enhanced Depth Imaging Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Macular Diseases. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupersmith, M.J. Baseline OCT measurements in the idiopathic intracranial hypertension treatment trial, part I: Quality control, comparisons, and variability. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 8180–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malmqvist, L.; Li, X.Q.; Hansen, M.H.; Thomsen, A.K.; Skovgaard, A.M.; Olsen, E.M.; Larsen, M.; Munch, I.C.; Hamann, S. Progression Over 5 Years of Prelaminar Hyperreflective Lines to Optic Disc Drusen in the Copenhagen Child Cohort 2000 Eye Study. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2020, 40, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skougaard, M.; Heegaard, S.; Malmqvist, L.; Hamann, S. Prevalence and histopathological signatures of optic disc drusen based on microscopy of 1713 enucleated eyes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, F.A.; Johnson, G.M.; Johnson, L.N.; Jun, B.; Machan, J.T. Increased Prevalence of Optic Disc Drusen after Papilloedema from Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: On the Possible Formation of Optic Disc Drusen. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2016, 40, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malmqvist, L.; Bursztyn, L.; Costello, F.; Digre, K.; Fraser, J.A.; Fraser, C.; Katz, B.; Lawlor, M.; Petzold, A.; Sibony, P.; et al. The Optic Disc Drusen Studies Consortium Recommendations for Diagnosis of Optic Disc Drusen Using Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2018, 38, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, J.A.; Sibony, P.A.; Petzold, A.; Thaung, C.; Hamann, S. ODDS Consortium Peripapillary Hyper-reflective Ovoid Mass-like Structure (PHOMS): An Optical Coherence Tomography Marker of Axoplasmic Stasis in the Optic Nerve Head. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, F.; Malmqvist, L.; Hamann, S. The Role of Optical Coherence Tomography in Differentiating Optic Disc Drusen from Optic Disc Edema. Asia-Pacific J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 7, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmqvist, L.; Li, X.Q.; Eckmann, C.L.; Skovgaard, A.M.; Olsen, E.M.; Larsen, M.; Munch, I.C.; Hamann, S. Optic Disc Drusen in Children: The Copenhagen Child Cohort 2000 Eye Study. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2018, 38, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, J.B.; Gusek, G.C.; Guggenmoos-Holzmann, I.; Naumann, G.O.H. Optic nerve head drusen associated with abnormally small optic discs. Int. Ophthalmol. 1987, 11, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Malmqvist, L.; Rothenbuehler, S.P.; Hamann, S. OCT based interpretation of the optic nerve head anatomy in young adults with retinal vascular occlusions and ischemic optic neuropathy. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghassibi, M.P.; Chien, J.L.; Abumasmah, R.K.; Liebmann, J.M.; Ritch, R.; Park, S.C. Optic Nerve Head Drusen Prevalence and Associated Factors in Clinically Normal Subjects Measured Using Optical Coherence Tomography. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wågström, J.; Malmqvist, L.; Hamann, S. Optic Nerve Head Blood Flow Analysis in Patients with Optic Disc Drusen Using Laser Speckle Flowgraphy. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.A.; Vandewalle, E.; Neves, C.M.; Stalmans, I. Visual field loss in optic disc drusen patients correlates with central retinal artery blood velocity patterns. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014, 92, e286–e291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, S.G.; Mansour, A.M. Central retinal artery occlusion and optic disc drusen. Eye 1998, 12, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmqvist, L.; Sibony, P.A.; Fraser, C.L.; Wegener, M.; Heegaard, S.; Skougaard, M.; Hamann, S.; Biousse, V.; Bursztyn, L.; Costello, F.; et al. Peripapillary Ovoid Hyperreflectivity in Optic Disc Edema and Pseudopapilledema. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1662–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichi, F.; Romano, S.; Villani, E.; Lembo, A.; Gilardoni, F.; Morara, M.; Ciardella, A.P.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; Nucci, P. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography findings in pediatric tilted disc syndrome. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2014, 252, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No ODD or HL | ODD | HL | PHOMS | No PHOMS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 65.6 | 3.1 | 31.3 | 81.3 | 21.2 |
| Male/female | 2/19 | 0/1 | 0/10 | 0/26 | 2/4 |
| Median age [range] (years) | 30 [22–66] | 24 | 31 [27–49] | 31 [22–66] | 29 [23–49] |
| Median RNFL [range] (µm) | 96 [60–109] | 105/92 | 103 † [55–123] | 96 [60–119] | 98 ^ [55–123] |
| Median GCL [range] (mm3) | 1,07 [0.79–1.34] | 1.26/1.22 | 1.03 †† [0.85–1.35] | 1.07 [0.79–1.35] | 1.07 ^^ [0.97–0.23] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wibroe, E.A.; Malmqvist, L.; Hamann, S. OCT Based Interpretation of the Optic Nerve Head Anatomy and Prevalence of Optic Disc Drusen in Patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH). Life 2021, 11, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060584
Wibroe EA, Malmqvist L, Hamann S. OCT Based Interpretation of the Optic Nerve Head Anatomy and Prevalence of Optic Disc Drusen in Patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH). Life. 2021; 11(6):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060584
Chicago/Turabian StyleWibroe, Elisabeth Arnberg, Lasse Malmqvist, and Steffen Hamann. 2021. "OCT Based Interpretation of the Optic Nerve Head Anatomy and Prevalence of Optic Disc Drusen in Patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH)" Life 11, no. 6: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060584
APA StyleWibroe, E. A., Malmqvist, L., & Hamann, S. (2021). OCT Based Interpretation of the Optic Nerve Head Anatomy and Prevalence of Optic Disc Drusen in Patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH). Life, 11(6), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11060584







