The Role of the Songbird Trade as an Anthropogenic Vector in the Spread of Invasive Non-Native Mynas in Indonesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Potentially Invasive Mynas on Java, Bali and Lombok
2.2. Data Acquisition—Animal Market Surveys
2.3. Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Invasive Non-Native Mynas in Trade
3.2. Determinants of Invasive Non-Native Mynas in Trade
4. Discussion
4.1. Invasive Non-Native Birds in Java, Bali and Lombok
4.2. National Policies and Strategies Concerning Invasive Non-Native Birds
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nijman, V. An overview of international wildlife trade from Southeast Asia. Biodiv. Conserv. 2010, 19, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nijman, V.; Nekaris, K.A.I. The Harry Potter effect: The rise in trade of owls as pets in Java and Bali, Indonesia. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 11, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thạch, H.M.; Le, M.D.; Vũ, N.B.; Panariello, A.; Sethi, G.; Sterling, E.J.; Blair, M.E. Slow loris trade in Vietnam: Exploring diverse knowledge and values. Folia Primatol. 2018, 89, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symes, W.S.; McGrath, F.L.; Rao, M.; Carrasco, L.R. The gravity of wildlife trade. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 218, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.B.C.; Green, J.M.; Prawiradilaga, D.M.; Giam, X.; Hikmatullah, D.; Putra, C.A.; Wilcove, D.S. Using market data and expert opinion to identify overexploited species in the wild bird trade. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 187, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gippet, J.M.; Bertelsmeier, C. Invasiveness is linked to greater commercial success in the global pet trade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2016337118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, T.M.; Lockwood, J.; Cassey, P. Avian Invasions: The Ecology and Evolution of Exotic Birds; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hulme, P.E. Trade, transport and trouble: Managing invasive species pathways in an era of globalization. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, S.; Maraver, A.; Anadón, J.D.; Tella, J.L. A survey of recent introduction events, spread and mitigation efforts of mynas (Acridotheres sp.) in Spain and Portugal. Anim. Biodiv. Conserv. 2015, 38, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.; Yong, D.L. Saving two birds with one stone: Solving the quandary of introduced, threatened species. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vall-llosera, M.; Cassey, P. Leaky doors: Private captivity as a prominent source of bird introductions in Australia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selge, S.; Fischer, A.; van der Wal, R. Public and professional views on invasive non-native species–A qualitative social scientific investigation. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 3089–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.A.; Pescott, O.L.; Peyton, J.; Adriaens, T.; Cottier-Cook, E.J.; Key, G.; Rabitsch, W.; Tricarico, E.; Barnes, D.K.; Baxter, N.; et al. Invasive non-native species likely to threaten biodiversity and ecosystems in the Antarctic Peninsula region. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 2702–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, B.; Zieritz, A.; Adriaens, T.; Bellard, C.; Boets, P.; Britton, J.R.; Newman, J.R.; van Valkenburg, J.L.; Aldridge, D.C. Trans-national horizon scanning for invasive non-native species: A case study in western Europe. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewel, J.J. Invasibility: Lessons from south Florida. Pages 214–230. In Ecology of Biological Invasions of North. America and Hawaii; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Carrete, M.; Tella, J. Wild-bird trade and exotic invasions: A new link of conservation concern? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardador, L.; Tella, J.L.; Anadón, J.D.; Abellán, P.; Carrete, M. The European trade ban on wild birds reduced invasion risks. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, a12631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species: A Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database; Invasive Species Specialist Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Feare, C.J.; Waters, J.; Fenn, S.R.; Larose, C.S.; Retief, T.; Havemann, C.; Ahlen, P.A.; Waters, C.; Little, M.K.; Atkinson, S.; et al. Eradication of invasive common mynas Acridotheres tristis from North Island, Seychelles, with recommendations for planning eradication attempts elsewhere. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2021, 12, 700–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corlett, R.T.; Leven, M.R.; Yong, D.L.; Eaton, J.A.; Round, P.D. Continental Analysis of Invasive Birds: Asia. In Invasive Birds: Global Trends and Impacts; Downs, C.T., Hart, L.A., Eds.; CABI: Cape Town, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.A.; Sodhi, N.S. Southeast Asian invasive birds: Ecology, impact and management. Ornithol. Sci. 2004, 3, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, H.; Collar, N.J.; Lees, A.C.; Moss, A.; Yuda, P.; Marsden, S.J. Spatio-temporal dynamics of consumer demand driving the Asian Songbird Crisis. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 241, a108237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collar, N.J.; Gardner, L.; Jeggo, D.F.; Marcordes, B.; Owen, A.; Pagel, T.; Pes, T.; Vaidl, A.; Wilkinson, R.; Wirth, R. Conservation breeding and the most threatened birds in Asia. Bird. Asia 2012, 18, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chng, S.; Eaton, J.A.; Krishnasamy, K.; Shepherd, C.R.; Nijman, V. In the Market for Extinction: An Inventory of Jakarta’s Bird Markets; TRAFFIC: Petaling Jaya, Malaysia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Whitten, A.J.; Soeriaatmadja, R.S.; Soeriaatmadja, R.E.; Afiff, S.A. Ecology of Java and Bali; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, P.; Ladle, R.J. Developing new policy instruments to regulate consumption of wild birds: Sociodemographic characteristics of bird-keeping in Java and Bali. Oryx 2009, 43, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Bertelsmeier, C.; Luque, G.M.; Courchamp, F. Increase in quantity and quality of suitable areas for invasive species as climate changes. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 27, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Balen, S. Birds on Fragmented Islands: Persistence in the Forests of Java and Bali. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Collar, N.J. Threatened Birds of Asia. The BirdLife International Red Data Book; Birdlife: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, T.M.; Dor, R. The effect of local species composition on the distribution of an avian invader. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, J.A.; van Balen, B.; Brickle, N.W.; Rheindt, F.E. Birds of the Indonesian Archipelago; Lynx: Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Berthouly-Salazar, C.; van Rensburg, B.J.; Le Roux, J.J.; Van Vuuren, B.J.; Hui, C. Spatial sorting drives morphological variation in the invasive bird, Acridotheris tristis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ewart, K.M.; Griffin, A.S.; Johnson, R.N.; Kark, S.; Magory Cohen, T.; Lo, N.; Major, R.E. Two speed invasion: Assisted and intrinsic dispersal of common mynas over 150 years of colonization. J. Biogeogr. 2019, 46, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nijman, V.; Langgeng, A.; Birot, H.; Imron, M.A.; Nekaris, K.A.I. Wildlife trade, captive breeding and the imminent extinction of a songbird. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 15, a00425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basuni, S.; Setiyani, G. Studi perdagangan burung di pasar Pramuka, Jakarta dan teknik penangkapan burung di alam. Media Konserv. 1989, 2, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, S. Sold for a Song: The Trade in Southeast. Asian Non-CITES Birds; TRAFFIC International: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Haryoko, T. Komposisi jenis dan jumlah burung liar yang perdagangkan di Jawa Barat. Ber. Biol. 2010, 10, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, T.M.; McKinney, M.; Kark, S.; Dor, R. Global invasion in progress: Modeling the past, current and potential global distribution of the common myna. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, F.; Saba, M.; Alshamlih, M. Anthropogenic not climatic correlates are the main drivers of expansion of non-native common myna Acridotheres tristis in Jordan. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2021, 12, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsalu, T.; Vilo, J. ClustVis: A web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using Principal Component Analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.M. Glmmtmb Balances Speed and Flexibility Among Packages for Zero-inflated Generalized Linear Mixed Modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartig, J. DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level/Mixed) Regression Models. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/DHARMa (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Hernández-Brito, D.; Carrete, M.; Popa-Lisseanu, A.G.; Ibáñez, C.; Tella, J.L. Crowding in the city: Losing and winning competitors of an invasive bird. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Cassey, P.; Blackburn, T.M. The wildlife pet trade as a driver of introduction and establishment in alien birds in Taiwan. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djuwantoko. Trade Traffic and Management of Wild Birds and Mammals in Semarang and Yogyakarta, Central Java, Indonesia. Master’s Thesis, University of the Philippines, Los Banos, Philippines, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, G.; Farmer, M. Reducing the risk of biological invasion by creating incentives for pet sellers and owners to do the right thing. J. Herpetol. 2011, 45, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soehartono, T.; Mardiastuti, A. CITES Implementation in Indonesia; Nagao Natural Environment Foundation: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Naysmith, S. Observations from a live bird market in Indonesia following a contained outbreak of avian influenza A (H5N1). EcoHealth 2014, 11, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelps, J.; Webb, E.L.; Bickford, D.; Nijman, V.; Sodhi, N.S. Boosting CITES. Science 2010, 330, 1752–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmadi, Y.Y. BBKSDA Sumut Sita Dan Lepas Ribuan Jalak, Murai Ke Habitatnya; Betahita: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ardiyanta, A. Ratusan Ekor Burung Dan Satwa Liar Dilepas Lairkan Ke Habitat Asal; RRI Bandar Lampung: Lampung, Indonesia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Eni. BKSDA-SKP Parepare Lepas Ratusan Burung Jalak Kerbau Kembali Ke Habitatnya; AkarBerita: Sulawesi Selatan, Indonesia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fachri, F. BKSDA Lepas 32 Ekor Burung Jalak Kerbau Dari Perdagangan Buring; Republika: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous, Balai Besar KSDA. Riau Bersama Para Pihak Lepas Liarkan 2 Ekor Burung Elang Dan 10 Ekor Burung Jalak Kebo; BKSDA: Pekanbaru, Indonesia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huda, K. Ratusan Burung Jalak Kerbau Dilepas Ke Alam; Koran Jakarta: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yuwono, A.; Awang, S.A.; Harpini, B.; Prasmadji, N. Strategi Nasional dan Arahan Rencana Aksi Pengelolaan Jenis Asing Invasif di Indonesia; Ministry of Environment and Forestry: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2015.
- Partasasmita, R.; Supian, S.; Adiana, G.; Juahir, H.; Yusra, A.I.; Umar, R. Status of population, occupation and seasonal habitat displacement of alien bird species in West Java Tropical Forest, Indonesia. J. Fundam. Appl. Sc. 2018, 10, 552–564. [Google Scholar]
- Nijman, V.; Langgeng, A.; Ardiansyah, A.; Imron, M.A.; Nekaris, K.A.I. Grosbeak starling Scissirostrum dubium in the cage-bird trade in Indonesia. BirdingASIA 2018, 30, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Prawira, A.M.; Taufiqurrahman, I.; Iqbal, M.; Wicaksono, G. Records of grosbeak starling Scissirostrum dubium from Kalimantan, Borneo, and its widespread occurrence on Java. BirdingASIA 2018, 29, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
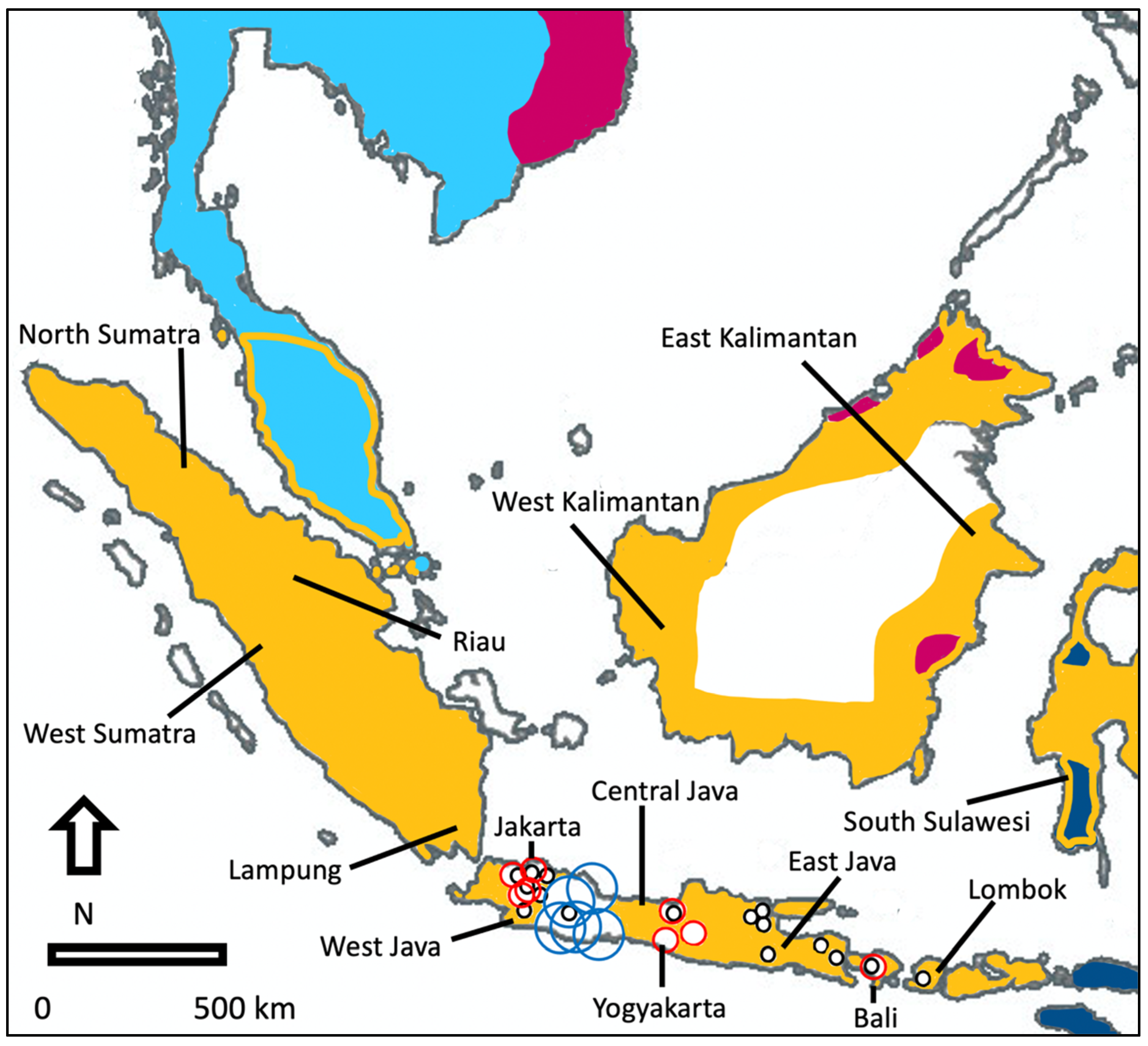


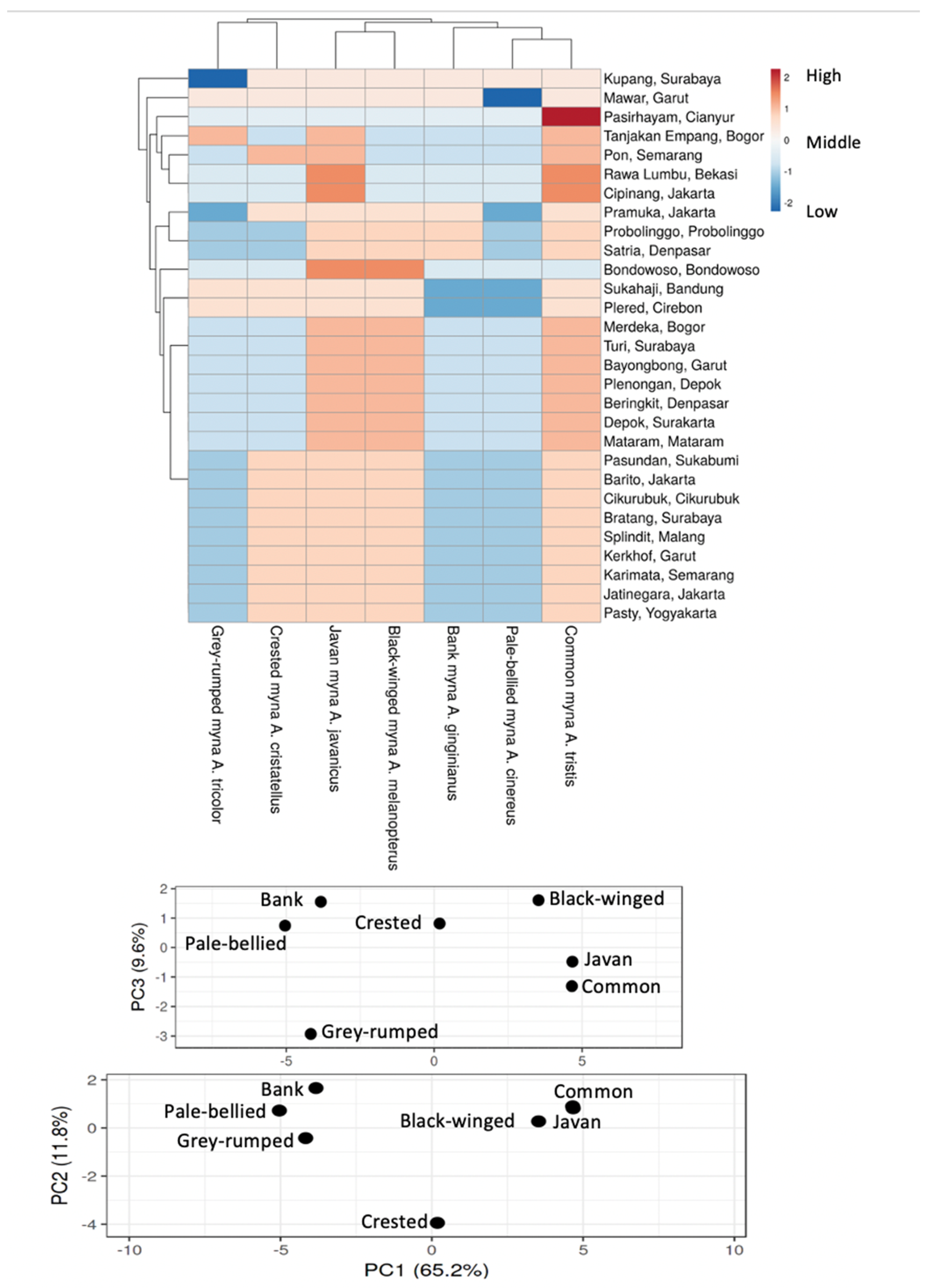

| Species | Native Range | Survey Region for Invasive Species | Survey Effort (Number of Markets) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank myna (A. ginginianus) | South Asia | Java, Bali, Lombok | 241 (28) |
| Black-winged myna (A. melanopterus) | Java minus easternmost part | Easternmost Java, Bali, Lombok | 21 (5) |
| Common myna (A. tristis) | Asia, incl. mainland SE Asia | Java, Bali, Lombok | 241 (28) |
| Crested myna (A. cristatellus) | China, Indochina | Java, Bali, Lombok | 241 (28) |
| Grey-rumped myna (A. tricolor) | Bali, Lombok | Java | 226 (25) |
| Javan myna (A. javanicus) | Java and Bali | Lombok | 3 (1) |
| Pale-bellied myna (A. cinereus) | South Sulawesi | Java, Bali, Lombok | 241 (28)) |
| Market, City (Number of Surveys) | javan | melan | trico | ciner | gingi | trist | crist | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pramuka, Jakarta (14) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0.4 (6) | 174.3 (2441) | 9.5 (133) | 184.3 |
| Depok, Surakarta, C. Java (6) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 142.0 (852) | 0 | 142.0 |
| Mataram, Lombok (4) | 100.5 (402) | 10.5 (42) | - | 0 | 0 | 3.0 (12) | 0 | 115.0 |
| Jatinegara, Jakarta (10) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33.7 (337) | 1.1 (11) | 34.8 |
| Pasty, Yogyakarta (6) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 23.3 (140) | 0.8 (5) | 24.2 |
| Sukahaji, Bandung, W. Java (23) | - | - | 1.3 (29) | 0 | 0 | 19.2 (443) | 2.9 (66) | 23.4 |
| Plered, Cirebon, W. Java (17) | - | - | 0.6 (10) | 0 | 0 | 21.0 (357) | 0.4 (7) | 22.0 |
| Karimata, Semarang, C. Java (7) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15.0 (105) | 2.0 (14) | 17.0 |
| Pon, Semarang, C. Java (3) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11.0 (33) | 0.7 (2) | 11.7 |
| Kerkhof, Garut, W. Java (35) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.7 (374) | 0.8 (29) | 11.5 |
| Splindit, Malang, E. Java (3) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9.7 (29) | 0.3 (1) | 10.0 |
| Bratang, Surabaya, E. Java (3) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6.0 (18) | 2.0 (6) | 8.0 |
| Cikurubuk, Tasikmalaya W Java (21) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.5 (157) | 0.1 (1) | 7.5 |
| Kupang, Surabaya, E. Java (3) | - | - | 0 | 1.0 (3) | 0.7 (2) | 2.7 (8) | 2.7 (8) | 7.0 |
| Mawar, Garut, W. Java (26) | - | - | 0.5 (13) | 0 | 0.1 (1) | 5.7 (149) | 0.3 (7) | 6.5 |
| Probolinggo, E. Java (3) | - | 4.7 (14) | 0 | 0 | 0.3 (1) | 1.3 (4) | 0 | 6.3 |
| Satria, Denpasar, Bali (7) | - | 4.7 (33) | - | 0 | 0.3 (2) | 1.3 (9) | 0 | 6.3 |
| Beringkit, Denpasar, Bali (5) | - | 0.8 (4) | - | 0 | 0 | 4.2 (21) | 0 | 5.0 |
| Plenongan, Depok, W. Java. (3) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.0 (12) | 0 | 4.0 |
| Barito, Jakarta (15) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.8 (42) | 0.6 (9) | 3.4 |
| Pasundan, Sukabumi, W. Java (4) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.5 (6) | 0.5 (2) | 2.0 |
| Bayongbong, Garut, W. Java (3) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.0 (6) | 0 | 2.0 |
| Rawa Lumbu, Bekasi, W. Java (3) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.0 (3) | 0 | 1.0 |
| Pasirhayam, Cianyur, W. Java (3) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.0 (3) | 0 | 1.0 |
| TanjakanEmpang, Bogor, W. Java (6) | - | - | 0.3 (2) | 0 | 0 | 0.3 (2) | 0 | 0.7 |
| Turi, Surabaya, E. Java (3) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.7 (5) | 0 | 0.7 |
| Bondowoso, E. Java (3) | - | 0.7 (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.7 |
| Merdeka, Bogor, W. Java (8) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 (2) | 0 | 0.3 |
| Cipinang, Jakarta (3) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 (1) | 0 | 0.3 |
| Kebayoran Lama, Jakarta (4) | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total outside range | 402 | 95 | 74 | 3 | 12 | 5569 | 301 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nijman, V.; Campera, M.; Imron, M.A.; Ardiansyah, A.; Langgeng, A.; Dewi, T.; Hedger, K.; Hendrik, R.; Nekaris, K.A.-I. The Role of the Songbird Trade as an Anthropogenic Vector in the Spread of Invasive Non-Native Mynas in Indonesia. Life 2021, 11, 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11080814
Nijman V, Campera M, Imron MA, Ardiansyah A, Langgeng A, Dewi T, Hedger K, Hendrik R, Nekaris KA-I. The Role of the Songbird Trade as an Anthropogenic Vector in the Spread of Invasive Non-Native Mynas in Indonesia. Life. 2021; 11(8):814. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11080814
Chicago/Turabian StyleNijman, Vincent, Marco Campera, Muhammad Ali Imron, Ahmad Ardiansyah, Abdullah Langgeng, Tungga Dewi, Katherine Hedger, Rifqi Hendrik, and K. Anne-Isola Nekaris. 2021. "The Role of the Songbird Trade as an Anthropogenic Vector in the Spread of Invasive Non-Native Mynas in Indonesia" Life 11, no. 8: 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11080814
APA StyleNijman, V., Campera, M., Imron, M. A., Ardiansyah, A., Langgeng, A., Dewi, T., Hedger, K., Hendrik, R., & Nekaris, K. A. -I. (2021). The Role of the Songbird Trade as an Anthropogenic Vector in the Spread of Invasive Non-Native Mynas in Indonesia. Life, 11(8), 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11080814






