Computational Insights into the Interaction between Cytoadherence Receptor gC1qR and the DBLβ12 Domain of a Plasmodium falciparum PfEMP1 Ligand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Data Retrieval
- Identification of DBLβ12 Domain in PfEMP1 Protein
- Molecular Modeling of the DBLβ12 Domain
- Protein–Protein Docking
- Analysis of Protein–Protein Complex
- Sequence Alignment Analysis
- Molecular Dynamic Simulation
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Model of DBLβ12 Domain
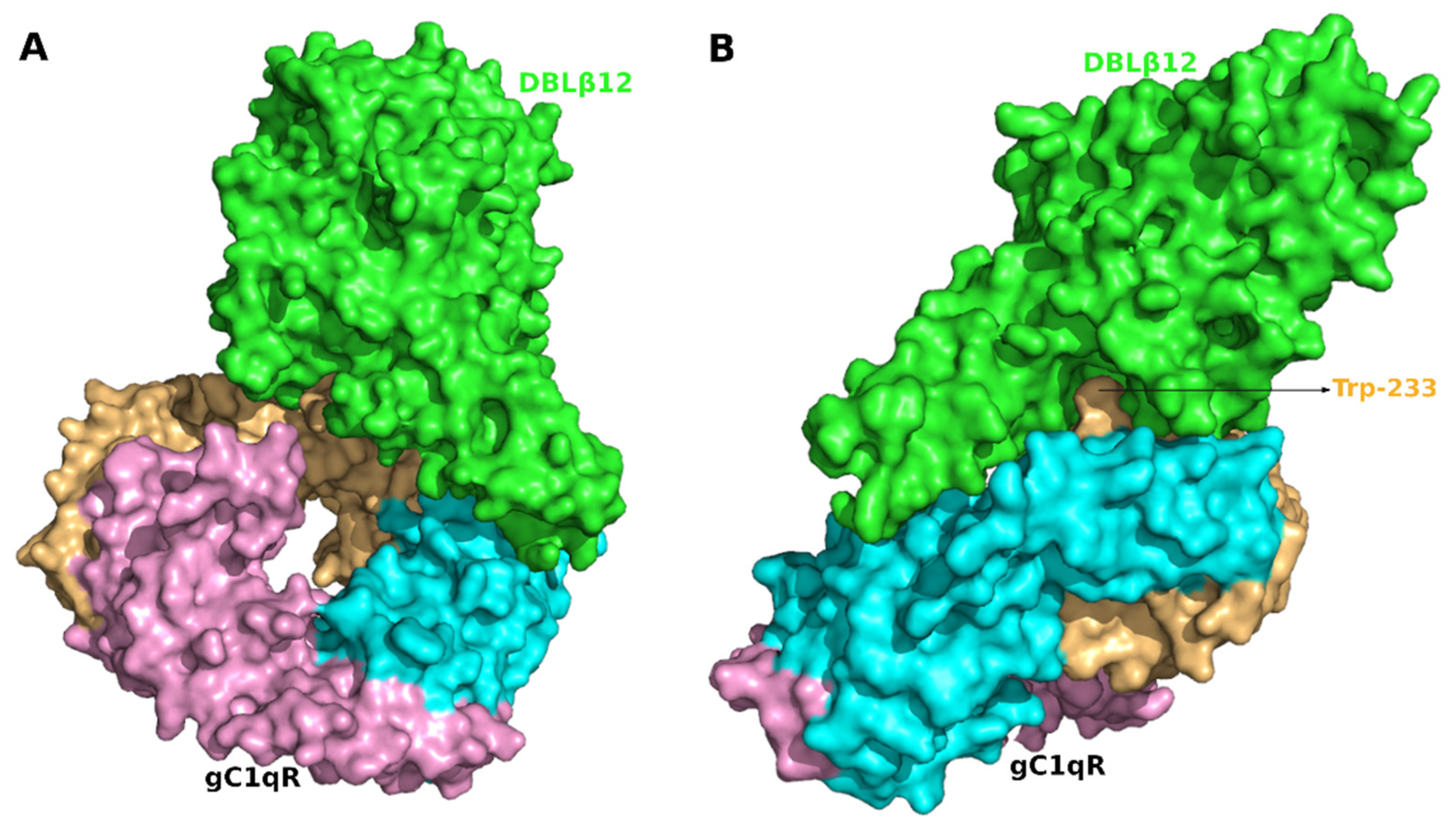
3.2. Molecular Recognition of Human Receptor gC1qR by the DBLβ12 Domain
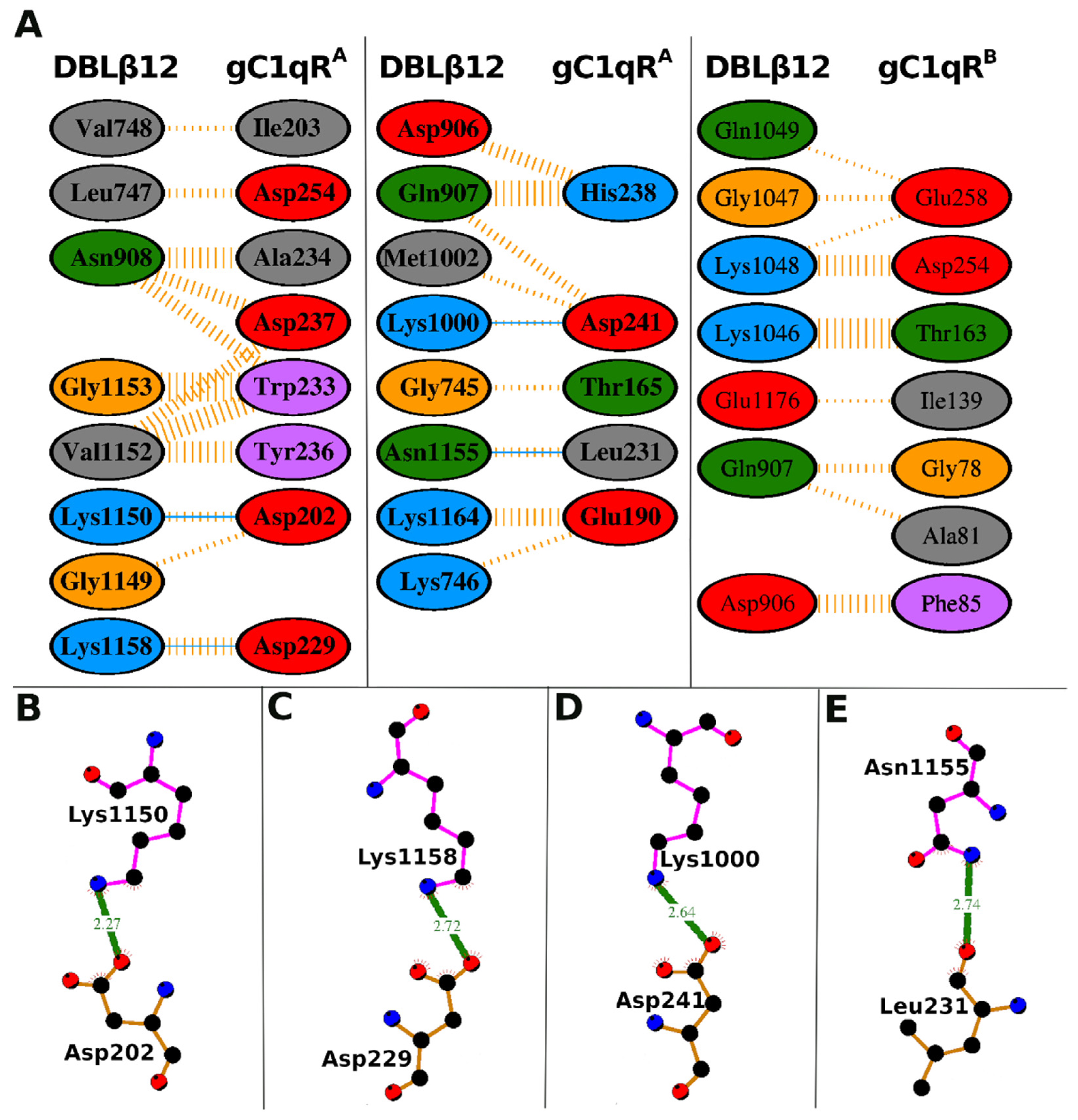
3.3. Interface Area and Interacting Residues of DBLβ12-gC1qR Complex
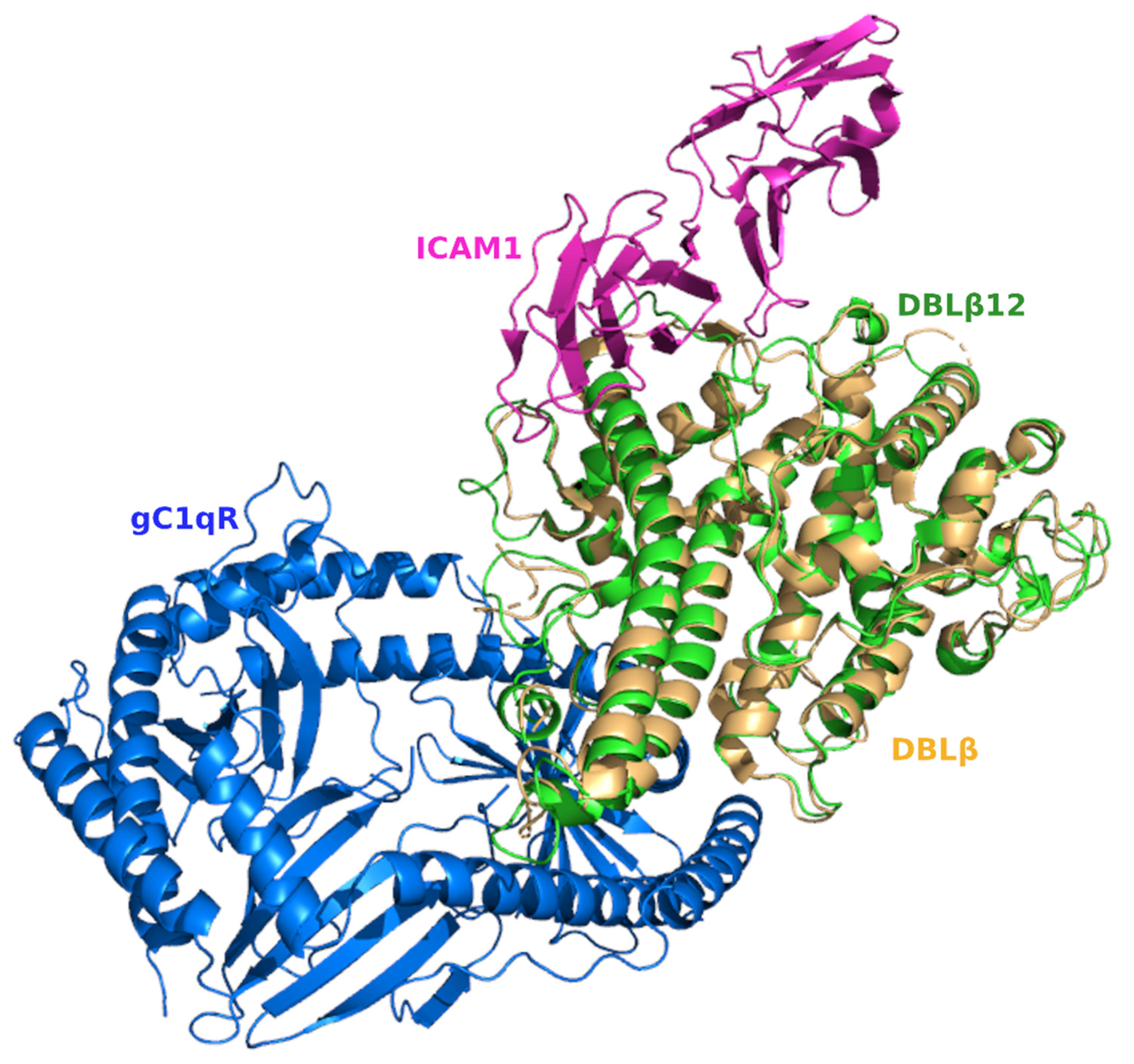
3.4. Comparative Analysis of gC1qR-Binding Site and ICAM1 Binding Sites in DBL Domains
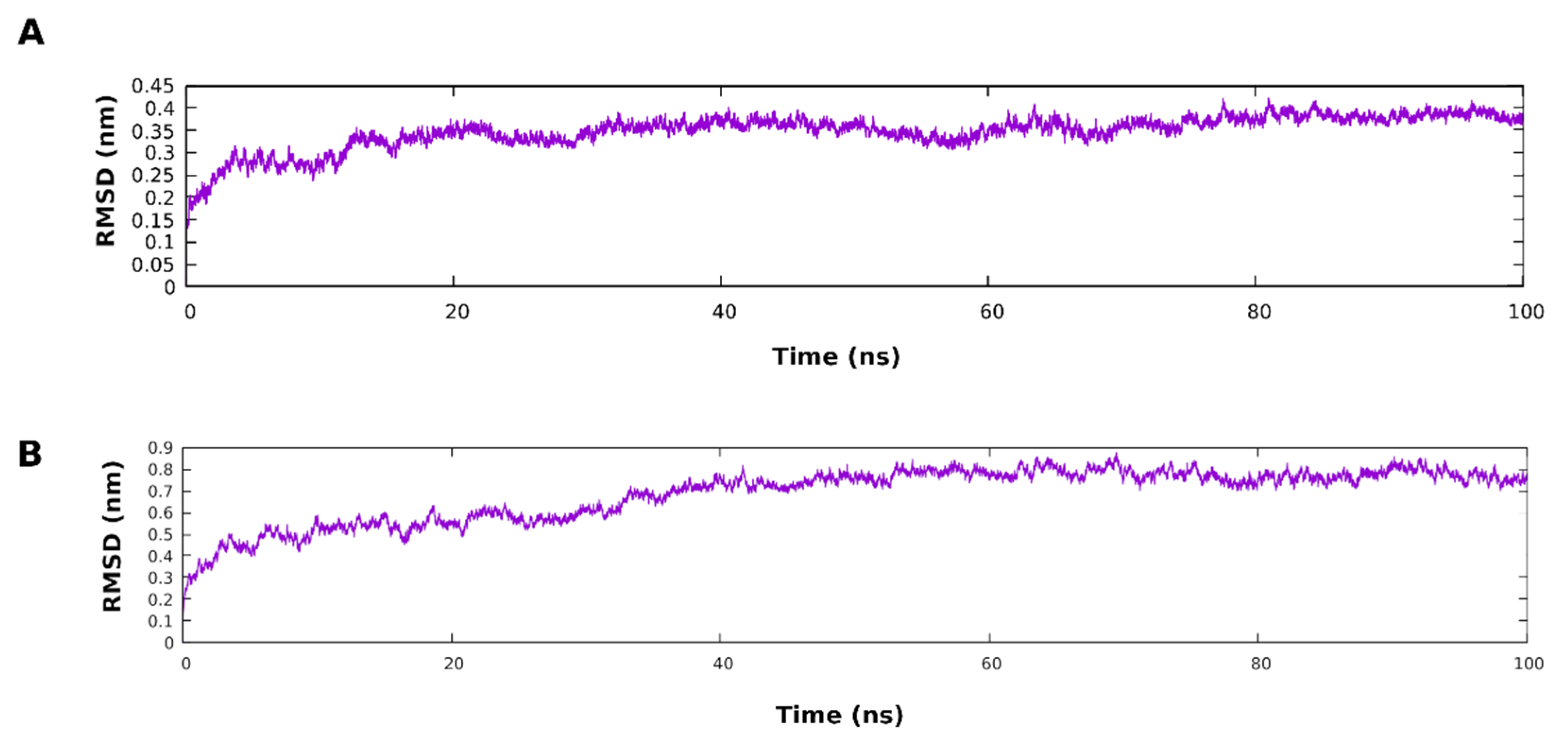
3.5. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- World Malaria Report 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Turner, G.D.; Morrison, H.; Jones, M.; Davis, T.M.; Looareesuwan, S.; Buley, I.D.; Gatter, K.C.; Newbold, C.I.; Pukritayakamee, S.; Nagachinta, B. An immunohistochemical study of the pathology of fatal malaria. Evidence for widespread endothelial activation and a potential role for intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in cerebral sequestration. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castillo, P.; Menéndez, C.; Mayor, A.; Carrilho, C.; Ismail, M.R.; Lorenzoni, C.; Machungo, F.; Osman, N.; Quintó, L.; Romagosa, C.; et al. Massive Plasmodium falciparum visceral sequestration: A cause of maternal death in Africa. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.R.; Adams, Y.; Hviid, L. Cerebral Plasmodium falciparum malaria: The role of PfEMP1 in its pathogenesis and immunity, and PfEMP1-based vaccines to prevent it. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 293, 230–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, M.; Duffy, P.E. Designing a VAR2CSA-based vaccine to prevent placental malaria. Vaccine 2015, 33, 7483–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockenhouse, C.F.; Tandon, N.N.; Magowan, C.; Jamieson, G.A.; Chulay, J.D. Identification of a platelet membrane glycoprotein as a falciparum malaria sequestration receptor. Science 1989, 243, 1469–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendt, A.R.; Simmons, D.L.; Tansey, J.; Newbold, C.I.; Marsh, K. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is an endothelial cell adhesion receptor for Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 1989, 341, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogerson, S.J.; Chaiyaroj, S.C.; Ng, K.; Reeder, J.C.; Brown, G.V. Chondroitin sulfate A is a cell surface receptor for Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.; Lavstsen, T.; Berger, S.S.; Wang, C.W.; Petersen, J.E.; Avril, M.; Brazier, A.J.; Freeth, J.; Jespersen, J.S.; Nielsen, M.A.; et al. Severe malaria is associated with parasite binding to endothelial protein C receptor. Nature 2013, 498, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.K.; Hafiz, A.; Banerjee, B.; Kim, K.S.; Datta, K.; Chitnis, C.E. Plasmodium falciparum uses gC1qR/HABP1/p32 as a receptor to bind to vascular endothelium and for platelet-mediated clumping. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.Z.; Heatwole, V.M.; Wertheimer, S.P.; Guinet, F.; Herrfeldt, J.A.; Peterson, D.S.; Ravetch, J.A.; Wellems, T.E. The large diverse gene family var encodes proteins involved in cytoadherence and antigenic variation of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Cell 1995, 82, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, P.C.; Lowe, B.S.; Kortok, M.; Molyneux, C.S.; Newbold, C.I.; Marsh, K. Parasite antigens on the infected red cell surface are targets for naturally acquired immunity to malaria. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikowski, R.; Frank, M.; Deitsch, K. Mutually exclusive expression of virulence genes by malaria parasites is regulated independently of antigen production. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavstsen, T.; Salanti, A.; Jensen, A.T.; Arnot, D.E.; Theander, T.G. Sub-grouping of Plasmodium falciparum 3D7 var genes based on sequence analysis of coding and non-coding regions. Malar. J. 2003, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rask, T.S.; Hansen, D.A.; Theander, T.G.; Gorm Pedersen, A.; Lavstsen, T. Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 diversity in seven genomes--divide and conquer. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayor, A.; Hafiz, A.; Bassat, Q.; Rovira-Vallbona, E.; Sanz, S.; Machevo, S.; Aguilar, R.; Cisteró, P.; Sigaúque, B.; Menéndez, C.; et al. Association of severe malaria outcomes with platelet-mediated clumping and adhesion to a novel host receptor. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, A.; Adams, Y.; Ghumra, A.; Lindergard, G.; Buchan, C.C.; Andisi, C.; Bull, P.C.; Mok, S.; Gupta, A.P.; Wang, C.W.; et al. A subset of group A-like var genes encodes the malaria parasite ligands for binding to human brain endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1772–E1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peerschke, E.I.; Ghebrehiwet, B. The contribution of gC1qR/p33 in infection and inflammation. Immunobiology 2007, 212, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerschke, E.I.; Brandwijk, R.J.; Dembitzer, F.R.; Kinoshita, Y.; Ghebrehiwet, B. Soluble gC1qR in Blood and Body Fluids: Examination in a Pancreatic Cancer Patient Cohort. Int. J. Cancer Res. Mol. Mech. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, P.D.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Peerschke, E.I.; Ghebrehiwet, B. The C1q-binding cell membrane proteins cC1q-R and gC1q-R are released from activated cells: Subcellular distribution and immunochemical characterization. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 84, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Ji, Y.; Valentino, A.; Pednekar, L.; Ramadass, M.; Habiel, D.; Kew, R.R.; Hosszu, K.H.; Galanakis, D.K.; Kishore, U.; et al. Soluble gC1qR is an autocrine signal that induces B1R expression on endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, A. gC1qR Mediated Receptor-Ligand Interactions in Plasmodium falciparum Malaria. Ph.D. Thesis, Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi, India, 25 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Magallón-Tejada, A.; Machevo, S.; Cisteró, P.; Lavstsen, T.; Aide, P.; Rubio, M.; Jiménez, A.; Turner, L.; Valmaseda, A.; Gupta, H.; et al. Cytoadhesion to gC1qR through Plasmodium falciparum Erythrocyte Membrane Protein 1 in Severe Malaria. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1006011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdar, W.S. Scoring residue conservation. Proteins 2002, 48, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, K.; Rehan, M.; Lynn, A.M.; Prasad, R. Employing information theoretic measures and mutagenesis to identify residues critical for drug-proton antiport function in Mdr1p of Candida albicans. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Dos Santos, R.N.; Oliva, G.; Andricopulo, A.D. Molecular docking and structure-based drug design strategies. Molecules 2015, 20, 13384–13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehan, M. Anticancer compound XL765 as PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor: A structural insight into the inhibitory mechanism using computational approaches. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Release 52. Available online: https://plasmodb.org/plasmo/app (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Pfam 34.0. Available online: http://pfam.xfam.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Hodsdon, M.E.; Ponder, J.W.; Cistola, D.P. The NMR solution structure of intestinal fatty acid-binding protein complexed with palmitate: Application of a novel distance geometry algorithm. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 264, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Inbar, Y.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. PatchDock and SymmDock: Servers for rigid and symmetric docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W363–W367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrusier, N.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. FireDock: Fast interaction refinement in molecular docking. Proteins 2007, 69, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hema, K.; Ahamad, S.; Joon, H.K.; Pandey, R.; Gupta, D. Atomic Resolution Homology Models and Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Plasmodium falciparum Tubulins. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 17510–17522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaira, B.G.; Slater, A.; McCrae, K.R.; Dreveny, I.; Sumya, U.; Mutch, N.J.; Searle, M.; Emsley, J. Factor XII and kininogen asymmetric assembly with gC1qR/C1QBP/P32 is governed by allostery. Blood 2020, 136, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, D.P.; Samudrala, R.; Smith, J.D. Disguising itself—Insights into Plasmodium falciparum binding and immune evasion from the DBL crystal structure. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 148, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittlesen, D.J.; Chianese-Bullock, K.A.; Yao, Z.Q.; Braciale, T.J.; Hahn, Y.S. Interaction between complement receptor gC1qR and hepatitis C virus core protein inhibits T-lymphocyte proliferation. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Jesty, J.; Xu, S.; Vinayagasundaram, R.; Vinayagasundaram, U.; Ji, Y.; Valentino, A.; Hosszu, K.K.; Mathew, S.; Joseph, K.; et al. Structure-function studies using deletion mutants identify domains of gC1qR/p33 as potential therapeutic targets for vascular permeability and inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2011, 2, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Jesty, J.; Peerschke, E.I. gC1q-R/p33: Structure-function predictions from the crystal structure. Immunobiology 2002, 205, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerschke, E.I.; Ghebrehiwet, B. cC1qR/CR and gC1qR/p33: Observations in cancer. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 61, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, T.; Liu, P. Globular C1q Receptor (gC1qR/p32/HABP1) Suppresses the Tumor-Inhibiting Role of C1q and Promotes Tumor Proliferation in 1q21-Amplified Multiple Myeloma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanti, A.; Clausen, T.M.; Agerbæk M, Ø.; Al Nakouzi, N.; Dahlbäck, M.; Oo, H.Z.; Lee, S.; Gustavsson, T.; Rich, J.R.; Hedberg, B.J.; et al. Targeting Human Cancer by a Glycosaminoglycan Binding Malaria Protein. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Protein | Status of the Residues in Ramachandran Plot | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Most Favourable | Additional Allowed | Generously Allowed | Disallowed | |
| Template | 89.0% | 10.3% | 0.5% | 0.3% |
| Model | 87.3% | 10.4% | 2.0% | 0.3% |
| DBLβ12 Residues | gC1qR Residues | Hydrogen Bonds | Non-Bonded Contacts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gly-745 | Thr-165 (A) | 1 | |
| Lys-746 | Glu-190 (A) | 1 | |
| Leu-747 | Asp-254 (A) | 2 | |
| Val-748 | Ile-203 (A) | 1 | |
| Asp-906 | His-238 (A) | 3 | |
| Gln-907 | His-238 (A) | 6 | |
| Gln-907 | Asp-241 (A) | 2 | |
| Asn-908 | Asp-237 (A) | 3 | |
| Asn-908 | Trp-233 (A) | 3 | |
| Asn-908 | Ala-234 (A) | 5 | |
| Lys-1000 | Asp-241 (A) | 1 | 1 |
| Met-1002 | Asp-241 (A) | 1 | |
| Gly-1149 | Asp-202 (A) | 1 | |
| Lys-1150 | Asp-202 (A) | 1 | 2 |
| Val-1152 | Trp-233 (A) | 5 | |
| Val-1152 | Tyr-236 (A) | 5 | |
| Val-1152 | Asp-237 (A) | 3 | |
| Gly-1153 | Trp-233 (A) | 7 | |
| Asn-1155 | Leu-231 (A) | 1 | 2 |
| Lys-1158 | Asp-229 (A) | 1 | 4 |
| Lys-1164 | Glu-190 (A) | 4 | |
| Asp-906 | Phe-85 (B) | 7 | |
| Gln-907 | Gly-78 (B) | 3 | |
| Gln-907 | Ala-81 (B) | 2 | |
| Lys-1046 | Thr-163 (B) | 12 | |
| Gly-1047 | Glu-258 (B) | 2 | |
| Lys-1048 | Glu-258 (B) | 1 | |
| Lys-1048 | Asp-254 (B) | 8 | |
| Gln-1049 | Glu-258 (B) | 1 | |
| Glu-1176 | Ile-139 (B) | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakri, R.; Rehan, M.; Shamshad, H.; Hafiz, A. Computational Insights into the Interaction between Cytoadherence Receptor gC1qR and the DBLβ12 Domain of a Plasmodium falciparum PfEMP1 Ligand. Life 2021, 11, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090993
Bakri R, Rehan M, Shamshad H, Hafiz A. Computational Insights into the Interaction between Cytoadherence Receptor gC1qR and the DBLβ12 Domain of a Plasmodium falciparum PfEMP1 Ligand. Life. 2021; 11(9):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090993
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakri, Rowaida, Mohd Rehan, Hina Shamshad, and Abdul Hafiz. 2021. "Computational Insights into the Interaction between Cytoadherence Receptor gC1qR and the DBLβ12 Domain of a Plasmodium falciparum PfEMP1 Ligand" Life 11, no. 9: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090993
APA StyleBakri, R., Rehan, M., Shamshad, H., & Hafiz, A. (2021). Computational Insights into the Interaction between Cytoadherence Receptor gC1qR and the DBLβ12 Domain of a Plasmodium falciparum PfEMP1 Ligand. Life, 11(9), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090993





