Ameliorative Effect of D-Carvone against Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Injury in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Acquisition and Ethical Approval
2.2. Hep I/R Injury Procedure
2.3. Experimental Design and Sample Obtainment
2.4. Assessment of Liver Function Parameters
2.5. Assessment of Parameters in Liver Tissues
2.5.1. Histopathological and Immunohistochemistry Investigations
2.5.2. Assessment of Hepatic Oxidative Stress Status
2.5.3. Gene Expression Experiments (Real-Time PCR)
2.5.4. Determination of Inflammation and Apoptotic Signaling Markers
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
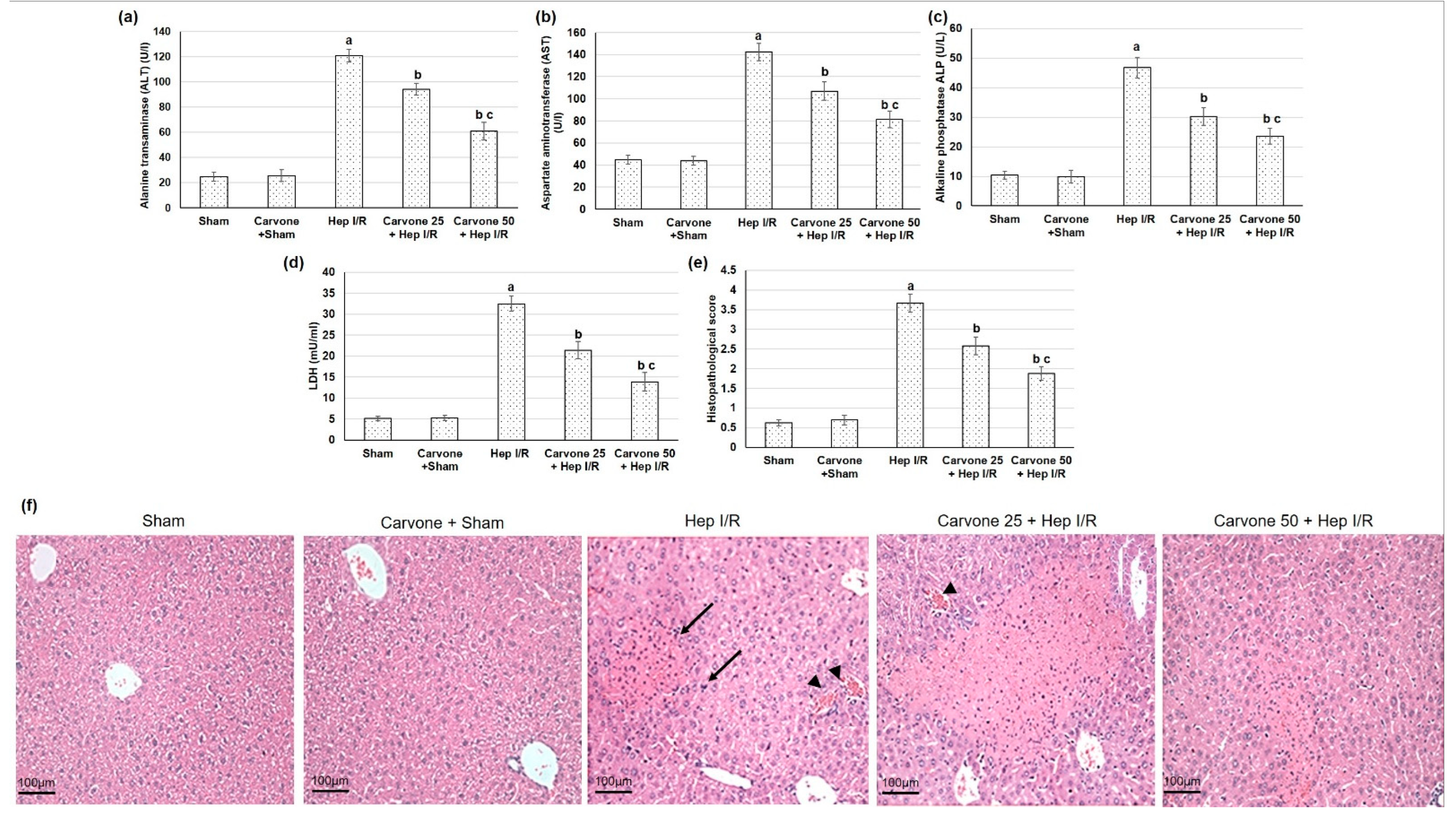
3.1. D-Carvone Pretreatment Improved Hepatic Function Tests in Hep I/R
3.2. Histopathological Examination
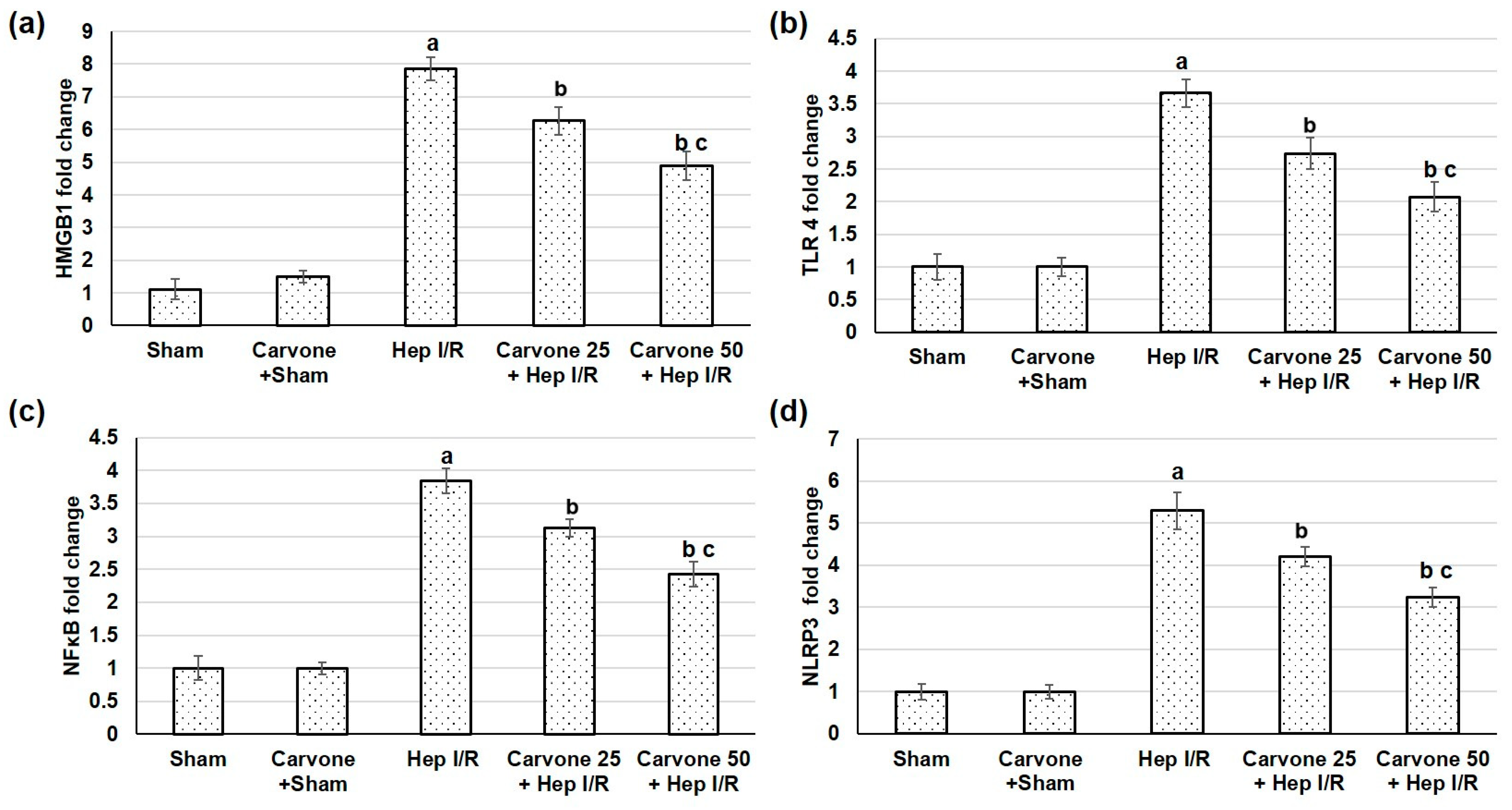
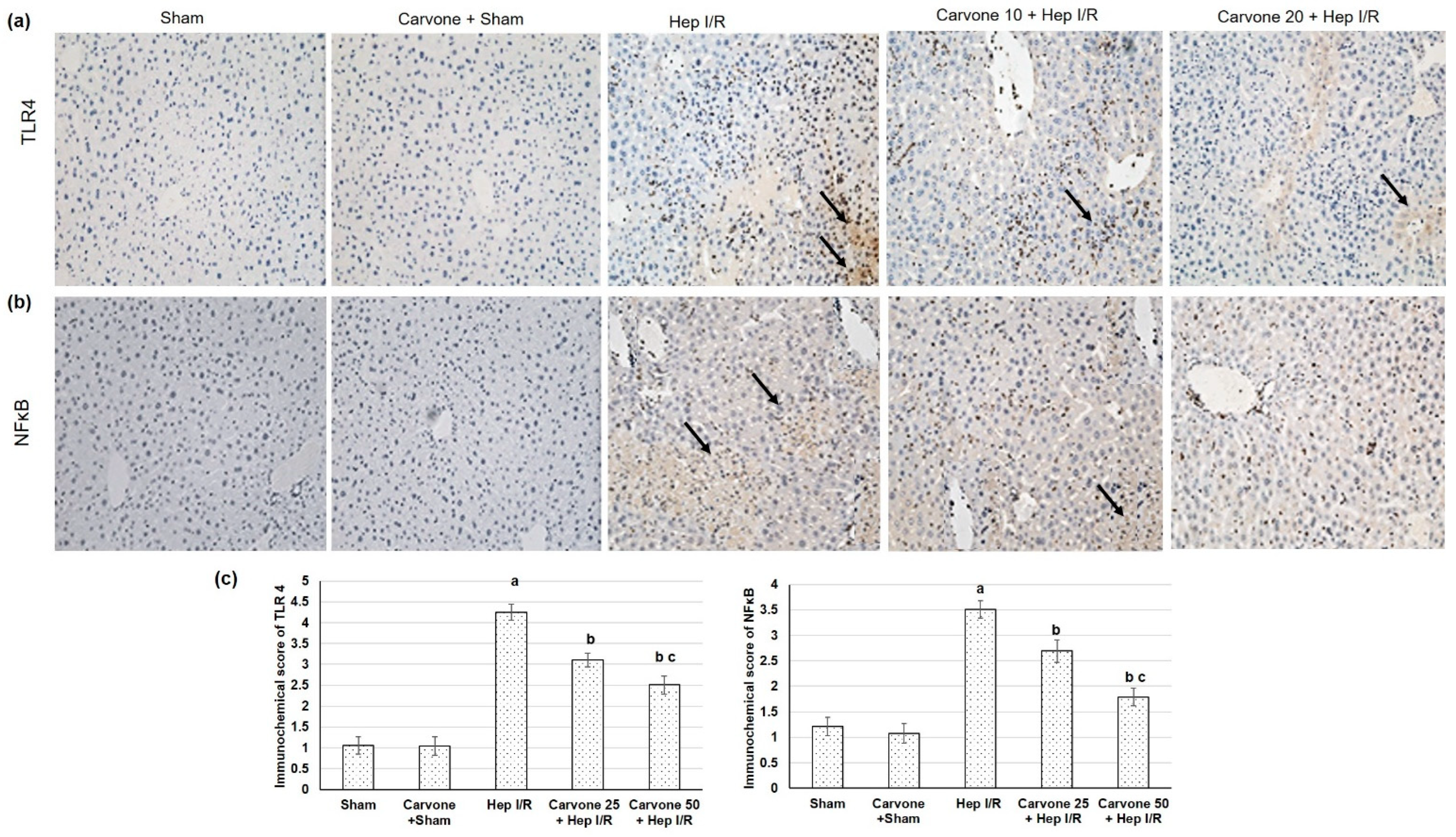
3.3. D-Carvone Pretreatment Reduced HMGB1/TLR4/NFκB/NLP3 Signaling in Hep I/R
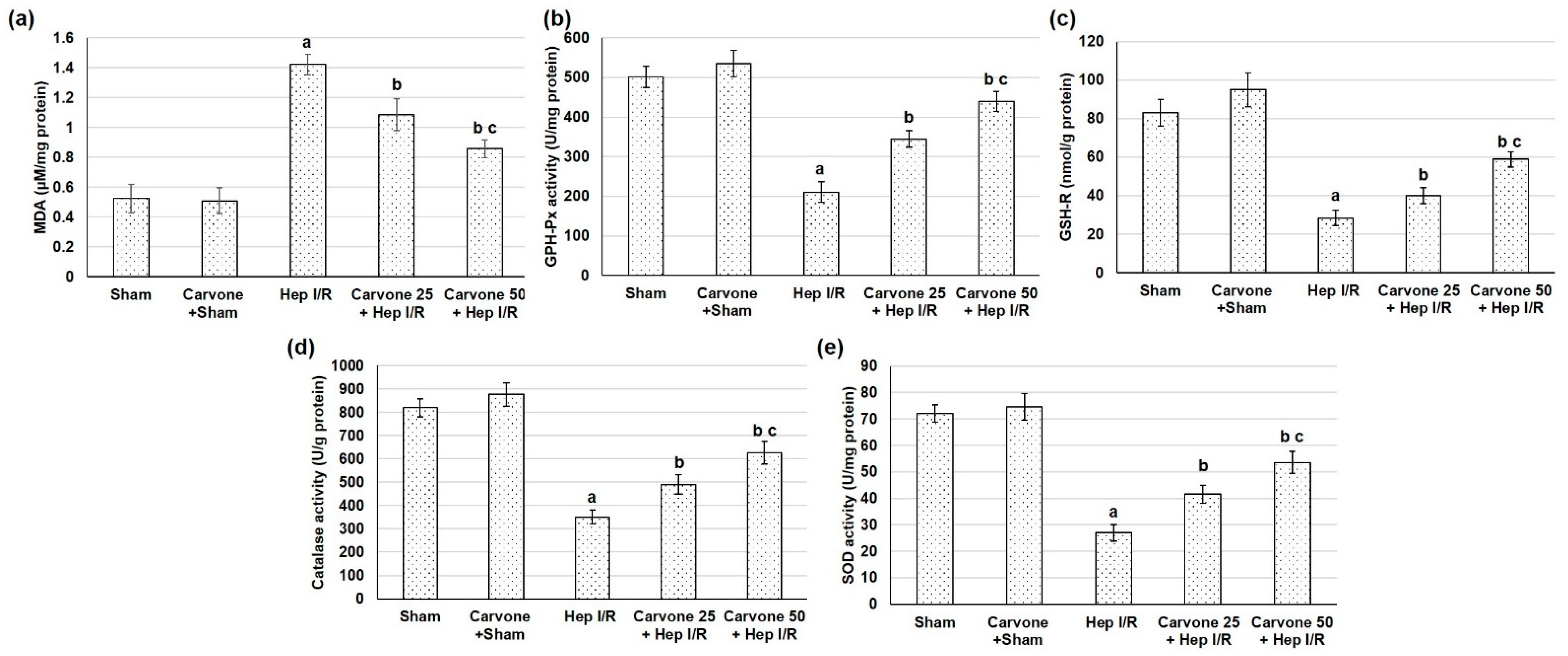
3.4. D-Carvone Pretreatment Improved Anti-Oxidant Capacity in Hep I/R
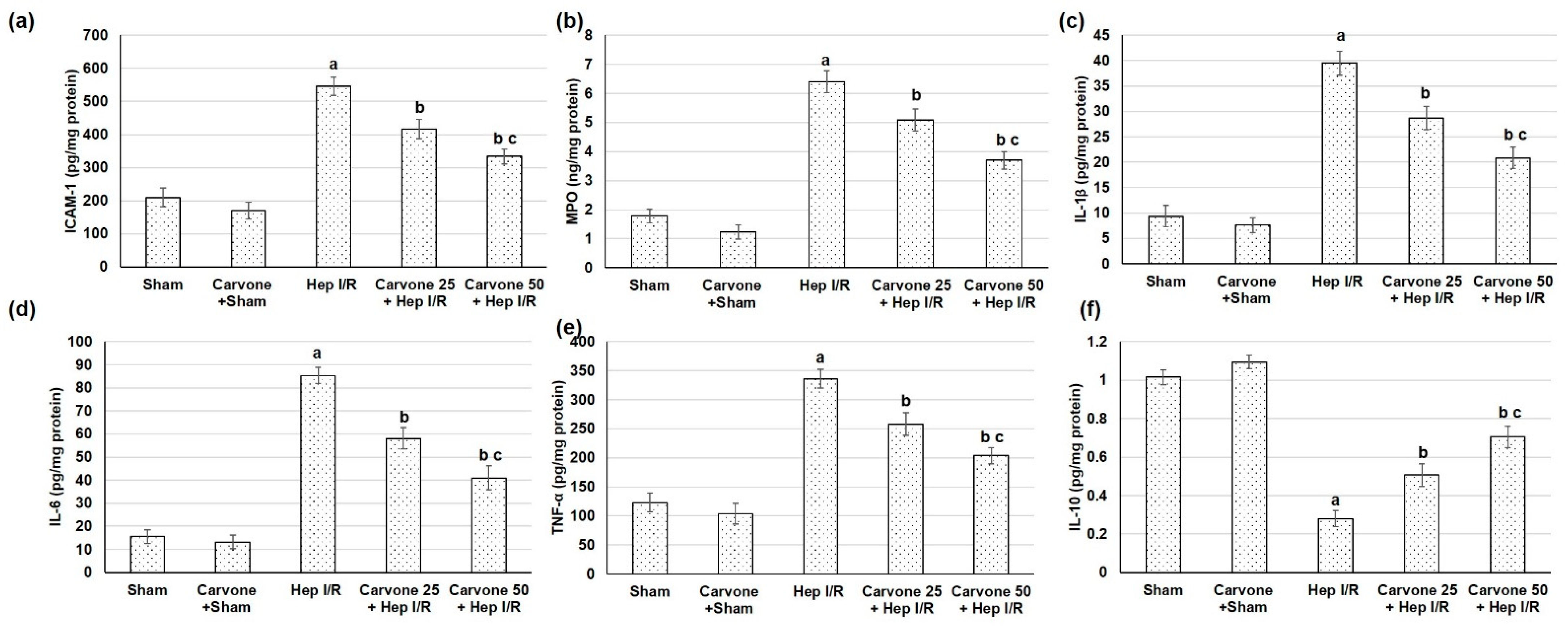
3.5. D-Carvone Pretreatment Reduced Neutrophils Infiltration and Inflammation Associated with Hep I/R
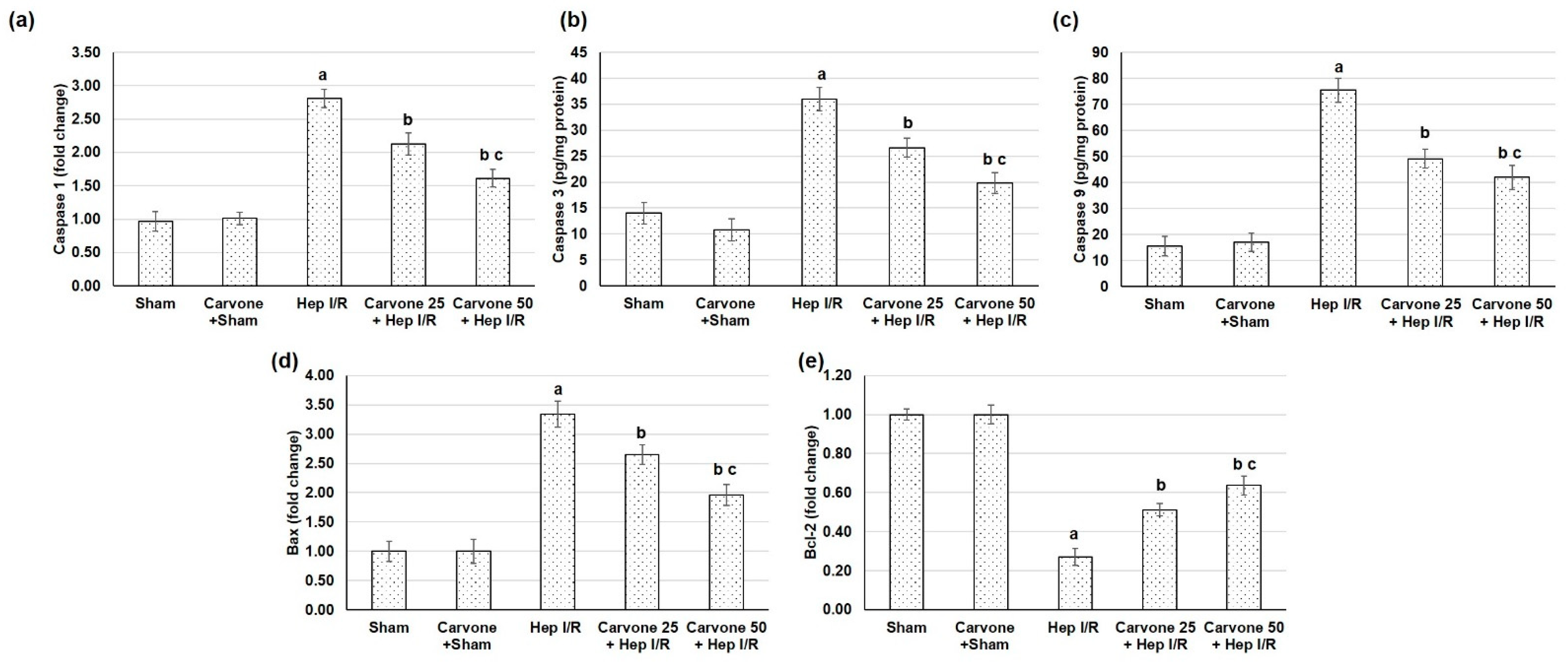
3.6. D-Carvone Pretreatment Reduced the Apoptosis Response Associated with Hep I/R
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, T.; Li, K.; Gong, X.; Jiang, R.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Tie, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, S.; Wan, J.; et al. Paeoniflorin protects against liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice via inhibiting HMGB1-TLR4 signaling pathway. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2247–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, T.V.; Okun, E.; Tang, S.C.; Thundyil, J.; Taylor, S.M.; Woodruff, T.M. Toll-like receptors in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Shock 2009, 32, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Nakamura, T.; Inouye, K.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Lundbäck, P.; Valdes-Ferrer, S.I.; Olofsson, P.S.; Kalb, T.; Roth, J.; et al. Novel role of PKR in inflammasome activation and HMGB1 release. Nature 2012, 488, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, U.; Tracey, K.J. HMGB1 is a therapeutic target for sterile inflammation and infection. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.A.; Chen, H.; Nie, H.; Zheng, B.; Gong, Q. HMGB1: An overview of its roles in the pathogenesis of liver disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 110, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsung, A.; Hoffman, R.A.; Izuishi, K.; Critchlow, N.D.; Nakao, A.; Chan, M.H.; Lotze, M.T.; Geller, D.A.; Billiar, T.R. Hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury involves functional TLR4 signaling in nonparenchymal cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 7661–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.S.; Zhang, J.X.; Wang, L.; Tian, Y.; Wang, H.; Rotstein, O. Toll-like receptor 4 involvement in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2004, 3, 250–253. [Google Scholar]
- Szabo, G.; Csak, T. Inflammasomes in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; Mechchate, H.; Benali, T.; Ghchime, R.; Charfi, S.; Balahbib, A.; Burkov, P.; Shariati, M.A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Omari, N.E. Health Benefits and Pharmacological Properties of Carvone. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, R. Carvone Content and Chemical Composition in Spearmint (Mentha spicata Var. Viridis L.) as Affected by Herb Storage under Ambient Temperature. J. Food Nutr. Popul. Health 2016, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Prajapati, V.; Kumar, S. Bioactivities of l-carvone, d-carvone, and dihydrocarvone toward three stored product beetles. J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkumar, R.; Sudha, M.; Viswanathan, P.; Kabalimoorthy, J.; Balasubramanian, T.; Nalini, N. Modulating effect of d-carvone on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced pre-neoplastic lesions, oxidative stress and biotransforming enzymes, in an experimental model of rat colon carcinogenesis. Cell Prolif. 2013, 46, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsanea, S.; Liu, D. BITC and S-Carvone Restrain High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Ameliorate Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 2241–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganathan, U.; Srinivasan, S. Beneficial effect of carvone, a dietary monoterpene ameliorates hyperglycemia by regulating the key enzymes activities of carbohydrate metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.M.; Kandil, Y.; Abbas, M.A. R-(-)-carvone Attenuated Doxorubicin Induced Cardiotoxicity In Vivo and Potentiated Its Anticancer Toxicity In Vitro. Balkan Med. J. 2020, 37, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogaly, H.A.; Aldulmani, S.A.A.; Al-Zahrani, F.A.M.; Abd-Elsalam, R.M. D-Carvone Attenuates CCl(4)-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and TGF-ß 1/SMAD3 Signaling Pathway. Biology 2022, 11, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asle-Rousta, M.; Amini, R.; Aghazadeh, S. Carvone suppresses oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver of immobilised rats. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Song, Y.; Ma, F.; Ma, Y. Anti-arthritic activity of D-carvone against complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats through modulation of inflammatory cytokines. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 24, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Chen, H. Anticancer effects of Carvone in myeloma cells is mediated through the inhibition of p38 MAPK signalling pathway, apoptosis induction and inhibition of cell invasion. JBUON 2018, 23, 747–751. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, J.C.; Oliveira Fde, S.; Benedito, R.B.; de Sousa, D.P.; de Almeida, R.N.; de Araújo, D.A. Antinociceptive activity of (-)-carvone: Evidence of association with decreased peripheral nerve excitability. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, G.; Wu, S.; Li, C. Protective Effect of D-Carvone against Dextran Sulfate Sodium Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Balb/c Mice and LPS Induced RAW Cells via the Inhibition of COX-2 and TNF-α. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2020, 39, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendy, A.; Elnagar, M.R.; Soubh, A.; Al-Mokaddem, A.; El-Haddad, A.; El-Sayed, M.K. Morin alleviates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion-induced mischief: In vivo and in silico contribution of Nrf2, TLR4, and NLRP3. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Feng, Z.; Gao, W.; Duan, Y.; Fan, G.; Geng, X.; Wu, B.; Li, K.; Liu, K.; Peng, C. Aucubin Attenuates Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR-4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Madden, J.F.; Gao, W.; Selvan, R.S.; Clavien, P. Interleukin-6 protects liver against warm ischemia/reperfusion injury and promotes hepatocyte proliferation in the rodent. Hepatology 1997, 26, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.E.; Abduldaium, Y.S.; Younis, N.S. Ameliorative Effect of Linalool in Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity: The Role of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB and Nrf2/HO1 Pathways. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sisi, A.E.E.; Sokar, S.S.; Shebl, A.M.; Mohamed, D.Z.; Abu-Risha, S.E. Octreotide and melatonin alleviate inflammasome-induced pyroptosis through inhibition of TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 pathway in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 410, 115340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendy, A.M.; Abdallah, D.M.; El-Abhar, H.S. The potential curative effect of rebamipide in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2017, 390, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannistrà, M.; Ruggiero, M.; Zullo, A.; Gallelli, G.; Serafini, S.; Maria, M.; Naso, A.; Grande, R.; Serra, R.; Nardo, B. Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: A systematic review of literature and the role of current drugs and biomarkers. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 33, S57–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias-Miró, M.; Jiménez-Castro, M.B.; Rodés, J.; Peralta, C. Current knowledge on oxidative stress in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Shirasuna, K.; Kimura, H.; Usui, F.; Kawashima, A.; Karasawa, T.; Tago, K.; Dezaki, K.; Nishimura, S.; Sagara, J.; et al. NLRP3 regulates neutrophil functions and contributes to hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury independently of inflammasomes. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 4342–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhong, F.; Cheng, H.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Tan, P.; Huang, M.; Liang, T.; Liu, Y.; Xia, X.; et al. The Dietary Supplement γ-Oryzanol Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion Injury via Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and HMGB1/NLRP3 Inflammasome. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 4628050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuishi, K.; Tsung, A.; Jeyabalan, G.; Critchlow, N.D.; Li, J.; Tracey, K.J.; Demarco, R.A.; Lotze, M.T.; Fink, M.P.; Geller, D.A.; et al. Cutting edge: High-mobility group box 1 preconditioning protects against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 7154–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.M.; El-Tanbouly, D.M.; Abdelsalam, R.M.; Zaki, H.F. Plumbagin ameliorates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: Role of high mobility group box 1 in inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.F.; Gamal, S.; El-Fayoumi, H.M. Limonin attenuates hepatocellular injury following liver ischemia and reperfusion in rats via toll-like receptor dependent pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ge, F.; Hu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Guo, K.; Miao, C. Sevoflurane Postconditioning Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Limiting HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB Pathway via Modulating microRNA-142 in vivo and in vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 646307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabie, M.A.; Zaki, H.F.; Sayed, H.M. Telluric acid ameliorates hepatic ischemia reperfusion-induced injury in rats: Involvement of TLR4, Nrf2, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 168, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendy, A.M.; Elnagar, M.R.; Allam, M.M.; Mousa, M.R.; Khodir, A.E.; El-Haddad, A.E.; Elnahas, O.S.; Fayez, S.M.; El-Mancy, S.S. Berberine-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers mitigate warm hepatic ischemia/reperfusion-induced lesion through modulation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling and autophagy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.; Cavalu, S.; Saber, S.; Youssef, M.E.; Abdelhamid, A.M.; Elagamy, H.I.; Kamal, I.; Gaafar, A.G.A.; El-Ahwany, E.; Amin, N.A.; et al. Canagliflozin-loaded chitosan-hyaluronic acid microspheres modulate AMPK/NF-κB/NLRP3 axis: A new paradigm in the rectal therapy of ulcerative colitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Duan, L.; Chen, J.; Xiong, A.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, F.; Tan, Z.; Gong, F.; Fang, M. Gene silencing of NALP3 protects against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Hum. Gene. Ther. 2011, 22, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Bai, C.; Sheng, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; et al. N-acetyl-L-tryptophan attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury via regulating TLR4/NLRP3 signaling pathway in rats. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, Q.; Geng, L.; Zhou, L.; Xie, H.; et al. Galectin-1 attenuates hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.I.; Ali, F.E.; Shalkami, A.S. Role of TLR-4/IL-6/TNF-α, COX-II and eNOS/iNOS pathways in the impact of carvedilol against hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1362–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Filho, J.; da Silva Brandi, J.; Ferreira Costa, H.; Carla de Paula Medeiros, K.; Alves Leite, J.; Pergentino de Sousa, D.; Regina Piuvezam, M. Carvone Enantiomers Differentially Modulate IgE-Mediated Airway Inflammation in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Markers | Accession Number (Genbank) | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward Primer | Reverse Primers | ||
| HMGB-1 | XM_039100270 | 5′-AGGCTGACAAGGCTCGTTATG-3′ | 3′-TGTCATCCGCAGCAGTGTTG-5′ |
| TLR4 | NM_019178 | 5′-GCTGCCAACATCATCCAGGAAGG-3′ | 3′-TGATGCCAGAGCGGCTACTCAG-5 |
| NFκB | L26267.1 | 5′-TGGGACGACACCTCTACACA-3′ | 3′-GGAGCTCATCTCATAGTTGTCC-5′ |
| NLRP3 | NM_00111642.1 | 5′-CAGACCTCCAAGACCACGACTG-3′ | 3′-CATCCGCAGCCAATGAACAGAG-5′ |
| Caspase 1 | NM_012762.3 | 5′-TGCCTGGTCTTGTGACTTGGAG-3′ | 3′-ATGTCCTGGGAAGAGGTAGAAACG-3′ |
| Bcl-2 | NM_016993.1 | 5′-CCGGGAGATCGTGATGAAGT-3′ | 3′-ATCCCAGCCTCCGTTATCCT-5′ |
| Bax | NM_017059.2 | 5′-GTGGTTGCCCTCTTCTACTTTG-3′ | 3′-CACAAAGATGGTCACTGTCTGC-5′ |
| β-actin | NM_0 3144.3 | 5′-TGACAGGATGCAGAAGGAGA-3′ | 3′-TAGAGCCACCAATCCACACA-5′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, M.E.; Younis, N.S. Ameliorative Effect of D-Carvone against Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Injury in Rats. Life 2022, 12, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101502
Mohamed ME, Younis NS. Ameliorative Effect of D-Carvone against Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Injury in Rats. Life. 2022; 12(10):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101502
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Maged E., and Nancy S. Younis. 2022. "Ameliorative Effect of D-Carvone against Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Injury in Rats" Life 12, no. 10: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101502
APA StyleMohamed, M. E., & Younis, N. S. (2022). Ameliorative Effect of D-Carvone against Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Injury in Rats. Life, 12(10), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101502








