A Pair of Prognostic Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: KLK10 and KLK11 mRNA Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
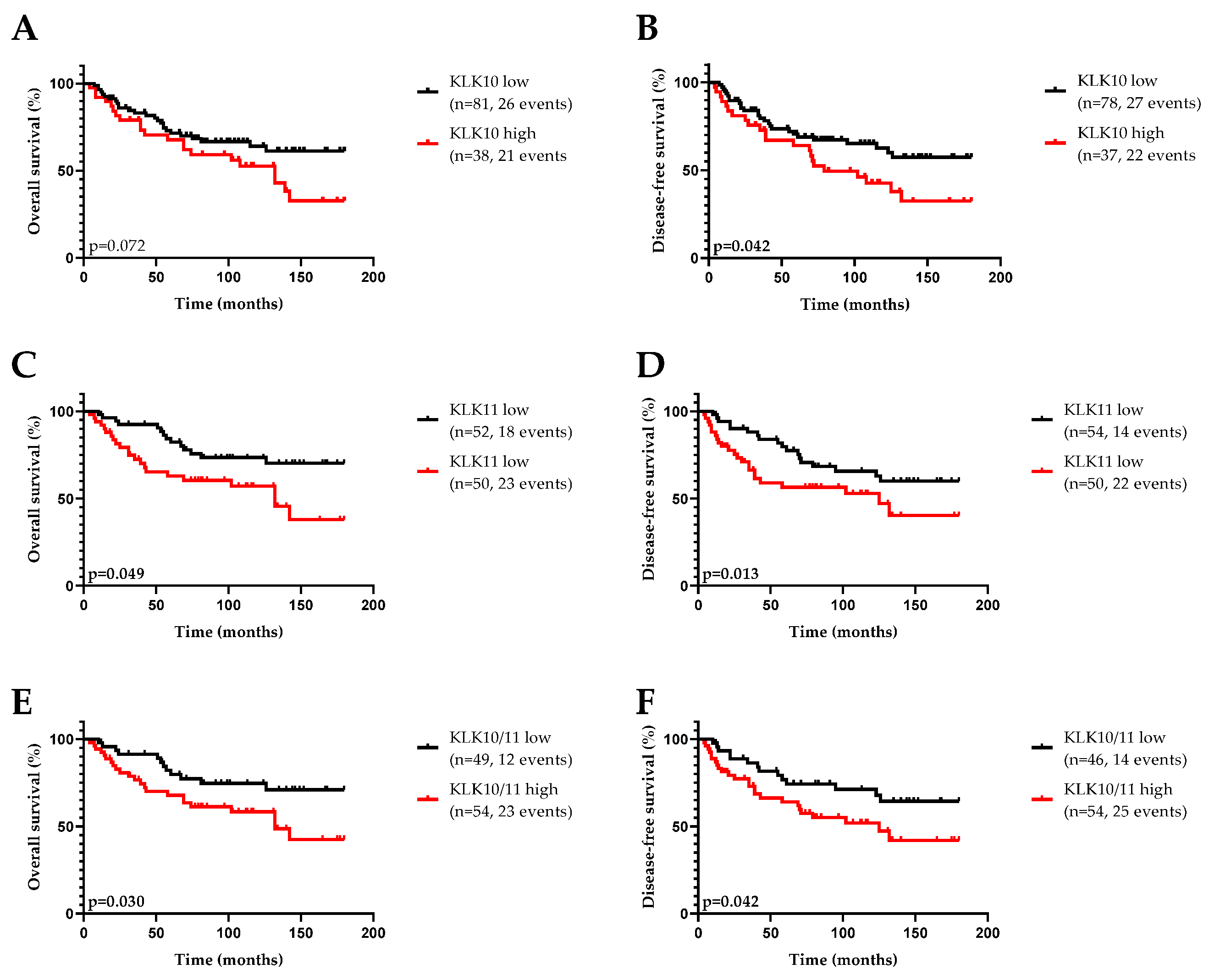
3. Results
3.1. KLK10 and KLK11 Expression in Tumor Tissues of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
3.2. Association of KLK10 and KLK11 mRNA Expression Levels with Disease-Free (DFS) and Overall (OS) Survival and Clinical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lebert, J.M.; Lester, R.; Powell, E.; Seal, M.; McCarthy, J. Advances in the Systemic Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25 (Suppl. S1), S142–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, F.; Enright, K.; Dent, R.; Dranitsaris, G.; Myers, J.; Flynn, C.; Fralick, M.; Kumar, R.; Clemons, M. Survival Outcomes for Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Implications for Clinical Practice and Trial Design. Clin. Breast Cancer 2009, 9, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Filho, J.S.; Tutt, A.N.J. Triple Negative Tumours: A Critical Review. Histopathology 2008, 52, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, G.; Frasci, G.; Chirico, A.; Esposito, E.; Siani, C.; Saturnino, C.; Arra, C.; Ciliberto, G.; Giordano, A.; D’Aiuto, M. Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Looking for the Missing Link between Biology and Treatments. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26560–26574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, M.; Im, S.-A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Domchek, S.M.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Tung, N.; Armstrong, A.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer in Patients with a Germline BRCA Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Cescon, D.W.; Rugo, H.S.; Nowecki, Z.; Im, S.A.; Yusof, M.M.; Gallardo, C.; Lipatov, O.; Barrios, C.H.; Holgado, E.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy versus Placebo plus Chemotherapy for Previously Untreated Locally Recurrent Inoperable or Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (KEYNOTE-355): A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Clinical Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, K.-L.; Huober, J.; Joerger, M. New Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) in Breast Cancer—An Overview of ADCs Recently Approved and in Later Stages of Development. Explor. Target. Anti-Tumor Ther. 2022, 3, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgoño, C.A.; Diamandis, E.P. The Emerging Roles of Human Tissue Kallikreins in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, M.; Magdolen, V.; Yang, F.; Kiechle, M.; Bayani, J.; Yousef, G.M.; Scorilas, A.; Diamandis, E.P.; Dorn, J. Emerging Clinical Importance of the Cancer Biomarkers Kallikrein-Related Peptidases (KLK) in Female and Male Reproductive Organ Malignancies. Radiol. Oncol. 2013, 47, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, C.D.; Molina, L.; Bhoola, K.D.; Ehrenfeld, P. Overview of Tissue Kallikrein and Kallikrein-Related Peptidases in Breast Cancer. Biol. Chem. 2018, 399, 937–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haritos, C.; Michaelidou, K.; Mavridis, K.; Missitzis, I.; Ardavanis, A.; Griniatsos, J.; Scorilas, A. Kallikrein-Related Peptidase 6 (KLK6) Expression Differentiates Tumor Subtypes and Predicts Clinical Outcome in Breast Cancer Patients. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelidou, K.; Ardavanis, A.; Scorilas, A. Clinical Relevance of the Deregulated Kallikrein-Related Peptidase 8 mRNA Expression in Breast Cancer: A Novel Independent Indicator of Disease-Free Survival. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 152, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Liu, Y.; Preis, S.; Geng, X.; Petit-Courty, A.; Kiechle, M.; Muckenhuber, A.; Dreyer, T.; Dorn, J.; Courty, Y.; et al. Prognostic Value of Kallikrein-Related Peptidase 12 (KLK12) mRNA Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Liu, Y.; Dreyer, T.; Bronger, H.; Drecoll, E.; Magdolen, V.; Dorn, J. Elevated Tumor Tissue Protein Expression Levels of Kallikrein-Related Peptidases KLK10 and KLK11 Are Associated with a Better Prognosis in Advanced High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Patients. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1856–1864. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.Y.; Diamandis, E.P.; Look, M.P.; Soosaipillai, A.P.; Foekens, J.A. Higher Expression of Human Kallikrein 10 in Breast Cancer Tissue Predicts Tamoxifen Resistance. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tailor, P.D.; Kodeboyina, S.K.; Bai, S.; Patel, N.; Sharma, S.; Ratnani, A.; Copland, J.A.; She, J.X.; Sharma, A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker Potential of Kallikrein Family Genes in Different Cancer Types. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Xu, W.B.; Zheng, M.H.; Ma, J.J.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, J.; Lu, A.G.; Qu, Y.; Li, J.W.; et al. Clinical Significance of Human Kallikrein 10 Gene Expression in Colorectal Cancer and Gastric Cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulou, D.K.; Papadopoulos, I.N.; Scorilas, A. Clinical Significance of Kallikrein-Related Peptidase (KLK10) mRNA Expression in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lei, H.; Fei, X.; Liang, S.; Xu, H.; Qin, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, B. NES1/KLK10 Gene Represses Proliferation, Enhances Apoptosis and down-Regulates Glucose Metabolism of PC3 Prostate Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunes, M.J.; Neuschatz, A.C.; Bornstein, L.E.; Naber, S.P.; Band, V.; Wazer, D.E. Loss of Expression of the Putative Tumor Suppressor NES1 Gene in Biopsy-Proven Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Predicts for Invasive Carcinoma at Definitive Surgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 56, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, G.M.; Yacoub, G.M.; Polymeris, M.E.; Popalis, C.; Soosaipillai, A.; Diamandis, E.P. Kallikrein Gene Downregulation in Breast Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, S.; Bhargava, R.; Yunes, M.; Li, B.; Goyal, J.; Naber, S.P.; Wazer, D.E.; Band, V. Analysis of Normal Epithelial Cell Specific-1 (NES1)/Kallikrein 10 mRNA Expression by in Situ Hybridization, a Novel Marker for Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 3393–3398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.Y.; De Meyts, E.R.; Jung, K.; Diamandis, E.P. Expression of the Normal Epithelial Cell-Specific 1 (NES1; KLK10) Candidate Tumour Suppressor Gene in Normal and Malignant Testicular Tissue. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 85, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ruan, B.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Xu, W.; Feng, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, X. Identification of KLK10 as a Therapeutic Target to Reverse Trastuzumab Resistance in Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 79494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loessner, D.; Goettig, P.; Preis, S.; Felber, J.; Bronger, H.; Clements, J.A.; Dorn, J.; Magdolen, V. Kallikrein-Related Peptidases Represent Attractive Therapeutic Targets for Ovarian Cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Liu, Y.; Diersch, S.; Kotzsch, M.; Grill, S.; Weichert, W.; Kiechle, M.; Magdolen, V.; Dorn, J. Clinical Relevance of Kallikrein-Related Peptidase 9, 10, 11, and 15 mRNA Expression in Advanced High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsis, C.; Yiotakis, I.; Scorilas, A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Significance of Human Kallikrein 11 (KLK11) mRNA Expression Levels in Patients with Laryngeal Cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, D.; Tasdemir, A.; Oguz, A.; Eroglu, C.; Cihan, Y.B.; Turak, E.E.; Karaman, H.; Soyuer, S. Is Human Kallikrein-11 in Gastric Cancer Treated with Surgery and Adjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Associated with Survival? Pathol. Res. Pract. 2013, 209, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Meng, F.; Qin, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, Y. KLK11 Suppresses Cellular Proliferation via Inhibition of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2264. [Google Scholar]
- Alexopoulou, D.K.; Kontos, C.K.; Christodoulou, S.; Papadopoulos, I.N.; Scorilas, A. KLK11 mRNA Expression Predicts Poor Disease-Free and Overall Survival in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Patients. Biomark. Med. 2014, 8, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Tang, H.Y.; Li, X.R.; He, X.W.; Xiang, K.M. Over-Expression of Human Kallikrein 11 Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Low Rectal Carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2010, 27, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, A.; Sangai, T.; Maeda, H.; Nakamura, M.; Hasebe, T.; Ochiai, A. Kallikrein 11 Expressed in Human Breast Cancer Cells Releases Insulin-like Growth Factor through Degradation of IGFBP-3. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 30, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ahmed, N.; Dorn, J.; Napieralski, R.; Drecoll, E.; Kotzsch, M.; Goettig, P.; Zein, E.; Avril, S.; Kiechle, M.; Diamandis, E.P.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Kallikrein-Related Peptidase 6 (KLK6) and 8 (KLK8) mRNA Expression in Advanced Serous Ovarian Cancer. Biol. Chem. 2016, 397, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and Quantifying Mammalian Transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate Transcript Quantification from RNA-Seq Data with or without a Reference Genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulou, P.; Gregorakis, A.K.; Plebani, M.; Scorilas, A. Expression Analysis and Prognostic Significance of Human Kallikrein 11 in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 357, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terayama, R.; Bando, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Yoshida, S. Differential Expression of Neuropsin and Protease M/Neurosin in Oligodendrocytes after Injury to the Spinal Cord. Glia 2004, 48, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, T.; Kain, E.Z.; Tuzuner, M.B.; Diren, A.; Batur, S.; Yilmaz-Aydogan, H.; Ozturk, O.; Isbir, T. Kallikrein 11 Down-Regulation in Breast Carcinoma: Correlation with Prognostic Parameters. In Vivo 2021, 35, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Lai, J.; Clements, J.A. Kallikreins on Steroids: Structure, Function, and Hormonal Regulation of Prostate-Specific Antigen and the Extended Kallikrein Locus. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 407–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.Y.; Grass, L.; Diamandis, E.P. Steroid Hormone Regulation of the Human Kallikrein 10 (KLK10) Gene in Cancer Cell Lines and Functional Characterization of the KLK10 Gene Promoter. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 337, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucalp, A.; Traina, T.A. The Androgen Receptor: Is It a Promising Target? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 2876–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulou, G.; Pampalakis, G.; Diamandis, E.P. Functional Roles of Human Kallikrein-Related Peptidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32989–32994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Laxmikanthan, G.; Lee, J.; Blaber, S.I.; Rodriguez, A.; Kogot, J.M.; Scarisbrick, I.A.; Blaber, M. Activation Profiles and Regulatory Cascades of the Human Kallikrein-Related Peptidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 31852–31864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomopoulou, K.; Hansen, K.K.; Saifeddine, M.; Tea, I.; Blaber, M.; Blaber, S.I.; Scarisbrick, I.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Cottrell, G.S.; Bunnett, N.W.; et al. Proteinase-Activated Receptors, Targets for Kallikrein Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 32095–32112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettig, P.; Magdolen, V.; Brandstetter, H. Natural and Synthetic Inhibitors of Kallikrein-Related Peptidases (KLKs). Biochimie 2010, 92, 1546–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debela, M.; Magdolen, V.; Schechter, N.; Valachova, M.; Lottspeich, F.; Craik, C.S.; Choe, Y.; Bode, W.; Goettig, P. Specificity Profiling of Seven Human Tissue Kallikreins Reveals Individual Subsite Preferences. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25678–25688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, J.; Abisoye-Ogunniyan, A.; Metcalf, K.J.; Werb, Z. Concepts of Extracellular Matrix Remodelling in Tumour Progression and Metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Loessner, D.; Irving-Rodgers, H.; Obermair, A.; Nicklin, J.L.; Clements, J.A. Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer Is Mediated by Kallikrein Related Peptidases. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2014, 31, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliendo, G.; Santagada, V.; Perissutti, E.; Severino, B.; Fiorino, F.; Frecentese, F.; Juliano, L. Kallikrein Protease Activated Receptor (PAR) Axis: An Attractive Target for Drug Development. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6669–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefansson, K.; Brattsand, M.; Roosterman, D.; Kempkes, C.; Bocheva, G.; Steinhoff, M.; Egelrud, T. Activation of Proteinase-Activated Receptor-2 by Human Kallikrein-Related Peptidases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulou, G.; Pampalakis, G. Kallikrein-Related Peptidases: Bridges between Immune Functions and Extracellular Matrix Degradation. Biol. Chem. 2010, 391, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisert, R.D.; Chamberlain, C.S.; Vonnahme, K.A.; Malayer, J.R.; Spicer, L.J. Possible Role of Kallikrein in Proteolysis of Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins during the Oestrous Cycle and Early Pregnancy in Pigs. Reproduction 2001, 121, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronger, H.; Magdolen, V.; Goettig, P.; Dreyer, T. Proteolytic Chemokine Cleavage as a Regulator of Lymphocytic Infiltration in Solid Tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Lu, W.; Kulkarni, B.; Pejovic, T.; Yan, X.; Chiang, J.H.; Hood, L.; Odunsi, K.; Lin, B. Analysis of Chemotherapy Response Programs in Ovarian Cancers by the Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2010, 117, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, K.L.; Cree, I.A.; Savage, R.S. Prediction of Resistance to Chemotherapy in Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, N.; Fan, N.; Meng, Q.; Luo, W.; Lv, L.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, F.; et al. Upregulated KLK10 Inhibits Esophageal Cancer Proliferation and Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity in Vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chi, P.; Lu, X. Knockdown of KLK11 Reverses Oxaliplatin Resistance by Inhibiting Proliferation and Activating Apoptosis via Suppressing the PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway in Colorectal Cancer Cell. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.D.; Parveen, A.; Yadav, D.K. Role of PARP in TNBC: Mechanism of Inhibition, Clinical Applications, and Resistance. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghban, R.; Roshangar, L.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Seidi, K.; Ebrahimi-Kalan, A.; Jaymand, M.; Kolahian, S.; Javaheri, T.; Zare, P. Tumor Microenvironment Complexity and Therapeutic Implications at a Glance. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TCGA Breast Cancer Data Set. Available online: http://www.xenabrowser.net (accessed on 16 September 2022).

| Clinicopathological Parameters | KLK10 a | KLK11 a | KLK10+11 a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low/High | Low/High | Low/Others b | |
| Age | p = 0.294 | p = 0.761 | p = 0.390 |
| ≤60 years | 43/25 | 33/28 | 26/35 |
| >60 years | 39/15 | 23/22 | 22/21 |
| Lymph node status | p = 0.990 | p = 0.473 | p = 0.626 |
| N0 | 45/22 | 33/26 | 28/30 |
| N+ | 37/18 | 23/24 | 20/26 |
| Tumor Size | p = 0.207 | p = 0.665 | p = 0.831 |
| ≤20 mm | 25/8 | 15/15 | 14/15 |
| >20 mm | 56/32 | 41/34 | 34/40 |
| Clinicopathological Parameters | DFS | OS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No a | HR (95% CI) b | p | No a | HR (95% CI) b | p | |
| Age | 0.005 | <0.001 | ||||
| ≤60 years | 65 | 1 | 65 | 1 | ||
| >60 years | 52 | 2.09 (1.25–3.52) | 56 | 2.76 (1.62–4.70) | ||
| Lymph node status | 0.023 | 0.018 | ||||
| N0 | 63 | 1 | 65 | 1 | ||
| N+ | 54 | 1.82 (1.09–3.05) | 56 | 1.86 (1.11–3.10) | ||
| Tumor Size | 0.058 | 0.076 | ||||
| ≤20 mm | 32 | 1 | 33 | 1 | ||
| >20 mm | 84 | 1.89 (0.98–3.64) | 87 | 1.85 (0.94–3.66) | ||
| KLK10 mRNA c | 0.045 | 0.076 | ||||
| low | 78 | 1 | 81 | 1 | ||
| high | 37 | 1.78 (1.01–3.12) | 38 | 1.68 (0.95–2.99) | ||
| KLK11 mRNA c | 0.053 | 0.016 | ||||
| low | 52 | 1 | 54 | 1 | ||
| high | 50 | 1.85 (0.99–3.44) | 50 | 2.29 (1.17–4.49) | ||
| KLK10+11 mRNA d | 0.046 | 0.035 | ||||
| low | 46 | 1 | 48 | 1 | ||
| high | 54 | 1.95 (1.01–3.78) | 54 | 2.12 (1.05–4.28) | ||
| Chemotherapy | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| no | 28 | 1 | 30 | 1 | ||
| yes | 87 | 0.31 (0.172–0.546) | 88 | 0.31 (0.173–0.562) |
| Clinicopathological Parameters | DFS | OS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No a | HR (95% CI) b | p | No a | HR (95% CI) b | p | |
| Age | 0.025 | 0.002 | ||||
| ≤60 years | 54 | 1 | 54 | 1 | ||
| >60 years | 41 | 1.61 (0.–4.09) | 43 | 3.18 (1.53–6.59) | ||
| Lymph node status | 0.236 | 0.286 | ||||
| N0 | 51 | 1 | 53 | 1 | ||
| N+ | 44 | 1.49 (0.77–2.87) | 44 | 1.46 (0.73–2.94) | ||
| Tumor Size | 0.305 | 0.423 | ||||
| ≤20 mm | 28 | 1 | 29 | 1 | ||
| >20 mm | 67 | 1.51 (0.69–3.33) | 68 | 1.41 (0.61–3.29) | ||
| KLK10 mRNA c | 0.019 | 0.058 | ||||
| low | 63 | 1 | 79 | 1 | ||
| high | 32 | 2.19 (1.14–4.20) | 36 | 1.95 (0.98–3.91) | ||
| KLK11 mRNA c | 0.113 | 0.044 | ||||
| low | 51 | 1 | 53 | 1 | ||
| high | 44 | 1.70 (0.88–3.26) | 44 | 2.06 (1.02–4.14) | ||
| KLK10+11 mRNA d | 0.049 | 0.054 | ||||
| low | 45 | 1 | 47 | 1 | ||
| high | 50 | 1.97 (1.00–3.86) | 50 | 2.03 (0.99–4.17) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Gong, W.; Preis, S.; Dorn, J.; Kiechle, M.; Reuning, U.; Magdolen, V.; Dreyer, T.F. A Pair of Prognostic Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: KLK10 and KLK11 mRNA Expression. Life 2022, 12, 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101517
Liu Y, Gong W, Preis S, Dorn J, Kiechle M, Reuning U, Magdolen V, Dreyer TF. A Pair of Prognostic Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: KLK10 and KLK11 mRNA Expression. Life. 2022; 12(10):1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101517
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yueyang, Weiwei Gong, Sarah Preis, Julia Dorn, Marion Kiechle, Ute Reuning, Viktor Magdolen, and Tobias F. Dreyer. 2022. "A Pair of Prognostic Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: KLK10 and KLK11 mRNA Expression" Life 12, no. 10: 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101517
APA StyleLiu, Y., Gong, W., Preis, S., Dorn, J., Kiechle, M., Reuning, U., Magdolen, V., & Dreyer, T. F. (2022). A Pair of Prognostic Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: KLK10 and KLK11 mRNA Expression. Life, 12(10), 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101517







