Cebidae Alu Element Alignments and a Complex Non-Human Primate Radiation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lineage-Specific Alu Elements
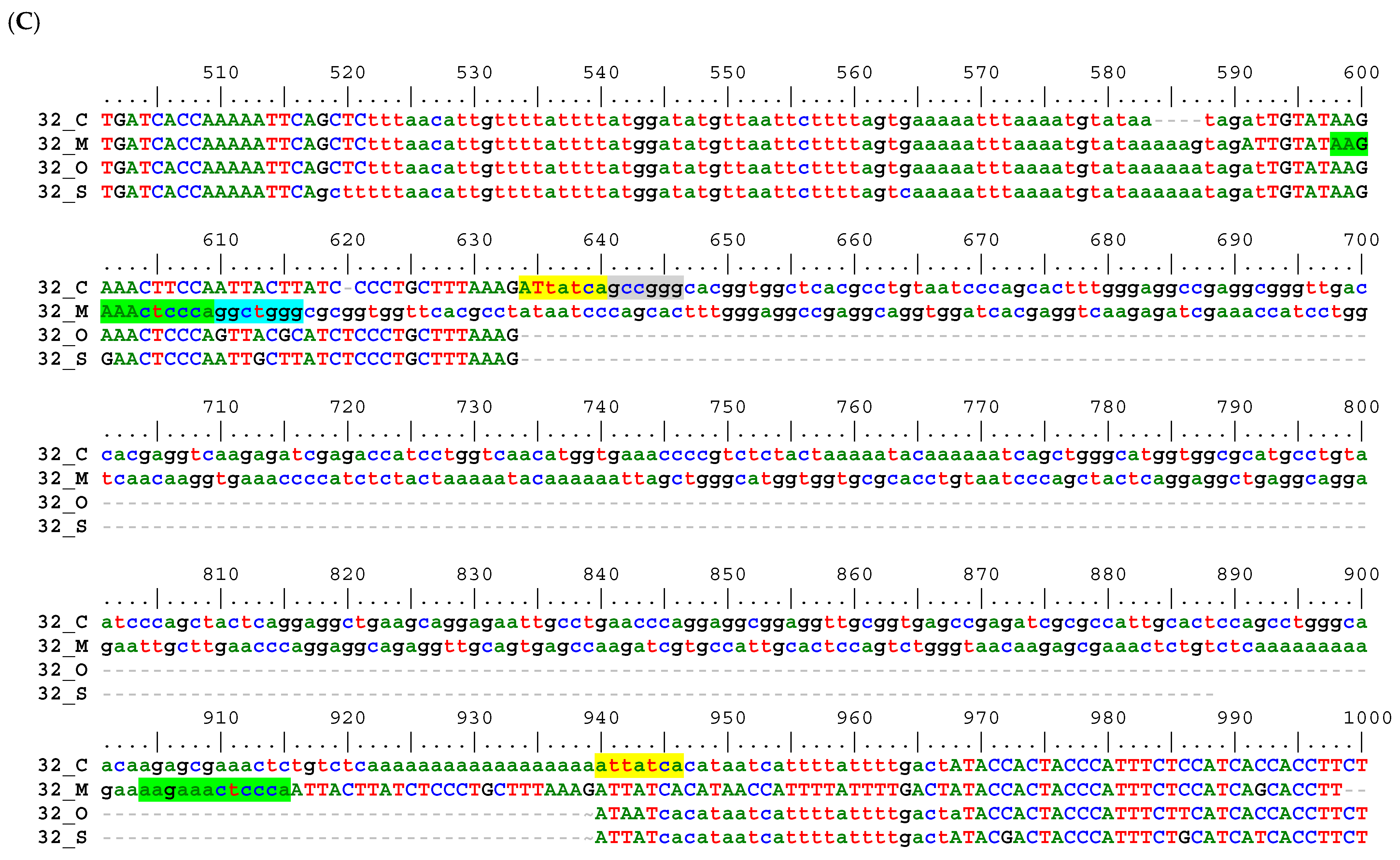
2.2. Sequence Alignment Inspection
2.3. Oligonucleotide Primers for PCR
2.4. DNA Samples
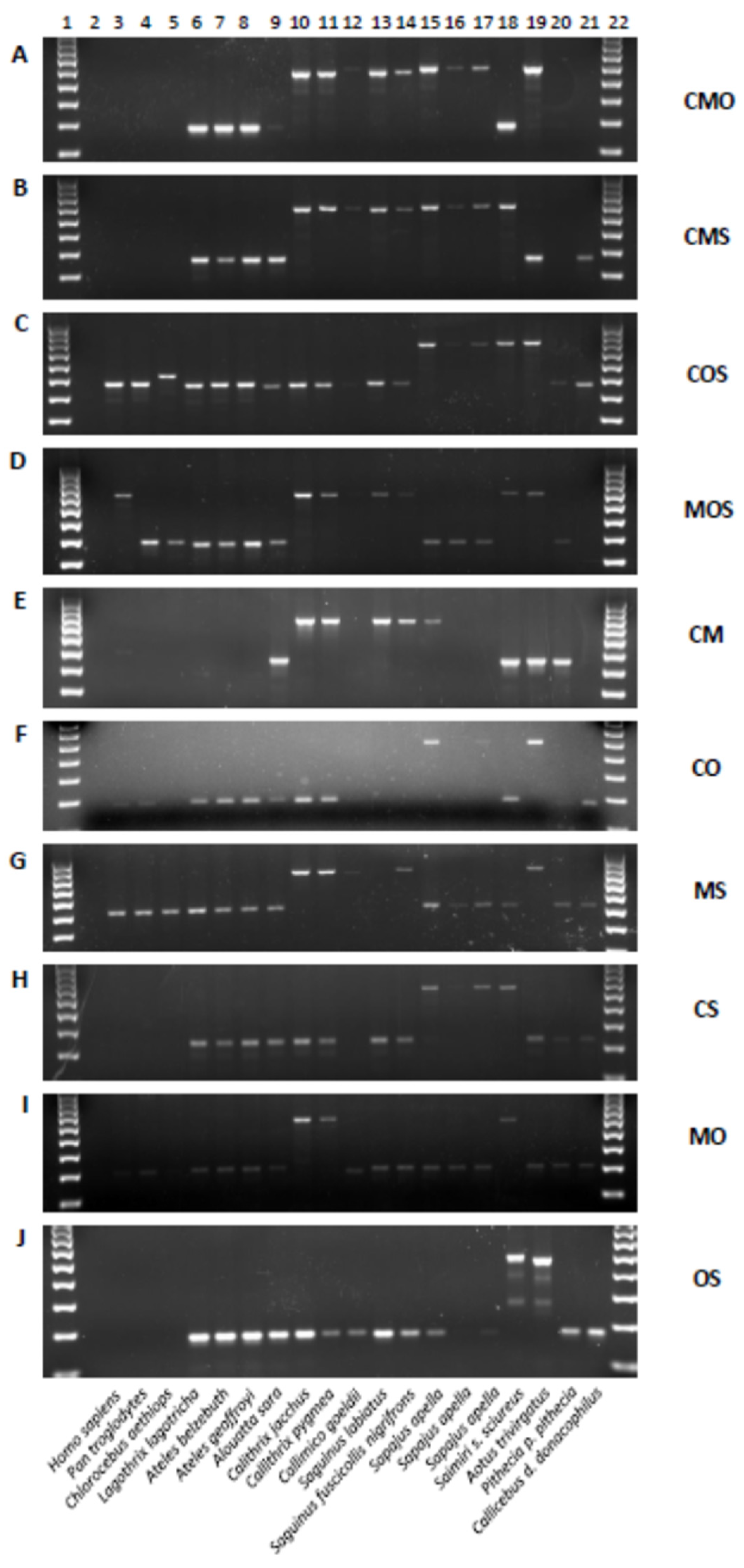
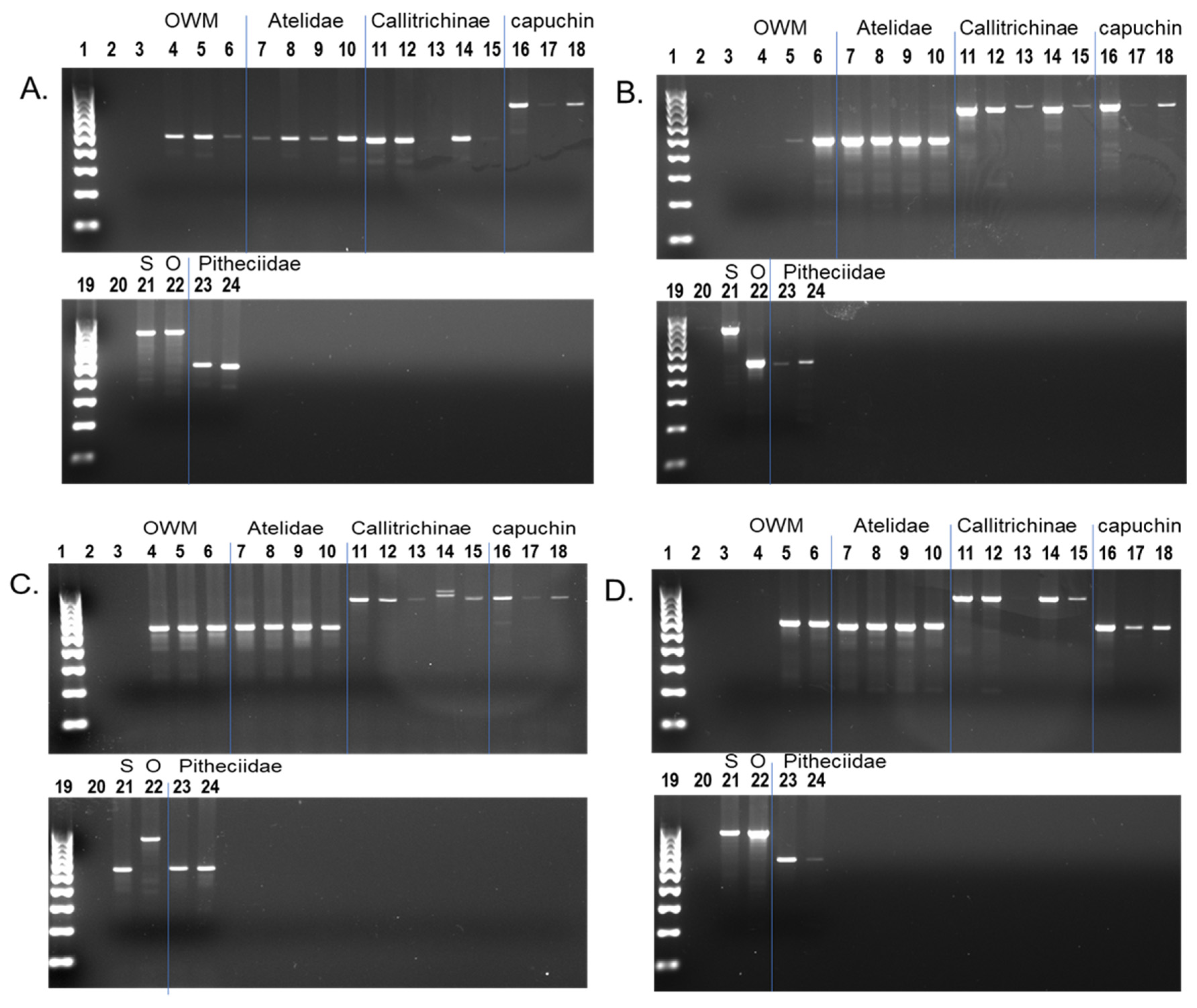
2.5. PCR Amplification
3. Results
3.1. Shared Alu Insertions
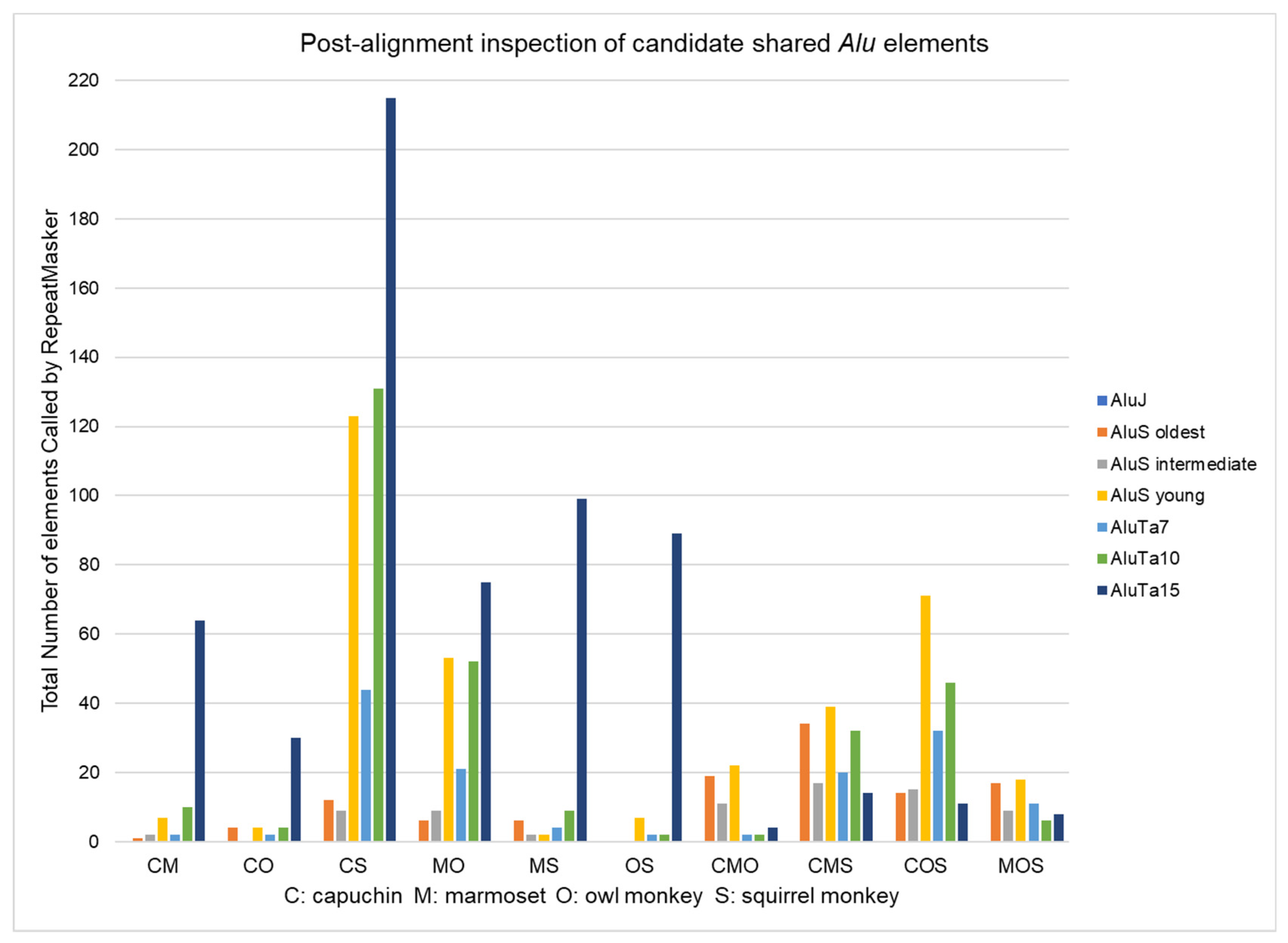
3.2. Alu Subfamily Distribution
3.3. Sequence Alignment-Based Phylogeny
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, D.A.; Batzer, M.A. Tracking Alu evolution in New World primates. BMC Evol. Biol. 2005, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ray, D.A.; Xing, J.; Hedges, D.J.; Hall, M.A.; Laborde, M.E.; Anders, B.A.; White, B.R.; Stoilova, N.; Fowlkes, J.D.; Landry, K.E.; et al. Alu insertion loci and platyrrhine primate phylogeny. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2005, 35, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, H. The current status of the New World monkey phylogeny. An. Da Acad. Bras. De Cienc. 2000, 72, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singer, S.S.; Schmitz, J.; Schwiegk, C.; Zischler, H. Molecular cladistic markers in New World monkey phylogeny (Platyrrhini, Primates). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2003, 26, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterholz, M.; Walter, L.; Roos, C. Retropositional events consolidate the branching order among New World monkey genera. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2009, 50, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameson Kiesling, N.M.; Yi, S.V.; Xu, K.; Gianluca Sperone, F.; Wildman, D.E. The tempo and mode of New World monkey evolution and biogeography in the context of phylogenomic analysis. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2015, 82, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, L.M.; Martins, A.; Ortiz, E.M.; Di Fiore, A. A RAD-sequencing approach to genome-wide marker discovery, genotyping, and phylogenetic inference in a diverse radiation of primates. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, H.; Sampaio, I. The systematics and evolution of New World primates—A review. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2015, 82, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrago, C.G.; Seuánez, H.N. Large ancestral effective population size explains the difficult phylogenetic placement of owl monkeys. Am. J. Primatol. 2019, 81, e22955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, V.E.; Walker, J.A.; Beckstrom, T.O.; Steely, C.J.; McDaniel, C.L.; St Romain, C.P.; Worley, K.C.; Phillips-Conroy, J.; Jolly, C.J.; Rogers, J.; et al. A computational reconstruction of Papio phylogeny using Alu insertion polymorphisms. Mob. DNA 2018, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storer, J.M.; Walker, J.A.; Jordan, V.E.; Batzer, M.A. Sensitivity of the polyDetect computational pipeline for phylogenetic analyses. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 593, 113516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelman, P.; Johnson, W.E.; Roos, C.; Seuánez, H.N.; Horvath, J.E.; Moreira, M.A.; Kessing, B.; Pontius, J.; Roelke, M.; Rumpler, Y.; et al. A molecular phylogeny of living primates. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smit, A.F.A.; Hubley, R.; Green, P. 2013–2015, RepeatMasker Open-4.0. 2015. Available online: http://www.repeatmasker.org (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Kent, W.J. BLAT—The BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordaux, R.; Hedges, D.J.; Batzer, M.A. Retrotransposition of Alu elements: How many sources? Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.; Canavez, F.C.; Sampaio, I.; Moreira, M.A.; Tagliaro, C.H.; Seuánez, H.N. Can molecular data place each neotropical monkey in its own branch? Chromosoma 2001, 109, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.A.; Xing, J.; Salem, A.H.; Batzer, M.A. SINEs of a nearly perfect character. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroig, G. When size makes a difference: Allometry, life-history and morphological evolution of capuchins (Cebus) and squirrels (Saimiri) monkeys (Cebinae, Platyrrhini). BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.M., Jr.; Amorim, N.; Carneiro, J.C.; de Mello Affonso, P.R.; Sampaio, I.; Schneider, H. Alu elements and the phylogeny of capuchin (Cebus and Sapajus) monkeys. Am. J. Primatol. 2015, 77, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins-Junior, A.M.G.; Carneiro, J.; Sampaio, I.; Ferrari, S.F.; Schneider, H. Phylogenetic relationships among Capuchin (Cebidae, Platyrrhini) lineages: An old event of sympatry explains the current distribution of Cebus and Sapajus. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2018, 41, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Storer, J. Characterization and Amplification of Retrotransposable Elements Platy-1 and Alu in the Cebidae Lineage of Platyrrhine Primates. Ph.D. Thesis, Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2019; p. 5053. Available online: https://digitalcommons.lsu.edu/gradschool_dissertations/5053 (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Storer, J.M.; Mierl, J.R.; Brantley, S.A.; Threeton, B.; Sukharutski, Y.; Rewerts, L.C.; St Romain, C.P.; Foreman, M.M.; Baker, J.N.; Walker, J.A.; et al. Amplification Dynamics of Platy-1 Retrotransposons in the Cebidae Platyrrhine Lineage. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konkel, M.K.; Ullmer, B.; Arceneaux, E.L.; Sanampudi, S.; Brantley, S.A.; Hubley, R.; Smit, A.F.; Batzer, M.A. Discovery of a new repeat family in the Callithrix jacchus genome. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rhoads, A.; Au, K.F. PacBio Sequencing and Its Applications. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goto, Y.; Akahori, R.; Yanagi, I.; Takeda, K.I. Solid-state nanopores towards single-molecule DNA sequencing. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 65, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buermans, H.P.; den Dunnen, J.T. Next generation sequencing technology: Advances and applications. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belton, J.M.; McCord, R.P.; Gibcus, J.H.; Naumova, N.; Zhan, Y.; Dekker, J. Hi-C: A comprehensive technique to capture the conformation of genomes. Methods 2012, 58, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsen, P.A.; Harris, R.A.; Liu, Y.; Murali, S.C.; Campbell, C.R.; Brown, A.D.; Sullivan, B.A.; Shelton, J.; Brown, S.J.; Raveendran, M.; et al. Hybrid de novo genome assembly and centromere characterization of the gray mouse lemur (Microcebus murinus). BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
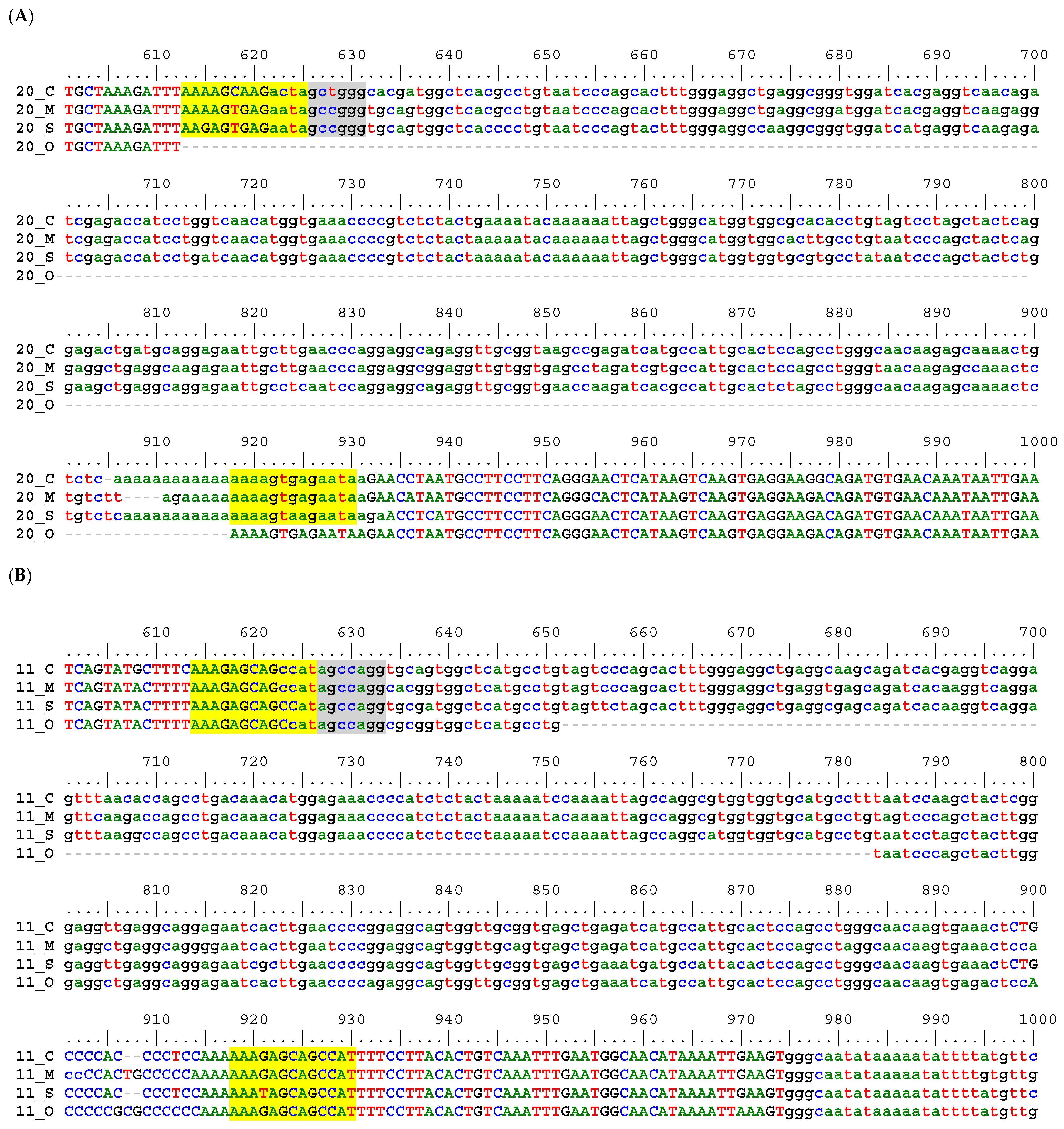
| Capuchin Monkey | Marmoset | Owl Monkey | Squirrel Monkey | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMOS | x | x | x | x |
| CMO | x | x | x | n/a |
| COS | x | n/a | x | x |
| CMS | x | x | n/a | x |
| MOS | n/a | x | x | x |
| CM | x | x | n/a | n/a |
| CO | x | n/a | x | n/a |
| CS | x | n/a | n/a | x |
| MO | n/a | x | x | n/a |
| MS | n/a | x | n/a | x |
| OS | n/a | n/a | x | x |
| C | x | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| M | n/a | x | n/a | n/a |
| O | n/a | n/a | x | n/a |
| S | n/a | n/a | n/a | x |
| Genome Ascertained | C | M | C | O | C | S | M | O | M | S | O | S | C | M | O | C | M | S | C | O | S | M | O | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Set # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| Candidates by set | 95 | 75 | 39 | 53 | 342 | 175 | 122 | 184 | 154 | 90 | 146 | 50 | 97 | 101 | 147 | 169 | 127 | 85 | 168 | 220 | 79 | 85 | 123 | 47 |
| Shared category | CM | CO | CS | MO | MS | OS | CMO | CMS | COS | MOS | ||||||||||||||
| a. Total Candidates | 170 | 92 | 517 | 306 | 244 | 196 | 345 | 381 | 467 | 255 | ||||||||||||||
| b. In multiple sets | 38 | 19 | 106 | 83 | 42 | 31 | 153 | 143 | 181 | 96 | ||||||||||||||
| Unique calls (a–b) | 132 | 73 | 411 | 223 | 202 | 165 | 192 | 238 | 286 | 159 | ||||||||||||||
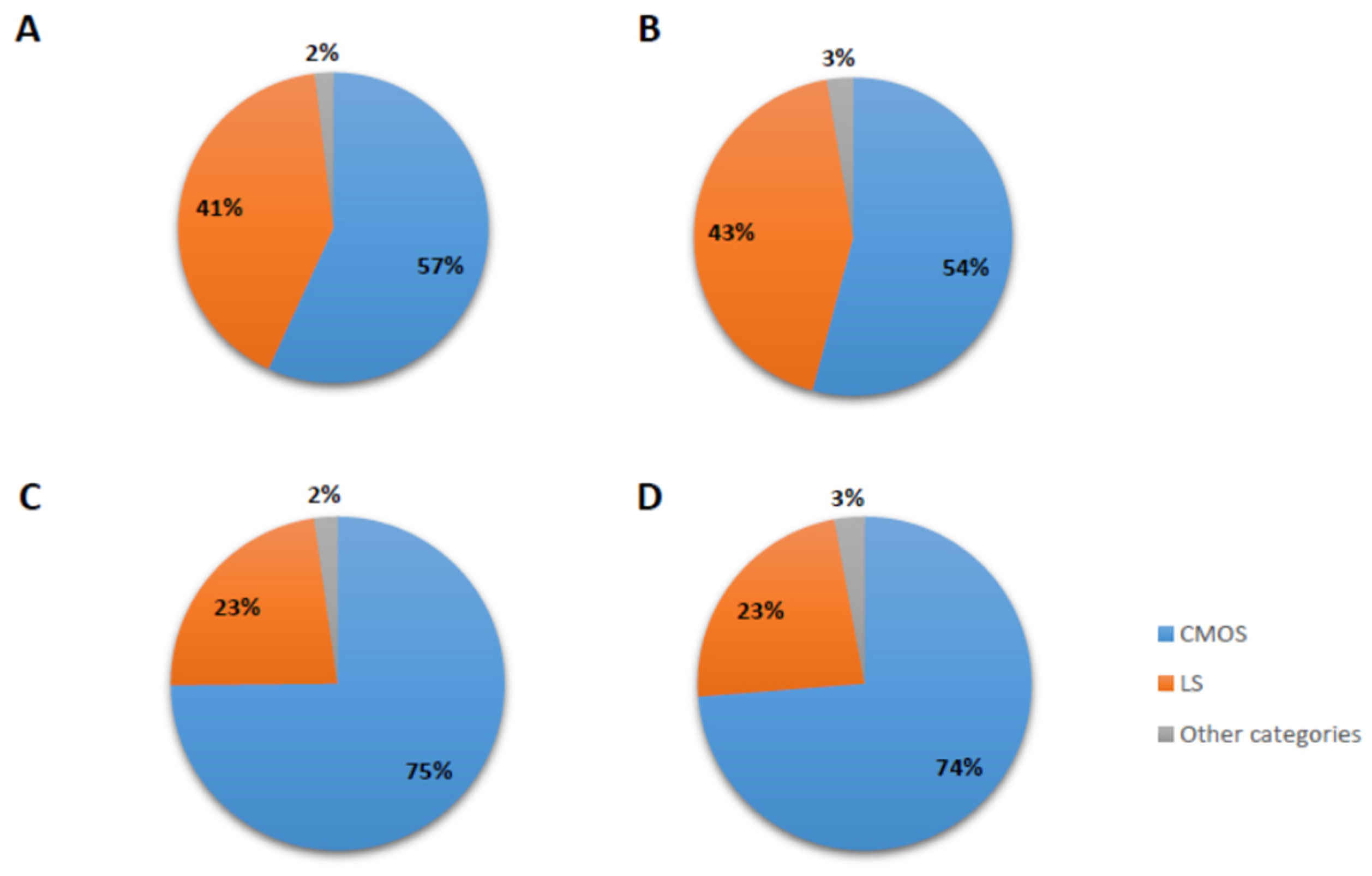
| Post-align Inspection | 43 | 22 | 267 | 108 | 61 | 50 | 20 | 52 | 63 | 23 | ||||||||||||||
| % retained | 33% | 30% | 65% | 48% | 30% | 30% | 10% | 22% | 22% | 14% | ||||||||||||||
| Shared Category | CM | CO | CS | MO | MS | OS | CMO | CMS | COS | MOS | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unique calls | 132 | 73 | 411 | 223 | 202 | 165 | 192 | 238 | 286 | 159 | 2081 | |
| Post-align shared | 43 | 22 | 267 | 108 | 61 | 50 | 20 | 52 | 63 | 23 | 709 | 34.1% |
| Post-align NP | 45 | 22 | 44 | 77 | 99 | 81 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 382 | 18.4% |
| Post-align other* | 44 | 29 | 100 | 38 | 42 | 34 | 169 | 181 | 221 | 132 | 990 | 47.6% |
| Shared Category | CMO | CMS | COS | MOS | All |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-align shared | 20 | 52 | 63 | 23 | 158 |
| Analyzed by PCR | 10 | 32 | 40 | 16 | 98 |
| PCR confirmed | 4 | 14 | 16 | 3 | 37 |
| % confirmed by PCR | 4/10 (40%) | 14/32 (44%) | 16/40 (40%) | 3/16 (19%) | 37/98 (38%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Storer, J.M.; Walker, J.A.; Brown, M.A.; Batzer, M.A. Cebidae Alu Element Alignments and a Complex Non-Human Primate Radiation. Life 2022, 12, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101655
Storer JM, Walker JA, Brown MA, Batzer MA. Cebidae Alu Element Alignments and a Complex Non-Human Primate Radiation. Life. 2022; 12(10):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101655
Chicago/Turabian StyleStorer, Jessica M., Jerilyn A. Walker, Morgan A. Brown, and Mark A. Batzer. 2022. "Cebidae Alu Element Alignments and a Complex Non-Human Primate Radiation" Life 12, no. 10: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101655
APA StyleStorer, J. M., Walker, J. A., Brown, M. A., & Batzer, M. A. (2022). Cebidae Alu Element Alignments and a Complex Non-Human Primate Radiation. Life, 12(10), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101655






