Deep Learning Approaches for Prognosis of Automated Skin Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review
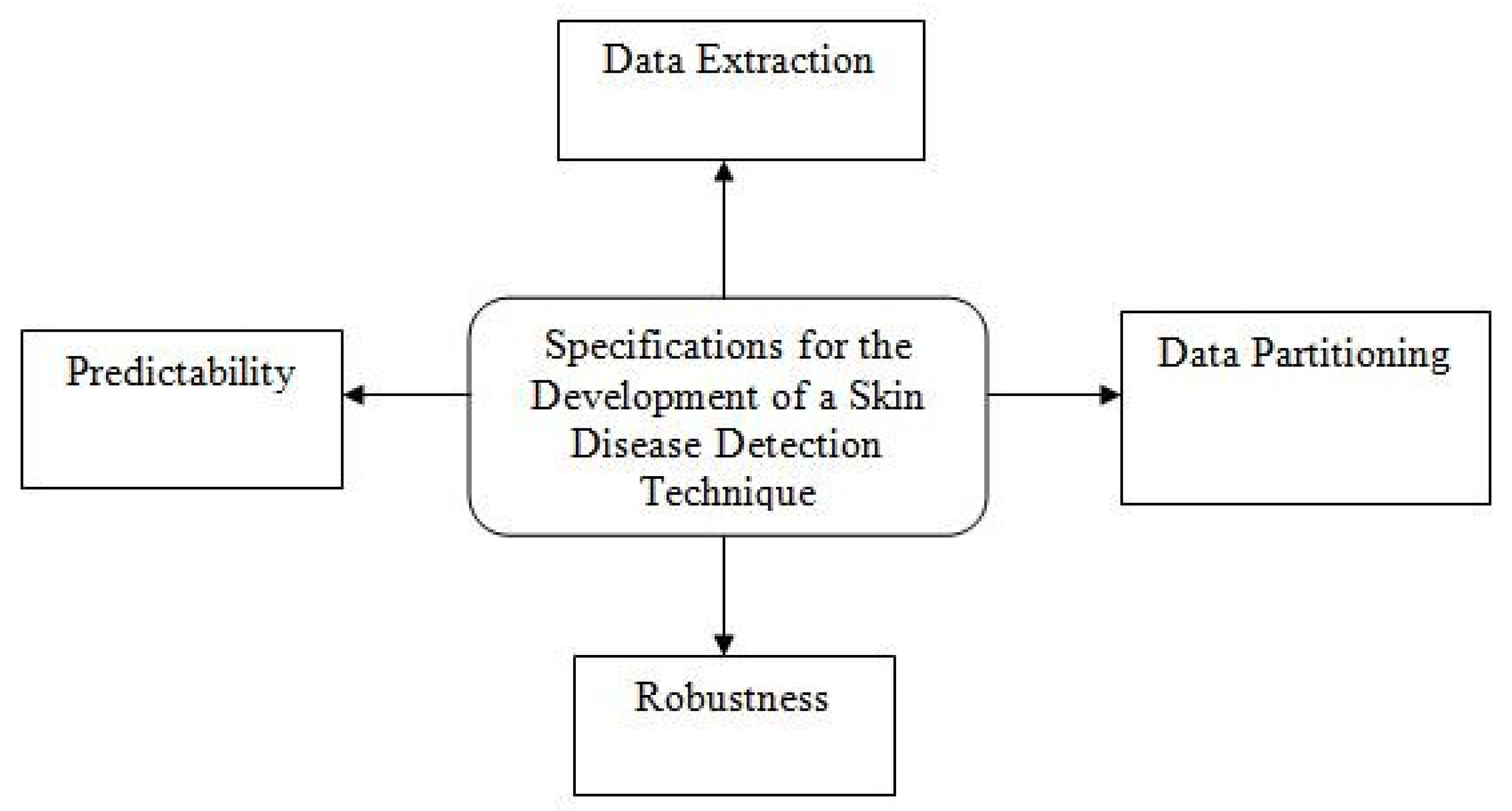
1.2. Research Gap and Design Parameters
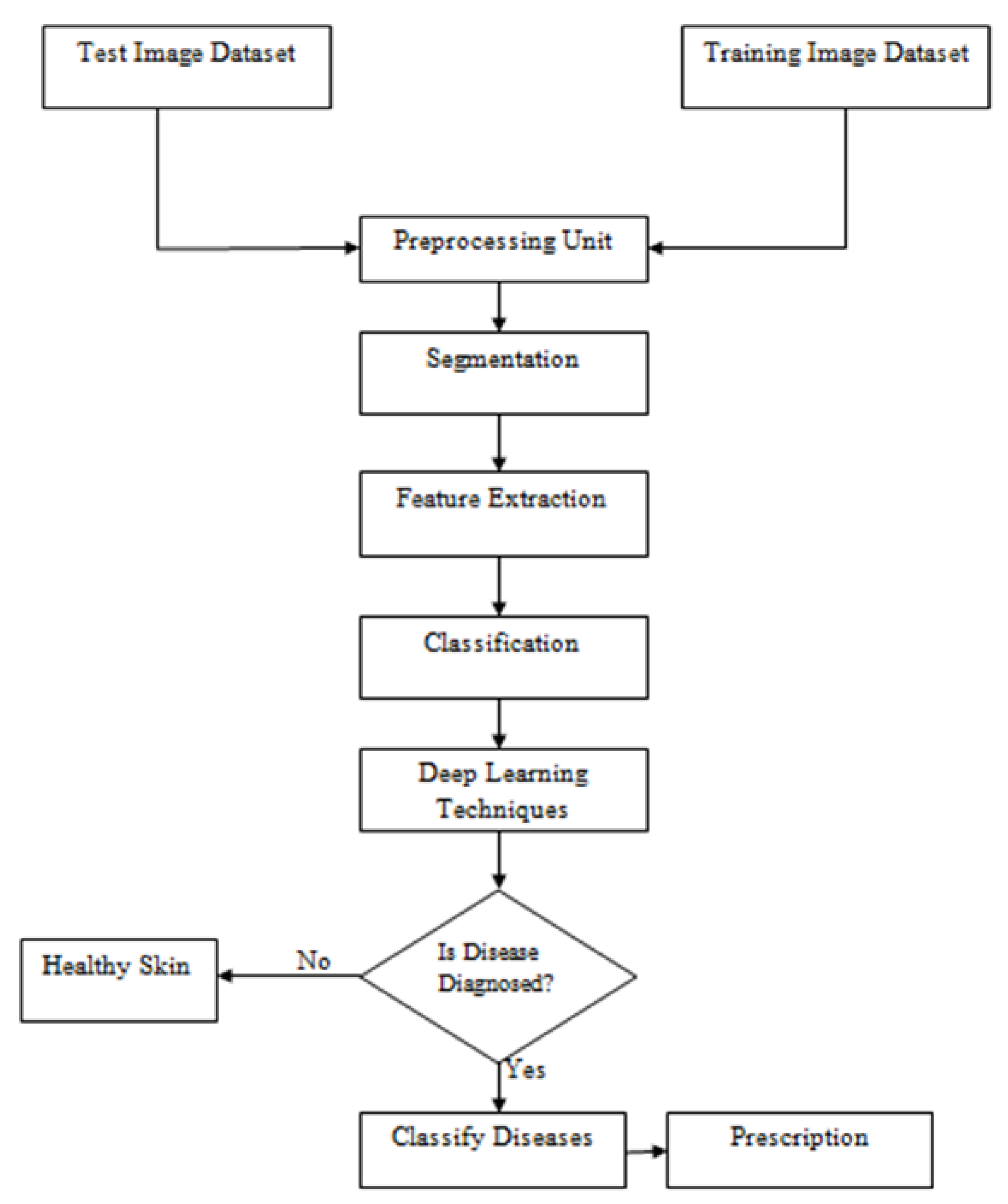
2. System Model
2.1. Motivation of Proposed Work: A Design Plan
2.2. Dermatological Disease Analyses of Diagnostic Systems
3. Input Design Data and Optimization
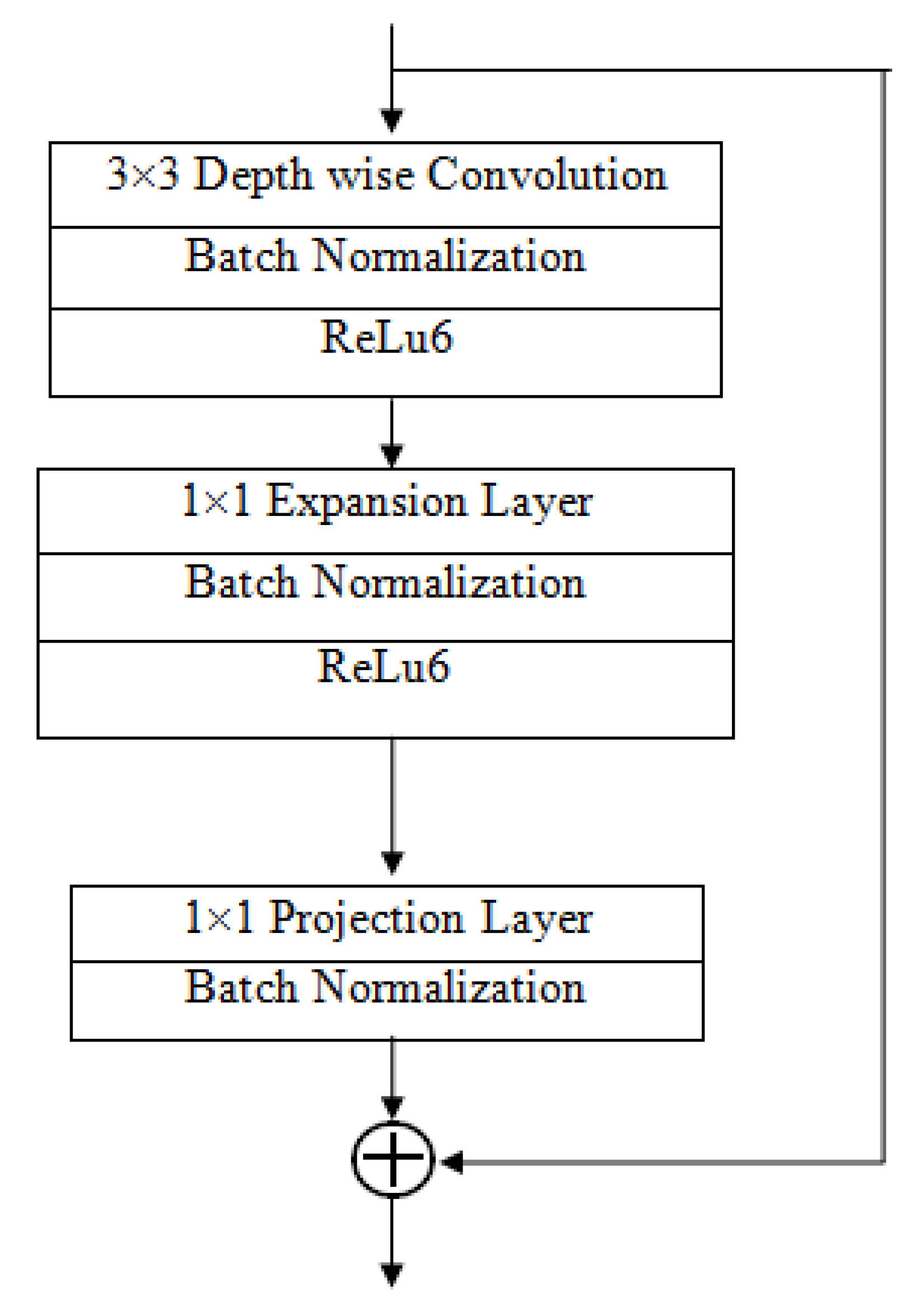
Importance of MobileNet V2 and LSTM
4. Discussion
4.1. Training Dataset
4.2. Progress of the Disease Growth
4.3. Execution Time
4.4. Preprocessing Factors
4.4.1. Incinerate Lightning Module
4.4.2. Viewpoint of Images
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deepalakshmi, P.; Prudhvi, K.T.; Siri, C.S.; Lavanya, K.; Srinivasu, P.N. Plant Leaf Disease Detection Using CNN Algorithm. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Model. Des. 2021, 12, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, G.P.H.; Anitha, J.; Jacinth, P.J. Identification of Melanoma in Dermoscopy Images Using Image Processing Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Control, Power, Communication and Computing Technologies (ICCPCCT), Kannur, India, 23–24 March 2018; pp. 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, K.; Chaudhuri, S.S.; Ghosh, S.; Dutta, S.K.; Chakraborty, P.; Sarkar, R. Skin Disease detection based on different Segmentation Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Opto-Electronics and Applied Optics (Optronix), Kolkata, India, 18–20 March 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kshirsagar, P.; Balakrishnan, N.; Yadav, A.D. Modelling of optimised neural network for classification and prediction of benchmark datasets. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2020, 8, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkur, S.; Kalbande, D.; Shimpi, P.; Bapat, C.; Jatakia, J. Human Skin Detection Using RGB, HSV and YCbCr Color Models. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.02694. [Google Scholar]
- Kotian, A.L.; Deepa, K. Detection and classification of skin diseases by image analysis using Matlab. Int. J. Emerg. Res. Manag. Technol. 2017, 6, 779–784. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaramurthy, S.; Saravanabhavan, C.; Kshirsagar, P. Prediction and Classification of Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Ensemble Machine Learning Approaches. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Application (DASA), Sakheer, Bahrain, 8–9 November 2020; pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gound, R.S.; Gadre, P.S.; Gaikwad, J.B.; Wagh, P.K. Skin Disease Diagnosis System using Image Processing and Data Mining. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2018, 179, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Liang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Chi, T. SOR: An optimised semantic ontology retrieval algorithm for heterogeneous multimedia big data. J. Comput. Sci. 2018, 28, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Q.; Hussain, A.; Ur Rehman, S.; Khan, U.; Maqsood, M.; Mehmood, K.; Khan, M.A. Classification of Melanoma and Nevus in Digital Images for Diagnosis of Skin Cancer. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 90132–90144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitharth, S.; Prasad, K.M.; Sangeetha, K.; Kshirsagar, P.R.; Babu, T.S.; Alhelou, H.H. An Enriched RPCO-BCNN Mechanisms for Attack Detection and Classification in SCADA Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 156297–156312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, N.; Shabut, A.M.; Hossain, M.A. Multi-Class Skin Diseases Classification Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network and Support Vector Machine. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Software, Knowledge, Information Management & Applications (SKIMA), Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 3–5 December 2018; Volume 1, pp. 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, N.; Shabut, A.M.; Hossain, M.A. A Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Classifying Prominent Skin Lesions Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 10th Computer Science and Electronic Engineering (CEEC), Colchester, UK, 19–21 September 2018; Volume 1, pp. 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Liu, Y.; He, W.; Li, X. Skin Roughness Evaluation Method Based on Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrix. In Proceedings of the 31st Chinese Control and Decision Conference (2019 CCDC), Nanchang, China, 3–5 June 2019; Volume 8, pp. 5671–5674. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, G.B.; Shitharth, S. Wireless sensor network and IoT based systems for healthcare application. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mamun, M.; Uddin, M.S. A Comparative Study among Segmentation Techniques for Skin Disease Detection Systems. In Proceedings of International Conference on Trends in Computational and Cognitive Engineering-TCCE 2020; Kaiser, M.S., Bandyopadhyay, A., Mahmud, M., Ray, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 1309, pp. 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alquran, H.; Abu Qasmieh, I.; Alqudah, A.M.; Alhammouri, S.; Alawneh, E.; Abughazaleh, A.; Hasayen, F. The Melanoma Skin Cancer Detection and Classification using Support Vector Machine. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Jordan Conference on Applied Electrical Engineering and Computing Technologies (AEECT), Aqaba, Jordan, 11–13 October 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-Kim, W.; Wettayaprasit, W.; Aiyarak, P. Convolutional neural networks using MobileNet for skin lesion classification. In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering, Chonburi, Thailand, 10–12 July 2019; pp. 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Thirumaleshwari Devi, B.; Shitharth, S. Multiple Face Detection Using Haar-AdaBoosting, LBP-AdaBoosting and Neural Networks. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1042, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SivaSai, J.G.; Srinivasu, P.N.; Sindhuri, M.N.; Rohitha, K.; Deepika, S. An Automated Segmentation of Brain MR Image through Fuzzy Recurrent Neural Network. In Bio-Inspired Neurocomputing; Studies in Computational Intelligence; Bhoi, A., Mallick, P., Liu, C.M., Balas, V., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 903. [Google Scholar]
- Ajith, A.; Goel, V.; Vazirani, P.; Roja, M.M. Digital Dermatology: Skin Disease Detection Model Using Image Processing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 15–16 June 2017; Volume 1, pp. 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Lali, I.U.; Saba TIqbal, T. An Improved Strategy for Skin Lesion Detection and Classification Using Uniform Segmentation and Feature Selection Based Approach. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018, 81, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kshirsagar, P.R.; Manoharan, H.; Tirth, V.; Naved, M.; Siddiqui, A.T.; Sharma, A.K. Automation Monitoring with Sensors For Detecting Covid Using Backpropagation Algorithm. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2021, 15, 2414–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.; Ema, R.R.; Islam, T. An Automated Dermatological Images Segmentation Based on a New Hybrid Intelligent ACO-GA Algorithm and Diseases Identification Using TSVM Classifier. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Advances in Science, Engineering and Robotics Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 3–5 May 2019; pp. 894–899. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Maisano, R.; Tomaselli, V.; Capra, A.; Longo, F.; Puliafito, A. Reducing Complexity of 3D Indoor Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 4th International Forum on Research and Technology for Society and Industry (RTSI), Palermo, Italy, 10–13 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.-W.; Hong, S.-N. Indoor Localization with WiFi Fingerprinting Using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 Tenth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Prague, Czech Republic, 3–6 July 2018; pp. 753–758. [Google Scholar]
- Selvarajan, S.; Shaik, M.; Ameerjohn, S.; Kannan, S. Mining of intrusion attack in SCADA network using clustering and genetically seeded flora based optimal classification algorithm. IET Inf. Secur. 2019, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, S.L.; Dharuman, C.; Venkatesan, P. Disease Classification Using Machine Learning Algorithms—A Comparative Study. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2017, 114, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sunny, A.D.; Kulshreshtha, S.; Singh, S.; Srinabh, B.M.; Sarojadevi, H. Disease Diagnosis System By Exploring Machine Learning Algorithms. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. (IJIET) 2018, 10, 014–021. [Google Scholar]
- Kshirsagar, P.R.; Akojwar, S.G.; Dhanoriya, R. Classification of ECG signals using artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Technologies and Engineering Systems; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 345. [Google Scholar]
- Kolkur, M.S.; Kalbande, D.R.; Kharkar, V. Machine Learning Approaches to Multi-Class Human Skin Disease Detection. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Res. 2018, 14, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hekler, A.; Utikal, J.S.; Enk, A.H.; Berking, C.; Klode, J.; Schadendorf, D.; Jansen, P.; Franklin, C.; Holland-Letz, T.; Krah, D.; et al. Pathologist-level classification of histopathological melanoma images with deep neural networks. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 115, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kshirsgar, P.; More, V.; Hendre, V.; Chippalkatti, P.; Paliwal, K. IOT Based Baby Incubator for Clinic. In ICCCE 2019; Lecture Notes in Electrical, Engineering; Kumar, A., Mozar, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, G.; García-Doval, I.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Descalzo-Gallego, M.A.; Taberner, R.; Gilaberte, Y.; Buendía-Eisman, A.; Fernández-Peñas, P. Difficulties coding dermatological disorders using the ICD-10: The DIADERM study. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. 2018, 109, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aractingi, S. Classifying skin diseases: Until where should we go. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 6, 681–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bram, H.J.; Frauendorfer, M.; Spencer, S.; Hartos, J.L. Does the Prevalence of Skin Cancer Differ by Metropolitan Status for Males and Females in the United States? J. Prev. Med. 2017, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, P.; Akojwar, S.; Bajaj, N.D. A hybridised neural network and optimisation algorithms for prediction and classification of neurological disorders. Int. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 2018, 28, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Kim, M.S.; Lim, W.; Park, G.H.; Park, I.; Chang, S.E. Classification of the clinical images for benign and malignant cutaneous tumours using a deep learning algorithm. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haenssle, H.A.; Fink, C.; Schneiderbauer, R.; Toberer, F.; Buhl, T.; Blum, A.; Kalloo, A.; HadjHassen, A.B.; Thomas, L.; Enk, A.; et al. Man against machine: Diagnostic performance of a deep learning convolutional neural network for dermoscopic melanoma recognition in comparison to 58 dermatologists. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitharth, S.; Meshram, P.; Kshirsagar, P.R.; Manoharan, H.; Tirth, V.; Sundramurthy, V.P. Impact of Big Data Analysis on Nanosensors for Applied Sciences using Neural Networks. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 4927607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, J. Large-Scale Semi-Supervised Learning; NEC LABS America, Inc.: Princeton, NJ, USA; Available online: http://www.thespermwhale.com/jaseweston/papers/largesemi.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2018).
- Padmaja, M.; Shitharth, S.; Prasuna, K.; Chaturvedi, A.; Kshirsagar, P.R.; Vani, A. Growth of Artificail Intelligence to Challenge Security in IoT Application. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demyanov, S.; Chakravorty, R.; Abedini, M.; Halpern, A.; Garnavi, R. Classification of dermoscopy patterns using deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Prague, Czech Republic, 16 June 2016; pp. 364–368. [Google Scholar]



| Diseases | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Acne vulgaris | Marks on the face, little pustules, and small lumps |
| Atopic dermatitis | Itching and irritation, rough, hypersensitivity skin that is genetic, with a red rash and crusty, thick skin |
| Benign skin tumors | Development that is not harmful, black drawing on the skin, and a smooth, rough, and oily texture |
| Mastitis | Infectious, heated, and uncomfortable tumor in a woman’s breast |
| Viral warts | Infection, any region of the organism, exfoliation of the afflicted area |
| Diaper candidiasis | Fungal, a diaper worn across two legs, urine exposure, red, swelling, seeping, and fluid |
| Folliculitis | Bacterial, tiny pus vesicles, and little red lumps |
| Carbuncle | Infection, compromised immune system, diabetes mellitus, and little pimples on the afflicted area |
| Eczema | Discoloration, cracking, and peeling |
| Number of States | Input Gate | Forget Gate | Cell State Gate | Reference Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 139 | 124 | 144 | 135.66 |
| 2 | 126 | 121 | 128 | 125 |
| 3 | 143 | 125 | 168 | 145.33 |
| 4 | 159 | 121 | 182 | 154 |
| 5 | 170 | 147 | 188 | 168.33 |
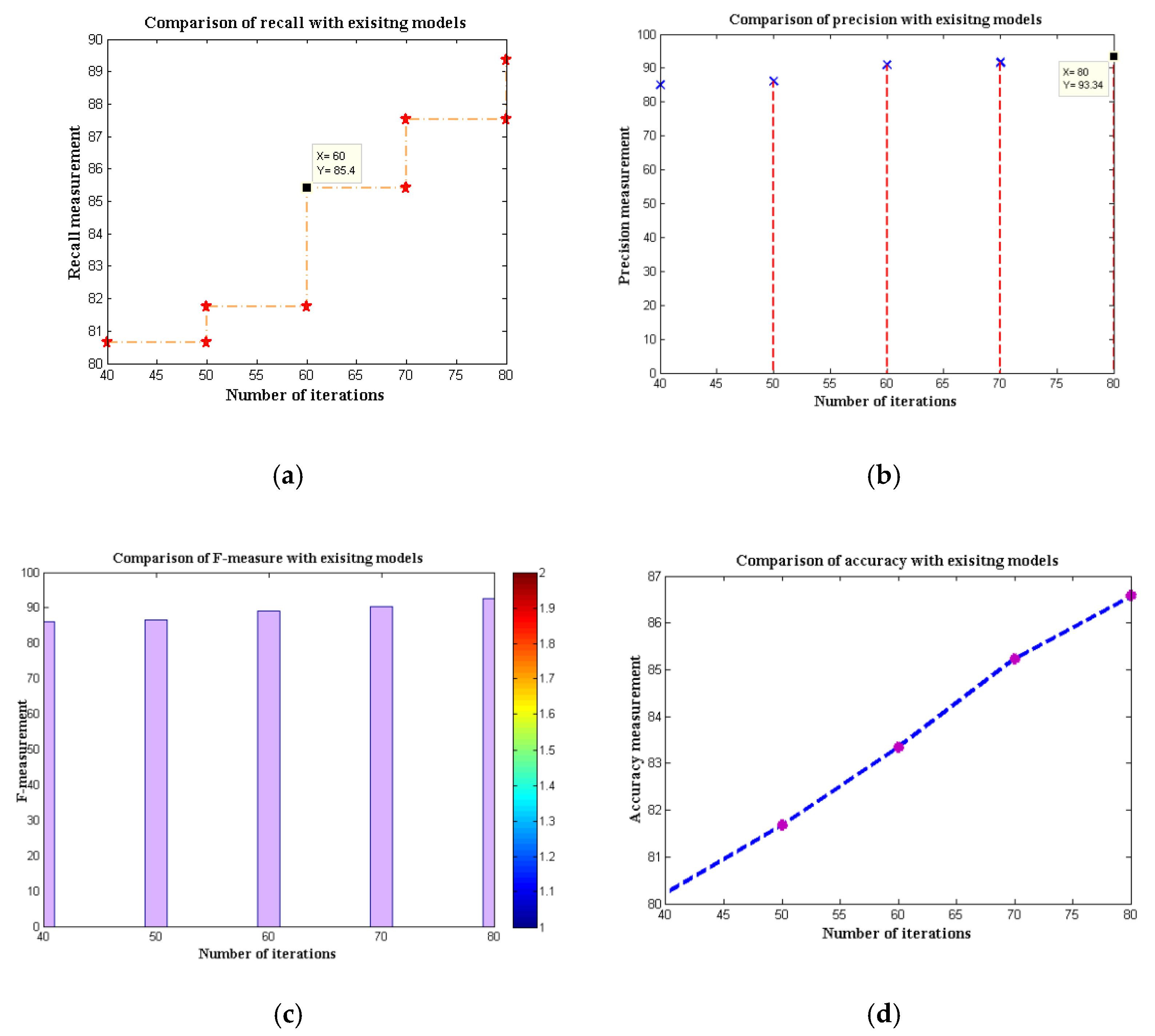
| Algorithms | Recall | Precision | F-Measure | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTNN | 80.65 | 85.07 | 86.07 | 80.23 |
| CNN | 81.75 | 86.07 | 86.61 | 81.67 |
| Depth-based CNN | 80.23 | 80.49 | 82.56 | 82.93 |
| Channel boost CNN | 81.24 | 82.39 | 82.98 | 83.45 |
| MobileNet V1 | 85.40 | 90.92 | 89.12 | 83.34 |
| MobileNet V2 | 87.51 | 91.69 | 90.23 | 85.23 |
| MobileNet V2–LSTM | 89.34 | 93.34 | 92.68 | 86.57 |
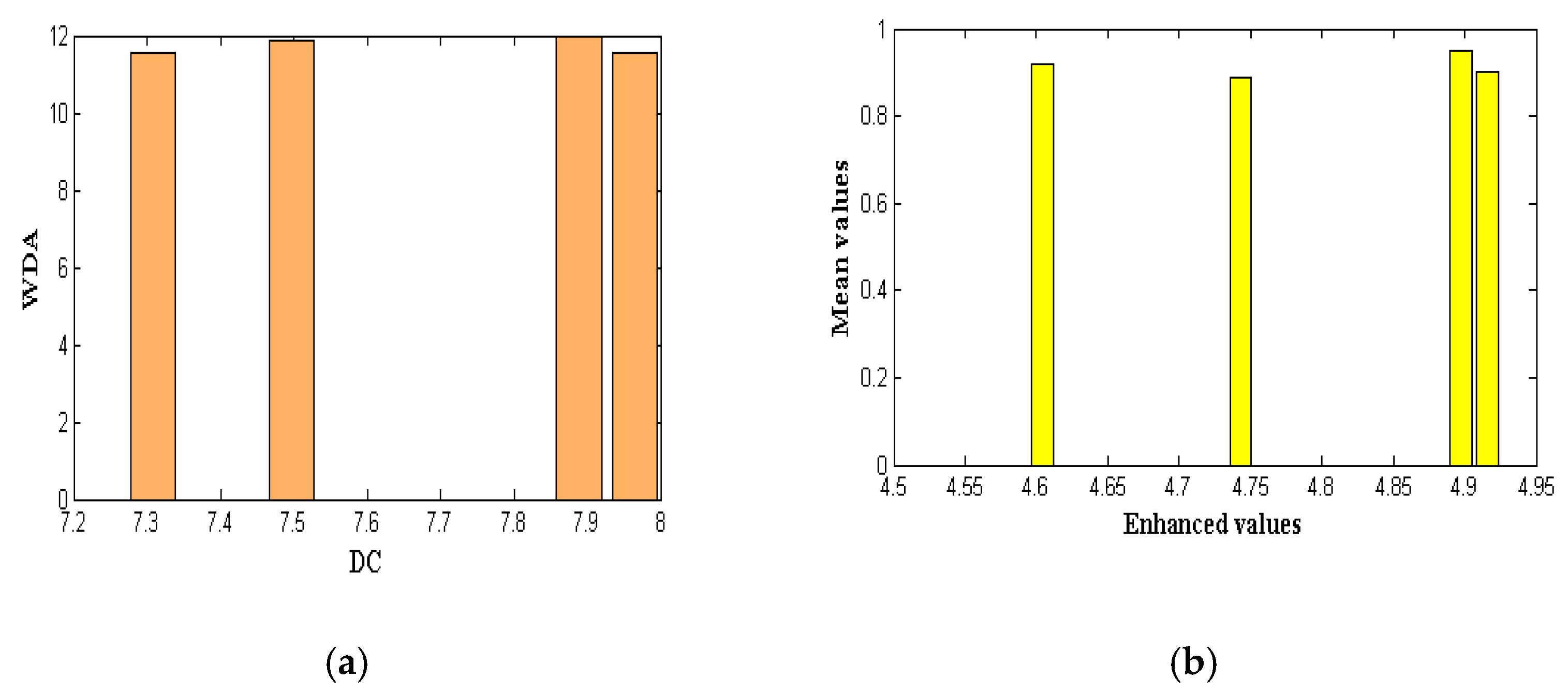
| Algorithms | Core of Disease (DC) | Whole Disease Area (WDA) | Enhanced | Mean Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 7.965 | 11.567 | 4.743 | 0.89 |
| Depth-based CNN | 7.234 | 11.459 | 4.369 | 0.72 |
| Channel boost CNN | 7.348 | 11.270 | 4.421 | 0.81 |
| MobileNet V1 | 7.309 | 11.552 | 4.916 | 0.90 |
| MobileNet V2 | 7.498 | 11.894 | 4.604 | 0.92 |
| MobileNet V2–LSTM | 7.889 | 11.999 | 4.897 | 0.95 |
| Algorithms | Maximum Iteration | Time of Execution |
|---|---|---|
| CNN | 90 | 162.32 |
| Depth-based CNN | 90 | 167.90 |
| Channel boost CNN | 80 | 156.23 |
| MobileNet V1 | 90 | 118.15 |
| MobileNet V2 | 70 | 107.89 |
| MobileNet V2–LSTM | 60 | 99.67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kshirsagar, P.R.; Manoharan, H.; Shitharth, S.; Alshareef, A.M.; Albishry, N.; Balachandran, P.K. Deep Learning Approaches for Prognosis of Automated Skin Disease. Life 2022, 12, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030426
Kshirsagar PR, Manoharan H, Shitharth S, Alshareef AM, Albishry N, Balachandran PK. Deep Learning Approaches for Prognosis of Automated Skin Disease. Life. 2022; 12(3):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030426
Chicago/Turabian StyleKshirsagar, Pravin R., Hariprasath Manoharan, S. Shitharth, Abdulrhman M. Alshareef, Nabeel Albishry, and Praveen Kumar Balachandran. 2022. "Deep Learning Approaches for Prognosis of Automated Skin Disease" Life 12, no. 3: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030426
APA StyleKshirsagar, P. R., Manoharan, H., Shitharth, S., Alshareef, A. M., Albishry, N., & Balachandran, P. K. (2022). Deep Learning Approaches for Prognosis of Automated Skin Disease. Life, 12(3), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030426







