Abstract
Glyphosate is the world’s most widely used agrochemical. Its use in agriculture and gardening has been proclaimed safe because humans and other animals do not have the target enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). However, increasing numbers of studies have demonstrated risks to humans and animals because the shikimate metabolic pathway is present in many microbes. Here, we assess the potential effect of glyphosate on healthy human microbiota. Our results demonstrate that more than one-half of human microbiome are intrinsically sensitive to glyphosate. However, further empirical studies are needed to determine the effect of glyphosate on healthy human microbiota.
1. Introduction
Glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine) is globally the most commonly used herbicide in agriculture, horticulture, silviculture, recreational areas, and home gardens [1,2]. The popularization of glyphosate-based herbicides (GBHs) has been associated with an increased detection of glyphosate and its by-product aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) in soil and water [3,4,5]. Here, we perceive the risk that glyphosate may modulate microbes that are essential to human well-being because the targeted shikimate pathway is present in many microbes [6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. The herbicide inactivates the central enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS), an almos-universal enzyme in plants, fungi, and prokaryotes, for the synthesis of three aromatic amino acids [13,14]. Some species have evolved a variety of resistance mechanisms to glyphosate (Figure 1), including target-site resistance (TSR), i.e., the direct effect of glyphosate on the EPSPS enzyme [6], and non-target-site resistance (NTSR) [15]. TSR adaptations can be determined based on amino acid biomarkers in the EPSPS active site that classify the enzyme as potentially sensitive or resistant to glyphosate [6]. Currently, four classes of EPSPS enzymes have been recognized as potentially sensitive (class I) or resistant (class II–IV) and can be determined based on bioinformatic methods. NTSR mechanisms may reduce the sensitivity of organisms to glyphosate by efflux pumps and the overexpression of the epsps gene [16]. Alternatively, they may increase sensitivity via the mitochondrial transport chain [17].
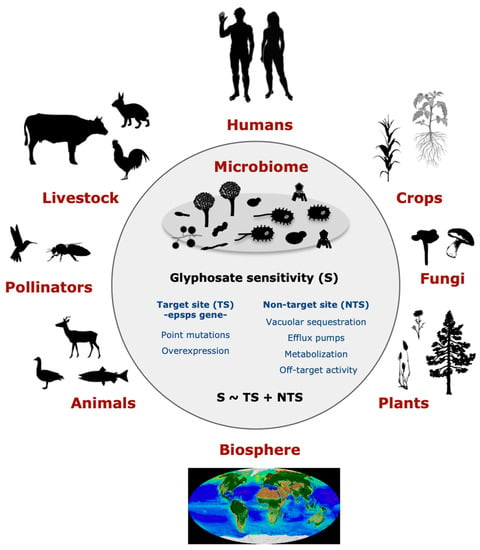
Figure 1.
Potential effects of glyphosate on the microbiome may have an impact on environmental health, human health, and sustainability. Glyphosate may influence healthy microbiota due to its action on the EPSPS enzyme, glyphosate target site (TS), and other non-target site (NTS) mechanisms. A healthy microbiota presents diverse species that are either sensitive or resistant to the herbicide. Thus, the heavy use of glyphosate-based products may lead to microbial dysbiosis by enhancing the spread of resistant and fast-evolving bacteria and selecting against sensitive ones. The consequences of this imbalance in the microbiota may have a wide-ranging ecological impact.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset of EPSPS Proteins
A dataset of the 732 bacterial genomes was obtained from the Human Microbiome Project (HMP) [18]. Genomes were mapped through BLAST searches onto the COG0128 from the database of Cluster of Orthologous Groups (COG) [19] to identify EPSPS proteins. The dataset is available in Supplementary Table S1.
2.2. Potential Sensitivity and Resistance to Glyphosate
Glyphosate targets the EPSPS enzyme by competing for the binding site with phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP) [20]. The enzyme has been categorized into four classes based on its potential sensitivity to glyphosate [6,21]. Classes I, II, and IV were determined based on the presence and absence of amino acid markers in active sites, whereas Class III was categorized based on a series of motifs. Biomarkers were identified based on amino acid residues in the EPSPS of Vibrio cholerae (Class I), Coxiella burnetii (Class II), Brevundimonas vesicularis (Class III), and Streptomyces davawensis (Class IV). These reference sequences are used on the web server http://ppuigbo.me/programs/EPSPSClass/ (accessed on 1 December 2021) to determine the intrinsic sensitivity of EPSPS enzymes.
3. Results and Discussion
Recently, we combined closely related bacterial species and different strains within species to identify changes in their sensitivity to glyphosate [7] under the microevolutionary perspective of Alignable Tight Genomic Clusters (ATGC) [22]. The study of the EPSPS enzyme showed that phylogenetic groups and bacterial lifestyle are key factors determining the intrinsic sensitivity to glyphosate, possibly resulting from thicker cell walls in addition to differences in EPSPS type [7,8]. Specifically, Firmicutes were significantly more resistant to glyphosate than the most sensitive Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria groups. Moreover, a bacterial lifestyle was strongly associated with sensitivity, because facultative host-associated and parasitic bacteria are more sensitive to the herbicide than free-living bacteria. However, Van Bruggen et al. showed that pathogens are generally less sensitive to glyphosate than host-associated and free-living bacteria, by analyzing literature data on minimal inhibitory concentrations for a large number of bacteria [8]. The microevolutionary analysis further revealed that bacteria may easily become resistant to glyphosate through small changes in the EPSPS active site in the short evolutionary time of ATGC with non-synonymous mutations and horizontal gene transfers [7]. Thus, the heavy use of glyphosate may have a strong impact on the species diversity and composition of microbial communities via (1) the purifying selection against sensitive bacteria, (2) the rapid adaptation of some bacterial groups to become resistant to glyphosate, and (3) the potential glyphosate-related multidrug resistance in bacteria [7,12,23].
Humans may be exposed to glyphosate directly when applying glyphosate-based herbicides or indirectly via drinking water and foodstuffs containing glyphosate residues [24,25]. In traditional agricultural practices, glyphosate-based herbicides are applied before planting and after harvest, but in genetically modified glyphosate-resistant crops, they can be used during the growing season. In addition, glyphosate-based herbicides are commonly used to desiccate traditional grain and seed crops before harvest. These practices include the risks of inhalation and skin exposure to the applicator. Residues in ingested products may lead to the exposure of human gastrointestinal and urogenital systems’ microbiota to glyphosate and its metabolites. Human cells are presumably not directly affected by glyphosate due to the lack of the EPSPS enzyme. However, the effect of glyphosate on the host-associated microbiota has been suggested in several studies of insects, plants, and mammals [7,9,10,26,27,28]. In our previous study [6], we performed a survey of 890 EPSPS sequences to evaluate the potential sensitivity to glyphosate in 101 common human gut bacterial species [29]. We found that 54% of most common gut bacterial species are intrinsically sensitive to glyphosate, i.e., these species present amino acid biomarkers that determine the susceptibility to glyphosate: 29% are potentially resistant, 7% vary intraspecifically, and 10% are unclassified. Bacteria with sensitive copies of the EPSPS enzyme include Faecalibacterium, Bifidobacterium, and Citrobacter, whereas Clostridium, Dorea, and Ruminococcus mostly have resistant sequences. These genera have previously been associated with irritable bowel syndrome [30]. Gastrointestinal issues (such as IBS) and inflammatory conditions have been speculated to arise from gut dysbiosis resulting from glyphosate exposure via the foodstuffs frequently included in a Western diet [31,32].
Here, with an extended survey of the TSR mechanism for glyphosate in 732 bacteria from the Human Microbiome Project (HMP) [18], we reveal the intrinsic sensitivity of glyphosate in a set of bacterial species of the human microbiome (Figure 2). Analysis of the EPSPS enzyme showed that 55% of bacterial strains isolated from the human body are potentially sensitive to glyphosate, in agreement with our previous study [6], and 77.8% of the strains (732 out of 941) have at least one copy of the epsps gene. The breakdown of the dataset by the isolation site of the microbe in the human body revealed differential sensitivity to the herbicide (Supplementary Table S1). A larger proportion of strains inhabiting the oral cavity and airways were intrinsically resistant to glyphosate compared with most other body sites.
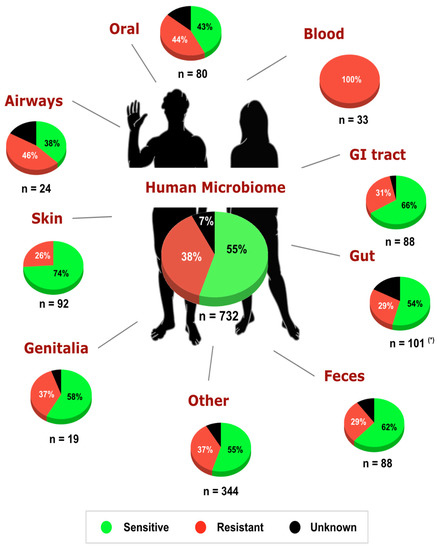
Figure 2.
Potential sensitivity to glyphosate in bacteria of the human microbiome project [18]. A total of 732 out of 941 (77.8%) bacterial species from the HMP have at least one copy of the epsps gene. Overall, in the human microbiome, the intrinsic sensitivity of bacteria to glyphosate is distributed as 55% sensitive, 38% resistant, and 7% unclassified. (*) Data concerning the sensitivity of gut microbiota were obtained from [6].
The airways are largely dominated by strains from the genera Neisseria (including both sensitive and unclassified strains), Staphylococcus (all strains are resistant to glyphosate), and Streptococcus (all strains are resistant to glyphosate). In the oral cavity, Streptococcus strains are dominated by resistant strains, whereas Prevotella strains are mostly sensitive to glyphosate. The skin microbiota is dominated by commensal and opportunistically pathogenic species [33] mostly sensitive to the herbicide. For example, the human skin is dominated by Propionibacterium acnes (all stains are sensitive to glyphosate) and Staphylococcus epidermidis (all strains are resistant to glyphosate). Moreover, 58% of the strains from the urogenital tract and vagina were intrinsically sensitive to the herbicide. Interestingly, all strains isolated from human blood are opportunistic pathogens, in agreement with [34], and intrinsically resistant to glyphosate (Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus sanguinis, Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Sporosarcina newyorkensis, and Psychrobacter sanguinis). Associations between microbiome dysbiosis and bloodstream infections (BSIs) have been suggested in immunocompromised [35] and COVID-19 [36] patients. Thus, it is possible that exposure to glyphosate may provide conditions that increase BSI-causing bacteria while decreasing sensitive commensal bacteria.
Recent studies with several animal species suggest that traces of glyphosate in food may lead to alterations of the gut microbiota [6,9,11,26,27,37,38] and changes in the urine metabolome [27,39]. The main elimination route of glyphosate is via urine excretion; thus, glyphosate is frequently found in the urine [40,41]. Glyphosate exposure via nutrition, inhalation, or dermal absorption has been proven by the urinal glyphosate residues detected in several studies [40,42]. Moreover, microbes inhabiting the human oral cavity and airways could be exposed to glyphosate via nutrition and inhalation routes. Dermal exposure, caused mainly by occupational use or the handling of glyphosate [43], may disrupt the skin microbiota.
A healthy human microbiota is defined by its microbial composition, function, dynamics, and ecology [44,45]. Distinctions in glyphosate sensitivity/resistance among bacteria, including the TSR and NTSR mechanisms, may lead to the dysbiosis of normal flora due to differential selection pressure [6,7,27]. The sheer number of intrinsically sensitive bacteria to glyphosate may lead to a potentially emerging disease due to microbial dysbiosis [31]. This includes a possible reduction in bacterial diversity due to a decrease in sensitive bacteria and an increase in resistant and fast-evolving bacteria, which are often pathogenic [46,47,48]. Pathogens tend to have superior stress responses due to their higher adaptiveness under stress conditions; for example, the transition from the environment into their host [46,47]. Thus, glyphosate as a stress factor may reduce bacterial susceptibility, either as a stress response or via mutations and change the bacterial response to antibiotics [12,49,50,51,52,53]. In turn, the heavy use of antibiotics and other chemicals may lead to bacterial co- and cross-resistance to glyphosate and other antimicrobials [8,46,54]. Notably, however, sensitivity towards antimicrobial compounds depends on the given concentration; thus, it is necessary to empirically determine at which level of glyphosate, and GBH, bacteria are resistant or susceptible.
4. Conclusions
Hence, does glyphosate affect the human microbiota? Contemporary research points to the herbicide’s potential to disrupt healthy microbiomes, including the human microbiome. Several empirical studies have determined the impact of glyphosate-based products on wild- and host-associated microbiota and called to control the potentially negative consequences on environmental health and sustainability. However, further empirical studies are needed to find a “smoking gun” that determines the effect of glyphosate on the healthy human microbiota. Moreover, additional experimental and epidemiological studies are needed to determine these proposed effects of glyphosate-based products on wild and host-associated microbes to control their potentially negative consequences on human health and ecosystem functions and services.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/life12050707/s1, Table S1: Potential sensitivity of bacterial species from the human microbiome to glyphosate.
Author Contributions
Conception and design of the study: P.P. Data collection: P.P. and L.I.L. Data analysis: P.P. and L.I.L. Manuscript drafting: P.P., L.I.L. and M.J.R. Manuscript revision for critical intellectual content: P.P., L.I.L., M.J.R., K.S., I.S. and M.H. Writing the final version of the manuscript: P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was supported by funds from the Turku Collegium for Science, Medicine and Technology (P.P.) and the Academy of Finland (grant no. 311077 to MH). P.P.’s research is also funded by Torres de Quevedo grant PTQ2018-009846.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
EPSPS protein data is available at http://ppuigbo.me/programs/EPSPSClass (accessed on 20 April 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Myers, J.P.; Antoniou, M.N.; Blumberg, B.; Carroll, L.; Colborn, T.; Everett, L.G.; Hansen, M.; Landrigan, P.J.; Lanphear, B.P.; Mesnage, R.; et al. Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: A consensus statement. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodburn, A.T. Glyphosate: Production, pricing and use worldwide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2000, 56, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagner, M.; Mikola, J.; Saloniemi, I.; Saikkonen, K.; Helander, M. Effects of a glyphosate-based herbicide on soil animal trophic groups and associated ecosystem functioning in a northern agricultural field. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struger, J.; Van Stempvoort, D.R.; Brown, S.J. Sources of aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) in urban and rural catchments in Ontario, Canada: Glyphosate or phosphonates in wastewater? Environ. Pollut. 2015, 204, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglin, W.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Kuivila, K.M.; Dietze, J.E. Glyphosate and Its Degradation Product AMPA Occur Frequently and Widely in U.S. Soils, Surface Water, Groundwater, and Precipitation. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leino, L.; Tall, T.; Helander, M.; Saloniemi, I.; Saikkonen, K.; Ruuskanen, S.; Puigbò, P. Classification of the glyphosate target enzyme (5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase) for assessing sensitivity of organisms to the herbicide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 408, 124556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainio, M.J.; Ruuskanen, S.; Helander, M.; Saikkonen, K.; Saloniemi, I.; Puigbò, P. Adaptation of bacteria to glyphosate: A microevolutionary perspective of the enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2021, 13, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bruggen, A.H.; Finckh, M.R.; He, M.; Ritsema, C.J.; Harkes, P.; Knuth, D.; Geissen, V. Indirect effects of the herbicide glyphosate on plant, animal and human health through its effects on microbial communities. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 589618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, E.V.; Raymann, K.; Moran, N.A. Glyphosate perturbs the gut microbiota of honey bees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10305–10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gallego, C.; Rainio, M.J.; Collado, M.C.; Mantziari, A.; Salminen, S.; Saikkonen, K.; Helander, M. Glyphosate-Based herbicide affects the composition of microbes associated with Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2020, 367, fnaa050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruuskanen, S.; Rainio, M.J.; Gómez-Gallego, C.; Selenius, O.; Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Saikkonen, K.; Saloniemi, I.; Helander, M. Glyphosate-Based herbicides influence antioxidants, reproductive hormones and gut microbiome but not reproduction: A long-term experiment in an avian model. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoult, D.; Hadjadj, L.; Baron, S.A.; Rolain, J.-M. Role of glyphosate in the emergence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, G.F.; Kishore, G.M.; Padgette, S.R.; Stalling, W.C. Glyphosate-Tolerant 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-Phosphate Synthases. U.S. Patent 5,633,435, 27 May 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Healy-Fried, M.L.; Funke, T.; Priestman, M.A.; Han, H.; Schönbrunn, E. Structural Basis of Glyphosate Tolerance Resulting from Mutations of Pro101 in Escherichia coli 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate Synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 32949–32955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaines, T.A.; Duke, S.O.; Morran, S.; Rigon, C.A.G.; Tranel, P.J.; Küpper, A.; Dayan, F.E. Mechanisms of evolved herbicide resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 10307–10330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, J.M.; Brand, L.; Tran, M.; Kong, Y.; Rogers, S.G. Bacterial glyphosate resistance conferred by overexpression of an E. coli membrane efflux transporter. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 39, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.P.; Juneau, P. Oxidative stress in duckweed (Lemna minor L.) induced by glyphosate: Is the mitochondrial electron transport chain a target of this herbicide? Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The Human Microbiome Project. Nature 2007, 449, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galperin, M.; Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.; Koonin, E.V. Expanded microbial genome coverage and improved protein family annotation in the COG database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 43, D261–D269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbrunn, E.; Eschenburg, S.; Shuttleworth, W.A.; Schloss, J.V.; Amrhein, N.; Evans, J.N.S.; Kabsch, W. Interaction of the herbicide glyphosate with its target enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate synthase in atomic detail. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.A.; Muola, A.; Saikkonen, K.; Saloniemi, I.; Helander, M.; Puigbò, P. Quantification of the Potential Impact of Glyphosate-Based Products on Microbiomes. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 179, e63109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, D.M.; Wolf, Y.; Koonin, E.V. ATGC database and ATGC-COGs: An updated resource for micro- and macro-evolutionary studies of prokaryotic genomes and protein family annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D210–D218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Gefen, O.; Ronin, I.; Bar-Meir, M.; Balaban, N.Q. Effect of tolerance on the evolution of antibiotic resistance under drug combinations. Science 2020, 367, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centner, T.J.; Russell, L.; Mays, M. Viewing evidence of harm accompanying uses of glyphosate-based herbicides under US legal requirements. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 648, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartjes, F.A.; Van der Aa, M. Measures to reduce pesticides leaching into groundwater-based drinking water resources: An appeal to national and local governments, water boards and farmers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bali, Y.A.; Ba-M’Hamed, S.; Elhidar, N.; Nafis, A.; Soraa, N.; Bennis, M. Glyphosate based- herbicide exposure affects gut microbiota, anxiety and depression-like behaviors in mice. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2018, 67, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnage, R.; Teixeira, M.; Mandrioli, D.; Falcioni, L.; Ducarmon, Q.R.; Zwittink, R.D.; Mazzacuva, F.; Caldwell, A.; Halket, J.; Amiel, C.; et al. Use of Shotgun Metagenomics and Metabolomics to Evaluate the Impact of Glyphosate or Roundup MON 52276 on the Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolome of Sprague-Dawley Rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 17005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, E.V.S.; Mak, M.; De Jong, T.K.; Powell, J.E.; O’Donnell, A.; Suhr, K.J.; Riddington, I.M.; Moran, N.A. Oral or Topical Exposure to Glyphosate in Herbicide Formulation Impacts the Gut Microbiota and Survival Rates of Honey Bees. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Biagi, E.; Heilig, H.G.; Kajander, K.; Kekkonen, R.A.; Tims, S.; de Vos, W.M. Global and Deep Molecular Analysis of Microbiota Signatures in Fecal Samples from Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.A.; Gibson, D.L. Separating the Empirical Wheat from the Pseudoscientific Chaff: A Critical Review of the Literature Surrounding Glyphosate, Dysbiosis and Wheat-Sensitivity. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 556729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsel, A.; Seneff, S. Glyphosate, pathways to modern diseases II: Celiac sprue and gluten intolerance. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2013, 6, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achermann, Y.; Goldstein, E.J.C.; Coenye, T.; Shirtliff, M.E. Propionibacterium acnes: From Commensal to Opportunistic Biofilm-Associated Implant Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 419–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppli, M.; Aabenhus, R.; Harboe, Z.; Andersen, L.; Tvede, M.; Jensen, J.-U.S. Mortality in enterococcal bloodstream infections increases with inappropriate antimicrobial therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taur, Y.; Xavier, J.; Lipuma, L.; Ubeda, C.; Goldberg, J.; Gobourne, A.; Lee, Y.J.; Dubin, K.A.; Socci, N.D.; Viale, A.; et al. Intestinal Domination and the Risk of Bacteremia in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venzon, M.; Bernard-Raichon, L.; Klein, J.; Axelrad, J.; Hussey, G.; Sullivan, A.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Noval, M.; Valero-Jimenez, A.; Gago, J.; et al. Gut microbiome dysbiosis during COVID-19 is associated with increased risk for bacteremia and microbial translocation. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blot, N.; Veillat, L.; Rouzé, R.; Delatte, H. Glyphosate, but not its metabolite AMPA, alters the honeybee gut microbiota. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnage, R.; Antoniou, M.N. Computational modelling provides insight into the effects of glyphosate on the shikimate pathway in the human gut microbiome. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 1, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lesseur, C.; Miao, Y.; Manservisi, F.; Panzacchi, S.; Mandrioli, D.; Belpoggi, F.; Chen, J.; Petrick, L. Low-Dose exposure of glyphosate-based herbicides disrupt the urine metabolome and its interaction with gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, L.; Sieke, C.; Pfeil, R.; Solecki, R. A critical review of glyphosate findings in human urine samples and comparison with the exposure of operators and consumers. J. Verbr. Lebensm. 2015, 10, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, D.; Grau, N.; Gascuel, Q.; Paroissin, C.; Stratonovitch, C.; Lairon, D.; Devault, D.A.; Di Cristofaro, J. Quantifiable urine glyphosate levels detected in 99% of the French population, with higher values in men, in younger people, and in farmers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32882–32893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, M.; Schledorn, P.; Schrödl, W.; Hoppe, H.-W.; Lutz, W.; Shehata, A.A. Detection of glyphosate residues in animals and humans. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Acquavella, J.F.; Alexander, B.H.; Mandel, J.S.; Gustin, C.; Baker, B.; Chapman, P.; Bleeke, M. Glyphosate biomonitoring for farmers and their families: Results from the Farm Family Exposure Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Abu-Ali, G.; Huttenhower, C. The healthy human microbiome. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilenko, V.; Devyatkin, A.; Marsova, M.; Shibilova, M.; Ilyasov, R.; Shmyrev, V. Common Inflammatory Mechanisms in COVID-19 and Parkinson’s Diseases: The Role of Microbiome, Pharmabiotics and Postbiotics in Their Prevention. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 6349–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bote, K.; Pöppe, J.; Merle, R.; Makarova, O.; Roesler, U. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Glyphosate and of a Glyphosate-Containing Herbicide Formulation for Escherichia coli Isolates—Differences Between Pathogenicand Non-pathogenic Isolates and Between Host Species. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.; Sahu, G.K.; Das, J. Stress response in pathogenic bacteria. J. Biosci. 1996, 21, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.A.; Schrödl, W.; Aldin, A.A.; Hafez, H.M.; Krüger, M. The Effect of Glyphosate on Potential Pathogens and Beneficial Members of Poultry Microbiota In Vitro. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurenbach, B.; Gibson, P.S.; Hill, A.M.; Bitzer, A.S.; Silby, M.W.; Godsoe, W.; Heinemann, J.A. Herbicide ingredients change Salmonella enterica sv. Typhimurium and Escherichia coli antibiotic responses. Microbiology 2017, 163, 1791–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Cui, P.; Wen, C.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Tang, J.; Che, J.; et al. Herbicide Selection Promotes Antibiotic Resistance in Soil Microbiomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 2337–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bote, K.; Pöppe, J.; Riede, S.; Breves, G.; Roesler, U. Effect of a Glyphosate-Containing Herbicide on Escherichia coli and Salmonella Ser. Typhimurium in an In Vitro Rumen Simulation System. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 9, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurenbach, B.; Marjoshi, D.; Amábile-Cuevas, C.F.; Ferguson, G.C.; Godsoe, W.; Gibson, P.; Heinemann, J.A. Sublethal Exposure to Commercial Formulations of the Herbicides Dicamba, 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid, and Glyphosate Cause Changes in Antibiotic Susceptibility in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. mBio 2015, 6, e00009-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurenbach, B.; Hill, A.M.; Godsoe, W.; Van Hamelsveld, S.; Heinemann, J.A. Agrichemicals and antibiotics in combination increase antibiotic resistance evolution. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bruggen, A.H.; He, M.M.; Shin, K.; Mai, V.; Jeong, K.C.; Finckh, M.R.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Environmental and health effects of the herbicide glyphosate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).