Ginseng® Alleviates Malathion-Induced Hepatorenal Injury through Modulation of the Biochemical, Antioxidant, Anti-Apoptotic, and Anti-Inflammatory Markers in Male Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Animals, Treatment Design
2.3. Biochemical Investigation
2.4. Antioxidant Tissue Parameters Analysis
2.5. Gene Expression
2.6. Histopathological Examination
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bodyweight
3.2. Liver and Kidney Serum Markers
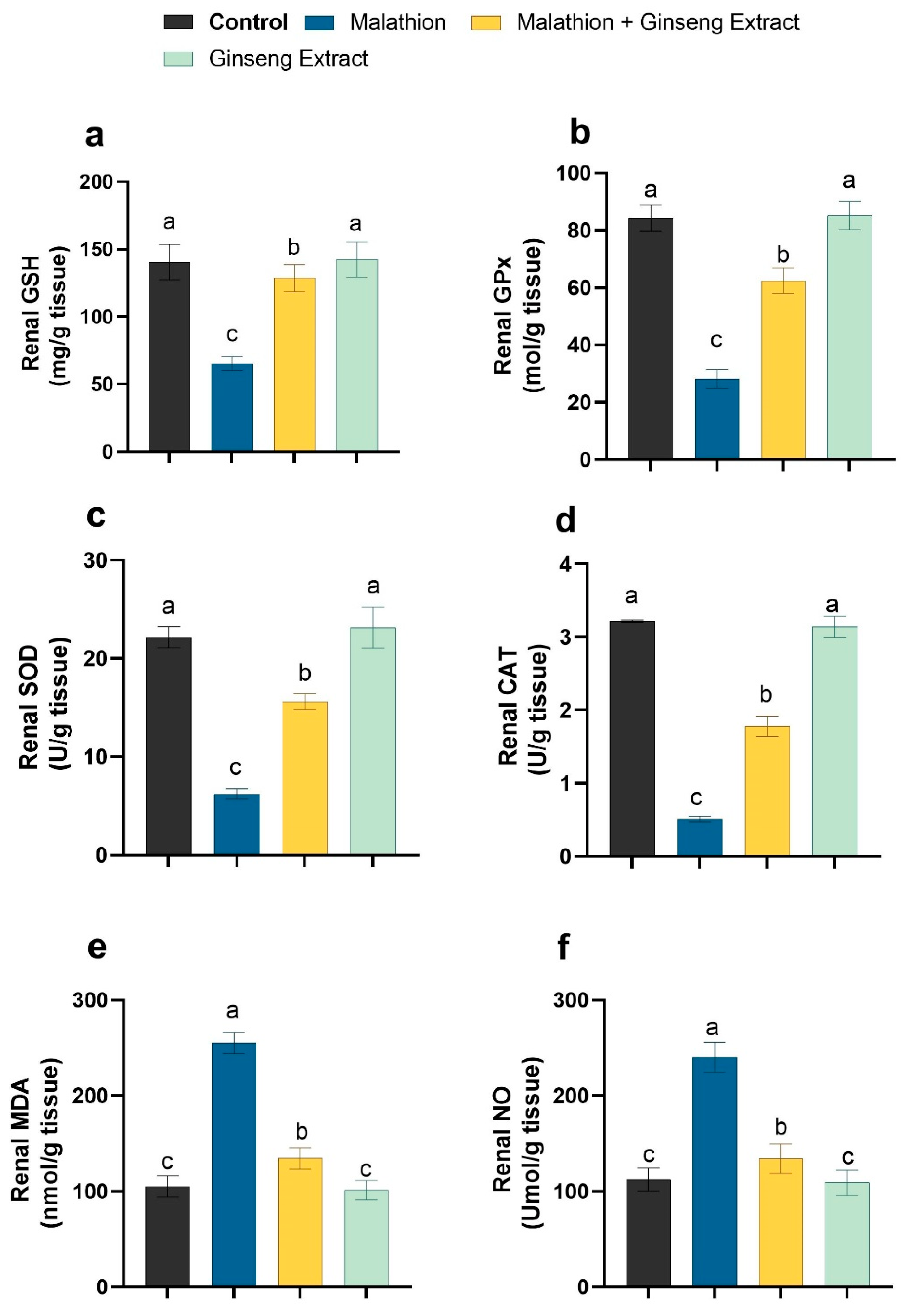
3.3. Hepatic and Renal Oxidative Stress Markers
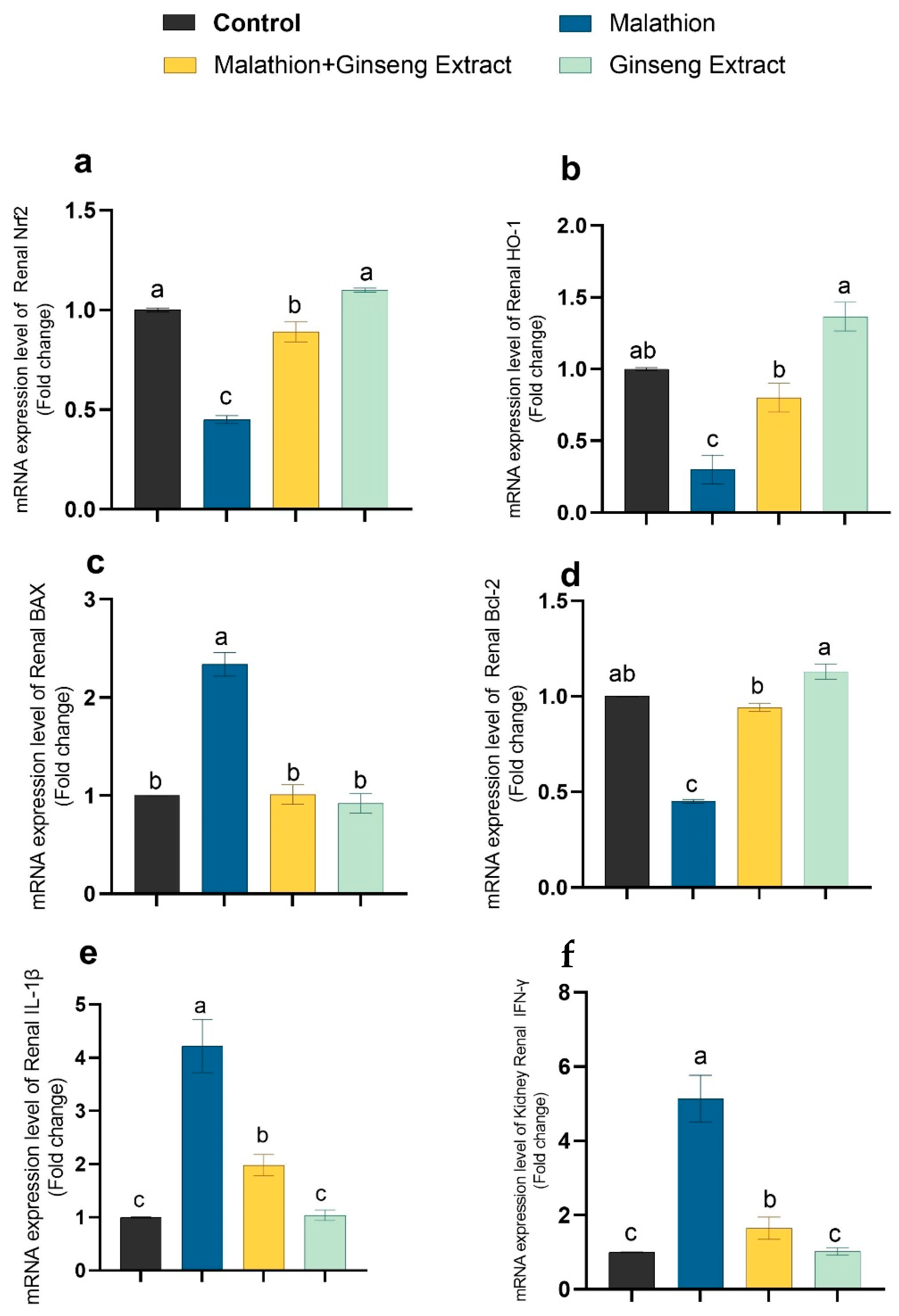
3.4. Genes Expression
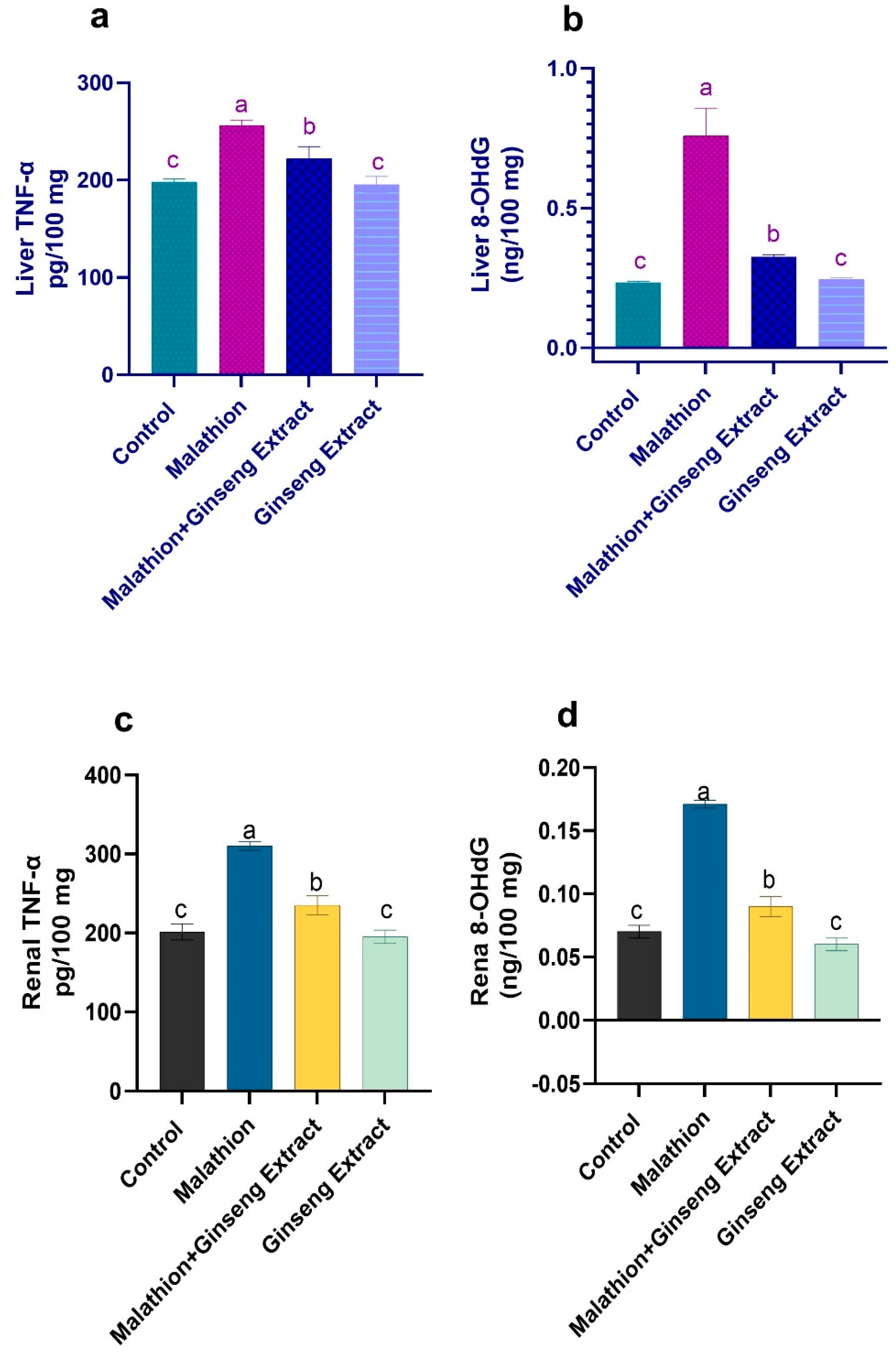
3.5. 8-OHdG and TNF-Alpha
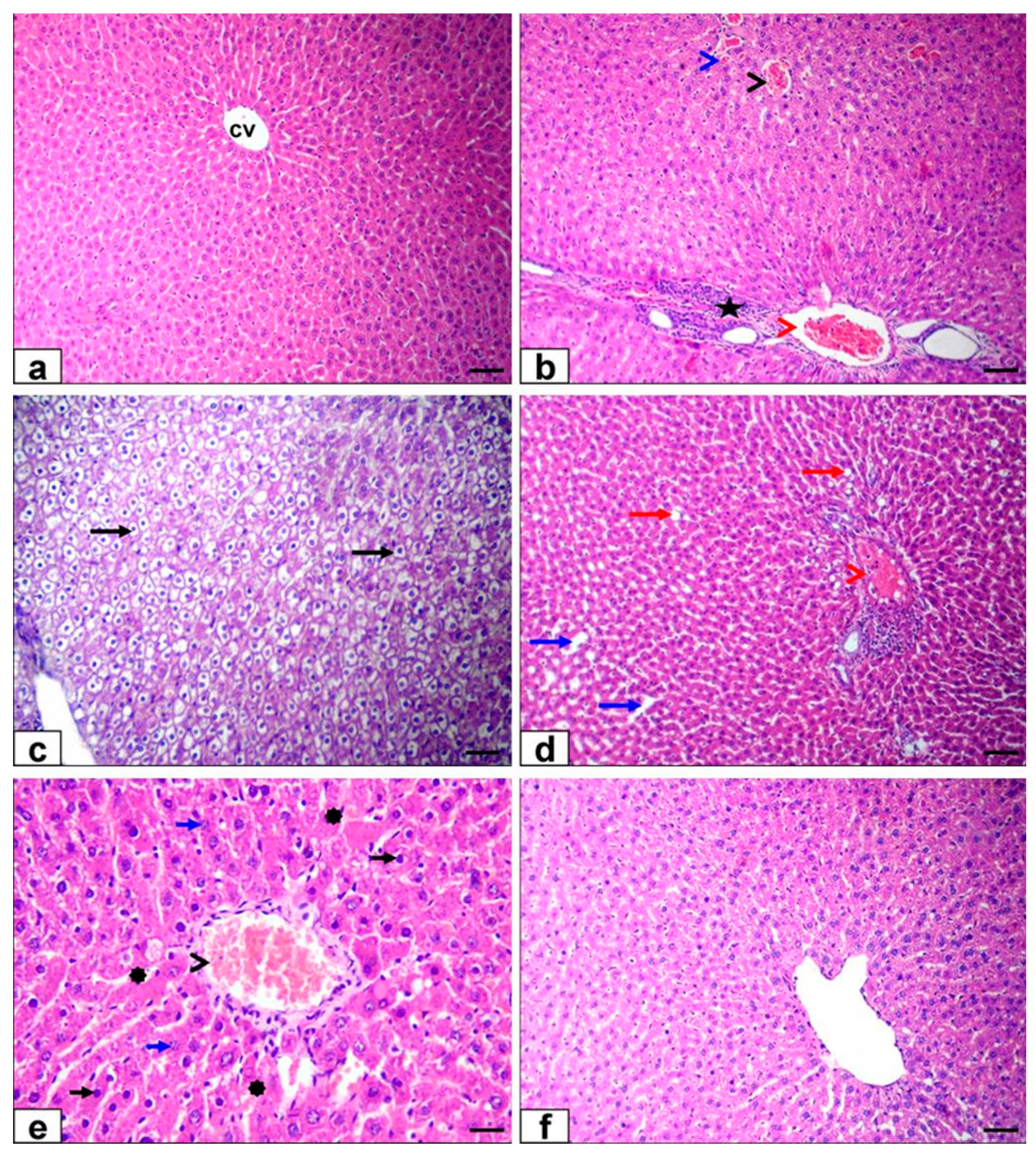
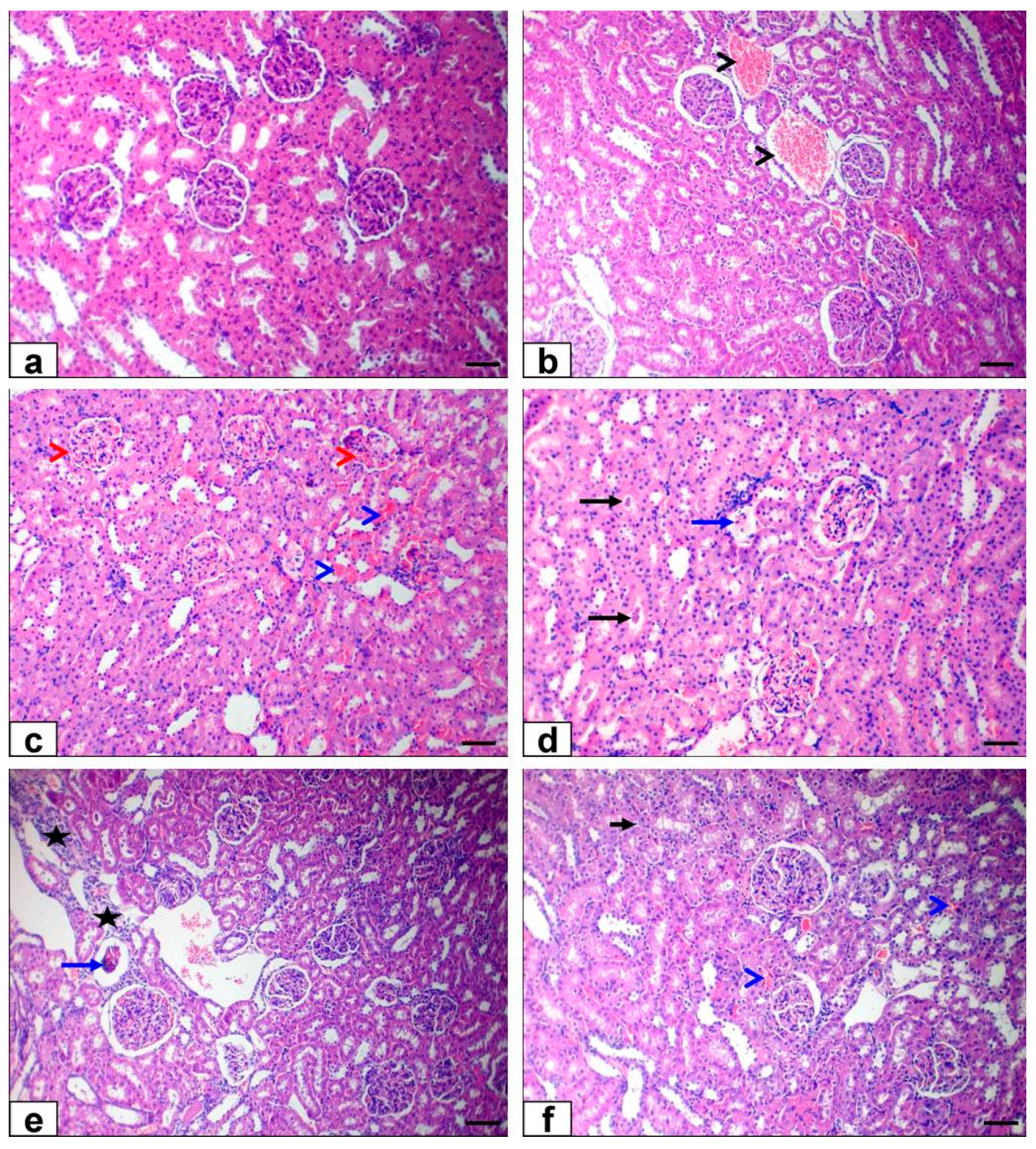
3.6. Histopathological Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selmi, S.; Rtibi, K.; Grami, D.; Sebai, H.; Marzouki, L. Malathion, an organophosphate insecticide, provokes metabolic, histopathologic and molecular disorders in liver and kidney in prepubertal male mice. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zidan, N.E.-H.A. Hepato-and nephrotoxicity in male albino rats exposed to malathion and spinosad in stored wheat grains. Acta Biol. Hung. 2015, 66, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Badr, A.M. Organophosphate toxicity: Updates of malathion potential toxic effects in mammals and potential treatments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26036–26057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, A.A.; Naime, A.A.; de Oliveira, J.; Colle, D.; Dos Santos, D.B.; Hort, M.A.; Moreira, E.L.G.; Suñol, C.; de Bem, A.F.; Farina, M. Long-term and low-dose malathion exposure causes cognitive impairment in adult mice: Evidence of hippocampal mitochondrial dysfunction, astrogliosis and apoptotic events. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete-Meneses, M.; Salas-Labadía, C.; Sanabrais-Jiménez, M.; Santana-Hernández, J.; Serrano-Cuevas, A.; Juárez-Velázquez, R.; Olaya-Vargas, A.; Pérez-Vera, P. Exposure to the insecticides permethrin and malathion induces leukemia and lymphoma-associated gene aberrations in vitro. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 44, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, S.; Başarslan, S.; Fırat, U.; Alp, H.; Uzar, E.; Arıkanoğlu, A.; Evliyaoğlu, O.; Acar, A.; Yücel, Y.; Kıbrıslı, E. Detection of borderline dosage of malathion intoxication in a rat’s brain. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 19, 2318–2323. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The World Health Report 2006: Working Together for Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health: Children & Youth Version: ICF-CY; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Selmi, S.; El-Fazaa, S.; Gharbi, N. Oxidative stress and cholinesterase inhibition in plasma, erythrocyte and brain of rats’ pups following lactational exposure to malathion. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.A.; dos Santos, D.B.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Colle, D.; Peres, K.C.; Hermes, J.; Barbosa, A.M.; Dafré, A.L.; de Bem, A.F.; Kuca, K. Effects of K074 and pralidoxime on antioxidant and acetylcholinesterase response in malathion-poisoned mice. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Xiang, B.; Wang, D.; Tang, S.; Teng, M.; Yan, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W. Different toxic effects of racemate, enantiomers, and metabolite of malathion on HepG2 cells using high-performance liquid chromatography–quadrupole–time-of-flight-based metabolomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, P.; Jan, C.-R.; Liang, W.-Z. The protective effects of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) against oxidative stress-associated apoptosis evoked by the organophosphorus insecticide malathion in normal human astrocytes. Toxicology 2019, 417, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, J.K.; Saraf, P.; Kumari, P.; Mittal, M.; Kumar, V. N-Acetyl-cysteine mediated inhibition of spermatogonial cells apoptosis against malathion exposure in testicular tissue. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Salam, O.M.; Youness, E.R.; Mohammed, N.A.; Yassen, N.N.; Khadrawy, Y.A.; El-Toukhy, S.E.; Sleem, A.A. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors protect against brain and liver damage caused by acute malathion intoxication. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbel, E.; Arslan-Acaroz, D.; Demirel, H.H.; Kucukkurt, I.; Ince, S. The subchronic exposure to malathion, an organophosphate pesticide, causes lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress, and tissue damage in rats: The protective role of resveratrol. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 7, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Choi, J.; Shin, S.S.; Yoon, M. Effects of Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) on obesity and adipose inflammation in ovariectomized mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 178, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-G.; Jang, S.-S.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Son, C.-G. Panax ginseng Meyer prevents radiation-induced liver injury via modulation of oxidative stress and apoptosis. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.R.; Ma, J.Y.; Sung, C.K. Chronic dietary ginseng extract administration ameliorates antioxidant and cholinergic systems in the brains of aged mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X. Ginseng: An nonnegligible natural remedy for healthy aging. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Fattah, S.M.; Safaa, M.; Sanad, M.; Helal, A.; Sarfinaz, S.; Abd ElGhany Ragaa, F.; Ghanem, F. Biochemical and histochemical studies on white ginseng roots for ameliorating aflatoxicosis in rats. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 458–473. [Google Scholar]
- Raheem, S.A.; Meselhy, A.R.; Hafiez, S.A.; Naby, N.A. Evaluation of the protective effect of ginseng against gentamicine-induced nephrotoxicity in adult, albino rats: A histochemical and immunohistochemical study. Al-Azhar Assiut. Med. J. 2017, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, G.A. Role of Ginseng as Hepatoprotective, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory against Methotrexate Induced Liver Injury in Rats. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2016, 62, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Uzun, F.G.; Kalender, S.; Durak, D.; Demir, F.; Kalender, Y. Malathion-induced testicular toxicity in male rats and the protective effect of vitamins C and E. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, H.N.; Dandin, V.S.; Paek, K.Y. Hepatoprotective activity of ginsenosides from Panax ginseng adventitious roots against carbon tetrachloride treated hepatic injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 158, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki, S.H.; Yang, J.H.; Ku, S.K.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, Y.W.; Cho, I.J. Red ginseng extract protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mostafa, R.E.; Shaffie, N.M.; Allam, R.M. Panax Ginseng alleviates thioacetamide-induced liver injury in ovariectomized rats: Crosstalk between inflammation and oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitman, S.; Frankel, S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1957, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietz, N.; Burtis, C.; Duncan, P.; Ervin, K.; Petitclerc, C.; Rinker, A.; Shuey, D.; Zygowicz, E. A reference method for measurement of alkaline phosphatase activity in human serum. Clin. Chem. 1983, 29, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumas, B.; Baysa, D.; Carter, R.; Peters, T.; Schaffer, R. Determination of serum total protein. Clin. Chem. 1981, 27, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulombe, J.J.; Favreau, L. A new simple semimicro method for colorimetric determination of urea. Clin. Chem. 1963, 9, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, H. Serum creatinine without interference. Clin. Chem. Acta 1972, 37, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraway, W.T.; Hald, P.M. Uric acid. In Standard Methods of Clinical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1963; Volume 4, pp. 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Virella, M.F.; Stone, P.G.; Colwell, J.A. Serum high density lipoprotein in diabetic patients. Diabetologia 1977, 13, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Oberley, L.W.; Li, Y. A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin. Chem. 1988, 34, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. [13] Catalase in vitro. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; Volume 105, pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Paglia, D.E.; Valentine, W.N. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1967, 70, 158–169. [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Gamble, M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafalou, S.; Eghbal, M.A.; Nili-Ahmadabadi, A.; Baeeri, M.; Abdollahi, M. Biochemical evidence on the potential role of organophosphates in hepatic glucose metabolism toward insulin resistance through inflammatory signaling and free radical pathways. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2012, 28, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasram, M.M.; Lamine, A.J.; Dhouib, I.B.; Bouzid, K.; Annabi, A.; Belhadjhmida, N.; Ahmed, M.B.; El Fazaa, S.; Abdelmoula, J.; Gharbi, N. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of N-acetylcysteine against malathion-induced liver damages and immunotoxicity in rats. Life Sci. 2014, 107, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possamai, F.; Fortunato, J.; Feier, G.; Agostinho, F.; Quevedo, J.; Wilhelm Filho, D.; Dal-Pizzol, F. Oxidative stress after acute and sub-chronic malathion intoxication in Wistar rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 23, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, J.J.; Feier, G.; Vitali, A.M.; Petronilho, F.C.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Quevedo, J. Malathion-induced oxidative stress in rat brain regions. Neurochem. Res. 2006, 31, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgade, C.; Barquet, A. Body distribution of malathion and its metabolites in a fatal poisoning by ingestion. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A Curr. Issues 1982, 10, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shinnawy, M.S.; Hassan, A.R.; Ismail, D.A.; Shahin, M.A. The potential protective and therapeutic effects of aloe vera juice on malathion induced hepatotoxicity in rabbits. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2014, 55, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flehi-Slim, I.; Chargui, I.; Boughattas, S.; El Mabrouk, A.; Belaïd-Nouira, Y.; Neffati, F.; Najjar, M.F.; Haouas, Z.; Cheikh, H.B. Malathion-induced hepatotoxicity in male Wistar rats: Biochemical and histopathological studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 17828–17838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, J.L.; Posser, T.; Mattos, J.J.; Trevisan, R.; Brocardo, P.S.; Rodrigues, A.L.S.; Leal, R.B.; Farina, M.; Marques, M.R.; Bainy, A.C. Zinc reverses malathion-induced impairment in antioxidant defenses. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 187, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, R.A. A comparison of the in vitro metabolism of parathion in the lung and liver of the rabbit. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1972, 23, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.C.; McLean, A.J.; Rivory, L.P.; Le Couteur, D.G. Hepatic disposition of neurotoxins and pesticides. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2000, 87, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błasiak, J.; Jałoszynski, P.; Trzeciak, A.; Szyfter, K. In vitro studies on the genotoxicity of the organophosphorus insecticide malathion and its two analogues. Mutat. Res. /Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 1999, 445, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Siddiqi, N.J.; Ojha, A.K.; Sharma, B. Hepatoprotective effect of Aloe vera against cartap-and malathion-induced toxicity in Wistar rats. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 18329–18343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kata, F.S. Short-time effects of malathion pesticide on functional and Histological changes of liver and kidney in female mice. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2020, 23, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Bansal, G. Enzymatic activity of liver and kidney altered by the different dose of organophosphate pesticide Malathion in albino rats. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2021, 9, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Ncibi, S.; Othman, M.B.; Akacha, A.; Krifi, M.N.; Zourgui, L. Opuntia ficus indica extract protects against chlorpyrifos-induced damage on mice liver. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogutcu, A.; Suludere, Z.; Kalender, Y. Dichlorvos-induced hepatotoxicity in rats and the protective effects of vitamins C and E. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 26, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fındıklı, H.A.; Bilge, Z.; Aydın, H.; Yüceer, M.M.; Algın, A.; Aydın, B. The combination of acute pancreatitis and toxic hepatitis developing secondary to exposure to malathion: A case report. Acta Gastro-Enterol. Belg. 2018, 81, 333–335. [Google Scholar]
- Gowda, S.; Desai, P.B.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Hull, V.V.; Math, A.A.; Vernekar, S.N. Markers of renal function tests. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 2, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy, L.; Alper, Y. The effects of royal jelly on oxidative stress and toxicity in tissues induced by malathion, an organophosphate insecticide. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2019, 70, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokota, K.; Fukuda, M.; Katafuchi, R.; Okamoto, T. Nephrotic syndrome and acute kidney injury induced by malathion toxicity. Case Rep. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.J. Cardiovascular drugs and serum uric acid. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2003, 17, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatma, U.; Kalender, Y. Protective effect of vitamins c and e on malathion-induced nephrotoxicity in male rats. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2011, 24, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Almalki, D.A. The potential protective effect of sesame oil and canola oil on rats exposed to malathion. Curr. Sci. Int. 2019, 8, 687–698. [Google Scholar]
- Buratti, F.M.; D’aniello, A.; Volpe, M.T.; Meneguz, A.; Testai, E. Malathion bioactivation in the human liver: The contribution of different cytochrome P450 isoforms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Salam, O.M.; Youness, E.R.; Mohammed, N.A.; Yassen, N.N.; Khadrawy, Y.A.; El-Toukhy, S.E.; Sleem, A.A. Novel neuroprotective and hepatoprotective effects of citric acid in acute malathion intoxication. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Salam, O.M.; Sleem, A.A.; Youness, E.R.; Shaffie, N.; Ibrahim, A.Y. Novel protective effects of brilliant blue G in acute malathion toxicity. React. Oxyg. Species 2018, 6, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severcan, Ç.; Ekremoglu, M.; Sen, B.; Pasaoglu, O.T.; Akyurek, N.; Severcan, S.M.; Pasaoglu, H. Acute effects of different doses of malathion on the rat liver. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2019, 5, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili, C.; Roshankhah, S.; Moradi, Y.; Salahshoor, M.R. Resveratrol attenuates malathion-induced renal damage by declining oxidative stress in rats. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 8, 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Kalender, S.; Ogutcu, A.; Uzunhisarcikli, M.; Açikgoz, F.; Durak, D.; Ulusoy, Y.; Kalender, Y. Diazinon-induced hepatotoxicity and protective effect of vitamin E on some biochemical indices and ultrastructural changes. Toxicology 2005, 211, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodeur, J.; DuBois, K. Studies on factors influencing the acute toxicity of malathion and malaoxon in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1967, 45, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, W.; Miles, J.; Mount, D.; Verschoyle, R. The toxicological properties of impurities in malathion. Arch. Toxicol. 1978, 42, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine; Oxford University Press: New York City, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbar, A.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Golestani, A.; Ghazi-Khansari, M.; Baeeri, M.; Abdollahi, M. Protection by pentoxifylline of malathion-induced toxic stress and mitochondrial damage in rat brain. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, G.; Husunet, M.T.; Guler, I.; Deveci, A.; Koc, E.; Nur, O.; Kilicle, P.A. The effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on hepatic histopathology and oxidative stress in rats treated with malathion. Med. Sci. 2018, 7, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, D.; Sánchez-Reus, I.; Bautista, M.; Cascales, M.A. Depletion of Kupffer cell function by gadolinium chloride attenuates thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity: Expression of metallothionein and HSP70. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakus, E.; Karadeniz, A.; Simsek, N.; Can, I.; Kara, A.; Yildirim, S.; Kalkan, Y.; Kisa, F. Protective effect of Panax ginseng against serum biochemical changes and apoptosis in liver of rats treated with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, Y.; Bae, J.; Jeong, J.H.; Ko, S.K.; Sohn, U.D. Protective effect of ultrasonication-processed ginseng berry extract on the D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury model in rats. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Eldaim, M.A.A.; Abd El Latif, A.S.; Hassan, A.; El-Borai, N.B. Ginseng attenuates fipronil-induced hepatorenal toxicity via its antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory activities in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45008–45017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Hamid, M.; Mohamed, H.M.; El-Twab, A.; Sanaa, M.; Zaied, K. Histological, ultrastructural, and biochemical study on the possible role of Panax ginseng in ameliorating liver injury induced by Lambda cyhalotherin. Beni-Suef. Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Gu, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Jia, X.; Liu, M.; Yao, D. Ginsenoside Rg5 improves cognitive dysfunction and beta-amyloid deposition in STZ-induced memory impaired rats via attenuating neuroinflammatory responses. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Park, J.; Kwon, S.; Park, M.-W.; Oh, S.-M.; Yeom, M.-J.; Shim, I.; Lee, H.-J.; Hahm, D.-H. Effect of wild ginseng on scopolamine-induced acetylcholine depletion in the rat hippocampus. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, S.; Demirtas, S.; Guclu, O.; Karahan, O.; Yavuz, C.; Caliskan, A.; Mavitas, B. Using oxidant and antioxidant levels to predict the duration of both acute peripheral and mesenteric ischemia. Perfusion 2014, 29, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-L.; Liu, D.-P.; Liang, C.-C. Paraoxonase gene polymorphisms, oxidative stress, and diseases. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 81, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, J.; El-Khayat, Z.; El-Toukhy, S.; El-Bana, M.; Medhat, D.; Morsy, S. Panax ginseng regulates brain monoamines in lipopolysaccharide-induced experimental brain injury. Der Pharma Chem. 2016, 8, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Reus, G.Z.; Valvassori, S.S.; Nuernberg, H.; Comim, C.M.; Stringari, R.B.; Padilha, P.T.; Leffa, D.D.; Tavares, P.; Dagostim, G.; Paula, M.M. DNA damage after acute and chronic treatment with malathion in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7560–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, M.I.; Hussien, H.M. Cisplatin-induced renal toxicity via tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin 6, tumor suppressor P53, DNA damage, xanthine oxidase, histological changes, oxidative stress and nitric oxide in rats: Protective effect of ginseng. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.-H.; Shin, B.-K.; Kim, N.J.; Chang, S.-Y.; Park, J.H. Protective effect of ginsenosides Rk3 and Rh4 on cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in vitro and in vivo. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, C.-H.; Seog, H.-M.; Choi, I.-W.; Choi, H.-D.; Cho, H.-Y. Effects of wild ginseng (Panax ginseng CA Meyer) leaves on lipid peroxidation levels and antioxidant enzyme activities in streptozotocin diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 98, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, T.; Kim, S.-W.; Sung, J.-H.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Sohn, S.-H.; Yoo, S.-K.; Kim, S.-K. Effect of fermented Panax ginseng extract (GINST) on oxidative stress and antioxidant activities in major organs of aged rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2012, 47, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Noh, J.-R.; Cho, E.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Son, H.-Y. Protective effect of Korean red ginseng against aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shukla, R.; Kumar, M. Role of Panax ginseng as an antioxidant after cadmium-induced hepatic injuries. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-F.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chu, C.-C.; Wu, S.-J.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Chao, J.C.-J. Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba, Panax ginseng, and Schizandra chinensis extract on liver injury in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2007, 35, 995–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.H.; Suk, K.T.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Sung, H.T.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, M.J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, M.Y. Anti-oxidant and natural killer cell activity of Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) and urushiol (Rhus vernicifera Stokes) on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease of rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.-H.; Bae, O.-N.; Park, J.H. Recent methodology in ginseng analysis. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pober, J.; Min, W. Endothelial cell dysfunction, injury and death. Vasc. Endothel. II 2006, 176, 135–156. [Google Scholar]
- Salmon, A.B.; Richardson, A.; Pérez, V.I. Update on the oxidative stress theory of aging: Does oxidative stress play a role in aging or healthy aging? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karabag-Coban, F.; Bulduk, I.; Liman, R.; Ince, S.; Cigerci, I.; Hazman, O. Oleuropein alleviates malathion-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in rats. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2016, 98, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasiak, J.; Stańkowska, D. Genotoxicity of Malaoxon: Induction of oxidized and methylated bases and protective effect of α-Tocopherol. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2001, 71, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzkeser, M.; Karakus, E.; Albayrak, A.; Bayir, Y.; Cadirci, E.; Unal, D.; Halici, Z.; Karadeniz, A. Protective effect of Panax ginseng against N-acetyl-p-aminophenol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 6, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doh, K.C.; Lim, S.W.; Piao, S.G.; Jin, L.; Heo, S.B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Bae, S.K.; Hwang, G.H.; Min, K.I.; Chung, B.H. Ginseng treatment attenuates chronic cyclosporine nephropathy via reducing oxidative stress in an experimental mouse model. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 37, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radad, K.; Gille, G.; Liu, L.; Rausch, W.-D. Use of ginseng in medicine with emphasis on neurodegenerative disorders. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 100, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasram, M.M.; Dhouib, I.B.; Bouzid, K.; Lamine, A.J.; Annabi, A.; Belhadjhmida, N.; Ahmed, M.B.; El Fazaa, S.; Abdelmoula, J.; Gharbi, N. Association of inflammatory response and oxidative injury in the pathogenesis of liver steatosis and insulin resistance following subchronic exposure to malathion in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Luong, T.T.; Kim, G.-L.; Pyo, S.; Rhee, D.-K. Korean Red Ginseng inhibits apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells via estrogen receptor β-mediated phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt signaling. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Okle, O.S.; Tohamy, H.G.; Althobaiti, S.A.; Soliman, M.M.; Ghamry, H.I.; Farrag, F.; Shukry, M. Ornipural®;Mitigates Malathion-Induced Hepato-Renal Damage in Rats via Amelioration of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers, Restoration of Antioxidant Activity, and Attenuation of Inflammatory Response. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Control | Malathion | Malathion + Ginseng® | Ginseng® | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial body Weight (g) | 145.02 ± 4.1 | 143.15 ± 3.4 | 147.1 ± 3.4 | 145.2 ± 3.5 |
| Final body Weight (g) | 265.14 ± 3.15 a | 231.2 ± 4.9 c | 245.65 ± 5.2 b | 266.15 ± 4.1 a |
| Bodyweight gain | 120.12 ± 3.8 a | 88.08 ± 3.1 c | 98.55 ± 2.15 b | 120.95 ± 3.9 a |
| Absolute Weight of Liver (g) | 4.59 ± 0.12 | 4.41 ± 0.10 | 4.83 ± 0.6 | 5.01 ± 0.1 |
| Relative liver weight (g/100 g BW) | 1.73 ± 0.10 | 1.90 ± 0.11 | 1.96 ± 0.12 | 1.88 ± 0.11 |
| Absolute Weight of Kidney (g) | 1.19 ± 0.11 | 1.22 ± 0.012 | 1.25 ± 0.01 | 1.26 ± 0.01 |
| Relative Weight of Kidney (g/100 g BW) | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.01 | 0.47 ± 0.1 |
| Control | Malathion | Malathion + Ginseng® | Ginseng® | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AST (U/mL) | 81.39 ± 3.2 c | 181.50 ± 10.1 a | 97.01 ± 5.4 b | 77.29 ± 3.2 c |
| ALT (U/mL) | 35.50 ± 1.2 c | 80.92 ± 3.2 a | 52.30 ± 3.1 b | 34.92 ± 1.4 c |
| ALP (U/L) | 86.05 ± 3.1 c | 212.61 ± 6.45 a | 107.81 ± 5.4 b | 85.67 ± 3.14 c |
| LDH (U/L) | 205.6 ± 10.14 c | 453.54 ± 10.4 a | 321.88 ± 12.4 b | 201.16 ± 11.2 c |
| ACP(U/L) | 105.12 ± 10.2 c | 172.3 ± 12.14 a | 129.34 ± 9.45 b | 101.14 ± 5.9 c |
| TP (g/L) | 5.15 ± 0.15 a | 3.59 ± 0.21 c | 4.54 ± 0.12 b | 5.23 ± 0.5 a |
| Albumin (g/L) | 4.06 ± 0.4 a | 2.67 ± 0.09 c | 3.74 ± 0.14 b | 4.19 ± 0.45 a |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 80.23 ± 5.45 c | 156.56 ± 7.1 a | 112.54 ± 6.14 b | 78.31 ± 3.4 c |
| TG (g/L) | 111.39 ± 10.2 a | 71.16 ± 4.1 c | 90.97 ± 5.14 b | 105.66 ± 7.4 a |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 22.05 ± 1.4 c | 77.69 ± 2.4 a | 43.48 ± 1.5 b | 20.19 ± 1.5 c |
| Creatinine (mg %) | 0.66 ± 0.01 c | 2.15 ± 0.1 a | 1.90 ± 0.04 b | 0.52 ± 0.01 c |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 25.71 ± 1.2 c | 84.06 ± 5.1 a | 44.34 ± 2.1 b | 23.07 ± 2.1 c |
| Paraoxonase (U/L) | 171.12 ± 12.5 a | 122.45 ± 12.15 c | 139.9 ± 5.15 b | 175.14 ± 10.2 a |
| AChE (U/L) | 240.15 ± 12.15 a | 86.15 ± 4.5 c | 133.15 ± 7.15 b | 238.15 ± 8.45 a |
| Ammonia (μmol/L) | 133.25 ± 5.45 c | 263.15 ± 15.2 a | 189.45 ± 10.2 b | 132.25 ± 10.25 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghamry, H.I.; Aboushouk, A.A.; Soliman, M.M.; Albogami, S.M.; Tohamy, H.G.; Okle, O.S.E.; Althobaiti, S.A.; Rezk, S.; Farrag, F.; Helal, A.I.; et al. Ginseng® Alleviates Malathion-Induced Hepatorenal Injury through Modulation of the Biochemical, Antioxidant, Anti-Apoptotic, and Anti-Inflammatory Markers in Male Rats. Life 2022, 12, 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050771
Ghamry HI, Aboushouk AA, Soliman MM, Albogami SM, Tohamy HG, Okle OSE, Althobaiti SA, Rezk S, Farrag F, Helal AI, et al. Ginseng® Alleviates Malathion-Induced Hepatorenal Injury through Modulation of the Biochemical, Antioxidant, Anti-Apoptotic, and Anti-Inflammatory Markers in Male Rats. Life. 2022; 12(5):771. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050771
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhamry, Heba I., Asmaa A. Aboushouk, Mohamed Mohamed Soliman, Sarah M. Albogami, Hossam G. Tohamy, Osama S. El Okle, Saed A. Althobaiti, Shaymaa Rezk, Foad Farrag, Azza I. Helal, and et al. 2022. "Ginseng® Alleviates Malathion-Induced Hepatorenal Injury through Modulation of the Biochemical, Antioxidant, Anti-Apoptotic, and Anti-Inflammatory Markers in Male Rats" Life 12, no. 5: 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050771
APA StyleGhamry, H. I., Aboushouk, A. A., Soliman, M. M., Albogami, S. M., Tohamy, H. G., Okle, O. S. E., Althobaiti, S. A., Rezk, S., Farrag, F., Helal, A. I., Ghoneim, H. A., & Shukry, M. (2022). Ginseng® Alleviates Malathion-Induced Hepatorenal Injury through Modulation of the Biochemical, Antioxidant, Anti-Apoptotic, and Anti-Inflammatory Markers in Male Rats. Life, 12(5), 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050771









