Circulating Neurovascular Guidance Molecules and Their Relationship with Peripheral Microvascular Impairment in Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
:Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients, Controls and Serum Sample Collection
2.2. Clinical Assessment
2.3. Assay for Serum sNRP1
2.4. Assay for Serum Sema3E
2.5. Assay for Serum Slit2
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
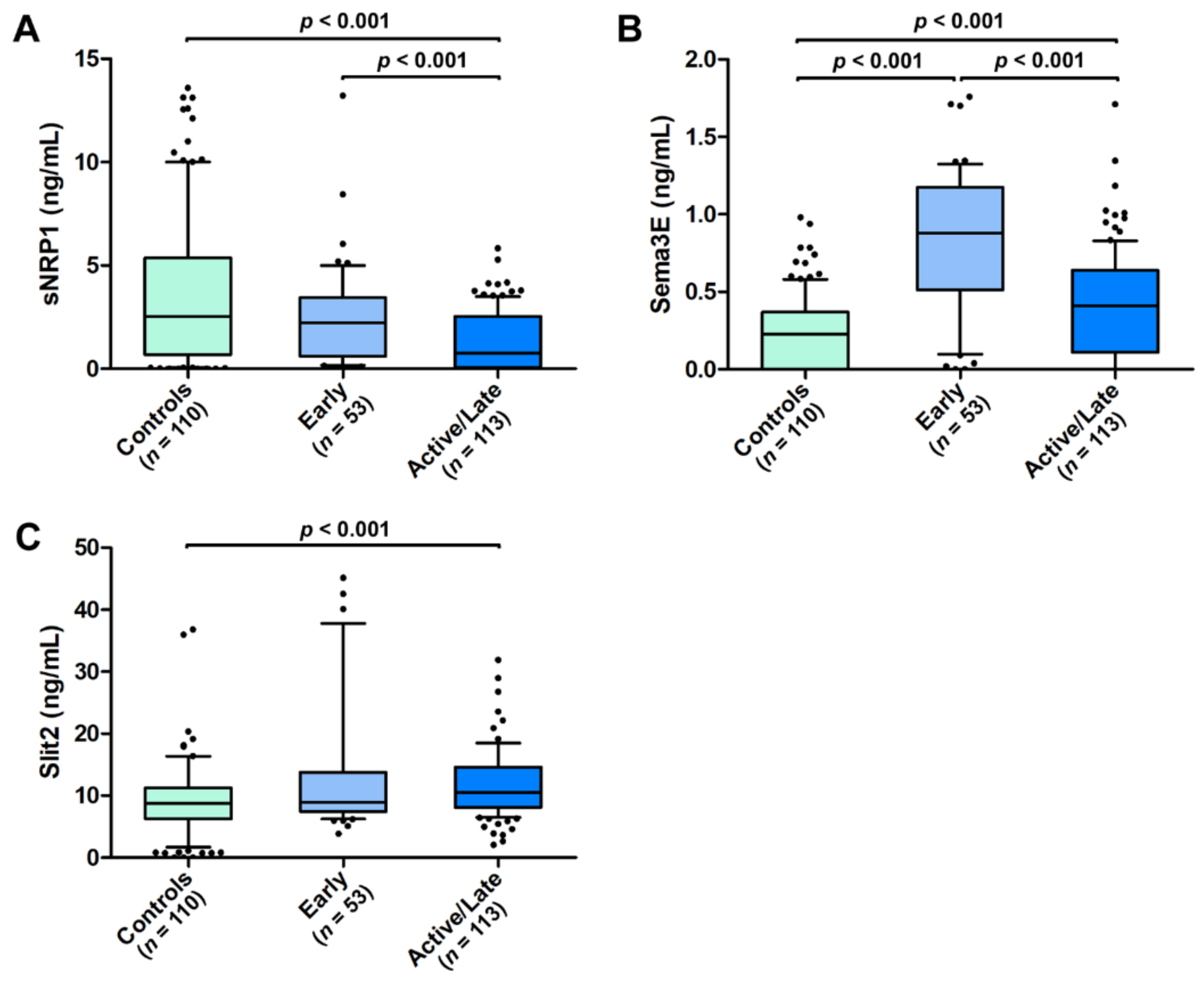
3.1. Serum sNRP1, Sema3E, and Slit2 Levels in SSc Patients
3.2. Diagnostic Accuracy of Circulating sNRP1, Sema3E, and Slit2 for SSc
3.3. Association of Serum sNRP1, Sema3E, and Slit2 Levels with the Severity of SSc-Related Peripheral Microvascular Damage
3.4. Logistic Regression Model Combining Serum sNRP1, Sema3E, and Slit2 Levels in SSc Patients
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lescoat, A.; Varga, J.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Khanna, D. New promising drugs for the treatment of systemic sclerosis: Pathogenic considerations, enhanced classifications, and personalized medicine. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2021, 30, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoreau, B.; Chaigne, B.; Renaud, A.; Mouthon, L. Pathophysiology of systemic sclerosis. Presse Med. 2021, 50, 104087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchetet, M.E.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Current concepts on the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin-Silva, D.C.; Santana-Gonçalves, M.; Kawashima-Vasconcelos, M.Y.; Oliveira, M.C. Management of endothelial dysfunction in systemic sclerosis: Current and developing strategies. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 788250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.; Allanore, Y.; El Aoufy, K.; Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D.; Krieg, T.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. A practical approach to the management of digital ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis: A narrative review. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. Common mechanisms of nerve and blood vessel wiring. Nature 2005, 436, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukouyama, Y.S.; Shin, D.; Britsch, S.; Taniguchi, M.; Anderson, D.J. Sensory nerves determine the pattern of arterial differentiation and blood vessel branching in the skin. Cell 2002, 109, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, R.H.; Eichmann, A. Axon guidance molecules in vascular patterning. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romano, E.; Rosa, I.; Fioretto, B.S.; Guiducci, S.; Manetti, M.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. A new avenue in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: The molecular interface between the endothelial and the nervous systems. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 119, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Vogenstahl, J.; Parrilla, M.; Acker-Palmer, A.; Segarra, M. Vascular regulation of developmental neurogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 890852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, B.; Liu, S.; Tan, X.; Lu, P.; Wang, D.; Xu, H. Class-3 semaphorins: Potent multifunctional modulators for angiogenesis-associated diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishide, M.; Kumanogoh, A. The role of semaphorins in immune responses and autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, S. Role of semaphorins in immunopathologies and rheumatic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avouac, J.; Pezet, S.; Vandebeuque, E.; Orvain, C.; Gonzalez, V.; Marin, G.; Mouterde, G.; Daïen, C.; Allanore, Y. Semaphorins: From angiogenesis to inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iragavarapu-Charyulu, V.; Wojcikiewicz, E.; Urdaneta, A. Semaphorins in angiogenesis and autoimmune diseases: Therapeutic targets? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumond, A.; Pagès, G. Neuropilins, as relevant oncology target: Their role in the tumoral microenvironment. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Qin, T.; Chen, X.; Wu, E.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Z. Targeting the SLIT/ROBO pathway in tumor progression: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919855238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, E.; Chora, I.; Manetti, M.; Mazzotta, C.; Rosa, I.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Blagojevic, J.; Soares, R.; Avouac, J.; Allanore, Y.; et al. Decreased expression of neuropilin-1 as a novel key factor contributing to peripheral microvasculopathy and defective angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, Y.; de Bernard, S.; Hickey, P.; Ballard, K.; Cruz, J.; Cornelisse, P.; Chadha-Boreham, H.; Distler, O.; Rosenberg, D.; Doelberg, M.; et al. Identifying early pulmonary arterial hypertension biomarkers in systemic sclerosis: Machine learning on proteomics from the DETECT cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2002591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chora, I.; Romano, E.; Manetti, M.; Mazzotta, C.; Costa, R.; Machado, V.; Cortez, A.; Bruni, C.; Lepri, G.; Guiducci, S.; et al. Evidence for a derangement of the microvascular system in patients with a very early diagnosis of systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, C.; Romano, E.; Bruni, C.; Manetti, M.; Lepri, G.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Blagojevic, J.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Guiducci, S. Plexin-D1/Semaphorin 3E pathway may contribute to dysregulation of vascular tone control and defective angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romano, E.; Manetti, M.; Rosa, I.; Fioretto, B.S.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Guiducci, S. Slit2/Robo4 axis may contribute to endothelial cell dysfunction and angiogenesis disturbance in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LeRoy, E.C.; Black, C.; Fleischmajer, R.; Jablonska, S.; Krieg, T.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Rowell, N.; Wollheim, F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): Classification, subsets, and pathogenesis. J. Rheumatol. 1988, 15, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valentini, G.; Matucci Cerinic, M. Disease-specific quality indicators, guidelines and outcome measures in scleroderma. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2007, 25, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Sulli, A.; Secchi, M.E.; Pizzorni, C.; Cutolo, M. Scoring the nailfold microvascular changes during the capillaroscopic analysis in systemic sclerosis patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, J.A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 1988, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Kahaleh, B.; Wigley, F.M. Review: Evidence that systemic sclerosis is a vascular disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Kuwana, M. Endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 7, S139–S146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, B.; Nallino, M.G.; Casabella, A.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; De Tanti, A.; Bruni, C. Monitoring the microcirculation in the diagnosis and follow-up of systemic sclerosis patients: Focus on pulmonary and peripheral vascular manifestations. Microcirculation 2020, 27, e12647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambova, S.N.; Müller-Ladner, U. Nailfold capillaroscopy in systemic sclerosis-state of the art: The evolving knowledge about capillaroscopic abnormalities in systemic sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2019, 4, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejewska, M.; Sikora, M.; Maciejewski, C.; Alda-Malicka, R.; Czuwara, J.; Rudnicka, L. Raynaud’s phenomenon with focus on systemic sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chora, I.; Guiducci, S.; Manetti, M.; Romano, E.; Mazzotta, C.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Soares, R. Vascular biomarkers and correlation with peripheral vasculopathy in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avouac, J.; Vallucci, M.; Smith, V.; Senet, P.; Ruiz, B.; Sulli, A.; Pizzorni, C.; Frances, C.; Chiocchia, G.; Cutolo, M.; et al. Correlations between angiogenic factors and capillaroscopic patterns in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larrivée, B.; Freitas, C.; Suchting, S.; Brunet, I.; Eichmann, A. Guidance of vascular development: Lessons from the nervous system. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cheng, H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wan, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, Z. Circulating soluble neuropilin-1 in patients with early cervical cancer and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia can be used as a valuable diagnostic biomarker. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 506428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tang, Y.; Dong, Z.; McElwee, K.J.; Li, G. Increased expression of neuropilin 1 in melanoma progression and its prognostic significance in patients with melanoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rachner, T.D.; Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Goebel, A.; Erdmann, K.; Hoffmann, O.; Rauner, M.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Kimmig, R.; Bittner, A.K. Soluble Neuropilin-1 is an independent marker of poor prognosis in early breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 2233–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, L.; Chen, N.; Ni, P.; Song, L.; Liu, X. Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) is a novel tumor marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2018, 485, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodink, I.; Kats, G.; van Kempen, L.; Grunberg, M.; Maass, C.; Verrijp, K.; Raats, J.; Leenders, W. Semaphorin 3E expression correlates inversely with Plexin D1 during tumor progression. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casazza, A.; Kigel, B.; Maione, F.; Capparuccia, L.; Kessler, O.; Giraudo, E.; Mazzone, M.; Neufeld, G.; Tamagnone, L. Tumour growth inhibition and anti-metastatic activity of a mutated furin-resistant Semaphorin 3E isoform. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xie, G.H.; Wang, W.W.; Yuan, X.L.; Xing, W.M.; Liu, H.J.; Chen, J.; Dou, M.; Shen, L.S. Epigenetically downregulated Semaphorin 3E contributes to gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20449–20465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabag, A.D.; Bode, J.; Fink, D.; Kigel, B.; Kugler, W.; Neufeld, G. Semaphorin-3D and semaphorin-3E inhibit the development of tumors from glioblastoma cells implanted in the cortex of the brain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Characteristics | SSc Patients (n = 166) |
|---|---|
| Mean ± SD age, years | 58.6 ± 13.7 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 22 (13.2) |
| Female | 144 (86.8) |
| Disease subset | |
| limited cutaneous SSc | 111 (66.9) |
| diffuse cutaneous SSc | 55 (33.1) |
| Autoantibody positivity | |
| Antinuclear | 153 (92.1) |
| Anticentromere | 81 (48.8) |
| Antitopoisomerase I | 57 (34.3) |
| Digital ulcers | 52 (31.3) |
| NVC pattern | |
| Early | 53 (32.0) |
| Active | 69 (41.5) |
| Late | 44 (26.5) |
| Active/Late NVC | DUs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| sNRP1 | OR (95% CI) | 0.65 (0.50–0.83) | 0.48 (0.35–0.66) |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Sema3E | OR (95% CI) | 0.07 (0.02–0.21) | 0.09 (0.02–0.30) |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Slit2 | OR (95% CI) | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) |
| p | 0.335 | 0.479 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romano, E.; Rosa, I.; Fioretto, B.S.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Manetti, M. Circulating Neurovascular Guidance Molecules and Their Relationship with Peripheral Microvascular Impairment in Systemic Sclerosis. Life 2022, 12, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12071056
Romano E, Rosa I, Fioretto BS, Matucci-Cerinic M, Manetti M. Circulating Neurovascular Guidance Molecules and Their Relationship with Peripheral Microvascular Impairment in Systemic Sclerosis. Life. 2022; 12(7):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12071056
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomano, Eloisa, Irene Rosa, Bianca Saveria Fioretto, Marco Matucci-Cerinic, and Mirko Manetti. 2022. "Circulating Neurovascular Guidance Molecules and Their Relationship with Peripheral Microvascular Impairment in Systemic Sclerosis" Life 12, no. 7: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12071056
APA StyleRomano, E., Rosa, I., Fioretto, B. S., Matucci-Cerinic, M., & Manetti, M. (2022). Circulating Neurovascular Guidance Molecules and Their Relationship with Peripheral Microvascular Impairment in Systemic Sclerosis. Life, 12(7), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12071056










