Federated Learning Approach with Pre-Trained Deep Learning Models for COVID-19 Detection from Unsegmented CT images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Detecting Lung Diseases on X-ray Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
2.2. Detecting Lung Diseases on Chest CT Scans Using CNNs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. TL
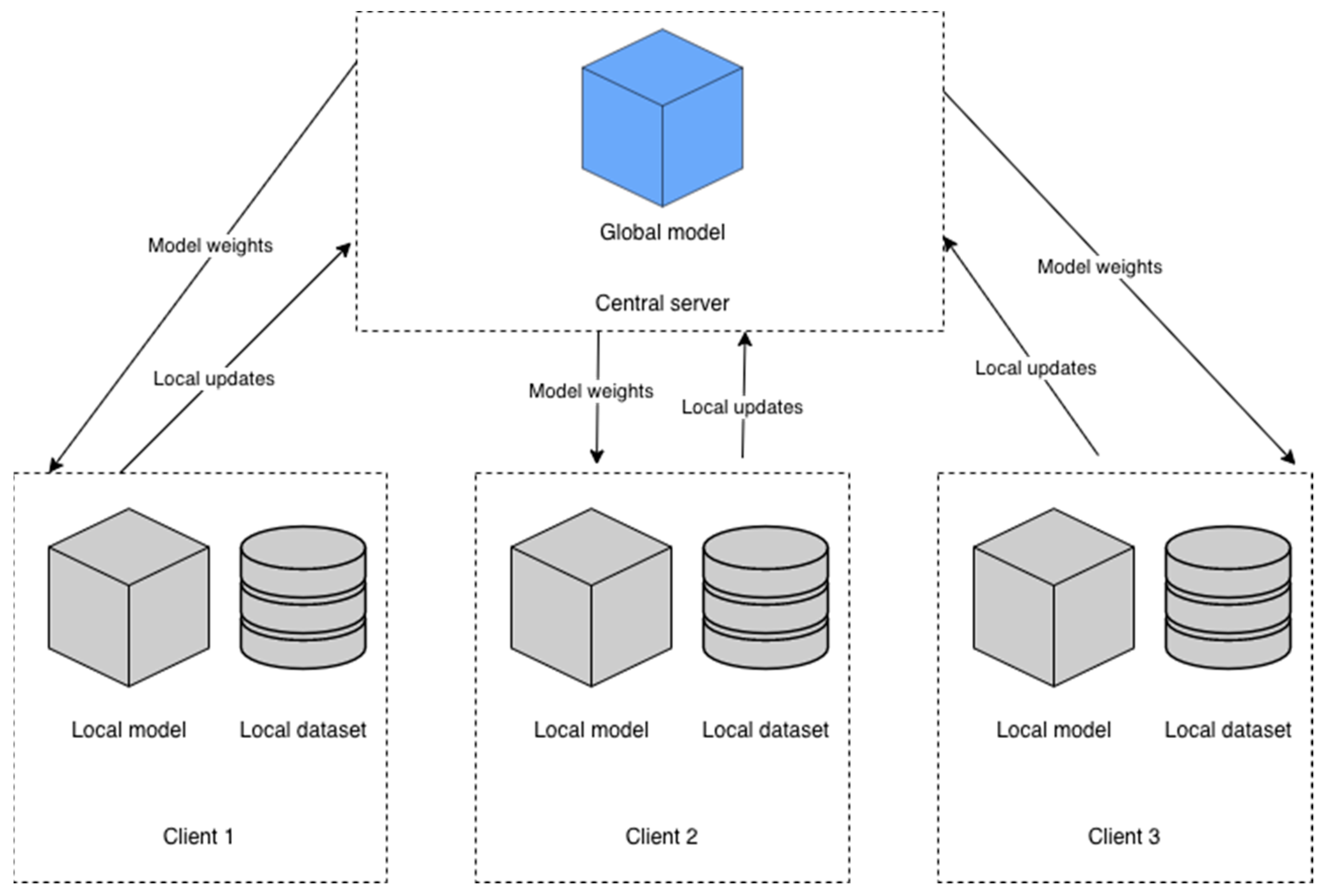
3.2.2. FL and Model Description
3.2.3. Hyperparameters and FL Configuration
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piret, J.; Boivin, G. Pandemics Throughout History. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 631736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Deng, Y.; Li, W. Coronavirus disease 2019: What we know? J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Bell, D.J. COVID-19|Radiology Reference Article|Radiopaedia.org. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/covid-19-4 (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobircă, A.; Bobircă, F.; Ancuța, I.; Florescu, A.; Bojincă, M.; Muscă, A.; Florescu, D.N.; Florescu, L.M.; Sima, R.M.; Florescu, A.; et al. COVID-19—A Trigger Factor for Severe Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis. Life 2022, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Radiology Assistant: COVID-19 Imaging Findings. Available online: https://radiologyassistant.nl/chest/covid-19/covid19-imaging-findings (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Ng, M.-Y.; Lee, E.Y.P.; Yang, J.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Lui, M.M.; Lo, C.S.-Y.; Leung, B.; Khong, P.-L.; et al. Imaging Profile of the COVID-19 Infection: Radiologic Findings and Literature Review. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tastanova, A.; Stoffel, C.I.; Dzung, A.; Cheng, P.F.; Bellini, E.; Johansen, P.; Duda, A.; Nobbe, S.; Lienhard, R.; Bosshard, P.P.; et al. A Comparative Study of Real-Time RT-PCR-Based SARS-CoV-2 Detection Methods and Its Application to Human-Derived and Surface Swabbed Material. J. Mol. Diagn. JMD 2021, 23, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şerbănescu, M.-S.; Oancea, C.-N.; Streba, C.T.; Pleşea, I.E.; Pirici, D.; Streba, L.; Pleşea, R.M. Agreement of two pre-trained deep-learning neural networks built with transfer learning with six pathologists on 6000 patches of prostate cancer from Gleason2019 Challenge. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2020, 61, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortani Barbosa, E.J.; Georgescu, B.; Chaganti, S.; Aleman, G.B.; Cabrero, J.B.; Chabin, G.; Flohr, T.; Grenier, P.; Grbic, S.; Gupta, N.; et al. Machine learning automatically detects COVID-19 using chest CTs in a large multicenter cohort. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 8775–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyasseri, Z.A.A.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Doush, I.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; Abasi, A.K.; Makhadmeh, S.N.; Alomari, O.A.; Abdulkareem, K.H.; Adam, A.; Damasevicius, R.; et al. Review on COVID-19 diagnosis models based on machine learning and deep learning approaches. Expert Syst. 2022, 39, e12759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazab, M.; Awajan, A.; Mesleh, A.; Abraham, A.; Jatana, V.; Alhyari, S. COVID-19 Prediction and Detection Using Deep Learning. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. Ind. Manag. Appl. 2020, 12, 168–181. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, P.; Sousa, O.; Magalhães, D.; Rabêlo, R.; Silva, R. Detecting pulmonary diseases using deep features in X-ray images. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 119, 108081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, M.F.; Unlersen, M.F.; Sabanci, K.; Durdu, A. CNN-based transfer learning–BiLSTM network: A novel approach for COVID-19 infection detection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 98, 106912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Mpesiana, T.A. COVID-19: Automatic detection from X-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmud, T.; Rahman, M.A.; Fattah, S.A. CovXNet: A multi-dilation convolutional neural network for automatic COVID-19 and other pneumonia detection from chest X-ray images with transferable multi-receptive feature optimization. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 122, 103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaraman, S.; Antani, S. Weakly Labeled Data Augmentation for Deep Learning: A Study on COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-rays. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Attar, A. A modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 and pneumonia from chest X-ray images based on the concatenation of Xception and ResNet50V2. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 19, 100360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Mazhar, R.; Kadir, M.A.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Islam, K.R.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Emadi, N.A.; et al. Can AI Help in Screening Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia? IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132665–132676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, S.; Kalantar, R.; Bhandari, M. Deep learning COVID-19 detection bias: Accuracy through artificial intelligence. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 1539–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunese, L.; Mercaldo, F.; Reginelli, A.; Santone, A. Explainable Deep Learning for Pulmonary Disease and Coronavirus COVID-19 Detection from X-rays. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Shah, J.L.; Bhat, M.M. CoroNet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismael, A.M.; Şengür, A. Deep learning approaches for COVID-19 detection based on chest X-ray images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 164, 114054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardakani, A.A.; Kanafi, A.R.; Acharya, U.R.; Khadem, N.; Mohammadi, A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, S.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Dey, N.; Rajinikanth, V.; Gandhi, T.K. Deep transfer learning-based automated detection of COVID-19 from lung CT scan slices. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.; Chung, H.; Kang, W.S.; Kim, K.W.; Shin, Y.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, N.Y.; Jung, H.; et al. COVID-19 Pneumonia Diagnosis Using a Simple 2D Deep Learning Framework With a Single Chest CT Image: Model Development and Validation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.; Zheng, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Chong, Y.; et al. Deep Learning Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) with CT Images. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2021, 18, 2775–2780. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zha, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Niu, M.; Wang, M.; Qiu, X.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; et al. A fully automatic deep learning system for COVID-19 diagnostic and prognostic analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozes, O.; Frid-Adar, M.; Greenspan, H.; Browning, P.D.; Zhang, H.; Ji, W.; Bernheim, A.; Siegel, E. Rapid AI Development Cycle for the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic: Initial Results for Automated Detection & Patient Monitoring using Deep Learning CT Image Analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.05037. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, M.; Yi, S.-L.; Zeng, Y.; Ye, F.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Ren, Y.-D.; Luo, L.; Pan, J.-S.; Zhang, Q. Deep Learning-Based Recognizing COVID-19 and other Common Infectious Diseases of the Lung by Chest CT Scan Images. medRxiv 2020, medrxiv-20046045. [Google Scholar]
- Feki, I.; Ammar, S.; Kessentini, Y.; Muhammad, K. Federated learning for COVID-19 screening from Chest X-ray images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 106, 107330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Khan, A.A.; Kumar, J.; Zakria; Golilarz, N.A.; Zhang, S.; Ting, Y.; Zheng, C.; Wang, W. Blockchain-Federated-Learning and Deep Learning Models for COVID-19 Detection Using CT Imaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 16301–16314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaLonde, R.; Bagci, U. Capsules for Object Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.04241. [Google Scholar]
- Sabour, S.; Frosst, N.; Hinton, G.E. Dynamic Routing Between Capsules. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.09829. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Yan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Experiments of Federated Learning for COVID-19 Chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.05592. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafavi, S.M. COVID19-CT-Dataset: An Open-Access Chest CT Image Repository of 1000+ Patients with Confirmed COVID-19 Diagnosis 2021. Available online: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/6ACUZJ (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Yan, T. COVID-19 and Common Pneumonia Chest CT Dataset (416 COVID-19 Positive CT Scans). 2020, Volume 2. Available online: https://doi.org/10.17632/3y55vgckg6.2 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Franquet, T. Imaging of pulmonary viral pneumonia. Radiology 2011, 260, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raharja, S.; Hussein, S. Radiographic development and resolution of lung abscess. Br. J. Hosp. Med. Lond. Engl. 2020, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choh, N.A.; Parry, A.H.; Wani, A.H.; Feroz, I.; Bhat, M.H.; Shaheen, F.A. The spectrum of imaging findings in pulmonary hydatid disease and the additive value of T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in its diagnosis. Pol. J. Radiol. 2021, 86, e53–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoura, E.; Zumla, A.; Bomanji, J. Imaging in tuberculosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2015, 32, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunihiro, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanaka, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Okada, M.; Kamiya, M.; Ueda, K.; Kawano, H.; Matsunaga, N. High-resolution CT findings of primary lung cancer with cavitation: A comparison between adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Radiol. 2016, 71, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.B.; Im, J.G.; Goo, J.M.; Chung, M.J.; Kim, M.Y. Atypical pulmonary metastases: Spectrum of radiologic findings. Radiogr. Rev. Publ. Radiol. Soc. N. Am. Inc 2001, 21, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T. COVID-19 and Common Pneumonia Chest CT Dataset (412 Common Pneumonia CT Scans). 2020, Volume 1. Available online: https://doi.org/10.17632/ygvgkdbmvt.1 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Li, P.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Lu, J.; HuangFu, Y.; Wang, D. A Large-Scale CT and PET/CT Dataset for Lung Cancer Diagnosis 2020. Available online: https://doi.org/10.7937/TCIA.2020.NNC2-0461 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Hopfield, J. Neural Networks and Physical Systems with Emergent Collective Computational Abilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2554–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hung, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-C.; Lai, P.-T.; Lin, C.-H.; Lee, C.-C. Comparing deep neural network and other machine learning algorithms for stroke prediction in a large-scale population-based electronic medical claims database. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 3110–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nica, R.-E.; Șerbănescu, M.-S.; Florescu, L.-M.; Camen, G.-C.; Streba, C.T.; Gheonea, I.-A. Deep Learning: A Promising Method for Histological Class Prediction of Breast Tumors in Mammography. J. Digit. Imaging 2021, 34, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolaccini, L.; Solli, P.; Pardolesi, A.; Pasini, A. An overview of the use of artificial neural networks in lung cancer research. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, R.Y.; Coyner, A.S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Chiang, M.F.; Campbell, J.P. Introduction to Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and Deep Learning. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Itoh, K.; Tanida, J.; Ichioka, Y. Parallel distributed processing model with local space-invariant interconnections and its optical architecture. Appl. Opt. 1990, 29, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Guan, Y.; Deng, B. Transfer learning based clinical concept extraction on data from multiple sources. J. Biomed. Inform. 2014, 52, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darzidehkalani, E.; Ghasemi-rad, M.; van Ooijen, P. Federated Learning in Medical Imaging: Part I: Toward Multicentral Health Care Ecosystems. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. JACR 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairouz, P.; McMahan, H.B.; Avent, B.; Bellet, A.; Bennis, M.; Bhagoji, A.N.; Bonawitz, K.; Charles, Z.; Cormode, G.; Cummings, R.; et al. Advances and Open Problems in Federated Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:1912.04977. [Google Scholar]
- Pokhrel, S.R.; Choi, J. Federated Learning With Blockchain for Autonomous Vehicles: Analysis and Design Challenges. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 4734–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, H.B.; Moore, E.; Ramage, D.; Hampson, S.; Arcas, B.A. Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1602.05629. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 22–24 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- TANG, W.; HU, J.; ZHANG, H.; WU, P.; HE, H. Kappa coefficient: A popular measure of rater agreement. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2015, 27, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandini, M.; Bagli, E.; Visani, G. Metrics for Multi-Class Classification: An Overview. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.05756. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-based Localization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar]
- Beutel, D.J.; Topal, T.; Mathur, A.; Qiu, X.; Fernandez-Marques, J.; Gao, Y.; Sani, L.; Li, K.H.; Parcollet, T.; de Gusmão, P.P.B.; et al. Flower: A Friendly Federated Learning Research Framework. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2007.14390. [Google Scholar]
- COVID-19 Pandemic in Romania—Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/COVID-19_pandemic_in_Romania (accessed on 8 January 2022).
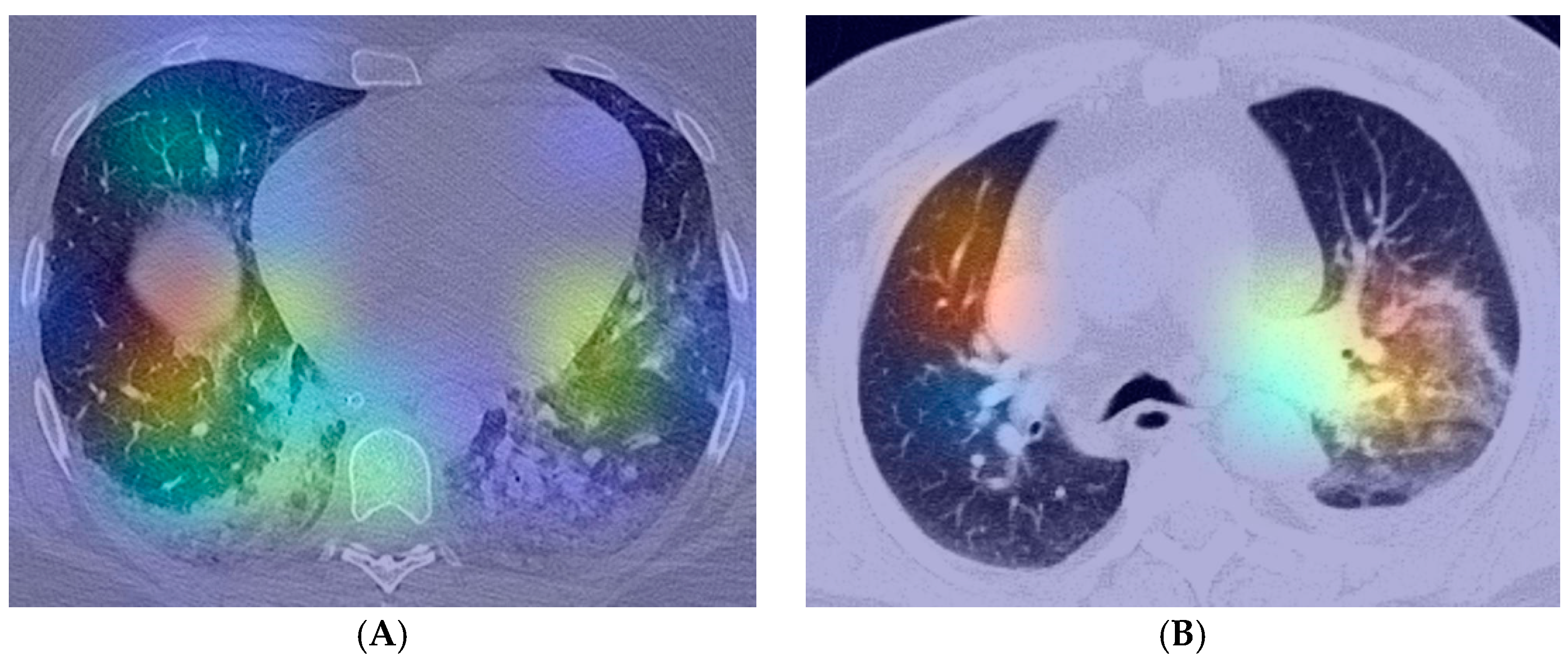
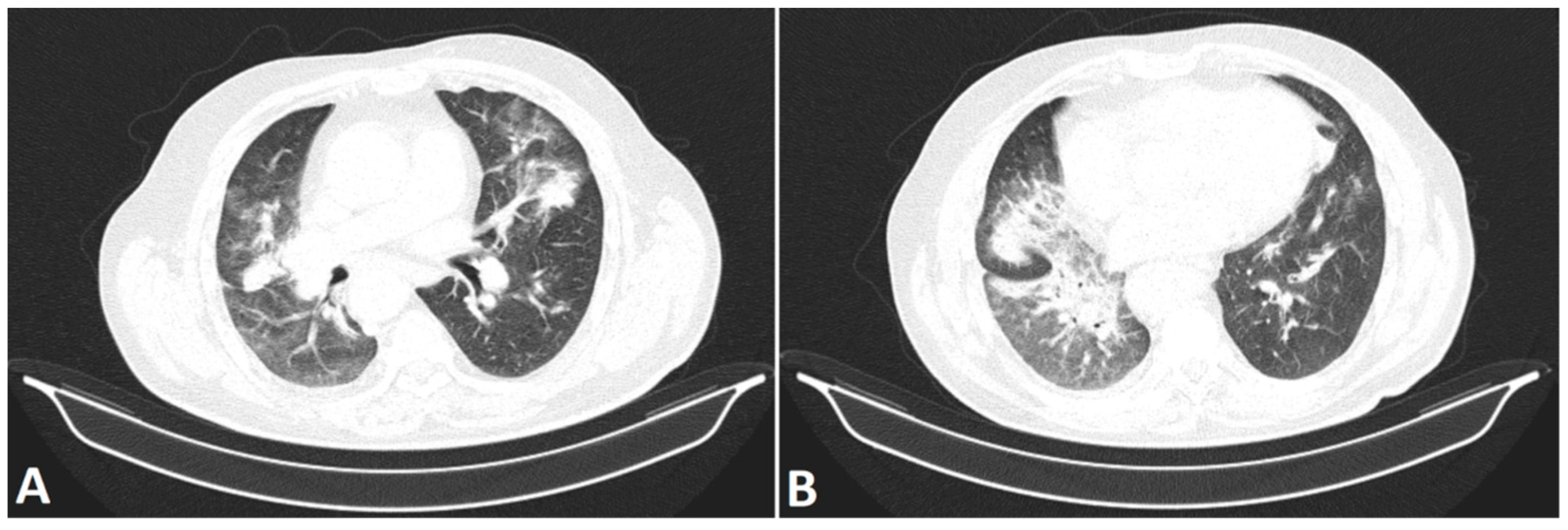
| Paper | Sample Size | Algorithm | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mahmud et al. [18] | 305 COVID-19, 1538 Normal aspect, 1493 Viral pneumonia, 3780 Bacterial pneumonia | ConvxNet | ACC: 0.900 Recall: 0.890 Spe: 0.890 |
| Rajaraman et al. [19] | 314 COVID-19, 1583 Normal aspect, 3780 Bacterial pneumonia, 1493 Viral pneumonia, 11,002 Varied pneumonia | U-Net, VGG-16, Inception-V3, Xception, DenseNet-121, NasNet-Mobile | ACC: 0.930 Sen: 0.970 Spe: 0.860 |
| Rahimzadeh et al. [20] | 180 COVID-19, 6054 Pneumonia, 8851 Normal aspect | ImageNet, Xception, ResNet50 | ACC: 0.914 |
| Chowdhurry et al. [21] | 423 COVID-19, 1485 Viral pneumonia, 1579 Normal aspect | MobileNetv2, SqueezeNet, ResNet18, ResNet101, DenseNet201, CheXNet, Inceptionv3, VGG19 | ACC 0.979 Sen 0.979 Spe 0.988 |
| Vaid et al. [22] | 181 COVID-19, 364 Normal aspect | Modified VGG19 | ACC: 0.963 |
| Brunese et al. [23] | 250 COVID-19, 3520 Normal aspect, 2753 Pneumonia | VGG16 | ACC: 0.960 Sen: 0.960 Spe: 0.980 |
| Khan et al. [24] | 284 COVID-19, 310 Normal aspect, 320 Bacterial pneumonia, 327 Viral pneumonia | CoroNet | ACC: 0.900 Spe: 0.960 Recall: 0.890 |
| Ismael et al. [25] | 180 COVID-19 200 Normal aspect | ResNet18, ResNet50, ResNet101, VGG16, VGG19 | ACC: 0.947 |
| Paper | Sample Size | Algorithm | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ko et al. [28] | 3993 Chest CT images COVID-19, Non-COVID-19 pneumonia, Non-pneumonia | VGG16, ResNet-50, Inception-v3, Xception | ResNet-50 ACC: 0.998 Sen: 0.995 Spe: 1.000 |
| Ying et al. [29] | 777 COVID-19, 708 Normal aspect, 505 Bacterial pneumonia | VGG16, DenseNet, ResNet, DRE-Net | DRE-Net ACC: 0.94 Recall: 0.93 AUC: 0.99 |
| Wang et al. [30] | 5372 Raw chest CT images COVID-19, Other pneumonia | DenseNet COVID-19Net | Training ACC: 0.812 Sen: 0.789 Spe: 0.899 Validation 1 ACC: 0.783 Sen: 0.803 Spe: 0.766 |
| Gozes et al. [31] | 157 Chest CT scans COVID-19, Non-COVID-19 aspect | ResNet-50-2 | Sen: 0.982 Spe: 0.922 |
| Fu M et al. [32] | 60,427 CT scans | ResNet-50 | ACC: 0.989 Sen: 0.967 Spe: 0.993 |
| Layer Id | D Configuration |
|---|---|
| 16 weight layers | |
| Input (224 × 244 × 3) | |
| 1 | conv3-64 conv3-64 |
| maxpool | |
| 2 | conv3-128 conv3-128 |
| maxpool | |
| 3 | conv3-256 conv3-256 conv3-256 |
| maxpool | |
| 4 | conv3-512 conv3-512 conv3-512 |
| maxpool | |
| 5 | conv3-512 conv3-512 conv3-512 |
| maxpool | |
| 6 | FC-128 |
| 7 | FC-3 |
| Softmax |
| Model | Categorical Accuracy | F1μ | F1M | Cohen’s Kappa Score | Matthews Correlation Coefficient | Training Time (Seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized VGG-16 | 0.9390 | 0.9390 | 0.9356 | 0.9053 | 0.9053 | 998.129 |
| Proposed method—FL VGG-16 | 0.8382 | 0.7865 | 0.8131 | 0.6816 | 0.6917 | 1960.73 |
| Model | Categorical Accuracy | F1μ | F1M | Cohen’s Kappa Score | Matthews Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized VGG-16 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.7741 | 0.6804 | 0.6856 |
| Proposed method—FL VGG-16 | 0.7932 | 0.7865 | 0.7246 | 0.6441 | 0.6894 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Florescu, L.M.; Streba, C.T.; Şerbănescu, M.-S.; Mămuleanu, M.; Florescu, D.N.; Teică, R.V.; Nica, R.E.; Gheonea, I.A. Federated Learning Approach with Pre-Trained Deep Learning Models for COVID-19 Detection from Unsegmented CT images. Life 2022, 12, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12070958
Florescu LM, Streba CT, Şerbănescu M-S, Mămuleanu M, Florescu DN, Teică RV, Nica RE, Gheonea IA. Federated Learning Approach with Pre-Trained Deep Learning Models for COVID-19 Detection from Unsegmented CT images. Life. 2022; 12(7):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12070958
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlorescu, Lucian Mihai, Costin Teodor Streba, Mircea-Sebastian Şerbănescu, Mădălin Mămuleanu, Dan Nicolae Florescu, Rossy Vlăduţ Teică, Raluca Elena Nica, and Ioana Andreea Gheonea. 2022. "Federated Learning Approach with Pre-Trained Deep Learning Models for COVID-19 Detection from Unsegmented CT images" Life 12, no. 7: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12070958
APA StyleFlorescu, L. M., Streba, C. T., Şerbănescu, M.-S., Mămuleanu, M., Florescu, D. N., Teică, R. V., Nica, R. E., & Gheonea, I. A. (2022). Federated Learning Approach with Pre-Trained Deep Learning Models for COVID-19 Detection from Unsegmented CT images. Life, 12(7), 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12070958








