Anti-MDA5 Amyopathic Dermatomyositis—A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge
Abstract
1. Introduction
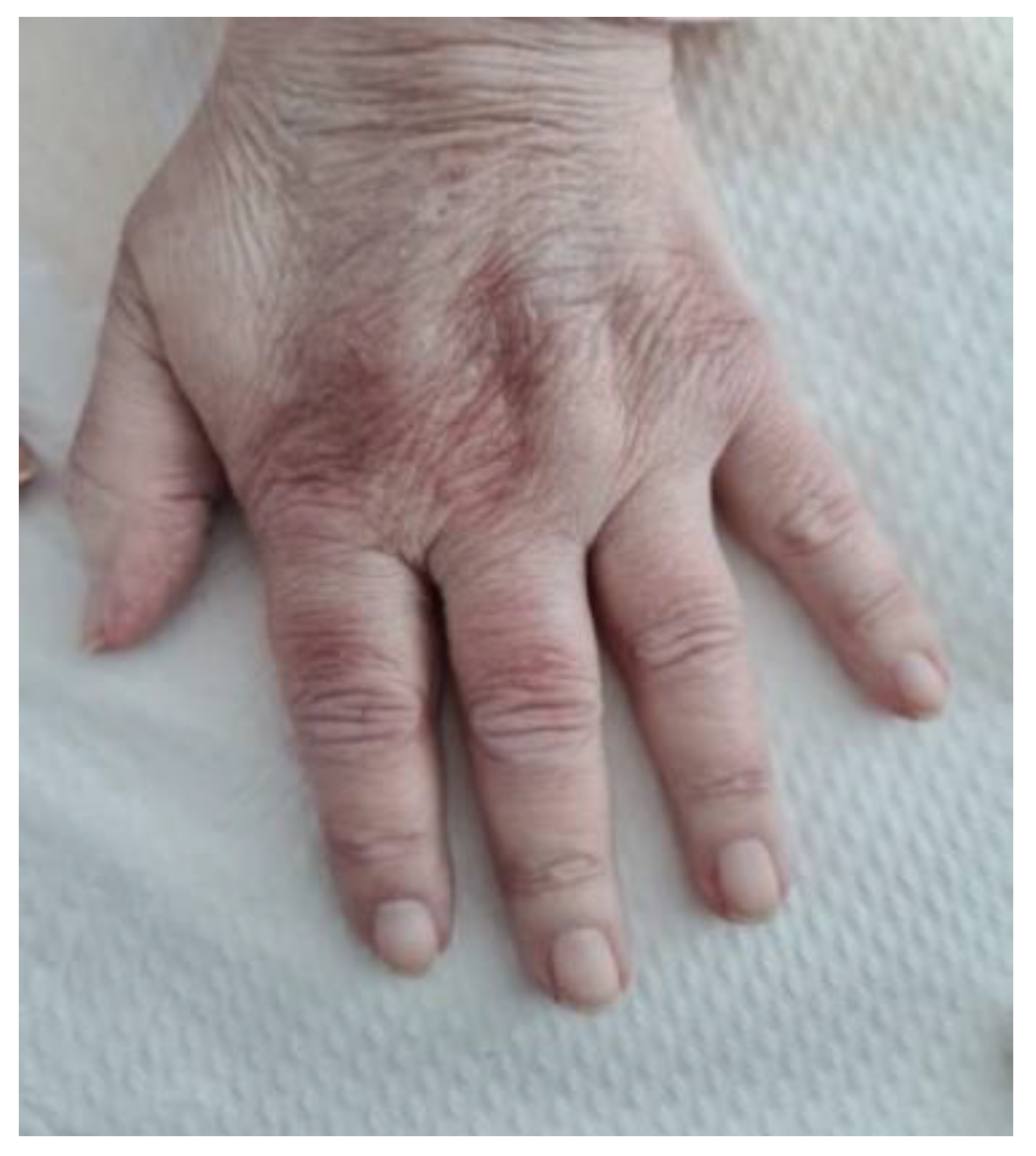
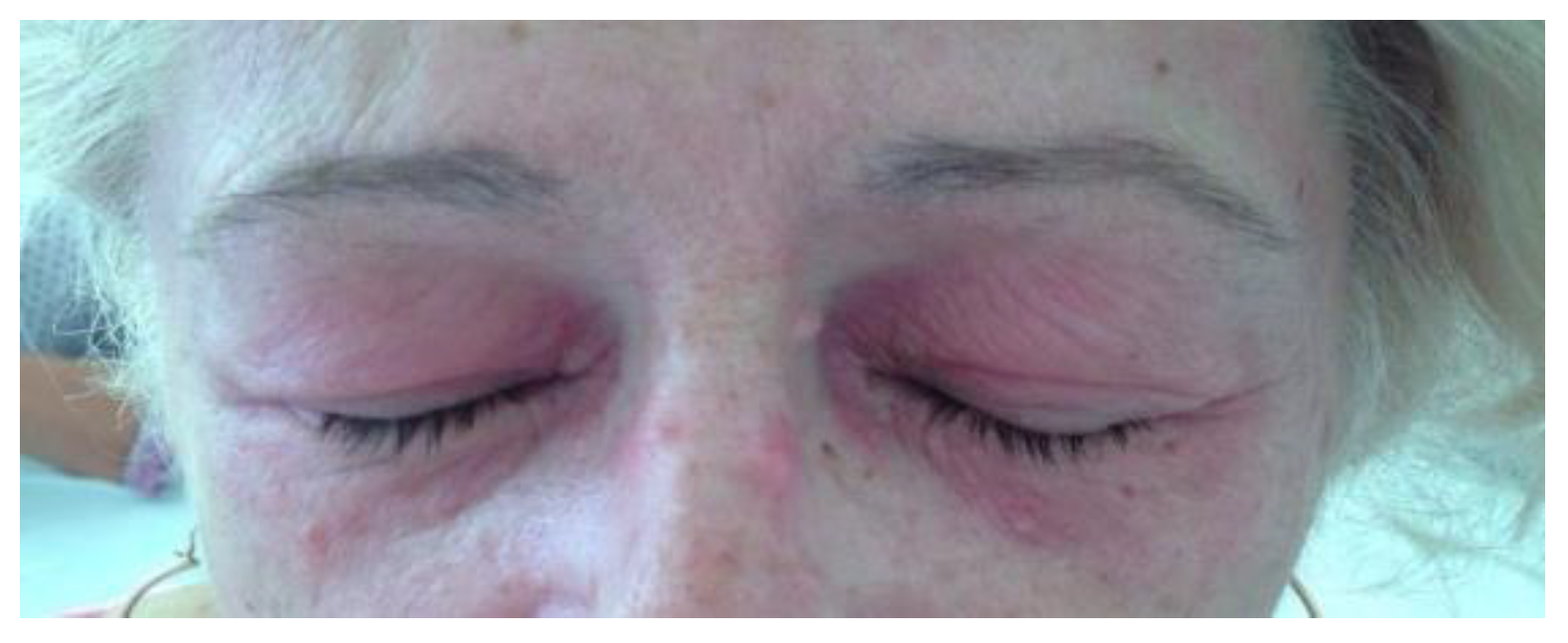
2. Clinical Experience—Case Report
3. Pathogenesis
4. Clinical and Paraclinical Features
5. Treatment
6. Prognosis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yanagihara, T.; Inoue, Y. Insights into pathogenesis and clinical implications in myositis-associated interstitial lung diseases. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2020, 26, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betteridge, Z.; McHugh, N. Myositis-specific autoantibodies: An important tool to support diagnosis of myositis. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 280, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Kuwana, M. Clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2010, 22, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontheimer, R.D. Would a new name hasten the acceptance of amyopathic dermatomyositis (dermatomyositis siné myositis) as a distinctive subset within the idiopathic inflammatory dermatomyopathies spectrum of clinical illness? J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 46, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Machado, P.M.; Gupta, L. Understanding and managing anti-MDA 5 dermatomyositis, including potential COVID-19 mimicry. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betteridge, Z.; Tansley, S.; Shaddick, G.; Chinoy, H.; Cooper, R.; New, R.; Lilleker, J.; Vencovsky, J.; Chazarain, L.; Danko, K.; et al. Frequency, mutual exclusivity and clinical associations of myositis autoantibodies in a combined European cohort of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy patients. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 101, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Sun, L.; Kuwana, M. Distinct profiles of myositis-specific autoantibodies in Chinese and Japanese patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Hirakata, M.; Kuwana, M.; Suwa, A.; Inada, S.; Mimori, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Oddis, C.V.; Ikeda, Y. Autoantibodies to a 140-kd polypeptide, CADM-140, in Japanese patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. Arthritis Care Res. 2005, 52, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosovsky, R.P.; Grodzin, C.; Channick, R.; Davis, G.A.; Giri, J.S.; Horowitz, J.; Kabrhel, C.; Lookstein, R.; Merli, G.; Morris, T.A.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. Chest 2020, 158, 2590–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Lundberg, I.; Tjärnlund, A.; Bottai, M.; Werth, V.P.; Pilkington, C.; De Visser, M.; Alfredsson, L.; Amato, A.; Barohn, R.J.; Liang, M.H.; et al. 2017 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landewé, R.B.M.; Kroon, F.P.B.; Alunno, A.; Najm, A.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Burmester, G.-R.R.; Caporali, R.; Combe, B.; Conway, R.; Curtis, J.R.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management and vaccination of people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases in the context of SARS-CoV-2: The November 2021 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rams, A.; Kosałka-Węgiel, J.; Kuszmiersz, P.; Matyja-Bednarczyk, A.; Polański, S.; Zaręba, L.; Bazan-Socha, S. Characteristics of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies with novel myositis-specific autoantibodies. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokiyama, K.; Tagawa, H.; Yokota, E.; Nagasawa, K.; Kusaba, T.; Tsuda, Y.; Niho, Y. Two cases of amyopathic dermatomyositis with fatal rapidly progressive interstitial pneumonitis. Ryumachi. Rheum. 1990, 30, 204–209. [Google Scholar]
- Nanke, Y.; Tateisi, M.; Yamagata, H.; Hara, M.; Kamatani, N. A case of amyopathic dermatomyositis with rapidly progressive interstitial pneumonia. Ryumachi. Rheum. 2000, 40, 705–710. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, S.; Hoshino, K.; Satoh, T.; Fujita, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Fujita, T.; Kuwana, M. RNA helicase encoded by melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 is a major autoantigen in patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: Association with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Care Res. 2009, 60, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Mizumaki, K.; Kano, M.; Yagi, N.; Tennichi, M.; Takeuchi, A.; Okamoto, Y.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Murakami, A.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Antimelanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 antibody level is a novel tool for monitoring disease activity in rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease with dermatomyositis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 176, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, Y.; Sugiura, K.; Hoshino, K.; Akiyama, M.; Tamakoshi, K. Epidemiologic study of clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis and anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibodies in central Japan. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainetti, C.; Beretta-Piccoli, B.T.; Selmi, C. Cutaneous Manifestations of Dermatomyositis: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 53, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisson, N.F.; Paik, J.; Orbai, A.-M.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Fiorentino, D.; Danoff, S.; Rosen, A. A Novel Dermato-Pulmonary Syndrome Associated With MDA-5 Antibodies. Medicine 2012, 91, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parperis, K.; Kiyani, A. Clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis associated with anti-MDA5 antibody. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nombel, A.; Fabien, N.; Coutant, F. Dermatomyositis with Anti-MDA5 Antibodies: Bioclinical Features, Pathogenesis and Emerging Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, N.; Kai, K.; Maruyama, A.; Sakai, M.; Sadanaga, Y.; Koarada, S.; Inoue, T.; Tada, Y. The relationship between type 1 IFN and vasculopathy in anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis patients. Rheumatology 2018, 58, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allenbach, Y.; Uzunhan, Y.; Toquet, S.; Leroux, G.; Gallay, L.; Marquet, A.; Meyer, A.; Guillaud, C.; Limal, N.; Gagnadoux, F.; et al. Different phenotypes in dermatomyositis associated with anti-MDA5 antibody. Neurology 2020, 95, e70–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzman, D.J.; Vleugels, R.A. Anti-melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 (MDA5) dermatomyositis: A concise review with an emphasis on distinctive clinical features. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, N.S.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Li, S.; Chung, L.; Fiorentino, D.F. Cutaneous Ulceration in Dermatomyositis: Association with Anti-Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Gene 5 Antibodies and Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 67, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Xia, Q.; Pan, M.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Shi, R.; Zhou, M.; Ding, X.; Kuwana, M.; Zheng, J. Gottron Papules and Gottron Sign with Ulceration: A Distinctive Cutaneous Feature in a Subset of Patients with Classic Dermatomyositis and Clinically Amyopathic Dermatomyositis. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, D.; Chung, L.; Zwerner, J.; Rosen, A.; Casciola-Rosen, L. The mucocutaneous and systemic phenotype of dermatomyositis patients with antibodies to MDA5 (CADM-140): A retrospective study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 65, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWane, M.E.; Waldman, R.; Lu, J. Dermatomyositis: Clinical features and pathogenesis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolazzi, C.; Cutolo, M.; Smith, V.; Gutierrez, M. State of the art on nailfold capillaroscopy in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 47, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, A.; Sebastiani, M.; Cassone, G.; Pipitone, N.; Giuggioli, D.; Colaci, M.; Salvarani, C.; Ferri, C. Nailfold capillaroscopic changes in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 34, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.C.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Samedy, L.-A.; Werner, J.; Owoyemi, K.; Danoff, S.; Christopher-Stine, L. Anti-Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Protein 5-Associated Dermatomyositis: Expanding the Clinical Spectrum. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervier, B.; Uzunhan, Y. Inflammatory Myopathy-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: From Pathophysiology to Treatment. Front. Med. 2020, 6, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurasawa, K.; Arai, S. Optimal management of interstitial lung disease associated with dermatomyositis/polymyositis: Lessons from the Japanese experience. Orphan Drugs Res. Rev. 2014, 4, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Misra, A.K.; Wong, N.L.; Healey, T.T.; Lally, E.V.; Shea, B.S. Interstitial lung disease is a dominant feature in patients with circulating myositis-specific antibodies. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, K.; Hagino, N. Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Report of 3 Cases in Japan. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wytrychowski, K.W.; Hans-Wytrychowska, A.; Piesiak, P.; Majewska-Pulsakowska, M.; Rożek-Piechura, K. Pulmonary rehabilitation in interstitial lung diseases: A review of the literature. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 29, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egashira, R. High-Resolution CT Findings of Myositis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease. Medicina 2021, 57, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorat, M.; Jurek, T.; Simon, K.; Guziński, M. The chest radiographic scoring system in initial diagnosis of COVID-19: Is a radiologist needed? Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacek, C.; Karolina, S.; Orzeł, A.; Frączek, M.; Tomasz, Z. Comparison of the clinical differences between COVID-19, SARS, influenza, and the common cold: A systematic literature review. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, A.; Gaini, S.; Sore, P. Rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease in a patient with anti-MDA5-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 47, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/cutaneous-dermatomyositis-in-adults-overview-and-initial-management?sectionName=Photoprotection&topicRef=5160&anchor=H13069036&source=see_link#H13069036 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Kawasumi, H.; Gono, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Yamanaka, H. Recent Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. Clin. Med. Insights Circ. Respir. Pulm. Med. 2015, 9s1, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, H.; Nakashima, R.; Hosono, Y.; Imura, Y.; Yagita, M.; Yoshifuji, H.; Hirata, S.; Nojima, T.; Sugiyama, E.; Hatta, K.; et al. Multicenter Prospective Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Combined Immunosuppressive Therapy with High-Dose Glucocorticoid, Tacrolimus, and Cyclophosphamide in Interstitial Lung Diseases Accompanied by Anti–Melanoma Differentiation–Associated Gene 5–Positive Dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 72, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, M.; Economidou, S.; Liampas, A.; Zis, P.; Parperis, K. Management of MDA-5 antibody positive clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis associated interstitial lung disease: A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 53, 151959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucur, S.; Savu, A.-P.; Stănescu, A.M.A.; Șerban, E.-D.; Nicolescu, A.-C.; Constantin, T.; Bobircă, A.; Constantin, M.-M. Oversight and Management of Women with Psoriasis in Childbearing Age. Medicina 2022, 58, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woytala, P.J.; Morgiel, E.; Łuczak, A.; Czesak-Woytala, K.; Wiland, P. The Safety of Intravenous Cyclophosphamide in the Treatment of Rheumatic Diseases. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 25, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Ye, S. Tofacitinib in Amyopathic Dermatomyositis–Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, T. Management of Myositis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Medicina 2021, 57, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Kishida, D.; Shimojima, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Sekijima, Y. Effective Administration of Rituximab in Anti-MDA5 Antibody–Positive Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease and Refractory Cutaneous Involvement: A Case Report and Literature Review. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2017, 2017, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felten, R.; Duret, P.M.; Bauer, E.; Ardizzone, M.; Djossou, H.J.; Salmon, J.H.; Fabre, C.; Walther, J.; Valckenaere, I.C.; Geoffroy, M.; et al. op0282 rituximab associated with severe covid-19 among patients with inflammatory arthritides: A 1-year multicenter study in 1116 successive patients receiving biologic agents. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 170–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, K.M.; A Bates, B.; Rashidi, E.S.; Olex, A.L.; Mannon, R.B.; Patel, R.C.; Singh, J.; Sun, J.; Auwaerter, P.G.; Ng, D.K.; et al. Long-term use of immunosuppressive medicines and in-hospital COVID-19 outcomes: A retrospective cohort study using data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 4, e33–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobircă, A.; Bobircă, F.; Ancuța, I.; Florescu, A.; Bojincă, M.; Muscă, A.; Florescu, D.N.; Florescu, L.M.; Sima, R.M.; Florescu, A.; et al. COVID-19—A Trigger Factor for Severe Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis. Life 2022, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, M.; Stoian, A.P.; Rizzo, M.; Serban, D.; Nuzzo, D.; Mazilu, L.; Suceveanu, A.I.; Dascalu, A.M.; Parepa, I.R. The Role of Endothelium in COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, S.; Kronbichler, A.; Salas, A.; Bruchfeld, A.; Geetha, D. Timing of COVID-19 Vaccine in the Setting of Anti-CD20 Therapy: A Primer for Nephrologists. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiapparoli, I.; Galluzzo, C.; Salvarani, C.; Pipitone, N. A glance into the future of myositis therapy. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 14, 1759720X2211002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaubitz, S.; Zeng, R.; Schmidt, J. New insights into the treatment of myositis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2020, 12, 1759720X1988649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penlioglou, T.; Stoian, A.P.; Papanas, N. Diabetes, Vascular Aging and Stroke: Old Dogs, New Tricks? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasin, L.; Cavalli, G.; Navalesi, P.; Sella, N.; Landoni, G.; Yavorovskiy, A.G.; Likhvantsev, V.V.; Zangrillo, A.; Dagna, L.; Monti, G. Anakinra for patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis of non-randomized cohort studies. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 86, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzetti, M.; Forastieri, A.; Borsa, N.; Pandolfo, A.; Molteni, C.; Borghesi, L.; Pontiggia, S.; Evasi, G.; Guiotto, L.; Erba, M.; et al. IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Anakinra in the Treatment of COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Retrospective, Observational Study. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, Y.; Yoshimi, R.; Tamura, M.; Takeno, M.; Kunishita, Y.; Kishimoto, D.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Takase-Minegishi, K.; Watanabe, T.; et al. The predictive prognostic factors for polymyositis/dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Bueno, F.; del Campo, P.D.; Trallero-Araguás, E.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, J.; Castellvi, I.; Rodriguez-Nieto, M.; Martínez-Becerra, M.; Sanchez-Pernaute, O.; Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Solanich, X.; et al. Recommendations for the treatment of anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5-positive dermatomyositis-associated rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofolean, D.E.; Mazilu, L.; Stăniceanu, F.; Mocanu, L.; Suceveanu, A.I.; Baz, R.O.; Parepa, R.I.; Suceveanu, A.P.; Bondari, S.; Bondari, D.; et al. Clinical presentation of a patient with cutis laxa with systemic involvement: A case report. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2015, 56, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Florescu, A.; Gherghina, F.L.; Mușetescu, A.E.; Pădureanu, V.; Roșu, A.; Florescu, M.M.; Criveanu, C.; Florescu, L.-M.; Bobircă, A. Novel Biomarkers, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis Interstitial Lung Disease—A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanizawa, K.; Handa, T.; Nakashima, R.; Kubo, T.; Hosono, Y.; Aihara, K.; Ikezoe, K.; Watanabe, K.; Taguchi, Y.; Hatta, K.; et al. The prognostic value of HRCT in myositis-associated interstitial lung disease. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gono, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Satoh, T.; Kuwana, M.; Katsumata, Y.; Takagi, K.; Masuda, I.; Tochimoto, A.; Baba, S.; Okamoto, Y.; et al. Clinical manifestation and prognostic factor in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-associated interstitial lung disease as a complication of dermatomyositis. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kashiwagi, C.; Sawada, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Umetsu, K.; Oshima, K.; Uchida, M.; Suzuki, M.; Kono, S.; et al. Differential clinical features of patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis who have circulating anti-MDA5 autoantibodies with or without myositis-associated autoantibodies. Respir. Med. 2018, 140, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bobirca, A.; Alexandru, C.; Musetescu, A.E.; Bobirca, F.; Florescu, A.T.; Constantin, M.; Tebeica, T.; Florescu, A.; Isac, S.; Bojinca, M.; et al. Anti-MDA5 Amyopathic Dermatomyositis—A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. Life 2022, 12, 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081108
Bobirca A, Alexandru C, Musetescu AE, Bobirca F, Florescu AT, Constantin M, Tebeica T, Florescu A, Isac S, Bojinca M, et al. Anti-MDA5 Amyopathic Dermatomyositis—A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. Life. 2022; 12(8):1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081108
Chicago/Turabian StyleBobirca, Anca, Cristina Alexandru, Anca Emanuela Musetescu, Florin Bobirca, Anca Teodora Florescu, Magdalena Constantin, Tiberiu Tebeica, Alesandra Florescu, Sebastian Isac, Mihai Bojinca, and et al. 2022. "Anti-MDA5 Amyopathic Dermatomyositis—A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge" Life 12, no. 8: 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081108
APA StyleBobirca, A., Alexandru, C., Musetescu, A. E., Bobirca, F., Florescu, A. T., Constantin, M., Tebeica, T., Florescu, A., Isac, S., Bojinca, M., & Ancuta, I. (2022). Anti-MDA5 Amyopathic Dermatomyositis—A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. Life, 12(8), 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081108







