Potential Role of miR-196a and miR-196b as Prognostic Biomarkers of Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Sources of Information, Research, and Selection
2.4. Data Collection Process, Data Characteristics
2.5. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies, Summary Measures, Summary of Results, Risk of Bias between Studies, Additional Measures
3. Results
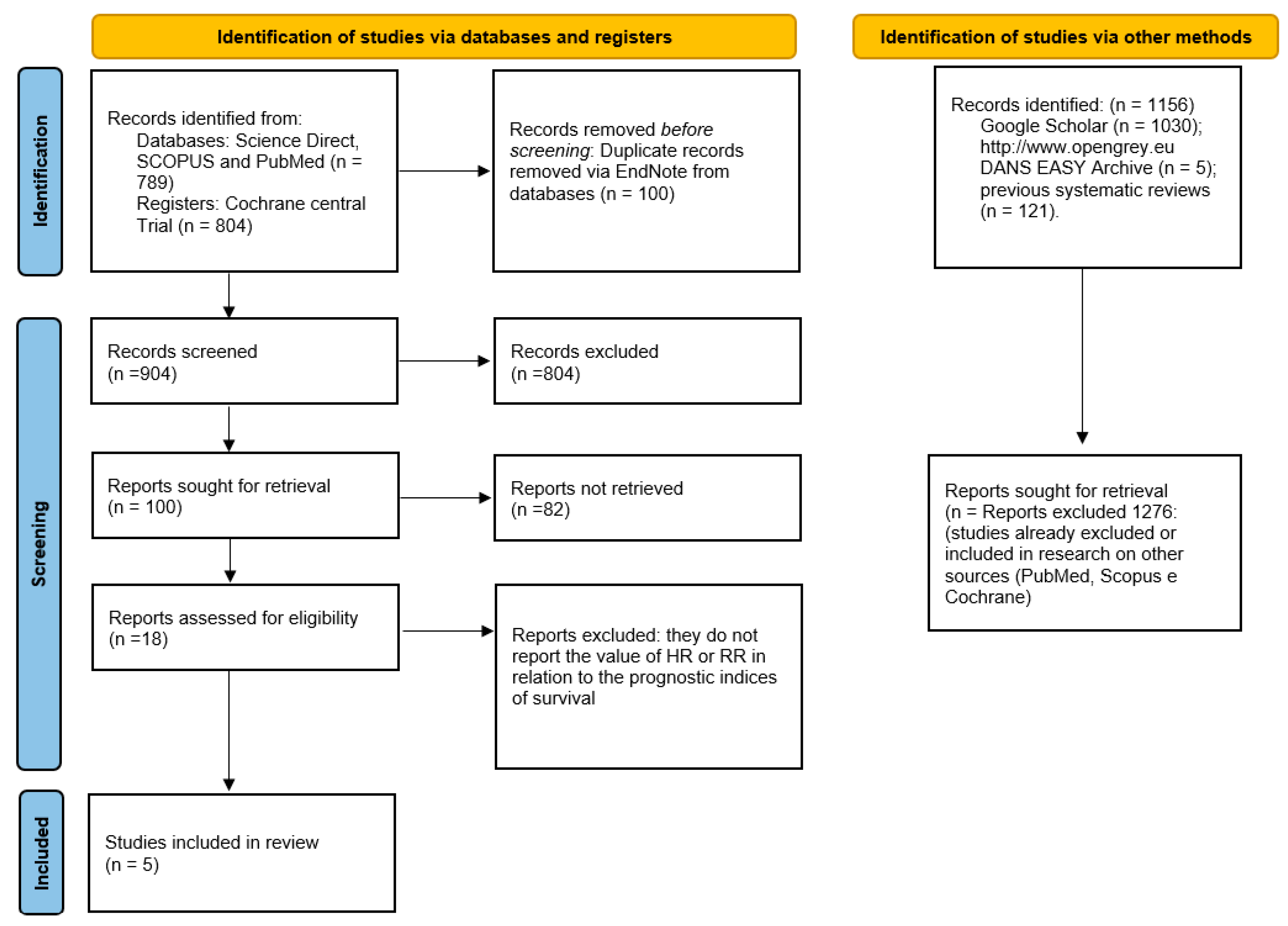
3.1. Selection of Studies
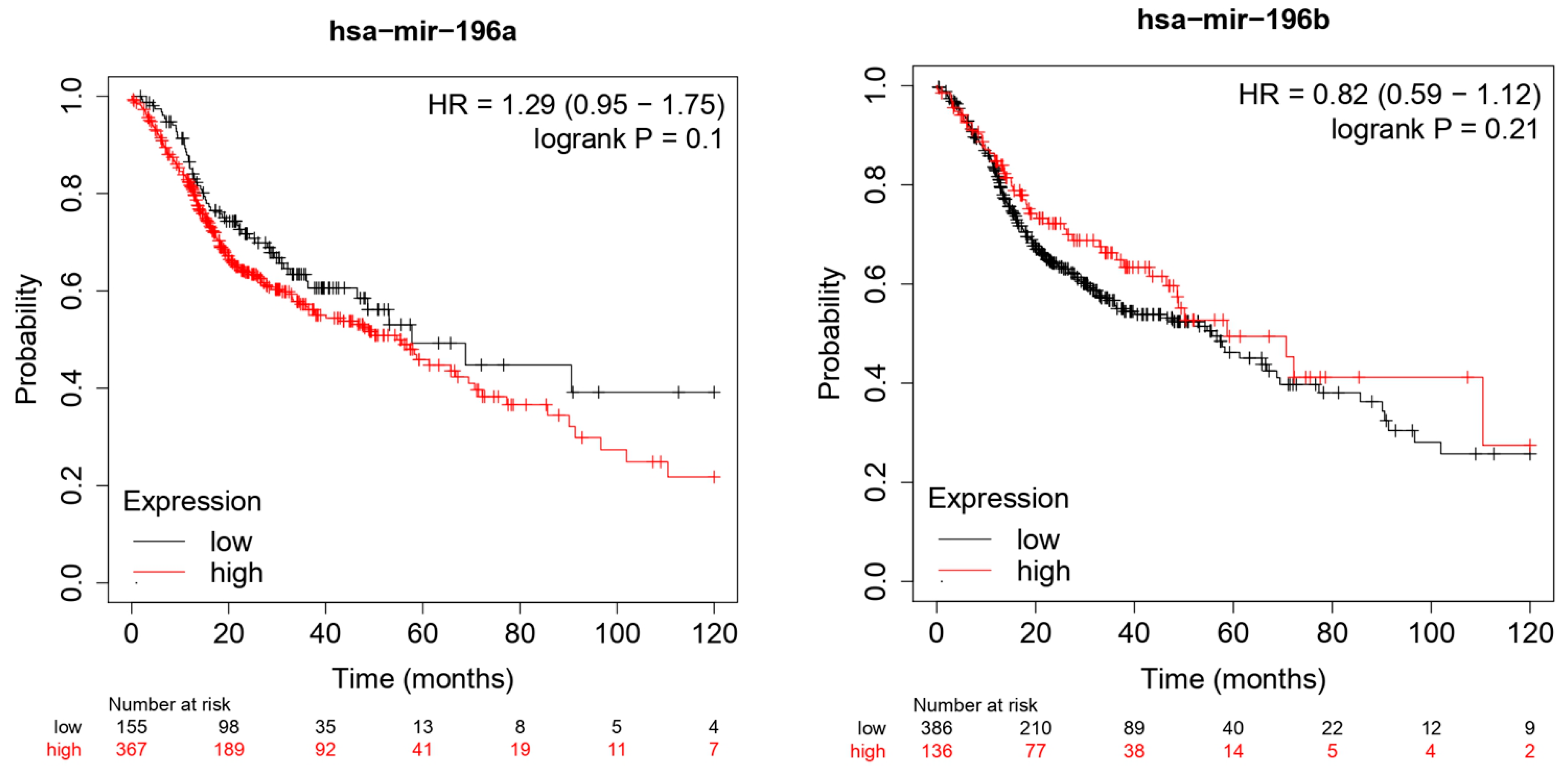
3.2. TGCA Cohort Analysis Results
3.3. Data Characteristics
3.4. Risk of Bias in Studies
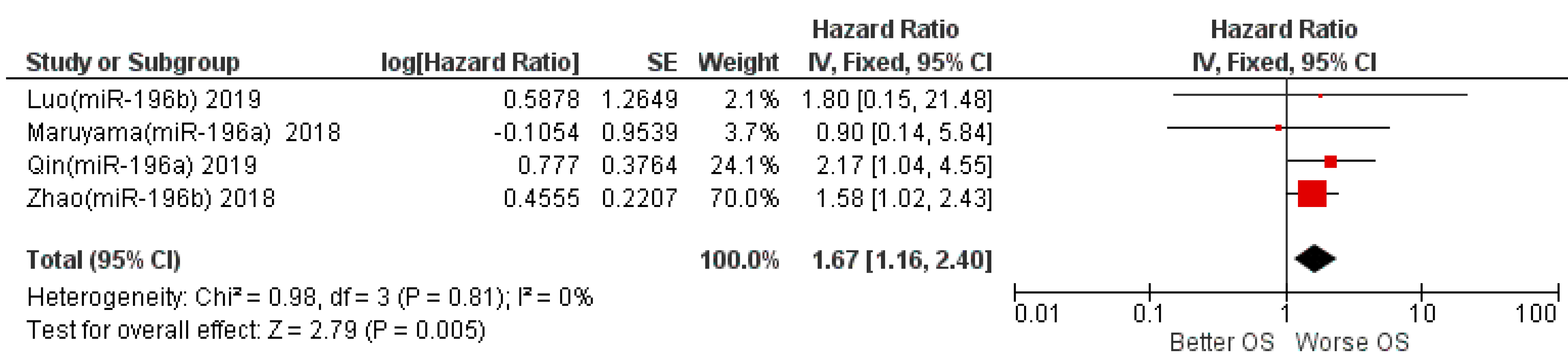
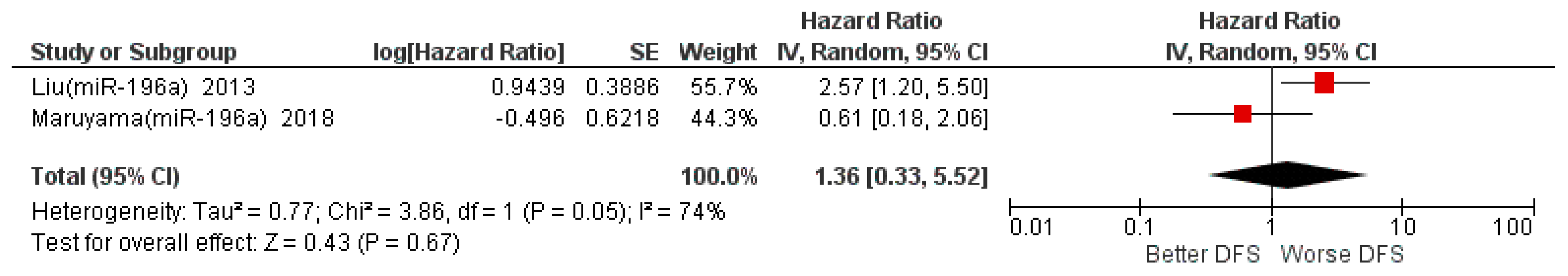
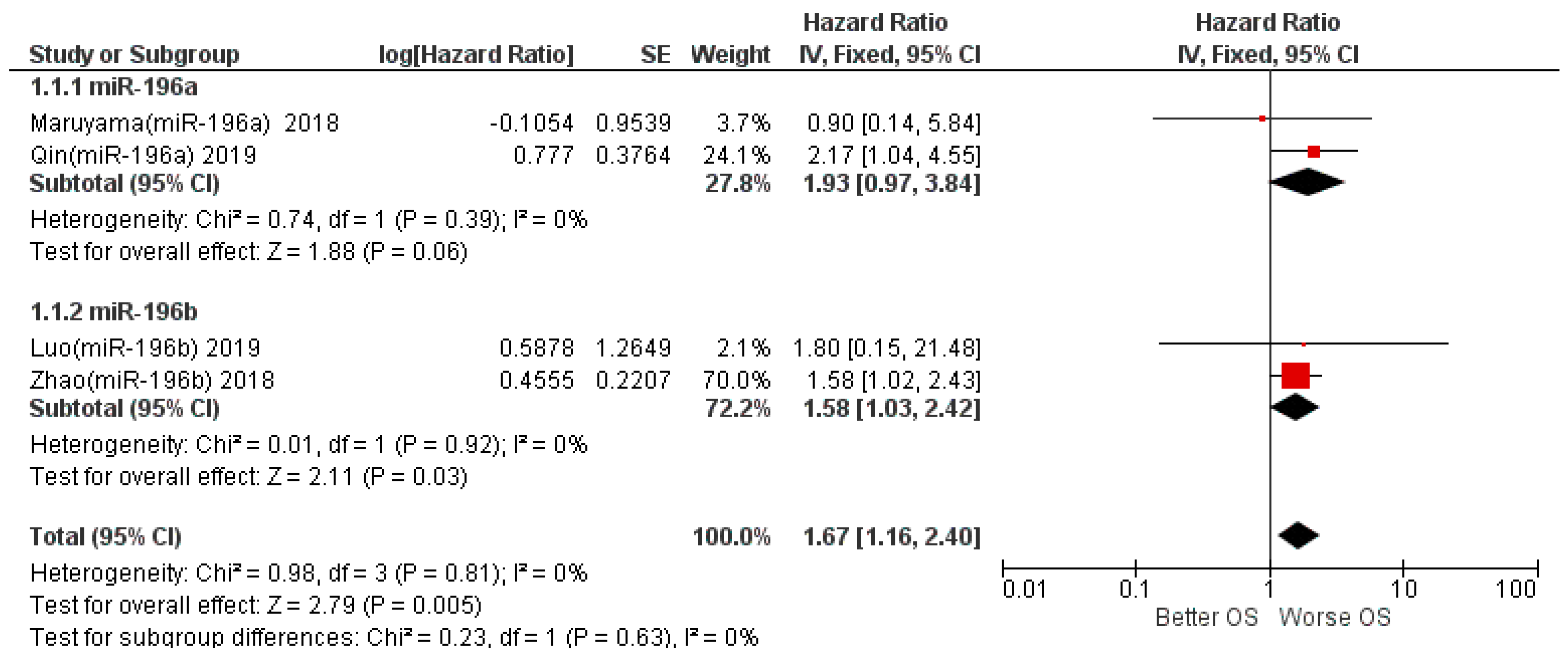
3.5. Meta-Analysis
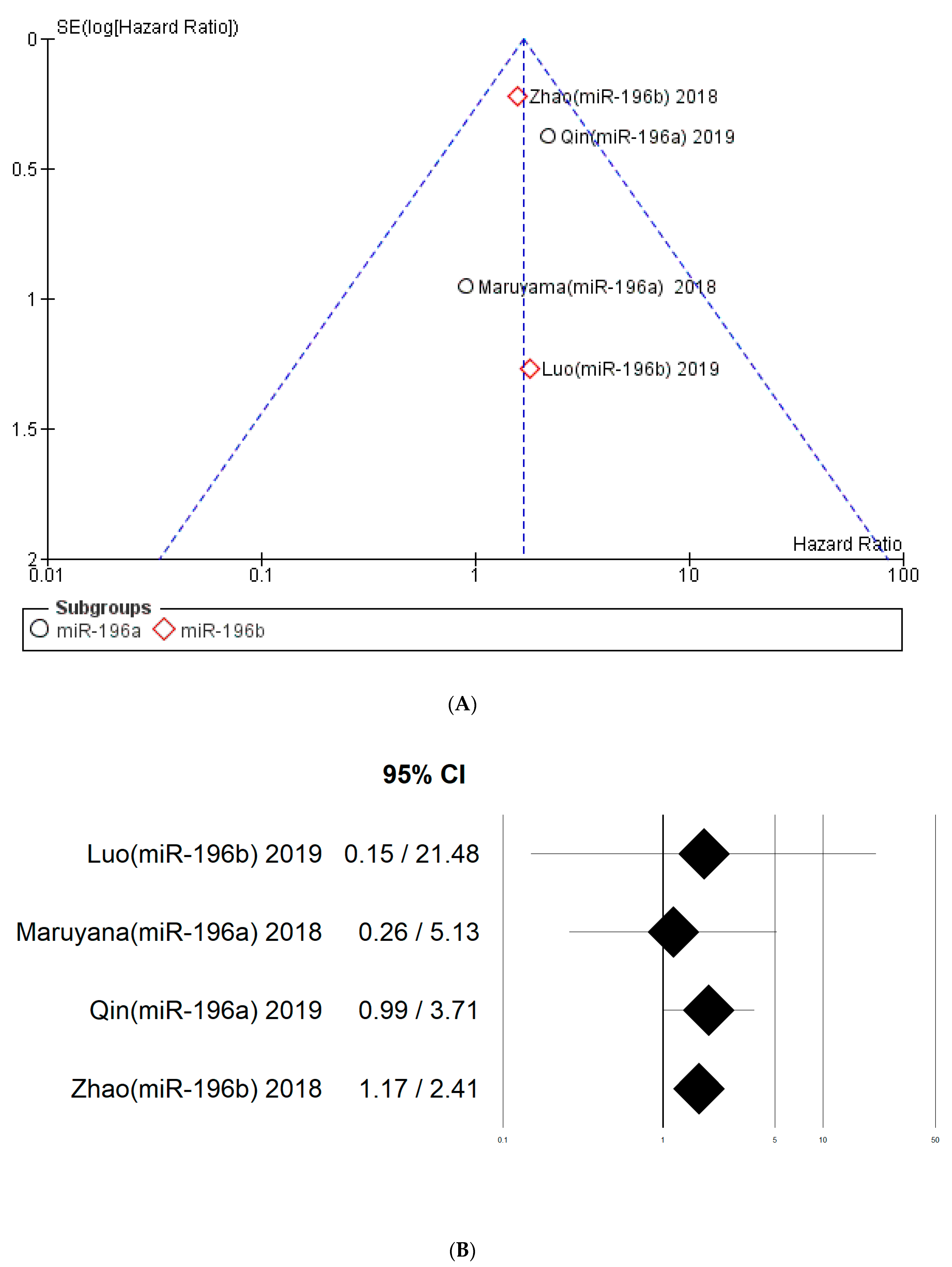
3.6. Risk of Bias across Study, Subgroup Analysis, Publication Bias
3.7. Trial Sequential Analysis, Grade
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.J.D.; Jackson, E.; Chew, J.; Nguyen, S.; Wu, J.; Poh, C.F.; Prisman, E. Combined chemoradiotherapy showed improved outcome with early-stage HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallus, R.; Gheit, T.; Holzinger, D.; Petrillo, M.; Rizzo, D.; Petrone, G.; Miccichè, F.; Mattiucci, G.C.; Arciuolo, D.; Capobianco, G.; et al. Prevalence of HPV Infection and p16(INK4a) Overexpression in Surgically Treated Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Vaccines 2022, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, S.-Y.; Chang, D.C.; Lin, S.-L. The microRNA (miRNA): Overview of the RNA genes that modulate gene function. Mol. Biotechnol. 2008, 38, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rawi, N.; Elmabrouk, N.; Abu Kou, R.; Mkadmi, S.; Rizvi, Z.; Hamdoon, Z. The role of differentially expressed salivary microRNA in oral squamous cell carcinoma. A systematic review. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 125, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Blood-based circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for predicting the prognosis of head and neck cancer-a systematic review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Caloro, G.A.; Laino, L.; Alovisi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Crincoli, V.; Aiuto, R.; Coccia, E.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. Circulating miR-21 as a Potential Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Spirito, F.; Sovereto, D.; Alovisi, M.; Troiano, G.; Aiuto, R.; Garcovich, D.; Crincoli, V.; Laino, L.; Cazzolla, A.P.; et al. MicroRNA-21 Expression as a Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Spirito, F.; Sovereto, D.; La Femina, L.; Campobasso, A.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Di Cosola, M.; Zhurakivska, K.; Cantore, S.; Ballini, A.; et al. Biological Prognostic Value of miR-155 for Survival Outcome in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Biology 2022, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Spirito, F.; Sovereto, D.; Alovisi, M.; Aiuto, R.; Garcovich, D.; Crincoli, V.; Laino, L.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Caloro, G.A.; et al. The Prognostic Role of miR-31 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.W.; Zhang, L. Expression of miR-195 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and its effect on proliferation and apoptosis of Hep-2. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 3232–3238. [Google Scholar]
- Mariani, P.; Russo, D.; Maisto, M.; Troiano, G.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Annunziata, M.; Laino, L. Pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is an independent prognostic factor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Oral Pathol. Am. Acad. Oral Pathol. 2022, 51, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Brüggemann, H.; Andreghetto, F.M.; Camps, C.; Klingbeil, M.d.F.G.; de Pereira, W.O.; Soares, R.M.; Moyses, R.; Wünsch-Filho, V.; Mathor, M.B.; et al. MicroRNA expression profile in head and neck cancer: HOX-cluster embedded microRNA-196a and microRNA-10b dysregulation implicated in cell proliferation. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Weakley, S.M.; Yao, Q. MicroRNA-196: Critical roles and clinical applications in development and cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, Z.; Jiang, H. EMT Participates in the Regulation of Exosomes Secretion and Function in Esophageal Cancer Cells. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211033077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Pan, S.; Yang, W.; Chen, S.; Shan, Y.; Shi, H. Serum miR-10a-5p and miR-196a-5p as non-invasive biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 773–780. [Google Scholar]
- Stenholm, L.; Stoehlmacher-Williams, J.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Heussen, N.; Akin, S.; Pauligk, C.; Lehmann, S.; Senff, T.; Hofheinz, R.D.; Ehninger, G.; et al. Prognostic role of microRNA polymorphisms in advanced gastric cancer: A translational study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie (AIO). Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2581–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Tsai, M.M.; Tu, H.F.; Lui, M.T.; Cheng, H.W.; Lin, S.C. miR-196a overexpression and miR-196a2 gene polymorphism are prognostic predictors of oral carcinomas. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20 (Suppl. 3), S406–S414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słotwiński, R.; Słotwińska, S.M. Diagnostic value of selected markers and apoptotic pathways for pancreatic cancer. Cent.-Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 41, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braig, S.; Mueller, D.W.; Rothhammer, T.; Bosserhoff, A.K. MicroRNA miR-196a is a central regulator of HOX-B7 and BMP4 expression in malignant melanoma. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2010, 67, 3535–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Mizoguchi, M.; Yoshimoto, K.; Hata, N.; Shono, T.; Suzuki, S.O.; Araki, Y.; Kuga, D.; Nakamizo, A.; Amano, T.; et al. MiRNA-196 is upregulated in glioblastoma but not in anaplastic astrocytoma and has prognostic significance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4289–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, L.; Leonardi, L.; Conti, A.; Novello, C.; Quattrini, I.; Montanini, L.; Roperto, F.; Del Piero, F.; Di Guardo, G.; Piro, F.; et al. miR-196a expression in human and canine osteosarcomas: A comparative study. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 99, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coira, I.F.; Rincón, R.; Cuendet, M. The Multiple Myeloma Landscape: Epigenetics and Non-Coding RNAs. Cancers 2022, 14, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Teijeiro, S.; Menéndez, S.T.; Villaronga, M.; Pena-Alonso, E.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Morgan, R.O.; Granda-Díaz, R.; Salom, C.; Fernandez, M.P.; García-Pedrero, J.M. Annexin A1 down-regulation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is mediated via transcriptional control with direct involvement of miR-196a/b. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, S. The microRNA Registry. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D109–D111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Fletcher, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D. Combined identification of three miRNAs in serum as effective diagnostic biomarkers for HNSCC. eBioMedicine 2019, 50, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Ji, W. miR-196b is a prognostic factor of human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and promotes tumor progression by targeting SOCS2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinichi, A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Online Kensaku 2014, 35, 154–155. [Google Scholar]
- Tierney, J.F.; Stewart, L.A.; Ghersi, D.; Burdett, S.; Sydes, M.R. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials 2007, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauerbrei, W.; Taube, S.E.; McShane, L.M.; Cavenagh, M.M.; Altman, D.G. Reporting Recommendations for Tumor Marker Prognostic Studies (REMARK): An Abridged Explanation and Elaboration. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, D.G.; McShane, L.M.; Sauerbrei, W.; Taube, S.E. Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies (REMARK): Explanation and elaboration. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.; Oxman, A.D.; Akl, E.A.; Kunz, R.; Vist, G.; Brozek, J.; Norris, S.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Glasziou, P.; DeBeer, H.; et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Á.; Munkácsy, G.; Győrffy, B. Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lánczky, A.; Győrffy, B. Web-Based Survival Analysis Tool Tailored for Medical Research (KMplot): Development and Implementation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Yan, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Shi, J.; Lu, E.; Chen, W.; et al. Exosomal miR-196a derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts confers cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer through targeting CDKN1B and ING5. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Nishihara, K.; Umikawa, M.; Arasaki, A.; Nakasone, T.; Nimura, F.; Matayoshi, A.; Takei, K.; Nakachi, S.; Kariya, K.-I.; et al. MicroRNA-196a-5p is a potential prognostic marker of delayed lymph node metastasis in early-stage tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2349–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Sun, G.; Sun, J.W. MiR-196b affects the progression and prognosis of human LSCC through targeting PCDH-17. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, D.G.; McShane, L.M.; Sauerbrei, W.; Taube, S.E. Reporting Recommendations for Tumor Marker Prognostic Studies (REMARK): Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miladinovic, B.; Hozo, I.; Djulbegovic, B. Trial Sequential Boundaries for Cumulative Meta-Analyses. Stata J. 2013, 13, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, Y.; Song, C.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, K.; Li, S.; Ma, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prognostic significance of microRNAs in cervical cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17141–17148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choupani, J.; Nariman-Saleh-Fam, Z.; Saadatian, Z.; Ouladsahebmadarek, E.; Masotti, A.; Bastami, M. Association of mir-196a-2 rs11614913 and mir-149 rs2292832 Polymorphisms with Risk of Cancer: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidoust, M.; Hamzehzadeh, L.; Rivandi, M.; Pasdar, A. Polymorphisms in non-coding RNAs and risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 132, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.G.; Jiang, L.Y.; Xu, Q. Comprehensive assessment for miRNA polymorphisms in hepatocellular cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaie, F.; Abedpoor, N.; Assareh, N.; Tabatabaiefar, M.A.; Shariati, L.; Zarrabi, A. The Importance of SNPs at miRNA Binding Sites as Biomarkers of Gastric and Colorectal Cancers: A Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.J.; You, G.R.; Lee, C.J.; Lu, Y.C.; Tang, S.J.; Huang, Y.F.; Huang, Y.C.; Lee, L.Y.; Fan, K.H.; Chen, Y.C.; et al. Systemic Investigation Identifying Salivary miR-196b as a Promising Biomarker for Early Detection of Head-Neck Cancer and Oral Precancer Lesions. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Chang, J.T.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, W.H.; Lee, L.Y.; Huang, B.S.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, H.F.; Cheng, A.J. Combined determination of circulating miR-196a and miR-196b levels produces high sensitivity and specificity for early detection of oral cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Pan, J.; Lu, X.; Chi, P. Role of miR-196 and its target gene HoxB8 in the development and proliferation of human colorectal cancer and the impact of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with FOLFOX4 on their expression. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4041–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, H.; Zheng, J.; Ning, N.; Tang, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Lowly-expressed lncRNA GAS5 facilitates progression of ovarian cancer through targeting miR-196-5p and thereby regulating HOXA5. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 151, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.D.; Hayden, J.A.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Moons, K.G.M.; Abrams, K.; Kyzas, P.A.; Malats, N.; Briggs, A.; Schroter, S.; Altman, D.G.; et al. Prognosis Research Strategy (PROGRESS) 2: Prognostic factor research. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Lead Author, Data | Country | Study Design | Average Age (M), Years (Y), N (Number of Patients) | Number of Patients Male (M), Female (F) | Grading (G1, G2, G3) | Staging (S) I–II, III–IV | Smoking History (Sm) Yes (Y), No (N) | Alcohol History Al Yes (Y), No (N) | Follow Up Max Months (m) or Range (R) | Tumor Type, Tumor Site | Cut-Off | miR | HR miR-196 Low and High Expression (OS, PFS, CSS, DFS, RFS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qin 2019 [38] | China | Prospective | ≥60 Y: 39 N <60 Y: 41 N | 80 (43 M, 37 F), | \ | S I–II: 33 S III–IV: 47 | Sm Y: 30 Sm N: 50 | Al Y: 24 Al N: 56 | 80 m | OSCC 80 (Tongue 30 Gingival 24 Cheek 13 Floor of Mouth 10 Oropharynx 3) | median | miR-196a | OS: HR ° 2.175 (1.455–4.034), p = 0.039 |
| Liu 2013 [18] | Taiwan | Prospective | M: 53.6 Y | 95 (90 M, 5 F) | \ | S I–III: 26 S IV: 69 | \ | \ | 85 m | OSCC 95 (Buccal mucosa 34, Tongue 25, Others 36) | median | miR-196a, miR-196a2 | DFS: HR 2.57 (1.20–5.48), p = 0.02 |
| Maruyama 2018 [39] | Japan | Retrospective | <60 Y: 21 N ≥60 Y: 29 N | 50 (24 M, 26 F), | G1 4: 31 G2: 16 G3: 0 G4: 1 | S I: 32 S II: 18 | Sm Y: 19 Sm N: 31 | Al Y: 22 Al N: 25 | 6o m | OSCC (TSCC 1) 50 | median | miR-196a, miR-10a miR-10b miR-196b | OS HR 0.91 (0.12–7.19) 2; DFS: HR 0.6 (0.18–2.06) 2 |
| Zhao 2018 [29] | China | Prospective | <60 Y: 42 N ≥60 Y: 71 N | 113 (96 M, 17 F), | \ | S II: 47 S III–IV: 66 | \ | R: 40–97 m | LSCC 113 (Glottic 70, Supraglottic 43) | median | miR-196b | OS: HR 3 1.577 (0.989–2.516), p = 0.039 | |
| Luo 2019 [40] | China | Prospective | M: 60.58 Y | 79 (66 M, 13 F), | G1: 11 G2: 32 G3: 36 | S I–II: 23 S III–IV: 56 | Sm Y: 52 exSm: 21 Sm N: 6 | Al Y: 58 exAl: 17 Al N: 4 | R: 5–60 m | LSCC 79 | median = 4.922 | miR-196b | OS: HR 1.80 (0.38–8.51) 2 |
| Lead Author, Data | Sample | Clinical Data | Marker Quantification | Prognostication | Statistics | Classical Prognostic Factors | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qin 2019 [38] | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 14 |
| Liu 2013 [18] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 12 |
| Maruyama 2018 [39] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 14 |
| Zhao 2018 [29] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 13 |
| Luo 2019 [40] | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 14 |
| Trial | Estimate | Z | p Val | PartN | UB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luo (miR-196b), 2019 [40] | 6.050 | 1.423 | 0.155 | 79 | 4.376 |
| Maruyama (miR-196a), 2018 [39] | 3.408 | 1.610 | 0.107 | 129 | 3.356 |
| Qin (miR-196a), 2019 [38] | 7.306 | 5.894 | 0.000 | 209 | 2.558 |
| Zhao (miR-196b), 2018 [29] | 5.476 | 9.206 | 0.000 | 322 | 1.990 |
| Certainty Assessment | No. of Patients | Effect | Certainty | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Studies | Study Design | Risk of Bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other Considerations | miR-196 | Relative (95% CI) | Absolute (95% CI) | |
| miR 196 | ||||||||||
| 4 | Randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | Serious 2 | publication bias strongly suspected 1 | -/322 | HR 1.67 (1.16 to 2.40) | 2 fewer per 1000 (from 2 fewer to 1 fewer) | ⨁⨁◯◯Low |
| miR subgroups—miR-196a | ||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | Serious 2 | publication bias strongly suspected 1 | -/130 | HR 1.93 (0.97 to 3.84) | 2 fewer per 1000 (from 4 fewer to 1 fewer) | ⨁⨁◯◯Low |
| miR subgroups—miR-196b | ||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | Serious 2 | publication bias strongly suspected 1 | -/192 | HR 1.58 (1.03 to 2.42) | 2 fewer per 1000 (from 2 fewer to 1 fewer) | ⨁⨁◯◯Low |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dioguardi, M.; Cantore, S.; Sovereto, D.; La Femina, L.; Caloro, G.A.; Spirito, F.; Scacco, S.; Di Cosola, M.; Lo Muzio, L.; Troiano, G.; et al. Potential Role of miR-196a and miR-196b as Prognostic Biomarkers of Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Life 2022, 12, 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081269
Dioguardi M, Cantore S, Sovereto D, La Femina L, Caloro GA, Spirito F, Scacco S, Di Cosola M, Lo Muzio L, Troiano G, et al. Potential Role of miR-196a and miR-196b as Prognostic Biomarkers of Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Life. 2022; 12(8):1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081269
Chicago/Turabian StyleDioguardi, Mario, Stefania Cantore, Diego Sovereto, Lucia La Femina, Giorgia Apollonia Caloro, Francesca Spirito, Salvatore Scacco, Michele Di Cosola, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Giuseppe Troiano, and et al. 2022. "Potential Role of miR-196a and miR-196b as Prognostic Biomarkers of Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis" Life 12, no. 8: 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081269
APA StyleDioguardi, M., Cantore, S., Sovereto, D., La Femina, L., Caloro, G. A., Spirito, F., Scacco, S., Di Cosola, M., Lo Muzio, L., Troiano, G., & Ballini, A. (2022). Potential Role of miR-196a and miR-196b as Prognostic Biomarkers of Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Life, 12(8), 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081269










