Abstract
The worsening of neurological status that occurs early after acute ischemic stroke (AIS) remains a serious issue, and the inflammatory response plays a key role in stroke pathobiology. Recently, endovascular treatment (EVT) has revolutionized the management and outcome of patients with AIS due to either extracranial carotid disease or intracranial disease. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) represents an easily available inflammatory biomarker. The aim of the study was to assess the relationship between the NLR at admission and the occurrence of early neurological deterioration (END) in patients with AIS who underwent EVT. Patients with AIS and proximal arterial occlusion in the anterior circulation undergoing EVT were retrospectively identified. Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) and absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) were collected from admission blood work to calculate the NLR. The study outcome was END defined as an increase in at least 4 points in NIHSS score or death between baseline and 24 h after the ischemic event. Patients included were 211, and END occurred in 30 (14.2%). Patients with older age (OR = 1.07, 95% CI: 1.02–1.13), higher serum glucose (OR = 1.01, 95% CI: 1.01–1.02), and higher NLR (OR = 1.011, 95% CI: 1.04–1.18) had an increased risk of END. The best predictive cut-off value of NLR was 6.4, and END occurred in 24.1% and 3.9% of the patients with NLR ≥ 6.4 and <6.4, respectively (p < 0.001). In patients with AIS undergoing EVT, higher NLR values predicted a higher risk of END. Biomarkers able to identify inflammatory mechanisms might identify novel treatment targets and enhance proof-of-concept trials of immunomodulation in stroke.
1. Introduction
Stroke is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide [1]. According to the epidemiological statistics of the global burden of disease, in 2019, there were 12.2 million incident cases and 101 million prevalent cases of stroke, with 6.55 million and 143 million disability-adjusted life years due to stroke [2]. Globally, stroke remains the second-leading cause of death and the third-leading cause of death and disability combined. Of note, the age-standardized rates of stroke-related mortality and stroke-related disability-adjusted life years were 3.6–3.7 times higher in the low- than high-income countries [2].
Ischemic stroke constitutes around 60–65% of all incident strokes. Although the endovascular treatment (EVT) has been demonstrated to represent a key therapy to improve clinical outcome, the rate of death and functional dependence is still high [3,4,5,6]. Importantly, the worsening of acute stroke early in its course remains a serious issue associated with poor outcome. Early neurological deterioration (END) has been reported to occur in 10% to 40% of stroke patients, and the differences in diagnostic criteria of clinical worsening, timing of assessment, and case mix of patients can account for the wide range in incidence [7]. Initial stroke severity has been shown to be a strong independent predictor of END [7,8]. Among biochemical biomarkers, high serum glucose levels and high high-sensitivity C-reactive protein were associated with clinical deterioration [7,9,10,11]. Low Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score (ASPECTS), poor collaterals, large vessel occlusion, extent of hypodensity > 33% in the middle cerebral territory, hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign, and cerebral edema on early brain CT may reflect severe initial stroke and have been found to be radiological predictors [12,13,14]. Age, history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and prestroke modified Rankin Scale score ≥ 2 were also recognized as risk factors for END in some studies, whereas the independent role of baseline blood pressure levels has not been established [8,12,13,15,16]. General anesthesia, unsatisfactory recanalization of occluded arteries, and number of EVT passes can further affect the risk of neurological worsening [8,12]. Thus far, only a few studies have investigated the occurrence and predictors of END in stroke patients undergoing EVT [8,13,17,18].
The inflammatory response plays a key role in the pathophysiology of ischemic stroke, and it has been shown to be involved in the secondary progression of ischemic lesion [11,19,20]. In this regard, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), which is easily calculated from the neutrophil and lymphocyte counts, represents a reliable and inexpensive measure of the inflammatory levels, and it is recently gaining attention as a prognostic biomarker in the field of acute cerebrovascular diseases. Previous studies have reported that the NLR may be a good predictor of mortality and short-term functional status, angiographic outcomes, intracerebral hemorrhage, and stroke-associated infection or pneumonia in patients with acute ischemic stroke, including stroke patients who receive reperfusion therapies [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Interestingly, the significant associations found between the NLR and the outcome of patients with either intracerebral hemorrhage or subarachnoid hemorrhage suggest how commonalities may exist in the inflammatory pathways underlying stroke-induced secondary brain damage [31,32,33].
The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between the NLR at admission and the occurrence of END in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) undergoing EVT.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Participants
In this retrospective cohort study, consecutive patients with AIS admitted (January 2016 to December 2019) at the Neurology Unit of the Marche Polytechnic University (Ancona, Italy) and treated with intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) plus EVT or EVT alone were identified. Patients were included if they had intracranial proximal arterial occlusion in the anterior circulation (i.e., intracranial carotid artery or M1/M2 segments of middle cerebral artery) and were treated with IVT within 4.5 h and EVT within 6.0 h after the stroke onset according to national and international stroke guidelines [34,35,36,37]. Endovascular treatment included mechanical thrombectomy with aspiration catheters alone, stent retrievers alone, or both, depending on occlusion type/location and the neurointerventionist’s choice; emergency carotid stent placement was decided by the treating neurointerventionist [38,39]. Demographics, clinical history, initial stroke severity by the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score [40], and extension of ischemic lesion by the ASPECTS [41] were retrieved, as previously detailed [42,43,44]. Total white blood cells, absolute neutrophil count (ANC), and absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) were collected from admission blood work within 24 h after stroke onset. The outcome measure was the END, defined as an increase of at least 4 points in NIHSS score or death between baseline and 24 h after the ischemic event [8]. Patients without laboratory values and/or data about 24 h neurological status available were excluded.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables were summarized as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median (quartile deviation(QD)), and categorical variables were presented as the number (%) of patients. The student t-test, Mann–Whitney test, or chi-squared test were used for univariate comparisons; the nonparametric Mann–Whitney test was used when the data did not have a normal distribution. Logistic regression was used to explore the relationship between the NLR and END. The variables with p-values < 0.05 from univariate analyses and associations with biologically plausible characteristics (i.e., age, sex, baseline NIHSS score, ASPECT score, and initial serum glucose [7]) were forced in the multivariate model. The ability of the NLR to predict the END was estimated through the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. The value with the highest Youden’s index was identified as the threshold able to better distinguish the presence of END [45]. Statistical significance was set at p-values < 0.05. STATA/IC 13.1 statistical package (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA) was used to perform statistical analysis.
3. Results
Patients included in the study were 211, and END occurred in 30 (14.2%) cases. The age of the study cohort was 74 [(10.5)] years, and 101 (47.9%) were men. Eighty-three patients underwent EVT alone, and 128 patients were treated with IVT plus EVT. Details about the procedures of mechanical thrombectomy were available for 205 patients: stent retrievers, aspiration catheters, and a combination of stent retrievers and aspiration catheters were used in 104, 65, and 36 patients, respectively. Carotid artery stent was placed in 21 patients; there was no statistically significant difference in the NLR values according to the stent placement (p = 0.311). The baseline characteristics of the participants with and without END are summarized in Table 1. The END group was older; had lower ASPECTS value; had more commonly intracranial occlusion at the level of the internal carotid artery, internal carotid artery terminus, and M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery; and had higher levels of serum glucose, higher white blood cells and neutrophil counts, lower lymphocyte count, and higher NLR values at admission compared with patients without END.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients.
Age, baseline serum glucose, and admission NLR resulted in independently being associated with END: participants who were older (odds ratio (OR) = 1.07, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.02–1.13, p = 0.005) and had higher serum glucose (OR = 1.01, 95% CI: 1.01–1.02, p = 0.002) and higher NLR (OR = 1.011, 95% CI: 1.04–1.18, p = 0.001) were at higher risk of END (Table 2). There was no collinearity in the multivariate model (variance inflation factors: 1.06 to 1.29).

Table 2.
Association between baseline characteristics and early neurological deterioration.
At the ROC analysis, the AUC of the NLR for END was 0.738 (95% CI: 0.638–0.837) with 6.4 × 109/L as the best predictive threshold of NLR (sensitivity: 86.7% (95% CI, 69.3–96.2%), specificity: 54.7% (95% CI, 47.1–62.1%), positive predictive value: 24.1% (95% CI, 20.4–28.2%), negative predictive value: 96.1% (95% CI, 90.8–98.4%), positive likelihood ratio (LR): 1.91 (95% CI, 1.55–2.37), negative LR: 0.24 (95% CI, 0.10–0.61)) (Figure 1). Early deterioration of neurological status occurred in 24.1% and 3.9% of the patients with NLR ≥ 6.4 and <6.4, respectively (p < 0.001). NLR ≥ 6.4 × 109/L was an independent predictor of END (OR = 7.85, 95% CI: 2.63–23.40, p < 0.001; ORadj = 6.68, 95% CI: 2.04–21.92, p = 0.002).
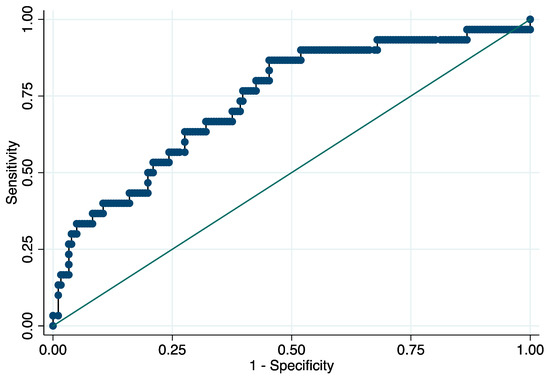
Figure 1.
Receiver operating characteristic curve for the prediction of early neurological deterioration. Predictive values of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for early neurological deterioration. Area under the curve 0.738 (95% CI: 0.638–0.837). Abbreviation: CI = confidence interval.
4. Discussion
The relationship between the NLR and the development of END in patients with AIS treated with EVT represents the main novelty provided by this research. Patients with ischemic stroke and higher NLR at admission were more likely to present early deterioration of the neurological status after stroke, and an NLR value of 6.4 resulted in the best discriminating threshold for the occurrence of END. These results support the increasing body of evidence that inflammatory pathways are crucial determinants of the pathophysiology and prognosis of acute vascular brain injury [46].
Inflammation may contribute to different mechanisms underlying END, including the formation of cerebral edema, progression of infarction, and hemorrhagic transformation [7]. The inflammatory response after stroke is triggered by the release of mediators from damaged brain tissue and develops early after cerebral infarct. Brain-resident macrophages are activated, and blood–brain barrier disruption favors the infiltration of peripheral immune cells into the site of injured tissue [47]. The prominent influx of polymorphonuclear cells and monocytes into the brain increases local inflammation. During the acute phase, leukocytes produce inflammatory cytotoxic mediators that favors cellular injury, promotes capillary permeability, and stimulates prothrombotic pathways that exacerbate edema development, ischemic damage, and secondary progression of brain injury [48,49]. Hemorrhagic transformation, which also represents a sign of endothelial disruption, has been linked to brain leukocyte infiltration [50]. The infiltration of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9)-positive neutrophils is associated with the breakdown of the blood–brain barrier and the degradation of basal lamina type IV collagen, which favors hemorrhagic complications [49,51]. The plugging of microvessels that follows endothelial activation, the recruitment of leukocytes, and the aggregation of platelets can impair the reperfusion of tissue and affect the viability of the penumbra area [52,53]. Thromboinflammatory pathways also contribute to the ischemia-reperfusion injury [54]; in this regard, the endothelium–leukocyte–platelet interaction is responsible for microvascular events and secondary thrombosis in the microvasculature that facilitate the growth of infarct size despite the recanalization of large vessels [54].
The insult to the central nervous system is also able to trigger the release of catecholamines and cortisol, which promote the death and functional impairment of peripheral lymphocytes [55]. Of note, the loss of subpopulations of regulatory lymphocytes that counteract the release of proinflammatory mediators and the activation of microglia may compromise the immune homeostasis and cause an imbalance between inflammatory and anti-inflammatory pathways [56,57,58]. In this regard, the SIRI can synthetize the balance between innate and adaptive immunity, with higher values indicating the increased activity of the former and the decreased activity of the latter.
Our data expand the already-accumulated evidence underlying the opportunity to enhance the prediction of the outcome of stroke patients by using serum indices. Of note, an increased peripheral inflammatory response measured by the NLR after stroke reperfusion therapy has been shown to correlate with the occurrence of hemorrhagic transformation and severity of cerebral edema, and a few studies have provided preliminary evidence about its relationship with the worsening of the neurological status [29,59,60]. In this context, it is worth emphasizing that indices incorporating different cellular types can ensure greater accuracy and represent more reliable indices to be used in real-world scenarios [61,62,63,64]. The assessment of a single cell line may be affected by conditions such as dehydration and overhydration and may be less accurate to synthetize the entanglement of the inflammatory pathways.
The real-world setting, which allows us to generalize the results to everyday clinical contexts, and the ready availability and cost effectiveness of the NLR, which is obtained from widely accessible and routinely collected variables, represent major study strengths. Different limits need, however, to be also acknowledged. The retrospective collection of data and the inclusion of patients admitted to one single academic center may have resulted in selection bias. The lack of information about the development of procedural complications, hemorrhagic transformation, and cerebral edema prevented us from exploring the relationship between the NLR and END according to the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms. Further, carotid artery stent was placed in a few patients, and any potential interference between stenting and NLR values could not be definitively explored. The current findings did not allow us to draw definitive conclusions about the causal association between the NLR and END but could stimulate speculations and generate hypotheses. Further studies characterized by larger samples and a prospective design with the assessment of variables such as the infarct volume, status of collaterals, and occurrence of early complications are warranted to confirm and externally validate these findings and provide additional clinical insights.
5. Conclusions
The NLR is a low-cost and readily available inflammatory biomarker that could be useful to identify stroke patients at higher risk of END after EVT. Interestingly, several pilot trials explored the role of immunomodulatory agents in ischemic stroke [65,66,67]. In this regard, biomarkers able to identify patients more prone to inflammation might also identify those patients who can benefit the most from such interventions and enhance the proof-of-concept trials of immunomodulation in stroke.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L.; methodology, S.L.; software, S.L.; formal analysis, S.L.; investigation, S.L., D.N. and S.B.; resources, S.L.; data curation, D.N. and S.B.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L.; writing—review and editing, S.L., S.M., M.Ś. and A.S.; supervision, S.L. and M.S.; project administration, S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Ethics Committee of Marche Polytechnic University approved the study (ID 57/2020). The study was performed following the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all patients or their representatives.
Data Availability Statement
Anonymized data will be shared by request from any qualified investigator.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, P.A.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e153–e639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, H.; Koot, J.; Hall, R.E.; O’Callaghan, C.; Bayley, M.; Corbett, D. Prevalence of individuals experiencing the effects of stroke in Canada: Trends and projections. Stroke 2015, 46, 2226–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, S.; Coccia, M.; Pulcini, A.; Cagnetti, C.; Galli, F.L.; Villani, L.; Campa, S.; Dobran, M.; Polonara, G.; Ceravolo, M.G.; et al. Endovascular treatment and cognitive outcome after anterior circulation ischemic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, S.; Rinaldi, C.; Cagnetti, C.; Foschi, N.; Norata, D.; Broggi, S.; Rocchi, C.; Silvestrini, M. Predictors of pharmaco-resistance in patients with post-stroke epilepsy. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, S.; Trinka, E.; Turcato, G.; Rinaldi, C.; Cagnetti, C.; Foschi, N.; Broggi, S.; Norata, D.; Brigo, F.; Silvestrini, M. Latency of poststroke epilepsy can predict drug resistance. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 2481–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanvi, B.; Treadwell, S.; Robinson, T. Early neurological deterioration in acute ischaemic stroke: Predictors, mechanisms and management. Postgrad. Med. J. 2008, 84, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girot, J.B.; Richard, S.; Gariel, F.; Sibon, I.; Labreuche, J.; Kyheng, M.; Gory, B.; Dargazanli, C.; Maier, B.; Consoli, A.; et al. Predictors of Unexplained Early Neurological Deterioration after Endovascular Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 2943–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, D.; Fiorelli, M.; Gentile, M.; Bastianello, S.; Sacchetti, M.L.; Argentino, C.; Pozzilli, C.; Fieschi, C. Progressing neurological deficit secondary to acute ischemic stroke. A study on predic-tability, pathogenesis, and prognosis. Arch. Neurol. 1995, 52, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos, A.; Cendra, E.; Teruel, J.; Martinez, M.; Genis, D. Deteriorating ischemic stroke: Risk factors and prognosis. Neurology 1990, 40, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Guo, W.; Tang, T.; Tao, L.; Gong, K.; Zhang, X. Relationship between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and early neurological deterioration in stroke patients with and without atrial fibrillation. Heart Lung 2020, 49, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Han, J.; Chu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z. Time Course and Clinical Relevance of Neurological Deterioration after Endovascular Recanalization Therapy for Anterior Circulation Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 651614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Su, Y.Y.; He, Y.B.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, G.; Fan, L.L. Early neurological deterioration after recanalization treatment in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A retrospective study. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davalos, A.; Toni, D.; Iweins, F.; Lesaffre, E.; Bastianello, S.; Castillo, J. Neurological deterioration in acute ischemic stroke: Potential predictors and associated factors in the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS) I. Stroke 1999, 30, 2631–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birschel, P.; Ellul, J.; Barer, D. Progressing stroke: Towards an internationally agreed definition. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2004, 17, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimar, C.; Mieck, T.; Buchthal, J.; Ehrenfeld, C.E.; Schmid, E.; Diener, H.-C. For the German Stroke Study Collaboration. Neurologic worsening during the acute phase of ischemic stroke. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Bae, J.H.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, W.J.; Byun, J.S.; Ahn, S.-W.; Shin, H.-W.; Han, S.-H.; Yoo, I.-H. Incidence and mechanism of early neurological deterioration after endovascular thrombectomy. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourcier, R.; Goyal, M.; Muir, K.W.; Desal, H.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; van Zwam, W.H.; Jovin, T.G.; Mitchell, P.J.; Demchuk, A.M.; et al. HERMES Trialists Collaboration. Risk factors of unexplained early neurological deterioration after treatment for ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion: A post hoc analysis of the HERMES study. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simats, A.; García-Berrocoso, T.; Montaner, J. Neuroinflammatory biomarkers: From stroke diagnosis and prognosis to therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangari, R.; Zanier, E.R.; Torgano, G.; Bersano, A.; Beretta, S.; Beghi, E.; Casolla, B.; Checcarelli, N.; Lanfranconi, S.; Maino, A.; et al. Early ficolin-1 is a sensitive prognostic marker for functional out-come in ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Song, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, S.; Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, M. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts poor outcomes after acute ischemic stroke: A cohort study and systematic review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 406, 116445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ren, Q.; Song, Y.; He, M.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J. Prognostic role of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Medicine 2017, 96, e8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, N.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Chang, J.J.; Malhotra, K.; Pandhi, A.; Ishfaq, M.F.; Alsbrook, D.; Arthur, A.S.; Elijovich, L.; Alexandrov, A.V. Admission neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic biomarker of outcomes in large vessel occlusion strokes. Stroke 2018, 49, 1985–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestrini, I.; Strbian, D.; Gautier, S.; Haapaniemi, E.; Moulin, S.; Sairanen, T.; Dequatre-Ponchelle, N.; Sibolt, G.; Cordonnier, C.; Melkas, S.; et al. Higher neutrophil counts before thrombolysis for cerebral ischemia predict worse outcomes. Neurology 2015, 85, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, K.; Goyal, N.; Chang, J.J.; Broce, M.; Pandhi, A.; Kerro, A.; Shahripour, R.B.; Alexandrov, A.V.; Tsivgoulis, G. Differential leukocyte counts on admission predict outcomes in patients with acute ischaemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Hao, Y.; Zi, W.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, W.; Lin, M.; Shi, Z.; et al. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts functional and safety outcomes after endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 45, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengeze, N.; Giray, S. The relationship between first pass recanalization of stent retriever-based thrombectomy and neutro-phil to lymphocyte ratio in middle cerebral artery occlusions. Int. J. Neurosci. 2021, 131, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, X.; Hu, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, J.; Chu, Z.; Xu, Y. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świtońska, M.; Piekuś-Słomka, N.; Słomka, A.; Sokal, P.; Zekanowska, E.; Lattanzi, S. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Symptomatic Hemorrhagic Transformation in Is-chemic Stroke Patients Undergoing Revascularization. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Spring, K.J.; Bhaskar, S.M.M. Role of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in the Prognosis of Acute Ischaemic Stroke after Reperfusion Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2022, 14, 11795735221092518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, S.; Brigo, F.; Trinka, E.; Cagnetti, C.; Di Napoli, M.; Silvestrini, M. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage: A System Review. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019, 10, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Yang, C.; Tang, Q.W.; Xiao, L.-F.; Chen, Z.-H.; Zhao, W.-Y. The Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 745560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.Y.; Zhao, X.X.; Rajah, G.; Hua, C.; Kang, R.J.; Han, Y.P.; Ding, Y.C.; Meng, R. Clinical significance of baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with ischemic stroke or hemorrhagic stroke: An updated meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SPREAD–Stroke Prevention and Educational Awareness Diffusion. Ictus Cerebrale: Linee Guida Italiane di Prevenzione e Trattamento. Available online: http://www.iso-spread.it/capitoli/LINEE_GUIDA_SPREAD_8a_EDIZIONE.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Jauch, E.C.; Saver, J.L.; Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bruno, A.; Connors, J.J.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Khatri, P.; McMullan, P.W., Jr.; Qureshi, A.I.; Rosenfield, K.; et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013, 44, 870–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. 2018 Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019, 50, e344–e418. [Google Scholar]
- Da Ros, V.; Scaggiante, J.; Sallustio, F.; Lattanzi, S.; Bandettini, M.; Sgreccia, A.; Rolla-Bigliani, C.; Lafe, E.; Sanfilippo, G.; Diomedi, M.; et al. Carotid Stenting and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke and Tandem Occlusions: Antithrombotic Treatment and Functional Outcome. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 2088–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Ros, V.; Scaggiante, J.; Pitocchi, F.; Sallustio, F.; Lattanzi, S.; Umana, G.E.; Chaurasia, B.; di Poggio, M.B.; Toscano, G.; Bigliani, C.R.; et al. Mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke with tandem occlusions: Impact of extracranial carotid lesion etiology on endovascular management and outcome. Neurosurg. Focus 2021, 51, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wityk, R.J.; Pessin, M.S.; Kaplan, R.F.; Caplan, L.R. Serial assessment of acute stroke using the NIH Stroke Scale. Stroke 1994, 25, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, P.A.; Demchuk, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Buchan, A.M. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. ASPECTS Study Group. Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score. Lancet 2000, 355, 1670–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, S.; Cagnetti, C.; Pulcini, A.; Morelli, M.; Maffei, S.; Provinciali, L.; Silvestrini, M. The P-wave terminal force in embolic strokes of undetermined source. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 375, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, S.; Pulcini, A.; Corradetti, T.; Rinaldi, C.; Zedde, M.L.; Ciliberti, G.; Silvestrini, M. Prediction of Outcome in Embolic Strokes of Undetermined Source. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, S.; Rinaldi, C.; Pulcini, A.; Corradetti, T.; Angelocola, S.; Zedde, M.L.; Ciliberti, G.; Silvestrini, M. Clinical phenotypes of embolic strokes of undetermined source. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. The immunology of stroke: From mechanisms to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Yang, G.; Li, G. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Role of inflammatory cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anrather, J.; Iadecola, C. Inflammation and Stroke: An Overview. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, S.; Di Napoli, M.; Ricci, S.; Divani, A.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerano, A.; Laredo, C.; Zhao, Y.; Rudilosso, S.; Renú, A.; Llull, L.; Amaro, S.; Obach, V.; Planas, A.M.; Urra, X.; et al. Leukocytes, collateral circulation, and reperfusion in ischemic stroke patients treated with mechanical thrombectomy. Stroke 2019, 50, 3456–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, A.; Cuadrado, E.; Ortega-Aznar, A.; Hernández-Guillamon, M.; Lo, E.H.; Montaner, J. MMP-9-positive neutrophil infiltration is associated to blood-brain barrier breakdown and basal lamina type IV collagen degradation during hemorrhagic transformation after human ischemic stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Duan, W.; Liu, L. Futile Recanalization after Endovascular Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. BioMed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 5879548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, S.F.; Denorme, F.; Langhauser, F.; Geuss, E.; Fluri, F.; Kleinschnitz, C. Thromboinflammation in Stroke Brain Damage. Stroke 2016, 47, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoll, G.; Nieswandt, B. Thrombo-inflammation in acute ischaemic stroke-implications for treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisel, C.; Schwab, J.; Prass, K.; Meisel, A.; Dirnagl, U. Central nervous system injury-induced immune deficiency syndrome. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urra, X.; Cervera, Á.; Villamor, N.; Planas, A.; Chamorro, Á. Harms and benefits of lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with acute stroke. Neuroradio 2009, 158, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wu, H.; Klebe, D.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J. Regulatory T Cell in Stroke: A New Paradigm for Immune Regulation. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 689827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brait, V.H.; Arumugam, T.; Drummond, G.; Sobey, C.G. Importance of T Lymphocytes in Brain Injury, Immunodeficiency, and Recovery after Cerebral Ischemia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 32, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, D.; Matias, M.; Neto, J.; Dias, R.; Moreira, G.; Petersen, N.; Azevedo, E.; Castro, P. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Cerebral Edema and Clinical Worsening Early after Reperfusion Therapy in Stroke. Stroke 2021, 52, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.W.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Jeong, H.B.; Yoon, B.W.; Ko, S.B. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts early worsening in stroke due to large vessel disease. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Shen, J.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, J.X.; Xia, Y.P. Prognostic value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in acute ischemic stroke after reperfusion therapy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, S.; Cagnetti, C.; Provinciali, L.; Silvestrini, M. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and neurological deterioration fol-lowing acute cerebral hemorrhage. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 57489–57494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, S.; Cagnetti, C.; Rinaldi, C.; Angelocola, S.; Provinciali, L.; Silvestrini, M. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio improves outcome prediction of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 387, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, S.; Norata, D.; Divani, A.A.; Di Napoli, M.; Broggi, S.; Rocchi, C.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Mansueto, G.; Silvestrini, M. Systemic Inflammatory Response Index and Futile Recanalization in Patients with Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Endovascular Treatment. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ren, L.; Yan, Y.; Sun, N.; Li, Y.-J.; Han, W.; Xue, R.; Liu, Q.; Hao, J.; et al. Impact of an immune modulator fingolimod on acute ischemic stroke. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18315–18320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, K.N.; Elm, J.J.; Molyneaux, B.J.; Hinson, H.; Beslow, L.A.; Sze, G.K.; Ostwaldt, A.-C.; del Zoppo, G.J.; Simard, J.M.; Jacobson, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of intravenous glyburide on brain swelling after large hemispheric infarction (GAMES-RP): A randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, J.; Veltkamp, R.; Montaner, J.; Johnston, S.C.; Singhal, A.B.; Becker, K.; Lansberg, M.G.; Tang, W.; Chang, I.; Muralidharan, K.; et al. Safety and efficacy of natalizumab in patients with acute ischaemic stroke (ACTION): A randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).