3D-QSAR Studies, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamic Simulation, and ADMET Proprieties of Novel Pteridinone Derivatives as PLK1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
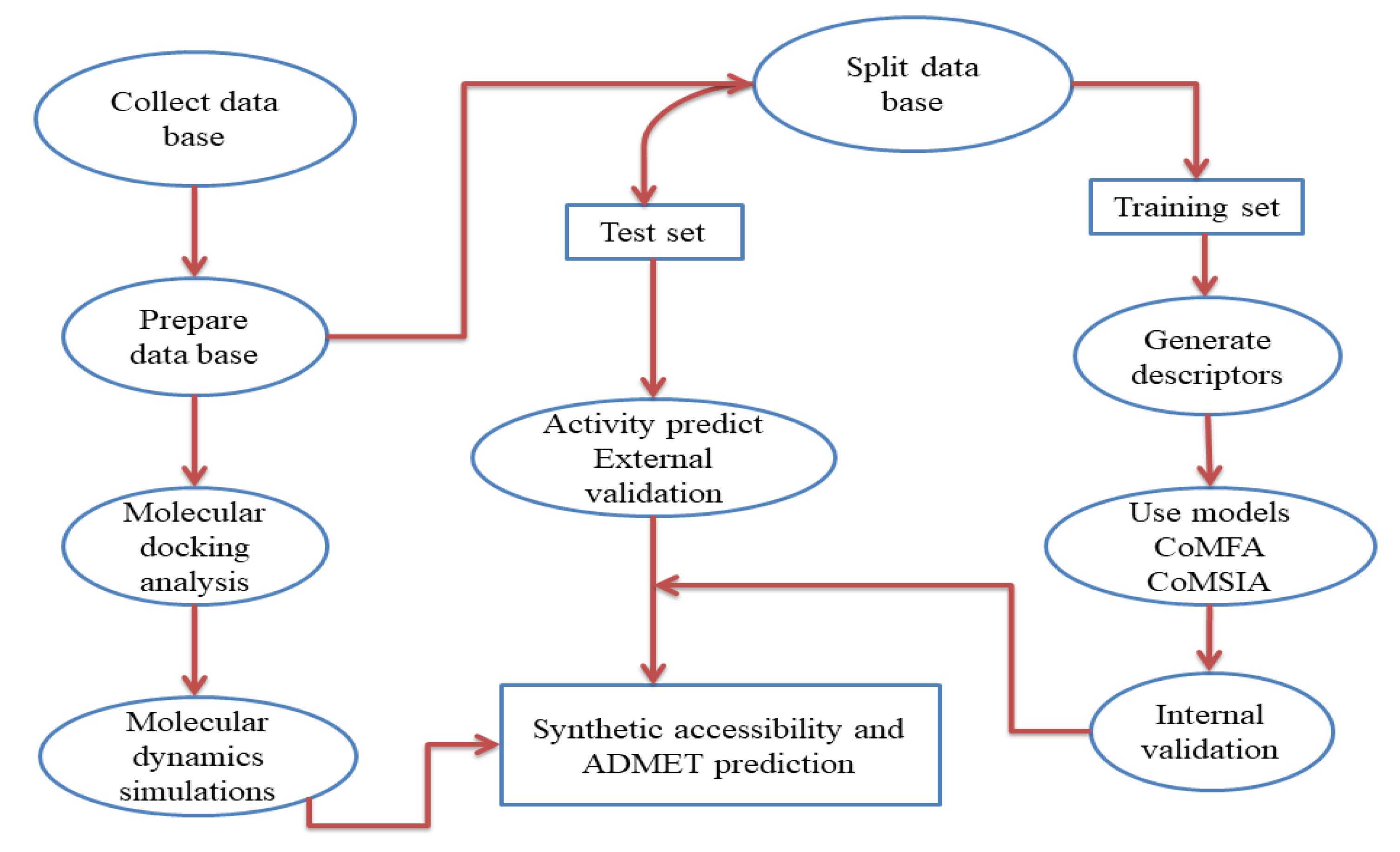
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Database and Biological Activity
2.2. Molecular Alignment and Generation of the Models
2.3. Molecular Docking
2.4. Molecular Dynamic (MD)
2.5. Synthetic Accessibility and ADMET Prediction
3. Results and Discussion
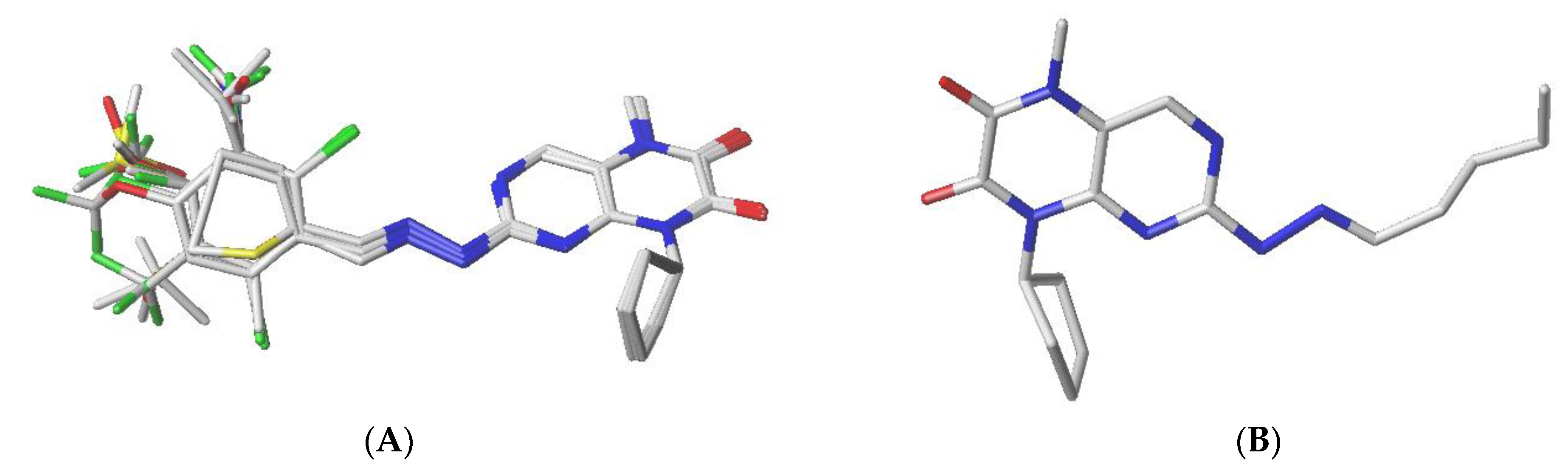
3.1. Distill Rigid Alignment
3.2. Generation of the CoMFA and CoMSIA Models
3.3. External Validation
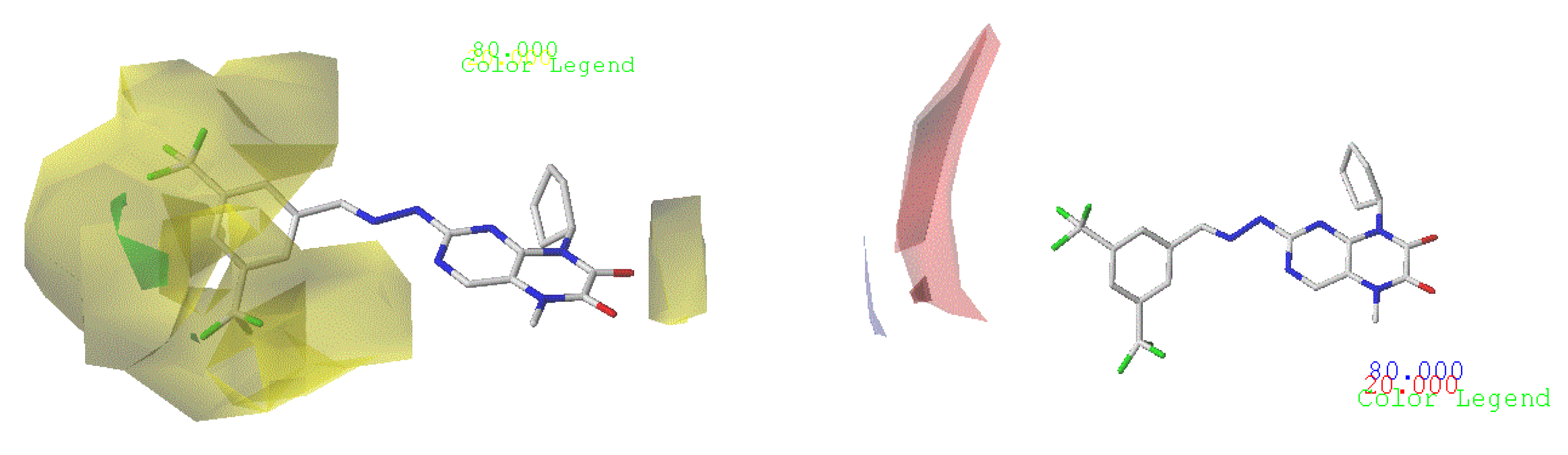
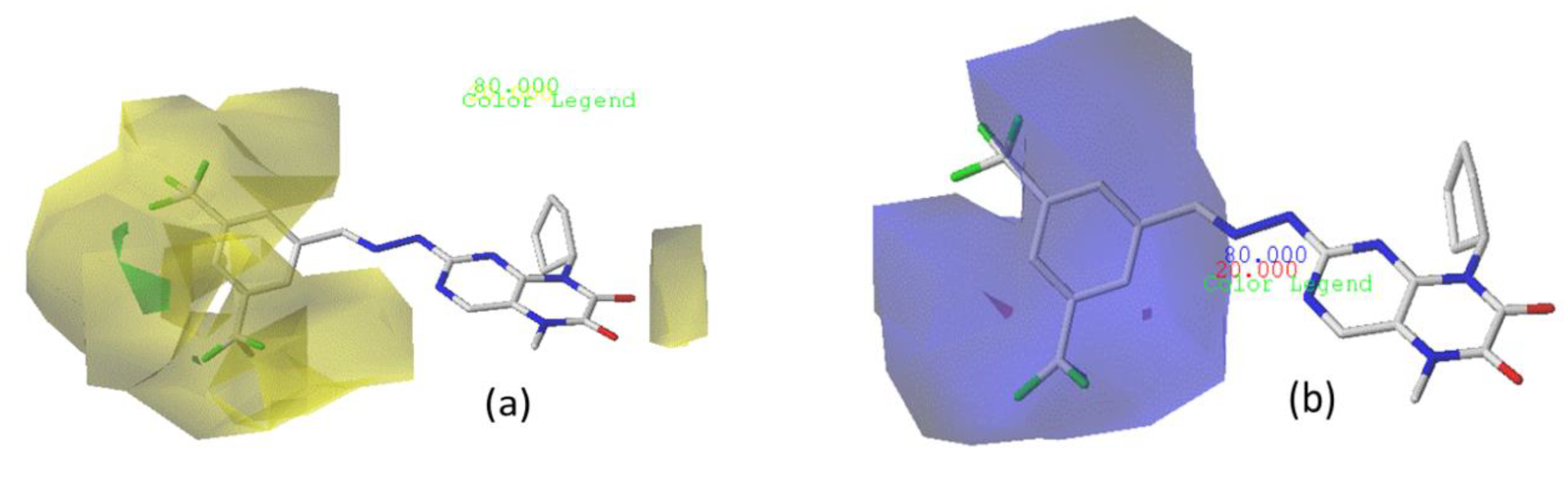
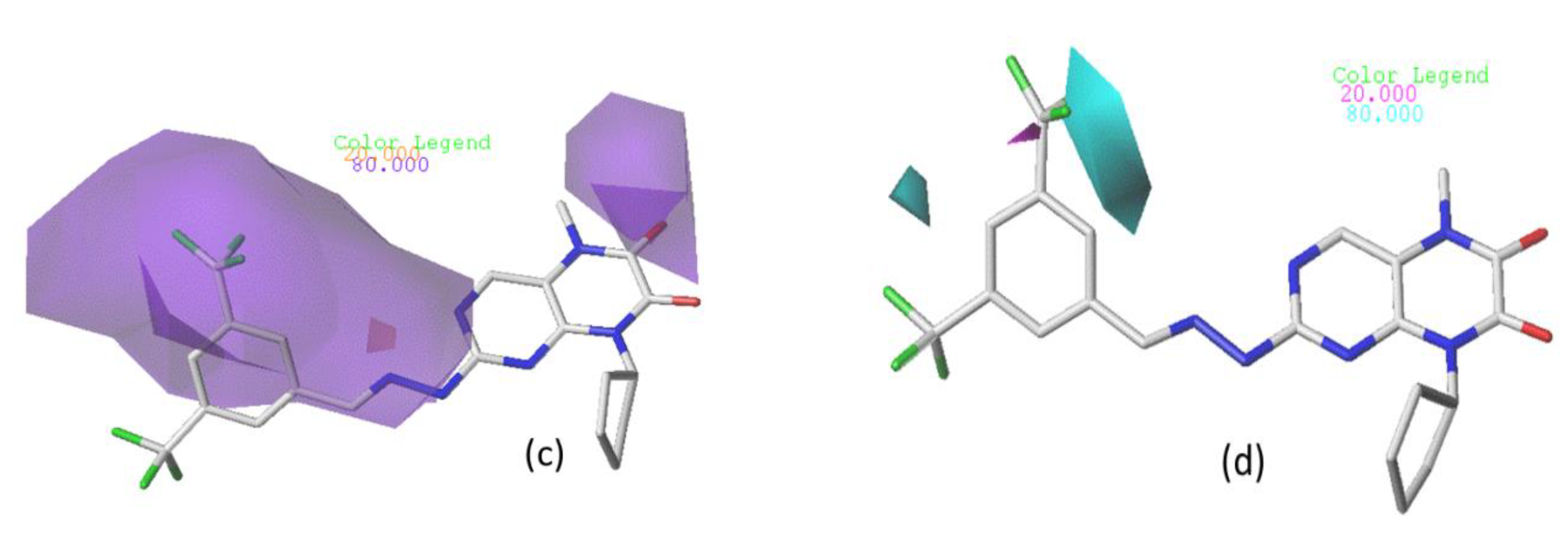
3.4. Analyzation of the CoMFA and CoMSIA Contour Charts
3.4.1. CoMFA Contour Chart
3.4.2. CoMSIA/SEA Contour Chart
3.5. Molecular Docking
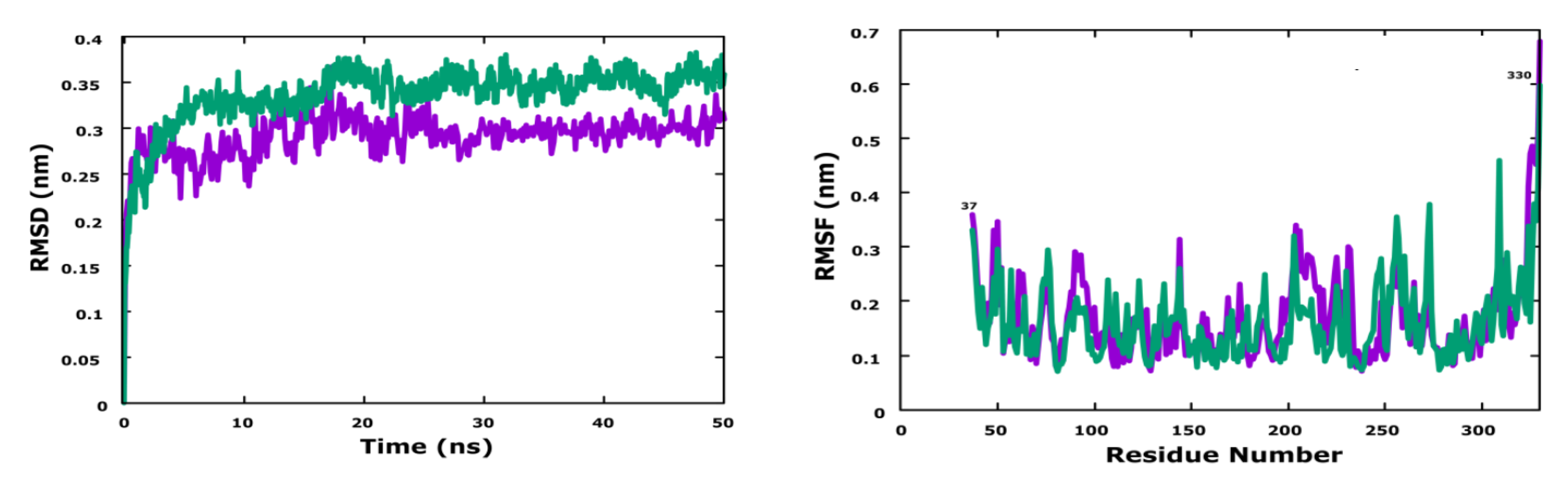
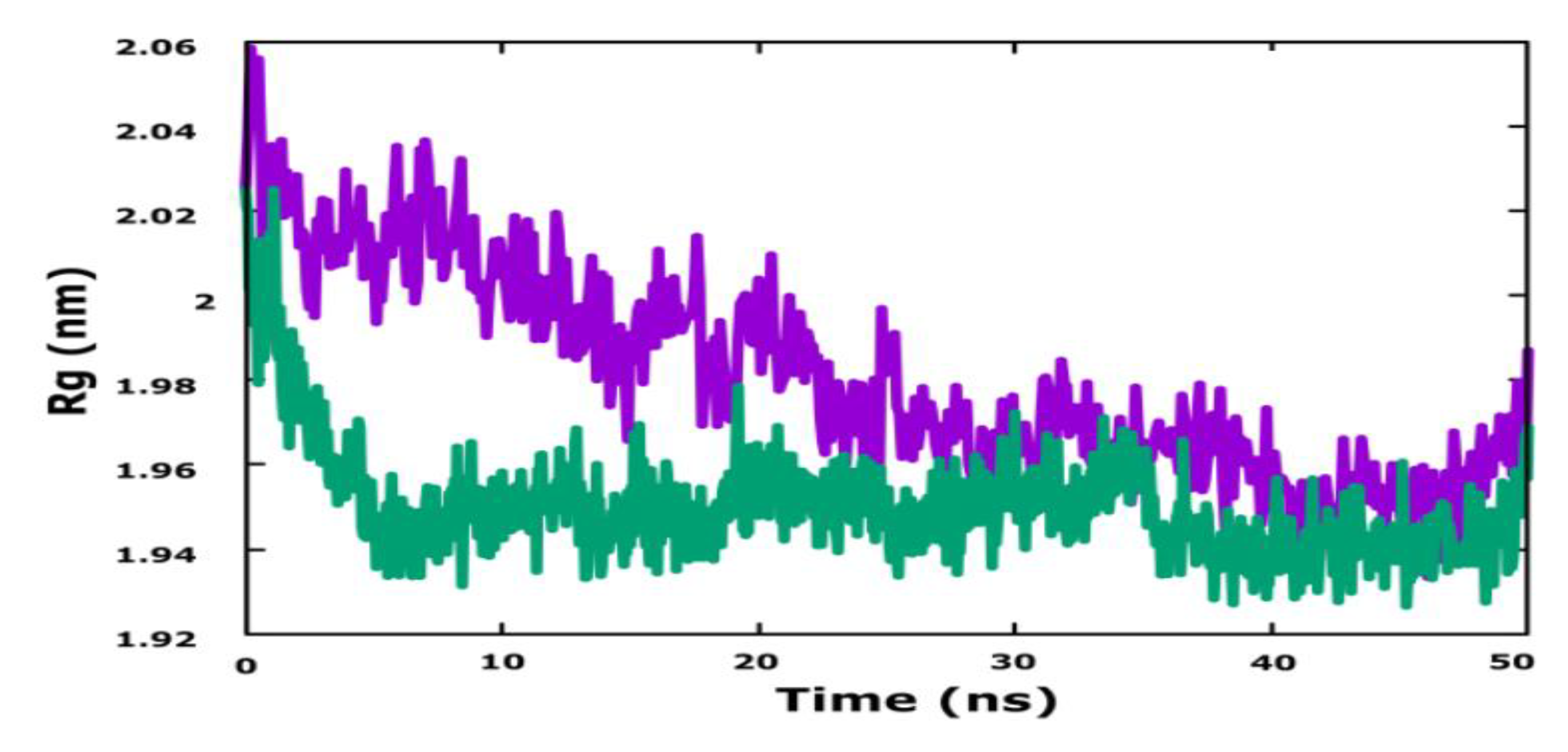
3.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.7. Synthetic Accessibility and Lipinski Rules
3.8. The Various ADMET Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, L.M.; Yeung, S.C.J.; Lee, M.H. Cancer Metabolic Reprogramming: Importance, Main Features, and Potentials for Precise Targeted Anti-Cancer Therapies. Cancer Biol. Med. 2014, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agamah, F.E.; Mazandu, G.K.; Hassan, R.; Bope, C.D.; Thomford, N.E.; Ghansah, A.; Chimusa, E.R. Computational/in Silico Methods in Drug Target and Lead Prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 21, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisiano, N.D.; Kasner, M.T. Polo-like Kinase and Its Inhibitors: Ready for the Match to Start? Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Hou, X.; Shao, C.; Li, J.; Cheng, J.X.; Kuang, S.; Ahmad, N.; Ratliff, T.; Liu, X. PIk1 Inhibition Enhances the Efficacy of Androgen Signaling Blockade in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6635–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, T.; Yin, B.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Y. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Pteridinone Derivatives Possessing a Hydrazone Moiety as Potent Plk1 Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er-rajy, M.; El Fadili, M.; Hadni, H.; Mrabti, N.N.; Zarougui, S.; Elhallaoui, M. 2D-QSAR Modeling, Drug-Likeness Studies, ADMET Prediction, and Molecular Docking for Anti-Lung Cancer Activity of 3-Substituted-5-(Phenylamino) Indolone Derivatives. Struct. Chem. 2022, 33, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, E.F.F.; Sippl, W.; de Castro Ramalho, T.; Ceva Antunes, O.A.; de Alencastro, R.B.; Albuquerque, M.G. 3D-QSAR CoMFA/CoMSIA Models Based on Theoretical Active Conformers of HOE/BAY-793 Analogs Derived from HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor Complexes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4344–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropsha, A.; Golbraikh, A. Predictive Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships Modeling: Development and Validation of QSAR Models. In Handbook of Chemoinformatics Algorithms; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2010; pp. 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.M.; Kumari, A.K.; Reddy, V.H.; Garcia, J.R. Novel Pyranopyrazole Derivatives Comprising a Benzoxazole Core as Antimicrobial Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Microbial Resistance and Machine Aided Results. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 100, 103908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Joy, M.N.; Sunil, K.; Sajith, A.M.; Santra, S.; Zyryanov, G.V.; Konovalova, O.A.; Butorin, I.I.; Muniraju, K. Towards Novel Tacrine Analogues: Pd(Dppf)Cl2·CH2Cl2 Catalyzed Improved Synthesis, in Silico Docking and Hepatotoxicity Studies. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 22476–22491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, R.; Jain, A.N. Surflex-Dock: Docking Benchmarks and Real-World Application. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, P.W.; Prlić, A.; Altunkaya, A.; Bi, C.; Bradley, A.R.; Christie, C.H.; Costanzo, L.D.; Duarte, J.M.; Dutta, S.; Feng, Z.; et al. The RCSB Protein Data Bank: Integrative View of Protein, Gene and 3D Structural Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D271–D281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El fadili, M.; Er-rajy, M.; Imtara, H.; Kara, M.; Zarougui, S.; Altwaijry, N.; Al kamaly, O.; Al Sfouk, A.; Elhallaoui, M. 3D-QSAR, ADME-Tox In Silico Prediction and Molecular Docking Studies for Modeling the Analgesic Activity against Neuropathic Pain of Novel NR2B-Selective NMDA Receptor Antagonists. Processes 2022, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Cramer, R.D.; Van Opdenbosch, N. Validation of the General Purpose Tripos 5.2 Force Field. J. Comput. Chem. 1989, 10, 982–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Sadeghi-Aliabadi, H.; Amanlou, M. 3D-QSAR, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamic Simulations for Prediction of New Hsp90 Inhibitors Based on Isoxazole Scaffold. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 36, 1463–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Khedkar, V.M.; Coutinho, E.C. 3D-QSAR in Drug Design—A Review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul-Haq, Z.; Wadood, A.; Uddin, R. CoMFA and CoMSIA 3D-QSAR Analysis on Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives as Urease Inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.-L.; Sun, P.-H.; Chen, W.-M. Exploring 3D-QSAR for Ketolide Derivatives as Antibacterial Agents Using CoMFA and CoMSIA. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2010, 7, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.R.; McKinnon, R.A.; Sorich, M.J. Effect of Steric Molecular Field Settings on CoMFA Predictivity. J. Mol. Model. 2007, 14, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mattos Oliveira, L.; Araújo, J.S.C.; Bacelar Costa Junior, D.; Santana, I.B.; Duarte, A.A.; Leite, F.H.A.; Benevides, R.G.; Coelho dos Santos Junior, M. Pharmacophore Modeling, Docking and Molecular Dynamics to Identify Leishmania Major Farnesyl Pyrophosphate Synthase Inhibitors. J. Mol. Model. 2018, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shan, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; He, L. Molecular Docking, 3D-QSAR Studies, and In Silico ADME Prediction of p-Aminosalicylic Acid Derivatives as Neuraminidase Inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 78, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Mitra, I.; Kar, S.; Ojha, P.K.; Das, R.N.; Kabir, H. Comparative Studies on Some Metrics for External Validation of QSPR Models. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golbraikh, A.; Tropsha, A. Beware of Q2! J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2002, 20, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, V.K.; Parikh, H.; Ghate, M. 3D QSAR Studies on 5-(2-Methylbenzimidazol-1-Yl)-N-Alkylthiophene-2-Carboxamide Derivatives as P. Falciparum Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase (PfDHODH) Inhibitors. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 22, 2235–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerasamy, R. Validation of QSAR Models-Strategies and Importance An Investigation on Male Contraception Activity of Extracts of Hibiscus Species-Mechanistic Studies (RM112200) View Project. Int. J. Drug Des. Discov. 2011, 3, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Free Download: BIOVIA Discovery Studio Visualizer—Dassault Systèmes. Available online: https://discover.3ds.com/discovery-studio-visualizer-download (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- AutoDock. Available online: https://autodock.scripps.edu/ (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RCSB PDB: Homepage. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/ (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Kothe, M.; Kohls, D.; Low, S.; Coli, R.; Rennie, G.R.; Feru, F.; Kuhn, C.; Ding, Y.-H. Research Article: Selectivity-Determining Residues in Plk1. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2007, 70, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, M.O.; Bhattacharje, G.; Al-Khafaji, K.; Taskin-Tok, T.; Alfasane, M.A.; Das, A.K.; Parvez, M.A.K.; Rahman, M.S. Combination of QSAR, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamic Simulation and MM-PBSA: Analogues of Lopinavir and Favipiravir as Potential Drug Candidates against COVID-19. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 3711–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welcome to GROMACS—GROMACS Webpage Https://Www.Gromacs.Org Documentation. Available online: https://www.gromacs.org/ (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- Stouten, P.F.W.; FrÖmmel, C.; Nakamura, H.; Sander, C. An Effective Solvation Term Based on Atomic Occupancies for Use in Protein Simulations. Mol. Simul. 2006, 10, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The PRODRG Server. Available online: http://davapc1.bioch.dundee.ac.uk/cgi-bin/prodrg (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- Ghosh, S.; Keretsu, S.; Cho, S.J. Computational Modeling of Novel Phosphoinositol-3-Kinase γ Inhibitors Using Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, and 3D-QSAR. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2021, 42, 1093–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Vandevondele, J.; William Kuo, I.F.; Sebastiani, D.; Ilja Siepmann, J.; Hutter, J.; Mundy, C.J. Isobaric−Isothermal Molecular Dynamics Simulations Utilizing Density Functional Theory: An Assessment of the Structure and Density of Water at Near-Ambient Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 11959–11964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El fadili, M.; Er-Rajy, M.; Kara, M.; Assouguem, A.; Belhassan, A.; Alotaibi, A.; Mrabti, N.N.; Fidan, H.; Ullah, R.; Ercisli, S.; et al. QSAR, ADMET In Silico Pharmacokinetics, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Studies of Novel Bicyclo (Aryl Methyl) Benzamides as Potent GlyT1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Schizophrenia. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, D.E.V.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: PkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SwissADME. Available online: http://www.swissadme.ch/index.php (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Zhang, M.Q.; Wilkinson, B. Drug Discovery beyond the “Rule-of-Five. ” Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Mitra, I. On Various Metrics Used for Validation of Predictive QSAR Models with Applications in Virtual Screening and Focused Library Design. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2011, 14, 450–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanbin, S.; Ahmad Fuad, F.A.; Abdul Hamid, A.A. Virtual Screening for Potential Inhibitors of Human Hexokinase II for the Development of Anti-Dengue Therapeutics. BioTech 2021, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.H.; Vomel, W.; Wochenschr, K.; Glazko, A.J.; Dill, W.A.; Kinkel, A.W.; Goulet, J.R.; Hollo-, W.J.; Brent, D.A.; Chandrasurin, P.; et al. Solubility and Partitioning I: Solubility of Nonelectrolytes in Water. J. Pharm. Sci. 1980, 69, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raevsky, O.; Egan, W.; Van De Waterbeemd, H.; Camenisch, G.; Hoffmann, F.; Folkers, G.; Raevsky, O.A. Estimation of Caco-2 Cell Permeability Using Calculated Molecular Descriptors Related Papers Est Imat Ion of Blood-Brain Barrier Crossing of Drugs Using Molecular Size and Shape, and H-B… Gerd Folkers Virt Ual Screening of Int Est Inal Drug Permeabilit y Per Art Ursson Predict Ion of Drug Absorpt Ion Using Mult Ivariat e St at Ist Ics Zy Estimation of Caco-2 Cell Permeability Using Calculated Molecular Descriptors. Quant StructAct Relat. 1996, 3, 48–90. [Google Scholar]
- Press, B.; Di Grandi, D. Permeability for Intestinal Absorption: Caco-2 Assay and Related Issues. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenderhauf, C.; Hammann, F.; Huwyler, J. Computational Prediction of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Using Decision Tree Induction. Molecules 2012, 17, 10429–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, Z.; Zhao, X.; Shin, J.-G.; Flockhart, D.A. Clinical Significance of the Cytochrome P450 2C19 Genetic Polymorphism. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 41, 913–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.W.; Chen, Y.Z. Prediction of Cytochrome P450 3A4, 2D6, and 2C9 Inhibitors and Substrates by Using Support Vector Machines. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Computer-Aided Prediction of Pharmacokinetic (ADMET) Properties—CHAPTER 21 Computer-Aided—Studocu. Available online: https://www.studocu.com/row/document/philadelphia-university-jordan/biology/computer-aided-prediction-of-pharmacokinetic-admet-properties/21421241 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Prediction of Human Clearance of Twenty-Nine Drugs from Hepatic Microsomal Intrinsic Clearance Data: An Examination of In Vitro Half-Life Approach and Nonspecific Binding to Microsomes | Drug Metabolism & Disposition. Available online: https://dmd.aspetjournals.org/content/27/11/1350.short (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Han, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, B.; Zhang, P. In Silico ADME and Toxicity Prediction of Ceftazidime and Its Impurities. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Comp | R | IC50 | pIC50 | Comp | R | IC50 | pIC50 * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 48.20 | 4.316 | 15 |  | 39.03 | 4.818 |
| 2 * | 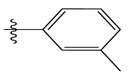 | 53.59 | 4.270 | 16 | 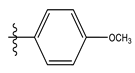 | 26.25 | 4.408 |
| 3 | 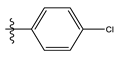 | 8.42 | 5.074 | 17 | 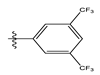 | 8.20 | 4.580 |
| 4 |  | 8.55 | 5.068 | 18 |  | 36.30 | 5.086 |
| 5 * |  | 26.59 | 4.575 | 19 * |  | 9.25 | 4.440 |
| 6 | 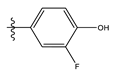 | 85.15 | 4.069 | 20 | 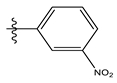 | 20.32 | 5.033 |
| 7 |  | 20.68 | 4.684 | 21 * | 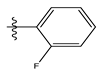 | 27.59 | 4.692 |
| 8 |  | 23.61 | 4.626 | 22 * | 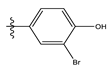 | 11.58 | 4.559 |
| 9 | 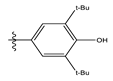 | 17.72 | 4.751 | 23 |  | 9.26 | 4.936 |
| 10 |  | 17.20 | 4.764 | 24 | 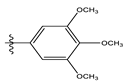 | 17.50 | 5.033 |
| 11 | 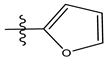 | 72.16 | 4.141 | 25 * | 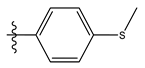 | 21.03 | 4.756 |
| 12 | 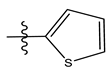 | 75.63 | 4.121 | 26 | 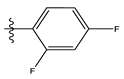 | 13.17 | 4.677 |
| 13 | 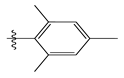 | 13.88 | 4.857 | 27 | 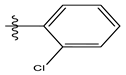 | 16.31 | 4.880 |
| 14 |  | 15.18 | 4.818 | 28 | 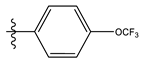 | 7.18 | 4.787 |
| pIC50 obs * | pIC50 Predict | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° | CoMFA | Residual | CoMSIA/SEAH | Residual | CoMSIA/SEH | Residual | |
| 1 * | 4.316 | 4.329 | −0.013 | 4.263 | 0.053 | 4.259 | 0.057 |
| 2 | 4.271 | 4.276 | −0.005 | 4.327 | −0.056 | 4.33 | −0.059 |
| 3 * | 5.074 | 4.471 | 0.603 | 4.492 | 0.582 | 4.486 | 0.588 |
| 4 * | 5.068 | 4.606 | 0.462 | 4.678 | 0.39 | 4.678 | 0.39 |
| 5 | 4.575 | 4.545 | 0.03 | 4.599 | −0.024 | 4.606 | −0.031 |
| 6 | 4.07 | 4.116 | −0.046 | 4.155 | −0.085 | 4.158 | −0.088 |
| 7 * | 4.684 | 4.328 | 0.356 | 4.315 | 0.369 | 4.308 | 0.376 |
| 8 | 4.626 | 4.631 | −0.005 | 4.605 | 0.021 | 4.603 | 0.023 |
| 9 | 4.751 | 4.745 | 0.006 | 4.755 | −0.004 | 4.745 | 0.006 |
| 10 | 4.764 | 4.779 | −0.015 | 4.129 | 0.635 | 4.784 | −0.02 |
| 11 | 4.141 | 4.123 | 0.018 | 4.122 | 0.019 | 4.124 | 0.017 |
| 12 | 4.121 | 4.152 | −0.031 | 4.178 | −0.057 | 4.176 | −0.055 |
| 13 | 4.857 | 4.883 | −0.026 | 4.835 | 0.022 | 4.833 | 0.024 |
| 14 | 4.818 | 4.831 | −0.013 | 4.835 | −0.017 | 4.849 | −0.031 |
| 15 | 4.409 | 4.343 | 0.066 | 4.44 | −0.031 | 4.439 | −0.03 |
| 16 | 4.581 | 4.58 | 0.001 | 4.556 | 0.025 | 4.559 | 0.022 |
| 17 | 5.086 | 5.091 | −0.005 | 5.126 | −0.04 | 5.12 | −0.034 |
| 18 | 4.440 | 4.394 | 0.046 | 4.286 | 0.154 | 4.282 | 0.158 |
| 19 | 5.034 | 5.028 | 0.006 | 4.986 | 0.048 | 4.986 | 0.048 |
| 20 | 4.692 | 4.717 | −0.025 | 4.692 | 0.000 | 4.69 | 0.002 |
| 21 | 4.559 | 4.549 | 0.01 | 4.509 | 0.050 | 4.511 | 0.048 |
| 22 * | 4.936 | 4.534 | 0.402 | 4.529 | 0.407 | 4.52 | 0.416 |
| 23 | 5.033 | 4.996 | 0.037 | 5.054 | −0.021 | 5.058 | −0.025 |
| 24 | 4.757 | 4.795 | −0.038 | 4.749 | 0.008 | 4.755 | 0.002 |
| 25 | 4.677 | 4.717 | −0.04 | 4.68 | −0.003 | 4.684 | −0.007 |
| 26 | 4.880 | 4.864 | 0.016 | 4.868 | 0.012 | 4.866 | 0.014 |
| 27 | 4.787 | 4.797 | −0.01 | 4.755 | 0.032 | 4.752 | 0.035 |
| 28 | 5.144 | 5.126 | 0.018 | 5.172 | −0.028 | 5.168 | −0.024 |
| Model | SEE | F-Value | NOC | Fraction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S * | E * | H * | D * | A * | |||||||
| CoMFA | 0.67 | 0.992 | 0.035 | 27.47 | 9 | 0.683 | 0.814 | 0.186 | - | - | - |
| CoMSIA/SHE | 0.69 | 0.974 | 0.059 | 15.52 | 7 | 0.758 | 0.069 | 0.135 | 0.797 | - | - |
| CoMSIA/SEAH | 0.66 | 0.975 | 0.057 | 12.30 | 7 | 0.767 | 0.067 | 0.138 | 0.779 | - | 0.016 |
| Statistical Parameters | CoMFA | CoMSIA/SEH | CoMSIA/SEAH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q² | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.66 |
| R² pred | 0.683 | 0.758 | 0.767 |
| K | 0.923 | 0.922 | 0.923 |
| K’ | 1.082 | 1.083 | 1.082 |
| Numbers of Compounds | Characteristic | Violations | S.A | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW | Nub-HA | Nub-HD | Nub-Rot | TPSA | LogP | Lipinski | Veber | Egan | ||
| Criteria | <500 | <10 | <5 | ≤10 | ≤140 | ≤5 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | 0 < S.A < 10 |
| 17 | 500.40 | 11 | 1 | 6 | 94.17 | 4.088 | Yes | Yes | Yes | 3.52 |
| 28 | 448.40 | 9 | 1 | 6 | 104.4 | 2.949 | Yes | Yes | Yes | 3.35 |
| Absorption | Distribution | Metabolism | Excretion | Toxicity | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Solubility | Intestinal Absorption | Caco2 Permeability | VDss | CNS Permeability | Substrate | Inhibitor | Global Clearance | AMES Toxicity | Skin Sensitization | ||||
| CYP 450 | |||||||||||||
| 2D6 | 3A4 | 1A2 | 2C19 | 2C9 | |||||||||
| Unit | log mol/Liter | Percent % | log Pap 10−6 cm/s | Log Liter/kg | Log PS | Yes or No | Log mL/min/kg | Yes or No | Yes or No | ||||
| 17 | −4.971 | 91.00 | 1.207 | −0.374 | −2.309 | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | 0.473 | No | No |
| 28 | −4.119 | 85.348 | 1.378 | −0.394 | −3.079 | No | Yes | No | No | No | 0.293 | No | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Er-rajy, M.; El fadili, M.; Imtara, H.; Saeed, A.; Ur Rehman, A.; Zarougui, S.; Abdullah, S.A.; Alahdab, A.; Parvez, M.K.; Elhallaoui, M. 3D-QSAR Studies, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamic Simulation, and ADMET Proprieties of Novel Pteridinone Derivatives as PLK1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Life 2023, 13, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010127
Er-rajy M, El fadili M, Imtara H, Saeed A, Ur Rehman A, Zarougui S, Abdullah SA, Alahdab A, Parvez MK, Elhallaoui M. 3D-QSAR Studies, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamic Simulation, and ADMET Proprieties of Novel Pteridinone Derivatives as PLK1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Life. 2023; 13(1):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010127
Chicago/Turabian StyleEr-rajy, Mohammed, Mohamed El fadili, Hamada Imtara, Aamir Saeed, Abid Ur Rehman, Sara Zarougui, Shaef A. Abdullah, Ahmad Alahdab, Mohammad Khalid Parvez, and Menana Elhallaoui. 2023. "3D-QSAR Studies, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamic Simulation, and ADMET Proprieties of Novel Pteridinone Derivatives as PLK1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer" Life 13, no. 1: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010127
APA StyleEr-rajy, M., El fadili, M., Imtara, H., Saeed, A., Ur Rehman, A., Zarougui, S., Abdullah, S. A., Alahdab, A., Parvez, M. K., & Elhallaoui, M. (2023). 3D-QSAR Studies, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamic Simulation, and ADMET Proprieties of Novel Pteridinone Derivatives as PLK1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Life, 13(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010127







