Intrinsic Therapeutic Link between Recuperative Cerebellar Con-Nectivity and Psychiatry Symptom in Schizophrenia Patients with Comorbidity of Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Imaging Data Acquisition
2.3. Imaging Data Preprocessing
2.4. Cerebello-Cortical Functional Connectivity Analysis
2.5. Assessments of Metabolic Syndrome
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of Cerebello-Cortical FC
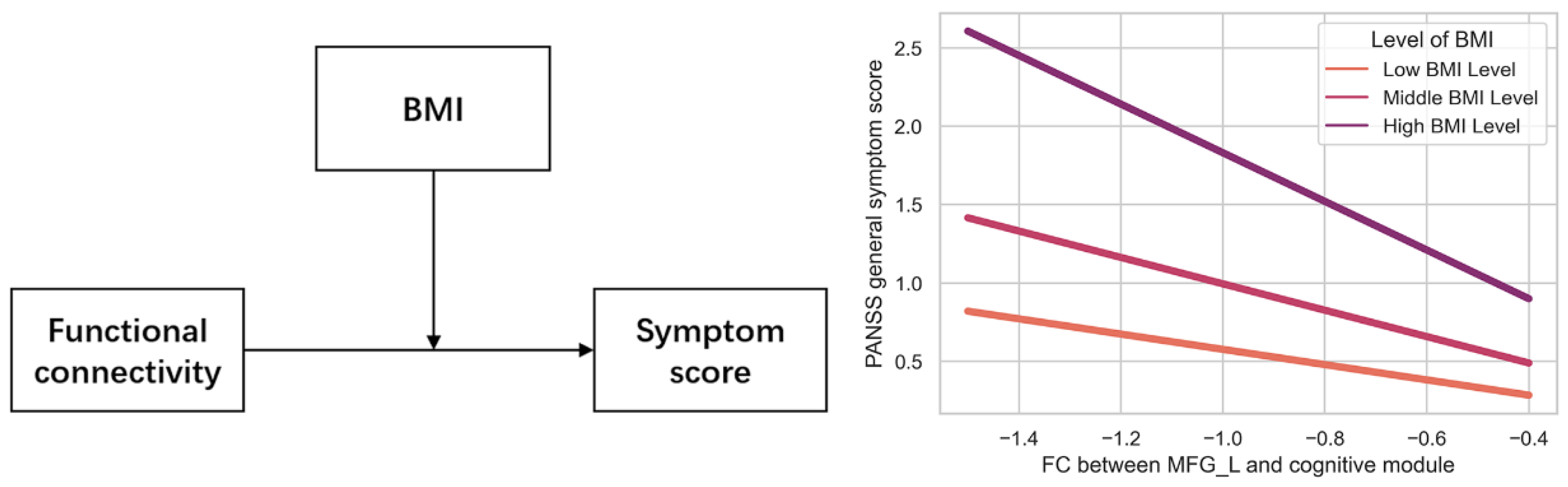
3.3. Relationship between FCs and Metabolic Syndrome, Psychiatric Symptoms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Owen, M.J.; Sawa, A.; Mortensen, P.B. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2016, 388, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goff, D.C. The Pharmacologic Treatment of Schizophrenia-2021. JAMA 2021, 325, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, C.U.; Detraux, J.; De Lepeleire, J.; De Hert, M. Effects of antipsychotics, antidepressants and mood stabilizers on risk for physical diseases in people with schizophrenia, depression and bipolar disorder. World Psychiatry 2015, 14, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Üçok, A.; Gaebel, W. Side effects of atypical antipsychotics: A brief overview. World Psychiatry 2008, 7, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, J.; Freemantle, N.; Harrison, P.; Bebbington, P. Atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia: Systematic overview and meta-regression analysis. BMJ 2000, 321, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deurenberg-Yap, M.; Chew, S.K.; Deurenberg, P. Elevated body fat percentage and cardiovascular risks at low body mass index levels among Singaporean Chinese, Malays and Indians. Obes. Rev. 2002, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, U.; Khaliq, S.; Ahmad, H.U.; Manzoor, S.; Lone, K.P. Metabolic syndrome: An update on diagnostic criteria, pathogenesis, and genetic links. Hormones 2018, 17, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J.; Vancampfort, D.; Sweers, K.; van Winkel, R.; Yu, W.; De Hert, M. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and metabolic abnormalities in schizophrenia and related disorders--a systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr. Bull. 2013, 39, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacKenzie, N.E.; Kowalchuk, C.; Agarwal, S.M.; Costa-Dookhan, K.A.; Caravaggio, F.; Gerretsen, P.; Chintoh, A.; Remington, G.J.; Taylor, V.H.; Mueller, D.J.; et al. Antipsychotics, Metabolic Adverse Effects, and Cognitive Function in Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grover, S.; Padmavati, R.; Sahoo, S.; Gopal, S.; Nehra, R.; Ganesh, A.; Raghavan, V.; Sankaranarayan, A. Relationship of metabolic syndrome and neurocognitive deficits in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 278, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, H.Y.; Perry, E.; Jayathilake, K. Clozapine-induced weight gain predicts improvement in psychopathology. Schizophr. Res. 2003, 59, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillinger, T.; McCutcheon, R.A.; Vano, L.; Mizuno, Y.; Arumuham, A.; Hindley, G.; Beck, K.; Natesan, S.; Efthimiou, O.; Cipriani, A.; et al. Comparative effects of 18 antipsychotics on metabolic function in patients with schizophrenia, predictors of metabolic dysregulation, and association with psychopathology: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terevnikov, V.; Stenberg, J.H.; Tiihonen, J.; Chukhin, E.; Joffe, M.; Burkin, M.; Joffe, G. Relationships between pharmacotherapy-induced metabolic changes and improved psychopathology in schizophrenia: Data from a mirtazapine and first-generation antipsychotics combination trial. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1661–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dursun, S.M.; Szemis, A.; Andrews, H.; Reveley, M.A. The effects of clozapine on levels of total cholesterol and related lipids in serum of patients with schizophrenia: A prospective study. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 1999, 24, 453. [Google Scholar]
- Raben, A.T.; Marshe, V.S.; Chintoh, A.; Gorbovskaya, I.; Muller, D.J.; Hahn, M.K. The Complex Relationship between Antipsychotic-Induced Weight Gain and Therapeutic Benefits: A Systematic Review and Implications for Treatment. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procyshyn, R.M.; Wasan, K.M.; Thornton, A.E.; Barr, A.M.; Chen, E.Y.; Pomarol-Clotet, E.; Stip, E.; Williams, R.; Macewan, G.W.; Birmingham, C.L.; et al. Clozapine and Risperidone Enhancement Study Group. Changes in serum lipids, independent of weight, are associated with changes in symptoms during long-term clozapine treatment. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2007, 32, 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Luckhoff, H.; Phahladira, L.; Scheffler, F.; Asmal, L.; du Plessis, S.; Chiliza, B.; Kilian, S.; Emsley, R. Weight gain and metabolic change as predictors of symptom improvement in first-episode schizophrenia spectrum disorder patients treated over 12months. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 206, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, M.; Miyata, J.; Hazama, M.; Fukuyama, H.; Murai, T.; Takahashi, H. Multimodal neuroimaging as a window into the pathological physiology of schizophrenia: Current trends and issues. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 102, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Chen, X.; He, H.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xie, Q.; Lai, Y.; Luo, C.; Yao, D. Altered Basal Ganglia Network Integration in Schizophrenia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuo, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J. Altered resting-state functional connectivity of the cerebellum in schizophrenia. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 12, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moberget, T.; Doan, N.T.; Alnaes, D.; Kaufmann, T.; Cordova-Palomera, A.; Lagerberg, T.V.; Diedrichsen, J.; Schwarz, E.; Zink, M.; Eisenacher, S.; et al. Cerebellar volume and cerebellocerebral structural covariance in schizophrenia: A multisite mega-analysis of 983 patients and 1349 healthy controls. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Luo, C.; Luo, Y.; Duan, M.; Yi, Q.; Biswal, B.B.; Yao, D. Reduction in gray matter of cerebellum in schizophrenia and its influence on static and dynamic connectivity. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J. Schizophrenia and the disconnection hypothesis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1999, 99, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Jiang, S.; Khundrakpam, B.S.; Duan, M.; Chen, X.; Yao, D. Evaluation of functional connectivity in subdivisions of the thalamus in schizophrenia. Br. J. Psychiatry 2019, 214, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honey, G.D.; Pomarol-Clotet, E.; Corlett, P.R.; Honey, R.A.; McKenna, P.J.; Bullmore, E.T.; Fletcher, P.C. Functional dysconnectivity in schizophrenia associated with attentional modulation of motor function. Brain 2005, 128, 2597–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brady, R.O., Jr.; Gonsalvez, I.; Lee, I.; Ongur, D.; Seidman, L.J.; Schmahmann, J.D.; Eack, S.M.; Keshavan, M.S.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Halko, M.A. Cerebellar-Prefrontal Network Connectivity and Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Cui, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Curtin, A.; Sheng, J.; et al. Functional reconfiguration of cerebellum-cerebral neural loop in schizophrenia following electroconvulsive therapy. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2022, 320, 111441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, C.J.; Schmahmann, J.D. Functional topography in the human cerebellum: A meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsters, J.H.; Laird, A.R.; Fox, P.T.; Eickhoff, S.B. Bridging the gap between functional and anatomical features of cortico-cerebellar circuits using meta-analytic connectivity modeling. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 3152–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, C.G.; Wang, X.D.; Zuo, X.N.; Zang, Y.F. DPABI: Data Processing & Analysis for (Resting-State) Brain Imaging. Neuroinformatics 2016, 14, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Luo, C.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Li, F.; Feng, H.; Li, J.; Gong, D.; Yao, D. Neuroscience Information Toolbox: An Open Source Toolbox for EEG-fMRI Multimodal Fusion Analysis. Front. Neuroinform. 2018, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.J.; Murray, J.D.; Repovs, G.; Cole, M.W.; Savic, A.; Glasser, M.F.; Pittenger, C.; Krystal, J.H.; Wang, X.J.; Pearlson, G.D.; et al. Altered global brain signal in schizophrenia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7438–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti KG, M.M.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. Metabolic syndrome--a new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ma, S.; Heng, D.; Tan, C.E.; Chew, S.K.; Hughes, K.; Tai, E.S. Should central obesity be an optional or essential component of the metabolic syndrome? Ischemic heart disease risk in the Singapore Cardiovascular Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-based Approach; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kobuch, S.; Macefield, V.G.; Henderson, L.A. Resting regional brain activity and connectivity vary with resting blood pressure but not muscle sympathetic nerve activity in normotensive humans: An exploratory study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 2433–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.; Kong, R.; Gordon, E.M.; Laumann, T.O.; Zuo, X.N.; Holmes, A.J.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Yeo, B.T.T. Local-Global Parcellation of the Human Cerebral Cortex from Intrinsic Functional Connectivity MRI. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 3095–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermes, E.; Nasrallah, H.; Davis, V.; Meyer, J.; McEvoy, J.; Goff, D.; Davis, S.; Stroup, T.S.; Swartz, M.; Lieberman, J.; et al. The association between weight change and symptom reduction in the CATIE schizophrenia trial. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 128, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konarzewska, B.; Waszkiewicz, N.; Galińska, B.; Szulc, A. Fasting insulin serum levels and psychopathology profiles in male schizophrenic inpatients treated with olanzapine or risperidone. Neuroendocr. Lett. 2013, 34, 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- Mezquida, G.; Savulich, G.; Garcia-Rizo, C.; Garcia-Portilla, M.P.; Toll, A.; Garcia-Alvarez, L.; Bobes, J.; Mane, A.; Bernardo, M.; Fernandez-Egea, E. Inverse association between negative symptoms and body mass index in chronic schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 192, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teff, K.L.; Rickels, M.R.; Grudziak, J.; Fuller, C.; Nguyen, H.-L.; Rickels, K. Antipsychotic-induced insulin resistance and postprandial hormonal dysregulation independent of weight gain or psychiatric disease. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3232–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wojciak, P.; Domowicz, K.; Rybakowski, J.K. Metabolic indices in schizophrenia: Association of negative symptoms with higher HDL cholesterol in female patients. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 22, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.F.; Hu, T.M.; Lan, T.H.; Chiu, H.J.; Sheen, L.Y.; Loh, E.W. Severity of psychosis syndrome and change of metabolic abnormality in chronic schizophrenia patients: Severe negative syndrome may be related to a distinct lipid pathophysiology. Eur. Psychiatry 2014, 29, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Reilly, J.X.; Beckmann, C.F.; Tomassini, V.; Ramnani, N.; Johansen-Berg, H. Distinct and overlapping functional zones in the cerebellum defined by resting state functional connectivity. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissenden, J.A.; Levin, E.J.; Osher, D.E.; Halko, M.A.; Somers, D.C. Functional Evidence for a Cerebellar Node of the Dorsal Attention Network. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 6083–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, W.; Liu, F.; Liu, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, C.; Zhai, J.; Zhao, J. Abnormal causal connectivity by structural deficits in first-episode, drug-naive schizophrenia at rest. Schizophr. Bull. 2015, 41, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, W.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, J.; Yu, L.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, J. Increased Cerebellar Functional Connectivity With the Default-Mode Network in Unaffected Siblings of Schizophrenia Patients at Rest. Schizophr. Bull. 2015, 41, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xi, Y.; Cui, L.B.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Fang, P.; Yin, H. Altered functional connectivity of the dentate nuclei in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2021, 233, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn, A.K.; Baker, J.T.; Lewandowski, K.E.; Ongur, D.; Cohen, B.M. Aberrant cerebellar connectivity in motor and association networks in schizophrenia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Botao, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Tang, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Qian, Z.; et al. Aberrant resting-state functional connectivity of salience network in first-episode schizophrenia. Brain Imaging Behav. 2020, 14, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjun, P.K.; Lalousis, P.A.; Dunne, T.F.; Heinze, K.; Reniers, R.L.; Broome, M.R.; Farmah, B.; Oyebode, F.; Wood, S.J.; Upthegrove, R. Aberrant salience network functional connectivity in auditory verbal hallucinations: A first episode psychosis sample. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, F.; Liu, F.; Chen, J.; Wu, R.; Chen, D.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, J.; Zhao, J. Cerebellar abnormalities in first-episode, drug-naive schizophrenia at rest. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2018, 276, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Ford, J.M. Default mode network activity and connectivity in psychopathology. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2012, 8, 49–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, M.; Park, H.J.; Pae, C.; Park, K.; Lee, E.; Lee, S.K.; An, S.K. Aberrant cerebro-cerebellar functional connectivity and minimal self-disturbance in individuals at ultra-high risk for psychosis and with first-episode schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 202, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; An, G.; Cai, W.; Ji, W.; Li, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy induces simultaneous changes in brain functions and structures that are associated with weight loss. Brain-Appar. Commun. J. Bacomics 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, B.; Dev, S.I.; Esterman, M.; Schwarz, N.F.; Ferland, T.; Fortenbaugh, F.C.; Milberg, W.P.; McGlinchey, R.E.; Salat, D.H.; Leritz, E.C. Aberrant patterns of default-mode network functional connectivity associated with metabolic syndrome: A resting-state study. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Cao, W.; Zhang, X.; Sun, B.; Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Yin, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, T.; et al. BOLD-fMRI reveals the association between renal oxygenation and functional connectivity in the aging brain. Neuroimage 2019, 186, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullmann, S.; Heni, M.; Veit, R.; Ketterer, C.; Schick, F.; Haring, H.U.; Fritsche, A.; Preissl, H. The obese brain: Association of body mass index and insulin sensitivity with resting state network functional connectivity. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ji, G.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, C.; von Deneen, K.M.; Han, Y.; et al. Altered Interactions Among Resting-State Networks in Individuals with Obesity. Obesity 2020, 28, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.D.; Cross, D.J.; Minoshima, S.; Belongia, D.; Watson, G.S.; Craft, S. Insulin resistance and Alzheimer-like reductions in regional cerebral glucose metabolism for cognitively normal adults with prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, E.; Meng, F.; Fujita, H.; Morgado, F.; Kazemi, Y.; Rice, L.C.; Ren, C.; Escamilla, C.O.; Gibson, J.M.; Sajadi, S.; et al. Regulation of autism-relevant behaviors by cerebellar-prefrontal cortical circuits. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, A.; Snyder, S.H. Schizophrenia: Diverse approaches to a complex disease. Science 2002, 296, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sathyanesan, A.; Zhou, J.; Scafidi, J.; Heck, D.H.; Sillitoe, R.V.; Gallo, V. Emerging connections between cerebellar development, behaviour and complex brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Duan, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Gong, J.; Dong, D.; Li, H.; Yi, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Aberrant Prefrontal-Thalamic-Cerebellar Circuit in Schizophrenia and Depression: Evidence From a Possible Causal Connectivity. Int. J. Neural. Syst. 2019, 29, 1850032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Chen, O.Y.; Chung, Y.; Forsyth, J.K.; McEwen, S.C.; Gee, D.G.; Bearden, C.E.; Addington, J.; Goodyear, B.; Cadenhead, K.S.; et al. Cerebello-thalamo-cortical hyperconnectivity as a state-independent functional neural signature for psychosis prediction and characterization. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girgis, R.R.; Javitch, J.A.; Lieberman, J.A. Antipsychotic drug mechanisms: Links between therapeutic effects, metabolic side effects and the insulin signaling pathway. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.M.; Caravaggio, F.; Costa-Dookhan, K.A.; Castellani, L.; Kowalchuk, C.; Asgariroozbehani, R.; Graff-Guerrero, A.; Hahn, M. Brain insulin action in schizophrenia: Something borrowed and something new. Neuropharmacology 2020, 163, 107633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Shu, H.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xie, C.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, F. Brain insulin resistance deteriorates cognition by altering the topological features of brain networks. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 13, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.M.; Young, R.L.; Leong, L.; Rogers, G.B.; Spencer, N.J.; Jessup, C.F.; Keating, D.J. The Diverse Metabolic Roles of Peripheral Serotonin. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1049–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitow, F.; Hirono, M.; Suzuki, H. Serotonin and Synaptic Transmission in the Cerebellum. In Handbook of the Cerebellum and Cerebellar Disorders; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 915–926. [Google Scholar]



| Characteristic | SCZ-MetS (n = 34) | SCZ-nMetS (n = 43) | HC (n = 35) | Unadjusted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p-Value | |
| Gender (male/female) | 27/7 | 28/15 | 26/9 | 0.199 |
| Age (years) | 44.42 (9.24) | 40.65 (12.24) | 39.49 (13.56) | 0.205 |
| Education (years) | 11.94 (2.66) | 11.42 (2.72) | 12.14 (5.08) | 0.657 |
| Medication dosage (chlorpromazine equivalent) | 337 (156) | 320 (137) | - | 0.683 |
| Illness duration | 20.3 (8.86) | 17.2 (11.7) | - | 0.2 |
| PANSS total score | 62.79 (14.11) | 61.8 (12.32) | - | 0.777 |
| PANSS positive symptom score | 11.5 (5.11) | 14.87 (5.75) | - | 0.022 * |
| PANSS negative symptom score | 22.54 (6.37) | 19.77 (5.94) | - | 0.092 |
| PANSS general symptom score | 28.75 (5.99) | 27.17 (5.37) | - | 0.293 |
| Characteristic | SCZ-MetS (n = 34) | SCZ-nMetS (n = 43) | Unadjusted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p-Value | |
| Body Mass Index | 25.28 (3.6) | 22.08 (3.63) | <0.001 *** |
| Fast blood glucose levels (mmol/L) | 5.43 (1.106) | 4.91 (0.7) | <0.05 * |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.59 (0.65) | 0.99 (0.43) | <0.001 *** |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 3.91 (0.96) | 3.96 (0.76) | 0.793 |
| High-density lipoprotein (mmol/L) | 0.996 (0.305) | 1.22 (0.29) | <0.01 ** |
| Low density lipoprotein (mmol/L) | 2.28 (0.28) | 2.2 (0.61) | 0.561 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 117.81 (10.1) | 116.38 (12.34) | 0.71 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 76.31 (7.22) | 76.11 (7.7) | 0.96 |
| Cluster | Brain Region | MNI | T Value | Cluster Size (Voxels) | Brain Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Left SFGmed | −1, 36, 30 | −5.05 | 276 | DMN |
| Left SFG | −3, 27, 60 | −3.13 | \ | DMN | |
| 2 | Left ITG | −48, −9, −18 | −4.88 | 113 | DAN |
| 3 | Right ITG | 51, −9, −39 | −4.46 | 256 | DAN |
| 4 | Left MFG | −36, 15, 60 | −4.12 | 69 | DMN |
| 5 | Right MFG | 44, 14, 51 | −3.16 | 49 | DMN |
| 6 | Right PreCG | 57, −15, 33 | 6.48 | 2884 | SMN |
| 7 | Left PoCG | −54, −24, 51 | 6.27 | 1867 | SMN |
| 8 | Left IPL | −59, −28, 43 | 5.36 | 230 | DAN |
| 9 | Left MCC | −12, −15, 39 | 5.28 | 38 | SVAN |
| 10 | Left LING | −6, −60, −3 | 5.10 | 172 | VN |
| 11 | Right LING | 6, −66, −3 | 5.07 | 155 | VN |
| 12 | Left MOG | −30, −81, 18 | 4.92 | 262 | VN |
| 13 | Right MOG | 42, −75, −3 | 4.72 | 138 | VN |
| 14 | Right Anterior PCUN | 9, −42, 52 | 3.76 | 155 | DMN |
| Left Anterior PCUN | −10, −43, 52 | 3.40 | \ | DMN | |
| 15 | Right INS | 36, 10, 12 | 3.26 | 104 | SVAN |
| 16 | Left INS | −30, 17, 12 | 3.22 | 137 | SVAN |
| Model | Dependent Variable | Independent Variable | R2 | F | p | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | PASSN general symptom score | Intercept | 0.07 | 4.30 * | 0.84 | [−0.24, 0.29] |
| BMI | 0.65 | [−0.21, 0.34] | ||||
| FC | 0.47 | [−0.50, 0.23] | ||||
| BMI × FC | 0.04 | [−0.70, 0.01] | ||||
| Model 2 | PASSN general symptom score | Intercept | 0.01 | 0.69 | 0.73 | [−0.23, 0.32] |
| FBG | 0.77 | [−0.22, 0.30] | ||||
| FC | 0.09 | [−0.64, 0.05] | ||||
| FBG × FC | 0.41 | [−0.24, 0.58] | ||||
| Model 3 | PASSN general symptom score | Intercept | 0.01 | 0.70 | 0.84 | [−0.25, 0.30] |
| TG | 0.66 | [−0.34,0.22] | ||||
| FC | 0.20 | [−0.60, 0.13] | ||||
| TG × FC | 0.41 | [−0.20, 0.49] | ||||
| Model 4 | PASSN general symptom score | Intercept | 0.001 | 0.03 | 0.79 | [−0.23, 0.31] |
| TC | 0.16 | [−0.50, 0.08] | ||||
| FC | 0.29 | [−0.67, 0.21] | ||||
| TC × FC | 0.85 | [−0.36, 0.44] | ||||
| Model 5 | PASSN general symptom score | Intercept | 0.06 | 0.33 | 0.78 | [−0.24, 0.31] |
| HDL | 0.67 | [−0.40, 0.26] | ||||
| FC | 0.13 | [−0.62, 0.08] | ||||
| HDL × FC | 0.57 | [−0.49, 0.27] | ||||
| Model 6 | PASSN general symptom score | Intercept | 0.003 | 0.1485 | 0.80 | [−0.24, 0.30] |
| LDL | 0.17 | [−0.51, 0.09] | ||||
| FC | 0.35 | [−0.65, 0.24] | ||||
| LDL × FC | 0.70 | [−0.30, 0.45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; Chang, X.; He, H.; Duan, M.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Tan, Y.; et al. Intrinsic Therapeutic Link between Recuperative Cerebellar Con-Nectivity and Psychiatry Symptom in Schizophrenia Patients with Comorbidity of Metabolic Syndrome. Life 2023, 13, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010144
Zhou J, Guo X, Liu X, Luo Y, Chang X, He H, Duan M, Li S, Li Q, Tan Y, et al. Intrinsic Therapeutic Link between Recuperative Cerebellar Con-Nectivity and Psychiatry Symptom in Schizophrenia Patients with Comorbidity of Metabolic Syndrome. Life. 2023; 13(1):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010144
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jingyu, Xiao Guo, Xiaoli Liu, Yuling Luo, Xin Chang, Hui He, Mingjun Duan, Shicai Li, Qifu Li, Ying Tan, and et al. 2023. "Intrinsic Therapeutic Link between Recuperative Cerebellar Con-Nectivity and Psychiatry Symptom in Schizophrenia Patients with Comorbidity of Metabolic Syndrome" Life 13, no. 1: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010144
APA StyleZhou, J., Guo, X., Liu, X., Luo, Y., Chang, X., He, H., Duan, M., Li, S., Li, Q., Tan, Y., Yao, G., Yao, D., & Luo, C. (2023). Intrinsic Therapeutic Link between Recuperative Cerebellar Con-Nectivity and Psychiatry Symptom in Schizophrenia Patients with Comorbidity of Metabolic Syndrome. Life, 13(1), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010144









