COVID-19 Inflammatory Markers and Vitamin D Relationship in Pediatric Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Laboratory Testing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. C Reactive Protein Analysis
3.2. Lactate Dehydrogenase Analysis
3.3. Creatine Kinase Analysis
3.4. Vitamin D Analysis
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cevik, M.; Tate, M.; Lloyd, O.; Maraolo, A.E.; Schafers, J.; Ho, A. SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV viral load dynamics, duration of viral shedding, and infectiousness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Microbe 2020, 2, e13–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V. Emerging Human Coronavirus Infections (SARS, MERS, and COVID-19): Where They Are Leading Us. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 40, 5–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Harrich, D.; Li, Z.; Hu, D.; Li, D. The unique features of SARS-CoV-2 transmission: Comparison with SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and 2009 H1N1 pandemic influenza virus. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, e2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdy, A.M.; Saad, M.A.; El Khateeb, A.F.; Ahmed, M.I.; Gamal El-Din, D.H. Comparative evaluation of semi-quantitative CT-severity scoring versus serum lactate dehydrogenase as prognostic biomarkers for disease severity and clinical outcome of COVID-19 patients. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdogan, D.; Guzel, M.; Tosun, D.; Akpinar, O. Diagnostic and early prognostic value of serum CRP and LDH levels in patients with possible COVID-19 at the first admission. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, N.; Yang, G.; Peng, W.; Tang, F.; Guo, C.; Chai, X. Serum lactate dehydrogenase level may predict acute respiratory distress syndrome of patients with fever infected by SARS-CoV-2. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.; Hu, H.; Liu, T. LDH, CRP and ALB predict nucleic acid turn negative within 14 days in symptomatic patients with COVID-19. Scott. Med. J. 2021, 66, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H. Effect of serum LDH and CK levels on condition and prognosis of COVID-patients. Med. J. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 42, 345–349. [Google Scholar]
- Bourkhissi, L.; El Fakiri, K.; Nassih, H.; El Qadiry, R.; Bourrahouat, A.; Sab, I.A.; Rada, N.; Draiss, G.; Bouskraoui, M. Laboratory abnormalities in children with novel Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Med. Insights Pediatr. 2020, 14, 1179556520955177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Upadhyaya, M.; Kandre, Y.; Pandya, A.; Saraf, V.; Saxena, D.; Mavalankar, D. Epidemiological, clinical and biomarker profile of pediatric patients infected with COVID-19. QJM Int. J. Med. 2021, 114, 476–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.-Y. Characteristics of abnormal serum creatine kinase-MB levels in children with COVID-19. World J. Pediatr. 2021, 17, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, D.; Guo, L.; et al. Elevated Serum Creatine Kinase as an Independent Prognostic Factor for Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Immunogenet 2020, 6, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Alpcan, A.; Tursun, S.; Kandur, Y. Vitamin D levels in children with COVID-19: A report from Turkey. Epidemiol. Infect. 2021, 149, E180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, K.; Şen, V. Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for COVID-19 in children? Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 3595–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Andreu, I.; Mariconda, A.; Saturnino, C.; Giuzio, F.; Longo, P.; Aquaro, S.; Catalano, A. Drugs for COVID-19: An Update. Molecules 2022, 27, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Catalano, A.; Saturnino, C.; Pellegrino, M.; Mariconda, A.; Longo, P.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Aquaro, S. COVID-19 at a Glance: An Up-to-Date Overview on Variants, Drug Design and Therapies. Viruses 2022, 14, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoğlu, E.; Akkoç, G.; Ağbaş, A.; Akgün, Ö.; Yurdakul, K.; Duru, H.N.S.; Elevli, M. The association between vitamin D levels and the clinical severity and inflammation markers in pediatric COVID-19 patients: Single-center experience from a pandemic hospital. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 2699–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Grant, W.B.; Frias-Toral, E.; Sarno, G.; Vetrani, C.; Ceriani, F.; Garcia-Velasquez, E.; Contreras-Briceño, J.; Savastano, S.; et al. Vitamin D: A Role Also in Long COVID-19? Nutrients 2022, 14, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerbu, B.; Pantea, S.; Bratosin, F.; Vidican, I.; Turaiche, M.; Frent, S.; Borsi, E.; Marincu, I. Liver Impairment and Hematological Changes in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C and COVID-19: A Retrospective Study after One Year of Pandemic. Medicina 2021, 57, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Tang, J. COVID-19 Infection Segmentation and Severity Assessment Using a Self-Supervised Learning Approach. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D status: Measurement, interpretation, and clinical application. Ann. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieth, R. Why the minimum desirable serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level should be 75 nmol/L (30 ng/mL). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 25, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorentz, K.; Röhle, G.; Siekmann, L. Einführung der neuen Standardmethoden 1994 zur Bestimmung der katalytischen Enzymkonzentrationen bei 37 °C. DG Klin. Chem. Mitt. 1995, 26, 290–293. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, G.; Dati, F. Vorläufige Referenzbereiche für 14 Proteins im Serum (für Erwachsene) nach Standardisierung immunochemischer Methoden unter Bezug auf das internationale Referenzmaterial CRM 470. Lab. Med. 1995, 19, 401–403. [Google Scholar]
- Cherian, A.G.; Hill, J.G. Age Dependence of Serum Enzymatic Activities (Alkaline Phosphatase, Aspartate Aminotransferase, and Creatine Kinase) in Healthy Children and Adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1978, 70, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamishi, S.; Olfat, M.; Pourakbari, B.; Eshaghi, H.; Abdolsalehi, M.R.; Shahbabaie, M.A.; Jalali, F.; Safari, F.; Mahmoudi, S. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in children: Update and new insights from the second report of an Iranian referral hospital. Epidemiol Infect. 2022, 150, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraglia Del Giudice, M.; Indolfi, C.; Dinardo, G.; Decimo, F.; Decimo, A.; Klain, A. Vitamin D status can affect COVID-19 outcomes also in pediatric population. PharmaNutrition 2022, 22, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Say, D.; Crawford, N.; McNab, S.; Wurzel, D.; Steer, A.; Tosif, S. Post-acute COVID-19 outcomes in children with mild and asymptomatic disease. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2021, 5, e22–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, K.R.; Sankar, J.; Das, R.R.; Ratageri, V.; Choudhary, B.; Bhat, J.I.; Mishra, B.; Collaborative Indian Pediatric COVID study group; Bhatnagar, S.; Behera, B.; et al. Clinical Profile and Risk Factors for Severe Disease in 402 Children Hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 from India: Collaborative Indian Pediatric COVID Study Group. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2021, 67, fmab048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.; Chorath, K.; Moreira, A.; Evans, M.; Burmeister-Morton, F.; Burmeister, F.; Naqvi, R.; Petershack, M.; Moreira, A. COVID-19 in 7780 pediatric patients: A systematic review. Eclinicalmedicine 2020, 24, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.M.; Oliveira, C.R.; Guerguis, S.; Eisenberg, R.; Choi, J.; Kim, M.; Abdelhemid, A.; Agha, R.; Agarwal, S.; Aschner, J.L.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Clinical Syndromes and Predictors of Disease Severity in Hospitalized Children and Youth. J. Pediatr. 2020, 230, 23–31.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; Ma, W.; Shi, X.; Li, S.; Hao, M.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, L. Clinical laboratory evaluation of COVID-19. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 519, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.; Celcilia, L. Levels of C-Reactive Protein, D-Dimer, And Lactate Dehydrogenase As Predictors Of Covid-19 Outcome In Children: A Systematic Review. Jimki 2021, 9, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Lorenzo, P.; Coya, O.N.; López-Jimenez, A.; Blázquez, A.; Delmiro, A.; Lucia, A.; Arenas, J.; Martín, M.A.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Cueto-Felgueroso, C.; et al. Plasma LDH: A specific biomarker for lung affectation in COVID-19? Pract. Lab. Med. 2021, 25, e00226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; Aggarwal, G.; Wong, J.; Benoit, S.; Vikse, J.; Plebani, M.; Lippi, G. Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-G.; Zhong, Z.-J.; Li, M.; Fu, J.; Su, Y.-H.; Ping, Y.-M.; Xu, Z.-J.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.-L. Coronavirus Disease 2019-Related Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biochem. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5596727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in children compared with adults in Shandong Province, China. Infection 2020, 48, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, A.; Verrengia, E.P.; Merlo, I.; Rea, F.; Siciliano, G.; Corrao, G.; Prelle, A. Muscle manifestations and CK levels in COVID infection: Results of a large cohort of patients inside a Pandemic COVID-19 Area. Acta Myol. 2021, 40, 119838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.A. Pediatric COVID-19: Systematic review of the literature. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, A.M.; Palumbo, N.; Nathan, S.K.; Singer, P.S.; Castellanos-Reyes, L.J.; Sethna, C.B. Pediatric COVID-19-associated rhabdomyolysis: A case report. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güllü, U.U.; Güngör, S.; Ipek, S.; Yurttutan, S.; Dilber, C. Predictive value of cardiac markers in the prognosis of COVID-19 in children. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 48, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Cheng, H.; Cao, Q.; Fei, A.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, L.; Fei, S.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Wu, J.; et al. Clinical features, laboratory findings and persistence of virus in 10 children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Biomed. J. 2020, 44, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feketea, G.; Vlacha, V.; Bocsan, I.C.; Vassilopoulou, E.; Stanciu, L.A.; Zdrenghea, M. Vitamin D in Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Related Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 648546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Huang, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y. Vitamin D levels and clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.2 in children: A longitudinal cohort study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 960859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshkhah, A.; Agrawal, V.; Eshein, A.; Subramanian, H.; Roy, H.K.; Backman, V. The Possible Role of Vitamin D in Suppressing Cytokine Storm and Associated Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. medRxiv 2020, PPR149846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, W.; Couture, A.D.; Swedlund, M.; Hampton, A.; Eglash, A.; Schrager, S. An Evidence-Based Review of Vitamin D for Common and High-Mortality Conditions. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2022, 35, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, S.-U.; Hong, T.M.; Joo, S.Y. Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency in Children with Fractures: Before and during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyazgül, G.; Bağ, Ö.; Yurtseven, I.; Coşkunol, F.; Başer, S.; Çiçek, D.; Kanberoğlu, G.I.; Çelik, F.; Nalbantoğlu, Ö.; Özkan, B. How Vitamin D Levels of Children Changed During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comparison of Pre-pandemic and Pandemic Periods. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2022, 14, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita-Cruz, J.; Fonseca-Tenorio, J.; Villasís-Keever, M.; López-Alarcón, M.; Parra-Ortega, I.; López-Martínez, B.; Miranda-Novales, G. Efficacy and safety of vitamin D supplementation in hospitalized COVID-19 pediatric patients: A randomized controlled trial. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 943529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 CRP values determined,
CRP values determined,  maximum normal CRP, 5 mg/L).
maximum normal CRP, 5 mg/L).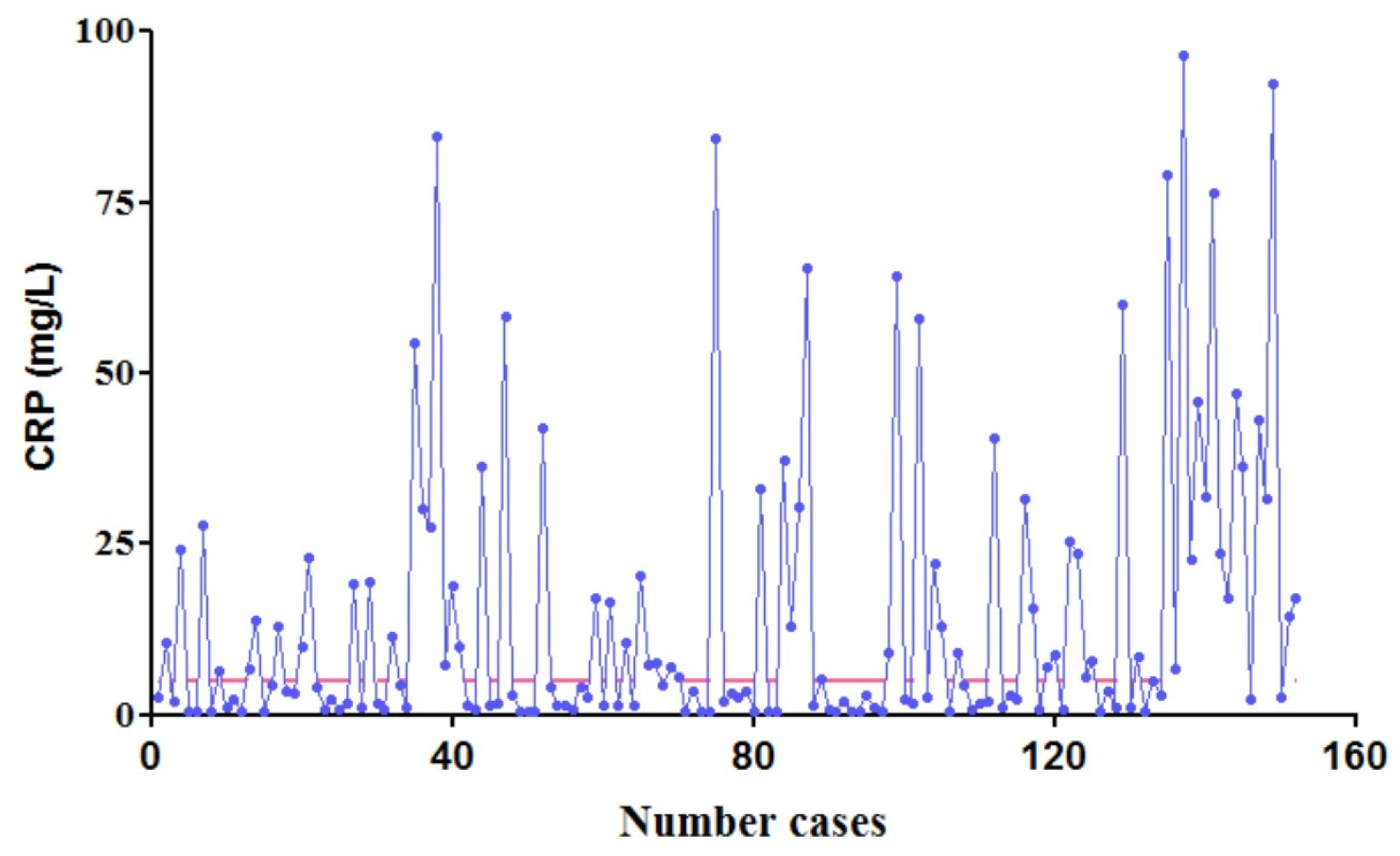

 determined LDH,
determined LDH,  minimum normal value,
minimum normal value,  maximum normal value; (b) Group 1–17 years:
maximum normal value; (b) Group 1–17 years:  determined LDH,
determined LDH,  minimum normal value,
minimum normal value,  maximum normal value.
maximum normal value.
 determined LDH,
determined LDH,  minimum normal value,
minimum normal value,  maximum normal value; (b) Group 1–17 years:
maximum normal value; (b) Group 1–17 years:  determined LDH,
determined LDH,  minimum normal value,
minimum normal value,  maximum normal value.
maximum normal value.

 0–4 years,
0–4 years,  4–7 years,
4–7 years,  maximum normal value for 0–4 years,
maximum normal value for 0–4 years,  maximum normal value for 4–7 years; (b) group 7–17 years:
maximum normal value for 4–7 years; (b) group 7–17 years:  7–13 years,
7–13 years,  13–17 years,
13–17 years,  7–13 years maximum normal value for males,
7–13 years maximum normal value for males,  13–17 years maximum normal value for males,
13–17 years maximum normal value for males,  7–13 years maximum normal value for females,
7–13 years maximum normal value for females,  13–17 years maximum normal value for females.
13–17 years maximum normal value for females.
 0–4 years,
0–4 years,  4–7 years,
4–7 years,  maximum normal value for 0–4 years,
maximum normal value for 0–4 years,  maximum normal value for 4–7 years; (b) group 7–17 years:
maximum normal value for 4–7 years; (b) group 7–17 years:  7–13 years,
7–13 years,  13–17 years,
13–17 years,  7–13 years maximum normal value for males,
7–13 years maximum normal value for males,  13–17 years maximum normal value for males,
13–17 years maximum normal value for males,  7–13 years maximum normal value for females,
7–13 years maximum normal value for females,  13–17 years maximum normal value for females.
13–17 years maximum normal value for females.
| CRP (mg/L) | LDH (U/L) 0–1 Years | LDH (U/L) 1–17 Years | CK (U/L) 0–4 Years | CK (U/L) 4–7 Years | CK (U/L) 7–13 Years | CK (U/L) 13–17 Years | 25-OHD (ng/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | <5 | 225–600 | 120–300 | 24–228 | 24–149 | 24–154 | 24–123 | >30 |
| Female | <5 | 225–600 | 120–300 | 24–228 | 24–149 | 24–247 | 24–270 | >30 |
| High CRP | Normal CRP | p | High LDH | Normal LDH | p | High CK | Normal CK | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Respiratory symptoms | 7 | 2 | 0.0399 | 6 | 2 | <0.0001 | 2 | 5 | 0.7242 |
| No respiratory symptoms | 61 | 82 | 2 | 34 | 6 | 21 |
| No. | CRP (mg/L) | LDH (U/L) | 25-OHD | Clinical Signs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.02 | 313 | 39.01 | - |
| 2 | 84.39 | 400 | 9.51 | - |
| 3 | 0.60 | 397 | 31.33 | Pneumonia |
| 4 | 7.90 | 404 | 22.17 | - |
| 5 | 25.29 | 354 | 25.64 | Pneumonia |
| 6 | 7.38 | 147 | 23.23 | Pneumonia |
| 7 | 18.91 | 224 | 31.33 | - |
| 8 | 16.38 | 273 | 18.13 | - |
| 9 | 7.18 | 265 | 34.78 | - |
| 10 | 30.39 | 265 | 24.55 | - |
| 11 | 0.60 | 162 | 62.75 | - |
| 12 | 9.84 | 237 | 26.11 | - |
| 13 | 10.56 | 287 | 29.63 | - |
| 14 | 24.20 | 250 | 27.95 | Acute laryngitis |
| 15 | 65.38 | 264 | 12.00 | - |
| 16 | 22.02 | 311 | 21.75 | - |
| 17 | 25.29 | 404 | 19.37 | Pneumonia |
| 18 | 22.60 | 183 | 30.94 | Pneumonia |
| 19 | 4.59 | 213 | 54.64 | - |
| 20 | 4.23 | 280 | 46.21 | - |
| 21 | 43.65 | 341 | 18.89 | - |
| 22 | 84.32 | 367 | 7.12 | Acute laryngitis |
| 23 | 2.69 | 304 | 35.65 | - |
| 24 | 76.31 | 257 | 17.07 | - |
| 25 | 24.33 | 260 | 29.29 | - |
| 26 | 1.49 | 228 | 46.51 | Pneumonia |
| 27 | 1.02 | 313 | 39.01 | - |
| Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient | Clinical Signs | CRP | LDH | 25-OHD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical signs | 1 | 0.3958 (p = 0.0401) | 0.5521 (p = 0.0028) | −0.3854 (p = 0.0471) |
| CRP | 0.3958 (p = 0.0401) | 1 | 0.2024 (p = 0.3114) | −0.8409 (p = <0.0001) |
| LDH | 0.5521 (p = 0.0028) | 0.2024 (p = 0.3114) | 1 | −0.3823 (p = 0.4904) |
| 25-OHD | −0.3854 (p = 0.0471) | −0.8409 (p = <0.0001) | −0.3823 (p = 0.4904) | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bagiu, I.C.; Scurtu, I.L.; Horhat, D.I.; Mot, I.C.; Horhat, R.M.; Bagiu, R.V.; Capraru, I.D.; Diaconu, M.M.; Adam, O.; Ciornei, B.; et al. COVID-19 Inflammatory Markers and Vitamin D Relationship in Pediatric Patients. Life 2023, 13, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010091
Bagiu IC, Scurtu IL, Horhat DI, Mot IC, Horhat RM, Bagiu RV, Capraru ID, Diaconu MM, Adam O, Ciornei B, et al. COVID-19 Inflammatory Markers and Vitamin D Relationship in Pediatric Patients. Life. 2023; 13(1):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010091
Chicago/Turabian StyleBagiu, Iulia Cristina, Ileana Luminita Scurtu, Delia Ioana Horhat, Ion Cristian Mot, Razvan Mihai Horhat, Radu Vasile Bagiu, Ionut Dragos Capraru, Mircea Mihai Diaconu, Ovidiu Adam, Bogdan Ciornei, and et al. 2023. "COVID-19 Inflammatory Markers and Vitamin D Relationship in Pediatric Patients" Life 13, no. 1: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010091
APA StyleBagiu, I. C., Scurtu, I. L., Horhat, D. I., Mot, I. C., Horhat, R. M., Bagiu, R. V., Capraru, I. D., Diaconu, M. M., Adam, O., Ciornei, B., Vulcanescu, D. D., Juganaru, I., Bondar, A.-C., & Horhat, F. G. (2023). COVID-19 Inflammatory Markers and Vitamin D Relationship in Pediatric Patients. Life, 13(1), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010091








