Improvement of Pain and Function by Using Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection in Patients with an Osteoarthritic Knee with Patellar Malalignment: An Electromyographic Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Injection of BTA
2.3. Clinical Assessment
2.4. Isokinetic Test
2.5. EMG Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
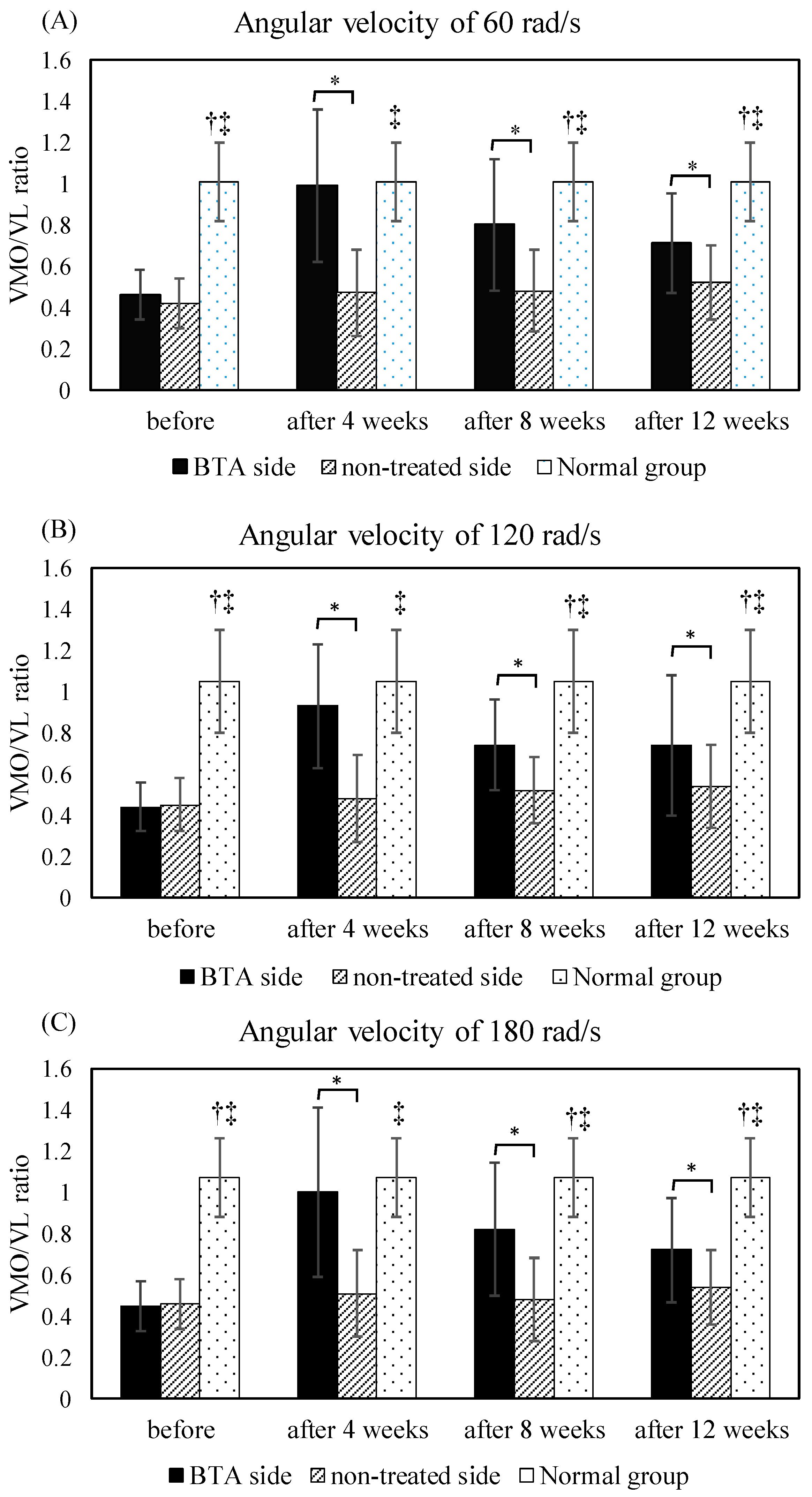
3. Results
3.1. VMO/VL Ratio before and after BTA Injection
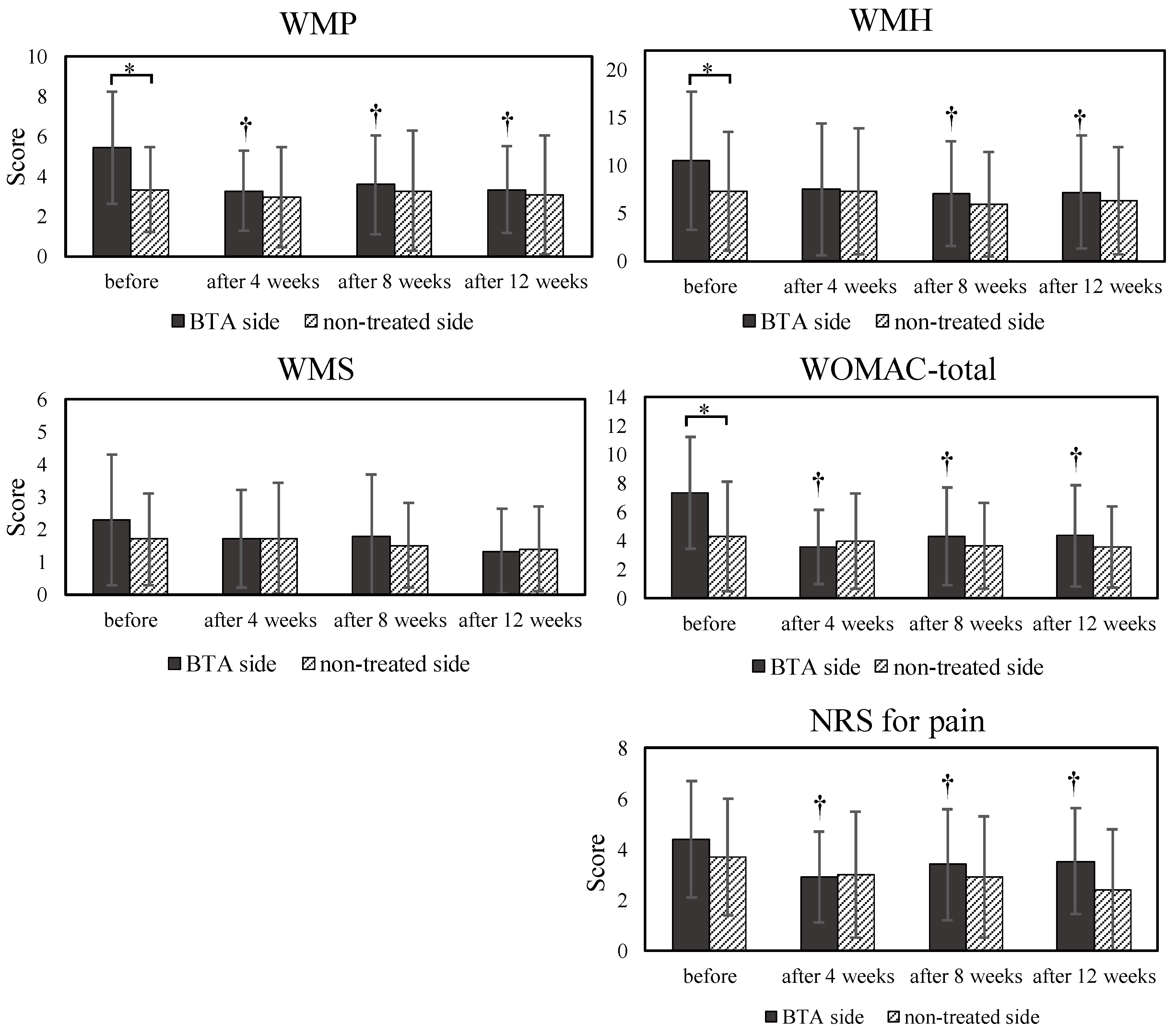
3.2. WOMAC Questionnaire and NRS
3.3. Associations of EMG Ratios with WOMAC and NRS
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petersen, W.; Ellermann, A.; Gösele-Koppenburg, A.; Best, R.; Rembitzki, I.V.; Brüggemann, G.P.; Liebau, C. Patellofemoral pain syndrome. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 2264–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boling, M.; Padua, D.; Marshall, S.; Guskiewicz, K.; Pyne, S.; Beutler, A. Gender differences in the incidence and prevalence of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blønd, L.; Hansen, L. Patellofemoral pain syndrome in athletes: A 5.7-year retrospective follow-up study of 250 athletes. Acta Orthop. Belg. 1998, 64, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kujala, U.M.; Jaakkola, L.H.; Koskinen, S.K.; Taimela, S.; Hurme, M.; Nelimarkka, O. Scoring of patellofemoral disorders. Arthroscopy 1993, 9, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Draper, C.E.; Fredericson, M.; Gold, G.E.; Delp, S.L.; Beaupre, G.; Besier, T. Patellar maltracking correlates with vastus medialis activation delay in patellofemoral pain patients. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, S.M.; Bennell, K.; Hodges, P.; Crossley, K.; McConnell, J. Delayed onset of electromyographic activity of vastus medialis obliquus relative to vastus lateralis in subjects with patellofemoral pain syndrome. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 82, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonner, J.H. Patellofemoral arthroplasty. Orthopedics 2010, 33, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.J.; Wood, L.; Selfe, J.; Peat, G. Anterior knee pain in younger adults as a precursor to subsequent patellofemoral osteoarthritis: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2010, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, A.; McElrath, C.; Wadhwa, V.; Shah, J.P.; Chhabra, A. Current clinical, radiological and treatment perspectives of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, N.M.; van Linschoten, R.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.; van Middelkoop, M. The additional effect of orthotic devices on exercise therapy for patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome: A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 46, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, M.J.; Selfe, J. Patellar taping for patellofemoral pain syndrome in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 4, CD006717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, S. Anterior knee pain: An update of physical therapy. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, S.; Arvidsson, H.; Eriksson, E. Electrical stimulation of vastus medialis and stretching of lateral thigh muscles in patients with patello-femoral symptoms. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 1993, 1, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, M.T.; Foxworth, J.L. The role of foot orthoses as an intervention for patellofemoral pain. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2003, 33, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiener-Ogilvie, S.; Jones, R.B. A randomized trial of exercise therapy and foot orthoses as treatment for knee pain in primary care. Br. J. Podiatry 2004, 7, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Crossley, K.; Bennell, K.; Green, S.; McConnell, J. A systematic review of physical interventions for patellofemoral pain syndrome. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2001, 11, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltychev, M.; Dutton, R.; Laimi, K.; Beaupré, G.; Virolainen, P.; Fredericson, M. Effectiveness of conservative treatment for patellofemoral pain syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 50, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazzuti, L.; Merlo, A.; Orlandi, F.; Campanini, I. Delayed onset of electromyographic activity of vastus medialis obliquus relative to vastus lateralis in subjects with patellofemoral pain syndrome. Gait Posture 2010, 32, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Chien, C.-C.; Wu, S.-K.; Liau, J.-J.; Jan, M.-H. Electromechanical delay of the vastus medialis obliquus and vastus lateralis in individuals with patellofemoral pain syndrome. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2012, 42, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.R.; Gross, M.T. Comparison of vastus medialis obliquus: Vastus lateralis muscle integrated electromyographic ratios between healthy subjects and patients with patellofemoral pain. Phys. Ther. 1991, 71, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcconnell, J. The management of chondromalacia patellae: A long term solution. Aust. J. Physiother. 1986, 32, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollnick, P.D.; Armstrong, R.B.; Saubert, C.W.; Piehl, K.; Saltin, B. Enzyme activity and fiber composition in skeletal muscle of untrained and trained men. J. Appl. Physiol. 1972, 33, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesary, Y.; Singh, V.; Frenkel-Rutenberg, T.; Greenberg, A.; Dekel, S.; Schwarzkopf, R.; Snir, N. Botulinum toxin injections as salvage therapy is beneficial for management of patellofemoral pain syndrome [published correction appears in Knee Surg Relat Res. 2022 Feb 1;34:2]. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2021, 33, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogozhin, A.; Pang, K.K.; Bukharaeva, E.; Young, C.; Slater, C.R. Recovery of mouse neuromuscular junctions from single and repeated injections of botulinum neurotoxin A. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 3163–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, H.E.; Frizelle, S.; McGarraugh, P.; Mahowald, M.L. Pain behavior measures to quantitate joint pain and response to neurotoxin treatment in murine models of arthritis. Pain Med. 2009, 10, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanshan, N.; Mahowald, M.L.; Dorman, C.; Frizelle, S.; Krug, H.E. The analgesic effect of intraarticular OnabotulinumtoxinA in a female murine model of collagenase induced chronic degenerative monoarthritis. Toxicon 2019, 158, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora, V.R.M.M.; Clemente-Napimoga, J.T.; Abdalla, H.B.; Macedo, C.G.; de la Canales, G.; Barbosa, C.M.R. Botulinum toxin type A reduces inflammatory hypernociception induced by arthritis in the temporomadibular joint of rats. Toxicon 2017, 129, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, H.M.; Hielm-Björkman, A.K.; Innes, J.F.; Laitinen-Vapaavuori, O.M. The effect of intra-articular botulinum toxin A on substance P, prostaglandin E2, and tumor necrosis factor alpha in the canine osteoarthritic joint. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, F.; Rossi, C.; Gianfranceschi, L.; Rossetto, O.; Caleo, M. Long-distance retrograde effects of botulinum neurotoxin A. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, G.W.; Benton, M.G.; Akerley, W.; Mayhew, G.F.; Moehlenkamp, C.; Raterman, D.; Burgess, D.L.; Rowell, W.J.; Lambert, C.; Eng, K.; et al. Structural variation and its potential impact on genome instability: Novel discoveries in the EGFR landscape by long-read sequencing. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, B.J.; Silbert, P.L.; Dunne, J.W.; Song, S.; Singer, K.P. An open label pilot investigation of the efficacy of Botulinum toxin type A [Dysport] injection in the rehabilitation of chronic anterior knee pain. Disabil. Rehabil. 2006, 28, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, B.J.; Silbert, P.L.; Song, S.; Dunne, J.W.; Singer, K.P. Treatment of refractory anterior knee pain using botulinum toxin type A (Dysport) injection to the distal vastus lateralis muscle: A randomized placebo controlled crossover trial. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silbert, B.I.; Singer, B.J.; Silbert, P.L.; Gibbons, J.T.; Singer, K.P. Enduring efficacy of Botulinum toxin type A injection for refractory anterior knee pain. Disabil. Rehabil. 2012, 34, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, S.M.; Bennell, K.L.; Crossley, K.M.; Hodges, P.W.; Mcconnell, J. Physical therapy alters recruitment of the vasti in patellofemoral pain syndrome. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudon, B.; Poussel, M.; Billon-Grumillier, C.; Beyaert, C.; Paysant, J. Knee kinetic pattern during gait and anterior knee pain before and after rehabilitation in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Biomechanics of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome. (2021, June 5). Physiopedia. Retrieved 06:25. Available online: https://www.physio-pedia.com/index.php?title=Clinical_Biomechanics_of_Patellofemoral_Pain_Syndrome&oldid=275659 (accessed on 24 December 2022).
- Criswell, E. Cram’s Introduction to Surface Electromyography, 2nd ed.; Jones and Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011; p. 365. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, G.M.; Watson, D.J.; Bellamay, N. Comparison of the responsiveness and relative effect size of the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index and Short-Form Medical Outcomes Study Survey in a randomized clinical trail of osteoarthritis patients. Arthritis. Care Res. 1999, 12, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angst, F.; Aeschlimann, A.; Steiner, W.; Stucki, G. Responsiveness of the WOMAC Osteoarthritis Index as compared with SF-36 in patients with osteoarthritis of legs undergoing a comprehensive rehabilitation program. Ann. Rheum. Dis 2001, 60, 834–840. [Google Scholar]
- Basmajian, J.V.; Blumenstein, R. Electrode Placement in EMG Biofeedback; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Chu, N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Tang, S. Relationship between the EMG ratio of muscle activation and bony structure in osteoarthritic knee patients with and without patellar malalignment. J. Rehabil. Med. 2008, 40, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mostamand, J.; Bader, D.L.; Hudson, Z. The effect of patellar taping on EMG activity of vasti muscles during squatting in individuals with patellofemoral pain syndrome. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossley, K.M.; Stefanik, J.J.; Selfe, J.; Collins, N.; Davis, I.S.; Powers, C.M.; McConnell, J.; Vicenzino, B.; Bazett-Jones, D.M.; Esculier, J.-F.; et al. 2016 Patellofemoral pain consensus statement from the 4th International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat, Manchester. Part 1: Terminology, definitions, clinical examination, natural history, patellofemoral osteoarthritis and patient-reported outcome measures. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, P.; Moghaddamshahabi, R.; Webster, T.J.; Koyuncu, A.C.C.; Ahmadian, E.; Khan, W.S.; Mohamed, A.J.; Eftekhari, A. The Use of Infrapatellar Fat Pad-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Articular Cartilage Regeneration: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paiva, A.; Meunier, F.A.; Molgo, J.; Aoki, K.R.; Dolly, J.O. Functional repair of motor endplates after botulinum toxin type A poisoning: Biphasic switch of synaptic activity between nerve sprouts and their parent terminals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999, 96, 3200–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intiso, D. Therapeutic use of botulinum toxin in neurorehabilitation. J. Toxicol. 2012, 2012, 802–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.A.; Paz, L.B.; Frank, M.I.; Engelmann, A.M.; Krause, A.; De La Côrte, F.D. Safety and Synovial Inflammatory Response After Intra-articular Injection of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Healthy Horses. J. Equine. Vet. Sci. 2022, 110, 103865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Huang, B.; Yu, K. The efficacy and safety of Botulinum Toxin Type A in painful knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060519895868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mitsudomi, T. Not all epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer are created equal: Perspectives for individualized treatment strategy. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.H.; Mori, D.; Kobayashi, H.; Mori, Y.; Nakamoto, H.; Okada, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sugita, S.; Yano, F.; Chung, U.-I.; et al. Excessive mechanical loading promotes osteoarthritis through the gremlin-1-NF-κB pathway. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matak, I.; Bölcskei, K.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Helyes, Z. Mechanisms of Botulinum Toxin Type A Action on Pain. Toxins 2019, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Lee, S.-K.; Ahnn, J. Botulinum Toxin as a Pain Killer: Players and Actions in Antinociception. Toxins 2015, 7, 2435–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Meng, H. Combination of Botulinum Toxin and minocycline Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain Through Antioxidant Stress and Anti-Inflammation via Promoting SIRT1 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 602417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotkin, L.I.; Manolagas, S.C.; Bellido, T. Transduction of cell survival signals by connexin-43 hemichannels. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8648–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago-Fuentes, R.; Fernández-Puente, P.; Megias, D.; Carpintero-Fernández, P.; Mateos, J.; Acea, B.; Fonseca, E.; Blanco, F.J.; Mayan, M.D. Proteomic Analysis of Connexin 43 Reveals Novel Interactors Related to Osteoarthritis. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 2015, 14, 1831–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, F.; Krattinger, N.; Mazzolai, L.; Simon, A.; Waeber, G.; Meda, P.; Haefliger, J.-A. An angiotensin II- and NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism increases connexin 43 in murine arteries targeted by renin-dependent hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, T.; Muto, T.; Barrette, K.; Challyandra, L.; Roy, S. Downregulation of Connexin 43 promotes vascular cell loss and excess permeability associated with the development of vascular lesions in the diabetic retina. Mol. Vis. 2014, 20, 732–741. [Google Scholar]
- Jhang, J.-F.; Kuo, H.-C. Novel Applications of Non-Invasive Intravesical Botulinum Toxin a Delivery in the Treatment of Functional Bladder Disorders. Toxins 2021, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, F.-C.; Kuo, H.-C. Liposome-Encapsulated Botulinum Toxin A in Treatment of Functional Bladder Disorders. Toxins 2022, 14, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.-N.; Tang, A.C.-W.; Lin, S.-C.; Tang, S.F.-T. Anterior knee pain caused by patellofemoral pain syndrome can be relieved by Botulinum toxin type A injection. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 129, S27–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Groups | PFPS Group (n = 15) | Normal Group (n = 15) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Data | ||||
| Male/Female | 1/14 | 2/13 | 0.543 | |
| Age (years) | 47.5 ± 9.5 | 50.3 ± 5.5 | 0.322 | |
| Body height (cm) | 159.9 ± 7.8 | 159.2 ± 6.5 | 0.783 | |
| Body mass (kg) | 60.3 ± 12.3 | 59.7 ± 10.4 | 0.874 | |
| BMI | 23.4 ± 3.2 | 34.4 ± 3.0 | 0.986 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, A.C.W.; Chen, C.-K.; Wu, S.Y.; Tang, S.F.T. Improvement of Pain and Function by Using Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection in Patients with an Osteoarthritic Knee with Patellar Malalignment: An Electromyographic Study. Life 2023, 13, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010095
Tang ACW, Chen C-K, Wu SY, Tang SFT. Improvement of Pain and Function by Using Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection in Patients with an Osteoarthritic Knee with Patellar Malalignment: An Electromyographic Study. Life. 2023; 13(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Alice Chu Wen, Chih-Kuang Chen, Szu Yuan Wu, and Simon F. T. Tang. 2023. "Improvement of Pain and Function by Using Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection in Patients with an Osteoarthritic Knee with Patellar Malalignment: An Electromyographic Study" Life 13, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010095
APA StyleTang, A. C. W., Chen, C.-K., Wu, S. Y., & Tang, S. F. T. (2023). Improvement of Pain and Function by Using Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection in Patients with an Osteoarthritic Knee with Patellar Malalignment: An Electromyographic Study. Life, 13(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010095






