Treatment Algorithm for Management of Benign Prostatic Obstruction: An Overview of Current Techniques
Abstract
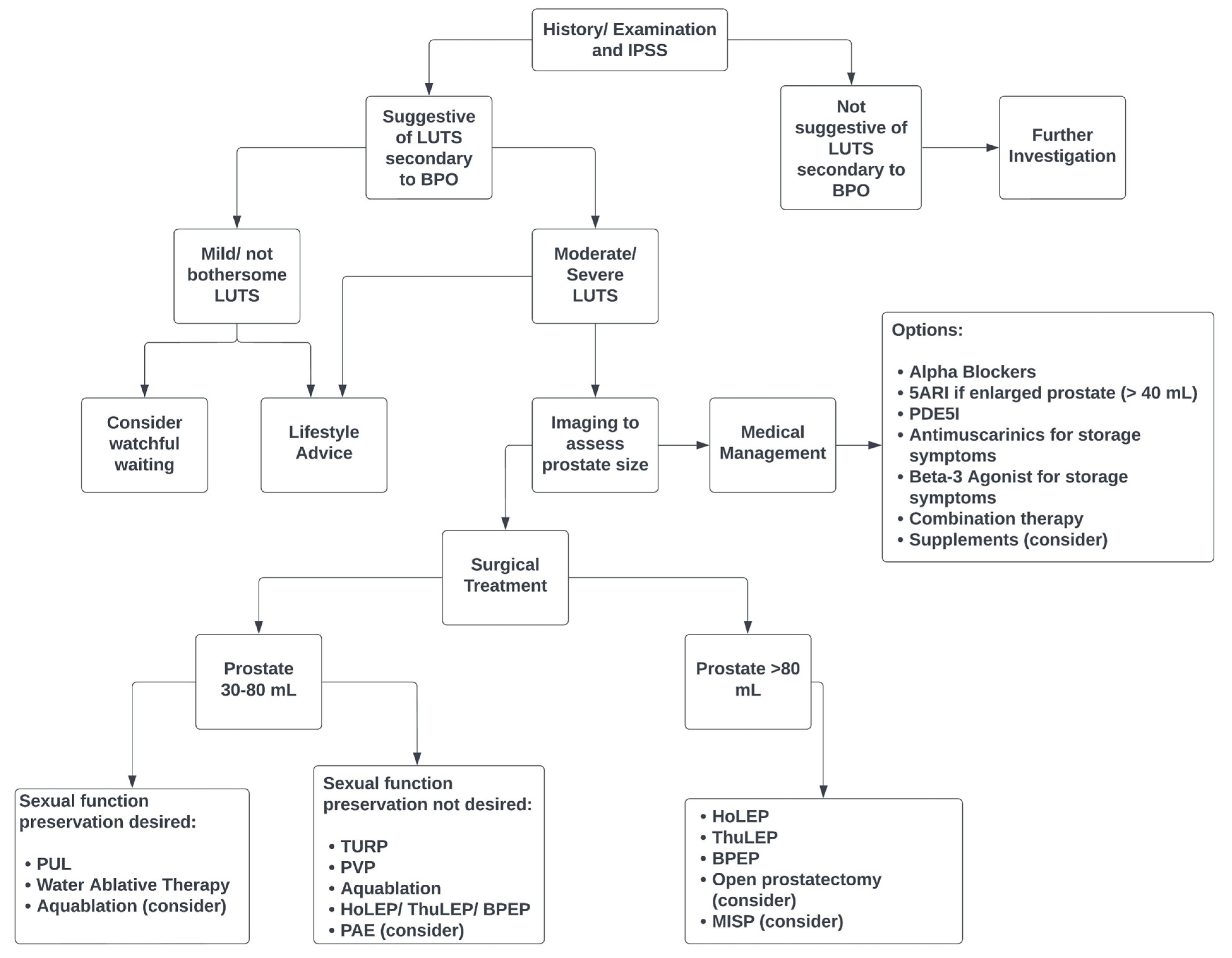
:1. Introduction
2. Diagnostic Workup
3. Management
4. Conservative Management
5. Medical Management
5.1. Alpha Blockers
5.2. 5-Alpha Reductase
5.3. Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors
5.4. Other Medications
5.5. Combination Therapy
5.6. Supplements
6. Surgical Management
6.1. Transurethral Resection of Prostate
6.2. Open Simple Prostatectomy
6.3. Minimally Invasive Simple Prostatectomy
6.4. Laser
- A.
- Photoselective Vaporisation of Prostate (PVP)
- B. Holmium Laser Enucleation of Prostate (HoLEP)
- C. Thulium Laser
6.5. Bipolar Transurethral Enucleation of Prostate
7. Alternative Modalities
7.1. Aquablation
7.2. Rezūm™
7.3. Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE)
7.4. Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL)
8. Future Modalities
8.1. iTind
8.2. Optilume
9. Cost-Effectiveness
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roehrborn, C.G. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: An Overview. Rev. Urol. 2005, 7, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.H.; Chan, E.M.C.; Lai, Y.K. The Global Burden of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Suggestive of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awedew, A.F.; Han, H.; Abbasi, B.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Ahmed, M.B.; Almidani, O.; Amini, E.; Arabloo, J.; Argaw, A.M.; Athari, S.S.; et al. The Global, Regional, and National Burden of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in 204 Countries and Territories from 2000 to 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022, 3, e754–e776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, C.; Link, C.L.; Onel, E.; Mazzetta, C.; Keech, M.; Hobbs, R.; Fourcade, R.; Kiemeney, L.; Lee, C.; Boyle, P.; et al. The Impact of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Comorbidities on Quality of Life: The BACH and UREPIK Studies. BJU Int. 2007, 99, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, E.D.; Wilson, S.S.; McConnell, J.D.; Slawin, K.M.; Lieber, M.C.; Smith, J.A.; Meehan, A.G.; Bautista, O.M.; Noble, W.R.; Kusek, J.W.; et al. Baseline Factors as Predictors of Clinical Progression of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Men Treated with Placebo. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassweiler, J.; Teber, D.; Kuntz, R.; Hofmann, R. Complications of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP)--Incidence, Management, and Prevention. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 969–979, discussion 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malde, S.; Umbach, R.; Wheeler, J.R.; Lytvyn, L.; Cornu, J.-N.; Gacci, M.; Gratzke, C.; Herrmann, T.R.W.; Mamoulakis, C.; Rieken, M.; et al. A Systematic Review of Patients’ Values, Preferences, and Expectations for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwun-Chung Cheng, B.; Kar-Kei Yuen, S.; Castellani, D.; Wroclawski, M.L.; Zhao, H.; Chiruvella, M.; Chua, W.-J.; Tiong, H.-Y.; Tanidir, Y.; Rosette, J.D.L.; et al. Defining Minimal Invasive Surgical Therapy for Benign Prostatic Obstruction Surgery: Perspectives from a Global Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Survey. Asian J. Urol. 2022, S221438822200090X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EAU. Guidelines on the Management of Non-Neurogenic Male LUTS. Available online: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/management-of-non-neurogenic-male-luts (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Lerner, L.B.; McVary, K.T.; Barry, M.J.; Bixler, B.R.; Dahm, P.; Das, A.K.; Gandhi, M.C.; Kaplan, S.A.; Kohler, T.S.; Martin, L.; et al. Management of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Attributed to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: AUA Guideline Part I—Initial Work-up and Medical Management. J. Urol. 2021, 206, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, L.B.; McVary, K.T.; Barry, M.J.; Bixler, B.R.; Dahm, P.; Das, A.K.; Gandhi, M.C.; Kaplan, S.A.; Kohler, T.S.; Martin, L.; et al. Management of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Attributed to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: AUA Guideline Part II—Surgical Evaluation and Treatment. J. Urol. 2021, 206, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrborn, C.G.; Girman, C.J.; Rhodes, T.; Hanson, K.A.; Collins, G.N.; Sech, S.M.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Garraway, W.M.; Lieber, M.M. Correlation between Prostate Size Estimated by Digital Rectal Examination and Measured by Transrectal Ultrasound. Urology 1997, 49, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, M.J.; Fowler, F.J.; O’Leary, M.P.; Bruskewitz, R.C.; Holtgrewe, H.L.; Mebust, W.K.; Cockett, A.T. The American Urological Association Symptom Index for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. The Measurement Committee of the American Urological Association. J. Urol. 1992, 148, 1549–1557, discussion 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhushankha, M.; Jayarajah, U.; Kuruppu, C.; Goonewardena, S.A.; Abeygunasekera, A.M. Clinical Characteristics and Outcome of High-Pressure Chronic Urinary Retention: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Urol. 2022, 15, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, M.; Gray, D.; Golding, S.E.; Hindley, R. Reaching a Tipping Point: A Qualitative Exploration of Quality of Life and Treatment Decision-Making in People Living with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Qual. Health Res. 2022, 32, 1979–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.L.; Brown, C.; Cromwell, D.A.; van der Meulen, J.; Emberton, M. The Impact of Self-Management of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms on Frequency-Volume Chart Measures. BJU Int. 2009, 104, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.C.; Vrydag, W. A1-, A2- and β-Adrenoceptors in the Urinary Bladder, Urethra and Prostate. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S88–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djavan, B.; Chapple, C.; Milani, S.; Marberger, M. State of the Art on the Efficacy and Tolerability of Alpha1-Adrenoceptor Antagonists in Patients with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Suggestive of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Urology 2004, 64, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwon, Y.N.; Park, J.J.; Yang, W.J.; Doo, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.K. Comparing Effects of Alpha-Blocker Management on Acute Urinary Retention Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Prostate Int. 2023, 11, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.-Q.; Mao, C.; Wong, S.Y.-S.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Fu, X.-H.; Dai, X.-Y.; Tang, J.-L. Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Monodrug Therapies for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Associated with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Network Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welk, B.; McArthur, E.; Fraser, L.-A.; Hayward, J.; Dixon, S.; Hwang, Y.J.; Ordon, M. The Risk of Fall and Fracture with the Initiation of a Prostate-Selective α Antagonist: A Population Based Cohort Study. BMJ 2015, 351, h5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatziralli, I.P.; Sergentanis, T.N. Risk Factors for Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacci, M.; Ficarra, V.; Sebastianelli, A.; Corona, G.; Serni, S.; Shariat, S.F.; Maggi, M.; Zattoni, F.; Carini, M.; Novara, G. Impact of Medical Treatments for Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia on Ejaculatory Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Sex. Med. 2014, 11, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, M.M.; de la Rosette, J.J.M.C.H.; Michel, M.C. Effects of Alpha(1)-Adrenoceptor Antagonists on Male Sexual Function. Drugs 2006, 66, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrborn, C.G.; Siami, P.; Barkin, J.; Damião, R.; Major-Walker, K.; Nandy, I.; Morrill, B.B.; Gagnier, R.P.; Montorsi, F.; CombAT Study Group. The Effects of Combination Therapy with Dutasteride and Tamsulosin on Clinical Outcomes in Men with Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: 4-Year Results from the CombAT Study. Eur. Urol. 2010, 57, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriole, G.; Bruchovsky, N.; Chung, L.W.K.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Rittmaster, R.; Roehrborn, C.; Russell, D.; Tindall, D. Dihydrotestosterone and the Prostate: The Scientific Rationale for 5alpha-Reductase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.V.; Hermann, D.J.; Cunningham, G.R.; Wilson, T.H.; Morrill, B.B.; Hobbs, S. Marked Suppression of Dihydrotestosterone in Men with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Dutasteride, a Dual 5α-Reductase Inhibitor. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2179–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittmaster, R.S.; Norman, R.W.; Thomas, L.N.; Rowden, G. Evidence for Atrophy and Apoptosis in the Prostates of Men given Finasteride. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guess, H.A.; Gormley, G.J.; Stoner, E.; Oesterling, J.E. The Effect of Finasteride on Prostate Specific Antigen: Review of Available Data. J. Urol. 1996, 155, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häggström, S.; T’rring, N.; M’ller, K.; Jensen, E.; Lund, L.; Nielsen, J.E.; Bergh, A.; Damber, J.-E. Effects of Finasteride on Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2002, 36, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, S.J.; Soloman, L.Z.; Wedderburn, A.W.; Kashif, K.M.; Summerton, D.; Basketter, V.; Holmes, S.A. A Prospective Study of the Natural History of Hematuria Associated with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and the Effect of Finasteride. J. Urol. 2000, 163, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-P.; Dai, B.; Zhang, H.-L.; Shi, G.; Ye, D.-W. Impact of Preoperative 5α-Reductase Inhibitors on Perioperative Blood Loss in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naslund, M.J.; Miner, M. A Review of the Clinical Efficacy and Safety of 5alpha-Reductase Inhibitors for the Enlarged Prostate. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mónica, F.Z.; De Nucci, G. Tadalafil for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2019, 20, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Liu, J.; Duan, L.; Cui, Y. Tadalafil 5 Mg Once Daily Improves Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Erectile Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Low. Urin. Tract. Symptoms 2018, 10, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gacci, M.; Corona, G.; Salvi, M.; Vignozzi, L.; McVary, K.T.; Kaplan, S.A.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Serni, S.; Mirone, V.; Carini, M.; et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Use of Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors Alone or in Combination with α-Blockers for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, P.; Kaplan, S.; De Koning Gans, H.J.; Millard, R. Safety and Tolerability of Tolterodine for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Men with Bladder Outlet Obstruction. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 999–1004, discussion 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, C.R.; Nazir, J.; Hakimi, Z.; Bowditch, S.; Fatoye, F.; Guelfucci, F.; Khemiri, A.; Siddiqui, E.; Wagg, A. Persistence and Adherence with Mirabegron versus Antimuscarinic Agents in Patients with Overactive Bladder: A Retrospective Observational Study in UK Clinical Practice. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.-H.; Kuo, H.-C. Mirabegron 25 Mg Monotherapy Is Safe but Less Effective in Male Patients with Overactive Bladder and Bladder Outlet Obstruction. Urology 2018, 117, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasopoulos, A.; Chapple, C.; Fowler, C.; Gratzke, C.; Kaplan, S.; Stief, C.; Tubaro, A. The Role of Antimuscarinics in the Management of Men with Symptoms of Overactive Bladder Associated with Concomitant Bladder Outlet Obstruction: An Update. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizaki, H.; Lee, K.-S.; Yamamoto, O.; Jong, J.J.; Katou, D.; Sumarsono, B.; Uno, S.; Yamaguchi, O. Mirabegron Add-on Therapy to Tamsulosin for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study (MATCH). Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Che, X.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, Y. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Tamsulosin Plus Tadalafil Compared with Tamsulosin Alone in Treating Males with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostrate Hyperplasia. Am. J. Mens. Health 2023, 17, 15579883231155096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamalunas, A.; Wendt, A.; Springer, F.; Vigodski, V.; Ciotkowska, A.; Rutz, B.; Wang, R.; Huang, R.; Liu, Y.; Schulz, H.; et al. Permixon®, Hexane-Extracted Serenoa Repens, Inhibits Human Prostate and Bladder Smooth Muscle Contraction and Exerts Growth-Related Functions in Human Prostate Stromal Cells. Life Sci. 2022, 308, 120931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vela-Navarrete, R.; Alcaraz, A.; Rodríguez-Antolín, A.; Miñana López, B.; Fernández-Gómez, J.M.; Angulo, J.C.; Castro Díaz, D.; Romero-Otero, J.; Brenes, F.J.; Carballido, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Hexanic Extract of Serenoa Repens (Permixon®) for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Associated with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (LUTS/BPH): Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials and Observational Studies. BJU Int. 2018, 122, 1049–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, J.V.; Trivisonno, L.; Sgarbossa, N.J.; Alvez, G.A.; Fieiras, C.; Escobar Liquitay, C.M.; Jung, J.H. Serenoa Repens for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Benign Prostatic Enlargement. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2023, CD001423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nunzio, C.; Salonia, A.; Gacci, M.; Ficarra, V. The Role of Combination Therapy with α-Blockers and Hexanic Extract of Serenoa Repens in the Treatment of LUTS/BPH. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavitakis, M.; Kyriazis, I.; Omar, M.I.; Gravas, S.; Cornu, J.-N.; Drake, M.J.; Gacci, M.; Gratzke, C.; Herrmann, T.R.W.; Madersbacher, S.; et al. Management of Urinary Retention in Patients with Benign Prostatic Obstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornu, J.-N.; Ahyai, S.; Bachmann, A.; de la Rosette, J.; Gilling, P.; Gratzke, C.; McVary, K.; Novara, G.; Woo, H.; Madersbacher, S. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Functional Outcomes and Complications Following Transurethral Procedures for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Resulting from Benign Prostatic Obstruction: An Update. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 1066–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, O.; Gratzke, C.; Bachmann, A.; Seitz, M.; Schlenker, B.; Hermanek, P.; Lack, N.; Stief, C.G.; Urology Section of the Bavarian Working Group for Quality Assurance. Morbidity, Mortality and Early Outcome of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate: A Prospective Multicenter Evaluation of 10,654 Patients. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eredics, K.; Wachabauer, D.; Röthlin, F.; Madersbacher, S.; Schauer, I. Reoperation Rates and Mortality After Transurethral and Open Prostatectomy in a Long-Term Nationwide Analysis: Have We Improved Over a Decade? Urology 2018, 118, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.E.; Scullion, M.M.; Omar, M.I.; Yuan, Y.; Mamoulakis, C.; N’Dow, J.M.; Chen, C.; Lam, T.B. Bipolar versus Monopolar Transurethral Resection of the Prostate for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Obstruction. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD009629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dong, W.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, Z.; Hai, B.; Pang, Z. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Efficacy and Safety Comparing Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate with Transurethral Resection of the Prostate for Patients with Prostate Volume Less than 100 ML or 100 g. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2022, 11, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.K.; Kroeze, S.G.C.; Chopra, S.; Bottle, A.; Patel, A. Examining the “Gold Standard”: A Comparative Critical Analysis of Three Consecutive Decades of Monopolar Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Outcomes. BJU Int. 2012, 110, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavan, L.; Kyriazis, G.; Mbiabjeu, D.; Gormley, R.; Hall, S.; Robinson, R.; Hodgson, D. Day-Case Surgery Is Possible in the Majority of Men Undergoing Transurethral Resection of the Prostate—A Report on over 1000 Cases. J. Clin. Urol. 2018, 11, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, A.; Ren, R.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Y.; Zou, Y.; Gong, M.; Liu, C.; Su, Z.; et al. Transurethral Enucleation of the Prostate versus Transvesical Open Prostatectomy for Large Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. World J. Urol. 2016, 34, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qiu, J.; Hou, Q.; Wang, D.; Huang, W.; Hu, C.; Li, K.; Gao, X. Endoscopic Enucleation versus Open Prostatectomy for Treating Large Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariser, J.J.; Packiam, V.T.; Adamsky, M.A.; Bales, G.T. Trends in Simple Prostatectomy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2016, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levasseur-Fortin, P.; Law, K.W.; Nguyen, D.-D.; Zakaria, A.; Misrai, V.; Elterman, D.; Bhojani, N.; Rijo, E.; Zorn, K.C. National Discrepancies in Residency Training of Open Simple Prostatectomy for Benign Prostatic Enlargement: Redefining Our Gold Standard. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2020, 14, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, D.; Peng, L.; Ren, Z.; Gou, H.; Li, Y.; Wei, Q. Comparison Between Minimally Invasive Simple Prostatectomy and Open Simple Prostatectomy for Large Prostates: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Trials. J. Endourol. 2019, 33, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuschi, A.; Al Salhi, Y.; Velotti, G.; Capone, L.; Martoccia, A.; Suraci, P.P.; Scalzo, S.; Annino, F.; Khorrami, S.; Asimakopoulos, A.; et al. Holmium Laser Enucleation of Prostate versus Minimally Invasive Simple Prostatectomy for Large Volume (≥120 ML) Prostate Glands: A Prospective Multicenter Randomized Study. Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 73, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravas, S.; Bachmann, A.; Reich, O.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Gilling, P.J.; De La Rosette, J. Critical Review of Lasers in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). BJU Int. 2011, 107, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, A.; Tubaro, A.; Barber, N.; d’Ancona, F.; Muir, G.; Witzsch, U.; Grimm, M.-O.; Benejam, J.; Stolzenburg, J.-U.; Riddick, A.; et al. 180-W XPS GreenLight Laser Vaporisation versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Obstruction: 6-Month Safety and Efficacy Results of a European Multicentre Randomised Trial—The GOLIATH Study. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.A.; Tubaro, A.; Barber, N.; d’Ancona, F.; Muir, G.; Witzsch, U.; Grimm, M.-O.; Benejam, J.; Stolzenburg, J.-U.; Riddick, A.; et al. A Multicenter Randomized Noninferiority Trial Comparing GreenLight-XPS Laser Vaporization of the Prostate and Transurethral Resection of the Prostate for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Obstruction: Two-Yr Outcomes of the GOLIATH Study. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichy, I.; Law, K.; Tholomier, C.; Nguyen, D.-D.; Sadri, I.; Bouhadana, D.; Couture, F.; Zakaria, A.S.; Bhojani, N.; Zorn, K.C.; et al. Global Experience and Progress in GreenLight-XPS 180-Watt Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshal, A.M.; Soltan, M.; El-Tabey, N.A.; Laymon, M.; Nabeeh, A. Randomised Trial of Bipolar Resection vs Holmium Laser Enucleation vs Greenlight Laser Vapo-enucleation of the Prostate for Treatment of Large Benign Prostate Obstruction: 3-years Outcomes. BJU Int. 2020, 126, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmivalli, A.; Ettala, O.; Nurminen, P.; Kinnala, P.; Boström, P.J.; Kytö, V. Short- and Long-Term Risks of Photoselective Laser Vaporization of the Prostate: A Population-Based Comparison with Transurethral Resection of the Prostate. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallara, G.; Capogrosso, P.; Schifano, N.; Costa, A.; Candela, L.; Cazzaniga, W.; Boeri, L.; Belladelli, F.; Scattoni, V.; Salonia, A.; et al. Ten-Year Follow-up Results After Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate. Eur. Urol. Focus 2021, 7, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Yao, H.; Bao, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, J. The Efficacy and Safety of HoLEP for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with Large Volume: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Mens. Health 2022, 16, 15579883221113204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiba, M.; Hoeh, B.; Welte, M.N.; Krimphove, M.J.; Vitucci, K.; Lindemann, N.; Schröder, J.; Jost, L.; Schmidt, F.E.; von Hollen, A.; et al. Learning Curve and Functional Outcomes after Laser Enucleation of the Prostate for Benign Prostate Hyperplasia According to Surgeon’s Caseload. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 3007–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottingham, C.U.; Large, T.; Agarwal, D.K.; Rivera, M.E.; Krambeck, A.E. Comparison of Newly Optimized Moses Technology vs Standard Holmium:YAG for Endoscopic Laser Enucleation of the Prostate. J. Endourol. 2021, 35, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, M.M.; Sriprasad, S.; Bhat, T.; Madaan, S. Is Thulium Laser Enucleation of Prostate an Alternative to Holmium and TURP Surgeries—A Systematic Review? Turk. J. Urol. 2020, 46, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartung, F.O.; Kowalewski, K.-F.; von Hardenberg, J.; Worst, T.S.; Kriegmair, M.C.; Nuhn, P.; Herrmann, T.R.W.; Michel, M.S.; Herrmann, J. Holmium Versus Thulium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Eur. Urol. Focus 2022, 8, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H.; Lin, T.-P.; Chang, Y.-H.; Huang, W.J.S.; Lin, A.T.L.; Chen, K.-K. Vapoenucleation of the Prostate Using a High-Power Thulium Laser: A One-Year Follow-up Study. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcaniolo, D.; Manfredi, C.; Veccia, A.; Herrmann, T.R.W.; Lima, E.; Mirone, V.; Fusco, F.; Fiori, C.; Antonelli, A.; Rassweiler, J.; et al. Bipolar Endoscopic Enucleation versus Bipolar Transurethral Resection of the Prostate: An ESUT Systematic Review and Cumulative Analysis. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRae, C.; Gilling, P. How I Do It: Aquablation of the Prostate Using the AquaBeam System. Can. J. Urol. 2016, 23, 8590–8593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taktak, S.; Jones, P.; Haq, A.; Rai, B.P.; Somani, B.K. Aquablation: A Novel and Minimally Invasive Surgery for Benign Prostate Enlargement. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2018, 10, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilling, P.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Anderson, P.; Sutton, M.; Aho, T.; Kramolowsky, E.; Thomas, A.; Cowan, B.; Kaufman, R.P.; et al. WATER: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Aquablation® vs Transurethral Resection of the Prostate in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Urol. 2018, 199, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilling, P.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Anderson, P.; Sutton, M.; Aho, T.; Kramolowsky, E.; Thomas, A.; Cowan, B.; Kaufman, R.P.; et al. Three-Year Outcomes after Aquablation Therapy Compared to TURP: Results from a Blinded Randomized Trial. Can. J. Urol. 2020, 27, 10072–10079. [Google Scholar]
- Zorn, K.C.; Bidair, M.; Trainer, A.; Arther, A.; Kramolowsky, E.; Desai, M.; Doumanian, L.; Elterman, D.; Kaufman, R.P.; Lingeman, J.; et al. Aquablation Therapy in Large Prostates (80–150 Cc) for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: WATER II 3-Year Trial Results. BJUI Compass 2022, 3, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.C.; Qu, L.; Webb, H.; Qin, K.; Chislett, B.; Xue, A.; Khaleel, S.; De Jesus Escano, M.; Chung, E.; Adam, A.; et al. Aquablation in Men with Benign Prostate Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Urol. 2023, 17, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, T.; Gilling, P.; El Hajj, A.; Anderson, P.; Barber, N. First Multi-Center All-Comers Study for the Aquablation Procedure. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.; Geraghty, R.; Jones, P.; Rai, B.P.; Somani, B.K. Rezum: A New Transurethral Water Vapour Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2018, 10, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McVary, K.T.; Gange, S.N.; Gittelman, M.C.; Goldberg, K.A.; Patel, K.; Shore, N.D.; Levin, R.M.; Rousseau, M.; Beahrs, J.R.; Kaminetsky, J.; et al. Erectile and Ejaculatory Function Preserved with Convective Water Vapor Energy Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Randomized Controlled Study. J. Sex. Med. 2016, 13, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, M.; Loloi, J.; Tang, K.; Syed, U.; Ciatto, M. Emerging Outcomes of Water Vapor Thermal Therapy (Rezum) in a Broad Range of Patients with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review. Low. Urin. Tract. Symptoms 2022, 14, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinos, T.; Katafigiotis, I.; Leotsakos, I.; Grivas, N.; Zabaftis, C.; Ermidis, D.; Sfoungaristos, S.; Karavitakis, M. Rezūm Water Vapor Therapy for the Treatment of Patients with Urinary Retention and Permanent Catheter Dependence Secondary to Benign Prostate Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review of the Literature. World J. Urol. 2023, 41, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisco, J.M.; Bilhim, T.; Costa, N.V.; Torres, D.; Pisco, J.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Oliveira, A.G. Randomised Clinical Trial of Prostatic Artery Embolisation Versus a Sham Procedure for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumstein, V.; Betschart, P.; Vetterlein, M.W.; Kluth, L.A.; Hechelhammer, L.; Mordasini, L.; Engeler, D.S.; Kessler, T.M.; Schmid, H.-P.; Abt, D. Prostatic Artery Embolization versus Standard Surgical Treatment for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Li, J.; Huang, X.Z.; Liu, Q. An Updated Meta-Analysis of Prostatic Arterial Embolization versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 2455–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, D.; Harris, M.; Drake, T.; Maher, B.; Modi, S.; Dyer, J.; Somani, B.; Hacking, N.; Bryant, T. Factors Predicting a Good Symptomatic Outcome After Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE). Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 41, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNicholas, T.A.; Woo, H.H.; Chin, P.T.; Bolton, D.; Fernández Arjona, M.; Sievert, K.-D.; Schoenthaler, M.; Wetterauer, U.; Vrijhof, E.J.E.J.; Gange, S.; et al. Minimally Invasive Prostatic Urethral Lift: Surgical Technique and Multinational Experience. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eure, G.; Rukstalis, D.; Roehrborn, C. Prostatic Urethral Lift for Obstructive Median Lobes: Consistent Results Across Controlled Trial and Real-World Settings. J. Endourol. 2023, 37, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Rajkumar, G.N.; Rai, B.P.; Aboumarzouk, O.M.; Cleaveland, P.; Srirangam, S.J.; Somani, B.K. Medium-Term Outcomes of Urolift (Minimum 12 Months Follow-up): Evidence From a Systematic Review. Urology 2016, 97, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrborn, C.G.; Barkin, J.; Gange, S.N.; Shore, N.D.; Giddens, J.L.; Bolton, D.M.; Cowan, B.E.; Cantwell, A.L.; McVary, K.T.; Te, A.E.; et al. Five Year Results of the Prospective Randomized Controlled Prostatic Urethral L.I.F.T. Study. Can. J. Urol. 2017, 24, 8802–8813. [Google Scholar]
- Sønksen, J.; Barber, N.J.; Speakman, M.J.; Berges, R.; Wetterauer, U.; Greene, D.; Sievert, K.-D.; Chapple, C.R.; Montorsi, F.; Patterson, J.M.; et al. Prospective, Randomized, Multinational Study of Prostatic Urethral Lift Versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate: 12-Month Results from the BPH6 Study. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.B.; Tayon, K.; Madiraju, S.; Carrion, R.E.; Perito, P. Prostatic Urethral Lift: Does Size Matter? J. Endourol. 2018, 32, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.E.; Chughtai, B.; Dornbier, R.A.; McVary, K.T. Surgical Reintervention Rate after Prostatic Urethral Lift: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Involving over 2,000 Patients. J. Urol. 2020, 204, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, L.; Dale, M.; Cleves, A.; Pelekanou, C.; Morris, R. UroLift for Treating Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A NICE Medical Technology Guidance Update. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 2022, 20, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, D.; Jones, P.; Somani, B.K. ITIND: The Second-Generation Temporary Implantable Nitinol Device for Minimally Invasive Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2020, 12, 1756287220934355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chughtai, B.; Elterman, D.; Shore, N.; Gittleman, M.; Motola, J.; Pike, S.; Hermann, C.; Terrens, W.; Kohan, A.; Gonzalez, R.R.; et al. The ITind Temporarily Implanted Nitinol Device for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Urology 2021, 153, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, S.A.; Pichardo, M.; Rijo, E.; Espino, G.; Lay, R.R.; Estrella, R. One-Year Outcomes after Treatment with a Drug-Coated Balloon Catheter System for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Related to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021, 24, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, S.A.; Moss, J.; Freedman, S.; Coutinho, K.; Wu, N.; Efros, M.; Elterman, D.; D’Anna, R.; Padron, O.; Robertson, K.J.; et al. The PINNACLE Study: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Sham-Controlled Study Evaluating the Optilume BPH Catheter System for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Urol. 2023, 210, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.; Jack, G.; Witjes, W.; Bjartell, A.; Caris, C.; Patel, A.; Taille, A.; Bolton, D.; Tubaro, A. Medical Therapy versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) for the Treatment of Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Enlargement (BPE): A Cost Minimisation Analysis. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wymer, K.M.; Narang, G.; Slade, A.; Sharma, V.; Thao, V.; Borah, B.J.; Rivera, M.; Cheney, S.; Humphreys, M.R. Evaluation of the Cost-Effectiveness of Surgical Treatment Options for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Urology 2023, 171, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Modality | Advantages | Disadvantages | AUA Recommendations | EAU Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) |
|
|
|
|
| Photoselective Vaporisation of Prostate (PVP)—‘Greenlight laser’ |
|
|
|
|
| Holmium Laser Enucleation of Prostate (HoLEP) |
|
|
|
|
| Thulium Laser |
|
|
|
|
| Open Prostatectomy (OSP) |
|
|
|
|
| Laparoscopic/Robotic Prostatectomy |
|
|
|
|
| Aquablation |
|
|
|
|
| Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) |
|
|
|
|
| Water Ablative Therapy (Rezūm) |
|
|
|
|
| Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL)—Urolift |
|
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hughes, T.; Harper, P.; Somani, B.K. Treatment Algorithm for Management of Benign Prostatic Obstruction: An Overview of Current Techniques. Life 2023, 13, 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13102077
Hughes T, Harper P, Somani BK. Treatment Algorithm for Management of Benign Prostatic Obstruction: An Overview of Current Techniques. Life. 2023; 13(10):2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13102077
Chicago/Turabian StyleHughes, Thomas, Philip Harper, and Bhaskar K. Somani. 2023. "Treatment Algorithm for Management of Benign Prostatic Obstruction: An Overview of Current Techniques" Life 13, no. 10: 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13102077
APA StyleHughes, T., Harper, P., & Somani, B. K. (2023). Treatment Algorithm for Management of Benign Prostatic Obstruction: An Overview of Current Techniques. Life, 13(10), 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13102077






