Oral Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil Orally Disintegrating Tablets under Various Gastric pH Levels Following Administration of Omeprazole in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Solubility of Sildenafil Is Affected by the pH
1.2. Sildenafil and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
1.3. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
1.4. Three-Dimensional Printing of the Sildenafil Orally Disintegrating Tablet (ODT) Formulation
2. Result
2.1. Dissolution Test
2.2. Gastric pH Changed Following Oral Administration of Omeprazole
2.3. Plasma Concentration and Pharmacokinetic Parameters of ODT and RLD (with and without Pretreatment with Omeprazole)
2.4. The Absorption Effect of Sildenafil with and without Pretreatment with Omeprazole
3. Materials
3.1. PPIs (Proton Pump Inhibitors)
3.2. RLD (Sildenafil Citrate Commercial Tablet as Reference Drug)
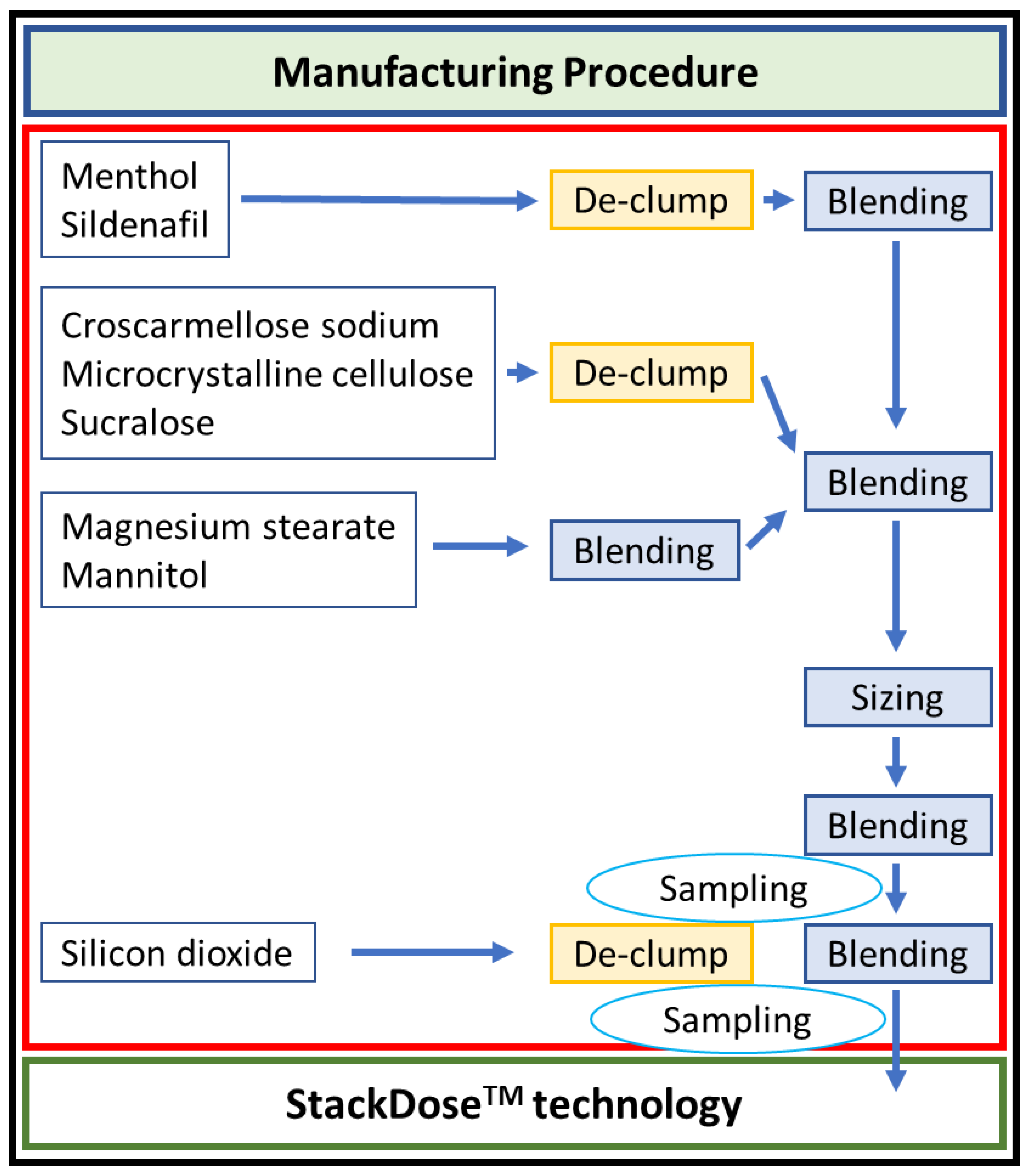
3.3. ODT (Orally Disintegrating Tablet)
3.4. Dissolution Test
3.5. Animals
3.6. Influence of Omeprazole on Gastric Acid
3.7. Sildenafil Citrate ODT or RLD Pharmacokinetics Study with and without Omeprazole
3.8. Preparation of Samples
3.9. Instrumentation and Chromatographic Conditions
3.10. Pharmacokinetics and Statistical Analysis of Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldstein, I.; Lue, T.F.; Padma-Nathan, H.; Rosen, R.C.; Steers, W.D.; Wicker, P.A. Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Sildenafil Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonia, A.; Rigatti, P.; Montorsi, F. Sildenafil in erectile dysfunction: A critical review. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2003, 19, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, H.A.; Mac Donald, R.; Rutks, I.R.; Nelson, D.B.; Wilt, T.J. Sildenafil for male erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatdee, S.; Atipairin, A.; Yoon, A.S.; Srichana, T.; Changsan, N.; Suwandecha, T.; Chanthorn, W.; Phoem, A. Oral bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of sildenafil citrate dry foam tablets in rats. Cogent Med. 2018, 5, 1510821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.Y.; Seo, Y.G.; Kim, G.K.; Woo, J.S.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.G. Comparison of the solubility and pharmacokinetics of sildenafil salts. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akula, P.; Lakshmi, P.K. Effect of pH on weakly acidic and basic model drugs and determination of their ex vivo transdermal permeation routes. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 54, e000070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.; Gingell, C.; Collins, M.; Wicker, P.A.; Osterloh, I.H. Clinical safety of oral sildenafil citrate (VIAGRA) in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 1998, 10, 69–73, discussion 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; Tack, J. The effect of sildenafil on gastric motility and satiation in healthy controls. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Conklin, J.L.; Park, H. The effect of sildenafil on segmental oesophageal motility and gastro-oesophageal reflux. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.; Horn, J. Clinical pharmacology of proton pump inhibitors: What the practising physician needs to know. Drugs 2003, 63, 2739–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Klotz, U. Proton pump inhibitors: An update of their clinical use and pharmacokinetics. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 64, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.E.; Peura, D.; Benjamin, S.B.; Joelsson, B.; Whipple, J. Efficacy of omeprazole for the treatment of symptomatic acid reflux disease without esophagitis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 1810–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, X.; Chen, R.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, N.; Gao, X.; Zheng, A. Innovative color jet 3D printing of levetiracetam personalized paediatric preparations. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Luo, B.Y.; LaBadie, R.R.; Zhu, H.; Feng, Y.; Ernst, C.; Crownover, P.H.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, Q. Bioequivalence and Bioavailability of an Orodispersible Tablet of Sildenafil Citrate in Healthy Chinese Male Subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2020, 9, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, M.; Kutinova-Canova, N.; Rysanek, P.; Horinkova, J.; Moskorova, D.; Slanar, O. Gastric pH in Rats: Key Determinant for Preclinical Evaluation of pH-dependent Oral Drug Absorption. Prague Med. Rep. 2019, 120, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressman, J.B.; Berardi, R.R.; Dermentzoglou, L.C.; Russell, T.L.; Schmaltz, S.P.; Barnett, J.L.; Jarvenpaa, K.M. Upper gastrointestinal (GI) pH in young, healthy men and women. Pharm. Res. 1990, 7, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumuro, O.; Uchida, S.; Kashiwagura, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Tanaka, S.; Inui, N.; Watanabe, H.; Namiki, N. Changes in gefitinib, erlotinib and osimertinib pharmacokinetics under various gastric pH levels following oral administration of omeprazole and vonoprazan in rats. Xenobiotica 2018, 48, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambayashi, A.; Kiyota, T. A physiologically-based drug absorption modeling for orally disintegrating tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 152, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choonara, B.F.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Tomar, L.K.; Tyagi, C.; Pillay, V. A menthol-based solid dispersion technique for enhanced solubility and dissolution of sulfamethoxazole from an oral tablet matrix. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madgulkar, A.; Bandivadekar, M.; Shid, T.; Rao, S. Sugars as solid dispersion carrier to improve solubility and dissolution of the BCS class II drug: Clotrimazole. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.; Perez-Rodriguez, Z.; Hernandez-Armengol, R.; Quinones-Garcia, Y.; Betancourt-Puron, T.; Cabrera-Perez, M.A. Biowaiver or Bioequivalence: Ambiguity in Sildenafil Citrate BCS Classification. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Shin, S.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, J.B.; Shin, B.S. Physiologically Relevant In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation (IVIVC) Approach for Sildenafil with Site-Dependent Dissolution. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedberg, D.E.; Lebwohl, B.; Abrams, J.A. The impact of proton pump inhibitors on the human gastrointestinal microbiome. Clin. Lab. Med. 2014, 34, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
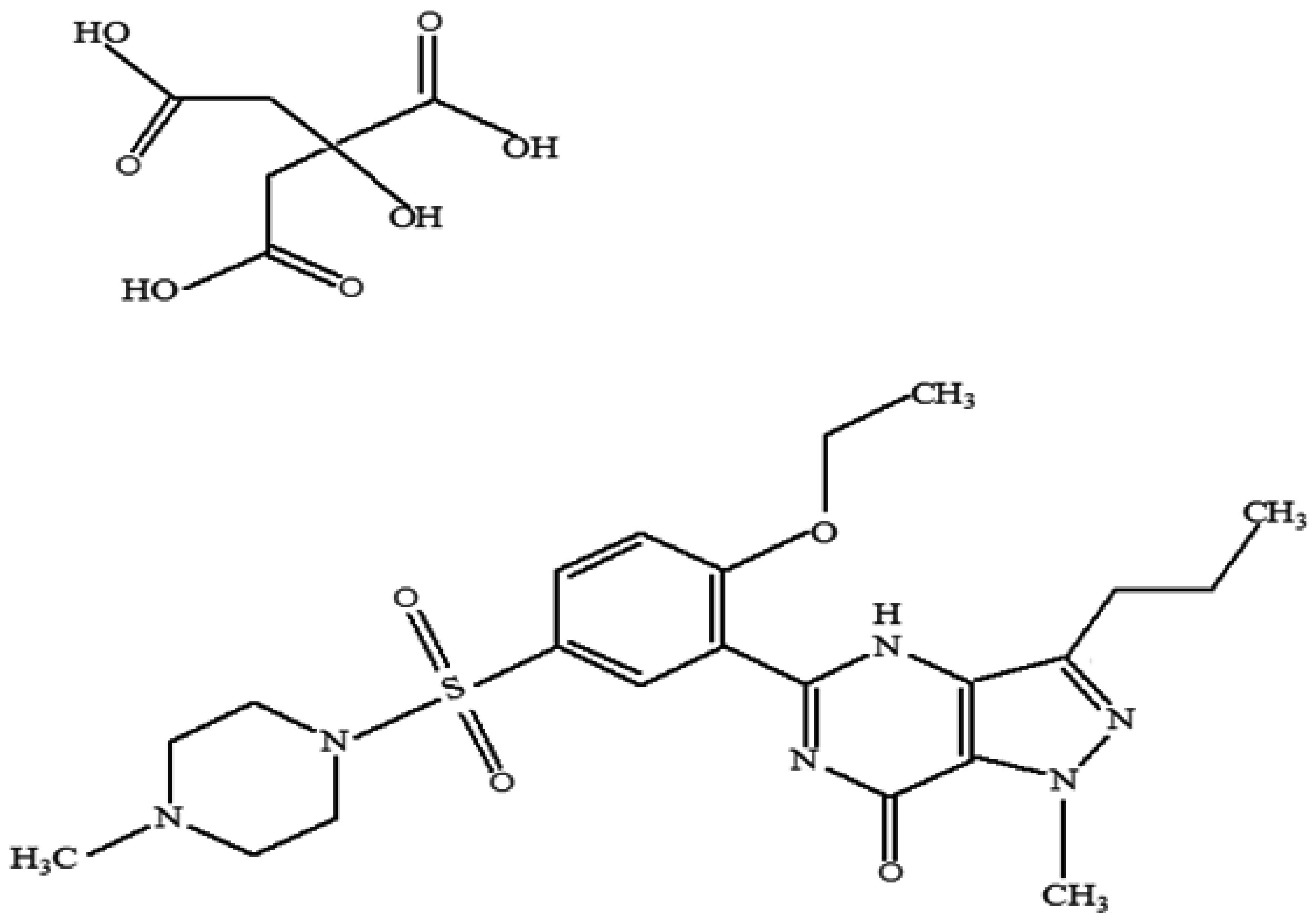




| pH | Solubility (mg/mL) in 37 °C Water |
|---|---|
| 1.2 | 37.25 |
| 4 | 21.19 |
| 5 | 18.53 |
| 6.8 | 0.4 |
| 7.4 | 0.24 |
| 8 | 0.22 |
| RLD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | AUC0–t | AUC0–∞ | Cmax | Tmax | T1/2 |
| (ng/mL × h) | (ng/mL × h) | (ng/mL) | (h) | (h) | |
| Mean | 126.1 | 159.5 | 92.102 | 0.94 | 1.90 |
| SD | 33.2 | 38.8 | 37.486 | 1.38 | 1.35 |
| CV(%) | 26.3 | 24.3 | 40.7 | 146.8 | 71.1 |
| Geometric Mean | 122.3 | 155.3 | 85.353 | 0.57 | 1.47 |
| Maximum | 162.2 | 198.3 | 133.953 | 3.00 | 3.66 |
| Minimum | 86.4 | 107.6 | 49.867 | 0.25 | 0.55 |
| Median | 127.9 | 169.4 | 92.295 | 0.38 | 1.64 |
| ODT | |||||
| Parameters | AUC0–t | AUC0–∞ | Cmax | Tmax | T1/2 |
| (ng/mL × h) | (ng/mL × h) | (ng/mL) | (h) | (h) | |
| Mean | 167.2 | 230.9 | 111.823 | 0.25 | 2.79 |
| SD | 73.2 | 33.3 | 47.649 | 0.00 | 1.13 |
| CV(%) | 43.8 | 14.4 | 42.6 | 0.0 | 40.4 |
| Geometric Mean | 153.5 | 228.9 | 103.873 | 0.25 | 2.58 |
| Maximum | 262.2 | 267.5 | 180.070 | 0.25 | 4.04 |
| Minimum | 88.7 | 193.5 | 64.174 | 0.25 | 1.39 |
| Median | 158.9 | 231.3 | 95.709 | 0.25 | 2.86 |
| RLD(PPI) | |||||
| Parameters | AUC0–t | AUC0–∞ | Cmax | Tmax | T1/2 |
| (ng/mL × h) | (ng/mL × h) | (ng/mL) | (h) | (h) | |
| Mean | 72.8 | 94.8 | 44.035 | 1.13 | 2.36 |
| SD | 36.8 | 42.2 | 29.625 | 1.15 | 1.60 |
| CV(%) | 50.6 | 44.5 | 67.3 | 102.1 | 67.6 |
| Geometric Mean | 63.2 | 85.0 | 35.137 | 0.67 | 1.89 |
| Maximum | 109.6 | 137.0 | 80.202 | 3.00 | 4.53 |
| Minimum | 25.1 | 35.4 | 13.932 | 0.25 | 0.76 |
| Median | 81.3 | 105.0 | 40.785 | 0.63 | 2.04 |
| ODT(PPI) | |||||
| Parameters | AUC0–t | AUC0–∞ | Cmax | Tmax | T1/2 |
| (ng/mL × h) | (ng/mL × h) | (ng/mL) | (h) | (h) | |
| Mean | 230.2 | 260.5 | 98.251 | 0.44 | 2.07 |
| SD | 185.0 | 175.0 | 49.279 | 0.38 | 1.66 |
| CV(%) | 80.4 | 67.2 | 50.2 | 86.4 | 80.3 |
| Geometric Mean | 155.9 | 201.3 | 84.781 | 0.40 | 1.44 |
| Maximum | 483.4 | 486.3 | 174.165 | 1.00 | 4.19 |
| Minimum | 40.4 | 60.2 | 42.382 | 0.25 | 0.52 |
| Median | 198.4 | 247.7 | 87.570 | 0.25 | 1.79 |
| Sildenafil Citrate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ODT * | RLD * (with PPI) | ODT * (with PPI) | ODT ** (with PPI) | |
| Cmax Geometric ratio (90 % CI) | 121.7 (77.8~190.3) | 41.2 ( 20.9~81.6) | 91.1 (50.7~163.5) | 221.2 (102.4~477.7) |
| AUC0–t Geometric ratio (90 % CI) | 125.5 (84.4~186.6) | 51.7 (31.3~85.5) | 127.4 (56.3~288.5) | 246.4 (98.7~615.5) |
| AUC0–∞ Geometric ratio (90 % CI) | 147.4 (118.3~183.7) | 54.7 (34.8~85.9) | 129.7 (66.9~251.2) | 237.0 (111.6~503.3) |
| Bioavailability F (%) *** | 144.0 | 59.4 | 163.0 | 274.8 |
| Ingredient | Amount (%) | Company | Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sildenafil citrate | 14.05 | Heteor | Telangana, India |
| Mannitol | 69.85 | ROQUETTE | Beinheim, France |
| AVICEL PH-102 NF microcrystalline cellulose | 5.6 | DuPont Nutrition | Wilmington, United States of America |
| Ac-Di Sol® SD711 NF croscarmellose sodium | 6 | DuPont Nutrition | Wilmington, United States of America |
| Silicon dioxide (Sylysia #350) | 0.5 | Fuji Silysia | Kasugai-shi, Japan |
| Magnesium stearate | 2 | Peter Greven Asia Sdn. Bhd. | Penang, Malaysia |
| Sucralose | 1 | Merck | Darmstadt, Germany |
| Menthol | 1 | BASF | Ludwigshafen, Germany |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shih, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-T.; Liao, Y.-J.; Liang, Y.-J. Oral Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil Orally Disintegrating Tablets under Various Gastric pH Levels Following Administration of Omeprazole in Rats. Life 2023, 13, 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13112126
Shih C-Y, Chen C-Y, Lin H-T, Liao Y-J, Liang Y-J. Oral Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil Orally Disintegrating Tablets under Various Gastric pH Levels Following Administration of Omeprazole in Rats. Life. 2023; 13(11):2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13112126
Chicago/Turabian StyleShih, Chin-Yu, Chao-Yi Chen, Hsien-Te Lin, Ying-Ju Liao, and Yao-Jen Liang. 2023. "Oral Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil Orally Disintegrating Tablets under Various Gastric pH Levels Following Administration of Omeprazole in Rats" Life 13, no. 11: 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13112126
APA StyleShih, C.-Y., Chen, C.-Y., Lin, H.-T., Liao, Y.-J., & Liang, Y.-J. (2023). Oral Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of Sildenafil Orally Disintegrating Tablets under Various Gastric pH Levels Following Administration of Omeprazole in Rats. Life, 13(11), 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13112126








