Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: An Update on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers, and Current Guidelines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
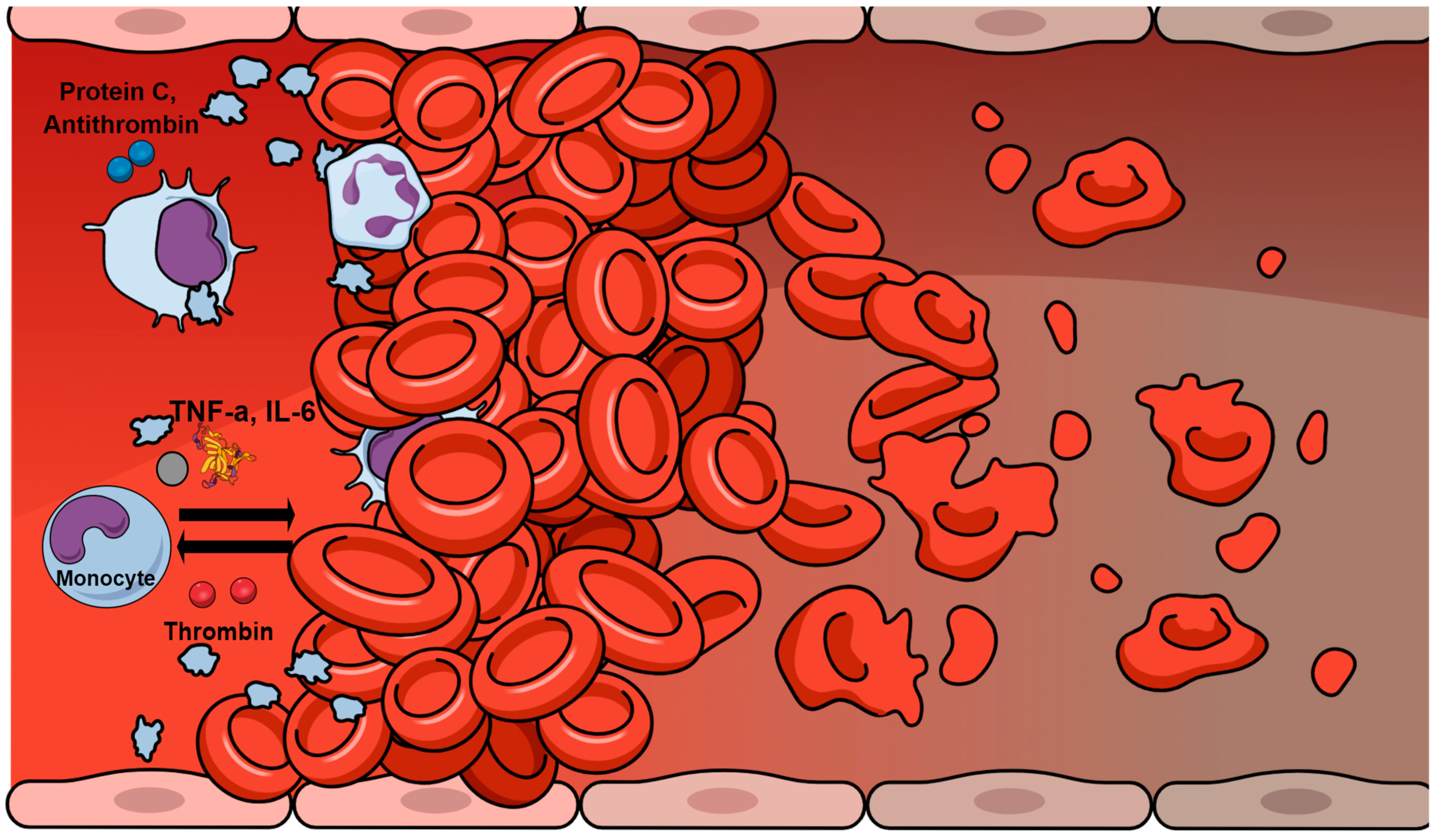
2. Hemostatic Abnormalities in Sepsis
3. Inflammation–Hemostasis Cross Talk
4. Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy and Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
5. Conventional Hemostatic Tests and Markers in Sepsis
5.1. Thrombocytopenia
5.2. Fibrin Degradation Products
5.3. Fibrinogen
5.4. Standard Coagulation Tests
6. Nonconventional Hemostatic Tests and Markers in Sepsis
6.1. Viscoelastic Tests
6.2. Measurement of Nuclear Materials
6.3. Measurement of Anticoagulant Proteins
6.4. Other Markers of Interest
7. From Guidelines to Clinical Practice
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustozzi, M.; Ehrlinder, H.; Bongiovanni, D.; Borovac, J.A.; Guerreiro, R.A.; Gąsecka, A.; Papakonstantinou, P.E.; Parker, W.A. Coagulopathy and sepsis: Pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and treatment. Blood Rev. 2021, 50, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.S.; Mannino, D.M.; Eaton, S.; Moss, M. The Epidemiology of Sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cecconi, M.; Evans, L.; Levy, M.; Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018, 392, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; van der Poll, T. Coagulation and sepsis. Thromb. Res. 2017, 149, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungurlu, S.; Kuppy, J.; Balk, R.A. Role of Antithrombin III and Tissue Factor Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis. Crit. Care Clin. 2020, 36, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, N.-L.; Aziz, M.; Gurien, S.D.; Wang, P. DAMPs and NETs in Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levi, M.; van der Poll, T. Inflammation and coagulation. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, S26–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; Poll, T. Coagulation in patients with severe sepsis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 41, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gando, S. Role of Fibrinolysis in Sepsis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2013, 39, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, J.L.; Bugge, T.H.; Goguen, J.D. Fibrin and fibrinolysis in infection and host defense. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, S.; Hammerschmidt, S. Fibrinolysis and host response in bacterial infections. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 98, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petros, S.; Kliem, P.; Siegemund, T. Thrombin generation in severe sepsis. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, S.R. Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature 2000, 407, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, T.; Ito, T.; Maruyama, I.; Jilma, B.; Brenner, T.; Müller, M.C.; Juffermans, N.P.; Thachil, J. Potential diagnostic markers for disseminated intravascular coagulation of sepsis. Blood Rev. 2016, 30, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, M.; Okajima, K.; Uchiba, M.; Horiuchi, S.; Okabe, H. Activated protein C inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by inhibiting activation of both nuclear factor-kappa B and activator protein-1 in human monocytes. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 88, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, A.P.; Bernard, G.R. Treating Patients with Severe Sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, F.B.; Toh, C.H.; Hoots, W.K.; Wada, H.; Levi, M. Towards definition, clinical and laboratory criteria, and a scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gando, S.; Levi, M.; Toh, C.H. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H. Sepsis-induced Coagulopathy and Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Anesthesiology 2020, 132, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H.; Warkentin, T.E.; Thachil, J.; van der Poll, T.; Levi, M. Diagnosis and management of sepsis-induced coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gando, S.; Iba, T.; Eguchi, Y.; Ohtomo, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Koseki, K.; Mayumi, T.; Murata, A.; Ikeda, T.; Ishikura, H.; et al. A multicenter, prospective validation of disseminated intravascular coagulation diagnostic criteria for critically ill patients: Comparing current criteria. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; Sivapalaratnam, S. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: An update on pathogenesis and diagnosis. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2018, 11, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, T.; Levi, M.; Levy, J.H. Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy and Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2020, 46, 089–095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Di Nisio, M.; Levy, J.H.; Kitamura, N.; Thachil, J. New criteria for sepsis-induced coagulopathy (SIC) following the revised sepsis definition: A retrospective analysis of a nationwide survey. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koyama, K.; Madoiwa, S.; Nunomiya, S.; Koinuma, T.; Wada, M.; Sakata, A.; Ohmori, T.; Mimuro, J.; Sakata, Y. Combination of thrombin-antithrombin complex, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, and protein C activity for early identification of severe coagulopathy in initial phase of sepsis: A prospective observational study. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hack, C.E. Fibrinolysis in Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2001, 27, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, B.; Massberg, S. Thrombosis as an intravascular effector of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.C.F.; Manolov, V.; Morgenstern, J.; Fleming, T.; Heitmeier, S.; Uhle, F.; Al-Saeedi, M.; Hackert, T.; Bruckner, T.; Schöchl, H.; et al. Acute fibrinolysis shutdown occurs early in septic shock and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality: Results of an observational pilot study. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, H. Classifying types of disseminated intravascular coagulation: Clinical and animal models. J. Intensive Care 2014, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Di Nisio, M.; Thachil, J.; Wada, H.; Asakura, H.; Sato, K.; Saitoh, D. A Proposal of the Modification of Japanese Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis (JSTH) Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Diagnostic Criteria for Sepsis-Associated DIC. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2018, 24, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iba, T.; Arakawa, M.; Di Nisio, M.; Gando, S.; Anan, H.; Sato, K.; Ueki, Y.; Levy, J.H.; Thachil, J. Newly Proposed Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy Precedes International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis Overt-Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation and Predicts High Mortality. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, T.; Arakawa, M.; Levy, J.H.; Yamakawa, K.; Koami, H.; Hifumi, T.; Sato, K. Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy and Japanese Association for Acute Medicine DIC in Coagulopathic Patients with Decreased Antithrombin and Treated by Antithrombin. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2018, 24, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamakawa, K.; Yoshimura, J.; Ito, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Hamasaki, T.; Fujimi, S. External Validation of the Two Newly Proposed Criteria for Assessing Coagulopathy in Sepsis. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folman, C.C.; Linthorst, G.E.; van Mourik, J.; van Willigen, G.; de Jonge, E.; Levi, M.; von dem Borne, A.E. Platelets release thrombopoietin (Tpo) upon activation: Another regulatory loop in thrombocytopoiesis? Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 83, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, O. The role of platelets in sepsis. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 5, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkata, C.; Kashyap, R.; Farmer, J.C.; Afessa, B. Thrombocytopenia in adult patients with sepsis: Incidence, risk factors, and its association with clinical outcome. J. Intensive Care 2013, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderschueren, S.; De Weerdt, A.; Malbrain, M.; Vankersschaever, D.; Frans, E.; Wilmer, A.; Bobbaers, H. Thrombocytopenia and prognosis in intensive care. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 1871–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawaz, M.; Fateh-Moghadam, S.; Pilz, G.; Gurland, H.-J.; Werdan, K. Platelet activation and interaction with leucocytes in patients with sepsis or multiple organ failure. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 25, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Damien, P.; Chabert, A.; Pozzetto, B.; Cognasse, F.; Garraud, O. Platelets and Infections—Complex Interactions with Bacteria. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, R.M.E.; Rodrigues, M.V.; Andreguetto, B.D.; Santos, T.M.; Gilberti, M.D.F.P.; de Castro, V.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M.; Dragosavac, D.; Carvalho-Filho, M.A.; De Paula, E.V. Association of the immature platelet fraction with sepsis diagnosis and severity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep08019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horan, J.T.; Francis, C.W. Fibrin Degradation Products, Fibrin Monomer and Soluble Fibrin in Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2001, 27, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeraro, F.; Ammollo, C.T.; Caironi, P.; Masson, S.; Latini, R.; Panigada, M.; Colucci, M. Low D-dimer levels in sepsis: Good or bad? Thromb. Res. 2019, 174, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favresse, J.; Lippi, G.; Roy, P.M.; Chatelain, B.; Jacqmin, H.; Ten Cate, H.; Mullier, F. D-dimer: Preanalytical, analytical, postanalytical variables, and clinical applications. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 548–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, J.M.; Ken-Dror, G.; Downey, C.; Abrams, S.T. The clinical utility of fibrin-related biomarkers in sepsis. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2013, 24, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelborg, K.; Larsen, J.B.; Hvas, A. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: Epidemiology, biomarkers, and management. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; Meijers, J.C. DIC: Which laboratory tests are most useful. Blood Rev. 2011, 25, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.H.; Tefferi, A.; Pruthi, R.K. How to Interpret and Pursue an Abnormal Prothrombin Time, Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, and Bleeding Time in Adults. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2007, 82, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarlatescu, E.; Juffermans, N.P.; Thachil, J. The current status of viscoelastic testing in septic coagulopathy. Thromb. Res. 2019, 183, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlinger, K.; Pérez-Ferrer, A.; Dirkmann, D.; Saner, F.; Maegele, M.; Calatayud, Á.A.P.; Kim, T.-Y. The role of evidence-based algorithms for rotational thromboelastometry-guided bleeding management. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2019, 72, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadou, P.; Sokou, R.; Tsantes, A.G.; Parastatidou, S.; Konstantinidi, A.; Houhoula, D.; Kokoris, S.; Iacovidou, N.; Tsantes, A.E. The Non-Activated Thromboelastometry (NATEM) Assay’s Application among Adults and Neonatal/Pediatric Population: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokou, R.; Ioakeimidis, G.; Piovani, D.; Parastatidou, S.; Konstantinidi, A.; Tsantes, A.G.; Lampridou, M.; Houhoula, D.; Iacovidou, N.; Kokoris, S.; et al. Development and validation of a sepsis diagnostic scoring model for neonates with suspected sepsis. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 1004727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokou, R.; Tritzali, M.; Piovani, D.; Konstantinidi, A.; Tsantes, A.G.; Ioakeimidis, G.; Lampridou, M.; Parastatidou, S.; Iacovidou, N.; Kokoris, S.; et al. Comparative Performance of Four Established Neonatal Disease Scoring Systems in Predicting In-Hospital Mortality and the Potential Role of Thromboelastometry. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsantes, A.G.; Sokou, R.; Konstantinidi, A.; Ioakeimidis, G.; Lampridou, M.; Parastatidou, S.; Theodoraki, M.; Piovani, D.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Boutsikou, T.; et al. Rotational Thromboelastometry in Neonates Admitted to a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Large Cross-sectional Study. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 47, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.C.; Meijers, J.C.; Vroom, M.B.; Juffermans, N.P. Utility of thromboelastography and/or thromboelastometry in adults with sepsis: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.L.; McRae, H.L.; Refaai, M.A. Efficacy of viscoelastic hemostatic assay testing in patients with sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsaras, G.; Sokou, R.; Tsantes, A.G.; Piovani, D.; Bonovas, S.; Konstantinidi, A.; Ioakeimidis, G.; Parastatidou, S.; Gialamprinou, D.; Makrogianni, A.; et al. The use of thromboelastography (TEG) and rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM) in neonates: A systematic review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 3455–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampridou, M.; Sokou, R.; Tsantes, A.G.; Theodoraki, M.; Konstantinidi, A.; Ioakeimidis, G.; Bonovas, S.; Politou, M.; Valsami, S.; Iliodromiti, Z.; et al. ROTEM diagnostic capacity for measuring fibrinolysis in neonatal sepsis. Thromb. Res. 2020, 192, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamik, B.; Gozdzik, W.; Jakubczyk, D.; Welna, M.; Kübler, A. Coagulation abnormalities identified by thromboelastometry in patients with severe sepsis: The relationship to endotoxemia and mortality. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2017, 28, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivula, M.; Pettilä, V.; Niemi, T.T.; Varpula, M.; Kuitunen, A.H. Thromboelastometry in patients with severe sepsis and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2009, 20, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.R.; Lawrence, M.; Pillai, S.; Mills, G.M.; Aubrey, R.; Thomas, D.; Williams, R.; Morris, K.; Evans, P.A. The effect of sepsis and septic shock on the viscoelastic properties of clot quality and mass using rotational thromboelastometry: A prospective observational study. J. Crit. Care 2018, 44, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Saxena, R. A Novel Thromboelastographic Score to Identify Overt Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Resulting in a Hypocoagulable State. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 134, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koami, H.; Sakamoto, Y.; Ohta, M.; Goto, A.; Narumi, S.; Imahase, H.; Inoue, S. Can rotational thromboelastometry predict septic disseminated intravascular coagulation? Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2015, 26, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wan, D.; Luo, X.; Song, T.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Liao, R.; Zhao, W.; Su, B. Circulating Histones in Sepsis: Potential Outcome Predictors and Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 650184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, U.; Tracey, K.J. HMGB1 Is a Therapeutic Target for Sterile Inflammation and Infection. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Kawahara, K.; Nakamura, T.; Yamada, S.; Nakamura, T.; Abeyama, K.; Hashiguchi, T.; Maruyama, I. High-mobility group box 1 protein promotes development of microvascular thrombosis in rats. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatada, T.; Nobori, T.; Okabayashi, K.; Maruyama, K.; Abe, Y.; Uemoto, S.; Yamada, S.; Maruyama, I.; Wada, H. Plasma concentrations and importance of high mobility group box protein in the prognosis of organ failure in patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimont, L.; Dechamps, M.; David, C.; Bouvy, C.; Gillot, C.; Haguet, H.; Favresse, J.; Ronvaux, L.; Candiracci, J.; Herzog, M.; et al. NETosis and Nucleosome Biomarkers in Septic Shock and Critical COVID-19 Patients: An Observational Study. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ye, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Lou, T.; Qiu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, B.; Fang, X. Circulating nucleosomes as a predictor of sepsis and organ dysfunction in critically ill patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, e558–e564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Pelayo, R.; Monestier, M.; Ammollo, C.T.; Semeraro, F.; Taylor, F.B.; Esmon, N.L.; Lupu, F.; Esmon, C.T. Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, M.; Ito, T.; Kawahara, K.-I.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagasato, T.; Shrestha, B.; Yamada, S.; Miyauchi, T.; Higuchi, K.; Takenaka, T.; et al. Recombinant Thrombomodulin Protects Mice against Histone-Induced Lethal Thromboembolism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abrams, S.T.; Zhang, N.; Manson, J.; Liu, T.; Dart, C.; Baluwa, F.; Toh, C.H. Circulating histones are mediators of trauma-associated lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dwivedi, D.J.; Toltl, L.J.; Swystun, L.L.; Pogue, J.; Liaw, K.-L.; Weitz, J.I.; Cook, D.J.; Fox-Robichaud, A.E.; Liaw, P.C.; Canadian Critical Care Translational Biology Group. Prognostic utility and characterization of cell-free DNA in patients with severe sepsis. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H. Inflammation and thrombosis: Roles of neutrophils, platelets and endothelial cells and their interactions in thrombus formation during sepsis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levi, M.; de Jonge, E.; van der Poll, T. Rationale for restoration of physiological anticoagulant pathways in patients with sepsis and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, S90–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levi, M.M.; Toh, C.H.; Thachil, J.; Watson, H.G. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Kidokoro, A.; Yagi, Y. The Role of the Endothelium in Changes in Procoagulant Activity in Sepsis. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 1998, 187, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, B.L.; Eid, A.; Singer, P.; Pillay, S.S.; Carl, P.; Novak, I.; Chalupa, P.; Atherstone, A.; Pénzes, I.; Kübler, A.; et al. High-dose antithrombin III in severe sepsis: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2001, 286, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederwanger, C.; Hell, T.; Hofer, S.; Salvador, C.; Michel, M.; Schenk, B.; Treml, B.; Bachler, M. Antithrombin deficiency is associated with mortality and impaired organ function in septic pediatric patients: A retrospective study. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martí-Carvajal, A.J.; Solà, I.; Gluud, C.; Lathyris, D.; Anand, V. Human recombinant protein C for severe sepsis and septic shock in adult and paediatric patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 12, CD004388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitton, C.; Gérard, N.; Sébille, V.; Bretonnière, C.; Zambon, O.; Villers, D.; Charreau, B. Early rise in circulating endothelial protein C receptor correlates with poor outcome in severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 37, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Cai, S.; Su, J. The Pathogenesis of Sepsis and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conway, E.M. Thrombomodulin and its role in inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2011, 34, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuno, T.; Mitsuyama, T.; Hidaka, K.; Tanaka, T.; Hara, N. The Role of Neutrophil Elastase in Human Pulmonary Artery Endothelial Cell Injury. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1997, 112, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinasewitz, G.T.; Yan, S.B.; Basson, B.; Comp, P.; Russell, J.A.; Cariou, A.; Um, S.L.; Utterback, B.; Laterre, P.-F.; Dhainaut, J.-F. Universal changes in biomarkers of coagulation and inflammation occur in patients with severe sepsis, regardless of causative micro-organism [ISRCTN74215569]. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R82–R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehme, M.W.; Deng, Y.; Raeth, U.; Bierhaus, A.; Ziegler, R.; Stremmel, W.; Nawroth, P.P. Release of thrombomodulin from endothelial cells by concerted action of TNF-alpha and neutrophils: In vivo and in vitro studies. Immunology 1996, 87, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kushimoto, S.; Wada, H.; Kawasugi, K.; Okamoto, K.; Uchiyama, T.; Seki, Y.; Hatada, T.; Imai, H.; Nobori, T.; Subcommittee, J.S.O.T.H. Increased Ratio of Soluble Fibrin Formation/Thrombin Generation in Patients With DIC. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2012, 18, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, L.; Huang, R.; Su, L.; Hou, M.; Wang, X.; Deng, J.; Hu, Y. Evaluation the combined diagnostic value of TAT, PIC, tPAIC, and sTM in disseminated intravascular coagulation: A multi-center prospective observational study. Thromb. Res. 2018, 173, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, K.; Kitamura, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Irie, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Kawano, Y.; Ishikura, H. Usefulness of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 as a predictive marker of mortality in sepsis. J. Intensive Care 2017, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipoe, T.L.; Wu, W.K.K.; Chung, L.; Gong, M.; Dong, M.; Liu, T.; Roever, L.; Ho, J.; Wong, M.C.S.; Chan, M.T.V.; et al. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 for Predicting Sepsis Severity and Mortality Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elad, B.; Avraham, G.; Schwartz, N.; Elias, A.; Elias, M. Role of a thrombin generation assay in the prediction of infection severity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihajlovic, D.; Brkic, S.; Lendak, D.; Mikic, A.N.; Draskovic, B.; Mitic, G. Endogenous thrombin potential as marker of procoagulant response that can be useful in early stage of sepsis. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2017, 28, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; Vincent, J.-L.; Tanaka, K.; Radford, A.H.; Kayanoki, T.; Fineberg, D.A.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Fareed, J. Effect of a Recombinant Human Soluble Thrombomodulin on Baseline Coagulation Biomarker Levels and Mortality Outcome in Patients with Sepsis-Associated Coagulopathy. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakura, H.; Takahashi, H.; Uchiyama, T.; Eguchi, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Kawasugi, K.; Madoiwa, S.; Wada, H.; DIC Subcommittee of the Japanese Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Proposal for new diagnostic criteria for DIC from the Japanese Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Thromb. J. 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Chung, D.; Takayama, T.K.; Majerus, E.M.; Sadler, J.E.; Fujikawa, K. Structure of von Willebrand Factor-cleaving Protease (ADAMTS13), a Metalloprotease Involved in Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 41059–41063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levi, M.; Scully, M.; Singer, M. The role of ADAMTS -13 in the coagulopathy of sepsis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; Mcintyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1181–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egi, M.; Ogura, H.; Yatabe, T.; Atagi, K.; Inoue, S.; Iba, T.; Kakihana, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Kushimoto, S.; Kuroda, Y.; et al. The Japanese Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2020 (J-SSCG 2020). Acute Med. Surg. 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inata, Y. Should we treat sepsis-induced DIC with anticoagulants? J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienast, J.; Juers, M.; Wiedermann, C.J.; Hoffmann, J.N.; Ostermann, H.; Strauss, R.; Keinecke, H.-O.; Warren, B.L.; Opal, S.M.; The KyberSept Investigators. Treatment effects of high-dose antithrombin without concomitant heparin in patients with severe sepsis with or without disseminated intravascular coagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Francois, B.; Zabolotskikh, I.; Daga, M.K.; Lascarrou, J.B.; Kirov, M.Y.; SCARLET Trial Group. Effect of a recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin on mortality in patients with sepsis-associated coagulopathy: The SCARLET randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarlatescu, E.; Tomescu, D.; Arama, S.S. Review. Anticoagulant Therapy in Sepsis. The Importance of Timing. J. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 3, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Item | Score | Overt DIC | SIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Range | ||
| Platelet count (×109/L) | 2 1 | <50 ≥50, <100 | <100 ≥100, <150 |
| FDP/D-dimers | 3 2 | Strong increase Moderate increase | - - |
| Prothrombin time (PT ratio) | 2 1 | ≥6 s ≥3 s, <6 s | (>1.4) (>1.2, ≤1.4) |
| Fibrinogen (g/mL) | 1 | <100 | - |
| SOFA score | 2 1 | - - | ≥2 1 |
| Total score for DIC or SIC | ≥5 | ≥4 |
| Treatment Options | Comments | References |
|---|---|---|
| Heparin and heparinoids | Their effectiveness in sepsis-induced coagulopathy is debatable and limited to preventing deep vein thrombosis. | Iba et al. [99] |
| Antithrombin, activated protein C, and tissue factor pathway inhibitors | Potential survival benefit with antithrombin administration. | Kienast et al. [100] |
| Fresh frozen plasma | No evidence supporting its use unless there are specific indications for bleeding or factor depletion beyond antithrombin | Iba et al. [99] |
| Recombinant thrombomodulin | It may improve overall mortality in patients with SIC | Vincent et al. [101] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsantes, A.G.; Parastatidou, S.; Tsantes, E.A.; Bonova, E.; Tsante, K.A.; Mantzios, P.G.; Vaiopoulos, A.G.; Tsalas, S.; Konstantinidi, A.; Houhoula, D.; et al. Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: An Update on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers, and Current Guidelines. Life 2023, 13, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020350
Tsantes AG, Parastatidou S, Tsantes EA, Bonova E, Tsante KA, Mantzios PG, Vaiopoulos AG, Tsalas S, Konstantinidi A, Houhoula D, et al. Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: An Update on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers, and Current Guidelines. Life. 2023; 13(2):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020350
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsantes, Andreas G., Stavroula Parastatidou, Emmanuel A. Tsantes, Elli Bonova, Konstantina A. Tsante, Petros G. Mantzios, Aristeidis G. Vaiopoulos, Stavros Tsalas, Aikaterini Konstantinidi, Dimitra Houhoula, and et al. 2023. "Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: An Update on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers, and Current Guidelines" Life 13, no. 2: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020350
APA StyleTsantes, A. G., Parastatidou, S., Tsantes, E. A., Bonova, E., Tsante, K. A., Mantzios, P. G., Vaiopoulos, A. G., Tsalas, S., Konstantinidi, A., Houhoula, D., Iacovidou, N., Piovani, D., Nikolopoulos, G. K., & Sokou, R. (2023). Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: An Update on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers, and Current Guidelines. Life, 13(2), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020350










