Keep the Right in Mind—A Focused Approach to Right Ventricle-Predominant Cardiogenic Shock
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Definition and Classification of Cardiogenic Shock
- (1)
- Hypotension—with a systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg for at least 30 min or the requirement of supportive measures to maintain the systolic blood pressure at 90 mm Hg.AND
- (2)
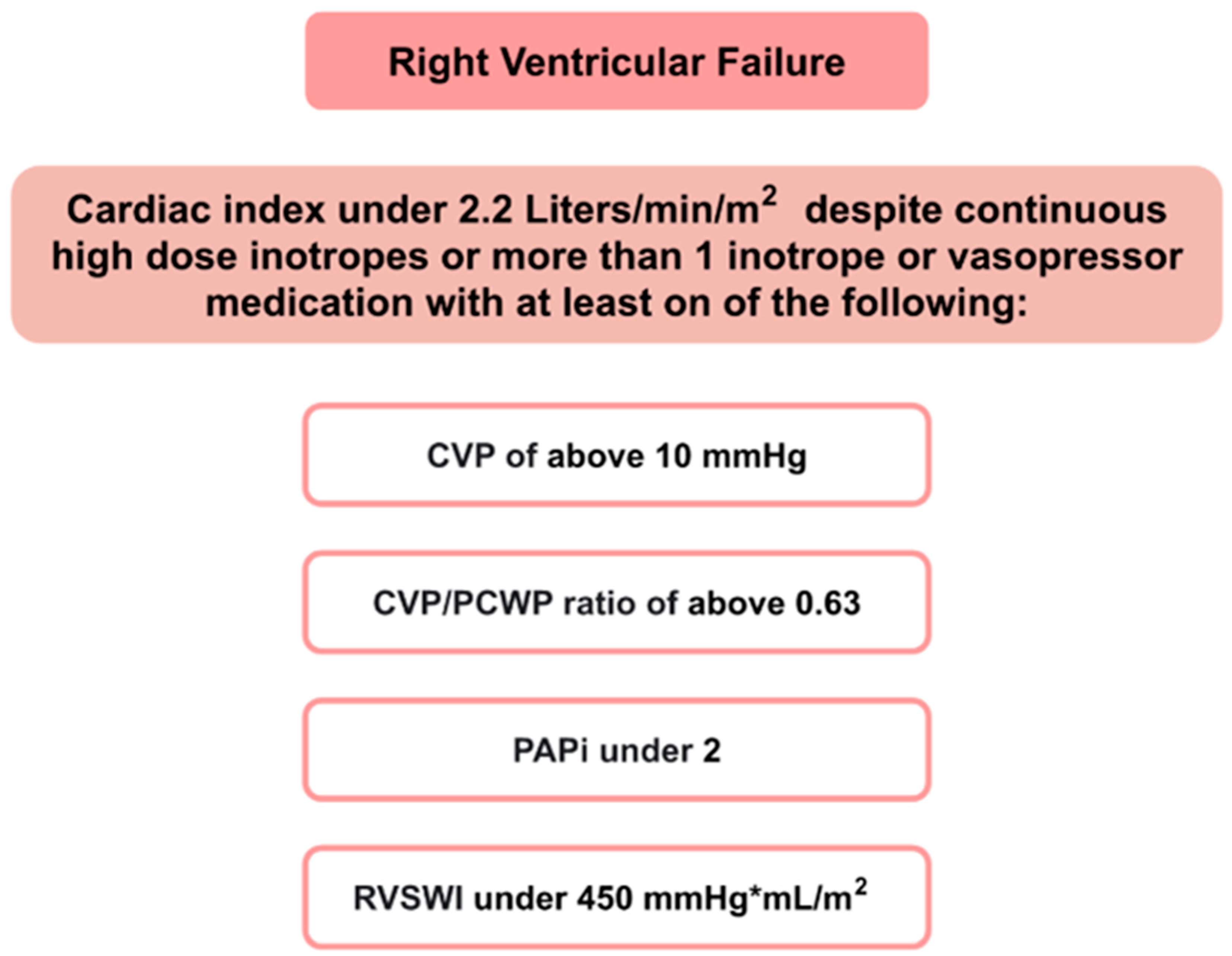
- Cardiac index ≤ 2.2 L/min/m2.AND
- (3)
- Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure greater than or equal to 15 mm Hg.
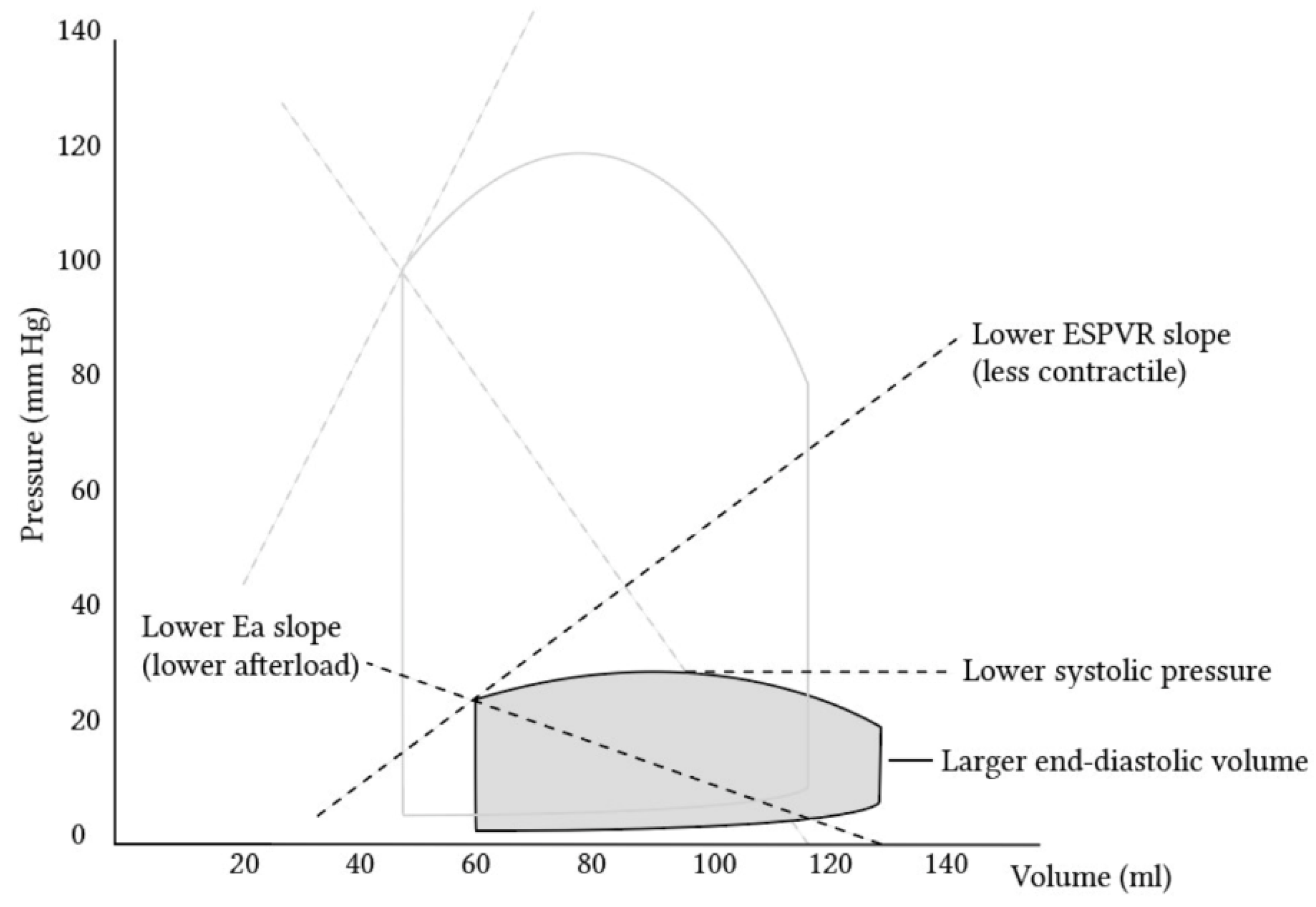
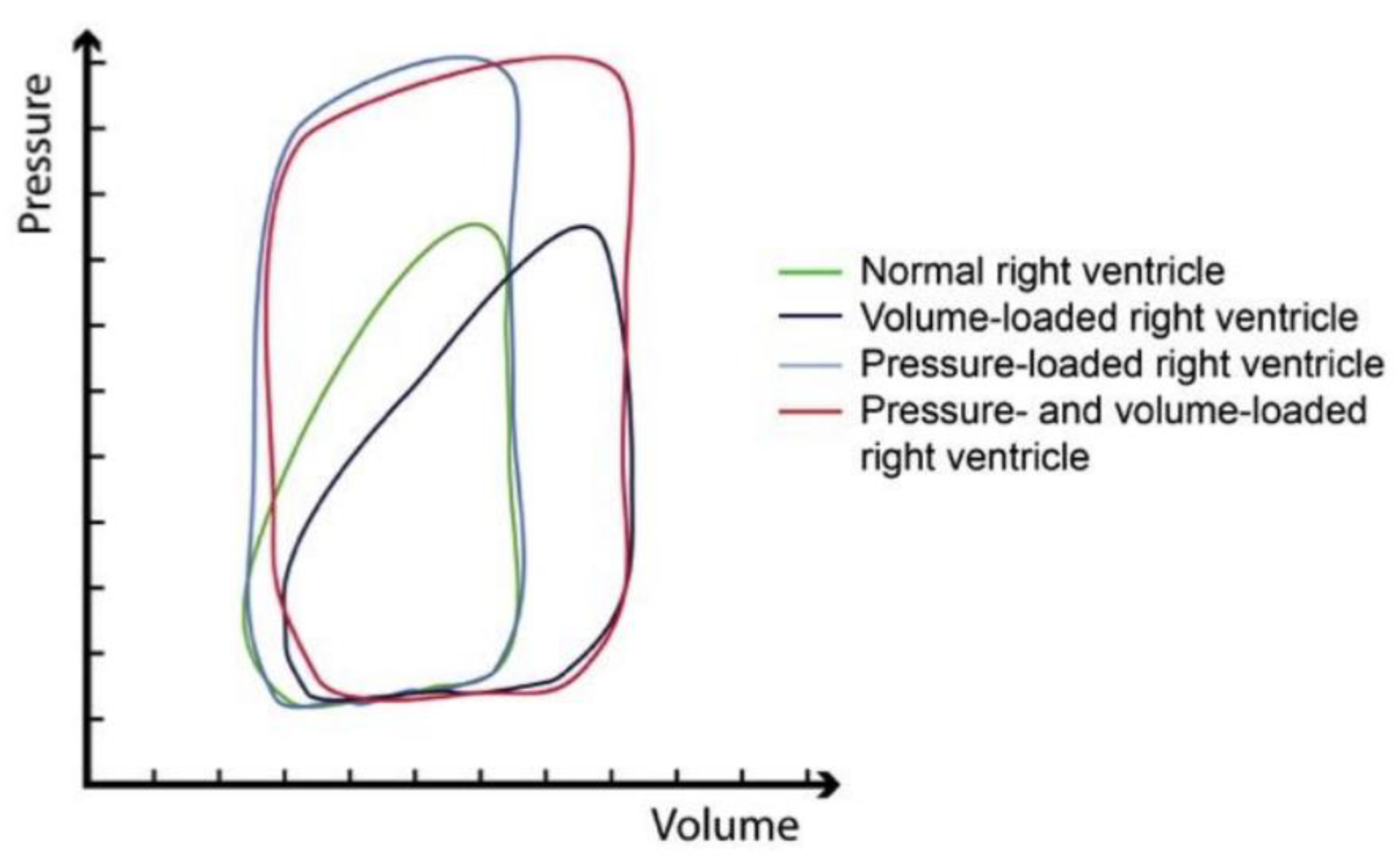
3. The Right Ventricle—Hemodynamics and Anatomical Characteristics
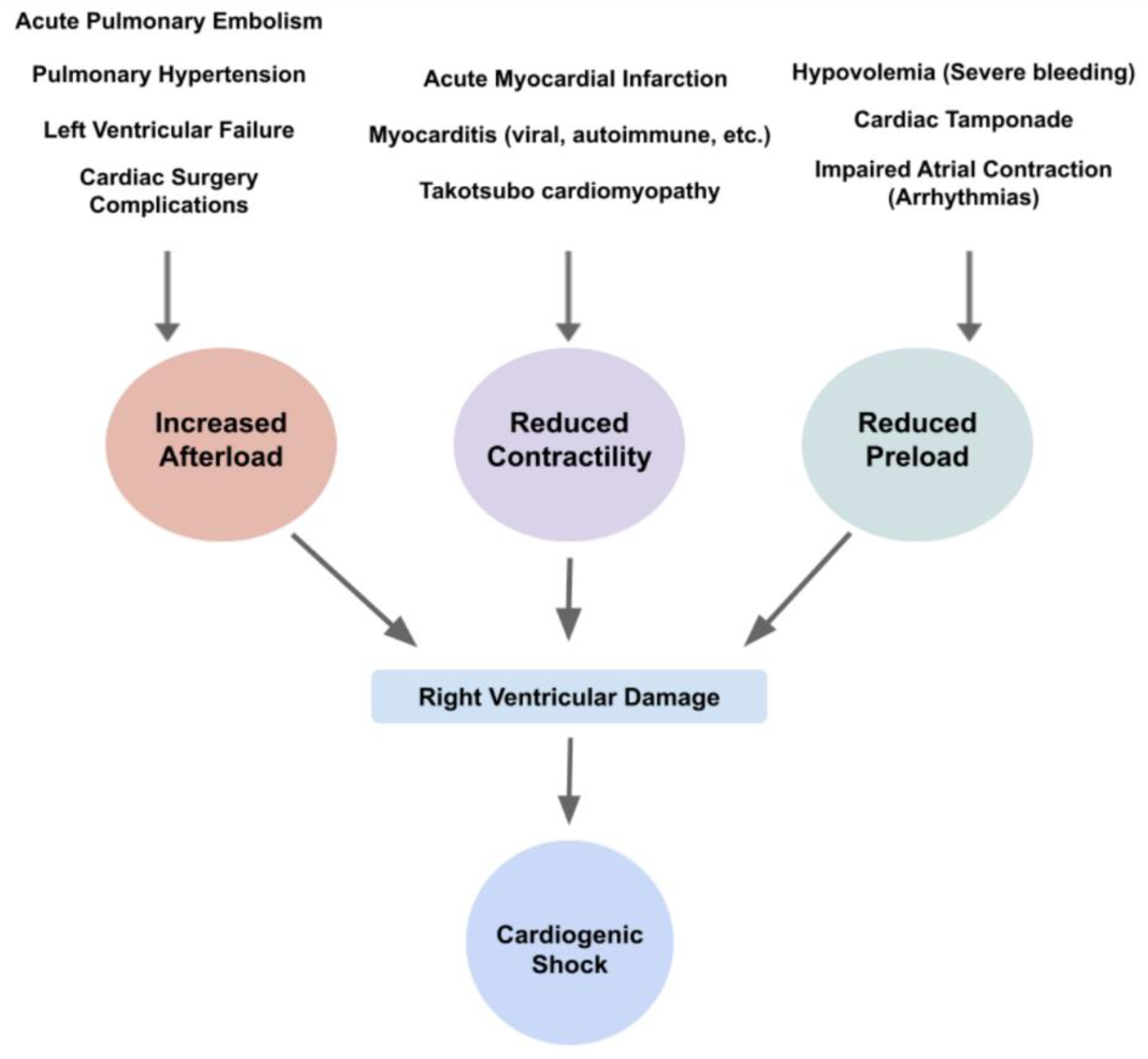
4. Etiology and Pathophysiology of CS
4.1. Acute RHF
4.2. Acute on Chronic RHF
5. Signs and Symptoms
5.1. Patient Presentation
5.2. Physical Examination
5.3. Hemodynamic Alterations
5.4. ECG
5.5. Laboratory Findings
6. Investigation Modalities
6.1. Non-Invasive Modalities
6.2. Invasive Modalities
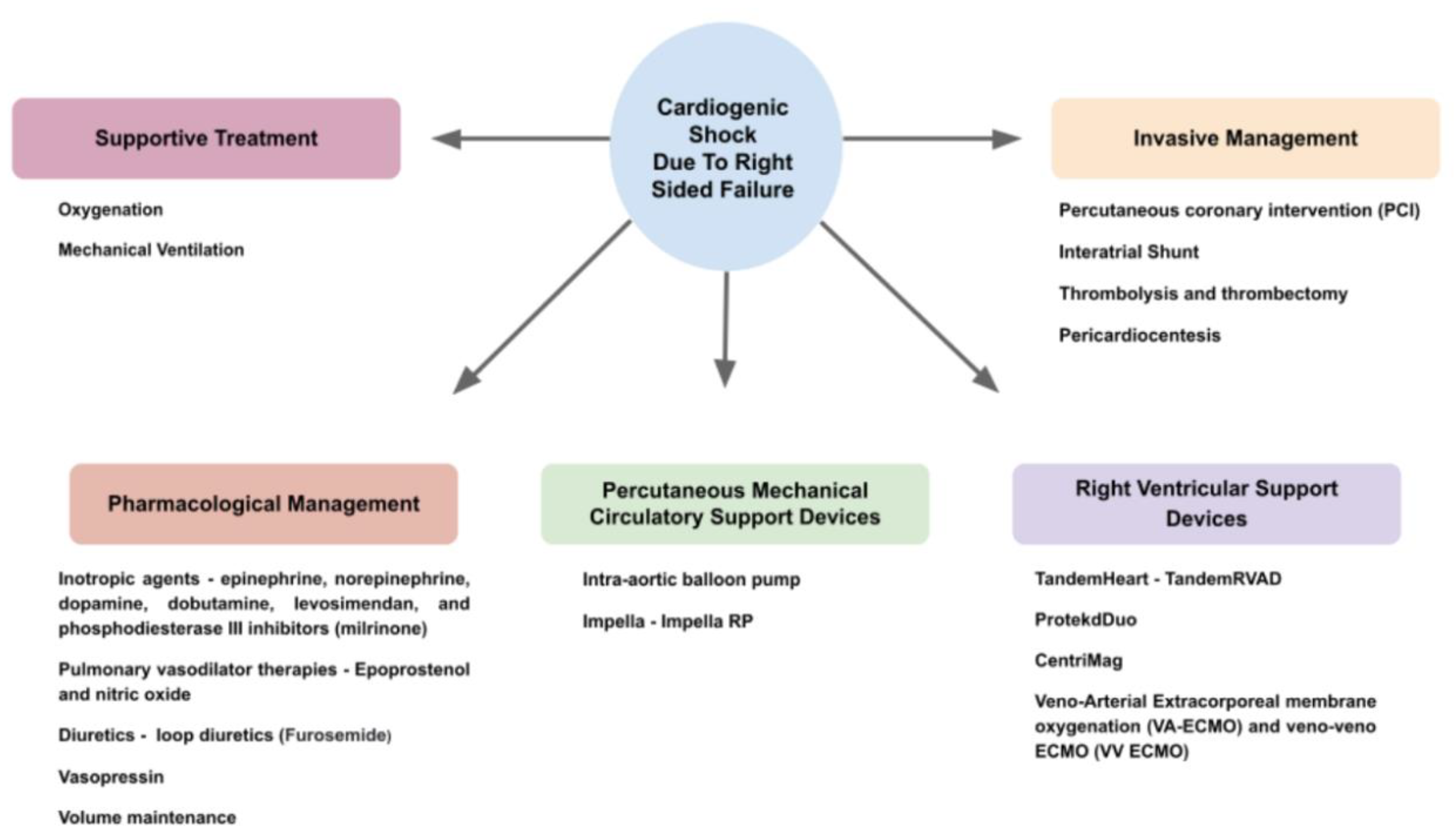
7. Management
7.1. Pharmacological
7.2. Invasive
7.3. Supportive Treatment
7.4. Percutaneous Mechanical Circulatory Support Device (PMCS)
7.5. Right Ventricular Support Device (RVAD)
8. Future Directions
9. Prognosis
10. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chioncel, O.; Mebazaa, A.; Harjola, V.-P.; Coats, A.J.; Piepoli, M.F.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Laroche, C.; Seferovic, P.M.; Anker, S.D.; Ferrari, R.; et al. Clinical phenotypes and outcome of patients hospitalized for acute heart failure: The ESC Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ordonez, C.P.; Garan, A.R. The landscape of cardiogenic shock: Epidemiology and current definitions. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2022, 37, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, V.L. Epidemiology of Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandras, S.A.; Desai, S. Right Heart Failure. [Updated 18 July 2022]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459381/ (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Albakri, A. Right heart failure: A review of clinical status and meta-analysis of diagnosis and clinical management methods. Intern. Med. Care 2018, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, M.K.; Everett, K.D.; Gulati, G.; Brener, M.I.; Kapur, N.K. Epidemiology and management of right ventricular-predominant heart failure and shock in the cardiac intensive care unit. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2022, 11, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorter, T.M.; Hoendermis, E.S.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Voors, A.A.; Lam, C.S.P.; Geelhoed, B.; Willems, T.P.; Van Melle, J.P. Right ventricular dysfunction in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 1472–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harjola, V.P.V.; Mebazaa, A.; Čelutkiene, J.J.; Bettex, D.D.; Bueno, H.; Chioncel, O.O.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Falk, V.; Filippatos, G.; Gibbs, S.S.; et al. Contemporary management of acute right ventricular failure: A statement from the Heart Failure Association and the Working Group on Pulmonary Circulation and Right Ventricular Function of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, N.K.; Esposito, M.L.; Bader, Y.; Morine, K.J.; Kiernan, M.S.; Pham, D.T.; Burkhoff, D. Mechanical Circulatory Support Devices for Acute Right Ventricular Failure. Circulation 2017, 136, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, P.; Thayer, K.L.; Abraham, J.; Everett, K.D.; Pahuja, M.; Whitehead, E.H.; Schwartz, B.P.; Lala, A.; Sinha, S.S.; Kanwar, M.K.; et al. Right Ventricular Dysfunction Is Common and Identifies Patients at Risk of Dying in Cardiogenic Shock. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 27, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Blumer, V.; Burkhoff, D.; Pahuja, M.; Sinha, S.S.; Rosner, C.; Vorovich, E.; Grafton, G.; Bagnola, A.; Hernandez-Montfort, J.A.; et al. Heart Failure-Related Cardiogenic Shock: Pathophysiology, Evaluation and Management Considerations: Review of Heart Failure-Related Cardiogenic Shock. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 27, 1126–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohria, A.; Tsang, S.W.; Fang, J.C.; Lewis, E.F.; Jarcho, J.A.; Mudge, G.H.; Stevenson, L.W. Clinical assessment identifies hemodynamic profiles that predict outcomes in patients admitted with heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zern, E.K.; Wang, D.; Rambarat, P.; Bernard, S.; Paniagua, S.M.; Liu, E.E.; McNeill, J.; Wang, J.K.; Andrews, C.T.; Pomerantsev, E.V.; et al. Association of Pulmonary Artery Pulsatility Index with Adverse Cardiovascular Events Across a Hospital-Based Sample. Circ. Heart Fail. 2022, 15, e009085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choung, J.; Ng, B.; Fitzpatrick, M. Comparison of Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure Measured on Right Heart Catheterisation and Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure Calculated from Nagueh’s Formula in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension. Heart Lung Circ. 2017, 26, S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanjanahattakij, N.; Sirinvaravong, N.; Aguilar, F.; Agrawal, A.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Gupta, S. High Right Ventricular Stroke Work Index Is Associated with Worse Kidney Function in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Cardiorenal Med. 2018, 8, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, N.K.; Davila, C.D.; Jumean, M.F. Integrating Interventional Cardiology and Heart Failure Management for Cardiogenic Shock. Interv. Cardiol. Clin. 2017, 6, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelios, C.J.; Lund, L.H.; Wever-Pinzon, O.; Selzman, C.H.; Myers, S.L.; Cantor, R.S.; Stehlik, J.; Chamogeorgakis, T.; McKellar, S.H.; Koliopoulou, A.; et al. Right Heart Failure Following Left Ventricular Device Implantation: Natural History, Risk Factors, and Outcomes: An Analysis of the STS INTERMACS Database. Circ. Heart Fail. 2022, 15, e008706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.A.; Copeland, H.; Alam, A.; Joseph, S.M. The “Right” Definition for Post–Left Ventricular Assist Device Right Heart Failure: The More We Learn, the Less We Know. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstam, M.A.; Kiernan, M.S.; Bernstein, D.; Bozkurt, B.; Jacob, M.; Kapur, N.K.; Kociol, R.D.; Lewis, E.F.; Mehra, M.R.; Pagani, F.D.; et al. Evaluation and Management of Right-Sided Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e578–e622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, F.; Redington, A. The right ventricle: Anatomy, physiology and clinical imaging. Heart 2008, 94, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redington, A.N.; Gray, H.H.; Hodson, M.E.; Rigby, M.L.; Oldershaw, P.J. Characterisation of the normal right ventricular pres-sure-volume relation by biplane angiography and simultaneous micromanometer pressure measurements. Br. Heart J. 1988, 59, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maughan, W.L.; Shoukas, A.A.; Sagawa, K.; Weisfeldt, M.L. Instantaneous pressure-volume relationship of the canine right ventricle. Circ. Res. 1979, 44, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, S.Y.; Nihoyannopoulos, P. Anatomy, echocardiography, and normal right ventricular dimensions. Heart 2006, 92, i2–i13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- A Website Edited by Alex Yartsev. Available online: https://derangedphysiology.com (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 1–39.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whiteman, S.; Alimi, Y.; Carrasco, M.; Gielecki, J.; Zurada, A.; Loukas, M. Anatomy of the cardiac chambers: A review of the left ventricle. Transl. Res. Anat. 2021, 23, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsky, M.D.; Morrow, D.A.; Proudfoot, A.G.; Hochman, J.S.; Thiele, H.; Rao, S.V. Cardiogenic Shock After Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 1840–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfisterer, M. Right ventricular involvement in myocardial infarction and cardiogenic shock. Lancet 2003, 362, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.; Ginsberg, F.; Parrillo, J.E. Cardiogenic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, S66–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFilippis, E.M.; Topkara, V.K.; Kirtane, A.J.; Takeda, K.; Naka, Y.; Garan, A.R. Mechanical Circulatory Support for Right Ventricular Failure. Card. Fail. Rev. 2022, 8, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meester, P. Tricuspid Regurgitation in Different Loading Conditions. Epidemiology, Determinants and Management. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- van Diepen, S.; Katz, J.N.; Albert, N.M.; Henry, T.D.; Jacobs, A.K.; Kapur, N.K.; Kilic, A.; Menon, V.; Ohman, E.M.; Sweitzer, N.K.; et al. Contemporary Management of Cardiogenic Shock: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 136, e232–e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrus, T.; Kanovsky, J.; Novotny, T.; Andrsova, I.; Spinar, J.; Kala, P. Right ventricular myocardial infarction: From pathophysi-ology to prognosis. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2013, 18, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Josiassen, J.; Helgestad, O.K.L.; Møller, J.E.; Schmidt, H.; Jensen, L.O.; Holmvang, L.; Ravn, H.B.; Hassager, C. Cardiogenic shock due to predominantly right ventricular failure complicating acute myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2020, 10, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukla, P.; McIntyre, W.F.; Fijorek, K.; Mirek-Bryniarska, E.; Bryniarski, L.; Krupa, E.; Jastrzębski, M.; Bryniarski, K.L.; Zhong-Qun, Z.; Baranchuk, A. Electrocardiographic abnormalities in patients with acute pulmonary embolism complicated by cardiogenic shock. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 32, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, V.; Goyal, A. Acute Pulmonary Embolism. [Updated 8 August 2022]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Appleton, C.; Gillam, L.; Koulogiannis, K. Cardiac Tamponade. Cardiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagar, S.; Liu, P.P.; Cooper, L.T., Jr. Myocarditis. Lancet 2012, 379, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawakami, R.; Sakamoto, A.; Kawai, K.; Gianatti, A.; Pellegrini, D.; Nasr, A.; Kutys, B.; Guo, L.; Cornelissen, A.; Mori, M.; et al. Pathological Evidence for SARS-CoV-2 as a Cause of Myocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.; May, C.W.; Williams, J.; Shlobin, O.A. Management of Right Heart Failure in the Critically Ill. Crit. Care Clin. 2014, 30, 475–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, M.; Jessup, M.; Mullens, W.; Reza, N.; Shah, A.M.; Sliwa, K.; Mebazaa, A. Acute heart failure. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, R.J.; Moul, M.S.; Beckman, D.; Slim, A.M. Isolated Right Ventricular Failure in Hyperthyroidism: A Clinical Dilemma. Heart Int. 2011, 6, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brailovsky, Y.; Sayer, G. The “Right” Side of Cardiogenic Shock. JACC Case Rep. 2020, 2, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portnoy, S.G.; Rudski, L.G. Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Right Ventricle: A 2014 Perspective. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2015, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, G.M.; Ciarka, A.; Biniecka, M.; Ceranowicz, P. Right Heart Catheterization—Background, Physiological Basics, and Clinical Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Ziccardi, M.; Pendela, V.S.; Singhal, M. Cardiac Cirrhosis. [Updated 18 July 2022]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo, M.; Huber, L.C.; Winnik, S.; Mikulicic, F.; Guidetti, F.; Frank, M.; Flammer, A.J.; Ruschitzka, F. Right Ventricular Failure: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. Card. Fail. Rev. 2019, 5, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerrero-Miranda, C.Y.; Hall, S.A. Cardiogenic Shock in Patients with Advanced Chronic Heart Failure. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc. J. 2020, 16, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandavarayan, R.A.; Chitturi, K.R.; Guha, A. Pathophysiology of Acute and Chronic Right Heart Failure. Cardiol. Clin. 2020, 38, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greyson, C.R. Pathophysiology of right ventricular failure. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, S57–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cochran, J.M.; Alam, A.; Guerrero-Miranda, C.Y. Importance of right heart catheterization in advanced heart failure management. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J.B.; Levy, Z.D.; Slesinger, T.L. Cardiogenic Shock. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 33, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, M.; Wu, Y.; Hazen, S.L.; Tang, W.H.W. Cystatin C Identifies Patients with Stable Chronic Heart Failure at Increased Risk for Adverse Cardiovascular Events. Circ. Heart Fail. 2012, 5, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chia, Y.C.; Kieneker, L.M.; van Hassel, G.; Binnenmars, S.H.; Nolte, I.M.; van Zanden, J.J.; van der Meer, P.; Navis, G.; Voors, A.A.; Bakker, S.J.L.; et al. Interleukin 6 and Development of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction in the General Population. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e018549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostura, M.; Smalley, C.; Koyfman, A.; Long, B. Right heart failure: A narrative review for emergency clinicians. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 58, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudski, L.G.; Lai, W.W.; Afilalo, J.; Hua, L.; Handschumacher, M.D.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Solomon, S.D.; Louie, E.K.; Schiller, N.B. Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of the Right Heart in Adults: A Report from the American Society of Echocardiography: Endorsed by the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2010, 23, 685–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleister, A.; Kahwash, R.; Haas, G.; Ghio, S.; Cittadini, A.; Baliga, R.R. Echocardiography and Heart Failure: A Glimpse of the Right Heart. Echocardiography 2014, 32, S95–S107. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/echo.12678 (accessed on 8 January 2023). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranka, S.; Mastoris, I.; Kapur, N.K.; Tedford, R.J.; Rali, A.; Acharya, P.; Weidling, R.; Goyal, A.; Sauer, A.J.; Gupta, B.; et al. Right Heart Catheterization in Cardiogenic Shock Is Associated with Improved Outcomes: Insights from the Nationwide Readmissions Database. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, B.; Klein, T.; Kimmoun, A. Vasopressor use in cardiogenic shock. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2020, 26, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassady, S.J.; Ramani, G.V. Right Heart Failure in Pulmonary Hypertension. Cardiol. Clin. 2020, 38, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, B.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Legras, A.; Morichau-Beauchant, T.; Leone, M.; Frederique, G.; Quenot, J.-P.; Kimmoun, A.; Cariou, A.; Lassus, J.; et al. Epinephrine Versus Norepinephrine for Cardiogenic Shock After Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, R.; Di Santo, P.; Jung, R.G.; Marbach, J.A.; Hutson, J.; Simard, T.; Ramirez, F.D.; Harnett, D.T.; Merdad, A.; Almufleh, A.; et al. Milrinone as Compared with Dobutamine in the Treatment of Cardiogenic Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binanay, C.; Califf, R.M.; Hasselblad, V.; O’Connor, C.M.; Shah, M.R.; Sopko, G.; Stevenson, L.W.; Francis, G.S.; Leier, C.V.; Miller, L.W.; et al. Evaluation Study of Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Effectiveness. JAMA 2005, 294, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiele, H.; Akin, I.; Sandri, M.; Fuernau, G.; De Waha, S.; Meyer-Saraei, R.; Nordbeck, P.; Geisler, T.; Landmesser, U.; Skurk, C.; et al. PCI Strategies in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Cardiogenic Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2419–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koc, L.; Ondrus, T.; Fila, P.; Richter, S.; Kala, P. Right ventricular myocardial infarction in the era of primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2021, 122, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruopp, N.F.; Cockrill, B.A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Review. JAMA 2022, 327, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzevich, K.M.; Chohan, H.; Grinnan, D.C. Management of pulmonary vasodilator therapy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension during critical illness. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biering-Sørensen, T.; Minamisawa, M.; Liu, J.; Claggett, B.; Papolos, A.I.; Felker, G.M.; McMurray, J.J.; Legg, J.C.; Malik, F.I.; Honarpour, N.; et al. The effect of the cardiac myosin activator, omecamtiv mecarbil, on right ventricular structure and function in chronic systolic heart failure (COSMIC—HF). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essien, E.-O.; Rali, P.; Mathai, S.C. Pulmonary Embolism. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, S. Pulmonary embolism an update. Aust. Fam. Physician 2017, 46, 816–820. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.-P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giri, J.; Sista, A.; Weinberg, I.; Kearon, C.; Kumbhani, D.J.; Desai, N.D.; Piazza, G.; Gladwin, M.T.; Chatterjee, S.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Interventional Therapies for Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Current Status and Principles for the Development of Novel Evidence: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, e774–e801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorjani, N.; Price, S. Massive Pulmonary Embolism. Cardiol. Clin. 2013, 31, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakaramakkil, M.J.; Sivathasan, C. ECMO and Short-term Support for Cardiogenic Shock in Heart Failure. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, J.A.; Nair, A.; Takeda, K.; Clerkin, K.; Topkara, V.K.; Masoumi, A.; Yuzefpolskaya, M.; Takayama, H.; Naka, Y.; Burkhoff, D.; et al. Clinical and hemodynamic effects of intra-aortic balloon pump therapy in chronic heart failure patients with cardiogenic shock. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2018, 37, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sultan, I.; Kilic, A.; Kilic, A. Short-Term Circulatory and Right Ventricle Support in Cardiogenic Shock: Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation, Tandem Heart, CentriMag, and Impella. Heart Fail. Clin. 2018, 14, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeken, U.; Feindt, P.; Litmathe, J.; Kurt, M.; Gams, E. Intraaortic Balloon Pumping in Patients with Right Ventricular Insufficiency after Cardiac Surgery: Parameters to Predict Failure of IABP Support. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 57, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, A.; Devore, A.D.; Sun, J.-L.; Barnett, A.S.; Samsky, M.D.; Shaw, L.K.; Chiswell, K.; Patel, C.B.; Patel, M.R. The impact of a failing right heart in patients supported by intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2016, 6, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrage, B.; Westermann, D. Mechanical circulatory support devices in cardiogenic shock and acute heart failure: Current evi-dence. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2019, 25, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basir, M.B.; Kapur, N.K.; Patel, K.; Salam, M.A.; Schreiber, T.; Kaki, A.; Hanson, I.; Almany, S.; Timmis, S.; Dixon, S.; et al. Improved Outcomes Associated with the use of Shock Protocols: Updates from the National Cardiogenic Shock Initiative. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 93, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.B.; Goldstein, J.; Milano, C.; Morris, L.D.; Kormos, R.L.; Bhama, J.; Kapur, N.K.; Bansal, A.; Garcia, J.; Baker, J.N.; et al. Benefits of a novel percutaneous ventricular assist device for right heart failure: The prospective RECOVER RIGHT study of the Impella RP device. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2015, 34, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramegna, M.; Beneduce, A.; Bertoldi, L.F.; Pagnesi, M.; Marini, C.; Pazzanese, V.; Camici, P.G.; Chieffo, A.; Pappalardo, F. Impella RP support in refractory right ventricular failure complicating acute myocardial infarction with unsuccessful right coronary artery revascularization. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 302, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.; Richards, J.B.; Frakes, M.; Cohen, J.; Wilcox, S.R. ECMO and Right Ventricular Failure: Review of the Literature. J. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 36, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, E.; Sklar, M.C.; Lequier, L.; Fan, E.; Kanji, H.D. Anticoagulation practices and the prevalence of major bleeding, thromboembolic events, and mortality in venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Crit. Care 2017, 39, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Khalpey, Z.; Smith, R.; Burkhoff, D.; Kociol, R.D.; Mehmood, M.; Alhussein, M.; Moayedi, Y.; Posada, J.D.; Ross, H.; et al. Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Cardiogenic Shock and Cardiac Arrest. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.W.; Schulze, P.C.; Kretzschmar, D. Acute right heart failure: Future perspective with the PERKAT RV pulsatile right ventricular support device. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753944719895902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzschmar, D.; Schulze, P.C.; Ferrari, M.W. Concept, Evaluation, and Future Perspectives of PERKAT® RV—A Novel Right Ventricular Assist Device. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2018, 12, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zymliński, R.; Dierckx, R.; Biegus, J.; Vanderheyden, M.; Bartunek, J.; Ponikowski, P. Novel IVC Doraya Catheter Provides Congestion Relief in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2022, 7, 326–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chioncel, O.; Parissis, J.; Mebazaa, A.; Thiele, H.; Desch, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Harjola, V.; Antohi, E.; Arrigo, M.; Ben Gal, T.; et al. Epidemiology, pathophysiology and contemporary management of cardiogenic shock—A position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1315–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furer, A.; Wessler, J.; Burkhoff, D. Hemodynamics of Cardiogenic Shock. Interv. Cardiol. Clin. 2017, 6, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniau, B.; Picod, A.; Azibani, F.; Gayat, E.; Mebazaa, A.; Blet, A. The CLIP -based mortality score in cardiogenic shock: Suitable only for cardiogenic shock? Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentzer, J.C.; van Diepen, S.; Barsness, G.W.; Henry, T.D.; Menon, V.; Rihal, C.S.; Naidu, S.S.; Baran, D.A. Cardiogenic Shock Classification to Predict Mortality in the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentzer, J.C.; Rayfield, C.; Soussi, S.; Berg, D.D.; Kennedy, J.N.; Sinha, S.S.; Baran, D.A.; Brant, E.; Mebazaa, A.; Billia, F.; et al. Advances in the Staging and Phenotyping of Cardiogenic Shock. JACC Adv. 2022, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, S.S.; Baran, D.A.; Jentzer, J.C.; Hollenberg, S.M.; van Diepen, S.; Basir, M.B.; Grines, C.L.; Diercks, D.B.; Hall, S.; Kapur, N.K.; et al. SCAI SHOCK Stage Classification Expert Consensus Update: A Review and Incorporation of Validation Studies: This statement was endorsed by the American College of Cardiology (ACC), American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP), American Heart Association (AHA), European Society of Car-diology (ESC) Association for Acute Cardiovascular Care (ACVC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplanta-tion (ISHLT), Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) in December 2021. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Copeland, V.J.; Fardman, A.; Furer, A. Keep the Right in Mind—A Focused Approach to Right Ventricle-Predominant Cardiogenic Shock. Life 2023, 13, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020379
Copeland VJ, Fardman A, Furer A. Keep the Right in Mind—A Focused Approach to Right Ventricle-Predominant Cardiogenic Shock. Life. 2023; 13(2):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020379
Chicago/Turabian StyleCopeland, Viana Jacquline, Alexander Fardman, and Ariel Furer. 2023. "Keep the Right in Mind—A Focused Approach to Right Ventricle-Predominant Cardiogenic Shock" Life 13, no. 2: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020379
APA StyleCopeland, V. J., Fardman, A., & Furer, A. (2023). Keep the Right in Mind—A Focused Approach to Right Ventricle-Predominant Cardiogenic Shock. Life, 13(2), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020379





