Epstein–Barr Virus and the Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
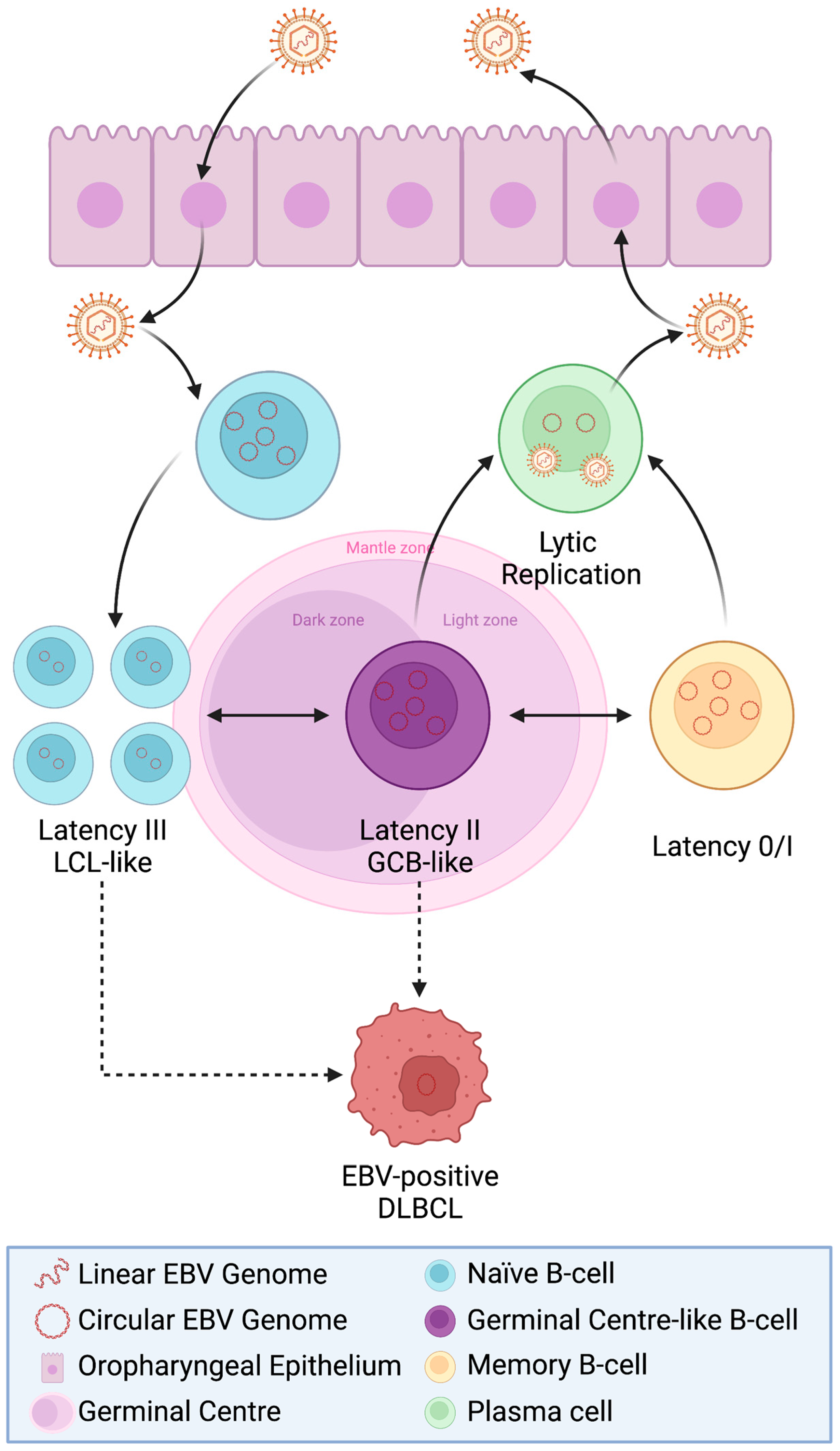
:1. Introduction
2. EBV Is Transforming in B-Cells
The Nature of Asymptomatic EBV Carriage in B-Cells
3. EBV+ Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
3.1. Evolution of DLBCL Classification and EBV
3.2. Other EBV-Associated Large B-Cell Malignancies
3.3. Prevalence of EBV+ DLBCL
3.4. Viral Gene Expression in EBV+ DLBCL
3.5. Cellular Genetics of EBV+ DLBCL
3.6. The Tumour Microenvironment of EBV+ DLBCL
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chabay, P. Advances in the Pathogenesis of EBV-Associated Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Zakeri, A.; Tabibzadeh, A.; Zakeri, A.M.; Zandi, M.; Siavoshi, S.; Seifpour, S.; Farahani, A. A review on EBV encoded and EBV-induced host microRNAs expression profile in different lymphoma types. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 1801–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.D.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: Lymphoid neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, M.; Neelapu, S.S.; Farooq, U.; Van Den Neste, E.; Kuruvilla, J.; Westin, J.; Link, B.K.; Hay, A.; Cerhan, J.R.; Zhu, L. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2017, 130, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muris, J.; Ylstra, B.; Cillessen, S.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Kluin-Nelemans, J.; Eijk, P.; Nota, B.; Tijssen, M.; De Boer, W.; Van De Wiel, M. Profiling of apoptosis genes allows for clinical stratification of primary nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 136, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Czuczman, M.S. ABC, GCB, and double-hit diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Does subtype make a difference in therapy selection? Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2015, 35, e449–e457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickinson, A.B.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr Virus. In Fields Virology, 3rd ed.; Field, B.N., Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott-Raven Publishers: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996; pp. 2397–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Baer, R.; Bankier, A.T.; Biggin, M.D.; Deininger, P.L.; Farrell, P.J.; Gibson, T.J.; Hatfull, G.; Hudson, G.S.; Satchwell, S.C.; Séguin, C.; et al. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein—Barr virus genome. Nature 1984, 310, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, O.; Smith, P.R.; Spender, L.C.; Karstegl, C.E.; Niller, H.H.; Huang, D.; Farrell, P.J. Updated Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) DNA sequence and analysis of a promoter for the BART (CST, BARF0) RNAs of EBV. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uner, A.; Akyurek, N.; Saglam, A.; Abdullazade, S.; Uzum, N.; Onder, S.; Barista, I.; Benekli, M. The presence of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) in Turkey: Special emphasis on ‘EBV-positive DLBCL of the elderly’. Apmis 2011, 119, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-G.; Huang, J.-J.; Li, Y.-J.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X.-W.; Jiang, W.-Q.; Huang, H.-Q.; Lin, T.-Y.; Li, Z.-M. Epstein-barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the elderly: A matched case-control analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.W. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2008; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A.B.; Bell, A.I. Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphomas. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpica, L.; Marques-Piubelli, M.L.; Beltran, B.E.; Chavez, J.C.; Miranda, R.N.; Castillo, J.J. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: 2022 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 951–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlers, B.; Spieß, K.; Leendertz, F.; Peeters, M.; Boesch, C.; Gatherer, D.; McGeoch, D.J. Lymphocryptovirus phylogeny and the origins of Epstein-Barr virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 91, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.A.; Achong, B.G.; Barr, Y.M. Virus particles in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s lymphoma. Lancet 1964, 283, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henle, G.; Henle, W.; Diehl, V. Relation of Burkitt’s tumor-associated herpes-type virus to infectious mononucleosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1968, 59, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, F.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Mundo, L.; Laginestra, M.A.; Fuligni, F.; Rossi, M.; Zairis, S.; Gazaneo, S.; De Falco, G.; Lazzi, S.; et al. Distinct viral and mutational spectrum of endemic Burkitt lymphoma. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henle, G.; Henle, W.; Clifford, P.; Diehl, V.; Kafuko, G.W.; Kirya, B.G.; Klein, G.; Morrow, R.H.; Munube, G.M.; Pike, P. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt’s lymphoma and control groups. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1969, 43, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederman, J.C.; Miller, G.; Pearson, H.A.; Pagano, J.S.; Dowaliby, J.M. Infectious Mononucleosis: Epstein–Barr-Virus Shedding in Saliva and the Oropharynx. N. Engl. J. Med. 1976, 294, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henle, W.; Diehl, V.; Kohn, G.; zur Hausen, H.; Henle, G. Herpes-Type virus and chromosome marker in normal Leukocytes after growth with irradiated Burkitt cells. Science 1967, 157, 1064–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.H. Establishment of cell lines from peripheral Leucocytes in infectious Mononucleosis. Nature 1967, 216, 810–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, M.; Fitzsimmons, L.; Bell, A.I. Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt lymphoma. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, A.; Barriga, F.; Inghirami, G.; Knowles, D.M.; Neequaye, J.; Magrath, I.T.; Dalla-Favera, R. Epstein-Barr virus infection precedes clonal expansion in Burkitt’s and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated lymphoma [see comments]. Blood 1991, 77, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, G.; MacArthur, G.; Farrell, P. Epstein–Barr virus and Burkitt lymphoma. Postgrad. Med. J. 2008, 84, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, H.C.; Pei, Y.; Robertson, E.S. Epstein–Barr virus: Diseases linked to infection and transformation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.P.; Kurzrock, R. Epstein-Barr virus and cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 803–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, B.M.; Lear, A.L.; Rowe, M.; Croom-Carter, D.; Young, L.S.; Rookes, S.M.; Gallimore, P.H.; Rickinson, A.B. Three transcriptionally distinct forms of epstein-barr virus latency in somatic cell hybrids: Cell phenotype dependence of virus promoter usage. Virology 1992, 187, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, S. Identification of virus-encoded MicroRNAs. Science 2004, 304, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, S.; Meister, G.; Grässer, F.A. EBV-encoded miRNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2011, 1809, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab-Traub, N. Novel mechanisms of EBV-induced oncogenesis. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, C.Y.; Papathomas, T.G.; Medeiros, L.J.; Young, K.H. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2013, 122, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.-T.; Guo, J.-R.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.-Z.; Shen, H.-R.; Kong, Y.-L.; Xia, Y.; Li, J.-Y.; Liang, J.-H.; Xu, W. EBV-Mir-BART5-5p targets p53 independent pathway in cytoplasm: Potential role in EBV lymphomagenesis. Genes Dis. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.H.; Macsween, K.F.; Higgins, C.D.; Thomas, R.; McAulay, K.; Williams, H.; Harrison, N.; Reid, S.; Conacher, M.; Douglas, J.; et al. A cohort study among university students: Identification of risk factors for Epstein-Barr virus Seroconversion and infectious Mononucleosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.H.; Swerdlow, A.J.; Higgins, C.; McAulay, K.; Harrison, N.; Williams, H.; Britton, K.; Macsween, K.F. Sexual history and Epstein-Barr virus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.D.; Swerdlow, A.J.; Macsween, K.F.; Harrison, N.; Williams, H.; McAulay, K.; Thomas, R.; Reid, S.; Conacher, M.; Britton, K.; et al. A study of risk factors for acquisition of Epstein-Barr virus and its subtypes. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemerow, G.; Mold, C.; Schwend, V.K.; Tollefson, V.; Cooper, N. Identification of gp350 as the viral glycoprotein mediating attachment of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) to the EBV/C3d receptor of B cells: Sequence homology of gp350 and C3 complement fragment C3d. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Spriggs, M.K.; Kovats, S.; Turk, S.M.; Comeau, M.R.; Nepom, B.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Epstein-Barr virus uses HLA class II as a cofactor for infection of B lymphocytes. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4657–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, G.J.; Decker, L.L.; Volk, M.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. EBV persistence in memory B cells in vivo. Immunity 1998, 9, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurth, J.; Spieker, T.; Wustrow, J.; Strickler, J.G.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Rajewsky, K.; Küppers, R. EBV-Infected B cells in infectious Mononucleosis. Immunity 2000, 13, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurth, J.; Hansmann, M.L.; Rajewsky, K.; Kuppers, R. Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells expanding in germinal centers of infectious mononucleosis patients do not participate in the germinal center reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4730–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunmire, S.K.; Verghese, P.S.; Balfour Jr, H.H. Primary epstein-barr virus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 102, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odumade, O.A.; Hogquist, K.A.; Balfour Jr, H.H. Progress and problems in understanding and managing primary Epstein-Barr virus infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, M.; Hammerschmidt, W. Epstein-Barr virus provides a new paradigm: A requirement for the immediate inhibition of apoptosis. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, G.J.; Hochberg, D.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. The expression pattern of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes in vivo is dependent upon the differentiation stage of the infected B cell. Immunity 2000, 13, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gires, O.; Zimber-Strobl, U.; Gonnella, R.; Ueffing, M.; Marschall, G.; Zeidler, R.; Pich, D.; Hammerschmidt, W. Latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus mimics a constitutively active receptor molecule. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 6131–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, R.G.; Wilson, J.B.; Anderson, S.J.; Longnecker, R. Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A drives B cell development and survival in the absence of normal B cell receptor signals. Immunity 1998, 9, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laichalk, L.L.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. Terminal differentiation into plasma cells initiates the Replicative cycle of Epstein-Barr virus in vivo. J. Virol. 2004, 79, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, P.; Bonzheim, I.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martínez, L. Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the elderly. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2011, 18, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münz, C. Epstein–Barr virus-specific immune control by innate lymphocytes. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Piubelli, M.L.; Salas, Y.I.; Pachas, C.; Becker-Hecker, R.; Vega, F.; Miranda, R.N. Epstein–Barr virus-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders and lymphomas: A review. Pathology 2020, 52, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.-X.; Liang, J.-H.; Miao, Y.; Fan, L.; Wang, L.; Qu, X.-Y.; Cao, L.; Gong, Q.-X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.-H. Epstein-Barr virus positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma predict poor outcome, regardless of the age. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatter, K.; Pezzella, F. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Diagn. Histopathol. 2010, 16, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, J. World Health Organization classification of malignant lymphomas. Exp. Oncol. 2001, 23, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Said, J.W. Aggressive B-cell lymphomas: How many categories do we need? Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, S42–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittaluga, S.; Jaffe, E.S. T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2010, 95, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrzalikova, K.; Vockerodt, M.; Leonard, S.; Bell, A.; Wei, W.; Schrader, A.; Wright, K.L.; Kube, D.; Rowe, M.; Woodman, C.B. Down-regulation of BLIMP1α by the EBV oncogene, LMP-1, disrupts the plasma cell differentiation program and prevents viral replication in B cells: Implications for the pathogenesis of EBV-associated B-cell lymphomas. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2011, 117, 5907–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrzalikova, K.; Leonard, S.; Fan, Y.; Bell, A.; Vockerodt, M.; Flodr, P.; Wright, K.L.; Rowe, M.; Tao, Q.; Murray, P.G. Hypomethylation and over-expression of the beta isoform of BLIMP1 is induced by Epstein-Barr virus infection of B cells; potential implications for the pathogenesis of EBV-associated lymphomas. Pathogens 2012, 1, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrzalikova, K.; John Woodman, C.B.; Murray, P.G. BLIMP1α, the master regulator of plasma cell differentiation is a tumor supressor gene in B cell lymphomas. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Palacky Univ. Olomouc 2012, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.W.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Piris, M.A.; Banham, A.H.; Delabie, J.; Braziel, R.M.; Geng, H.; Iqbal, J.; Lenz, G. A new immunostain algorithm classifies diffuse large B-cell lymphoma into molecular subtypes with high accuracy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5494–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roosbroeck, K.; Cools, J.; Dierickx, D.; Thomas, J.; Vandenberghe, P.; Stul, M.; Delabie, J.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Marynen, P.; Wlodarska, I. ALK-positive large B-cell lymphomas with cryptic SEC31A-ALK and NPM1-ALK fusions. Haematologica 2010, 95, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukema, S.M.; Siebert, R.; Schuuring, E.; van Imhoff, G.W.; Kluin-Nelemans, H.C.; Boerma, E.-J.; Kluin, P.M. Double-hit B-cell lymphomas. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2011, 117, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S.; Cook, J.R.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Anderson, K.C.; Brousset, P.; Cerroni, L.; de Leval, L.; Dirnhofer, S. The International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms: A Report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2022, 140, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.D.; Arthur, S.E.; Hodson, D.J. Molecular profiling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Why so many types of subtypes? Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 814–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuze, T.; Nakamura, N.; Hashimoto, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Abe, M. The Characteristics of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-positive Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Comparison between EBV+ and EBV-Cases in Japanese Population. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2000, 91, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, T.; Ichimura, K.; Suzuki, R.; Suzumiya, J.; Ohshima, K.; Yatabe, Y.; Yokoi, T.; Kojima, M.; Kamiya, Y.; Taji, H. Senile EBV+ B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders: A clinicopathologic study of 22 patients. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Yoon, D.; Suh, C.; Huh, J.; Do, I.-G.; Sohn, I.; Jo, J.; Jung, S.-H.; Hong, M.; Yoon, H. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in young adults: Is this a distinct disease entity? Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.J.; Beltran, B.E.; Miranda, R.N.; Young, K.H.; Chavez, J.C.; Sotomayor, E.M. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly: 2016 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, B.E.; Castro, D.; Paredes, S.; Miranda, R.N.; Castillo, J.J. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.J.; Beltran, B.E.; Miranda, R.N.; Young, K.H.; Chavez, J.C.; Sotomayor, E.M. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: 2018 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dojcinov, S.D.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L. EBV-positive lymphoproliferations of B-T-and NK-cell derivation in non-immunocompromised hosts. Pathogens 2018, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Martino, G.; Lazzi, S. A comparison of the International Consensus and 5th World Health Organization classifications of mature B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2022, 37, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, C.Y.; Li, L.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Visco, C.; Tzankov, A.; Manyam, G.C.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Dybaer, K.; Chiu, A.; Orazi, A. Prevalence and clinical implications of Epstein–Barr virus infection in de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Western countries. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donzel, M.; Bonjour, M.; Combes, J.-D.; Broussais, F.; Sesques, P.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; de Martel, C. Lymphomas associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection in 2020: Results from a large, unselected case series in France. Eclinicalmedicine 2022, 54, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Suh, C.H.; Won Kim, K.; Kim, H.S.; Armand, P.; Huang, R.Y.; Guenette, J.P. The incidence of Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodetskiy, V.; Probatova, N.; Obukhova, T.; Vasilyev, V. Analysis of prognostic factors in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with rheumatic diseases. Lupus Sci. Med. 2021, 8, e000561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yue, B. Clinical characteristics and prognostic significance of EBER positivity in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundo, L.; Del Porro, L.; Granai, M.; Siciliano, M.C.; Mancini, V.; Santi, R.; Marcar, L.; Vrzalikova, K.; Vergoni, F.; Di Stefano, G. Frequent traces of EBV infection in Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas classified as EBV-negative by routine methods: Expanding the landscape of EBV-related lymphomas. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2407–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.; De Matteo, E.; Narbaitz, M.; Carreño, F.A.; Preciado, M.V.; Chabay, P.A. Epstein–Barr virus presence in pediatric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma reveals a particular association and latency patterns: Analysis of viral role in tumor microenvironment. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.; Narbaitz, M.; Metrebian, F.; De Matteo, E.; Preciado, M.V.; Chabay, P.A. Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma association is not only restricted to elderly patients. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 2816–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolae, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Abdullah, S.; Steinberg, S.M.; Pham, T.A.; Davies-Hill, T.; Xi, L.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. EBV-positive large B-cell lymphomas in young patients: A nodal lymphoma with evidence for a tolerogenic immune environment. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2015, 126, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.S.; Rickinson, A.B. Epstein–Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, G.; Bell, A.; Rickinson, A. Epstein–Barr virus–associated Burkitt lymphomagenesis selects for downregulation of the nuclear antigen EBNA2. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, G.L.; Milner, A.E.; Tierney, R.J.; Croom-Carter, D.S.; Altmann, M.; Hammerschmidt, W.; Bell, A.I.; Rickinson, A.B. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2) gene deletion is consistently linked with EBNA3A,-3B, and-3C expression in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells and with increased resistance to apoptosis. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10709–10717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, G.L.; Long, H.M.; Stylianou, J.; Thomas, W.A.; Leese, A.; Bell, A.I.; Bornkamm, G.W.; Mautner, J.; Rickinson, A.B.; Rowe, M. An Epstein-Barr virus anti-apoptotic protein constitutively expressed in transformed cells and implicated in burkitt lymphomagenesis: The Wp/BHRF1 link. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderton, E.; Yee, J.; Smith, P.; Crook, T.; White, R.; Allday, M. Two Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) oncoproteins cooperate to repress expression of the proapoptotic tumour-suppressor Bim: Clues to the pathogenesis of Burkitt’s lymphoma. Oncogene 2008, 27, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.I.; Wang, F.; Mannick, J.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 is a key determinant of lymphocyte transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9558–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Romero-Masters, J.C.; Huebner, S.; Ohashi, M.; Hayes, M.; Bristol, J.A.; Nelson, S.E.; Eichelberg, M.R.; Van Sciver, N.; Ranheim, E.A.; et al. EBNA2-deleted Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) isolate, P3HR1, causes Hodgkin-like lymphomas and diffuse large B cell lymphomas with type II and Wp-restricted latency types in humanized mice. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirmeier, U.; Neuhierl, B.; Kilger, E.; Reisbach, G.; Sandberg, M.L.; Hammerschmidt, W. Latent membrane protein 1 is critical for efficient growth transformation of human B cells by Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 2982–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.-D.; Xu, X.; Plowshay, J.; Ranheim, E.A.; Burlingham, W.J.; Jensen, J.L.; Asimakopoulos, F.; Tang, W.; Gulley, M.L.; Cesarman, E.; et al. LMP1-deficient Epstein-Barr virus mutant requires T cells for lymphomagenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.-D.; Tsai, M.-H.; Romero-Masters, J.C.; Ranheim, E.A.; Huebner, S.M.; Bristol, J.A.; Delecluse, H.-J.; Kenney, S.C. Latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) and LMP2A collaborate to promote Epstein-Barr virus-induced B cell lymphomas in a cord blood-humanized mouse model but are not essential. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01928-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.E.; Rämer, P.C.; Naresh, K.N.; Meixlsperger, S.; Pinaud, L.; Rooney, C.; Savoldo, B.; Coutinho, R.; Bödör, C.; Gribben, J. EBNA3B-deficient EBV promotes B cell lymphomagenesis in humanized mice and is found in human tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1487–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruo, S.; Zhao, B.; Johannsen, E.; Kieff, E.; Zou, J.; Takada, K. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens 3C and 3A maintain lymphoblastoid cell growth by repressing p16INK4A and p14ARF expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.M.; Dai, J.; Bazot, Q.; Patel, L.; Nikitin, P.A.; Djavadian, R.; Winter, P.S.; Salinas, C.A.; Barry, A.P.; Wood, K.C. Epstein-Barr virus ensures B cell survival by uniquely modulating apoptosis at early and late times after infection. eLife 2017, 6, e22509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Masters, J.C.; Ohashi, M.; Djavadian, R.; Eichelberg, M.R.; Hayes, M.; Zumwalde, N.A.; Bristol, J.A.; Nelson, S.E.; Ma, S.; Ranheim, E.A.; et al. An EBNA3A-mutated Epstein-Barr virus retains the capacity for lymphomagenesis in a cord blood-humanized mouse model. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e02168-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, Y.; Murata, T.; Sato, Y.; Muramatsu, H.; Ito, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Okuno, T.; Murakami, N.; Yoshida, K.; Sawada, A. Defective Epstein–Barr virus in chronic active infection and haematological malignancy. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Okuno, Y.; Sato, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Murata, T. Deletion of Viral microRNAs in the Oncogenesis of Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Lymphoma. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 667968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Tsai, M.-H.; Shumilov, A.; Poirey, R.; Bannert, H.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Feederle, R.; Delecluse, H.-J. The Epstein-Barr virus BART miRNA cluster of the M81 strain modulates multiple functions in primary B cells. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, S.; Hijioka, F.; Watanabe, T.; Yanagi, Y.; Okuno, Y.; Masud, H.; Sato, Y.; Murata, T.; Kimura, H. Role of Epstein–Barr Virus C Promoter Deletion in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; Jiang, A.; et al. A probabilistic classification tool for genetic subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma with therapeutic implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontzek, F.; Staiger, A.M.; Wullenkord, R.; Grau, M.; Zapukhlyak, M.; Kurz, K.S.; Horn, H.; Erdmann, T.; Fend, F.; Richter, J.; et al. Molecular profiling of EBV associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crombie, J.L.; LaCasce, A.S. Epstein Barr virus associated B-cell lymphomas and iatrogenic lymphoproliferative disorders. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gebauer, N.; Künstner, A.; Ketzer, J.; Witte, H.M.; Rausch, T.; Benes, V.; Zimmermann, J.; Gebauer, J.; Merz, H.; Bernard, V. Genomic insights into the pathogenesis of Epstein–Barr virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by whole-genome and targeted amplicon sequencing. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebauer, N.; Gebauer, J.; Hardel, T.T.; Bernard, V.; Biersack, H.; Lehnert, H.; Rades, D.; Feller, A.C.; Thorns, C. Prevalence of targetable oncogenic mutations and genomic alterations in Epstein–Barr virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.N.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Lim, K.-H.; Kohlhammer, H.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature 2011, 470, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeelall, Y.S.; Horikawa, K. Oncogenic MYD88 mutation drives Toll pathway to lymphoma. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 659–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, G.; Xiao, H.; Yin, W.; Nakamura, S.; Rao, H. Genetic heterogeneity and mutational signature in Chinese Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lin, W.; Duan, Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, W.; Su, W.; Yan, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, L. Comprehensive genomic profiling of EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and the expression and clinicopathological correlations of some related genes. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.; Der, C.J. RHOA takes the RHOad less traveled to cancer. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Miyoshi, H.; Sakata, S.; Dobashi, A.; Couronné, L.; Kogure, Y.; Sato, Y.; Nishida, K.; Gion, Y.; Shiraishi, Y. Frequent structural variations involving programmed death ligands in Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphomas. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1687–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, X. The Spectrum of MYC alterations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Acta Haematol. 2020, 143, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedell, P.A.; Smith, S.M. Double hit and double expressors in lymphoma: Definition and treatment. Cancer 2018, 124, 4622–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Tang, G.; Wang, W.; Kim, Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Fedoriw, G.Y. EBV+ high-grade B cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements: A multi-institutional study. Histopathology 2022, 80, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran, B.E.; Morales, D.; Quiñones, P.; Medeiros, L.J.; Miranda, R.N.; Castillo, J.J. EBV-positive diffuse large b-cell lymphoma in young immunocompetent individuals. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011, 11, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, C.; Tobin, J.; Gunawardana, J.; Francis, S.; Gifford, G.; Gabrielli, S.; Gill, A.; Stevenson, W.; Talaulikar, D.; Gould, C. The tumour microenvironment is immuno-tolerogenic and a principal determinant of patient outcome in EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2019, 103, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.; Vistarop, A.G.; Huaman, F.; Narbaitz, M.; Metrebian, F.; De Matteo, E.; Preciado, M.V.; Chabay, P.A. Cytotoxic response against Epstein Barr virus coexists with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma tolerogenic microenvironment: Clinical features and survival impact. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Hiraiwa, S.; Miyaoka, M.; Tomita, S.; Ikoma, H.; Ito, A.; Kondo, Y.; Itoh, J.; Roncador, G. High PTX3 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.-D.; Xu, X.; Jones, R.; Delecluse, H.-J.; Zumwalde, N.A.; Sharma, A.; Gumperz, J.E.; Kenney, S.C. PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade inhibits Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoma growth in a cord blood humanized-mouse model. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| WHO Classification 2017 | WHO Classification 2022 | ICC Classification 2022 | EBV Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma NOS | 1. Large B-cell lymphomas | ||
| DLBCL, NOS | DLBCL | DLBCL | Negative by definition |
| 2. Other lymphomas of large B-cells | |||
| T-cell/histiocyte-rich LBCL | T-cell/histiocyte-rich LBCL | T-cell/histiocyte-rich LBCL | Negative |
| Primary DLBCL of the CNS | Primary large B-cell lymphoma of immune-privileged sites (CNS, vitreoretinal, testicular) | Primary DLBCL of immune-CNS, Primary DLBCL of testis * | Predominantly negative |
| Primary cutaneous DLBCL, leg type | Primary cutaneous DLBCL, leg type | Primary cutaneous DLBCL, leg type | Negative |
| EBV-positive DLBCL, NOS | EBV-positive DLBCL | EBV-positive DLBCL, NOS | 100% positive by definition |
| Primary mediastinal (thymic) LBCL | Primary mediastinal LBCL | Primary mediastinal LBCL | Rare examples of EBV-positive cases reported |
| Intravascular LBCL | Intravascular LBCL | Intravascular LBCL | Negative |
| DLBCL associated with chronic inflammation | DLBCL associated with chronic inflammation | DLBCL associated with chronic inflammation | 100% positive |
| Lymphomatoid granulomatosis | Lymphomatoid granulomatosis | Lymphomatoid granulomatosis | 100% positive |
| ALK-positive LBCL | ALK-positive LBCL | ALK-positive LBCL | Negative |
| Plasmablastic lymphoma | Plasmablastic lymphoma | Plasmablastic lymphoma | 70–80% positive |
| LBCL with IRF4 rearrangement | LBCL with IRF4 rearrangement | LBCL with IRF4 rearrangement * | Negative |
| Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration | High-grade B-cell lymphoma with 11q aberrations | LBCL with 11q aberrations | Negative |
| (Previously included in DLBCL associated with chronic inflammation) | Fibrin-associated LBCL | Fibrin-associated DLBCL | ~100% positive |
| (Not previously included) | Fluid overload-associated LBCL | HHV8 and EBV-negative PEL | WHO:13–30% positive. ICC: negative by definition. |
| 2. KSHV/HHV8-associated B-cell LPD | |||
| HHV8-positive DLBCL, NOS | KSHV/HHV8-positive DLBCL | HHV8+ DLBCL | Occasional cases are positive |
| Primary effusion lymphoma | Primary effusion lymphoma | Primary effusion lymphoma | Most cases positive |
| 3. B-cell lymphoma unclassifiable | 1. Large B-cell Lymphoma (continued) | ||
| B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between DLBCL and classical Hodgkin lymphoma | Mediastinal grey zone lymphoma | Mediastinal grey zone lymphoma | Negative |
| 4. High-grade B-cell lymphoma | |||
| High-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements | DLBCL/high grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 rearrangements | High grade B-cell lymphoma; MYC:BCL2 or MYC:BCL6 or MYC:BCL2:BCL6 | Negative (rare reported EBV-positive cases) |
| High-grade B-cell lymphoma, NOS | High-grade B-cell lymphoma, NOS | High-grade B-cell lymphoma, NOS | Negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ross, A.M.; Leahy, C.I.; Neylon, F.; Steigerova, J.; Flodr, P.; Navratilova, M.; Urbankova, H.; Vrzalikova, K.; Mundo, L.; Lazzi, S.; et al. Epstein–Barr Virus and the Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Life 2023, 13, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020521
Ross AM, Leahy CI, Neylon F, Steigerova J, Flodr P, Navratilova M, Urbankova H, Vrzalikova K, Mundo L, Lazzi S, et al. Epstein–Barr Virus and the Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Life. 2023; 13(2):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020521
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoss, Aisling M., Ciara I. Leahy, Fiona Neylon, Jana Steigerova, Patrik Flodr, Martina Navratilova, Helena Urbankova, Katerina Vrzalikova, Lucia Mundo, Stefano Lazzi, and et al. 2023. "Epstein–Barr Virus and the Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma" Life 13, no. 2: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020521
APA StyleRoss, A. M., Leahy, C. I., Neylon, F., Steigerova, J., Flodr, P., Navratilova, M., Urbankova, H., Vrzalikova, K., Mundo, L., Lazzi, S., Leoncini, L., Pugh, M., & Murray, P. G. (2023). Epstein–Barr Virus and the Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Life, 13(2), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020521







