Iron Fertilization Can Enhance the Mass Production of Copepod, Pseudodiaptomus annandalei, for Fish Aquaculture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Physicochemical Analyses
2.3. Biological Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
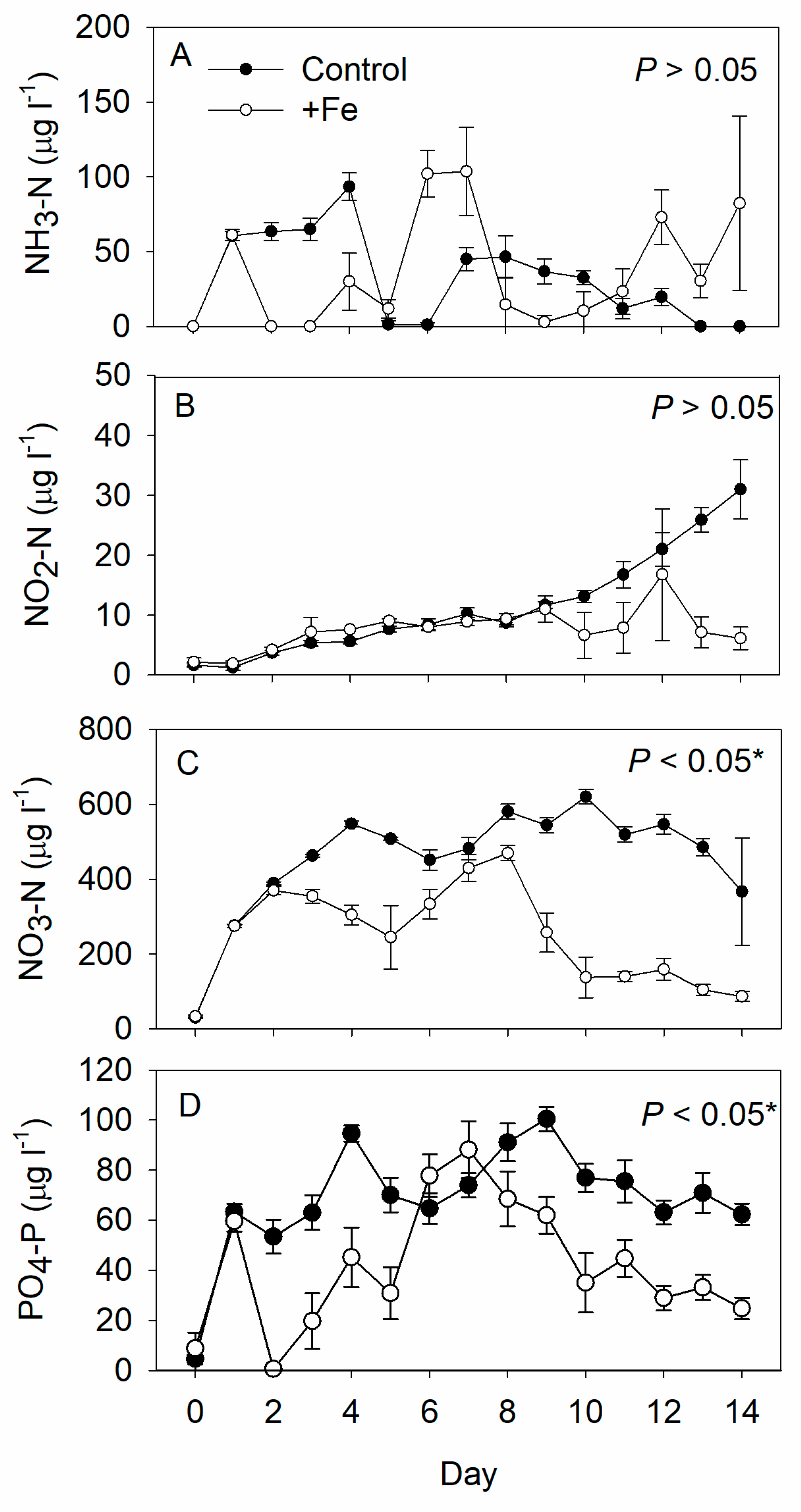
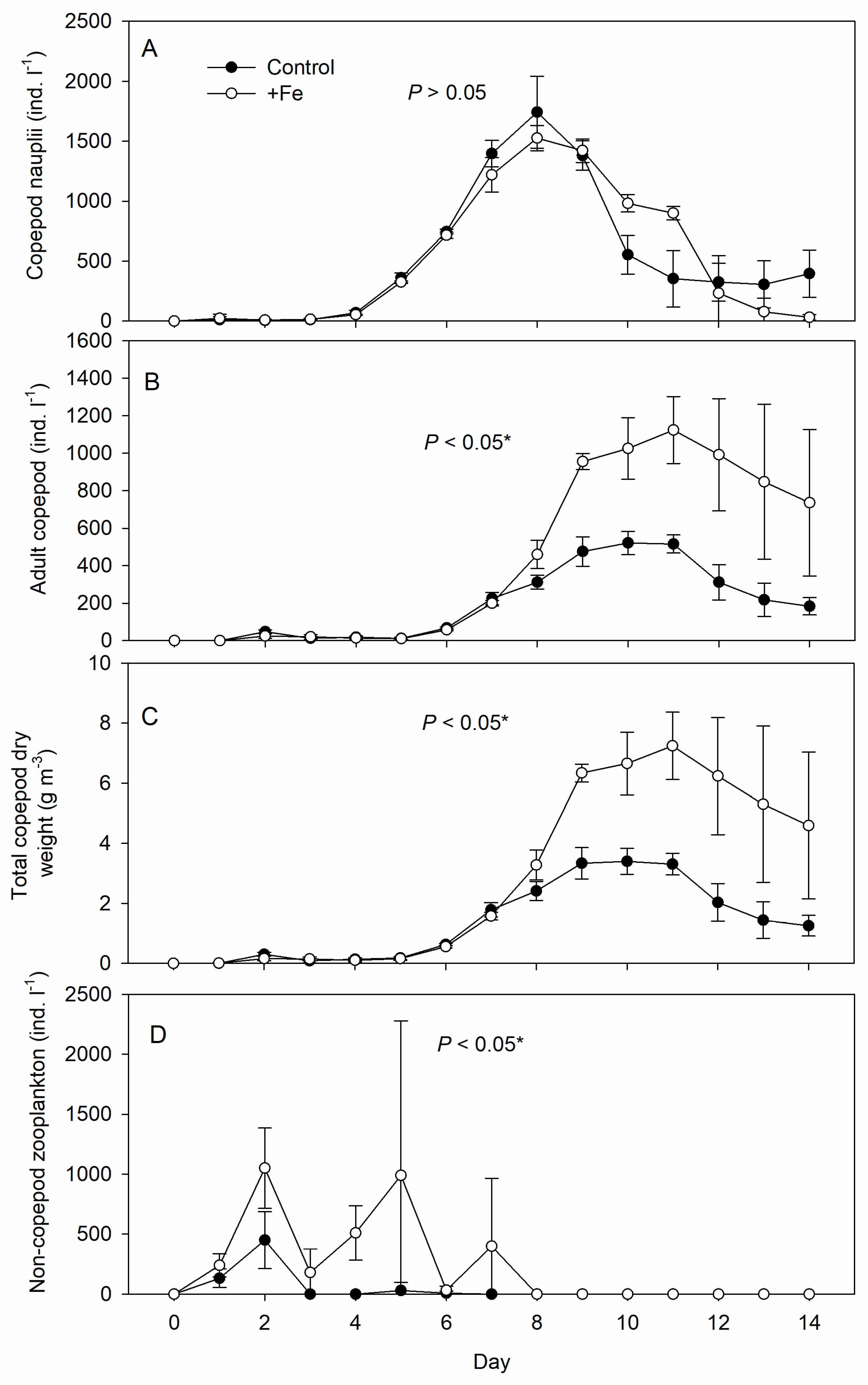
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, I.C.; Su, H.M.; Chang, E.Y. Techniques in finfish larviculture in Taiwan. Aquaculture 2001, 200, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de F Côrtes, G.; Tsuzuki, M.Y. Effect of different live food on survival and growth of first feeding barber goby, Elacatinus figaro (Sazima, Moura & Rosa 1997) larvae. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 831–834. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, X.; Lin, M. Effects of algae and live food density on the feeding ability, growth and survival of miiuy croaker during early development. Aquaculture 2014, 428, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, K.S.; Chang, Y.C.; Meng, P.J.; Leu, M.Y.; Glover, D.C. Towards sustainable exhibits-application of an inorganic fertilization method in coral reef fish larviculture in an aquarium. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2748–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, K.R.; AkbarAli, I.; Schmidt, B.V.; John, E.M.; Sureshkumar, S.; Thazhakot Vasunambesan, S. Improvement of nutritional quality of live feed for aquaculture: An overview. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara, A.; Marcial, H.S. The use of non-Brachionus plicatilis species complex rotifer in larviculture. Hydrobiologia 2019, 844, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, L.C.; Dhert, P.; Sorgeloos, P. Recent developments in the application of live feeds in the freshwater ornamental fish culture. Aquaculture 2003, 227, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, J.N.; Nagata, W.D. Carbohydrate and fatty acid composition of the rotifer, Brachionus plicatilis, fed monospecific diets of yeast or phytoplankton. Aquaculture 1990, 89, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, P.M.; van Someren Gréve, H.; Jørgensen, K.N.; Kjær, K.G.; Hansen, B.W. Evaluation of high-density tank cultivation of the live-feed cyclopoid copepod Apocyclops royi (Lindberg 1940). Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivotto, I.; Buttino, I.; Borroni, M.; Piccinetti, C.; Malzone, M.; Carnevali, O. The use of the Mediterranean calanoid copepod Centropages typicus in Yellowtail clownfish (Amphiprion clarkii) larviculture. Aquaculture 2008, 284, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivotto, I.; Capriotti, F.; Buttino, I.; Avella, A.; Vitiello, V.; Maradonna, F.; Carnevali, O. The use of harpacticoid copepods as live prey for Amphiprion clarkii larviculture: Effects on larval survival and growth. Aquaculture 2008, 274, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavens, P.; Sorgeloos, P. Manual on the Production and Use of Live Food for Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, R.J.; Bell, J.G.; Luizi, F.S.; Gara, B.; Bromage, N.R.; Sargent, J.R. Natural copepods are superior to enriched Artemia nauplii as feed for halibut larvae (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) in terms of survival, pigmentation and retinal morphology: Relation to dietary essential fatty acids. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, W.; Goodwin, A.E.; Eiras, J.C.; Nowak, B.F. Importance of Copepoda in freshwater aquaculture. Zool. Stud. 2004, 43, 193–205. [Google Scholar]
- Støttrup, J. The elusive copepods: Their production and suitability in marine aquaculture. Aquac. Res. 2000, 31, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, S.C.; Augustin, C.B.; Geffen, A.J.; Dinis, M.T. Growth, egg production and hatching success of Acartia tonsa cultured at high densities. Aquaculture 2017, 468, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasdi, N.W.; Qin, J.G. Copepod supplementation as a live food improved growth and survival of Asian seabass Lates calcarifer larvae. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 3606–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanda, E.; Drillet, G.; Huang, C.C.; Hwang, J.S.; Højgaard, J.K.; Jakobsen, H.H.; Rayner, T.A.; Su, H.M.; Hansen, B.W. An analysis of how to improve production of copepods as live feed from tropical Taiwanese outdoor aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, C.; Huang, X. Effect of diet on the development, survival, and reproduction of the calanoid copepod Pseudodiaptomus dubia. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1756–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Luo, X.; Huang, X.; Gu, B. Influences of temperature on development and survival, reproduction and growth of a calanoid copepod (Pseudodiaptomus dubia). Sci. World J. 2009, 9, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindley, L.C.; Phelps, R.P. Production and collection of copepod nauplii from brackish water ponds. J. Appl. Aquac. 2009, 21, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang’ombe, J.; Brown, J.A.; Halfyard, L.C. Effect of using different types of organic animal manure on plankton abundance, and on growth and survival of Tilapia rendalli (Boulenger) in ponds. Aquac. Res. 2006, 37, 1360–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, A. The growth and gonadal maturation of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell) broodstock fed differently heated soybean-based diets. Aquac. Nutr. 2006, 12, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaatz, S.E.; Morris, J.E.; Rudacille, J.B.; Johnson, J.A.; Clayton, R.D. Role of organic fertilizers in walleye (Sander vitreus) production in plastic-lined culture ponds. Aquac. Res. 2011, 42, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.K.; Tew, K.S. The Advantages of inorganic fertilization for the mass production of copepods as food for fish larvae in aquaculture. Life 2022, 12, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischke, C.C.; Zimba, P.V. Plankton community responses in earthen channel catfish nursery ponds under various fertilization regimes. Aquaculture 2004, 233, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Romano, N. Nitrogenous wastes: Often overlooked pollutants in aquatic environments. J. Mar. Sci. Res. Dev. 2013, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Nitrogen biogeochemistry of aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 1998, 166, 181–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasso, J. Toxicity of nitrogenous wastes to aquaculture animals. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1994, 2, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, A.T. Fertilizers and the environment. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 1999, 55, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Maranger, R.; Sobota, D.J.; Bouwman, L. The Haber Bosch–harmful algal bloom (HB–HAB) link. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.; Culver, D.A. The survival and growth of larval walleye, Stizostedion vitreum, and trophic dynamics in fertilized ponds. Aquaculture 1992, 108, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, K.S.; Meng, P.J.; Lin, H.S.; Chen, J.H.; Leu, M.Y. Experimental evaluation of inorganic fertilization in larval giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus Bloch) production. Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.P.; Culver, D.A. Experimental evaluation of the impacts of reduced inorganic phosphorus fertilization rates on juvenile saugeye production. Aquaculture 2010, 304, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, K.S.; Conroy, J.D.; Culver, D.A. Effects of lowered inorganic phosphorus fertilization rates on pond production of percid fingerlings. Aquaculture 2006, 255, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, D.A. Effects of the N: P ratio in fertilizer for fish hatchery ponds. Int. Ver. Für Theor. Und Angew. Limnol. Verh. 1991, 24, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Han, C.C.; Ju, Y.M.; Tew, K.S. Analyses of diet preference of larval orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) grown under inorganic fertilization method using next-generation sequencing. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, D.A.; Madon, S.P.; Qin, J. Percid pond production techniques: Timing, enrichment, and stocking density manipulation. J. Appl. Aquac. 1994, 2, 9–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Madon, S.P.; Culver, D.A. Effect of larval walleye (Stizostedion vitreum) and fertilization on the plankton community: Implications for larval fish culture. Aquaculture 1995, 130, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R.R.; Ryther, J.H. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 1962, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Camus, T.; Zeng, C.; McKinnon, A.D. Egg production, egg hatching success and population increase of the tropical paracalanid copepod, Bestiolina similis (Calanoida: Paracalanidae) fed different microalgal diets. Aquaculture 2009, 297, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-X.; Xu, D.-H. Feeding, egg production and laboratory culture of Schmackeria poplesia Shen (Copepoda: Calanoida). Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, N.; Sumares, B.; Andrade, C.A.P.; Afonso, A. The effects of temperature and photoperiod on egg hatching success, egg production and population growth of the calanoid copepod, Acartia grani (Calanoida: Acartiidae). Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, T.G.; Nielsen, R.; Nielsen, M.; Drillet, G.; Jepsen, P.M.; Hansen, B.W. Economic feasibility of copepod production for commercial use: Result from a prototype production facility. Aquaculture 2015, 436, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geider, R.J.; La Roche, J. The role of iron in phytoplankton photosynthesis, and the potential for iron-limitation of primary productivity in the sea. Photosynth. Res. 1994, 39, 275–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, J.L.; Geider, R.J.; Graziano, L.M.; Murray, H.; Lewis, K. Induction of specific proteins in eukaryotic algae grown under iron-, phosphorus-, or nitrogen-deficient conditions. J. Phycol. 1993, 29, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueler, J.G.; Ades, D.R. The role of iron nutrition in photosynthesis and nitrogen assimilation in Scenedesmus quadricauda (Chlorophyceae). J. Phycol. 1987, 23, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S. Influence of iron availability on nutrient consumption ratio of diatoms in oceanic waters. Nature 1998, 393, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.H.; Gordon, M.; Fitzwater, S.E. The case for iron. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, D.; Hare, C.; Weaver, R.; Zhang, Y.; Firme, G.; DiTullio, G.; Alm, M.; Riseman, S.; Maucher, J.; Geesey, M. Phytoplankton iron limitation in the Humboldt Current and Peru Upwelling. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, D.A.; Bruland, K.W. Iron-limited diatom growth and Si: N uptake ratios in a coastal upwelling regime. Nature 1998, 393, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasozi, N.; Tandlich, R.; Fick, M.; Kaiser, H.; Wilhelmi, B. Iron supplementation and management in aquaponic systems: A review. Aquac. Rep. 2019, 15, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, A.; Sourinejad, I.; Gharaei, A.; Johari, S.A.; Ghasemi, Z. The effects of diet supplementation with inorganic and nanoparticulate iron and copper on growth performance, blood biochemical parameters, antioxidant response and immune function of snow trout Schizothorax zarudnyi (Nikolskii, 1897). Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.; Liss, P.; Duce, R. Design of a small-scale in situ iron fertilization experiment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wakeham, S.G.; Fisher, N.S. Influence of iron on fatty acid and sterol composition of marine phytoplankton and copepod consumers. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.; Monteiro, M.; Robbs, P.; Leite, S. Growth and chemical composition of Spirulina Maxima and Spirulina Platensis biomass at different temperatures. Aquac. Int. 1999, 7, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, M.; Toledo, J.D.; Golez MS, N.; de los Santos, M.; Ohno, A. Preliminary investigation of feeding performance of larvae of early red-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides, reared with mixed zooplankton. In Live Food in Aquaculture; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.H.; Dahms, H.U.; Cheng, S.H.; Souissi, S.; Schmitt, F.G.; Kumar, R.; Hwang, J.S. Predation of Pseudodiaptomus annandalei (Copepoda: Calanoida) by the grouper fish fry Epinephelus coioides under different hydrodynamic conditions. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 393, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Sheng, J.; Lin, Q.; Gao, Y.; Lv, J. Effect of salinity on reproduction and survival of the copepod Pseudodiaptomus annandalei Sewell, 1919. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.C.; Riley, J.P. Determination of nitrate in the presence of nitrite in natural waters by flow injection analysis with a non-quantitative on-line cadmium redactor. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1994, 57, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanda, E.; Drillet, G.; Huang, C.C.; Hwang, J.S.; Jakobsen, H.H.; Rayner, T.A.; Su, H.M.; Wu, C.H.; Hansen, B.W. Trophic interactions and productivity of copepods as live feed from tropical Taiwanese outdoor aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 2015, 445, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, T.A.; Jørgensen, N.O.; Blanda, E.; Wu, C.H.; Huang, C.C.; Mortensen, J.; Hwang, J.S.; Hansen, B.W. Biochemical composition of the promising live feed tropical calanoid copepod Pseudodiaptomus annandalei (Sewell 1919) cultured in Taiwanese outdoor aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 2015, 441, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Dhanker, R.; Kumar, R. Does maternal exposure to diatom polyunsaturated aldehyde enhance offspring fitness in limnetic zooplankton Echinisca triserialis (Crustacea: Claodcera)? Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2022, 195, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, O.; Yakubu, A.; Adams, T.; Olaji, E.; Nwogu, N. A review of the use of copepods in marine fish larviculture. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2011, 21, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Zeng, C. The effects of live prey and greenwater on the early larval rearing of orchid dottyback Pseudochromis fridmani. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 737008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Shao, L.; Ricketts, A.; Moorhead, J. The importance of copepods as live feed for larval rearing of the green mandarin fish Synchiropus splendidus. Aquaculture 2018, 491, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisian, B.L.; Lemus, J.T.; Apeitos, A.; Blaylock, R.B.; Saillant, E.A. An intensive, large-scale batch culture system to produce the calanoid copepod, Acartia tonsa. Aquaculture 2019, 501, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Cabrero, A.; Herena-Garcia, R.; Nolan, J.M. Intensive production of the harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus californicus in a zero-effluent ‘green water’ bioreactor. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, M.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Tu, Y.H.; Chiu, P.S.; Yu, B.H.; Wang, J.B.; Tew, K.S.; Meng, P.J. Natural spawning, early development and first successful hatchery production of the bluestreak cleaner wrasse, Labroides dimidiatus (Valenciennes, 1839), with application of an inorganic fertilization method in larviculture. Aquaculture 2022, 553, 738056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, C.S. Potential fitness trade-offs for thermal tolerance in the intertidal copepod Tigriopus californicus. Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 2010, 64, 2521–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammock, B.G.; Lesmeister, S.; Flores, I.; Bradburd, G.S.; Hammock, F.H.; Teh, S.J. Low food availability narrows the tolerance of the copepod Eurytemora affinis to salinity, but not to temperature. Estuaries Coasts 2016, 39, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringler, N.H.; Hall, J.D. Effects of logging on water temperature, and dissolved oxygen in spawning beds. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1975, 104, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacek, C.; Marcus, N.H. Egg production of the copepod Acartia tonsa: The influence of hypoxia and food concentration. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecology. 2005, 318, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.W.; Hansen, P.J.; Nielsen, T.G.; Jepsen, P.M. Effects of elevated pH on marine copepods in mass cultivation systems: Practical implications. J. Plankton Res. 2017, 39, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, R.; Sommer, U. Food quantity and quality interactions at phytoplankton–zooplankton interface: Chemical and reproductive responses in a calanoid copepod. Front. Mar. Science. 2020, 7, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Anderson, R.S.; Spierling, R.; Leader, S.; Lesne, C.; Mahan, K.; Lundquist, T.; Benemann, J.R.; Lane, T.; Polle, J.E.W. Characterization of a novel strain of Tribonema minus demonstrating high biomass productivity in outdoor raceway ponds. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 331, 125007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Cheng, J.J.; Cobb, K.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, N.; Addy, M.; Chen, P.; Yan, X.; Ruan, R. Tribonema sp. and Chlorella zofingiensis co-culture to treat swine wastewater diluted with fishery wastewater to facilitate harvest. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, G.-K.; Kuo, J.; Tew, K.S. Iron Fertilization Can Enhance the Mass Production of Copepod, Pseudodiaptomus annandalei, for Fish Aquaculture. Life 2023, 13, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020529
Hong G-K, Kuo J, Tew KS. Iron Fertilization Can Enhance the Mass Production of Copepod, Pseudodiaptomus annandalei, for Fish Aquaculture. Life. 2023; 13(2):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020529
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Guo-Kai, Jimmy Kuo, and Kwee Siong Tew. 2023. "Iron Fertilization Can Enhance the Mass Production of Copepod, Pseudodiaptomus annandalei, for Fish Aquaculture" Life 13, no. 2: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020529
APA StyleHong, G.-K., Kuo, J., & Tew, K. S. (2023). Iron Fertilization Can Enhance the Mass Production of Copepod, Pseudodiaptomus annandalei, for Fish Aquaculture. Life, 13(2), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020529




