The Minimum Number of Ablation Lines for Complete Isolation of the Pulmonary Veins during Thoracoscopic Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
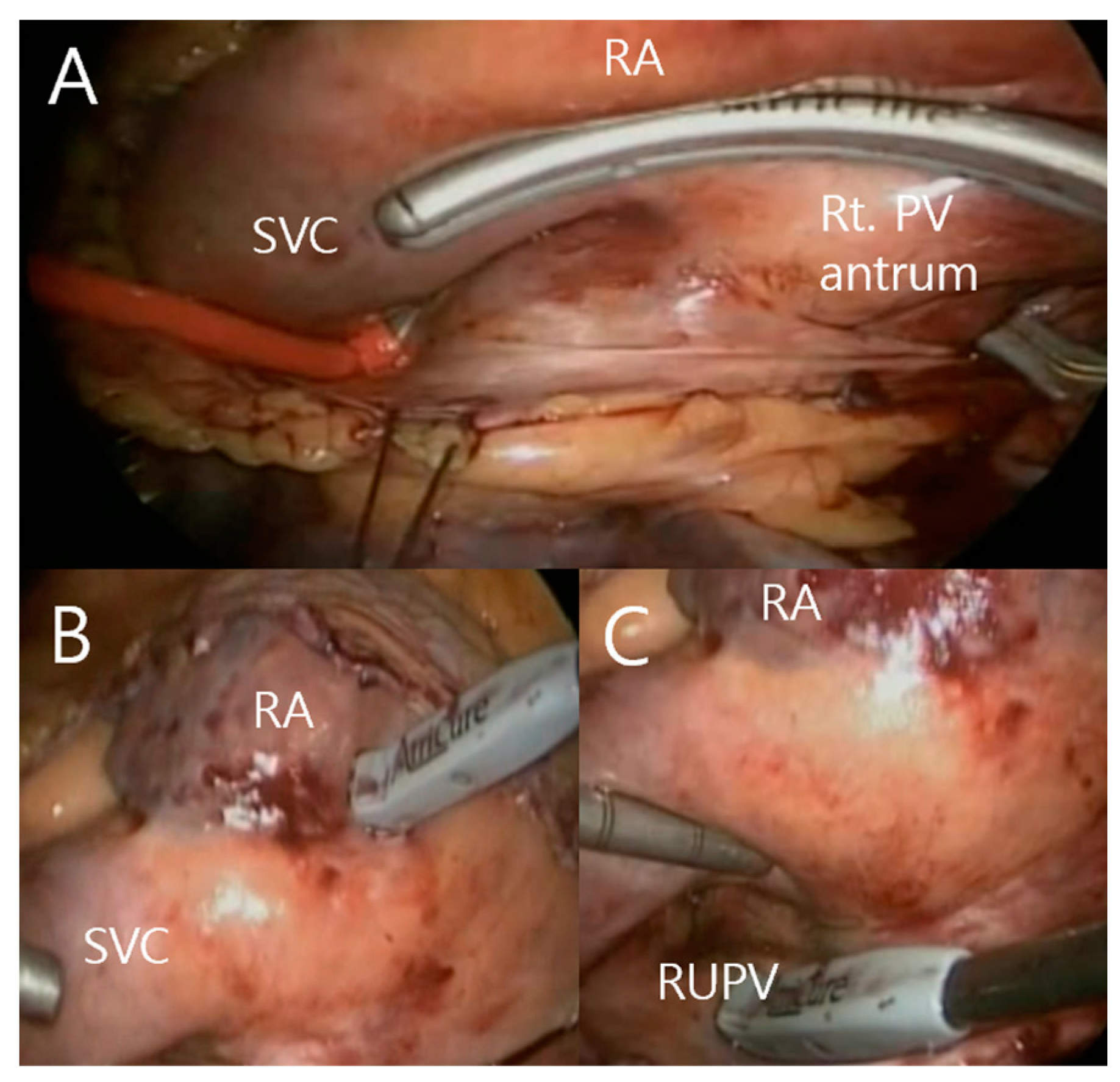
2.2. Totally Thoracoscopic Ablation
2.3. Conduction Block Test
2.4. Postoperative Management and Follow-Up
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Operative Data
3.3. Postoperative Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michaud, G.F.; Stevenson, W.G. Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Alpert, J.S.; Calkins, H.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C., Jr.; Conti, J.B.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, e1–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, G.G.; Gali, W.L.; Sarabanda, A.V.L.; Cunha, C.R.D.; Kessler, I.M.; Atik, F.A. Late Results of Cox Maze III Procedure in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Associated with Structural Heart Disease. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2017, 109, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.M.; Maniar, H.S.; Camillo, C.J.; Schuessler, R.B.; Boineau, J.P.; Sundt, T.M., III; Cox, J.L.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. The Cox maze III procedure for atrial fibrillation: Long-term efficacy in patients undergoing lone versus concomitant procedures. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2003, 126, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimar, T.; Schena, S.; Bailey, M.S.; Maniar, H.S.; Schuessler, R.B.; Cox, J.L.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. The cox-maze procedure for lone atrial fibrillation: A single-center experience over 2 decades. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2012, 5, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ad, N.; Suri, R.M.; Gammie, J.S.; Sheng, S.; O’Brien, S.M.; Henry, L. Surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation trends and outcomes in North America. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 144, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.M.; Maniar, H.S.; Schuessler, R.B.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Chronic transmural atrial ablation by using bipolar radiofrequency energy on the beating heart. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2002, 124, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Meir, M.; Gelsomino, S.; Lorusso, R.; Luca, F.; Pison, L.; Parise, O.; Wellens, F.; Gensini, G.F.; Maessen, J. The hybrid approach for the surgical treatment of lone atrial fibrillation: One-year results employing a monopolar radiofrequency source. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelsomino, S.; Van Breugel, H.N.; Pison, L.; Parise, O.; Crijns, H.J.; Wellens, F.; Maessen, J.G.; La Meir, M. Hybrid thoracoscopic and transvenous catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2014, 45, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Meir, M.; Gelsomino, S.; Luca, F.; Lorusso, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Pison, L.; Wellens, F.; Maessen, J. Minimally invasive thoracoscopic hybrid treatment of lone atrial fibrillation: Early results of monopolar versus bipolar radiofrequency source. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 14, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melby, S.J.; Gaynor, S.L.; Lubahn, J.G.; Lee, A.M.; Rahgozar, P.; Caruthers, S.D.; Williams, T.A.; Schuessler, R.B.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Efficacy and safety of right and left atrial ablations on the beating heart with irrigated bipolar radiofrequency energy: A long-term animal study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006, 132, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Meir, M. Surgical options for treatment of atrial fibrillation. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 3, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhwar, V.; Rankin, J.S.; Damiano, R.J., Jr.; Gillinov, A.M.; Bakaeen, F.G.; Edgerton, J.R.; Philpott, J.M.; McCarthy, P.M.; Bolling, S.F.; Roberts, H.G.; et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Surgical Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calkins, H.; Kuck, K.H.; Cappato, R.; Brugada, J.; Camm, A.J.; Chen, S.A.; Crijns, H.J.; Damiano, R.J., Jr.; Davies, D.W.; DiMarco, J.; et al. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: Recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design: A report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Developed in partnership with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society (ECAS); and in collaboration with the American College of Cardiology (ACC), American Heart Association (AHA), the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS). Endorsed by the governing bodies of the American College of Cardiology Foundation, the American Heart Association, the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society, the European Heart Rhythm Association, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society, and the Heart Rhythm Society. Heart Rhythm. 2012, 9, 632–696.e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, H.; Hindricks, G.; Cappato, R.; Kim, Y.H.; Saad, E.B.; Aguinaga, L.; Akar, J.G.; Badhwar, V.; Brugada, J.; Camm, J.; et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, e275–e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Geuzebroek, G.S.; Van Putte, B.P.; Boersma, L.V.; Sonker, U.; De Bakker, J.M.; Van Boven, W.J. Completely thoracoscopic pulmonary vein isolation with ganglionic plexus ablation and left atrial appendage amputation for treatment of atrial fibrillation. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2010, 38, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pojar, M.; Vojacek, J.; Haman, L.; Parizek, P.; Omran, N.; Vobornik, M.; Harrer, J. Thoracoscopic radiofrequency ablation for lone atrial fibrillation: Box-lesion technique. J. Card. Surg. 2014, 29, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotov, A.; Vachev, S.; Borisov, D.; Troitskiy, A.; Khabazov, R. Thoracoscopic Pulmonary Vein and Left Atrial Posterior Wall Isolation Combined with Left Atrial Appendage Resection in Patients with Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 35, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Greef, Y.; Ströker, E.; Schwagten, B.; Kupics, K.; De Cocker, J.; Chierchia, G.B.; de Asmundis, C.; Stockman, D.; Buysschaert, I. Complications of pulmonary vein isolation in atrial fibrillation: Predictors and comparison between four different ablation techniques: Results from the MIddelheim PVI-registry. Europace 2018, 20, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.J.; Jeong, D.S.; Park, S.J.; Park, K.M.; Kim, J.S.; On, Y.K. Long-term outcome of totally thoracoscopic surgical ablation in atrial fibrillation: A single-center experience. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2021, 36, 100861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.K.; Schneeberger, E.W.; Osterday, R.; Miller, D.; Merrill, W.; Flege, J.B., Jr.; Gillinov, A.M. Video-assisted bilateral pulmonary vein isolation and left atrial appendage exclusion for atrial fibrillation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2005, 130, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurfirst, V.; Mokracek, A.; Bulava, A.; Canadyova, J.; Hanis, J.; Pesl, L. Two-staged hybrid treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation: Short-term single-centre results. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 18, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirak, J.; Jones, D.; Sun, B.; Sai-Sudhakar, C.; Crestanello, J.; Firstenberg, M. Toward a definitive, totally thoracoscopic procedure for atrial fibrillation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2008, 86, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheitt, H.; Kim, H.; Wilton, S.; White, J.A.; Garcia, J. Left Atrial Flow Stasis in Patients Undergoing Pulmonary Vein Isolation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Using 4D-Flow Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral, H.; Latchamsetty, R. Atrial Fibrillation: Paroxysmal, Persistent, and Permanent. In Cardiac Electrophysiology from Cell to Bedside, 6th ed.; Zipes, D.P., Jalife, J., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.M.; Ungerleider, R.M.; Lofland, G.K.; Cox, J.L. Left atrial isolation: New technique for the treatment of supraventricular arrhythmias. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1980, 80, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graffigna, A.; Pagani, F.; Minzioni, G.; Salerno, J.; Vigano, M. Left atrial isolation associated with mitral valve operations. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1992, 54, 1093–1097; discussion 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiraudon, G.M. Combined sino-atrial node atrio-ventricular node isolation: A surgical alternative to His bundle ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation 1985, 72 (Suppl. 3), 220. [Google Scholar]
- Velimirovic, D.B.; Petrovic, P.; Djukic, P.; Vranes, M.; Pavlovic, S.U.; Zivkovic, M. Corridor procedure—Surgical option for treatment of chronic atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing mitral valve replacement. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1997, 5, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.L.; Schuessler, R.B.; D’Agostino, H.J., Jr.; Stone, C.M.; Chang, B.C.; Cain, M.E.; Corr, P.B.; Boineau, J.P. The surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. III. Development of a definitive surgical procedure. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1991, 101, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillinov, A.M.; McCarthy, P.M. Curative surgery for atrial fibrillation: Current status and minimally invasive approaches. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2003, 1, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamner, C.E.; Potter, D.D., Jr.; Cho, K.R.; Lutterman, A.; Francischelli, D.; Sundt, T.M., III; Schaff, H.V. Irrigated radiofrequency ablation with transmurality feedback reliably produces Cox maze lesions in vivo. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 80, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillinov, A.M.; McCarthy, P.M. Atricure bipolar radiofrequency clamp for intraoperative ablation of atrial fibrillation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 74, 2165–2168; discussion 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.A.; Ellenbogen, A.L.; Pathak, V.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Kasarajan, V. Efficacy of a cooled bipolar epicardial radiofrequency ablation probe for creating transmural myocardial lesions. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 139, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.M.; Maniar, H.S.; Diodato, M.D.; Schuessler, R.B.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Physiological consequences of bipolar radiofrequency energy on the atria and pulmonary veins: A chronic animal study. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 76, 836–841; discussion 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaynor, S.L.; Ishii, Y.; Diodato, M.D.; Prasad, S.M.; Barnett, K.M.; Damiano, N.R.; Byrd, G.D.; Wickline, S.A.; Schuessler, R.B.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Successful performance of Cox-Maze procedure on beating heart using bipolar radiofrequency ablation: A feasibility study in animals. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 78, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.M.; Aziz, A.; Clark, K.L.; Schuessler, R.B.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Chronic performance of a novel radiofrequency ablation device on the beating heart: Limitations of conduction delay to assess transmurality. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 144, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.M.; Aziz, A.; Sakamoto, S.I.; Schuessler, R.B.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Epicardial Ablation on the Beating Heart: Limited Efficacy of a Novel, Cooled Radiofrequency Ablation Device. Innovations 2009, 4, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Weimar, T.; Kazui, T.; Lee, U.; Schuessler, R.B.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Epicardial ablation performance of a novel radiofrequency device on the beating heart in pigs. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 97, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint, L.L.; Lawrance, C.P.; Okada, S.; Kazui, T.; Robertson, J.O.; Schuessler, R.B.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Performance of a novel bipolar/monopolar radiofrequency ablation device on the beating heart in an acute porcine model. Innovations 2013, 8, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Voeller, R.K.; Melby, S.J.; Lall, S.C.; Chang, N.L.; Schuessler, R.B.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation: The efficacy of a novel bipolar pen device in the cardioplegically arrested and beating heart. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 136, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuessler, R.B.; Lee, A.M.; Melby, S.J.; Voeller, R.K.; Gaynor, S.L.; Sakamoto, S.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Animal studies of epicardial atrial ablation. Heart Rhythm. 2009, 6, S41–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgerton, J.R.; Edgerton, Z.J.; Weaver, T.; Reed, K.; Prince, S.; Herbert, M.A.; Mack, M.J. Minimally invasive pulmonary vein isolation and partial autonomic denervation for surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2008, 86, 35–38; discussion 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgerton, J.R.; McClelland, J.H.; Duke, D.; Gerdisch, M.W.; Steinberg, B.M.; Bronleewe, S.H.; Prince, S.L.; Herbert, M.A.; Hoffman, S.; Mack, M.J. Minimally invasive surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: Six-month results. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 138, 109–113; discussion 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockwood, D.; Nakagawa, H.; Peyton, M.D.; Edgerton, J.R.; Scherlag, B.J.; Sivaram, C.A.; Po, S.S.; Beckman, K.J.; Abedin, M.; Jackman, W.M. Linear left atrial lesions in minimally invasive surgical ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation: Techniques for assessing conduction block across surgical lesions. Heart Rhythm 2009, 6, S50–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M.J. Current results of minimally invasive surgical ablation for isolated atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2009, 6, S46–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgerton, J.R.; Jackman, W.M.; Mack, M.J. A new epicardial lesion set for minimal access left atrial maze: The Dallas lesion set. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 88, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgerton, J.R.; Jackman, W.M.; Mahoney, C.; Mack, M.J. Totally thorascopic surgical ablation of persistent AF and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation using the “Dallas” lesion set. Heart Rhythm 2009, 6, S64–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Xin, M.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, T.G.; Wang, J.; Meng, F.; Meng, X. Ablation in selective patients with long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: Medium-term results of the Dallas lesion set. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 46, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirak, J.H.; Schwartzman, D. Interim results of the 5-box thoracoscopic maze procedure. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 94, 1880–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroomen, M.; Maesen, B.; Luermans, J.L.; Maessen, J.G.; Crijns, H.J.; La Meir, M.; Pison, L. Epicardial and Endocardial Validation of Conduction Block After Thoracoscopic Epicardial Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Innovations 2020, 15, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On, Y.K.; Park, K.M.; Jeong, D.S.; Park, P.W.; Lee, Y.T.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.S. Electrophysiologic Results After Thoracoscopic Ablation for Chronic Atrial Fibrillation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 1595–1602; discussion 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, M.; Khairy, P.; Mongeon, F.P.; Andrade, J.G.; Gomes, S.; Galvan, Z.; Weerasooriya, R.; Novak, P.; Nault, I.; Arentz, T.; et al. Pulmonary Vein Stenosis After Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: Insights From the ADVICE Trial. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.Z.; Zhu, D.; Bai, Z.X.; Shi, J.; Shi, Y.K.; Guo, Y.Q. A novel “box lesion” minimally invasive totally thoracoscopic surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2015, 44, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, S.L.; Diodato, M.D.; Prasad, S.M.; Ishii, Y.; Schuessler, R.B.; Bailey, M.S.; Damiano, N.R.; Bloch, J.B.; Moon, M.R.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. A prospective, single-center clinical trial of a modified Cox maze procedure with bipolar radiofrequency ablation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 128, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Age, years | 58.70 ± 10.17 |
| Female, n (%) | 1 (5) |
| AF duration, months | 88.15 ± 70.70 |
| Long-standing AF, n (%) | 19 (95) |
| Prior RFCA | 3 (15) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 8 (40) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 4 (20) |
| Congestive heart failure, n (%) | 6 (30) |
| Prior stroke, n (%) | 4 (20) |
| Thyroid disease, n (%) | 3 (15) |
| Echocardiographic parameters | |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction (%) | 56.63 ± 8.37 |
| Left atrial diameter (mm) | 46.47 ± 7.95 |
| Left atrial volume index (mL/min) | 53.92 ± 17.97 |
| Operative Data | |
|---|---|
| Operative time, minutes | 140.25 ± 16.02 |
| Right-side procedures | |
| Total number of ablations | 6.3 ± 0.47 |
| Confirmed PVI, n (%) | 18 (90) |
| Entrance block, n (%) | 18 (90) |
| Exit block, n (%) | 19 (90) |
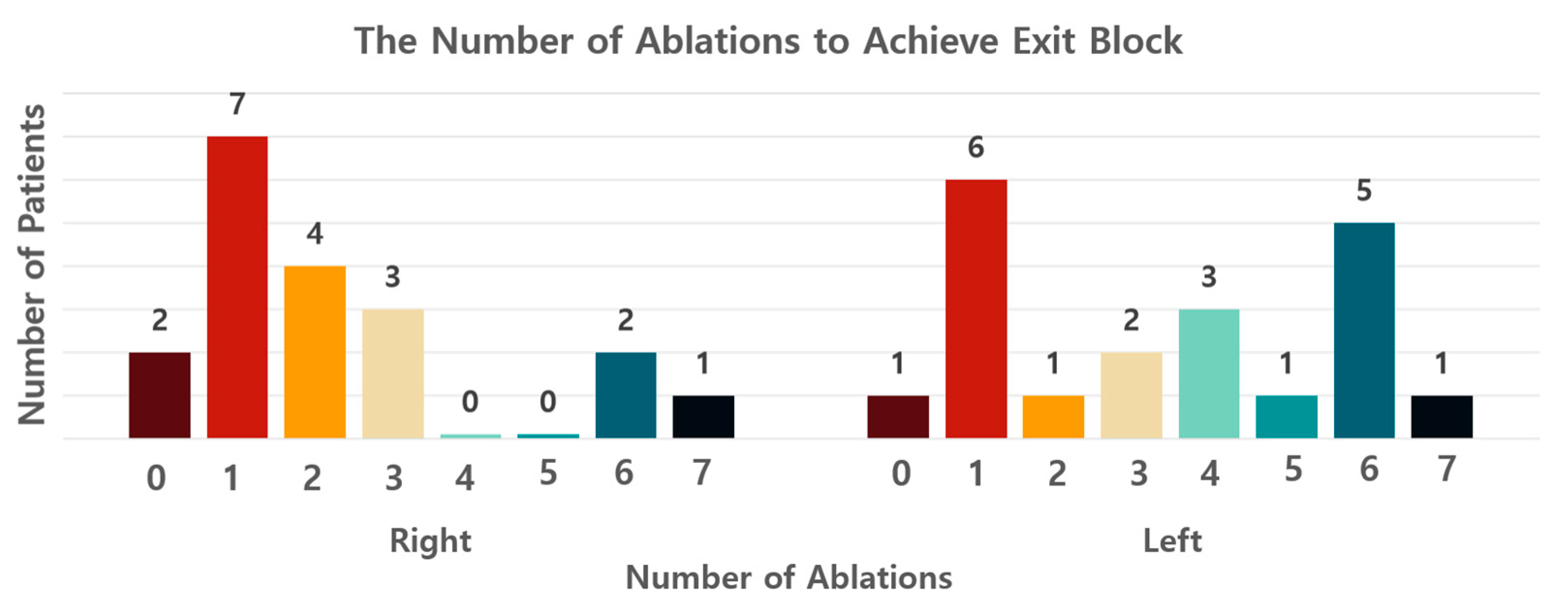
| Exit block, the minimum number of ablations (median, IQR) | 2 (1, 3) |
| Left side procedures | |
| Total number of ablations | 6.35 ± 0.49 |
| Confirmed PVI, n (%) | 18 (90) |
| Entrance block, n (%) | 18 (90) |
| Exit block, n (%) | 20 (100) |
| Exit block, the minimum number of ablations (median, IQR) | 3.5 (1, 6) |
| LA appendage exclusion, size, mm | 40 ± 3.35 |
| Postoperative Data | |
|---|---|
| Postoperative hospital stay, days | 6.4 ± 1.8 |
| Complication | |
| Reintubation, number of patients, n (%) | 0 (0) |
| Reoperation, number of patients, n (%) | 0 (0) |
| Incidence of pneumonia, n (%) | 0 (0) |
| Rhythm | |
| Cardioversion during admission, n (%) | 8 (40) |
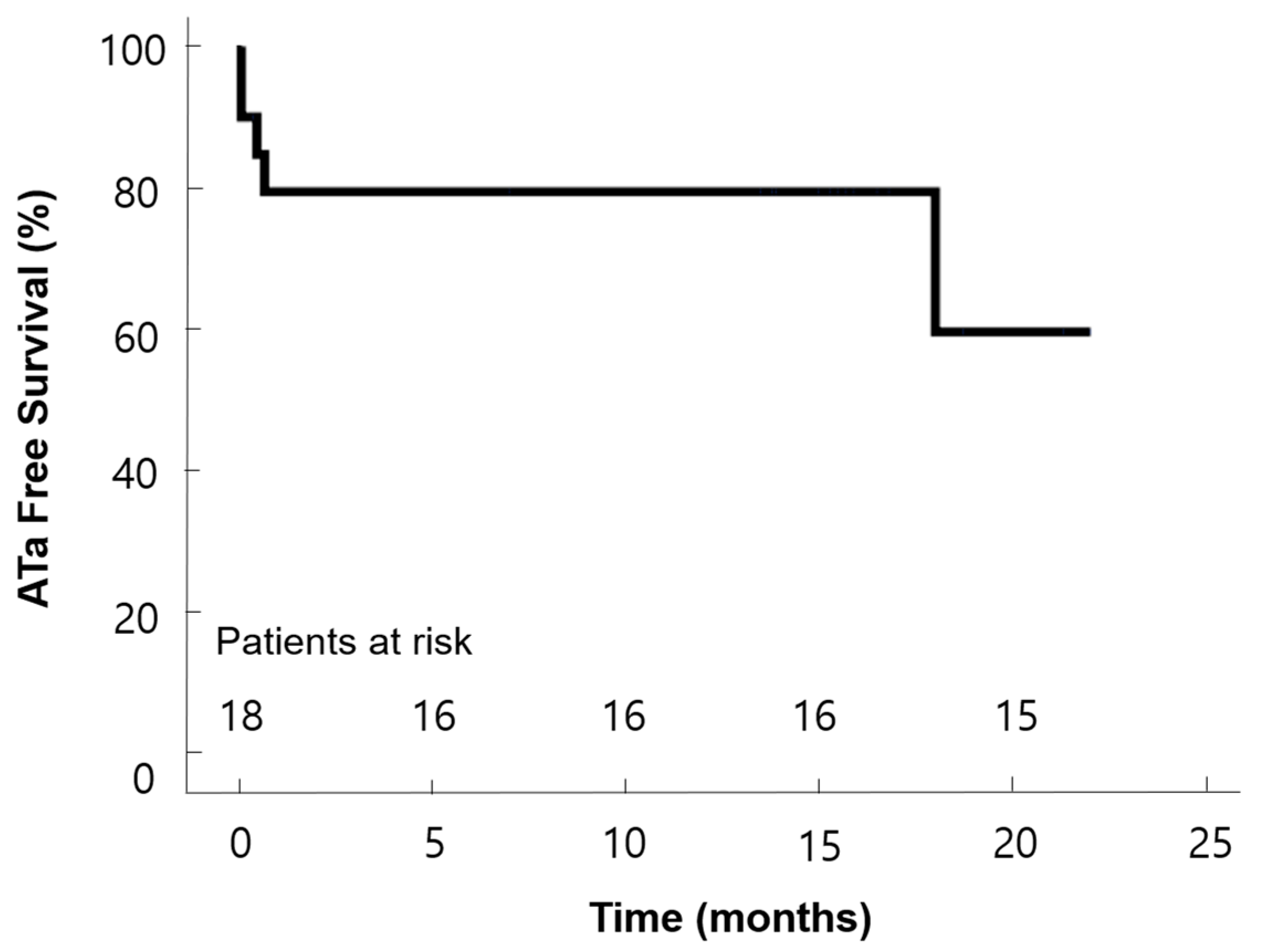
| Sinus rhythm at discharge, n (%) | 15 (75) |
| Sinus rhythm at 6 months, n (%) | 13 (68) |
| Sinus rhythm at the last follow-up, n (%) | 15 (75) |
| Echocardiographic parameters at 6 months | |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction (%) | 57.72 ± 6.53 |
| Left atrial diameter (mm) | 48.42 ± 7.11 |
| Left atrial volume index (mL/min) | 46.04 ± 13.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, M.S.; Lee, Y.; Jeong, D.S. The Minimum Number of Ablation Lines for Complete Isolation of the Pulmonary Veins during Thoracoscopic Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. Life 2023, 13, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030770
Choi MS, Lee Y, Jeong DS. The Minimum Number of Ablation Lines for Complete Isolation of the Pulmonary Veins during Thoracoscopic Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. Life. 2023; 13(3):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030770
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Min Suk, Yoonseo Lee, and Dong Seop Jeong. 2023. "The Minimum Number of Ablation Lines for Complete Isolation of the Pulmonary Veins during Thoracoscopic Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation" Life 13, no. 3: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030770
APA StyleChoi, M. S., Lee, Y., & Jeong, D. S. (2023). The Minimum Number of Ablation Lines for Complete Isolation of the Pulmonary Veins during Thoracoscopic Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. Life, 13(3), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030770







