Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer through the Multi-Ligand Binding of Prostate-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and miRNA Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
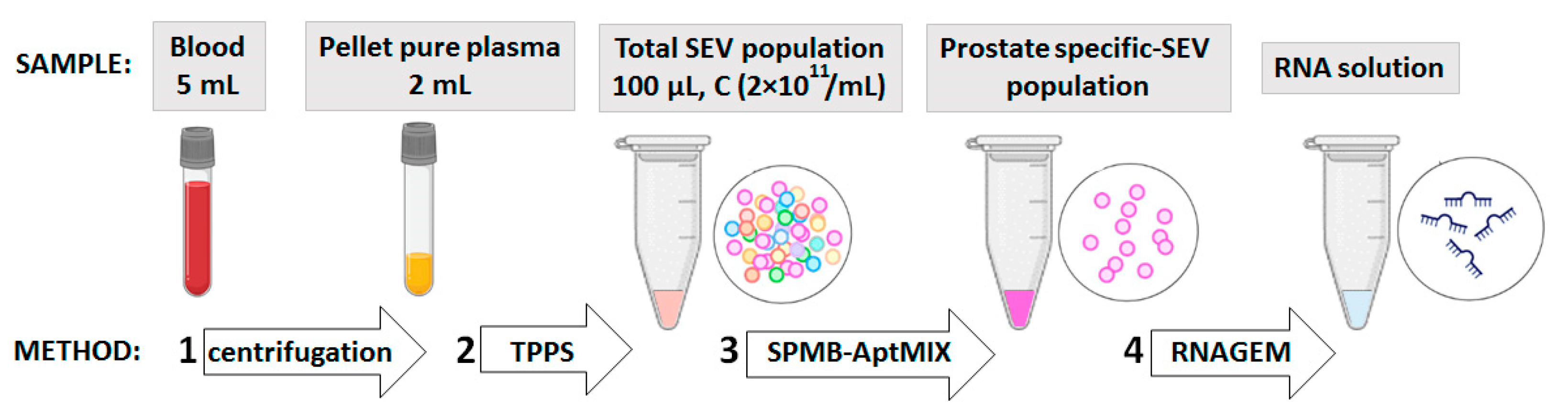
2.2. Plasma Sampling and SEV Isolation
2.3. Maintaining of PC Cell Cultures and SEV Isolation
2.4. SEV Labelling with CM-Dil
2.5. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.6. Low-Voltage Scanning Electron Microscopy (LVSEM)
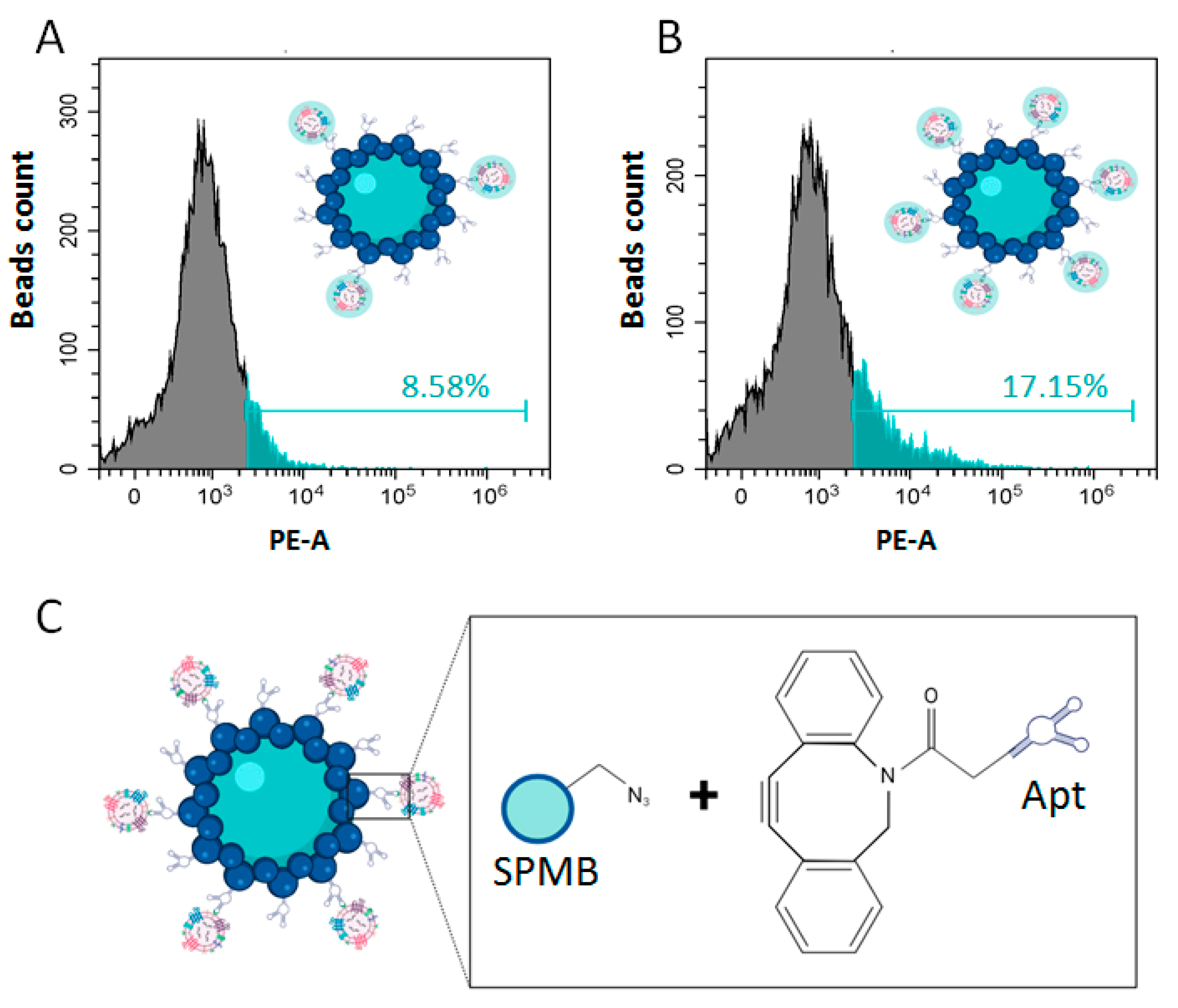
2.7. Bead-Assisted Flow Cytometry of the Total SEV Population
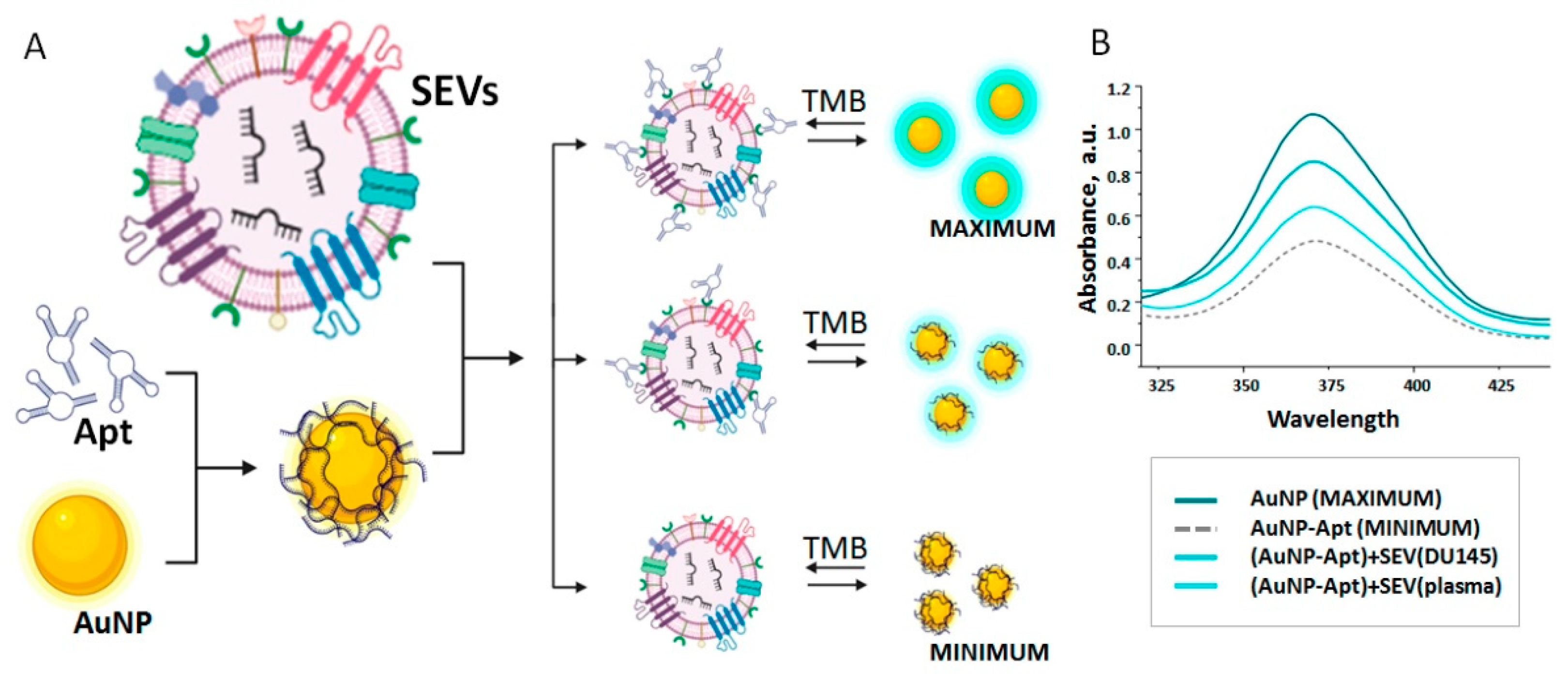
2.8. Aurum Nanoparticle and AuNP-Aptasensor
2.9. Formation of SPMB-Apt Complexes for Prostate-Derived SEV Isolation
2.10. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Small Extracellular Vesicles (SEVs) from Plasma
3.2. Selection of Most Effective DNA-Aptamers
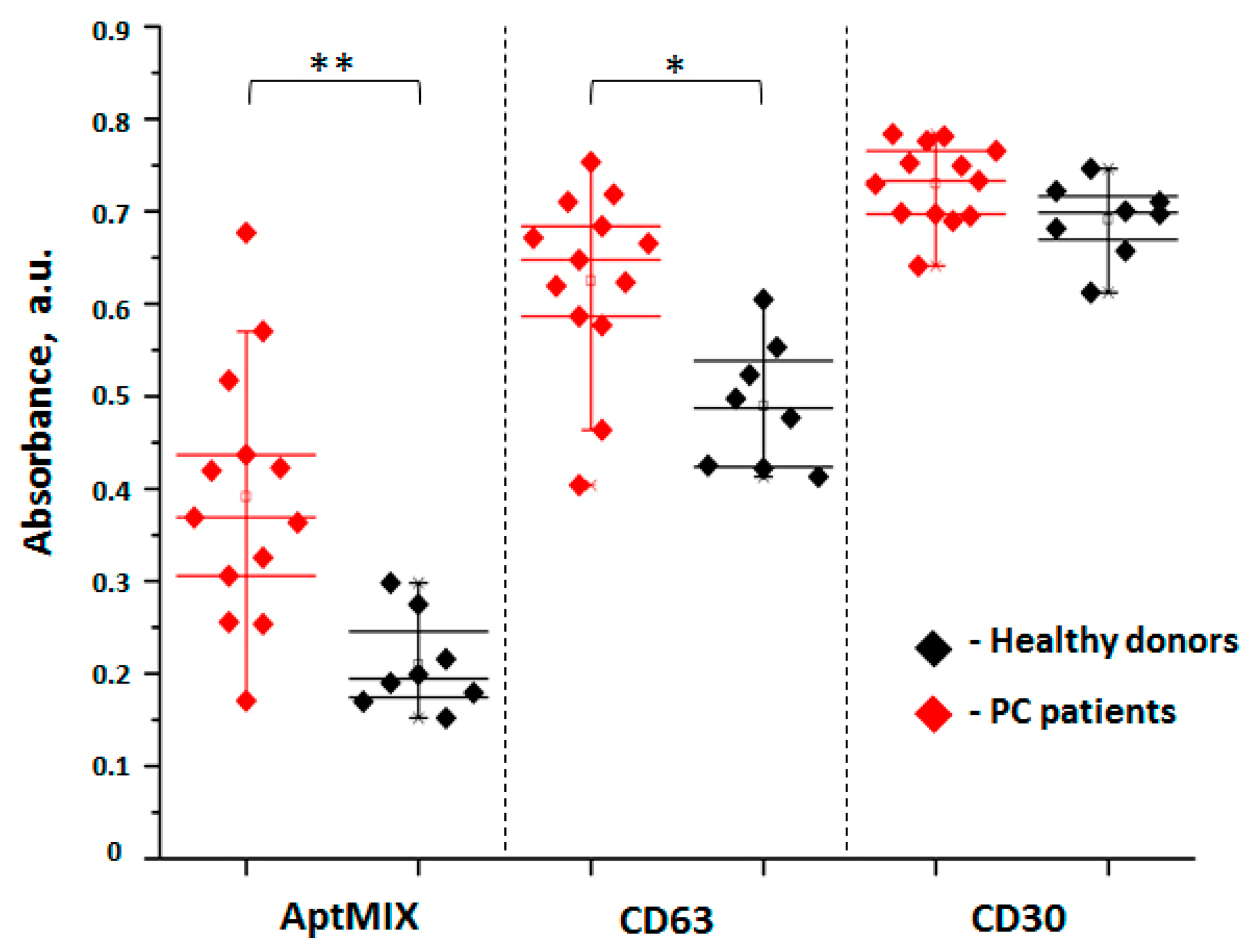
3.3. Relative Quantification of PC-Derived SEVs in Plasma of Healthy Donors and PC Patients
3.4. Isolation of pSEVs with Functionalized SPMP
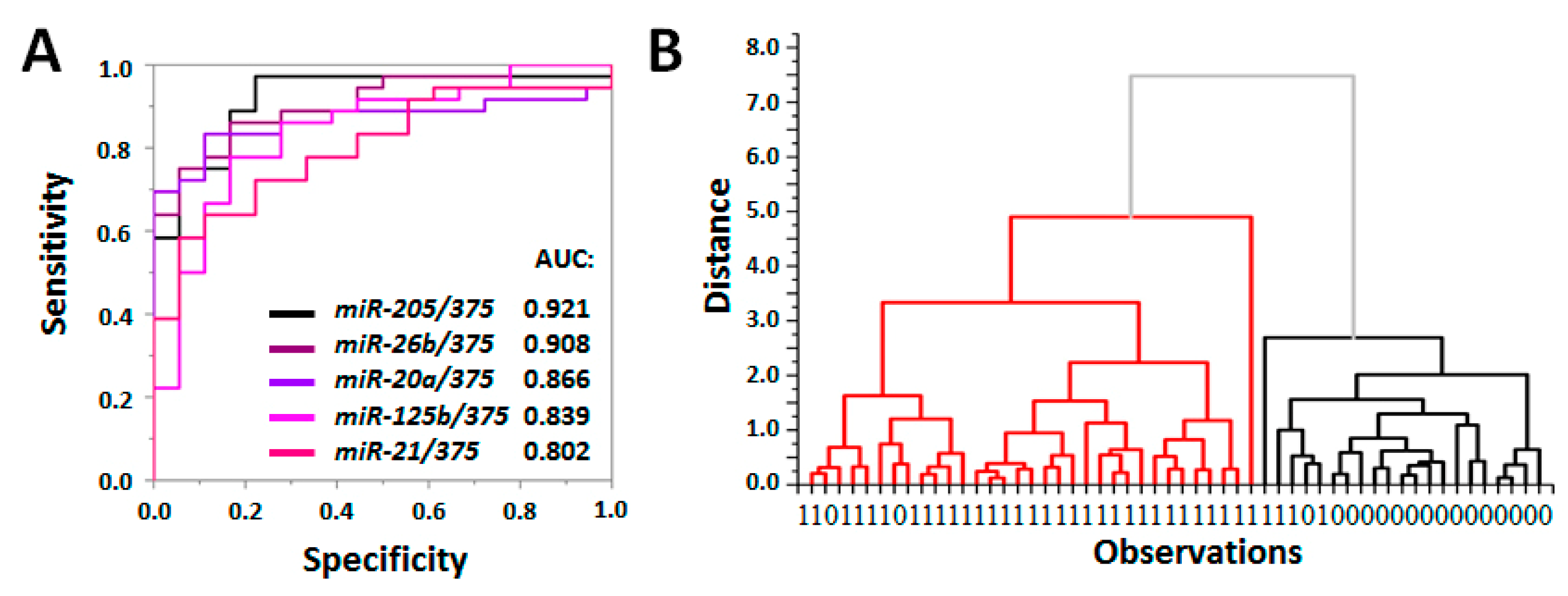
3.5. Evaluation of Diagnostic Value of PC-Associated miRNA in pSEVs
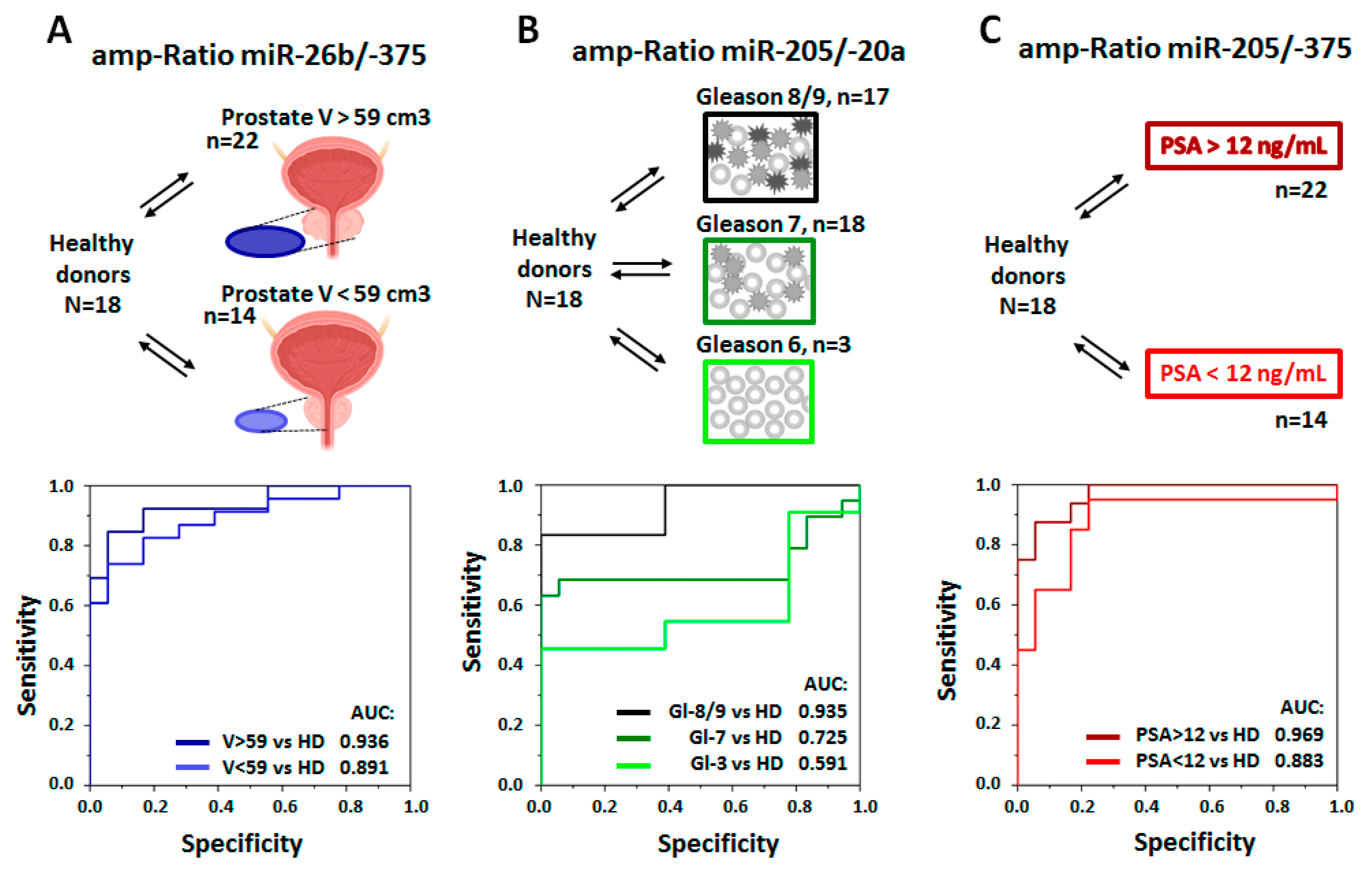
3.6. Clinical Significance of PC-Associated miRNA in pSEVs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catalona, W.J. Prostate Cancer Screening. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamaki, M.; Zoumpourlis, V. Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: From diagnosis to prognosis and precision-guided therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 228, 107932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.; Castro, E.; Fizazi, K.; Heidenreich, A.; Ost, P.; Procopio, G.; Tombal, B.; Gillessen, S. Prostate cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, M.G.; Cowling, T.E.; Sujenthiran, A.; Nossiter, J.; Berry, B.; Cathcart, P.; Aggarwal, A.; Payne, H.; van der Meulen, J.; Clarke, N.W.; et al. Risk stratification for prostate cancer management: Value of the Cambridge Prognostic Group classification for assessing treatment allocation. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova-Salas, I.; Athie, A.; Boutros, P.C.; Del Re, M.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Pienta, K.J.; Posadas, E.M.; Sowalsky, A.G.; Stenzl, A.; Wyatt, A.W.; et al. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Blood-based Liquid Biopsies to Inform Clinical Decision-making in Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porzycki, P.; Ciszkowicz, E. Modern biomarkers in prostate cancer diagnosis. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2020, 73, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukachinsky, H.; Madison, R.W.; Chung, J.H.; Gjoerup, O.V.; Severson, E.A.; Dennis, L.; Fendler, B.J.; Morley, S.; Zhong, L.; Graf, R.P.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA in 3334 Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer Identifies Targetable BRCA Alterations and AR Resistance Mechanisms. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3094–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosini, A.; Bernardi, S.; Foroni, C.; Pasinetti, N.; Guerini, A.E.; Russo, D.; Bresciani, R.; Tomasi, C.; Magrini, S.M.; Bardoscia, L.; et al. Stratification of Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer Patients by Liquid Biopsy: Clinical Insights from a Pilot Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaeminck-Guillem, V. Exosomes and prostate cancer management. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 86, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenc, T.; Klimczyk, K.; Michalczewska, I.; Słomka, M.; Kubiak-Tomaszewska, G.; Olejarz, W. Exosomes in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Hurley, J.; Roberts, D.; Chakrabortty, S.K.; Enderle, D.; Noerholm, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J.K. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: Opportunities and challenges. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaglani, S.; Gonzalez-Kozlova, E.; Lundon, D.J.; Tewari, A.K.; Dogra, N.; Kyprianou, N. Exosomes as A Next-Generation Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tool in Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Mendes, D.E.; Berkman, C.E. Functional prostate-specific membrane antigen is enriched in exosomes from prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nanou, A.; Coumans, F.A.W.; van Dalum, G.; Zeune, L.L.; Dolling, D.; Onstenk, W.; Crespo, M.; Fontes, M.S.; Rescigno, P.; Fowler, G.; et al. Circulating tumor cells, tumor-derived extracellular vesicles and plasma cytokeratins in castration-resistant prostate cancer patients. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19283–19293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foroni, C.; Zarovni, N.; Bianciardi, L.; Bernardi, S.; Triggiani, L.; Zocco, D.; Venturella, M.; Chiesi, A.; Valcamonico, F.; Berruti, A. When Less Is More: Specific Capture and Analysis of Tumor Exosomes in Plasma Increases the Sensitivity of Liquid Biopsy for Comprehensive Detection of Multiple Androgen Receptor Phenotypes in Advanced Prostate Cancer Patients. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furesi, G.; de Jesus Domingues, A.M.; Alexopoulou, D.; Dahl, A.; Hackl, M.; Schmidt, J.R.; Kalkhof, S.; Kurth, T.; Taipaleenmäki, H.; Conrad, S.; et al. Exosomal miRNAs from Prostate Cancer Impair Osteoblast Function in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKiernan, J.; Donovan, M.J.; O’Neill, V.; Bentink, S.; Noerholm, M.; Belzer, S.; Skog, J.; Kattan, M.W.; Partin, A.; Andriole, G.; et al. A Novel Urine Exosome Gene Expression Assay to Predict High-grade Prostate Cancer at Initial Biopsy. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zabegina, L.; Nazarova, I.; Knyazeva, M.; Nikiforova, N.; Slyusarenko, M.; Titov, S.; Vasilyev, D.; Sleptsov, I.; Malek, A. MiRNA let-7 from TPO(+) Extracellular Vesicles is a Potential Marker for a Differential Diagnosis of Follicular Thyroid Nodules. Cells 2020, 9, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabegina, L.; Nazarova, I.; Nikiforova, N.; Slyusarenko, M.; Sidina, E.; Knyazeva, M.; Tsyrlina, E.; Novikov, S.; Reva, S.; Malek, A. A New Approach for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis by miRNA Profiling of Prostate-Derived Plasma Small Extracellular Vesicles. Cells 2021, 10, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slyusarenko, M.; Shalaev, S.; Valitova, A.; Zabegina, L.; Nikiforova, N.; Nazarova, I.; Rudakovskaya, P.; Vorobiev, M.; Lezov, A.; Filatova, L.; et al. AuNP Aptasensor for Hodgkin Lymphoma Monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slyusarenko, M.; Nikiforova, N.; Sidina, E.; Nazarova, I.; Egorov, V.; Garmay, Y.; Merdalimova, A.; Yevlampieva, N.; Gorin, D.; Malek, A. Formation and evaluation of a two-phase polymer system in human plasma as a method for extracellular nanovesicle isolation. Polymers 2021, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtam, T.; Evtushenko, V.; Samsonov, R.; Zabrodskaya, Y.; Kamyshinsky, R.; Zabegina, L.; Verlov, N.; Burdakov, V.; Garaeva, L.; Slyusarenko, M.; et al. Evaluation of immune and chemical precipitation methods for plasma exosome isolation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiforova, N.; Chumachenko, M.; Nazarova, I.; Zabegina, L.; Slyusarenko, M.; Sidina, E.; Malek, A. CM-Dil Staining and SEC of Plasma as an Approach to Increase Sensitivity of Extracellular Nanovesicles Quantification by Bead-Assisted Flow Cytometry. Membranes 2021, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratov, K.A.; Petrova, T.A.; Mikhailovskii, V.Y.; Ivanova, A.N.; Kostareva, A.A.; Fedorov, A.V. A study of extracellular vesicles isolated from blood plasma conducted by low-voltage scanning electron microscopy. Cell Tissue Biol. 2017, 11, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piella, J.; Bastús, N.G.; Puntes, V. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Sub-10-nanometer Citrate-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles and Related Optical Properties. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Human Protein Atlas CD63 Protein Expression in Tumor Tissues. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000135404-CD63/pathology (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Li, P.; Yu, X.; Han, W.; Kong, Y.; Bao, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Gu, Y. Ultrasensitive and Reversible Nanoplatform of Urinary Exosomes for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. ACS Sensors 2019, 4, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, N.; Butler, S.; Mahal, B.A.; Trinh, Q.-D.; Rose, B.; King, M.; Orio, P.; Mouw, K.W.; Martin, N.; Leeman, J.E.; et al. Three-tiered Subclassification System of High-risk Prostate Cancer in Men Managed With Radical Prostatectomy: Implications for Treatment Decision-making. Urology 2020, 145, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokowy, T.; Wojtas, B.; Jarzab, B.; Krohn, K.; Fredman, D.; Dralle, H.; Musholt, T.; Hauptmann, S.; Lange, D.; Hegedüs, L.; et al. Two-miRNA classifiers differentiate mutation-negative follicular thyroid carcinomas and follicular thyroid adenomas in fine needle aspirations with high specificity. Endocrine 2016, 54, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Valbuena, G.N.; Curry, E.; Bevan, C.L.; Keun, H.C. MicroRNAs as biomarkers for prostate cancer prognosis: A systematic review and a systematic reanalysis of public data. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, F.; Jeet, V.; Moya, L.; Selth, L.A.; Chambers, S.; Clements, J.A.; Batra, J. A Plasma Biomarker Panel of Four MicroRNAs for the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paunescu, I.A.; Bardan, R.; Marcu, A.; Nitusca, D.; Dema, A.; Negru, S.; Balacescu, O.; Balacescu, L.; Cumpanas, A.; Sirbu, I.O.; et al. Biomarker Potential of Plasma MicroRNA-150-5p in Prostate Cancer. Medicina 2019, 55, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giglio, S.; De Nunzio, C.; Cirombella, R.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Faruq, O.; Volinia, S.; Baldassarre, G.; Tubaro, A.; Ishii, H.; Croce, C.M.; et al. A preliminary study of micro-RNAs as minimally invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis of prostate cancer patients. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samami, E.; Pourali, G.; Arabpour, M.; Fanipakdel, A.; Shahidsales, S.; Javadinia, S.A.; Hassanian, S.M.; Mohammadparast, S.; Avan, A. The Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Circulating MicroRNAs in the Assessment of Patients With Prostate Cancer: Rational and Progress. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 716831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevillet, J.R.; Kang, Q.; Ruf, I.K.; Briggs, H.A.; Vojtech, L.N.; Hughes, S.M.; Cheng, H.H.; Arroyo, J.D.; Meredith, E.K.; Gallichotte, E.N.; et al. Quantitative and stoichiometric analysis of the microRNA content of exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14888–14893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nazarova, I.; Slyusarenko, M.; Sidina, E.; Nikiforova, N.; Semiglazov, V.; Semiglazova, T.; Aigner, A.; Rybakov, E.; Malek, A. Evaluation of Colon-Specific Plasma Nanovesicles as New Markers of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Apt1 | Apt2 | Apt3 | Apt4 | Apt5 | Apt6 | Apt7 | Apt8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEV (plasma) | 6.61 | 19.91 | 17.53 | 7.15 | 6.34 | 10.69 | 14.78 | 8.96 |
| SEV (DU-145) | 36.9 | 77.7 | 63.87 | 63.24 | 81.42 | 72.63 | 73.83 | 63.49 |
| SEV (PC-3) | 62.42 | 60.76 | 55.37 | 60.46 | 64.89 | 63.7 | 63.83 | 67.49 |
| Delta 1 | 43.05 | 49.32 | 42.09 | 54.7 | 66.82 | 57.48 | 54.05 | 56.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zabegina, L.; Zyatchin, I.; Kniazeva, M.; Shalaev, A.; Berkut, M.; Sharoyko, V.; Mikhailovskii, V.; Kondratov, K.; Reva, S.; Nosov, A.; et al. Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer through the Multi-Ligand Binding of Prostate-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and miRNA Analysis. Life 2023, 13, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13040885
Zabegina L, Zyatchin I, Kniazeva M, Shalaev A, Berkut M, Sharoyko V, Mikhailovskii V, Kondratov K, Reva S, Nosov A, et al. Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer through the Multi-Ligand Binding of Prostate-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and miRNA Analysis. Life. 2023; 13(4):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13040885
Chicago/Turabian StyleZabegina, Lidia, Ilya Zyatchin, Margarita Kniazeva, Andrey Shalaev, Maria Berkut, Vladimir Sharoyko, Vladimir Mikhailovskii, Kirill Kondratov, Sergey Reva, Alexandr Nosov, and et al. 2023. "Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer through the Multi-Ligand Binding of Prostate-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and miRNA Analysis" Life 13, no. 4: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13040885
APA StyleZabegina, L., Zyatchin, I., Kniazeva, M., Shalaev, A., Berkut, M., Sharoyko, V., Mikhailovskii, V., Kondratov, K., Reva, S., Nosov, A., & Malek, A. (2023). Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer through the Multi-Ligand Binding of Prostate-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and miRNA Analysis. Life, 13(4), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13040885









