Morphological Changes of the Suboccipital Musculature in Women with Myofascial Temporomandibular Pain: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
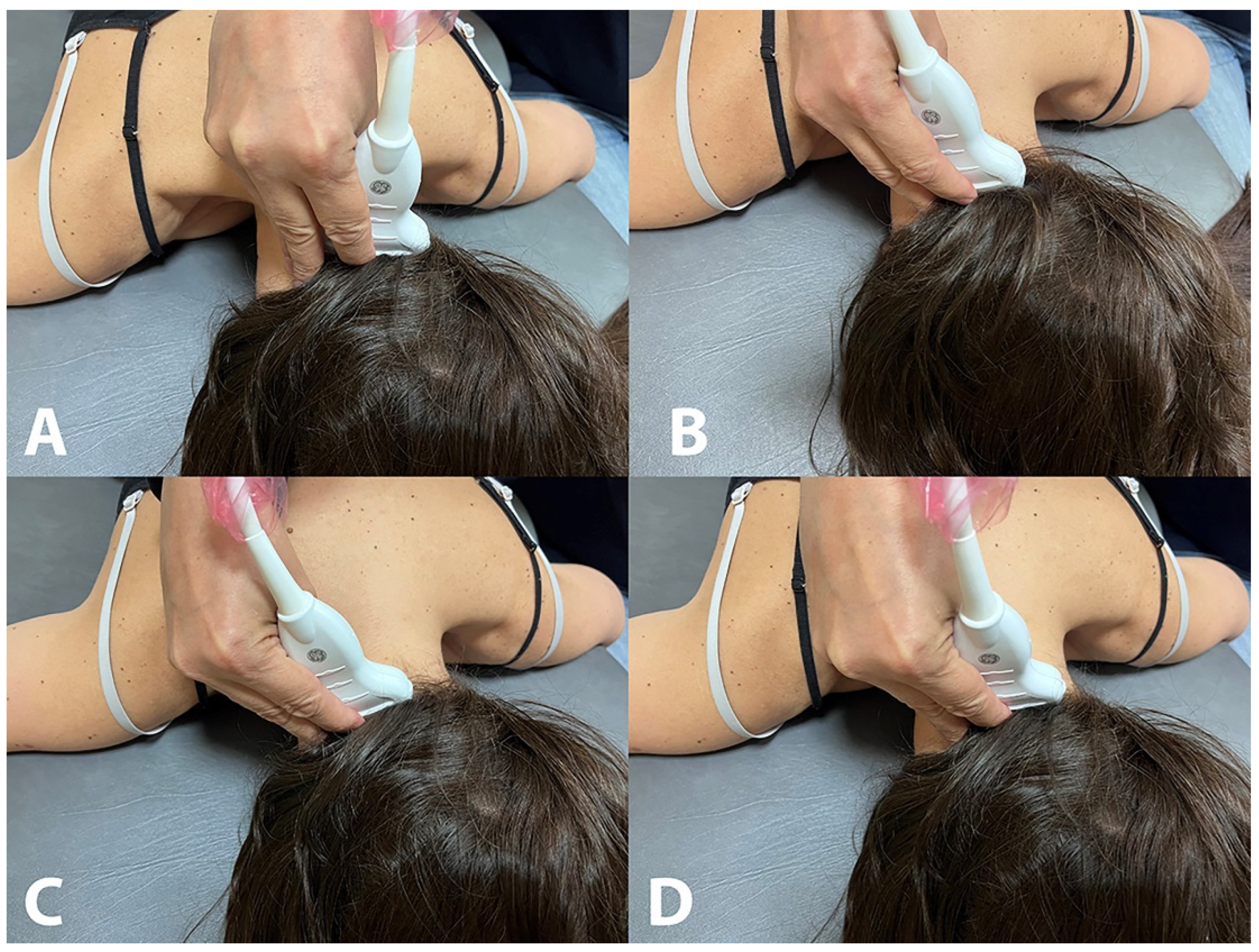
2.3. Ultrasound Assessment
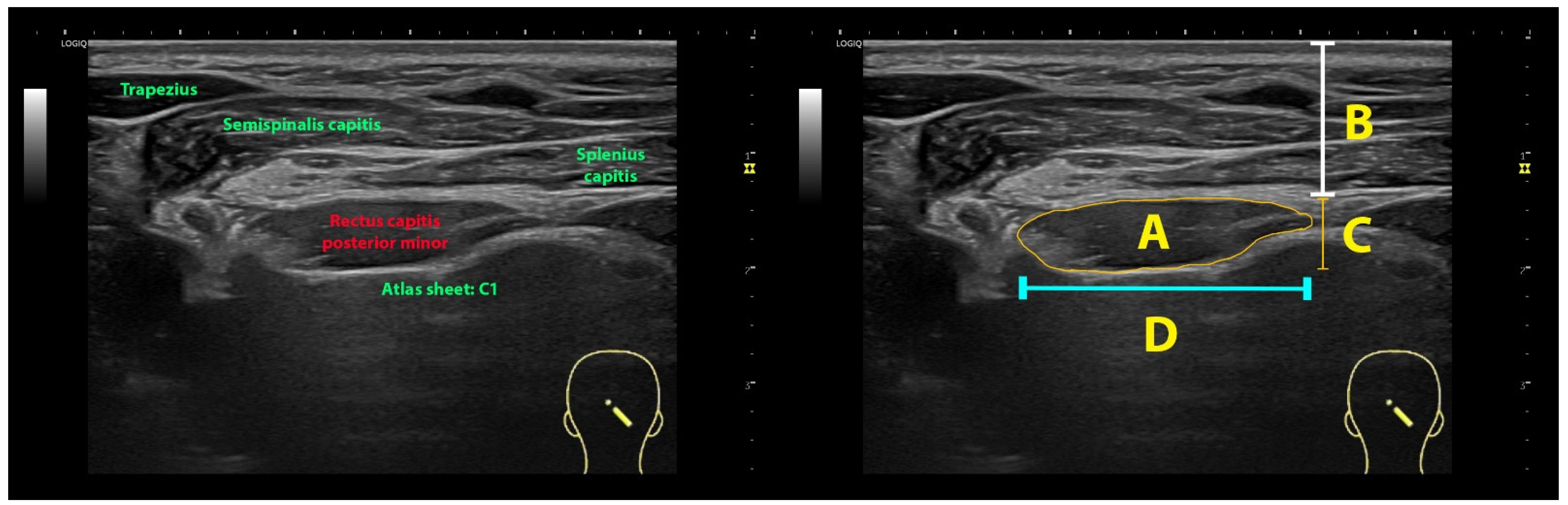
2.4. Imaging Management
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
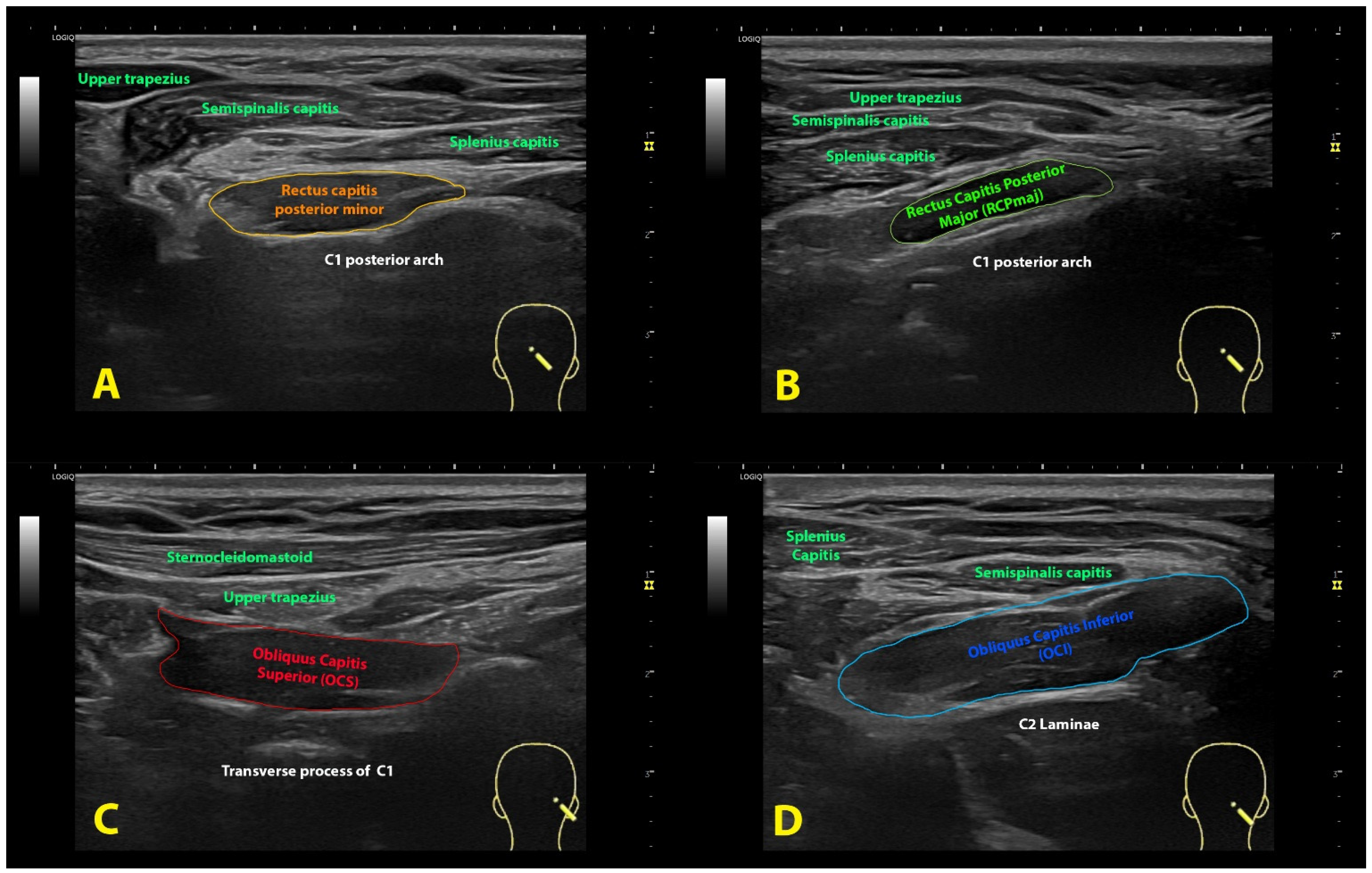
3.1. Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor (RCPmin) Muscle
3.2. Rectus Capitis Posterior Major (RCPmaj) Muscle
3.3. Oblique Capitis Superior (OCS) Muscle
3.4. Oblique Capitis Inferior (OCI) Muscle
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scrivani, S.J.; Keith, D.A.; Kaban, L.B. Temporomandibular disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2693–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-de-las-Peñas, C.; Svensson, P. Myofascial temporomandibular Disorder. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2016, 12, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, E.; Ohrbach, R.; Truelove, E.; Look, J.; Anderson, G.; Goulet, J.P.; Svensson, P.; Gonzalez, Y.; Lobbezoo, F.; Michelotti, A.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders (DC/TMD) for Clinical and Research Applications: Recommendations of the International RDC/TMD Consortium Network* and Orofacial Pain Special Interest Groupdagger. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2014, 28, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, D.; Guarda-Nardini, L.; Winocur, E.; Piccotti, F.; Ahlberg, J.; Lobbezoo, F. Research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders: A systematic review of axis I epidemiologic findings. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2011, 112, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poveda-Roda, R.; Bagan, J.V.; Sanchis, J.M.; Carbonell, E. Temporomandibular disorders. A case-control study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Y Cir. Bucal 2012, 17, e794–e800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapias Ledesma, M.A.; Martinez Dominguez, C.; Munoz Garcia, J.C.; Hernandez-Barrera, V. Factors associated with temporomandibular disorder in a health centre’s population. Aten. Primaria 2008, 40, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca-Martínez, F.; Herranz-Gómez, A.; Madroñero-Miguel, B.; Reina-Varona, Á.; La Touche, R.; Angulo-Díaz-Parreño, S.; Pardo-Montero, J.; Del Corral, T.; López-de-Uralde-Villanueva, I. Craniocervical and cervical spine features of patients with temporomandibular disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mørch, C.D.; Hu, J.W.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Sessle, B.J. Convergence of cutaneous, musculoskeletal, dural and visceral afferents onto nociceptive neurons in the first cervical dorsal horn. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.M.; Hancock, M.J.; Crawford, R.J.; Smith, A.C.; Walton, D.M. Advancing imaging technologies for patients with spinal pain: With a focus on whiplash injury. Spine J. 2018, 18, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Jull, G.; Noteboom, J.T.; Darnell, R.; Galloway, G.; Gibbon, W.W. Fatty infiltration in the cervical extensor muscles in persistent whiplash-associated disorders: A magnetic resonance imaging analysis. Spine 2006, 31, E847–E855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Bueno, A.; Ferrando, J.; Elliott, J.M.; Cuadrado, M.L.; Pareja, J.A. Magnetic resonance imaging study of the morphometry of cervical extensor muscles in chronic tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvedstrup, J.; Amin, F.M.; Hougaard, A.; Ashina, H.; Christensen, C.E.; Larsson, H.B.W.; Ashina, M.; Schytz, H.W. Volume of the rectus capitis posterior minor muscle in migraine patients: A cross-sectional structural MRI study. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.Y.; Yu, S.B.; Liu, C.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, J.F.; Chi, Y.Y.; Wang, X.G.; Lin, X.T.; Sui, H.J. Correlation between chronic headaches and the rectus capitis posterior minor muscle: A comparative analysis of cross-sectional trail. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera-Calero, J.A.; Sánchez-Jorge, S.; Álvarez-González, J.; Ortega-Santiago, R.; Cleland, J.A.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Arias-Buría, J.L. Intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of rehabilitative ultrasound imaging of cervical multifidus muscle in healthy people: Imaging capturing and imaging calculation. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2020, 48, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Kitamura, K.; Morita, S.; Nagakura, R.; Matsunaga, S.; Abe, S. Morphological classification and comparison of suboccipital muscle fiber characteristics. Anat. Cell Biol. 2017, 50, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadipoor, A.; Khademi-Kalantari, K.; Rezasoltani, A.; Naimi, S.S.; Akbarzadeh-Baghban, A. Assessing the reliability of echo intensity of craniovertebral muscle group using b-mode ultrasound: A technical note. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2021, 11, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.J.; Chai, H.M.; Wang, S.F. Reliability of thickness measurements of the dorsal muscles of the upper cervical spine: An ultrasonographic study. J. Orthop. Sport. Phys. Ther. 2009, 39, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øverås, C.K.; Myhrvold, B.L.; Røsok, G.; Magnesen, E. Musculoskeletal diagnostic ultrasound imaging for thickness measurement of four principal muscles of the cervical spine -a reliability and agreement study. Chiropr. Man. Ther. 2017, 25, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-de-las-Peñas, C.; Mesa-Jimenez, J.A.; Lopez-Davis, A.; Koppenhaver, S.L.; Arias-Buria, J.L. Cadaveric and ultrasonographic validation of needling placement in the obliquus capitis inferior muscle. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2020, 45, 102075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armijo-Olivo, S.; Fuentes, J.P.; da Costa, B.R.; Major, P.W.; Warren, S.; Thie, N.M.; Magee, D.J. Reduced endurance of the cervical flexor muscles in patients with concurrent temporomandibular disorders and neck disability. Man. Ther. 2010, 15, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armijo-Olivo, S.; Silvestre, R.; Fuentes, J.; da Costa, B.R.; Gadotti, I.C.; Warren, S.; Major, P.W.; Thie, N.M.; Magee, D.J. Electromyographic activity of the cervical flexor muscles in patients with temporomandibular disorders while performing the cranio-cervical flexion test: A cross-sectional study. Phys. Ther. 2011, 91, 1184–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomacher, J.; Falla, D. Function and structure of the deep cervical extensor muscles in patients with neck pain. Man. Ther. 2013, 18, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthaikhup, S.; Assapun, J.; Kothan, S.; Watcharasaksilp, K.; Elliott, J.M. Structural changes of the cervical muscles in elder women with cervicogenic headache. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Cai, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Samuel, O.C.; Zheng, N.; Chi, Y.Y.; Yu, S.B.; Sui, H.J.; Xu, Q.; et al. Anatomical parameters of the rectus capitis posterior major and obliques capitis inferior muscles based on an oblique Sagittal magnetic resonance scan method. Int. J. Morphol. 2018, 36, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, C.; Yuan, X.Y.; Chi, Y.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, J.F.; Sui, H.J.; Han, S.H.; Yu, S.B.; Lin, X.T. Anatomical parameters of the rectus capitis posterior minor muscle based on a new magnetic resonance scan method. Int. J. Morphol. 2017, 35, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, D.; Buxton, D.F.; Nitz, A. A comparison of spindle concentrations in large and small muscles acting in parallel combinations. J. Morphol. 1984, 180, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahkeshani, K.; Ward, P.J. Connection between the spinal dura mater and suboccipital musculature: Evidence for the myodural bridge and a route for its dissection: A review. Clin. Anat. 2012, 25, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.Y.; Sui, H.J.; Eteer, K.; Yu, S.B.; Hu, J.N. Utilization of MR imaging in myodural bridge complex with relevant muscles: Current status and future perspectives. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2020, 20, 382–389. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.Y.; Han, X.; Wang, M.Y.; Ning, D.X.; Xu, B.; Xie, L.Z.; Yu, S.B.; Sui, H.J. Relationship between the sectional area of the rectus capitis posterior minor and the to be named ligament from 3D MR imaging. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedhoseinpoor, T.; Taghipour, M.; Dadgoo, M.; Sanjari, M.A.; Takamjani, I.E.; Kazemnejad, A.; Khoshamooz, Y.; Hides, J. Alteration of lumbar muscle morphology and composition in relation to ow back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2022, 22, 660–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.P.; Croci, C.S.; Caria, P.H. Is there relationship between temporo-mandibular disorders and head and cervical posture? A systematic review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2013, 40, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenbaum, T.; Dvir, Z.; Reiter, S.; Winocur, E. Cervical flexion-rotation test and physiological range of motion—A comparative study of patients with myogenic temporomandibular disorder versus healthy subjects. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 27, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenbaum, T.; Dvir, Z.; Emodi-Perelmam, A.; Reiter, S.; Rubin, P.; Winocur, E. Relationship between specific temporo-mandibular disorders and impaired upper neck performance. Eur. J. Oral. Sci. 2020, 128, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calixtre, L.B.; Oliveira, A.B.; de Sena Rosa, L.R.; Armijo-Olivo, S.; Visscher, C.M.; Alburquerque-Sendín, F. Effectiveness of mobilisation of the upper cervical region and craniocervical flexor training on orofacial pain, mandibular function and headache in women with TMD. A randomised, controlled trial. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 46, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La-Touche, R.; Martínez-García, S.; Serrano-García, B.; Proy-Acosta, A.; Adraos-Juárez, D.; Fernández-Pérez, J.J.; Angulo-Díaz-Parreño, S.; Cuenca-Martínez, F.; Paris-Alemany, A.; Suso-Marti, L. Effect of manual therapy and therapeutic exercise applied to the cervical region on pain and pressure pain sensitivity in patients with temporomandibular disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| TMD (n = 20) | Healthy Controls (n = 20) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measure | Right Side | Left Side | Right Side | Left Side |
| CSA * | 0.35 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.7 (0.25) | 0.65 (0.2) |
| Perimeter * | 2.0 (0.3) | 1.9 (0.25) | 2.9 (0.45) | 2.85 (0.4) |
| Depth | 1.45 (0.2) | 1.5 (0.1) | 1.6 (0.2) | 1.6 (0.2) |
| Width | 4.1 (0.1) | 4.1 (0.15) | 4.2 (0.05) | 4.1 (0.1) |
| Thickness * | 0.65 (0.1) | 0.6 (0.05) | 0.9 (0.15) | 0.9 (0.1) |
| TMD (n = 20) | Healthy Controls (n = 20) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measure | Right Side | Left Side | Right Side | Left Side |
| CSA * | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.05) | 0.75 (0.2) | 0.7 (0.2) |
| Perimeter * | 2.0 (0.3) | 1.9 (0.25) | 3.0 (0.4) | 2.9 (0.4) |
| Depth | 1.5 (0.15) | 1.5 (0.15) | 1.65 (0.2) | 1.6 (0.2) |
| Width | 4.1 (0.1) | 4.05 (0.2) | 4.2 (0.1) | 4.15 (0.05) |
| Thickness * | 0.65 (0.1) | 0.6 (0.1) | 0.95 (0.15) | 0.9 (0.1) |
| TMD (n = 20) | Healthy Controls (n = 20) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measure | Right Side | Left Side | Right Side | Left Side |
| CSA * | 0.5 (0.3) | 0.45 (0.1) | 0.85 (0.3) | 0.8 (0.25) |
| Perimeter * | 2.2 (0.7) | 2.25 (0.3) | 2.8 (0.6) | 2.9 (0.5) |
| Depth | 1.6 (0.2) | 1.5 (0.15) | 1.55 (0.2) | 1.6 (0.15) |
| Width | 4.15 (0.05) | 4.1 (0.1) | 4.2 (0.25) | 4.15 (0.1) |
| Thickness * | 0.8 (0.2) | 0.75 (0.1) | 1.0 (0.15) | 1.0 (0.2) |
| TMD (n = 20) | Healthy Controls (n = 20) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measure | Right Side | Left Side | Right Side | Left Side |
| CSA * | 0.45 (0.2) | 0.45 (0.15) | 0.9 (0.25) | 0.9 (0.3) |
| Perimeter * | 2.25 (0.5) | 2.3 (0.45) | 3.3 (0.5) | 3.39 (0.5) |
| Depth | 1.5 (0.2) | 1.45 (0.15) | 1.6 (0.2) | 1.55 (0.2) |
| Width | 4.1 (0.15) | 4.1 (0.15) | 4.2 (0.1) | 4.15 (0.05) |
| Thickness * | 0.7 (0.15) | 0.75 (0.15) | 1.05 (0.15) | 1.05 (0.15) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ulman-Macón, D.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Angulo-Díaz-Parreño, S.; Arias-Buría, J.L.; Mesa-Jiménez, J.A. Morphological Changes of the Suboccipital Musculature in Women with Myofascial Temporomandibular Pain: A Case-Control Study. Life 2023, 13, 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051159
Ulman-Macón D, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Angulo-Díaz-Parreño S, Arias-Buría JL, Mesa-Jiménez JA. Morphological Changes of the Suboccipital Musculature in Women with Myofascial Temporomandibular Pain: A Case-Control Study. Life. 2023; 13(5):1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051159
Chicago/Turabian StyleUlman-Macón, Daniel, César Fernández-de-las-Peñas, Santiago Angulo-Díaz-Parreño, José L. Arias-Buría, and Juan A. Mesa-Jiménez. 2023. "Morphological Changes of the Suboccipital Musculature in Women with Myofascial Temporomandibular Pain: A Case-Control Study" Life 13, no. 5: 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051159
APA StyleUlman-Macón, D., Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C., Angulo-Díaz-Parreño, S., Arias-Buría, J. L., & Mesa-Jiménez, J. A. (2023). Morphological Changes of the Suboccipital Musculature in Women with Myofascial Temporomandibular Pain: A Case-Control Study. Life, 13(5), 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051159







