Localization of the Catalytic Domain of Copepod Luciferases: Analysis of Truncated Mutants of the Metridia longa Luciferase
Abstract
1. Introduction
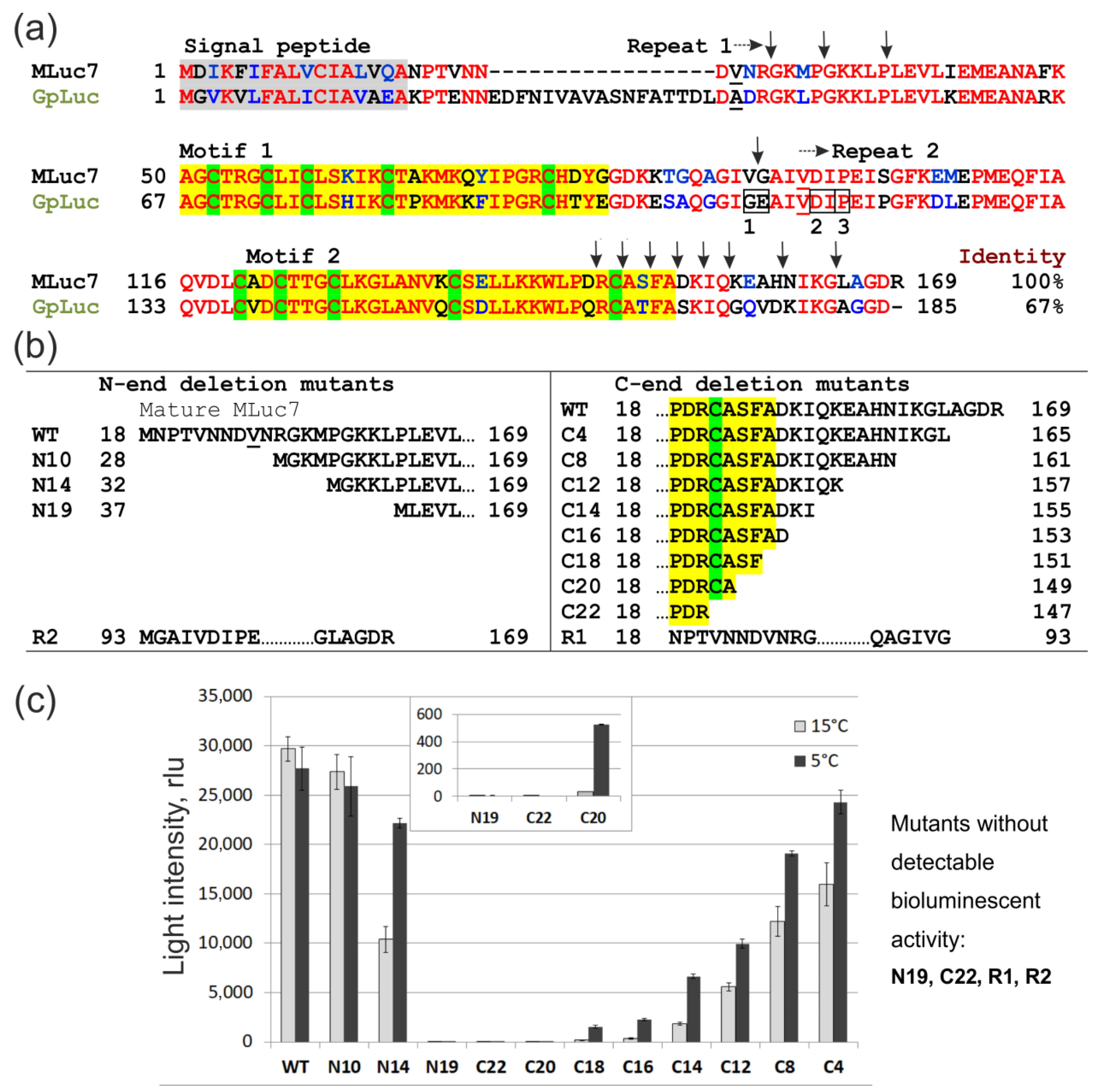
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Genetic Constructs
2.3. Expression in E. coli, Purification, and Preparation of Natively Folded Luciferases
2.4. Expression of MLuc7 and Its Mutants in Mammalian Cells
2.5. Bioluminescence Assay
2.6. Spectral Measurements
2.7. Structural Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Functional Analysis of Deletion Mutants in Crude E. coli Lysates
3.2. Bioluminescent Properties of High-Activity Deletion Mutants
3.3. Protein Spatial Structure Analysis
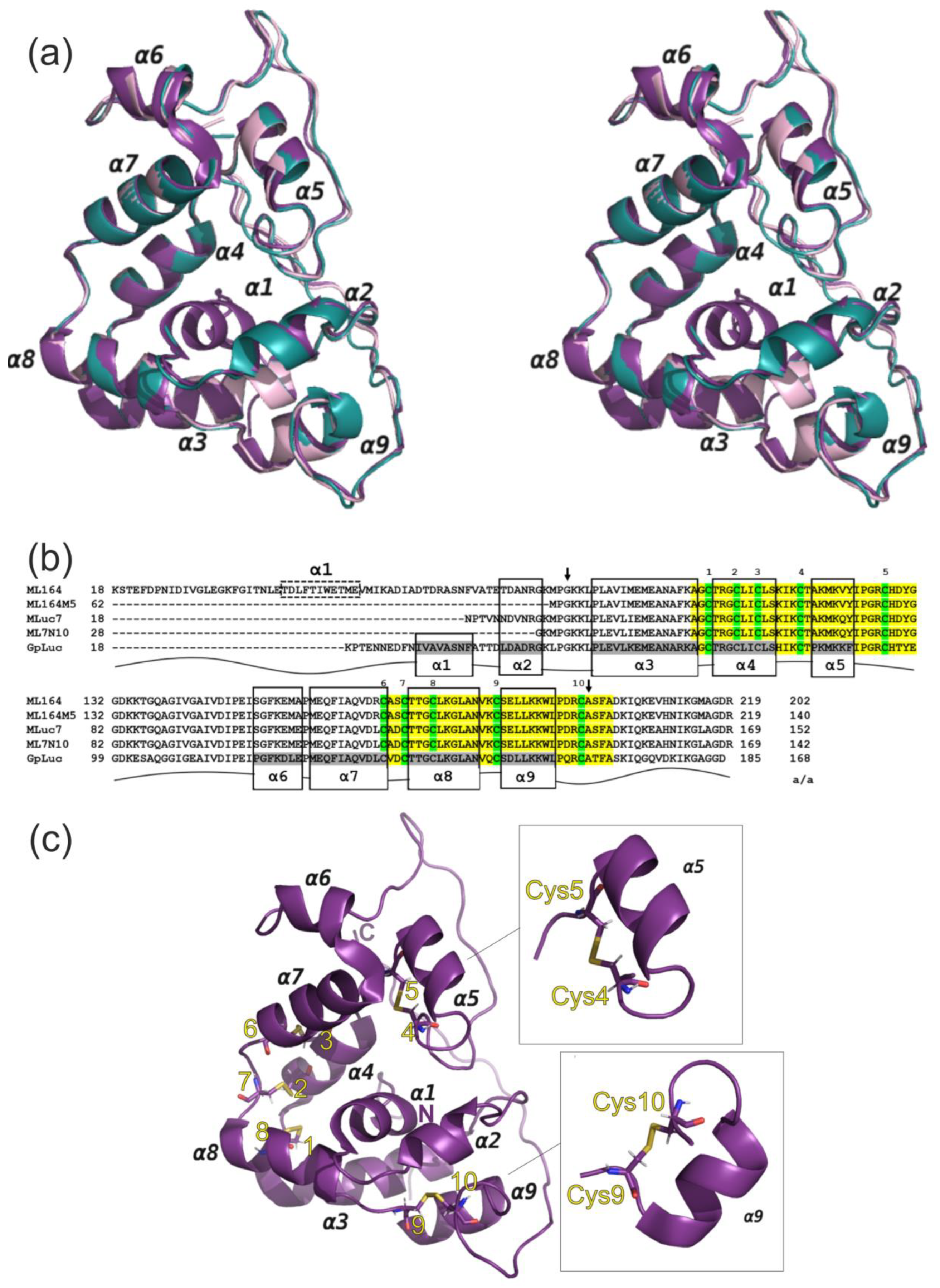
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Markova, S.V.; Golz, S.; Frank, L.A.; Kalthof, B.; Vysotski, E.S. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a luciferase from the marine copepod Metridia longa. A novel secreted bioluminescent reporter enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 3212–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markova, S.V.; Larionova, M.D.; Vysotski, E.S. Shining light on the secreted luciferases of marine copepods: Current knowledge and applications. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, B.; Szent-Gyorgi, C. Luciferases, Fluorescent Proteins, Nucleic Acids Encoding the Luciferases and Fluorescent Proteins and the Use Thereof in Diagnostics, High Throughput Screening and Novelty Items. U.S. Patent #6232107, 15 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.; Rathnayaka, T.; Kuroda, Y. Bacterial expression and re-engineering of Gaussia princeps luciferase and its use as a reporter protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1854, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisova, V.V.; Frank, L.A.; Markova, S.V.; Burakova, L.P.; Vysotski, E.S. Recombinant Metridia luciferase isoforms: Expression, refolding and applicability for in vitro assay. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2008, 7, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, S.V.; Larionova, M.D.; Burakova, L.P.; Vysotski, E.S. The smallest natural high-active luciferase: Cloning and characterization of novel 16.5-kDa luciferase from copepod Metridia longa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 457, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionova, M.D.; Markova, S.V.; Vysotski, E.S. The novel extremely psychrophilic luciferase from Metridia longa: Properties of a high-purity protein produced in insect cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, S.V.; Burakova, L.P.; Vysotski, E.S. High-active truncated luciferase of copepod Metridia longa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inouye, S.; Sahara, Y. Identification of two catalytic domains in a luciferase secreted by the copepod Gaussia princeps. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, Y.; Yamaguchi, A.; Tsuruoka, N.; Torimura, M.; Gojobori, T.; Shigeri, Y. Evolution of bioluminescence in marine planktonic copepods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionova, M.D.; Markova, S.V.; Vysotski, E.S. Bioluminescent and structural features of native folded Gaussia luciferase. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 183, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerke, A.R.; Loening, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Swartz, J.R. Cell-free metabolic engineering promotes high-level production of bioactive Gaussia princeps luciferase. Metab. Eng. 2008, 10, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Kobayashi, N.; Tsuda, K.; Unzai, S.; Saotome, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Yamazaki, T. Solution structure of Gaussia Luciferase with five disulfide bonds and identification of a putative coelenterazine binding cavity by heteronuclear NMR. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, E.A.; Moutsiopoulou, A.; Ioannou, S.; Ahern, K.; Woodward, K.; Dikici, E.; Daunert, S.; Deo, S. K Truncated variants of Gaussia luciferase with tyrosine linker for site-specific bioconjugate applications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 8, 26814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remy, I.; Michnick, S.W. A highly sensitive protein-protein interaction assay based on Gaussia luciferase. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 977–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolkhof, P.; Werthebach, M.; van de Venn, A.; Poschmann, G.; Chen, L.; Welte, M.; Stühler, K.; Beller, M. A luciferase-fragment complementation assay to detect lipid droplet-associated protein-protein interactions. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2017, 16, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markova, S.V.; Larionova, M.D.; Gorbunova, D.A.; Vysotski, E.S. The disulfide-rich Metridia luciferase refolded from E. coli inclusion bodies reveals the properties of a native folded enzyme produced in insect cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 175, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, S.V.; Larionova, M.D.; Vysotski, E.S. Production of Metridia luciferase in native form by oxidative refolding from E. coli inclusion bodies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2524, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkema, F.M.; Nordentoft, M.K.; Didriksen, A.K.; Corneliussen, A.S.; Willemoës, M.; Winther, J.R. Flash properties of Gaussia luciferase are the result of covalent inhibition after a limited number of cycles. Protein Sci. 2021, 3, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PymolWiki.org. Available online: https://pymolwiki.org/index.php/Color_h (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Yan, R.; Xu, D.; Yang, J.; Walker, S.; Zhang, Y. A comparative assessment and analysis of 20 representative sequence alignment methods for protein structure prediction. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmuro-Matsuyama, Y.; Furuta, T.; Matsui, H.; Kanai, M.; Ueda, H. Miniaturization of Bright Light-Emitting Luciferase ALuc: PicALuc. ACS Chem. Biol. 2022, 17, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.B.; Suzuki, H.; Sato, M.; Tao, H. Superluminescent variants of marine luciferases for bioassays. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8732–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degeling, M.H.; Bovenberg, M.S.; Lewandrowski, G.K.; de Gooijer, M.C.; Vleggeert-Lankamp, C.L.; Tannous, M.; Maguire, C.A.; Tannous, B.A. Directed molecular evolution reveals Gaussia luciferase variants with enhanced light output stability. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3006–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionova, M.D.; Markova, S.V.; Vysotski, E.S. Tyr72 and Tyr80 are involved in the formation of an active site of a luciferase of copepod Metridia longa. Photochem. Photobiol. 2017, 93, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Fu, Z.; Wang, T.; Cui, X.; Dong, J.; Du, F.; Huang, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, G.; Sun, J.; et al. A high-throughput in vivo selection method for luciferase variants. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayaka, T.; Tawa, M.; Nakamura, T.; Sohya, S.; Kuwajima, K.; Yohda, M.; Kuroda, Y. Solubilization and folding of a fully active recombinant Gaussia luciferase with native disulfide bonds by using a SEP-Tag. BBA-Proteins Proteom. 2011, 1814, 1775–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, D.; Schwarz, E.; Komaromy, M.; Wall, R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J. Mol. Biol. 1984, 179, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanyuk, G.A.; Xu, H.; Wu, C.K.; Markova, S.V.; Lee, J.; Vysotski, E.S.; Wang, B.C. Expression, purification and characterization of the secreted luciferase of the copepod Metridia longa from Sf9 insect cells. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 61, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenkmayerova, A.; Toul, M.; Pluskal, D.; Racha Baatallah, R.; Gagnot, G.; Pinto, G.P.; Santana, V.T.; Stuchla, M.; Neugebauer, P.; Chaiyen, P.; et al. Catalytic mechanism for Renilla-type luciferases. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessler, M.; Gaffney, J.P.; Crawford, J.M.; Trautman, E.; Gujarati, N.A.; Alatalo, P.; Pieribone, V.A.; Gruber, D.F. Luciferin production and luciferase transcription in the bioluminescent copepod Metridia lucens. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
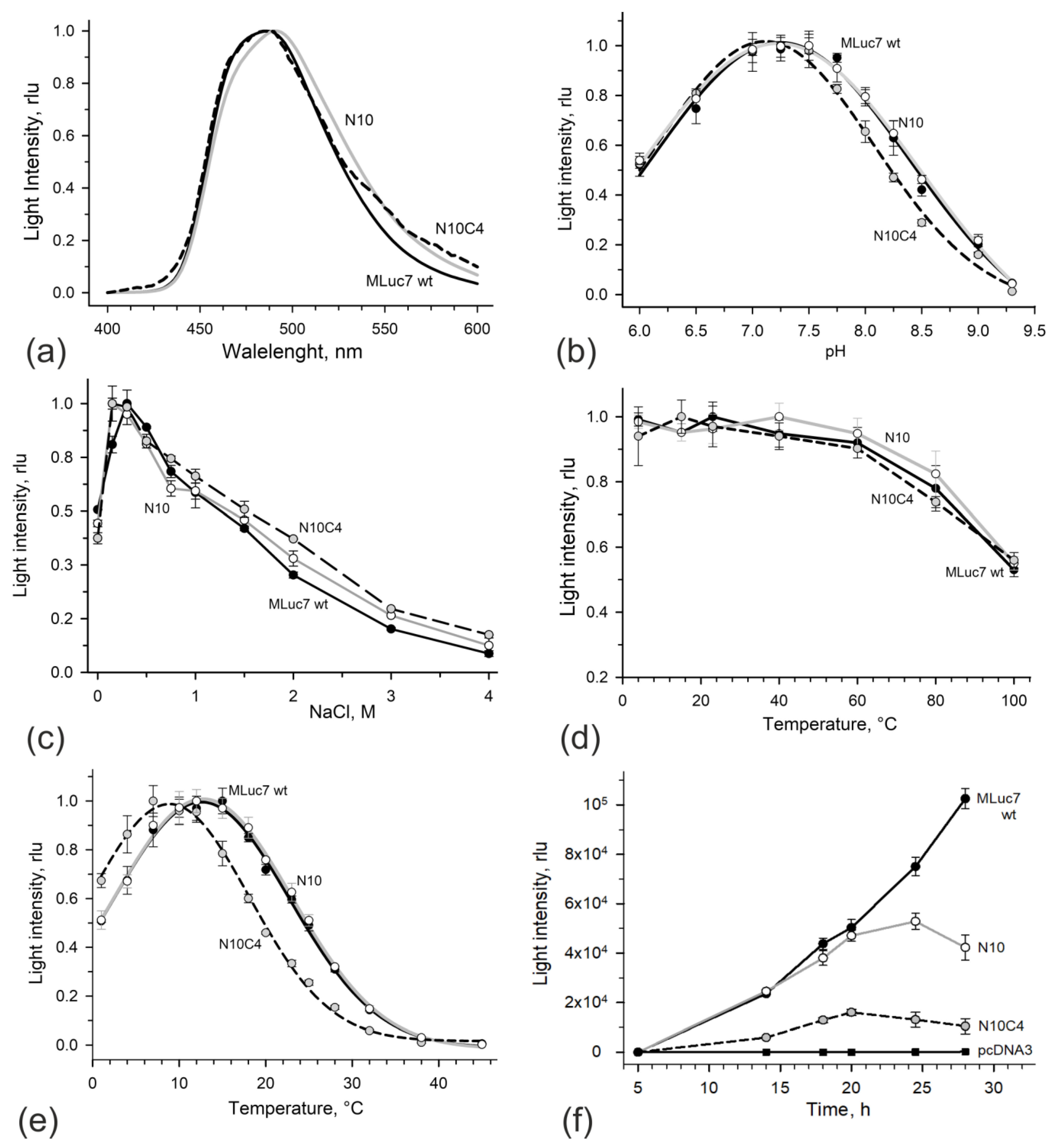

| Protein | Initial Bioluminescence Activity 1 (rlu/mg, ×109) | Relative Bioluminescence Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| MLuc7 | 12.9 ± 1.4 | 100 |
| ML7-N10 | 11.8 ± 1.1 | 92 |
| ML7-N10C4 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | 23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markova, S.V.; Larionova, M.D.; Korotov, I.A.; Vysotski, E.S. Localization of the Catalytic Domain of Copepod Luciferases: Analysis of Truncated Mutants of the Metridia longa Luciferase. Life 2023, 13, 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051222
Markova SV, Larionova MD, Korotov IA, Vysotski ES. Localization of the Catalytic Domain of Copepod Luciferases: Analysis of Truncated Mutants of the Metridia longa Luciferase. Life. 2023; 13(5):1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051222
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkova, Svetlana V., Marina D. Larionova, Igor A. Korotov, and Eugene S. Vysotski. 2023. "Localization of the Catalytic Domain of Copepod Luciferases: Analysis of Truncated Mutants of the Metridia longa Luciferase" Life 13, no. 5: 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051222
APA StyleMarkova, S. V., Larionova, M. D., Korotov, I. A., & Vysotski, E. S. (2023). Localization of the Catalytic Domain of Copepod Luciferases: Analysis of Truncated Mutants of the Metridia longa Luciferase. Life, 13(5), 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051222







