Early Detection of Secondary Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma and Disseminated Bone Metastases with Normal Prostate-Specific Antigen Level after Pelvic Salvage Radiotherapy in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
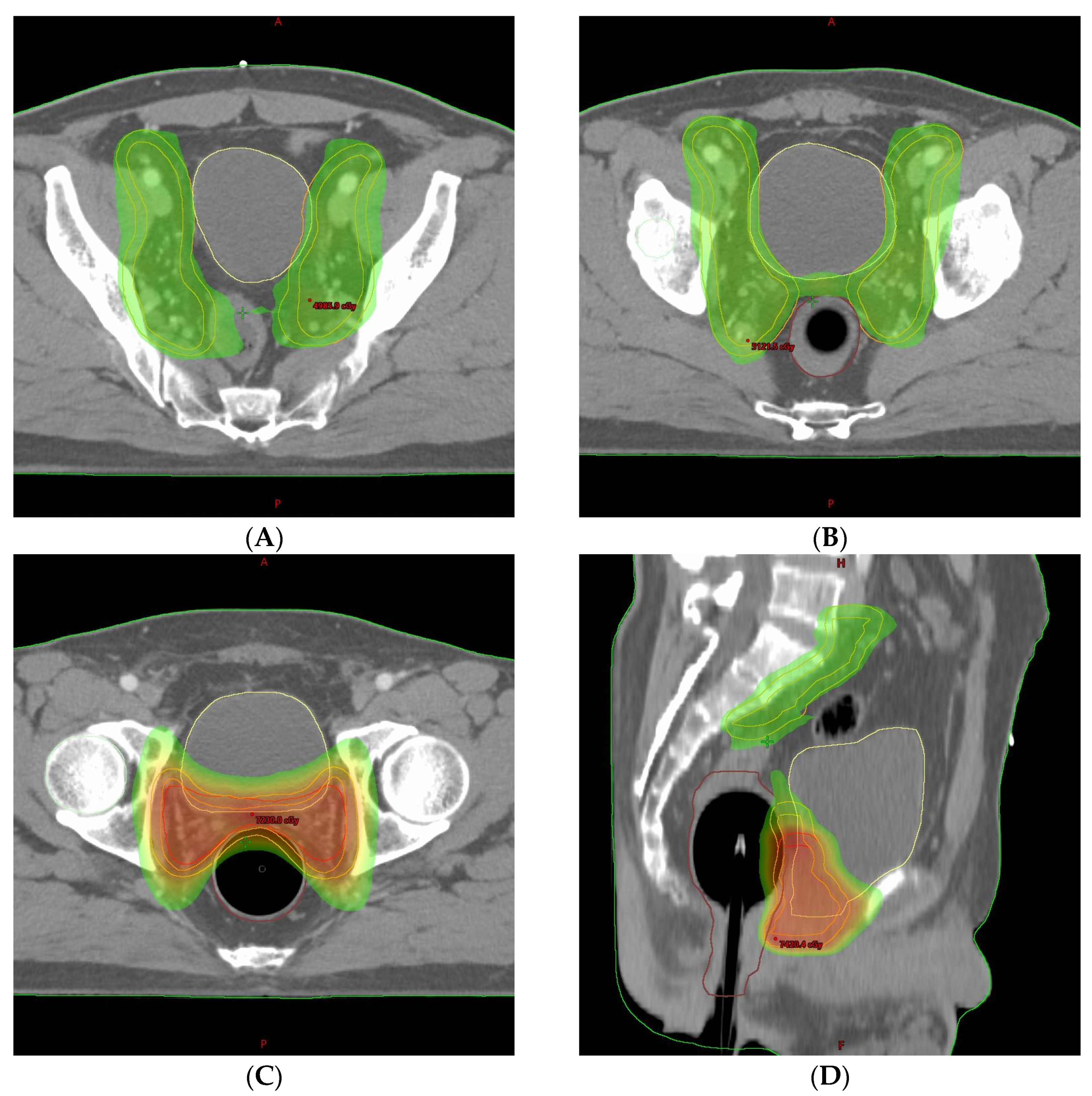
2. Detailed Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schaue, D.; McBride, W.H. Opportunities and challenges of radiotherapy for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raicu, M.; Vral, A.; Thierens, H.; De Ridder, L. Radiation damage to endothelial cells in vitro, as judged by the micronucleus assay. Mutagenesis 1993, 8, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Hu, W. Dosimetric impact of different bladder and rectum filling during prostate cancer radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miralbell, R.; Roberts, S.A.; Zubizarreta, E.; Hendry, J.H. Dose-fractionation sensitivity of prostate cancer deduced from radiotherapy outcomes of 5969 patients in seven international institutional datasets: α/β = 1.4 (0.9–2.2) Gy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, e17–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorbińska, J.; Krajewski, W.; Zdrojowy, R. Urological complications after radiation therapy-nothing ventured, nothing gained: A Narrative Review. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1096–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibovici, D.; Spiess, P.E.; Agarwal, P.K.; Tu, S.M.; Pettaway, C.A.; Hitzhusen, K.; Millikan, R.E.; Pisters, L.L. Prostate cancer progression in the presence of undetectable or low serum prostate-specific antigen level. Cancer 2007, 109, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtle, A.J.; Freeman, A.; Masters, J.R.; Payne, H.A.; Harland, S.J. Clinical features of patients who present with metastatic prostate carcinoma and serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels < 10 ng/mL: The “PSA negative” patients. Cancer 2003, 98, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oefelein, M.G.; Smith, N.; Carter, M.; Dalton, D.; Schaeffer, A. The incidence of prostate cancer progression with undetectable serum prostate specific antigen in a series of 394 radical prostatectomies. J. Urol. 1995, 154, 2128–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Ito, T.; Akiyama, A.; Aizawa, T.; Miki, M.; Tachibana, M. M1 prostate cancer with a serum level of prostate-specific antigen less than 10 ng/mL. Int. J. Urol. 2001, 8, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, A.J.; Kattan, M.W.; Eastham, J.A.; Dotan, Z.A.; Bianco, F.J., Jr.; Lilja, H.; Scardino, P.T. Defining biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy: A proposal for a standardized definition. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3973–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, W., Jr.; Bosch, W.R.; Harkenrider, M.M.; Strauss, J.B.; Abu-Rustum, N.; Albuquerque, K.V.; Beriwal, S.; Creutzberg, C.L.; Eifel, P.J.; Erickson, B.A.; et al. NRG Oncology/RTOG Consensus Guidelines for Delineation of Clinical Target Volume for Intensity Modulated Pelvic Radiation Therapy in Postoperative Treatment of Endometrial and Cervical Cancer: An Update. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, F.; Altobelli, E.; Sergi, F.; Buscarini, M. Bladder cancer after radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Rev. Urol. 2013, 15, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.D.; Stetz, J.; Pajak, T.F. Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 31, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, S.G.; Heyns, C.F. Management of radiation cystitis. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2010, 7, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautruche, A.; Delouya, G. A contemporary review about the management of radiation-induced hemorrhagic cystitis. Curr. Opin. Support Palliat. Care 2018, 12, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, C.J.; Mahar, A.L.; Choo, R.; Herschorn, S.; Kodama, R.T.; Shah, P.S.; Danjoux, C.; Narod, S.A.; Nam, R.K. Second malignancies after radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2016, 352, i851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.; Stukenborg, G.J.; Keim, J.; Theodorescu, D. Cancer incidence after localized therapy for prostate cancer. Cancer 2006, 107, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boorjian, S.; Cowan, J.E.; Konety, B.R.; DuChane, J.; Tewari, A.; Carroll, P.R.; Kane, C.J. Cancer of the Prostate Strategic Urologic Research Endeavor Investigators. Bladder cancer incidence and risk factors in men with prostate cancer: Results from Cancer of the Prostate Strategic Urologic Research Endeavor. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kestin, L.L.; Ye, H.; Wallace, M.; Martinez, A.A.; Vicini, F.A. Analysis of second malignancies after modern radiotherapy versus prostatectomy for localized prostate cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 98, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrouser, K.; Leibovich, B.; Bergstralh, E.; Zincke, H.; Blute, M. Bladder cancer risk following primary and adjuvant external beam radiation for prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2005, 174, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, L.; Henry, A.; Hoskin, P.; Siebert, F.A.; Venselaar, J. Second primary cancers after radiation for prostate cancer: A systematic review of the clinical data and impact of treatment technique. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 110, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, D.S.; Shariat, S.F.; Lowrance, W.T.; Sterbis, J.R.; Vora, K.C.; Bochner, B.H.; Donat, S.M.; Herr, H.W.; Dalbagni, G.; Sandhu, J.S. Impact of previous radiotherapy for prostate cancer on clinical outcomes of patients with bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Castelao, J.E.; Yuan, J.M.; Stern, M.C.; Conti, D.V.; Cortessis, V.K.; Pike, M.C.; Gago-Dominguez, M. Cigarette smoking and subtypes of bladder cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wei, R.; Yang, R.; Lu, Z.; Liu, E.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, M.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Risk and Prognosis of Secondary Bladder Cancer After Radiation Therapy for Rectal Cancer: A Large Population-Based Cohort Study. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 586401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Zhong, G.; Ren, M. Increased risk of secondary bladder cancer after radiation therapy for endometrial cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalken, J.A. Molecular and cellular prostate biology: Origin of prostate-specific antigen expression and implications for benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int. 2004, 93 (Suppl. S1), 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, Y.; Kihara, K.; Kamata, S.; Nagahama, K.; Yonese, J.; Fukuda, H.; Tosaka, A.; Nagamatsu, H.; Ishizaka, K.; Tsujii, T.; et al. Relationship between pretreatment serum levels of prostate specific antigen and bone metastasis in prostate cancer. Hinyokika Kiyo 1996, 42, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Combes, A.D.; Palma, C.A.; Calopedos, R.; Wen, L.; Woo, H.; Fulham, M.; Leslie, S. PSMA PET-CT in the Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, T.J.; Choe, M.; Kim, B.H.; Byun, S.J. Early Detection of Secondary Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma and Disseminated Bone Metastases with Normal Prostate-Specific Antigen Level after Pelvic Salvage Radiotherapy in Prostate Cancer. Life 2023, 13, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061249
Shin TJ, Choe M, Kim BH, Byun SJ. Early Detection of Secondary Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma and Disseminated Bone Metastases with Normal Prostate-Specific Antigen Level after Pelvic Salvage Radiotherapy in Prostate Cancer. Life. 2023; 13(6):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061249
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Teak Jun, Misun Choe, Byung Hoon Kim, and Sang Jun Byun. 2023. "Early Detection of Secondary Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma and Disseminated Bone Metastases with Normal Prostate-Specific Antigen Level after Pelvic Salvage Radiotherapy in Prostate Cancer" Life 13, no. 6: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061249
APA StyleShin, T. J., Choe, M., Kim, B. H., & Byun, S. J. (2023). Early Detection of Secondary Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma and Disseminated Bone Metastases with Normal Prostate-Specific Antigen Level after Pelvic Salvage Radiotherapy in Prostate Cancer. Life, 13(6), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061249




