Identification of Phase-Separation-Protein-Related Function Based on Gene Ontology by Using Machine Learning Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
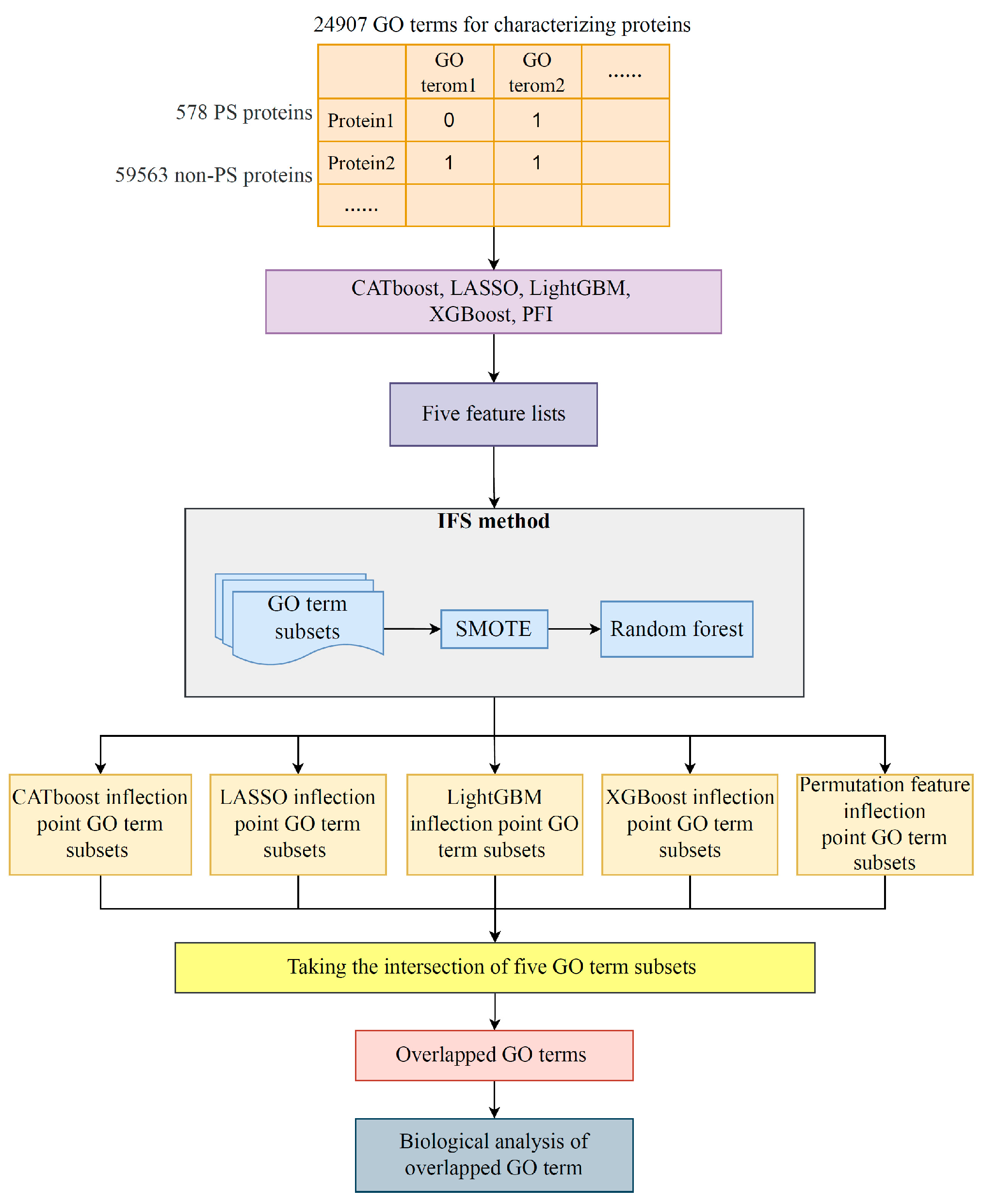
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Feature Ranking Algorithms
2.2.1. Categorical Boosting
2.2.2. Extreme Gradient Boosting
2.2.3. Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator
2.2.4. Light Gradient-Boosting Machine
2.2.5. Permutation Feature Importance
2.3. Incremental Feature Selection
2.4. Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique
2.5. Random Forest
2.6. Performance Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Feature Ranking Results
3.2. Results of IFS Method with Random Forest
3.3. Intersection of Most Essential Features Extracted from Different Feature Lists
4. Discussion
4.1. Phase Separation in RNA Binding-Related Biological Process
4.2. Phase Separation in Membrane Formation
4.3. Phase Separation at the Synapse
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boeynaems, S.; Alberti, S.; Fawzi, N.L.; Mittag, T.; Polymenidou, M.; Rousseau, F.; Schymkowitz, J.; Shorter, J.; Wolozin, B.; Van Den Bosch, L.; et al. Protein phase separation: A new phase in cell biology. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrea, D.M.; Kriwacki, R.W. Phase separation in biology; functional organization of a higher order. Cell Commun. Signal 2016, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Intrinsically disordered proteins in overcrowded milieu: Membrane-less organelles, phase separation, and intrinsic disorder. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 44, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banani, S.F.; Lee, H.O.; Hyman, A.A.; Rosen, M.K. Biomolecular condensates: Organizers of cellular biochemistry. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Brangwynne, C.P. Liquid phase condensation in cell physiology and disease. Science 2017, 357, eaaf4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron-Sandoval, L.P.; Safaee, N.; Michnick, S.W. Mechanisms and consequences of macromolecular phase separation. Cell 2016, 165, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, X.; Li, P.; Liu, C.; Lou, J.; Wang, Z.; Wen, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, X. Liquid-liquid phase separation in biology: Mechanisms, physiological functions and human diseases. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 953–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nott, T.J.; Petsalaki, E.; Farber, P.; Jervis, D.; Fussner, E.; Plochowietz, A.; Craggs, T.D.; Bazett-Jones, D.P.; Pawson, T.; Forman-Kay, J.D.; et al. Phase transition of a disordered nuage protein generates environmentally responsive membraneless organelles. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumiller, W.M., Jr.; Keating, C.D. Phosphorylation-mediated rna/peptide complex coacervation as a model for intracellular liquid organelles. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huai, Y.; Mao, W.; Wang, X.; Ru, K.; Qian, A.; Yang, H. Liquid-liquid phase separation of biomacromolecules and its roles in metabolic diseases. Cells 2022, 11, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broide, M.L.; Berland, C.R.; Pande, J.; Ogun, O.O.; Benedek, G.B. Binary-liquid phase separation of lens protein solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5660–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galkin, O.; Chen, K.; Nagel, R.L.; Hirsch, R.E.; Vekilov, P.G. Liquid-liquid separation in solutions of normal and sickle cell hemoglobin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8479–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, S.; Gladfelter, A.; Mittag, T. Considerations and challenges in studying liquid-liquid phase separation and biomolecular condensates. Cell 2019, 176, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, T.; Nozawa, R.S.; Jia, T.Z.; Saio, T.; Mori, E. Biological phase separation: Cell biology meets biophysics. Biophys. Rev. 2020, 12, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riback, J.A.; Katanski, C.D.; Kear-Scott, J.L.; Pilipenko, E.V.; Rojek, A.E.; Sosnick, T.R.; Drummond, D.A. Stress-triggered phase separation is an adaptive, evolutionarily tuned response. Cell 2017, 168, 1028–1040.e1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, R.M.; Chong, P.A.; Tsang, B.; Kim, T.H.; Bah, A.; Farber, P.; Lin, H.; Forman-Kay, J.D. Pi-pi contacts are an overlooked protein feature relevant to phase separation. eLife 2018, 7, e31486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.P.; Sawaya, M.R.; Boyer, D.R.; Goldschmidt, L.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Cascio, D.; Chong, L.; Gonen, T.; Eisenberg, D.S. Atomic structures of low-complexity protein segments reveal kinked β sheets that assemble networks. Science 2018, 359, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, A.K.; Nutter-Upham, A.; Lindquist, S.; King, O.D. Plaac: A web and command-line application to identify proteins with prion-like amino acid composition. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2501–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardenberg, M.; Horvath, A.; Ambrus, V.; Fuxreiter, M.; Vendruscolo, M. Widespread occurrence of the droplet state of proteins in the human proteome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33254–33262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Sun, T.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lai, L.; Pei, J. Prediction of liquid-liquid phase separating proteins using machine learning. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, R.M.; Forman-Kay, J.D. First-generation predictors of biological protein phase separation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 58, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorogush, A.V.; Ershov, V.; Gulin, A. Catboost: Gradient boosting with categorical features support. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.11363. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System; The 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani, R.J. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. B Methodol. 1996, 73, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finely, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. Lightgbm: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Rudin, C.; Dominici, F. All models are wrong, but many are useful: Learning a variable’s importance by studying an entire class of prediction models simultaneously. J. Mach. Learn Res. 2019, 20, 1–81. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.A.; Setiono, R. Incremental feature selection. Appl. Intell. 1998, 9, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hou, C.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Chen, T.; Shen, B.; Hou, Y.; Li, P.; Li, T. Screening membraneless organelle participants with machine-learning models that integrate multimodal features. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2115369119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zeng, T.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.D. Identifying methylation pattern and genes associated with breast cancer subtypes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Li, Z.; Zeng, T.; Pan, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Li, H.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.D. Distinguishing glioblastoma subtypes by methylation signatures. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 604336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohavi, R. A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence Volume 2; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 1995; pp. 1137–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. Smote: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Fu, M.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Feng, K.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Analysis and prediction of protein stability based on interaction network, gene ontology, and kegg pathway enrichment scores. BBA Proteins Proteom. 2023, 1871, 140889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Ma, Q.; Ren, J.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.-D. Identification of smoking associated transcriptome aberration in blood with machine learning methods. BioMed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 5333361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, B.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Han, Y.; Dai, Q. Drug-drug interactions prediction using fingerprint only. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 7818480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, L. Identification of drug–disease associations by using multiple drug and disease networks. Curr. Bioinform. 2022, 17, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, L. A model with deep analysis on a large drug network for drug classification. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2023, 20, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, D. Evaluation: From precision, recall and f-measure to roc., informedness, markedness & correlation. J. Mach. Learn. Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chen, L. Pmptce-hnea: Predicting metabolic pathway types of chemicals and enzymes with a heterogeneous network embedding algorithm. Curr. Bioinform. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Chen, L. Iatc-nfmlp: Identifying classes of anatomical therapeutic chemicals based on drug networks, fingerprints and multilayer perceptron. Curr. Bioinform. 2022, 17, 814–824. [Google Scholar]
- Hofweber, M.; Dormann, D. Friend or foe-post-translational modifications as regulators of phase separation and rnp granule dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 7137–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Fang, X. Phase separation in rna biology. J. Genet. Genom. 2021, 48, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, P.; Kedersha, N.; Anderson, P. Stress granules and processing bodies in translational control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2019, 11, a032813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Na, Z.; Slavoff, S.A. P-bodies: Composition, properties, and functions. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 2424–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standart, N.; Weil, D. P-bodies: Cytosolic droplets for coordinated mrna storage. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protter, D.S.W.; Parker, R. Principles and properties of stress granules. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, D.W.; Kedersha, N.; Lee, D.S.W.; Strom, A.R.; Drake, V.; Riback, J.A.; Bracha, D.; Eeftens, J.M.; Iwanicki, A.; Wang, A.; et al. Competing protein-rna interaction networks control multiphase intracellular organization. Cell 2020, 181, 306–324.e328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén-Boixet, J.; Kopach, A.; Holehouse, A.S.; Wittmann, S.; Jahnel, M.; Schlüßler, R.; Kim, K.; Trussina, I.; Wang, J.; Mateju, D.; et al. Rna-induced conformational switching and clustering of g3bp drive stress granule assembly by condensation. Cell 2020, 181, 346–361.e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Mathieu, C.; Kolaitis, R.M.; Zhang, P.; Messing, J.; Yurtsever, U.; Yang, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Pan, Q.; et al. G3bp1 is a tunable switch that triggers phase separation to assemble stress granules. Cell 2020, 181, 325–345.e328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caragine, C.M.; Haley, S.C.; Zidovska, A. Nucleolar dynamics and interactions with nucleoplasm in living cells. eLife 2019, 8, e47533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontaine, D.L.J.; Riback, J.A.; Bascetin, R.; Brangwynne, C.P. The nucleolus as a multiphase liquid condensate. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.W.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.; Shan, L.; Luan, P.F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Yang, L.Z.; Xing, Y.H.; Yang, L.; et al. Nascent pre-rrna sorting via phase separation drives the assembly of dense fibrillar components in the human nucleolus. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 767–783.e711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feric, M.; Vaidya, N.; Harmon, T.S.; Mitrea, D.M.; Zhu, L.; Richardson, T.M.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Pappu, R.V.; Brangwynne, C.P. Coexisting liquid phases underlie nucleolar subcompartments. Cell 2016, 165, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Zhang, H. Phase separation in membrane biology: The interplay between membrane-bound organelles and membraneless condensates. Dev. Cell 2020, 55, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Ditlev, J.A.; Hui, E.; Xing, W.; Banjade, S.; Okrut, J.; King, D.S.; Taunton, J.; Rosen, M.K.; Vale, R.D. Phase separation of signaling molecules promotes t cell receptor signal transduction. Science 2016, 352, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, L.B.; Zhang, X.; Ditlev, J.A.; Rosen, M.K. Stoichiometry controls activity of phase-separated clusters of actin signaling proteins. Science 2019, 363, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zihni, C.; Mills, C.; Matter, K.; Balda, M.S. Tight junctions: From simple barriers to multifunctional molecular gates. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 564–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutel, O.; Maraspini, R.; Pombo-García, K.; Martin-Lemaitre, C.; Honigmann, A. Phase separation of zonula occludens proteins drives formation of tight junctions. Cell 2019, 179, 923–936.e911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Mayr, C. A membraneless organelle associated with the endoplasmic reticulum enables 3’utr-mediated protein-protein interactions. Cell 2018, 175, 1492–1506.e1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zheng, G.; Xie, W.; Mayr, C. In vivo reconstitution finds multivalent rna-rna interactions as drivers of mesh-like condensates. eLife 2021, 10, e64252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, Y.; Alam, J.M.; Noshiro, D.; Mouri, K.; Ando, T.; Okada, Y.; May, A.I.; Knorr, R.L.; Suzuki, K.; Ohsumi, Y.; et al. Phase separation organizes the site of autophagosome formation. Nature 2020, 578, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, N.N.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Liquid-liquid phase separation in autophagy. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e202004062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itakura, E.; Mizushima, N. Characterization of autophagosome formation site by a hierarchical analysis of mammalian atg proteins. Autophagy 2010, 6, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Yoshimori, T.; Ohsumi, Y. The role of atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 27, 107–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, M. Phase separation at the synapse. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.M.; Weinberg, R.J. Ultrastructure of synapses in the mammalian brain. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2012, 4, a005587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Winters, C.; Azzam, R.; Li, X.; Galbraith, J.A.; Leapman, R.D.; Reese, T.S. Organization of the core structure of the postsynaptic density. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couteaux, R.; Pécot-Dechavassine, M. Synaptic vesicles and pouches at the level of “active zones” of the neuromuscular junction. C R Acad. Hebd Seances Acad. Sci. D 1970, 271, 2346–2349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Shang, Y.; Araki, Y.; Guo, T.; Huganir, R.L.; Zhang, M. Phase transition in postsynaptic densities underlies formation of synaptic complexes and synaptic plasticity. Cell 2016, 166, 1163–1175.e1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Díaz-Alonso, J.; Ye, F.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Ji, Z.; Nicoll, R.A.; Zhang, M. Phase separation-mediated tarp/maguk complex condensation and ampa receptor synaptic transmission. Neuron 2019, 104, 529–543.e526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vistrup-Parry, M.; Chen, X.; Johansen, T.L.; Bach, S.; Buch-Larsen, S.C.; Bartling, C.R.O.; Ma, C.; Clemmensen, L.S.; Nielsen, M.L.; Zhang, M.; et al. Site-specific phosphorylation of psd-95 dynamically regulates the postsynaptic density as observed by phase separation. Iscience 2021, 24, 103268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, N.A.; Fetter, R.D.; Shen, K. Assembly of synaptic active zones requires phase separation of scaffold molecules. Nature 2020, 588, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Südhof, T.C. The presynaptic active zone. Neuron 2012, 75, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Cai, Q.; Shen, Z.; Chen, X.; Zeng, M.; Du, S.; Zhang, M. Rim and rim-bp form presynaptic active-zone-like condensates via phase separation. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 971–984.e975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Feature List | Number of Features | Recall | Precision | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CATBoost feature list | 440 | 0.942 | 0.995 | 0.967 |
| 140 | 0.910 | 0.995 | 0.951 | |
| LASSO feature list | 2160 | 0.968 | 0.994 | 0.981 |
| 70 | 0.875 | 0.996 | 0.931 | |
| LightGBM feature list | 660 | 0.962 | 0.994 | 0.978 |
| 90 | 0.882 | 0.995 | 0.935 | |
| XGBoost feature list | 1410 | 0.964 | 0.995 | 0.979 |
| 360 | 0.947 | 0.995 | 0.970 | |
| PFI feature list | 760 | 0.967 | 0.994 | 0.980 |
| 190 | 0.949 | 0.995 | 0.971 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Q.; Huang, F.; Guo, W.; Feng, K.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y. Identification of Phase-Separation-Protein-Related Function Based on Gene Ontology by Using Machine Learning Methods. Life 2023, 13, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061306
Ma Q, Huang F, Guo W, Feng K, Huang T, Cai Y. Identification of Phase-Separation-Protein-Related Function Based on Gene Ontology by Using Machine Learning Methods. Life. 2023; 13(6):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061306
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Qinglan, FeiMing Huang, Wei Guo, KaiYan Feng, Tao Huang, and Yudong Cai. 2023. "Identification of Phase-Separation-Protein-Related Function Based on Gene Ontology by Using Machine Learning Methods" Life 13, no. 6: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061306
APA StyleMa, Q., Huang, F., Guo, W., Feng, K., Huang, T., & Cai, Y. (2023). Identification of Phase-Separation-Protein-Related Function Based on Gene Ontology by Using Machine Learning Methods. Life, 13(6), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061306








