Lessons from Polyomavirus Immunofluorescence Staining of Urinary Decoy Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Virus Genotype Definition
2.3. Cytopreparations
2.4. Immunofluorescence
3. Results
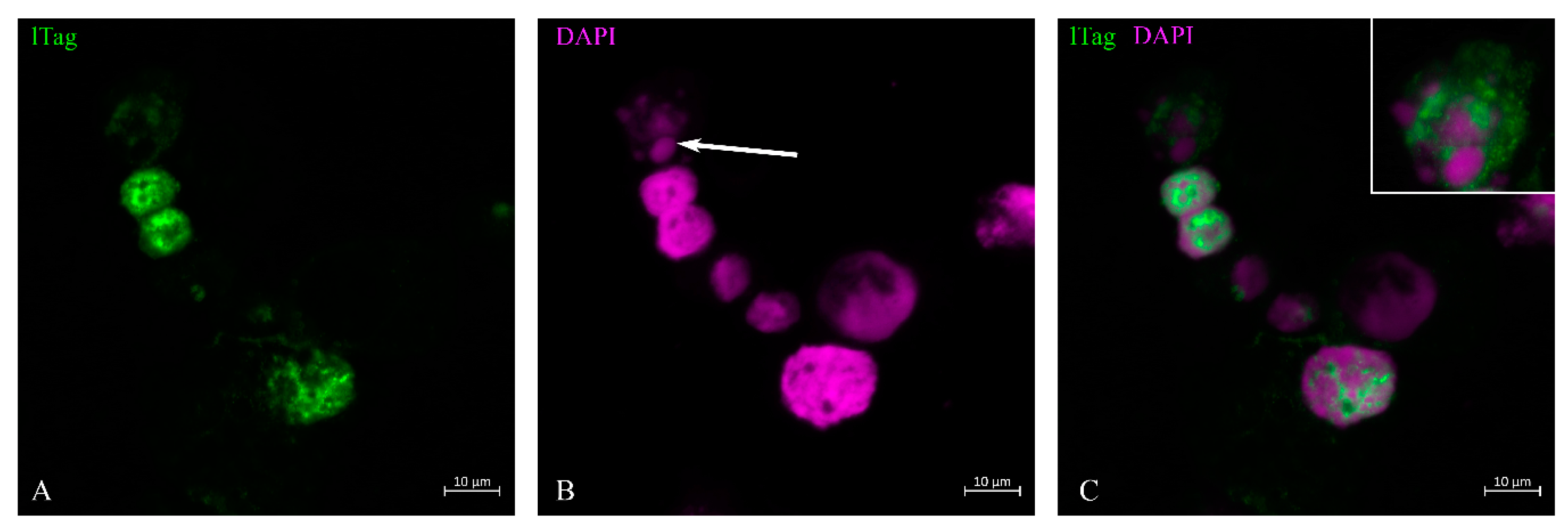
3.1. LTag Distribution
3.2. VP1 Translation and Distribution
3.3. VP1 and lTag-Positive Decoy Cells in Process of Apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of This Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hariharan, S.; Israni, A.K.; Danovitch, G. Long-Term Survival after Kidney Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.; Parajuli, S.; Muth, B.; Astor, B.C.; Panzer, S.E.; Mandelbrot, D.; Zhong, W.; Djamali, A. In kidney transplant recipients with BK polyomavirus infection, early BK nephropathy, microvascular inflammation, and serum creatinine are risk factors for graft loss. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2016, 18, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickeleit, V.; Singh, H.K.; Dadhania, D.; Cornea, V.; El-Husseini, A.; Castellanos, A.; Davis, V.G.; Waid, T.; Seshan, S.V. The 2018 Banff Working Group classification of definitive polyomavirus nephropathy: A multicenter validation study in the modern era. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Randhawa, P.S.; AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. BK polyomavirus in solid organ transplantation—Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.S.; Heyenbruch, D.; Rubinstein, J.D.; Sabulski, A.; Jodele, S.; Thomas, S.; Lutzko, C.; Zhu, X.; Leemhuis, T.; Cancelas, J.A.; et al. Virus-specific T-cell therapy to treat BK polyomavirus infection in bone marrow and solid organ transplant recipients. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5745–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, A.; Infanti, L.; Dumoulin, A.; Buser, A.; Samaridis, J.; Stebler, C.; Gosert, R.; Hirsch, H.H. Prevalence of polyomavirus BK and JC infection and replication in 400 healthy blood donors. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drachenberg, C.B.; Hirsch, H.H.; Papadimitriou, J.C.; Gosert, R.; Wali, R.K.; Munivenkatappa, R.; Nogueira, J.; Cangro, C.B.; Haririan, A.; Mendley, S.; et al. Polyomavirus BK versus JC replication and nephropathy in renal transplant recipients: A prospective evaluation. Transplantation 2007, 84, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.V.; Wolfendale, M.R.; Daniel, R.A.; Dhanjal, N.K.; Gardner, S.D.; Gibson, P.E.; Field, A.M. A prospective study of human polyomavirus infection in pregnancy. J. Infect. Dis. 1980, 142, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegley, N.; Walavalkar, V.; Aujla, H.; Chen, L.X.; Huang, Y.; Lee, B.K.; Jen, K.Y. Clinicopathologic Characteristics of JC Virus Nephropathy in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2021, 105, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Vincenti, F.; Friman, S.; Tuncer, M.; Citterio, F.; Wiecek, A.; Scheuermann, E.H.; Klinger, M.; Russ, G.; Pescovitz, M.D.; et al. Polyomavirus BK replication in de novo kidney transplant patients receiving tacrolimus or cyclosporine: A prospective, randomized, multicenter study. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaub, S.; Hirsch, H.H.; Dickenmann, M.; Steiger, J.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Hopfer, H.; Mayr, M. Reducing immunosuppression preserves allograft function in presumptive and definitive polyomavirus-associated nephropathy. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, R.; Elbahloul, O.; Gallichio, M.H.; Stellrecht, K.; Conti, D.J. Monthly screening for polyoma virus eliminates BK nephropathy and preserves renal function. Surg. Infect. 2009, 10, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Knowles, W.; Dickenmann, M.; Passweg, J.; Klimkait, T.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Steiger, J. Prospective study of polyomavirus type BK replication and nephropathy in renal-transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-T.; Chen, W.-F.; Hou, X.-T.; Yang, S.-C.; Yang, H.-F.; Li, J.; Deng, R.-H.; Huang, Y.; Nuertai, Y.; Wang, C.-X.; et al. Non-invasive urinary sediment double-immunostaining predicts BK polyomavirus associated-nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Ahn, B.Y.; Cho, Y. Structural basis for the inactivation of retinoblastoma tumor suppressor by SV40 large T antigen. Embo J. 2001, 20, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeCaprio, J.A.; Garcea, R.L. A cornucopia of human polyomaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.F.; Christensen, J.B.; Imperiale, M.J. BK virus large T antigen: Interactions with the retinoblastoma family of tumor suppressor proteins and effects on cellular growth control. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowd, G.A.; Fanning, E. A wolf in sheep’s clothing: SV40 co-opts host genome maintenance proteins to replicate viral DNA. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, M.; Lanfranco, G.; Segoloni, G.P. “Decoy cells” in urine. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 4309–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, T.M.; Silva, S.F.; Silva, S.L.; Holanda, M.C.; Nascimento, J.M.; Ferreira, M.V. Polyomavirus-infected decoy cells in cytocentrifuged urine cytology specimens from renal transplant recipients. Acta Cytol. 2011, 55, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drachenberg, C.B.; Beskow, C.O.; Cangro, C.B.; Bourquin, P.M.; Simsir, A.; Fink, J.; Weir, M.R.; Klassen, D.K.; Bartlett, S.T.; Papadimitriou, J.C. Human polyoma virus in renal allograft biopsies: Morphological findings and correlation with urine cytology. Hum. Pathol. 1999, 30, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickeleit, V.; Hirsch, H.H.; Binet, I.F.; Gudat, F.; Prince, O.; Dalquen, P.; Thiel, G.; Mihatsch, M.J. Polyomavirus infection of renal allograft recipients: From latent infection to manifest disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, P.; Cantalupo, P.G.; Zheng, W.; Saenz-Robles, M.T.; Duray, A.M.; Weitz, D.; Pipas, J.M. Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals a Heterogeneous Cellular Response to BK Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2021, 95, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.K.; Safak, M.; Khalili, K. Regulation of gene expression in primate polyomaviruses. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10846–10856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurdiss, D.L.; Morgan, E.L.; Thompson, R.F.; Prescott, E.L.; Panou, M.M.; Macdonald, A.; Ranson, N.A. New Structural Insights into the Genome and Minor Capsid Proteins of BK Polyomavirus using Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Structure 2016, 24, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meinke, G.; Phelan, P.J.; Kalekar, R.; Shin, J.; Archambault, J.; Bohm, A.; Bullock, P.A. Insights into the initiation of JC virus DNA replication derived from the crystal structure of the T-antigen origin binding domain. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.P.; Xu, M.; Machado, A.C.D.; Yu, X.J.; Rohs, R.; Chen, X.S. Mechanism of Origin DNA Recognition and Assembly of an Initiator-Helicase Complex by SV40 Large Tumor Antigen. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- David, A.; Dolan, B.P.; Hickman, H.D.; Knowlton, J.J.; Clavarino, G.; Pierre, P.; Bennink, J.R.; Yewdell, J.W. Nuclear translation visualized by ribosome-bound nascent chain puromycylation. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 197, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ou, W.C.; Wang, M.; Fung, C.Y.; Tsai, R.T.; Chao, P.C.; Hseu, T.H.; Chang, D. The major capsid protein, VP1, of human JC virus expressed in Escherichia coli is able to self-assemble into a capsid-like particle and deliver exogenous DNA into human kidney cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80 Pt 1, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cioni, M.; Leboeuf, C.; Comoli, P.; Ginevri, F.; Hirsch, H.H. Characterization of Immunodominant BK Polyomavirus 9mer Epitope T Cell Responses. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meier, R.P.H.; Muller, Y.D.; Dietrich, P.Y.; Tille, J.C.; Nikolaev, S.; Sartori, A.; Labidi-Galy, I.; Ernandez, T.; Kaur, A.; Hirsch, H.H.; et al. Immunologic Clearance of a BK Virus-associated Metastatic Renal Allograft Carcinoma. Transplantation 2021, 105, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Comoli, P.; Basso, S.; Azzi, A.; Moretta, A.; De Santis, R.; Del Galdo, F.; De Palma, R.; Valente, U.; Nocera, A.; Perfumo, F.; et al. Dendritic Cells Pulsed with Polyomavirus BK Antigen Induce Ex Vivo Polyoma BK Virus–Specific Cytotoxic T-Cell Lines in Seropositive Healthy Individuals and Renal Transplant Recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 3197–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanford, R.E.; Butel, J.S. Construction and characterization of an SV40 mutant defective in nuclear transport of T antigen. Cell 1984, 37, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abend, J.R.; Joseph, A.E.; Das, D.; Campbell-Cecen, D.B.; Imperiale, M.J. A truncated T antigen expressed from an alternatively spliced BK virus early mRNA. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, K.D.; Bouchet-Marquis, C.; Heiser, K.; Szomolanyi-Tsuda, E.; Mishra, R.; Lamothe, B.; Hoenger, A.; Garcea, R.L. Virion Assembly Factories in the Nucleus of Polyomavirus-Infected Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, G.G.; Negorev, D.; Bell, P.; Ishov, A.M. Review: Properties and assembly mechanisms of ND10, PML bodies, or PODs. J. Struct. Biol. 2000, 129, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannecchini, S. Evidence of the Mechanism by Which Polyomaviruses Exploit the Extracellular Vesicle Delivery System during Infection. Viruses 2020, 12, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris-Love, J.; O’Hara, B.A.; Gee, G.V.; Dugan, A.S.; O’Rourke, R.S.; Armstead, B.E.; Assetta, B.; Haley, S.A.; Atwood, W.J. Biogenesis of JC polyomavirus associated extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Biol. 2022, 1, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerges, D.; Hevesi, Z.; Schmidt, S.H.; Kapps, S.; Pajenda, S.; Geist, B.; Schmidt, A.; Wagner, L.; Winnicki, W. Tubular epithelial progenitors are excreted in urine during recovery from severe acute kidney injury and are able to expand and differentiate in vitro. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnermann, J.; Chou, C.L.; Ma, T.; Traynor, T.; Knepper, M.A.; Verkman, A.S. Defective proximal tubular fluid reabsorption in transgenic aquaporin-1 null mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9660–9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Guo, H.; Han, L.; Huang, H.; Shen, Y.; He, J.; Liu, J. Sternheimer-Malbin Staining to Detect Decoy Cells in Urine of 213 Kidney Transplant Patients. Transplant. Proc. 2020, 52, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekito, T.; Araki, M.; Yoshinaga, K.; Maruyama, Y.; Sadahira, T.; Nishimura, S.; Wada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Watanabe, T.; Tanabe, K.; et al. Presence of decoy cells for 6 months on urine cytology efficiently predicts BK virus nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Int. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickeleit, V.; Singh, H.K.; Randhawa, P.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Bhatnagar, R.; Bracamonte, E.; Chang, A.; Chon, W.J.; Dadhania, D.; Davis, V.G.; et al. The Banff Working Group Classification of Definitive Polyomavirus Nephropathy: Morphologic Definitions and Clinical Correlations. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müller, D.C.; Rämö, M.; Naegele, K.; Ribi, S.; Wetterauer, C.; Perrina, V.; Quagliata, L.; Vlajnic, T.; Ruiz, C.; Balitzki, B.; et al. Donor-derived, metastatic urothelial cancer after kidney transplantation associated with a potentially oncogenic BK polyomavirus. J. Pathol. 2018, 244, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | Case 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 61 | 58 | 52 | 60 | 51 | 60 |
| Gender | m | m | m | m | m | f |
| Underlying disease | ADPKD | ADPKD | Reflux NP | Diabetic NP. | Undefined | Undefined |
| eGFR (MDRD) mL/min | 15 | 32 | 12 | 42 | 24.51 | 24.51 |
| BK PCR (Plasma) | 5.2 × 104 | 4.1 × 105 | 1 × 102 | 2.3 × 104 | 4 × 103 | 3 × 108 |
| Decoy cells in urine (%) | 50 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 90 | 5 * |
| Months after KTX | 6 | 2 | 96 | 27 | 4 | 14 |
| Start of Virus Production at Nucleus (%) | Ghost Cells Membrane Damage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 6 | 94 |
| Case 2 | 18 | 82 |
| Case 3 | 20 | 80 |
| Case 4 | 16 | 84 |
| Case 5 | 21 | 79 |
| Case 6 | 32 | 68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pajenda, S.; Hevesi, Z.; Eder, M.; Gerges, D.; Aiad, M.; Koldyka, O.; Winnicki, W.; Wagner, L.; Eskandary, F.; Schmidt, A. Lessons from Polyomavirus Immunofluorescence Staining of Urinary Decoy Cells. Life 2023, 13, 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071526
Pajenda S, Hevesi Z, Eder M, Gerges D, Aiad M, Koldyka O, Winnicki W, Wagner L, Eskandary F, Schmidt A. Lessons from Polyomavirus Immunofluorescence Staining of Urinary Decoy Cells. Life. 2023; 13(7):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071526
Chicago/Turabian StylePajenda, Sahra, Zsofia Hevesi, Michael Eder, Daniela Gerges, Monika Aiad, Oliver Koldyka, Wolfgang Winnicki, Ludwig Wagner, Farsad Eskandary, and Alice Schmidt. 2023. "Lessons from Polyomavirus Immunofluorescence Staining of Urinary Decoy Cells" Life 13, no. 7: 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071526
APA StylePajenda, S., Hevesi, Z., Eder, M., Gerges, D., Aiad, M., Koldyka, O., Winnicki, W., Wagner, L., Eskandary, F., & Schmidt, A. (2023). Lessons from Polyomavirus Immunofluorescence Staining of Urinary Decoy Cells. Life, 13(7), 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071526






