Glycogen Metabolism and Its Role in Growth and Encystation in Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. E. histolytica Culture Maintenance
2.3. Vector Construction and Transfection
2.4. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
2.5. Growth Curves
2.6. Glycogen Determination
2.7. Encystation
3. Results
3.1. Cellular Glycogen Content Is Reduced during Growth in the Absence of Glucose
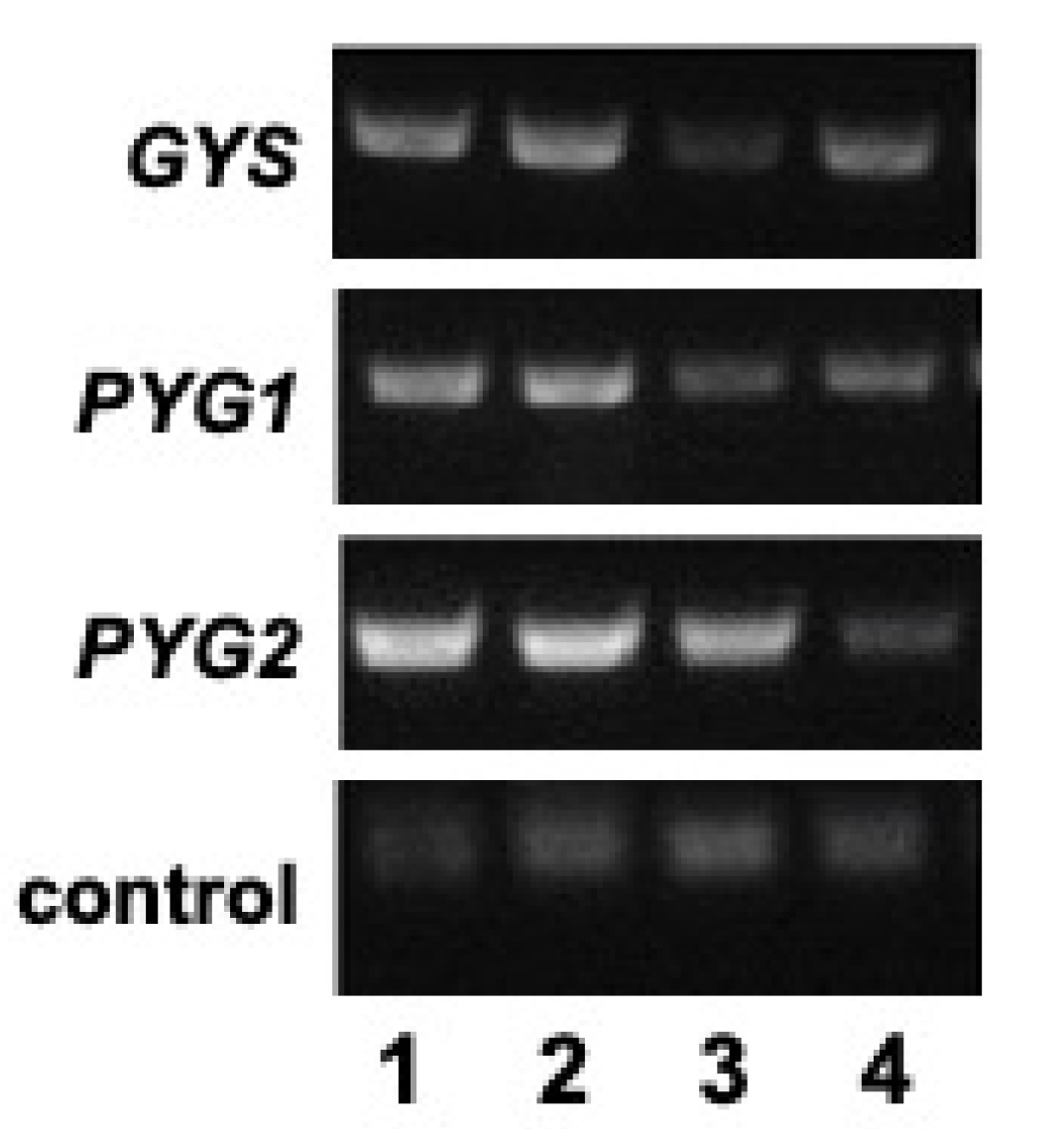
3.2. Trigger-Mediated RNAi Silencing of the Glycogen Synthase and Glycogen Phosphorylase Genes
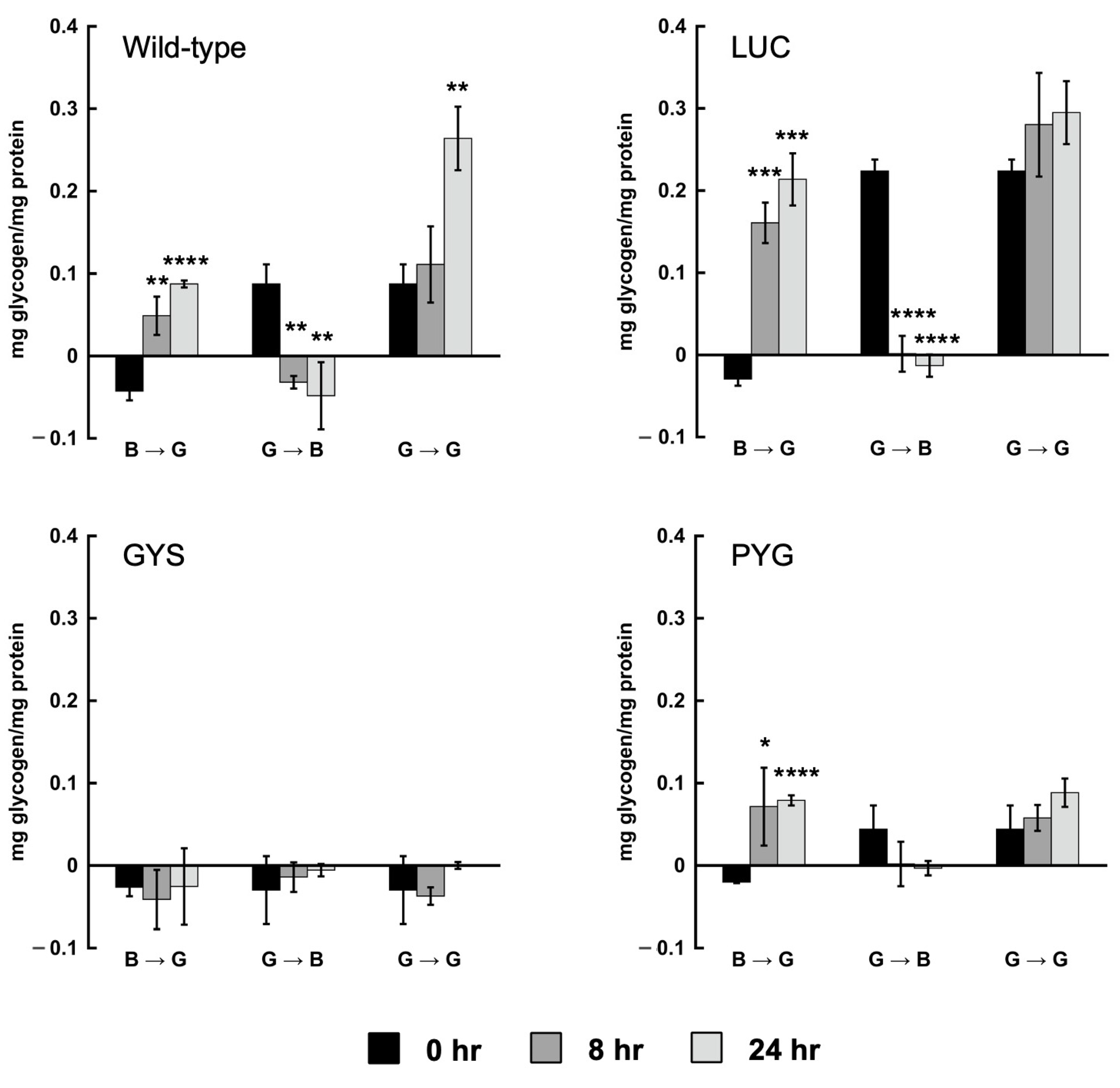
3.3. Cellular Glycogen Is Reduced in the Glycogen Synthase and Glycogen Phosphorylase RNAi Strains
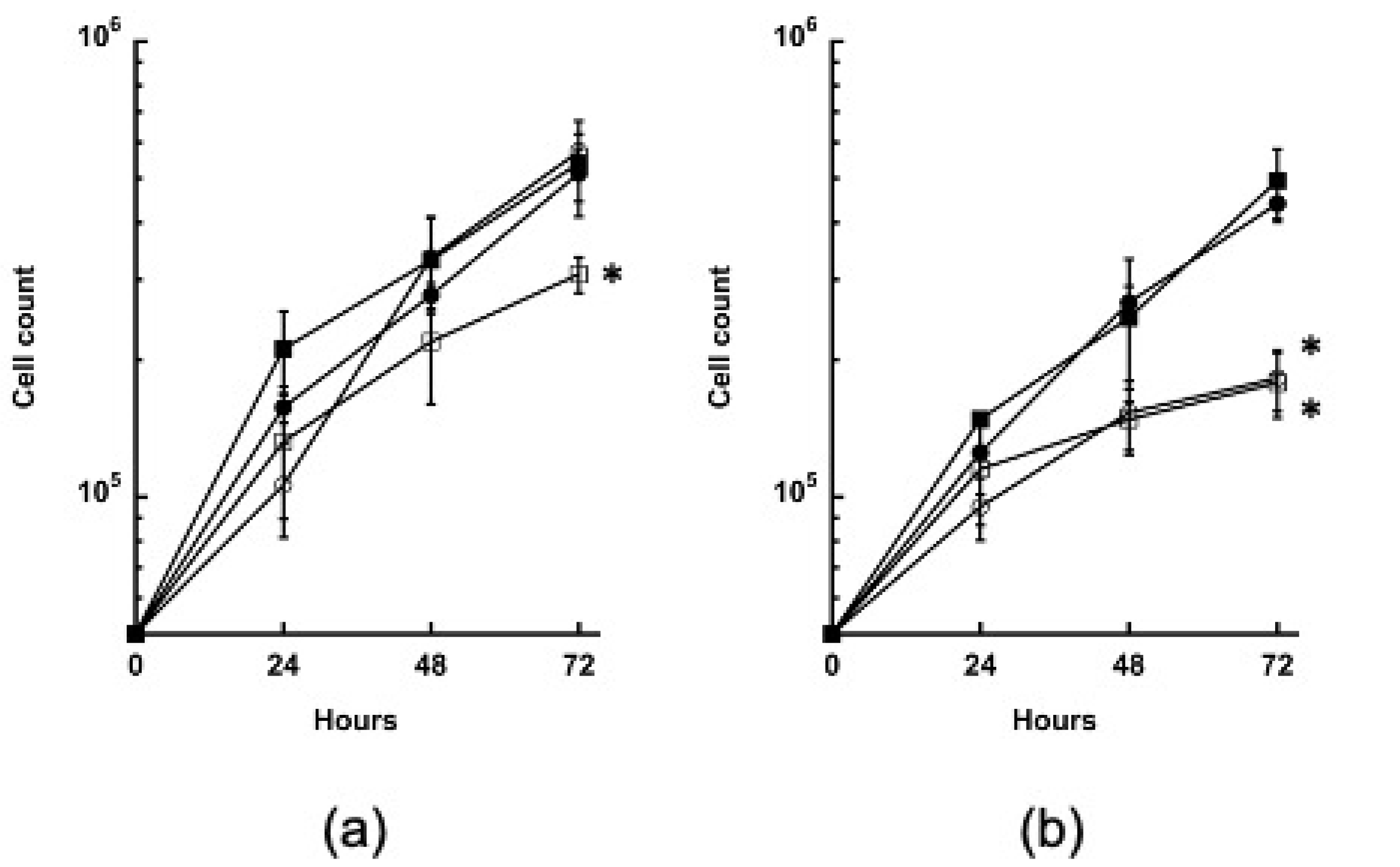
3.4. Growth of the GYS and PYG1+2 Strains Is Impaired in the Absence of Glucose
3.5. Encystation Is Impaired in the GYS and PYG1+2 RNAi Strains
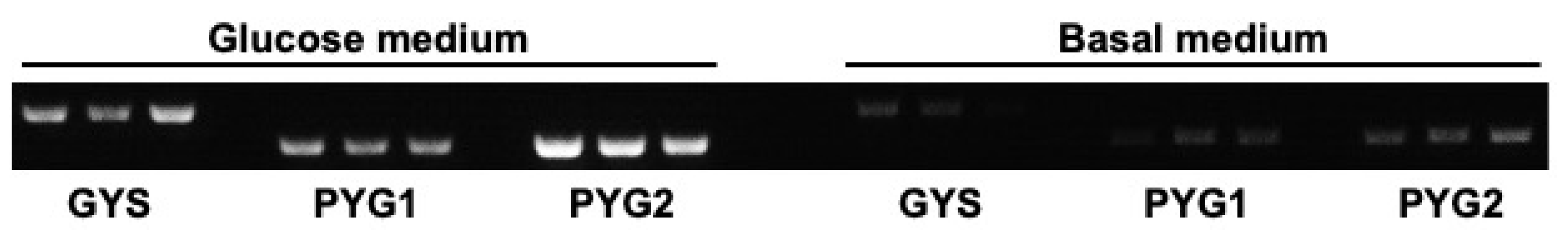
3.6. Expression of GYS, PYG1, and PYG2 Is Downregulated in the Absence of Glucose
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization; Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group. WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; 254p. [Google Scholar]
- Blessmann, J.; Ali, I.K.; Nu, P.A.; Dinh, B.T.; Viet, T.Q.; Van, A.L.; Clark, C.G.; Tannich, E. Longitudinal study of intestinal Entamoeba histolytica infections in asymptomatic adult carriers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4745–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhuri, G.; Prakash, V.; Kumar, A.; Shahi, S.K.; Sharma, M. Protective immunity to entamoeba histolytica infection in subjects with antiamoebic antibodies residing in a hyperendemic zone. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 23, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, R.; Ali, I.M.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Prevalence and immune response to Entamoeba histolytica infection in preschool children in Bangladesh. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, R.; Faruque, A.S.; Hahn, P.; Lyerly, D.M.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar infection in children in Bangladesh. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.M.; Ljungstrom, I.; Glass, R.I.; Lundin, L.; Stoll, B.J.; Huldt, G. Amoebiasis and giardiasis in Bangladesh: Parasitological and serological studies. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1983, 77, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.F. Entamoeba histolytica cyst passers—To treat or not to treat? S. Afr. Med. J. 1987, 72, 657–658. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, T.F.; Gathiram, V.; Simjee, A.E. Seroepidemiological study of antibody responses to the zymodemes of Entamoeba histolytica. Lancet 1985, 1, 716–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, R.; Baveja, U.; Anand, B.S. Entamoeba histolytica cyst passers: Clinical features and outcome in untreated subjects. Lancet 1984, 2, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Palomo, A.; Martinez-Baez, M. Selective primary health care: Strategies for control of disease in the developing world. X. Amebiasis. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1983, 5, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxt, L.A.; Singh, U. New insights into Entamoeba histolytica pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 21, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, B.; Anderson, I.; Davies, R.; Alsmark, U.C.; Samuelson, J.; Amedeo, P.; Roncaglia, P.; Berriman, M.; Hirt, R.P.; Mann, B.J.; et al. The genome of the protist parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Nature 2005, 433, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, B.J.; Hall, N. Entamoeba: Still more to be learned from the genome. Trends. Parasitol. 2005, 21, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, E.; Encalada, R.; Pineda, E.; Jasso-Chavez, R.; Moreno-Sanchez, R. Glycolysis in Entamoeba histolytica. Biochemical characterization of recombinant glycolytic enzymes and flux control analysis. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 1767–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, E.; Encalada, R.; Vazquez, C.; Olivos-Garcia, A.; Michels, P.A.M.; Moreno-Sanchez, R. Control and regulation of the pyrophosphate-dependent glucose metabolism in Entamoeba histolytica. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2019, 229, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, E.; Encalada, R.; Vazquez, C.; Nequiz, M.; Olivos-Garcia, A.; Moreno-Sanchez, R.; Saavedra, E. In vivo identification of the steps that control energy metabolism and survival of Entamoeba histolytica. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.P.; Ingram-Smith, C. Biochemical and kinetic characterization of the recombinant ADP-forming acetyl coenzyme A synthetase from the amitochondriate protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. Eukaryot Cell 2014, 13, 1530–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, A.; Kami, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Sugawara, M.; Toki, N.; Onozuka, H.; Kinoshita, T.; Saito, N.; Ochiai, A.; Tomita, M.; et al. Quantitative metabolome profiling of colon and stomach cancer microenvironment by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4918–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.E. Metabolism of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903. Adv Parasitol 1984, 23, 105–142. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, L.R.; Verma, A.K.; Paul, J.; Bhattacharya, A. Phagocytosis of Gut Bacteria by Entamoeba histolytica. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.G.; Alsmark, U.C.; Tazreiter, M.; Saito-Nakano, Y.; Ali, V.; Marion, S.; Weber, C.; Mukherjee, C.; Bruchhaus, I.; Tannich, E.; et al. Structure and content of the Entamoeba histolytica genome. Adv. Parasitol. 2007, 65, 51–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Coombs, G.H. Amino acid consumption by the parasitic, amoeboid protists Entamoeba histolytica and E. invadens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 130, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, R.M.; Wittner, M. Ultrastructure of bacterized and axenic trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica with particular reference to helical bodies. J. Cell Biol. 1970, 45, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura-Luna, J.J.; Calzado-Flores, C. Incorporation of 14C-glucose into cytoplasmic glycogen from Entamoeba invadens IP-1 strain. Arch. Med. Res. 2000, 31, S194–S195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumel-Alterzon, S.; Ankri, S. Entamoeba histolytica adaptation to glucose starvation: A matter of life and death. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 20, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker-Grunwald, T.; Martin, J.B.; Klein, G. Characterization of glycogen and amino acid pool of Entamoeba histolytica by 13C-NMR spectroscopy. J. Eukaryot Microbiol. 1995, 42, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.K.; Ghosh, S.K. The chitin biosynthesis pathway in Entamoeba and the role of glucosamine-6-P isomerase by RNA interference. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Ghosh, S.K.; Jang, K.; Bullitt, E.; Moore, L.; Robbins, P.W.; Samuelson, J. Evidence for a “wattle and daub” model of the cyst wall of entamoeba. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesel, J.; Shuman, J.; Bastuzel, I.; Dickerson, J.; Ingram-Smith, C. Encystation of Entamoeba histolytica in Axenic Culture. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, L.S. Techniques of axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae. J. Parasitol. 1968, 54, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morf, L.; Pearson, R.J.; Wang, A.S.; Singh, U. Robust gene silencing mediated by antisense small RNAs in the pathogenic protist Entamoeba histolytica. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2013, 41, 9424–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, L.; Nickel, R.; Tannich, E. Transfection and continuous expression of heterologous genes in the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8975–8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, W. Trypan blue exclusion test of cell viability. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, D. Encystation of entamoeba parasites. Bioessays 1997, 19, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquezdelara-Cisneros, L.G.; Arroyo-Begovich, A. Induction of encystation of Entamoeba invadens by removal of glucose from the culture medium. J. Parasitol. 1984, 70, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primer Sequence | |
|---|---|
| Cloning Primers | |
| GYS RNAi Forward | 5′-CGA CTC CCG GGA TGT CAA TTT CTA TCT CAT TAC CTA TTC TAG-3′ |
| GYS RNAi Reverse | 5′-CGA CTG GCC CTC GAG TTA AAG TTC AAA AAC AAA GAC TTT TTT C-3′ |
| PYG1 RNAi Forward | 5′-ATT GCA GCA TCA ACG CAA GAT GAC CAC ACA AAT TAG ACG-3′ |
| PYG1 RNAi Reverse | 5′-TTC ACT TGA TGA GGA TTT TTG CAT GAC TTT TTC ATC TTC TTA AAT CTT CTC ATT ACA-3′ |
| PYG2 RNAi Forward | 5′-TGT AAT GAG AAG ATT TAA GAA GAT GAA AAA GTC ATG CAA AAA TCC TCA TCA AGT-3′ |
| PYG2 RNAi Reverse | 5′-ACA TTT TAA GTT TAA AAA AGA AGA GTT CAA CAA TCT TCT AAC TAT ATC TTG-3′ |
| RT-PCR Primers | |
| GYS RT-PCR Forward | 5′-TGT CAC CAC AAG AAA TGG CTG-3′ |
| GYS RT-PCR Reverse | 5′-AAG GGA AGG AAG TTG TGG CA-3′ |
| PYG1 RT-PCR Forward | 5′-GAT GAC CAC ACA AAT TAG ACG ATC AGT TTC TAT G-3′ |
| PYG1 RT-PCR Reverse | 5′-GCA AGA GAA TCA AGG AAA CAT GCT GC-3′ |
| PYG2 RT-PCR Forward | 5′-GCA AAA ATC CTC ATC AAG TGA AGG AGT TTC TC-3′ |
| PYG2 RT-PCR Reverse | 5′-CCA AGT CCT CCT GAT CCA AGT GCA G-3′ |
| ssrRNA Forward | 5′-AGG CGC GTA AAT TAC CCA CTT TCG-3′ |
| ssrRNA Reverse | 5′-CAC CAG ACT TGC CCT CCA ATT GAT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wesel, J.; Ingram-Smith, C. Glycogen Metabolism and Its Role in Growth and Encystation in Entamoeba histolytica. Life 2023, 13, 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071529
Wesel J, Ingram-Smith C. Glycogen Metabolism and Its Role in Growth and Encystation in Entamoeba histolytica. Life. 2023; 13(7):1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071529
Chicago/Turabian StyleWesel, Jordan, and Cheryl Ingram-Smith. 2023. "Glycogen Metabolism and Its Role in Growth and Encystation in Entamoeba histolytica" Life 13, no. 7: 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071529
APA StyleWesel, J., & Ingram-Smith, C. (2023). Glycogen Metabolism and Its Role in Growth and Encystation in Entamoeba histolytica. Life, 13(7), 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071529





