Platelet-Rich Plasma in Dermatology: New Insights on the Cellular Mechanism of Skin Repair and Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Skin Functionality, Tissue Aggression, and Soft Tissue Lesions
1.1. The Haemostasis Phase
1.2. The Inflammatory Phase
1.3. The Proliferative Phase
1.4. The Maturation Phase
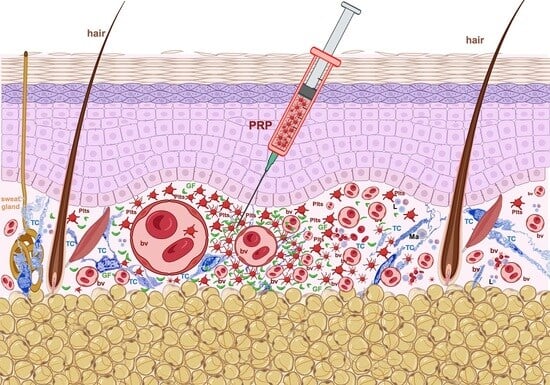
2. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Its Introduction in Tissue Repair
3. Potential Mechanisms Underlying PRP’s Effects
4. Thrombocyte’s Genesis and Phenotype
4.1. Development of Platelets
- Platelet budding from the megakaryocyte surface (apparently, these membrane blebs do not contain organelles) [93];
- Proplatelet formation, elongation, and branching is the process by which MKs form thin cellular prolongations with a moniliform aspect, typically presenting an alternation of dilated platelet-sized segments bounded by thin cytoplasmic bridges. The rupture of these cytoplasmic bridges releases fragments of the MKs’ cytoplasm (enwrapped in MK cell membrane) into circulation, also known as platelets [94];
- MKs cytoplasm fragmentation through the invagination membrane system (this functions as a reserve that is providing membranes for the proplatelets’ development) [95].
4.2. The Platelet’s Structure and Ultrastructure
4.3. Roles of Platelets
5. A Concise Evolution of the PRP Therapy Concept
- N1N2—platelet composition:
- -
- The pair of digits relates to the concentration of platelets in the PRP compared to the basal levels in the blood.
- -
- “1” represents a concentration range of 100,000–200,000 platelets/μL.
- -
- “2” represents a concentration range of 200,000–300,000 platelets/μL.
- -
- So “12” would mean that the PRP has twice the basal concentration of platelets, and the PRP’s platelet concentration is between 200,000–400,000 platelets/μL.
- N3N4—purity:
- -
- N3 indicates the absence (0) or presence (1) of erythrocytes (RBCs).
- -
- N4 represents the concentration of leukocytes, with “0” indicating no leukocytes and increasing numbers indicating higher concentrations.
- -
- For example, “11” would indicate the presence of erythrocytes and a low concentration of leukocytes in the PRP.
- -
- Both leukocytes and erythrocytes can affect the results obtained after PRP injections due to side effects and interferences [252].
- N5N6—activation:
- -
- N5 specifies whether the PRP is endogenously activated (0) or whether it is activated externally, before PRP injection (1).
- -
- N6 indicates whether calcium was added for activation, with “0” meaning no calcium added and “1” meaning calcium was added.
- -
- For instance, “00” would mean that the PRP is endogenously activated, and no calcium has been added.
- -
- Previous research has indicated that the level of calcium can impact the cellular and tissue reactions elicited by PRP [253].
6. Utility of PRP in Dermatological Practice
6.1. PRP in Skin Burns
6.2. PRP in Alopecia
6.2.1. Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA)
6.2.2. Alopecia Areata (AA)
6.2.3. Telogen Effluvium (TE)
6.3. PRP in Skin Ageing
6.4. PRP in Acne Scarring
6.5. PRP in Melasma
6.6. Limitations of PRP
7. Further Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Someya, T.; Amagai, M. Toward a New Generation of Smart Skins. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranduca, M.; Branisteanu, D.; Serban, D.; Branisteanu, D.; Stoleriu, G.; Manolache, N.; Serban, I. Synthesis and Physiological Implications of Melanic Pigments (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4183–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorg, H.; Tilkorn, D.J.; Hager, S.; Hauser, J.; Mirastschijski, U. Skin Wound Healing: An Update on the Current Knowledge and Concepts. Eur. Surg. Res. 2017, 58, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.A.F. Fibrin Is a Many Splendored Thing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, xxi–xxii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilgus, T.A.; Roy, S.; McDaniel, J.C. Neutrophils and Wound Repair: Positive Actions and Negative Reactions. Adv. Wound Care 2013, 2, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Barbul, A. Understanding the Role of Immune Regulation in Wound Healing. Am. J. Surg. 2004, 187, S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, T.J.; DiPietro, L.A. Inflammation and Wound Healing: The Role of the Macrophage. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2011, 13, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, L.C.; Jenkins, S.J.; Allen, J.E.; Taylor, P.R. Tissue-Resident Macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armulik, A.; Genové, G.; Betsholtz, C. Pericytes: Developmental, Physiological, and Pathological Perspectives, Problems, and Promises. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, D.M.; Izeta, A. Pericytes in Wound Healing: Friend or Foe? Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 833–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisan, M.; Yap, S.; Casteilla, L.; Chen, C.-W.; Corselli, M.; Park, T.S.; Andriolo, G.; Sun, B.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L.; et al. A Perivascular Origin for Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Multiple Human Organs. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahara, T.; Murohara, T.; Sullivan, A.; Silver, M.; van der Zee, R.; Li, T.; Witzenbichler, B.; Schatteman, G.; Isner, J.M. Isolation of Putative Progenitor Endothelial Cells for Angiogenesis. Science 1997, 275, 964–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceradini, D.J.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Callaghan, M.J.; Tepper, O.M.; Bastidas, N.; Kleinman, M.E.; Capla, J.M.; Galiano, R.D.; Levine, J.P.; Gurtner, G.C. Progenitor Cell Trafficking Is Regulated by Hypoxic Gradients through HIF-1 Induction of SDF-1. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaraju, R.; Rennert, R.C.; Maan, Z.N.; Duscher, D.; Barrera, J.; Whittam, A.J.; Januszyk, M.; Rajadas, J.; Rodrigues, M.; Gurtner, G.C. Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Seeded Hydrogels Increase Endogenous Progenitor Cell Recruitment and Neovascularization in Wounds. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2016, 22, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Krieg, T.; Smola, H. Keratinocyte–Fibroblast Interactions in Wound Healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, G.; Rognoni, E.; Hiratsuka, T.; Liakath-Ali, K.; Hoste, E.; Kar, G.; Kayikci, M.; Russell, R.; Kretzschmar, K.; Mulder, K.W.; et al. Wounding Induces Dedifferentiation of Epidermal Gata6+ Cells and Acquisition of Stem Cell Properties. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanpain, C.; Horsley, V.; Fuchs, E. Epithelial Stem Cells: Turning over New Leaves. Cell 2007, 128, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P. Wound Healing--Aiming for Perfect Skin Regeneration. Science 1997, 276, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B.R.; Hwang, C.; Talbot, S.; Hibler, B.; Matoori, S.; Mooney, D.J. Breakthrough Treatments for Accelerated Wound Healing. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushiken, L.F.S.; Beserra, F.P.; Bastos, J.K.; Jackson, C.J.; Pellizzon, C.H. Cutaneous Wound Healing: An Update from Physiopathology to Current Therapies. Life 2021, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.; Covington, S.; Sen, C.K.; Januszyk, M.; Kirsner, R.S.; Gurtner, G.C.; Shah, N.H. Rapid Identification of Slow Healing Wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2016, 24, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.P.; Taylor, K.R.; Jameson, J.M. Immunomodulation at Epithelial Sites by Obesity and Metabolic Disease. Immunol. Res. 2012, 52, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoedler, S.; Broichhausen, S.; Guo, R.; Dai, R.; Knoedler, L.; Kauke-Navarro, M.; Diatta, F.; Pomahac, B.; Machens, H.-G.; Jiang, D.; et al. Fibroblasts—The Cellular Choreographers of Wound Healing. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1233800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faour, S.; Farahat, M.; Aijaz, A.; Jeschke, M.G. Fibrosis in Burns: An Overview of Mechanisms and Therapies. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2023, 325, C1545–C1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duscher, D.; Maan, Z.N.; Wong, V.W.; Rennert, R.C.; Januszyk, M.; Rodrigues, M.; Hu, M.; Whitmore, A.J.; Whittam, A.J.; Longaker, M.T.; et al. Mechanotransduction and Fibrosis. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.; Rustad, K.C.; Akaishi, S.; Sorkin, M.; Glotzbach, J.P.; Januszyk, M.; Nelson, E.R.; Levi, K.; Paterno, J.; Vial, I.N.; et al. Focal Adhesion Kinase Links Mechanical Force to Skin Fibrosis via Inflammatory Signaling. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Lei, T. Effects of Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma Injections on Facial Skin Rejuvenation. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 3024–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Iwasaki, A.; Chien, A.L.; Kang, S. UVB-Mediated DNA Damage Induces Matrix Metalloproteinases to Promote Photoaging in an AhR- and SP1-Dependent Manner. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 7, e156344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersant, B.; Sid-Ahmed, M.; Braud, L.; Jourdan, M.; Baba-Amer, Y.; Meningaud, J.-P.; Rodriguez, A.-M. Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves the Wound Healing Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Paracrine and Metabolism Alterations. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 1234263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, N.; Abouelgoud, M.; Haiba, D.; Arakeep, H. Comparative Study on the Effect of Injectable Platelet Rich Plasma versus Its Topical Application in the Treatment of Thermal Burn in Adult Male Albino Rat: Histological and Immunohistochemical Study. Egypt. J. Histol. 2021, 45, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei-Dan, O.; Laver, L.; Nyska, M.; Mann, G. Platelet Rich Plasma—A New Biotechnology for Treatment of Sports Injuries. Harefuah 2011, 150, 453–457, 490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nurden, A. Platelets, Inflammation and Tissue Regeneration. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105, S13–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E.; Carlson, E.R.; Eichstaedt, R.M.; Schimmele, S.R.; Strauss, J.E.; Georgeff, K.R. Platelet-Rich Plasma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 1998, 85, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, B.J.; Seroyer, S.T.; Filardo, G.; Bajaj, S.; Fortier, L.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Where Are We Now and Where Are We Going? Sports Health A Multidiscip. Approach 2010, 2, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brass, L. Understanding and Evaluating Platelet Function. Hematology 2010, 2010, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): What Is PRP and What Is Not PRP? Implant. Dent. 2001, 10, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppley, B.L.; Woodell, J.E.; Higgins, J. Platelet Quantification and Growth Factor Analysis from Platelet-Rich Plasma: Implications for Wound Healing. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kalén, A.; Risto, O.; Wahlström, O. Fibroblast Proliferation Due to Exposure to a Platelet Concentrate in Vitro Is PH Dependent. Wound Repair Regen. 2002, 10, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.A.; Jolly, D.G.; Worden, C.E.; Hendren, D.G.; Kane, C.J.M. Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel Promotes Differentiation and Regeneration during Equine Wound Healing. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2003, 74, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppley, B.L.; Pietrzak, W.S.; Blanton, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Review of Biology and Applications in Plastic Surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 147e–159e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froum, S.J.; Wallace, S.S.; Tarnow, D.P.; Cho, S.-C. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Bone Growth and Osseointegration in Human Maxillary Sinus Grafts: Three Bilateral Case Reports. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2002, 22, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovic, V.; Ciric, M.; Jovanovic, V.; Stojanovic, P. Platelet Rich Plasma: A Short Overview of Certain Bioactive Components. Open Med. 2016, 11, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Domyati, M.; Abdel-Wahab, H.; Hossam, A. Combining Microneedling with Other Minimally Invasive Procedures for Facial Rejuvenation: A Split-face Comparative Study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stivala, S.; Sorrentino, S.; Gobbato, S.; Bonetti, N.R.; Camici, G.G.; Lüscher, T.F.; Medalia, O.; Beer, J.H. Glycoprotein Ib clustering in platelets can be inhibited by α-linolenic acid as revealed by cryo-electron tomography. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.K.; Gulati, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Healing Virtuoso. Blood Res. 2016, 51, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Evidence to Support Its Use. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senger, D.R.; Galli, S.J.; Dvorak, A.M.; Perruzzi, C.A.; Harvey, V.S.; Dvorak, H.F. Tumor Cells Secrete a Vascular Permeability Factor That Promotes Accumulation of Ascites Fluid. Science 1983, 219, 983–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S. Review of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Biology. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 59, S21–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefsson, E.C.; Vainchenker, W.; James, C. Regulation of Platelet Production and Life Span: Role of Bcl-XL and Potential Implications for Human Platelet Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, G.; Monzel, A.S.; Karan, K.R.; Michelson, J.; Ware, S.A.; Cardenas, A.; Lin, J.; Bris, C.; Santhanam, B.; Murphy, M.P.; et al. A Multi-Omics Longitudinal Aging Dataset in Primary Human Fibroblasts with Mitochondrial Perturbations. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolagas, S.C.; Parfitt, A.M. What Old Means to Bone. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, R.G.; Santos, G.S.; Alkass, N.; Chiesa, T.L.; Azzini, G.O.; da Fonseca, L.F.; dos Santos, A.F.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Mosaner, T.; Lana, J.F. The Regenerative Mechanisms of Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Review. Cytokine 2021, 144, 155560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, J.E. How Can We Use Proteomics to Learn More about Platelets? Platelets 2023, 34, 2217932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzek, S.; Betensky, M.; Di Paola, J.; Diacovo, T.; Goldenberg, N.; Ignjatovic, V. What Can the Plasma Proteome Tell Us about Platelets (and Vice Versa)? Platelets 2023, 34, 2186707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatlekar, S.; Manne, B.K.; Basak, I.; Edelstein, L.C.; Tugolukova, E.; Stoller, M.L.; Cody, M.J.; Morley, S.C.; Nagalla, S.; Weyrich, A.S.; et al. MiR-125a-5p Regulates Megakaryocyte Proplatelet Formation via the Actin-Bundling Protein L-Plastin. Blood 2020, 136, 1760–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caux, M.; Mansour, R.; Xuereb, J.-M.; Chicanne, G.; Viaud, J.; Vauclard, A.; Boal, F.; Payrastre, B.; Tronchère, H.; Severin, S. PIKfyve-Dependent Phosphoinositide Dynamics in Megakaryocyte/Platelet Granule Integrity and Platelet Functions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, 987–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirer, T.; Ilhan, O.; Arat, M.; Genç, Y.; Özcan, M.; Dalva, K.; Çelebi, H.; Beksaç, M.; Akan, H.; Gürman, G.; et al. CD41+ and CD42+ Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells May Predict Platelet Engraftment after Allogeneic Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Clin. Apher. 2001, 16, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machlus, K.R.; Italiano, J.E. Megakaryocyte Development and Platelet Formation. In Platelets; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 25–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Wang, D.; Han, X.; Chen, M.; Shi, G.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, M. CXCR4high Megakaryocytes Regulate Host-Defense Immunity against Bacterial Pathogens. Elife 2022, 11, e78662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thon, J.N.; Italiano, J.E. Platelets: Production, Morphology and Ultrastructure. In Antiplatelet Agents; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, E.M.; Norol, F.; Guichard, J.; Breton-Gorius, J.; Vainchenker, W.; Massé, J.-M.; Debili, N. Ultrastructure of Platelet Formation by Human Megakaryocytes Cultured With the Mpl Ligand. Blood 1997, 89, 2336–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.K.; Villacorta-Martin, C.; Hon, S.; Rock, J.R.; Murphy, G.J. Lung Megakaryocytes Display Distinct Transcriptional and Phenotypic Properties. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 6204–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livada, A.C.; Pariser, D.N.; Morrell, C.N. Megakaryocytes in the Lung: History and Future Perspectives. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 7, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Alibhai, D.; Walsh, T.G.; Tarassova, N.; Englert, M.; Birol, S.Z.; Li, Y.; Williams, C.M.; Neal, C.R.; Burkard, P.; et al. Highly Efficient Platelet Generation in Lung Vasculature Reproduced by Microfluidics. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noetzli, L.J.; French, S.L.; Machlus, K.R. New Insights Into the Differentiation of Megakaryocytes From Hematopoietic Progenitors. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machlus, K.R.; Italiano, J.E. The Incredible Journey: From Megakaryocyte Development to Platelet Formation. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 201, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainchenker, W.; Raslova, H. Megakaryocyte Polyploidization: Role in Platelet Production. Platelets 2020, 31, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Wang, X.; Qu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Jing, T.; Zhang, Q. Megakaryopoiesis and Platelet Production: Insight into Hematopoietic Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation. Stem Cell Investig. 2015, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzi, S.; Lordier, L.; Debili, N.; Raslova, H.; Vainchenker, W. Megakaryocyte and Polyploidization. Exp. Hematol. 2018, 57, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrançais, E.; Ortiz-Muñoz, G.; Caudrillier, A.; Mallavia, B.; Liu, F.; Sayah, D.M.; Thornton, E.E.; Headley, M.B.; David, T.; Coughlin, S.R.; et al. The Lung Is a Site of Platelet Biogenesis and a Reservoir for Haematopoietic Progenitors. Nature 2017, 544, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, H.; Korpal, M.; Hurov, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Zhang, J.; Cantley, L.C.; Graf, T.; Shivdasani, R.A. Characterization of the Megakaryocyte Demarcation Membrane System and Its Role in Thrombopoiesis. Blood 2006, 107, 3868–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowata, S.; Isogai, S.; Murai, K.; Ito, S.; Tohyama, K.; Hitomi, J.; Ishida, Y. Novel Concept of Platelet Production from Megakaryocyte in Intact Bone Marrow: Proplatelet and Thick Protrusion. Blood 2012, 120, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, H.F.G.; Korporaal, S.J.A. Platelet Morphology and Ultrastructure. In Platelets in Thrombotic and Non-Thrombotic Disorders; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, M.; Thon, J.N.; Ehrlicher, A.J.; Wu, S.; Mazutis, L.; Deschmann, E.; Sola-Visner, M.; Italiano, J.E.; Hartwig, J.H. Microtubule Sliding Drives Proplatelet Elongation and Is Dependent on Cytoplasmic Dynein. Blood 2015, 125, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, I.C.; Scheller, I.; Wackerbarth, L.M.; Beck, S.; Heib, T.; Aurbach, K.; Manukjan, G.; Gross, C.; Spindler, M.; Nagy, Z.; et al. Actin/Microtubule Crosstalk during Platelet Biogenesis in Mice Is Critically Regulated by Twinfilin1 and Cofilin1. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscher, J.; Guinard, I.; Eckly, A.; Lanza, F.; Léon, C. Blood Platelet Formation at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thon, J.N.; Montalvo, A.; Patel-Hett, S.; Devine, M.T.; Richardson, J.L.; Ehrlicher, A.; Larson, M.K.; Hoffmeister, K.; Hartwig, J.H.; Italiano, J.E. Cytoskeletal Mechanics of Proplatelet Maturation and Platelet Release. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, S.; Jeong, D.; Chung, J.; Kim, G.; Song, J.; Moon, E.; Huh, Y.H.; Kim, D. Super-Resolution Imaging Reveals Cytoskeleton-Dependent Organelle Rearrangement within Platelets at Intermediate Stages of Maturation. Structure 2021, 29, 810–822.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemble, S.; Dalby, A.; Lowe, G.C.; Nicolson, P.L.R.; Watson, S.P.; Senis, Y.; Thomas, S.G.; Harrison, P. Analysis of Preplatelets and Their Barbell Platelet Derivatives by Imaging Flow Cytometry. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 2932–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Storrie, B. The Cellular Basis of Platelet Secretion: Emerging Structure/Function Relationships. Platelets 2017, 28, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Williamson, J.K.; Aronova, M.A.; Prince, A.A.; Pokrovskaya, I.D.; Leapman, R.D.; Storrie, B. Golgi Proteins in Circulating Human Platelets Are Distributed across Non-Stacked, Scattered Structures. Platelets 2017, 28, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchinger, H.; Jain, K.; Tyagi, T.; Hwa, J. Role of Platelet Mitochondria: Life in a Nucleus-Free Zone. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. Shedding Light on the Cell Biology of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Biomedical Applications. Life 2023, 13, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soslau, G. Platelet Protein Synthesis, Regulation, and Post-Translational Modifications: Mechanics and Function. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyrich, A.S.; Schwertz, H.; Kraiss, L.W.; Zimmerman, G.A. Protein Synthesis by Platelets: Historical and New Perspectives. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, W.S.; Juang, L.J.; Mazinani, N.; Munro, L.; Jefferies, W.A.; Kastrup, C.J. Post-Translational Modifications of Platelet-Derived Amyloid Precursor Protein by Coagulation Factor XIII-A*. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 4449–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Solari, F.A.; Sickmann, A.; Garcia, A.; Jurk, K.; Heemskerk, J.W.M. Molecular Proteomics and Signalling of Human Platelets in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.; Moser, M.; Mann, M. Copy Number Analysis of the Murine Platelet Proteome Spanning the Complete Abundance Range. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 3435–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, J.M.; Gambaryan, S.; Watson, S.P.; Jurk, K.; Walter, U.; Sickmann, A.; Heemskerk, J.W.M.; Zahedi, R.P. What Can Proteomics Tell Us About Platelets? Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1204–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellner, M. How Can Platelet Proteomics Best Be Used to Interrogate Disease? Platelets 2023, 34, 2220046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, K.S.; Farley, A.; Dawson, C.A.; Rimes, J.; Biben, C.; de Graaf, C.; Potts, M.A.; Stonehouse, O.J.; Carmagnac, A.; Gangatirkar, P.; et al. Membrane Budding Is a Major Mechanism of in Vivo Platelet Biogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, H.; Stegner, D. Imaging Platelet Biogenesis in Vivo. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, X.; Poncz, M.; Gadue, P.; French, D.L. Understanding Platelet Generation from Megakaryocytes: Implications for in Vitro–Derived Platelets. Blood 2016, 127, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, N.; Eto, K. Generation and Manipulation of Human IPSC-Derived Platelets. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 3385–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Eguren, A.; Gómez-Álvarez, M.; Francés-Herrero, E.; Romeu, M.; Ferrero, H.; Seli, E.; Cervelló, I. Human Umbilical Cord-Based Therapeutics: Stem Cells and Blood Derivatives for Female Reproductive Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Dai, W.; Jiang, Y. Good Manufacturing Practice-Grade of Megakaryocytes Produced by a Novel Ex Vivo Culturing Platform. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zheng, J. Platelet Generation in Vivo and in Vitro. Springerplus 2016, 5, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca-Zamora, E.J.; Ferrer-Marín, F.; Rivera, J.; Teruel-Montoya, R. Tubulin in Platelets: When the Shape Matters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiano, J.E.; Lecine, P.; Shivdasani, R.A.; Hartwig, J.H. Blood Platelets Are Assembled Principally at the Ends of Proplatelet Processes Produced by Differentiated Megakaryocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, I.; Baaten, C.C.F.M.J.; Gibbins, J.M.; Ten Cate, H.; Heemskerk, J.W.M.; Jones, C.I.; van der Meijden, P.E.J. Repeated Platelet Activation and the Potential of Previously Activated Platelets to Contribute to Thrombus Formation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Liu, C.; Rosenberger, P. Platelet Formation and Activation Are Influenced by Neuronal Guidance Proteins. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1206906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muravlev, I.A.; Dobrovolsky, A.B.; Antonova, O.A.; Khaspekova, S.G.; Mazurov, A.V. Effects of Platelets Activated by Different Agonists on Fibrin Formation and Thrombin Generation. Platelets 2023, 34, 2139365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornert, A.; Boscher, J.; Pertuy, F.; Eckly, A.; Stegner, D.; Strassel, C.; Gachet, C.; Lanza, F.; Léon, C. Cytoskeletal-based mechanisms differently regulate in vivo and in vitro proplatelet formation. Haematologica 2020, 106, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, J.; Bompard, G.; Cau, J.; Kunishima, S.; Rabeharivelo, G.; Mateos-Langerak, J.; Cazevieille, C.; Cavelier, P.; Boizet-Bonhoure, B.; Delsert, C.; et al. Microtubule Polyglutamylation and Acetylation Drive Microtubule Dynamics Critical for Platelet Formation. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelená, A.; Blumberg, J.; Probst, D.; Gerasimaitė, R.; Lukinavičius, G.; Schwarz, U.S.; Köster, S. Force Generation in Human Blood Platelets by Filamentous Actomyosin Structures. Biophys. J. 2023, 122, 3340–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán-Saenz, N.Z.; Serrano-Puente, A.; Gallegos-Flores, P.I.; Mendoza-Almanza, B.D.; Esparza-Ibarra, E.L.; Godina-González, S.; González-Curiel, I.E.; Ayala-Luján, J.L.; Hernández-Barrales, M.; Cueto-Villalobos, C.F.; et al. Platelet Membrane: An Outstanding Factor in Cancer Metastasis. Membranes 2022, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protty, M.B.; Jenkins, P.V.; Collins, P.W.; O’Donnell, V.B. The Role of Procoagulant Phospholipids on the Surface of Circulating Blood Cells in Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Open Biol. 2022, 12, 210318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuragi, T.; Nagata, S. Regulation of Phospholipid Distribution in the Lipid Bilayer by Flippases and Scramblases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 576–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollet, H.; Conrard, L.; Cloos, A.-S.; Tyteca, D. Plasma Membrane Lipid Domains as Platforms for Vesicle Biogenesis and Shedding? Biomolecules 2018, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorent, J.H.; Levental, K.R.; Ganesan, L.; Rivera-Longsworth, G.; Sezgin, E.; Doktorova, M.; Lyman, E.; Levental, I. Author Correction: Plasma Membranes Are Asymmetric in Lipid Unsaturation, Packing and Protein Shape. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagoutte-Renosi, J.; Allemand, F.; Ramseyer, C.; Rabani, V.; Davani, S. Influence of Antiplatelet Agents on the Lipid Composition of Platelet Plasma Membrane: A Lipidomics Approach with Ticagrelor and Its Active Metabolite. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenna, A.; Nappi, F.; Lusini, M.; Satriano, U.M.; Schilirò, D.; Spadaccio, C.; Chello, M. Effect of Statins on Platelet Activation and Function: From Molecular Pathways to Clinical Effects. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6661847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.G. The Structure of Resting and Activated Platelets. In Platelets; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 47–77. [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns, S. Activation of Platelet Function Through G Protein–Coupled Receptors. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel-Hett, S.; Wang, H.; Begonja, A.J.; Thon, J.N.; Alden, E.C.; Wandersee, N.J.; An, X.; Mohandas, N.; Hartwig, J.H.; Italiano, J.E. The Spectrin-Based Membrane Skeleton Stabilizes Mouse Megakaryocyte Membrane Systems and Is Essential for Proplatelet and Platelet Formation. Blood 2011, 118, 1641–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, J.; Ranke, C.; Perego, E.; Köster, S. Human Blood Platelets Contract in Perpendicular Direction to Shear Flow. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 2009–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnke, O. The Formation of Fusiform Proplatelets and Their Transformation to Discoid Platelets. Platelets 1993, 4, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, Y.; Fitch-Tewfik, J.L.; Qiu, Y.; Ahn, B.; Myers, D.R.; Tran, R.; Fay, M.E.; Ding, L.; Spearman, P.W.; Michelson, A.D.; et al. Platelet Geometry Sensing Spatially Regulates α-Granule Secretion to Enable Matrix Self-Deposition. Blood 2015, 126, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalker, T.J.; Welsh, J.D.; Brass, L.F. Shaping the Platelet Response to Vascular Injury. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2014, 21, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, L.R.; Cahill, M.R.; Young, P.W. The Importance of Alpha-Actinin Proteins in Platelet Formation and Function, and Their Causative Role in Congenital Macrothrombocytopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woronowicz, K.; Dilks, J.R.; Rozenvayn, N.; Dowal, L.; Blair, P.S.; Peters, C.G.; Woronowicz, L.; Flaumenhaft, R. The Platelet Actin Cytoskeleton Associates with SNAREs and Participates in α-Granule Secretion. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4533–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golebiewska, E.M.; Poole, A.W. Secrets of Platelet Exocytosis—What Do We Really Know about Platelet Secretion Mechanisms? Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 165, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménasché, G.; Longé, C.; Bratti, M.; Blank, U. Cytoskeletal Transport, Reorganization, and Fusion Regulation in Mast Cell-Stimulus Secretion Coupling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.L.; Meneses-Salas, E.; Ramadass, M.; Monfregola, J.; Rahman, F.; Carvalho Gontijo, R.; Kiosses, W.B.; Pestonjamasp, K.; Allen, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. Differential Dysregulation of Granule Subsets in WASH-Deficient Neutrophil Leukocytes Resulting in Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebstrup, M.L.; Dias, C.; Heitmann, A.S.B.; Sønder, S.L.; Nylandsted, J. Actin Cytoskeletal Dynamics in Single-Cell Wound Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.G.; Clawson, C.C. The Surface-Connected Canalicular System of Blood Platelets--a Fenestrated Membrane System. Am. J. Pathol. 1980, 101, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pokrovskaya, I.D.; Tobin, M.; Desai, R.; Joshi, S.; Kamykowski, J.A.; Zhang, G.; Aronova, M.A.; Whiteheart, S.W.; Leapman, R.D.; Storrie, B. Canalicular System Reorganization during Mouse Platelet Activation as Revealed by 3D Ultrastructural Analysis. Platelets 2021, 32, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokrovskaya, I.D.; Aronova, M.A.; Kamykowski, J.A.; Prince, A.A.; Hoyne, J.D.; Calco, G.N.; Kuo, B.C.; He, Q.; Leapman, R.D.; Storrie, B. STEM Tomography Reveals That the Canalicular System and A-granules Remain Separate Compartments during Early Secretion Stages in Blood Platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumüller, J.; Ellinger, A.; Wagner, T. Transmission Electron Microscopy of Platelets FROM Apheresis and Buffy-Coat-Derived Platelet Concentrates. In The Transmission Electron Microscope—Theory and Applications; InTech: Sydney, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gruba, S.M.; Koseoglu, S.; Meyer, A.F.; Meyer, B.M.; Maurer-Jones, M.A.; Haynes, C.L. Platelet Membrane Variations and Their Effects on δ-Granule Secretion Kinetics and Aggregation Spreading among Different Species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escolar, G.; Leistikow, E.; White, J. The Fate of the Open Canalicular System in Surface and Suspension- Activated Platelets. Blood 1989, 74, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckly, A.; Heijnen, H.; Pertuy, F.; Geerts, W.; Proamer, F.; Rinckel, J.-Y.; Léon, C.; Lanza, F.; Gachet, C. Biogenesis of the Demarcation Membrane System (DMS) in Megakaryocytes. Blood 2014, 123, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvadurai, M.V.; Hamilton, J.R. Structure and Function of the Open Canalicular System—The Platelet’s Specialized Internal Membrane Network. Platelets 2018, 29, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, S.; Dalmay, D.; Mahaut-Smith, M. Fluorescence Approaches to Image and Quantify the Demarcation Membrane System in Living Megakaryocytes. In Platelets and Megakaryocytes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 195–215. [Google Scholar]
- Pokrovskaya, I.D.; Yadav, S.; Rao, A.; McBride, E.; Kamykowski, J.A.; Zhang, G.; Aronova, M.A.; Leapman, R.D.; Storrie, B. 3D Ultrastructural Analysis of A-granule, Dense Granule, Mitochondria, and Canalicular System Arrangement in Resting Human Platelets. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 4, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noetzli, L.J.; Italiano, J.E. Unlocking the Molecular Secrete(s) of α-Granule Biogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 2539–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, E.L.; Rao, A.; Zhang, G.; Hoyne, J.D.; Calco, G.N.; Kuo, B.C.; He, Q.; Prince, A.A.; Pokrovskaya, I.D.; Storrie, B.; et al. Comparison of 3D Cellular Imaging Techniques Based on Scanned Electron Probes: Serial Block Face SEM vs. Axial Bright-Field STEM Tomography. J. Struct. Biol. 2018, 202, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonnalagadda, D.; Izu, L.T.; Whiteheart, S.W. Platelet Secretion Is Kinetically Heterogeneous in an Agonist-Responsive Manner. Blood 2012, 120, 5209–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starlinger, P.; Haegele, S.; Offensperger, F.; Oehlberger, L.; Pereyra, D.; Kral, J.B.; Schrottmaier, W.C.; Badrnya, S.; Reiberger, T.; Ferlitsch, A.; et al. The Profile of Platelet A-granule Released Molecules Affects Postoperative Liver Regeneration. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Whiteheart, S.W. The Nuts and Bolts of the Platelet Release Reaction. Platelets 2017, 28, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, D.M.; Heijnen, H.F.G.; Gahl, W.A.; Gunay-Aygun, M. The A-granule Proteome: Novel Proteins in Normal and Ghost Granules in Gray Platelet Syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, D.M.; Heijnen, H.F.G.; Horne, M.K.; White, J.G.; Gahl, W.A. Proteomic Analysis of Platelet A-granules Using Mass Spectrometry. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosher, D.F.; Pesciotta, D.M.; Loftus, J.C.; Albrecht, R.M. Secreted Alpha Granule Proteins. In Platelet Membrane Glycoproteins; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 171–191. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, V.M.A.; Latorre-Rey, L.J.; Schenk, F.; Rommel, M.G.E.; Moritz, T.; Modlich, U. Targeting Transgenic Proteins to Alpha Granules for Platelet-Directed Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 27, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, G.; Masse, J.; Cramer, E. Alpha-Granule Membrane Mirrors the Platelet Plasma Membrane and Contains the Glycoproteins Ib, IX, and V. Blood 1996, 87, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, P.; Flaumenhaft, R. Platelet α-Granules: Basic Biology and Clinical Correlates. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, C.S. The Yin-Yang of Platelet Granules. Blood 2008, 111, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiano, J.E.; Richardson, J.L.; Patel-Hett, S.; Battinelli, E.; Zaslavsky, A.; Short, S.; Ryeom, S.; Folkman, J.; Klement, G.L. Angiogenesis Is Regulated by a Novel Mechanism: Pro- and Antiangiogenic Proteins Are Organized into Separate Platelet α Granules and Differentially Released. Blood 2008, 111, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everts, P.A.; Lana, J.F.; Onishi, K.; Buford, D.; Peng, J.; Mahmood, A.; Fonseca, L.F.; van Zundert, A.; Podesta, L. Angiogenesis and Tissue Repair Depend on Platelet Dosing and Bioformulation Strategies Following Orthobiological Platelet-Rich Plasma Procedures: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa Marques, R.; Simon, J.; d’Arros, C.; Landfester, K.; Jurk, K.; Mailänder, V. Proteomics Reveals Differential Adsorption of Angiogenic Platelet Lysate Proteins on Calcium Phosphate Bone Substitute Materials. Regen. Biomater. 2022, 9, rbac044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beirat, A.F.; Menakuru, S.R.; Kalra, M. Platelet Delta (δ)-Storage Pool Deficiency: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Hematol. Rep. 2023, 15, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, W.T.; Raghavan, M.; Calomeni, E.P.; Turner, J.N.; Roysam, B.; Roysam, S.; Smith, M.R.; Kouides, P.A.; Lachant, N.A. A Morphometric Analysis of Platelet Dense Granules of Patients with Unexplained Bleeding: A New Entity of Delta-Microgranular Storage Pool Deficiency. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W. Sorting Machineries: How Platelet-Dense Granules Differ from α-Granules. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaumenhaft, R.; Sharda, A. Platelet Secretion. In Platelets; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 349–370. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, M.-J.; Wang, J.-L.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Liang, Q.-L.; Chen, K.; Nie, L.-B.; Zhu, X.-Q. Functional Characterization of Dense Granule Proteins in Toxoplasma gondii RH Strain Using CRISPR-Cas9 System. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, M.B.; Pearce, C.S.; Heaslip, A.T. Dense Granule Biogenesis, Secretion, and Function in Toxoplasma gondii. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2022, 69, e12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Song, Y.; Hou, L.; Zhao, J.; Shen, B. Identification of Novel Dense-Granule Proteins in Toxoplasma gondii by Two Proximity-Based Biotinylation Approaches. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 18, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, J.; Badin, M.; Graf, L.; Rivard, G.E.; Paterson, A.D.; Pare, G.; Hayward, C.P.M. Bleeding Risks Associated with Confirmed Platelet Dense Granule Deficiency and/or Impaired Aggregation Responses. Blood 2016, 128, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatouk, A.F.; Brockington, J.; Gudena, V. A Case of Platelet Storage Pool Deficiency of Dense Granules (Delta SPD). Am. J. Case Rep. 2011, 12, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Leem, Y.-E.; Kwon, I.; Kang, J.-S.; Bae, Y.M.; Cho, H. Estrogen Modulates Serotonin Effects on Vasoconstriction through Src Inhibition. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Konradt, C.; Corken, A.; Ware, J.; Nieswandt, B.; Di Paola, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, D.; Nieman, M.T.; Whiteheart, S.W.; et al. Hemostasis vs. Homeostasis: Platelets Are Essential for Preserving Vascular Barrier Function in the Absence of Injury or Inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24316–24325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho-Tin-Noé, B.; Le Chapelain, O.; Camerer, E. Platelets Maintain Vascular Barrier Function in the Absence of Injury or Inflammation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golebiewska, E.M.; Poole, A.W. Platelet Secretion: From Haemostasis to Wound Healing and Beyond. Blood Rev. 2015, 29, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koupenova, M.; Clancy, L.; Corkrey, H.A.; Freedman, J.E. Circulating Platelets as Mediators of Immunity, Inflammation, and Thrombosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasek, J. Platelet Secretory Granules or Secretory Lysosomes? Platelets 2005, 16, 500–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monis, B.; Wasserkrug, H. Histochemistry of Glycosidases of Megakaryocytes and Platelets. Histochemie 1967, 10, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badimón, L.; Vilahur, G.; Padró, T. Lipoproteins, Platelets, and Atherothrombosis. Rev. Española Cardiol. Engl. Ed. 2009, 62, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovskaya, I.D.; Joshi, S.; Tobin, M.; Desai, R.; Aronova, M.A.; Kamykowski, J.A.; Zhang, G.; Whiteheart, S.W.; Leapman, R.D.; Storrie, B. SNARE-Dependent Membrane Fusion Initiates α-Granule Matrix Decondensation in Mouse Platelets. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2947–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaumenhaft, R. Molecular Basis of Platelet Granule Secretion. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Ma, J.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, G.; Kang, X. The Role of S100A6 in Human Diseases: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, C.; Xavier-Ferrucio, J.; Lu, Y.-C.; Min, E.; Zhang, P.-X.; Zou, S.; Kang, E.; Zhang, M.; Zerafati, G.; Gallagher, P.G.; et al. Adult Human Megakaryocyte-Erythroid Progenitors Are in the CD34+CD38mid Fraction. Blood 2016, 128, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muench, M.O.; Bárcena, A. Megakaryocyte Growth and Development Factor Is a Potent Growth Factor for Primitive Hematopoietic Progenitors in the Human Fetus. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 55, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawai, N.; Koike, K.; Higuchi, T.; Ogami, K.; Oda, M. Thrombopoietin Enhances the Production of Myeloid Cells, but Not Megakaryocytes, in Juvenile Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Blood 1998, 91, 4065–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, C.S.; Charó, N.; Tatti, S.; Gómez, R.M.; D’Atri, L.P.; Schattner, M. Regulation of Megakaryo/Thrombopoiesis by Endosomal Toll-like Receptor 7 and 8 Activation of CD34+ Cells in a Viral Infection Model. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 7, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydman, G.H.; Ellett, F.; Jorgensen, J.; Marand, A.L.; Zukerberg, L.; Selig, M.K.; Tessier, S.N.; Wong, K.H.K.; Olaleye, D.; Vanderburg, C.R.; et al. Megakaryocytes Respond during Sepsis and Display Innate Immune Cell Behaviors. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1083339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Cantor, A.B. Common Features of Megakaryocytes and Hematopoietic Stem Cells: What’s the Connection? J. Cell Biochem. 2009, 107, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendas, G.; Schlesinger, M. The GPIb-IX Complex on Platelets: Insight into Its Novel Physiological Functions Affecting Immune Surveillance, Hepatic Thrombopoietin Generation, Platelet Clearance and Its Relevance for Cancer Development and Metastasis. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzeffi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Wu, Y.-F.; Zhang, A.; Kareddy, N.; Tadjou Tito, E.; Rock, P.; Michelson, A.D.; Frelinger, A.L. Platelet Surface GPIbα, Activated GPIIb-IIIa, and P-Selectin Levels in Adult Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Patients. Platelets 2022, 33, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiro, O.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Molecular Basis of Leukocyte–Endothelium Interactions during the Inflammatory Response. Rev. Española Cardiol. Engl. Ed. 2009, 62, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilos, M.; Petousis, S.; Parthenakis, F. Interaction between Platelets and Endothelium: From Pathophysiology to New Therapeutic Options. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 8, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, K.; Kiryu, J.; Tsujikawa, A.; Miyamoto, K.; Honjo, M.; Tanihara, H.; Nonaka, A.; Yamashiro, K.; Katsuta, H.; Miyahara, S.; et al. Platelets Adhering to the Vascular Wall Mediate Postischemic Leukocyte–Endothelial Cell Interactions in Retinal Microcirculation. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, U.J.H. Interaction of Platelets, Leukocytes and the Endothelium*. Transfus. Med. Hemotherapy 2006, 33, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, K.; Zieger, B. Endothelial Cells and Coagulation. Cell Tissue Res. 2022, 387, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Oswald, B.E.; Sullivan, J.A.; Dahmani, F.Z.; Pasman, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, P.; Ni, H. Platelet Physiology and Immunology: Pathogenesis and Treatment of Classical and Non-Classical Fetal and Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia. Ann. Blood 2019, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalia, L. The Role of Platelet-Selectin as a Marker of Thrombocyte Aggregation on Cerebral Sinus Venous Thrombosis. J. Blood Med. 2022, 13, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricius, H.-Å.; Starzonek, S.; Lange, T. The Role of Platelet Cell Surface P-Selectin for the Direct Platelet-Tumor Cell Contact During Metastasis Formation in Human Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 642761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, H.E.; Sheats, M.K. Targeting Neutrophil Β2-Integrins: A Review of Relevant Resources, Tools, and Methods. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterbusch, M.; Schrottmaier, W.C.; Kral-Pointner, J.B.; Salzmann, M.; Assinger, A. Measuring and Interpreting Platelet-Leukocyte Aggregates. Platelets 2018, 29, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossaint, J.; Margraf, A.; Zarbock, A. Role of Platelets in Leukocyte Recruitment and Resolution of Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tang, C. Targeting Platelet in Atherosclerosis Plaque Formation: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnouf, T.; Chou, M.-L.; Lundy, D.J.; Chuang, E.-Y.; Tseng, C.-L.; Goubran, H. Expanding Applications of Allogeneic Platelets, Platelet Lysates, and Platelet Extracellular Vesicles in Cell Therapy, Regenerative Medicine, and Targeted Drug Delivery. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zhao, T.; Song, N.; Pan, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Xia, C. Platelets and Platelet Extracellular Vesicles in Drug Delivery Therapy: A Review of the Current Status and Future Prospects. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1026386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano Jerez, E.M.; Gibbins, J.M.; Hughes, C.E. Targeting Platelet Inhibition Receptors for Novel Therapies: PECAM-1 and G6b-B. Platelets 2021, 32, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M. Platelet Lipidome: Dismantling the “Trojan Horse” in the Bloodstream. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinczyk, N.; Misztal, T.; Gromotowicz-Poplawska, A.; Zebrowska, A.; Rusak, T.; Radziwon, P.; Chabielska, E. Utility of Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 in the Platelet Activity Assessment in Mouse and Human Blood. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, E.E.; Braun, A.; Jansen, P.; Hartmann, M. Platelet-Therapeutics to Improve Tissue Regeneration and Wound Healing—Physiological Background and Methods of Preparation. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boilard, E.; Bellio, M. Platelet Extracellular Vesicles and the Secretory Interactome Join Forces in Health and Disease. Immunol. Rev. 2022, 312, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsuya, K.; Kaneko, K.; Kasahara, K. Function of Platelet Glycosphingolipid Microdomains/Lipid Rafts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, M.; Ehrenberg, A.; Toska, L.M.; Metz, L.M.; Klier, M.; Krueger, I.; Reusswig, F.; Elvers, M. Molecular Drivers of Platelet Activation: Unraveling Novel Targets for Anti-Thrombotic and Anti-Thrombo-Inflammatory Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkaya Fırat, A. Chemokines Effective on Platelet Functions. In Chemokines Updates; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Giusti, I.; Rughetti, A.; D’Ascenzo, S.; Millimaggi, D.; Pavan, A.; Dell’Orso, L.; Dolo, V. Identification of an Optimal Concentration of Platelet Gel for Promoting Angiogenesis in Human Endothelial Cells. Transfusion 2009, 49, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roweth, H.G.; Battinelli, E.M. Platelets and (Lymph) Angiogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2023, 13, a041174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocansey, D.K.W.; Pei, B.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Olovo, C.V.; Mao, F. Cellular and Molecular Mediators of Lymphangiogenesis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Jang, J.H.; Oh, I.-Y.; Choi, J.-I.; Yun, J.-Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.-E.; Ko, S.-B.; Kang, J.-A.; Kang, J.; et al. Human Podoplanin-Positive Monocytes and Platelets Enhance Lymphangiogenesis Through the Activation of the Podoplanin/CLEC-2 Axis. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1518–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Yu, J.; Xu, W.; Gao, J.; Lv, X.; Wen, Z. The Role of Podoplanin in the Immune System and Inflammation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 3561–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Tsukiji, N.; Otake, S. Crosstalk between Hemostasis and Lymphangiogenesis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Tsukiji, N. Platelet CLEC-2 and Lung Development. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 4, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautch, V.L.; Caron, K.M. Blood and Lymphatic Vessel Formation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a008268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puricelli, C.; Boggio, E.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Stoppa, I.; Sutti, S.; Giordano, M.; Dianzani, U.; Rolla, R. Platelets, Protean Cells with All-Around Functions and Multifaceted Pharmacological Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Li, Z.-T.; Xu, L.-H.; Su, T.-Y.; Han, Y.; Bao, M.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.-J.; Lou, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Increase Col8a1 Secretion and Vascular Stiffness in Intimal Injury. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, S.; Zhang, Q.; D’Agostino, I.; Bruno, A.; Tacconelli, S.; Contursi, A.; Guarnieri, S.; Dovizio, M.; Falcone, L.; Ballerini, P.; et al. The Antiplatelet Agent Revacept Prevents the Increase of Systemic Thromboxane A2 Biosynthesis and Neointima Hyperplasia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbotin, V.M. Analysis of Arterial Intimal Hyperplasia: Review and Hypothesis. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2007, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Teng, F.; He, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Guo, D.; et al. The Role of Platelets in the Regulation of Tumor Growth and Metastasis: The Mechanisms and Targeted Therapy. MedComm 2023, 4, e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.; Yin, S.; Yang, S.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L. Roles of Platelets in Tumor Invasion and Metastasis: A Review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, M. Role of Platelets and Platelet Receptors in Cancer Metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, S.; Osei, E.; Maftoon, N. Interactions of Platelets with Circulating Tumor Cells Contribute to Cancer Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Almanza, G.; Burciaga-Hernández, L.; Maldonado, V.; Melendez-Zajgla, J.; Olmos, J. Role of Platelets and Breast Cancer Stem Cells in Metastasis. World J. Stem Cells 2020, 12, 1237–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisinger, F.; Patzelt, J.; Langer, H.F. The Platelet Response to Tissue Injury. Front Med. 2018, 5, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajdu, S.I. A Note from History: The Discovery of Blood Cells. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2003, 33, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stassen, J.M.; Nyström, Å. A Historical Review of Hemostasis, Thrombosis, and Antithrombotic Therapy. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1997, 39, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gaetano, G. Historical Overview of the Role of Platelets in Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Haematologica 2001, 86, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-González, D.J.; Méndez-Bolaina, E.; Trejo-Bahena, N.I. Platelet-Rich Plasma Peptides: Key for Regeneration. Int. J. Pept. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielins, E.R.; Atashroo, D.A.; Maan, Z.N.; Duscher, D.; Walmsley, G.G.; Hu, M.; Senarath-Yapa, K.; McArdle, A.; Tevlin, R.; Wearda, T.; et al. Wound Healing: An Update. Regen. Med. 2014, 9, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronkite, E.P. Use of Thrombin and Fibrinogen in Skin Grafting. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1944, 124, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeissadat, S.A.; Babaee, M.; Rayegani, S.M.; Hashemi, Z.; Hamidieh, A.A.; Mojgani, P.; Vanda, H.F. An Overview of Platelet Products (PRP, PRGF, PRF, Etc.) in the Iranian Studies. Future Sci. OA 2017, 3, FSO231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, L.; Li, H.; Eriksson, U. The PDGF Family: Four Gene Products Form Five Dimeric Isoforms. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2004, 15, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde Montero, E.; Fernández Santos, M.E.; Suárez Fernández, R. Plasma Rico En Plaquetas: Aplicaciones En Dermatología. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015, 106, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, B.; D’Autilio, M.F.L.M.; Orlandi, F.; Pepe, G.; Garcovich, S.; Scioli, M.G.; Orlandi, A.; Cervelli, V.; Gentile, P. Wound Healing: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of a Bio-Functionalized Scaffold Based on Hyaluronic Acid and Platelet-Rich Plasma in Chronic Ulcers. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Parayaruthottam, P.; Roshan, G.; Menon, V.; Fidha, M.; Fernandes, A. Platelets and Their Pathways in Dentistry: Systematic Review. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervelli, V.; Bocchini, I.; Di Pasquali, C.; De Angelis, B.; Cervelli, G.; Curcio, C.B.; Orlandi, A.; Scioli, M.G.; Tati, E.; Delogu, P.; et al. P.R.L. Platelet Rich Lipotransfert: Our Experience and Current State of Art in the Combined Use of Fat and PRP. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 434191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanaati, S.; Herrera-Vizcaino, C.; Al-Maawi, S.; Lorenz, J.; Miron, R.J.; Nelson, K.; Schwarz, F.; Choukroun, J.; Sader, R. Fifteen Years of Platelet Rich Fibrin in Dentistry and Oromaxillofacial Surgery: How High Is the Level of Scientific Evidence? J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 44, 471–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieslik-Bielecka, A.; Choukroun, J.; Odin, G.; Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M. L-PRP/L-PRF in Esthetic Plastic Surgery, Regenerative Medicine of the Skin and Chronic Wounds. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tözüm, T.F.; Demiralp, B. Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Promising Innovation in Dentistry. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2003, 69, 664. [Google Scholar]
- Anitua, E. Plasma Rich in Growth Factors: Preliminary Results of Use in the Preparation of Future Sites for Implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1999, 14, 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Ra Hara, G.; Basu, T. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Regenerative Medicine. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2014, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Hernandez, M.; Kandalam, U.; Zhang, Y.; Ghanaati, S.; Choukroun, J. Injectable Platelet Rich Fibrin (i-PRF): Opportunities in Regenerative Dentistry? Clin. Oral. Investig. 2017, 21, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel-Campbell, A.L.; Ismail, A.; Reynolds, K.A.; Poon, E.; Serrano, L.; Grushchak, S.; Farid, C.; West, D.P.; Alam, M. A Systematic Review of the Safety and Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) for Skin Aging. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 312, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, P.; Garcovich, S.; Bielli, A.; Scioli, M.G.; Orlandi, A.; Cervelli, V. The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Hair Regrowth: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Calabrese, C.; De Angelis, B.; Dionisi, L.; Pizzicannella, J.; Kothari, A.; De Fazio, D.; Garcovich, S. Impact of the Different Preparation Methods to Obtain Autologous Non-Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma (A-PRP) and Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma (AA-PRP) in Plastic Surgery: Wound Healing and Hair Regrowth Evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervelli, V.; Garcovich, S.; Bielli, A.; Cervelli, G.; Curcio, B.C.; Scioli, M.G.; Orlandi, A.; Gentile, P. The Effect of Autologous Activated Platelet Rich Plasma (AA-PRP) Injection on Pattern Hair Loss: Clinical and Histomorphometric Evaluation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 760709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uebel, C.O.; da Silva, J.B.; Cantarelli, D.; Martins, P. The Role of Platelet Plasma Growth Factors in Male Pattern Baldness Surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Taweel, A.I.; Al Refae, A.A.; Hamed, A.M.; Kamal, A.M. Comparative Study of the Efficacy of Platelet-rich Plasma Combined with Carboxytherapy vs Its Use with Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser in Atrophic Acne Scars. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Domyati, M.; Abdel-Wahab, H.; Hossam, A. Microneedling Combined with Platelet-rich Plasma or Trichloroacetic Acid Peeling for Management of Acne Scarring: A Split-face Clinical and Histologic Comparison. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos-Mikich, A.; de Oliveira, R.; Frantz, N. Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy and Reproductive Medicine. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2018, 35, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matz, E.L.; Pearlman, A.M.; Terlecki, R.P. Safety and Feasibility of Platelet Rich Fibrin Matrix Injections for Treatment of Common Urologic Conditions. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2018, 59, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Conca, V.; Abad-Collado, M.; Hueso-Abancens, J.R.; Mengual-Verdú, E.; Piñero, D.P.; Aguirre-Balsalobre, F.; Molina, J.C. Efficacy and Safety of Treatment of Hyposecretory Dry Eye with Platelet-rich Plasma. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, E170–E178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshdeep, M.; Kumaran, S. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Dermatology: Boon or a Bane? Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2014, 80, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Andia, I.; Zumstein, M.A.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Pinto, N.R.; Bielecki, T. Classification of Platelet Concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma-PRP, Platelet-Rich Fibrin-PRF) for Topical and Infiltrative Use in Orthopedic and Sports Medicine: Current Consensus, Clinical Implications and Perspectives. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014, 4, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, E.; Di Matteo, B.; Delgado, D.; Cole, B.J.; Dorotei, A.; Dragoo, J.L.; Filardo, G.; Fortier, L.A.; Giuffrida, A.; Jo, C.H.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: An Expert Opinion and Proposal for a Novel Classification and Coding System. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 1447–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everts, P.A.; Malanga, G.A.; Paul, R.V.; Rothenberg, J.B.; Stephens, N.; Mautner, K.R. Assessing Clinical Implications and Perspectives of the Pathophysiological Effects of Erythrocytes and Plasma Free Hemoglobin in Autologous Biologics for Use in Musculoskeletal Regenerative Medicine Therapies. A Review. Regen. Ther. 2019, 11, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oneto, P.; Zubiry, P.R.; Schattner, M.; Etulain, J. Anticoagulants Interfere With the Angiogenic and Regenerative Responses Mediated by Platelets. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerty, C.C.; Jeschke, M.G.; Branski, L.K.; Barret, J.P.; Dziewulski, P.; Herndon, D.N. Hypertrophic Scarring: The Greatest Unmet Challenge after Burn Injury. Lancet 2016, 388, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementoni, M.T.; B-Roscher, M.; Munavalli, G.S. Photodynamic Photorejuvenation of the Face with a Combination of Microneedling, Red Light, and Broadband Pulsed Light. Lasers Surg. Med. 2010, 42, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M. Evaluation of the Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Post-Burn Scars. Open Access J. Surg. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Liu, X.-L.; Kang, Z.-C.; Wang, Y.-S. Platelet-Rich Plasma Promotes Peripheral Nerve Regeneration after Sciatic Nerve Injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Nouri, M.; Zarrabi, M.; Fatemi, M.J.; Shpichka, A.; Timashev, P.; Hassan, M.; Vosough, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Regenerative Medicine: Possible Applications in Management of Burns and Post-Burn Scars: A Review. Cell J. 2023, 25, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgos, M.S.; Pop, O.L.; Sandor, M.; Borza, I.L.; Negrean, R.A.; Cote, A.; Neamtu, A.-A.; Grierosu, C.; Sachelarie, L.; Huniadi, A. Platelets Rich Plasma (PRP) Procedure in the Healing of Atonic Wounds. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, B.; Luo, G.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Accelerates Skin Wound Healing by Promoting Re-Epithelialization. Burns Trauma. 2020, 8, tkaa028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knightly, N.; Lee, C.; O’Brien, L.; Qayyum, T.; Hurley, C.; Kelly, J. Role for Platelet Rich Plasma as an Adjuvant Therapy in Wound Healing and Burns. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2023, 46, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, M.S.; Alotaibi, A.A.S.; Alotaibi, N.O.M.; Alosaimi, N.S.; Alotaibi, S.G.M.; Abdelrahim, M.E.A. Efficiency of Platelet-rich Plasma in the Management of Burn Wounds: A Meta-analysis. Int. Wound J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tammam, B.M.H.; Habotta, O.A.; El-khadragy, M.; Abdel Moneim, A.E.; Abdalla, M.S. Therapeutic Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Platelet-Rich Plasma on Skin Burn Healing and Rejuvenation: A Focus on Scar Regulation, Oxido-Inflammatory Stress and Apoptotic Mechanisms. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, S.; Sarangal, R. What′s New in Cicatricial Alopecia? Indian. J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2013, 79, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, K.; Rodrigues, T.S.; Ledon, J.; Savas, J.; Chacon, A. Comprehensive Overview and Treatment Update on Hair Loss. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2013, 3, 35881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadgrove, N.; Batra, S.; Barreto, D.; Rapaport, J. An Updated Etiology of Hair Loss and the New Cosmeceutical Paradigm in Therapy: Clearing ‘the Big Eight Strikes’. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbald, C. Alopecia Areata: An Updated Review for 2023. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2023, 27, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyadan, F.; Nambiar, A.; Vijayaraghavan, S. Androgenetic Alopecia: An Update. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2013, 79, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daunton, A.; Harries, M.; Sinclair, R.; Paus, R.; Tosti, A.; Messenger, A. Chronic Telogen Effluvium: Is It a Distinct Condition? A Systematic Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2023, 24, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindy Gasnier, R.B. Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma as a Treatment of Male Androgenetic Alopecia: Study of 14 Cases. J. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. Res. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, P.; Cole, J.; Cole, M.; Garcovich, S.; Bielli, A.; Scioli, M.; Orlandi, A.; Insalaco, C.; Cervelli, V. Evaluation of Not-Activated and Activated PRP in Hair Loss Treatment: Role of Growth Factor and Cytokine Concentrations Obtained by Different Collection Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, P.; Agarwal, S.; Dhot, P.; Sayal, S. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Treatment of Androgenic Alopecia. Asian J. Transfus. Sci. 2015, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatu, S.; More, Y.; Gokhale, N.; Chavhan, D.; Bendsure, N. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Androgenic Alopecia: Myth or an Effective Tool. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2014, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, J.; Brandt, R. The Effects of Autologus Platelet Rich Plasma and Various Growth Factors on Non-Transplanted Miniaturized Hair. Int. Soc. Hair Restor. Surg. 2009, 19, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.; Khetarpal, S. Platelet-rich plasma for androgenetic alopecia: A review of the literature and proposed treatment protocol. Int. J. Women Dermatol. 2019, 5, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S. Outcome of Intra-Operative Injected Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy during Follicular Unit Extraction Hair Transplant: A Prospective Randomised Study in Forty Patients. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2016, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarelli, N.; Gahoonia, N.; Sivamani, R.K. Integrative and Mechanistic Approach to the Hair Growth Cycle and Hair Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Ntege, E.H.; Sunami, H.; Inoue, Y. Regenerative Medicine Strategies for Hair Growth and Regeneration: A Narrative Review of Literature. Regen. Ther. 2022, 21, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-S.; Zheng, Z.; Choi, M.J.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, D.-Y.; Cho, S.B. The Effect of CD34+ Cell-containing Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma Injection on Pattern Hair Loss: A Preliminary Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Choi, H.-I.; Choi, D.-K.; Sohn, K.-C.; Im, M.; Seo, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, Y. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Potential Therapeutic Tool for Promoting Hair Growth. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.; Won, C.H.; Chung, W.-K.; Park, B.-S. Up-to-Date Clinical Trials of Hair Regeneration Using Conditioned Media of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in Male and Female Pattern Hair Loss. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 12, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, M.S.; Kumar, A.S.; Kirit, R.; Konathan, R.; Sivamani, R.K. Systematic Review of the Use of Platelet-rich Plasma in Aesthetic Dermatology. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2015, 14, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trink, A.; Sorbellini, E.; Bezzola, P.; Rodella, L.; Rezzani, R.; Ramot, Y.; Rinaldi, F. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo- and Active-Controlled, Half-Head Study to Evaluate the Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Alopecia Areata. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalifah, A.; Alsantali, A.; Wang, E.; McElwee, K.J.; Shapiro, J. Alopecia Areata Update. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, H.; Chen, H. Platelet-rich Plasma in the Treatment of Alopecia Areata after COVID-19 Vaccination. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorova, L.N.; Abadjieva, T.I. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Alopecia Areata: A Case Report With a Mini Review of Literature. Cureus 2023, 15, e38751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pensato, R.; Al-Amer, R.; La Padula, S. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Treating Androgenic Alopecia: A Systematic Review. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Role of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Chronic Alopecia Areata: Our Centre Experience. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2015, 48, 057–059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, J. Successful Treatment of Corticosteroid-Resistant Ophiasis-Type Alopecia Areata (AA) with Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP). JAAD Case Rep. 2015, 1, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Taieb, M.A.; Ibrahim, H.; Nada, E.A.; Seif Al-Din, M. Platelets Rich Plasma versus Minoxidil 5% in Treatment of Alopecia Areata: A Trichoscopic Evaluation. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 30, e12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, A.; Jin, A.; Kwiecien, G.J.; Gatherwright, J.; Khetarpal, S.; Zins, J.E. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Treatment of Hair Loss Improves Patient-Reported Quality of Life. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023, 47, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Dawla, R.E.; Abdelhaleem, M.; Abdelhamed, A. Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Female Patients with Chronic Telogen Effluvium: A Randomised, Controlled, Double-Blind, Pilot Clinical Trial. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2022, 89, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.-M.; Li, Z.-X.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Yang, Y.-C.; Fu, S.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Yang, R.-H.; Xiong, K. A Systematic Summary of Survival and Death Signalling during the Life of Hair Follicle Stem Cells. Stem. Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paththinige, N.D.; Akarawita, J.K.W.; Jeganathan, G. The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Autologous Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Androgenetic Alopecia. Skin. Appendage Disord. 2020, 6, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Garcovich, S. Systematic Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma Use in Androgenetic Alopecia Compared with Minoxidil®, Finasteride®, and Adult Stem Cell-Based Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, R.; Grimalt, R. A Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma: History, Biology, Mechanism of Action, and Classification. Skin. Appendage Disord. 2018, 4, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fakahany, H.; Raouf, H.A.; Medhat, W. Using Automated Microneedling with Platelet Rich Plasma for Treating Cicatricial Alopecia, Recalcitrant Alopecia Areata and Traction Alopecia, Case Report. Proc. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, AB140. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, R.; Kumar, S.; Garg, P.; Verma, Y.K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Comparative and Economical Therapy for Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Cell Tissue Bank. 2023, 24, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, K.; Saxena, D.; Savant, S. Successful Hair Transplant Outcome in Cicatricial Lichen Planus of the Scalp by Combining Scalp and Beard Hair along with Platelet Rich Plasma. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2016, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, G.F.; Mustoe, T.A.; Lingelbach, J.; Masakowski, V.R.; Griffin, G.L.; Senior, R.M.; Deuel, T.F. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor and Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Enhance Tissue Repair Activities by Unique Mechanisms. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddi, A.H. Role of Morphogenetic Proteins in Skeletal Tissue Engineering and Regeneration. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Davis-Smyth, T. The Biology of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Nan, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Si, H.; Yang, F.; Li, G. Epidermal Growth Factor Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Follicular Outer Root Sheath Cells via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, W.H.; Maciag, T. The Heparin-Binding (Fibroblast) Growth Factor Family of Proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1989, 58, 575–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redaelli, A.; Romano, D.; Marcianó, A. Face and Neck Revitalization with Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Clinical Outcome in a Series of 23 Consecutively Treated Patients. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2010, 9, 466–472. [Google Scholar]
- Elnehrawy, N.Y.; Ibrahim, Z.A.; Eltoukhy, A.M.; Nagy, H.M. Assessment of the Efficacy and Safety of Single Platelet-rich Plasma Injection on Different Types and Grades of Facial Wrinkles. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2017, 16, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, E.P.; Sahin, G.; Aydin, F.; Senturk, N.; Turanli, A.Y. Evaluation of Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Human Facial Skin. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2014, 16, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofny, E.R.M.; Abdel-Motaleb, A.A.; Ghazally, A.; Ahmed, A.M.; Hussein, M.R.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma Is a Useful Therapeutic Option in Melasma. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 30, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, N.; Mariano, M.; Cordone, I.; Abril, E.; Masi, S.; Foddai, M.L. Autologous Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma Dermal Injections for Facial Skin Rejuvenation: Clinical, Instrumental, and Flow Cytometry Assessment. Dermatol. Surg. 2017, 43, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BUZALAF, M.A.R.; LEVY, F.M. Autologous Platelet Concentrates for Facial Rejuvenation. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2022, 30, e20220020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.K.; Shin, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, N.I. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Wrinkles and Skin Tone in Asian Lower Eyelid Skin: Preliminary Results from a Prospective, Randomised, Split-Face Trial. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2014, 24, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehryan, P.; Zartab, H.; Rajabi, A.; Pazhoohi, N.; Firooz, A. Assessment of Efficacy of Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) on Infraorbital Dark Circles and Crow’s Feet Wrinkles. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2014, 13, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totey, S.; Dhurat, R.; Kadam, P.; Sevilla, G.; Shetty, G. Safety and Efficacy of Growth Factor Concentrate in the Treatment of Nasolabial Fold Correction: Split Face Pilot Study. Indian. J. Dermatol. 2015, 60, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sclafani, A.P. Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrix for Improvement of Deep Nasolabial Folds. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2010, 9, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everts, P.A.; Pinto, P.C.; Girão, L. Autologous Pure Platelet-rich Plasma Injections for Facial Skin Rejuvenation: Biometric Instrumental Evaluations and Patient-reported Outcomes to Support Antiaging Effects. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawdat, H.I.; Hegazy, R.A.; Fawzy, M.M.; Fathy, M. Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma: Topical Versus Intradermal After Fractional Ablative Carbon Dioxide Laser Treatment of Atrophic Acne Scars. Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S. Split Face Comparative Study of Microneedling with PRP versus Microneedling with Vitamin C in Treating Atrophic Post Acne Scars. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2014, 7, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alster, T.S.; Graham, P.M. Microneedling: A Review and Practical Guide. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 44, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Kanodia, S.; Singh, K. Combined Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma with Microneedling Verses Microneedling with Distilled Water in the Treatment of Atrophic Acne Scars: A Concurrent Split-face Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofal, E.; Helmy, A.; Nofal, A.; Alakad, R.; Nasr, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma versus CROSS Technique with 100% Trichloroacetic Acid versus Combined Skin Needling and Platelet Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Atrophic Acne Scars: A Comparative Study. Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, Z.A.; El-Ashmawy, A.A.; Shora, O.A. Therapeutic Effect of Microneedling and Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma in the Treatment of Atrophic Scars: A Randomized Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2017, 16, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.K.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Salem, A.M. Skin Microneedling plus Platelet-Rich Plasma versus Skin Microneedling Alone in the Treatment of Atrophic Post Acne Scars: A Split Face Comparative Study. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2018, 29, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faghihi, G.; Keyvan, S.; Asilian, A.; Nouraei, S.; Behfar, S.; Nilforoushzadeh, M. Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined with Fractional Ablative Carbon Dioxide Resurfacing Laser in Treatment of Facial Atrophic Acne Scars: A Split-Face Randomized Clinical Trial. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2016, 82, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, M.N.; Mun, S.K. The Efficacy of Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma Combined with Ablative Carbon Dioxide Fractional Resurfacing for Acne Scars: A Simultaneous Split-Face Trial. Dermatol. Surg. 2011, 37, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, B.; Raj, C. Fractional CO 2 Laser vs Fractional CO 2 with Topical Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Acne Scars: A Split-Face Comparison Trial. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2017, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Yoon, J.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Moon, J.; Kwon, H.H.; Suh, D.H. Combination of Platelet Rich Plasma in Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser Treatment Increased Clinical Efficacy of for Acne Scar by Enhancement of Collagen Production and Modulation of Laser-induced Inflammation. Lasers Surg. Med. 2018, 50, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-T.; Xuan, M.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Liu, H.-W.; Cai, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Xiang, X.-F.; Shan, G.-Q.; Cheng, B. The Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined with Erbium Fractional Laser Therapy for Facial Acne Scars or Acne. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, M.; Xiao, Q.; Zhou, R.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L.; Li, L. Efficacy and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Melasma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbechie-Godec, O.A.; Elbuluk, N. Melasma: An Up-to-Date Comprehensive Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 7, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddaleno, A.S.; Camargo, J.; Mitjans, M.; Vinardell, M.P. Melanogenesis and Melasma Treatment. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, Q.; Xia, Y. New Mechanistic Insights of Melasma. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgado-Carrasco, D.; Piquero-Casals, J.; Granger, C.; Trullàs, C.; Passeron, T. Melasma: The Need for Tailored Photoprotection to Improve Clinical Outcomes. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2022, 38, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qari, S.; Bader, M.; Farran, E.; Borrah, R.; Khamis, S.; Alharbi, Z. Combined Synergetic Effect of Lipoconcentrate Fat Grafting, Nanofat Transfer, Platelet-Rich Plasma, Microneedling, and CO2 Fractional Laser for Plastic Regenerative and Esthetic Surgery and Cosmetic Care. Cureus 2023, 15, e44035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, C.; Tuan, R.S. Biology of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Its Clinical Application in Cartilage Repair. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamata, E.S.; Bartlett, E.L.; Weir, D.; Rohrich, R.J. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Evolving Role in Plastic Surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 147, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Rasmusson, L.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of Platelet Concentrates: From Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma (P-PRP) to Leucocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalon, J.; Chateau, A.L.; Bertrand, B.; Louis, M.L.; Silvestre, A.; Giraudo, L.; Veran, J.; Sabatier, F. DEPA Classification: A Proposal for Standardising PRP Use and a Retrospective Application of Available Devices. BMJ Open Sport. Exerc. Med. 2016, 2, e000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wan, W.; Manole, C.G.; Zhang, Q. Skin Telocytes versus Fibroblasts: Two Distinct Dermal Cell Populations. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2530–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manole, C.G.; Simionescu, O. The Cutaneous Telocytes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 913, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manole, C.G.; Gherghiceanu, M.; Ceafalan, L.C.; Hinescu, M.E. Dermal Telocytes: A Different Viewpoint of Skin Repairing and Regeneration. Cells 2022, 11, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manole, C.G.; Cismaşiu, V.; Gherghiceanu, M.; Popescu, L.M. Experimental Acute Myocardial Infarction: Telocytes Involvement in Neo-Angiogenesis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 2284–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cismasiu, V.B.; Radu, E.; Popescu, L.M. MiR-193 Expression Differentiates Telocytes from Other Stromal Cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolescu, M.I.; Manole, C.G. Telocytes and Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 752.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Category | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| I | Pure PRP (P-PRP) | Leukocyte-poor preparations with a low-density fibrin network upon activation. |
| II | Leukocyte and platelet-rich plasma (L-PRP) | Contains leukocytes and forms a low-density fibrin network upon activation. |
| III | Pure platelet-rich fibrin (P-PRF) | Leukocyte-poor preparations with a high-density fibrin network. Mixed with an activator and requiring a specific separator gel. |
| IV | Leukocyte and PRF (L-PRF) | Contains leukocytes and has a high-density fibrin network. Blood is centrifuged immediately after collection without the use of anticoagulants, thrombin, or CaCl2. |
| Author(s) | Study Type | Number of Patients | Interventions | Duration and Frequency | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asif et al. [319] | Placebo-controlled, split-face study | 50 | Micro-needling + PRP vs. Micro-needling alone | Three monthly treatments | 62.2% improvement with PRP combination vs. 45.84% in the control group. |
| Nofal et al. [320] | Randomised, single-blinded, controlled trial | 45 | PRP injections vs. TCA CROSS technique vs. Micro-needling + PRP | Treatment every 2 weeks for 6 weeks | Significant improvement in all groups compared to baseline, but no difference between the groups at 14 weeks. |
| Ibrahim et al. [321] | Randomised, comparative trial | 90 | Micro-needling vs. PRP injections vs. Micro-needling alternating with PRP | Up to six sessions, every 2–4 weeks | Greatest improvement was in the micro-needling + PRP group, followed by PRP alone. Highest patient satisfaction in the combination group. |
| El-Domyati et al. [245] | Randomised, single-blinded, split-face trial | 24 | Micro-needling + PRP vs. micro-needling + TCA 15% vs. micro-needling alone | Treatments every 2 weeks, total of six sessions | At 3 months, combination groups showed higher mean scar improvement than micro-needling alone. No significant difference between combination treatments. |
| Ibrahim et al. [322] | Prospective, single-blinded, split-face clinical trial | 35 | Micro-needling + PRP vs. micro-needling | Treatments every 3 weeks, total of four treatments | No significant difference between the two groups. |
| Chawla et al. [317] | Prospective, comparative, split-face trial | 27 | Micro-needling + PRP vs. micro-needling + topical vitamin C 15% | Treatment every 4 weeks, total of four treatments | At 4 months, the PRP and micro-needling group’s satisfaction rate was higher than that of the micro-needling in association with topical vitamin C group’s. The percentage of patients included in the poor response category was lower in the PRP combination group (22.2%) than in the vitamin C combination group (37%). |
| Faghihi et al. [323] | Randomised, single-blinded, split-face trial | 16 | CO2 laser + PRP vs. CO2 laser | Two monthly treatments | Trend toward improved response with PRP. More erythema and oedema in the PRP group. |
| Lee et al. [324] | Randomised, split-face trial | 14 | CO2 laser + PRP vs. CO2 laser | Two monthly treatments | Faster improvement of laser-induced erythema in PRP group. Shorter mean duration of erythema, oedema, and crusting with PRP. |
| Gawdat et al. [316] | Randomised, split-face, single-blinded, placebo-controlled study | 30 | CO2 laser + PRP (topical/intradermal) vs. CO2 laser | Three monthly sessions | Significant improvement in skin smoothness with PRP. Shorter duration of adverse effects with PRP. |
| Kar and Raj [325] | Randomised, split-face trial | 30 | CO2 laser + PRP vs. CO2 laser | Three monthly sessions | No significant difference in scar scores between PRP and control. Less redness, pain, and swelling with PRP. |
| Min et al. [326] | Prospective, randomised, single-blinded, split-face trial | 25 | CO2 laser + PRP vs. CO2 laser | Two monthly sessions | Greater improvements and patient satisfaction with PRP. Significantly lower side effects with PRP. |
| Zhu et al. [327] | Clinical study | 22 | Erbium laser + topical PRP | Three treatments 1–2 months apart | Moderate clinical improvement post-treatment: 68% of patients rated it as excellent or markedly improved. 91% were satisfied or very satisfied. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manole, C.G.; Soare, C.; Ceafalan, L.C.; Voiculescu, V.M. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Dermatology: New Insights on the Cellular Mechanism of Skin Repair and Regeneration. Life 2024, 14, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010040
Manole CG, Soare C, Ceafalan LC, Voiculescu VM. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Dermatology: New Insights on the Cellular Mechanism of Skin Repair and Regeneration. Life. 2024; 14(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleManole, Catalin G., Cristina Soare, Laura Cristina Ceafalan, and Vlad M. Voiculescu. 2024. "Platelet-Rich Plasma in Dermatology: New Insights on the Cellular Mechanism of Skin Repair and Regeneration" Life 14, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010040
APA StyleManole, C. G., Soare, C., Ceafalan, L. C., & Voiculescu, V. M. (2024). Platelet-Rich Plasma in Dermatology: New Insights on the Cellular Mechanism of Skin Repair and Regeneration. Life, 14(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010040