Abstract
Postural disorders in children and adolescents have an increasing incidence. The aim of this study was to identify the type of postural defects in school-age and preschool children, as well as the external risk factors determined by an inadequate lifestyle. The research included 134 children aged between 5 and 18 years, in whom postural defects were identified. The project involved an examination of the children’s body posture, a survey of the parents to determine the children’s lifestyle, blood tests, and spinal X-rays. A significant percentage (76%) of the children included in the study were underweight. The examination of postural defects in the students revealed scoliosis in 21% of the patients, kyphosis in 7.5%, and lordosis in 1.5%, while 70% of the patients presented an association between at least two postural defects. As far as risk factors are concerned, we identified the presence of rickets sequelae in 70% of the patients, the presence of pectus excavatum in 43% of the patients, genu varum in 15%, and flat foot in 12%. Additionally, 90% of the children had an incorrect posture at the desk, while 42% incorrectly carried their backpack on one shoulder only. In terms of diet quality, associations between an inadequate diet and postural disorders were found for kyphosis, scoliosis, and other deformities. In conclusion, postural abnormalities in children have an increased incidence from an early age and are a result of the change in lifestyle in recent years, represented by sedentarism, a lack of physical activity, the excessive use of electronic devices, stress, and an inadequate diet.
1. Introduction
Characterized as a public health issue, postural changes in children and adolescents have an increasing prevalence, defined by some authors as a social epidemic. While the Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America reports the presence of postural disorders in 9.6 million children under 19 years of age [], studies in Poland report an incidence of between 34 and 69% [,], while in China, the prevalence reaches 80% [], of which 5% are severe deformities.
Although posture is primarily an innate manifestation, it is subject to change and improvement in the process of individual development. Posture is also determined by muscle balance, motor stereotypy, the characteristics of the individual’s higher nervous activity, and character [].
The causes of postural disorders are divided into congenital and acquired, as well as external and internal. Congenital causes include the various pathologies of intrauterine development, affecting the spine or the lower limbs, while acquired causes are represented by injuries or various pathologies such as rickets, tuberculosis, or the various characteristics of occupational activity (e.g., sitting in a chair with the head leaning forward).
The internal causes of postural disorders are represented by chronic diseases or various hearing and vision defects, which cause the patient to adopt incorrect positions in order to compensate for the deficit [].
The external causes of poor posture are determined by a person’s lifestyle. In the modern world of computer and electronic development, children choose forms of leisure that involve sitting in front of devices over physical activity []. Thus, the muscles in the abdomen and back become weakened over time, leading to a redistribution of the load on the passive structures of the spine and, therefore, contributing to a worsening muscle imbalance and the occurrence of postural disorders and pain in the lumbar spine [,].
An important effect on the correct development of the child is rationally organized physical activity during childhood, which contributes to forming and consolidating optimal motor patterns and is a predictor of activity in adulthood [].
Other causes of acquired postural defects in children are emotional problems, eating disorders, insufficient time for sleep, and the poor organization of work and play spaces—e.g., chairs or tables that are too high, insufficient desk space, etc., which lead to the adoption of wrong postures—and, over time, this static stereotype becomes fixed [].
Preventing postural defects is a complex procedure aimed at ensuring both physical and mental general health. This issue is particularly important in children and young people because during growth and maturation, posture can be influenced by many factors, and the most important is that the posture developed during this period prevails, to a large extent, throughout life [,].
The low effectiveness of measures for the timely diagnosis and correction of postural disorders leads to impaired cardiorespiratory function, impaired metabolism, and irreversible changes in the bone system [,,].
The aim of this study was to identify postural defects among school-age and preschool children, to determine their type, and to identify the external risk factors that are determined by an inappropriate lifestyle or unsatisfactory social conditions related to the occurrence of body posture abnormalities. To this end, we aimed to identify the relationships between the occurrence of postural defects and gender, age, and BMI z-score (WHO), as well as the students’ lifestyle in a broad sense (the extent of physical activity, the duration of homework, and nutrition).
2. Materials and Methods
This study involved 134 children aged 5–18 years who were admitted to the pediatric ward or came to the pediatric outpatient clinic and in whom postural defects were identified.
The participating students presented with varying numbers of hours at school or kindergarten, depending on the cycle of education that they were a part of; children were observed to be carrying backpacks of different weights; and school desks were identified as having different sizes.
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
The research took place between September 2023 and April 2024. The project involved examining the children’s body posture, surveying their parents in order to determine the children’s lifestyle, blood tests, and X-rays of the spine. A data analysis was used to establish the determining factors of postural defects. The parents gave their written consent for the examination of their children and for the questionnaire. Participation in the study was voluntary.
2.2. Measurements
The inclusion criteria were school age, the presence of postural defects, and the obtainment of written parental consent for examination. The exclusion criteria were posttraumatic musculoskeletal disorders, genetic defects affecting the musculoskeletal system, systemic diseases, joint and muscle diseases that were a contraindication for examination, significant vision and hearing impairments, and skin disorders.
The examination of the children consisted of
a. The measurement of the children’s height (in centimeters) and weight. Their BMI (body mass index) was calculated, and the BMI values were classified according to the 2007 WHO (World Health Organization) standards []. The z-score and BMI values’ classification into four categories were determined as underweight (a z-score below −2), normal weight (a z-score between −2 and 1), overweight (a z-score above 1), and obese (a z-score above 2).
b. A ruler, a plumb line, and a scoliometer were used to examine body posture.
The examination was performed as follows:
- -
- The child is in a standing position, with their back towards the examiner (who is positioned 1.5–2 m away);
- -
- The positions, the levels, and the inclinations of the different body segments (head, neck, shoulders, arms, and hemithorax) are examined;
- -
- The examination of the landmarks is carried out (posterosuperior iliac spine, iliac crests, scapular spines, shoulder blades, ribs, and vertebral spinous processes), and they are marked with a skin pencil, from bottom to top.
The assessment of specific signs is carried out, taking into account whether the child is right- or left-handed:
- -
- Lumbar bulge, protruding on the convex side of a lumbar curvature (given by the protrusion of the lumbar costiform processes through the muscle mass of the vertebral grooves);
- -
- Rib hump (hemithorax uneveness)—a prominence of the posterior arches of the ribs on the convex side of the thoracic curvature;
- -
- Shoulder asymmetry;
- -
- The unevenness and tilting of the scapular tips (on the convex side, the tip of the scapula is more elevated, more prominent);
- -
- The inequality of the “waist triangles” (between the lateral edges of the thorax and pelvis and the upper limb on that side)—on the concave side, the lower angle of this triangle is sharper and lower than on the opposite side;
- -
- Intergluteal fold—with the cranial extremity towards the convexity of the lumbar curvature;
- -
- Uneven subgluteal folds, lower on side of the convexity of the lumbar spine, the buttock is more prominent.
The examination of the child from the front is carried out, in order to assess the following:
- -
- The degree of symmetry and unevenness of the collarbones, shoulders, and breasts;
- -
- The anterior chondral rib hump (located in the concave part of the main curvature).
Lead wire test—the lead wire is placed at the apex of the C7 spinous process and its position at S1 is observed; if it passes over the S1 spinous process, the scoliosis is balanced; if it passes laterally, the scoliosis is unbalanced on that side; in normal children, the lead wire is placed at the tragus of the ear and it must pass in front of the shoulder and in line with the greater trochanter;
The dynamic examination of the spine is necessary to
- -
- Differentiate a scoliosis proper from a postural defect (scoliotic attitude); the scoliotic attitude is a longer curvature, largely reducible by the anterior flexion of the trunk or the suspension of the child by the head; there are no secondary changes (vertebral rotation); if the curvature persists during the anterior flexion, then the scoliosis is structural.
- -
- Assess, by lateral flexion (lifting the upper limbs from the side of the concavity or association with the lateral inclination of the trunk at 90° towards the convexity), the possibility of the reduction of the lateral inclination and the rotation of the vertebrae of the curvature.
Scoliosis is a deforming condition of the spine, characterized by one or more lateral curvatures visible in the frontal plane, accompanied by the rotation of the vertebrae, with the tendency toward the upper and lower compensation of these curvatures, but without the tendency to reduce them completely (by suspension or decubitus), having an impact on the morphology of the trunk.
Kyphosis is a deforming condition of the spine, characterized by an anterior (sagittal) tilt of the spine, often resulting in a dorsal protrusion, located in the continuity of the spinous processes of the vertebrae.
Hemithorax unevenness (a hump) is a unilateral deformity, seen as a protrusion outside of the spinous processes of the vertebrae, caused by the protrusion of the posterior arches of the ribs and transverse vertebral processes, a consequence of vertebral rotation.
Lordosis is the deforming condition of the spine, rare compared to the previous ones, characterized by a sagittal inclination of the spine, with the concavity oriented posteriorly, or by the accentuation of this curvature that exists physiologically.
c. For the assessment of muscle strength, we used a Saehan dynamometer. Muscle strength was measured with the children standing upright while squeezing the handle of the dynamometer with full force for 3–5 s. The children had three tries, and the best value was recorded. The results were interpreted according to age.
- 1.
- For boys:
- -
- For ages 8 to 11 years, weights ranged from 13.0 to 18.5 kg;
- -
- Ages 12 to 15 years—from 21.6 to 37.6 kg;
- -
- Ages 16 to 19 years—from 45.9 to 51.0 kg.
- 2.
- For girls:
- -
- For ages 8 to 11 years, the standard was from 9.8 to 17.1 kg;
- -
- For ages 12 to 15 years, the standard was from 19.9 to 28.3;
- -
- Ages 16 to 19 years—from 31.3 to 33.8 kg.
The second part of the research process consisted of a self-constructed parent/guardian questionnaire, which contained metric questions and detailed questions about the children’s living conditions, eating habits, time spent in front of the computer for study or fun, physical activity, position at their desk, how they wore their backpack, and the length of their study hours.
Subsequently we took blood samples for hemograms and biochemical tests (calcinemia, creatine kinase, alkaline phosphatase, and vitamin D3). In children with scoliosis, we performed X-rays of the spine in order to calculate the Cobb angle.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The data was processed with IBM SPSS 27. Numerical variables (e.g., age, weight, BMI, hours of classes, hours of play, Cobb angle, etc.) were described as the mean, standard deviation, amplitude and median, as appropriate; to facilitate the risk analysis, for each subject included in the study, the BMI z-score was calculated, with the individual BMI being in relation to the WHO standard values for the age and sex of the subject; categorical variables (e.g., postural deformities, muscle strength, etc.) were presented as absolute and relative frequencies; for normally distributed quantitative variables, the “Independent-Samples T Test” or the ANOVA test were applied; non-parametric tests (the Mann–Whitney U Test or the Kruskal–Wallis test) were used for the asymmetrical distributions; the Pearson Chi Square test or the Fischer’s Exact Test were used to test the association between the risk factors and various postural disorders; the correlation analysis and bivariate logistic analysis were applied and the OR risk was calculated for the various risk factors studied; the results were interpreted for their significance level, assumed at p ≤ 0.05.
2.4. Ethical Considerations
The research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice in Research. The Ethics Committee of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova, Romania, granted the ethical approval for the study: 244/25 October 2023. Participation was voluntary and the participants were informed about the project.
3. Results
- 1.
- General characteristics of the study group
A total of 134 children aged 5–18 years participated in the study, of whom 82 (61%) were boys and 52 (39%) were girls, with the majority (61%) of the subjects coming from urban areas.
In terms of their educational level, most of the subjects attended middle school (34%), followed by primary school (33%), and high school (25%); only 6% of the subjects were preschoolers.
Both the weight and the height of the children varied significantly from a statistical point of view (p < 0.05) between the sexes, with girls being thinner and shorter on average than boys; the BMI (kg/m2), calculated knowing the height and the weight of the children, varied globally between 10.6 and 23.9, with an average of 16.9 ± 2.7. According to this classification, a significant proportion of patients (76%) were underweight; the values of the standardized BMI score [BMI z-score (WHO)] ranged between −4.7 and 2.3 globally, with an average of −0.8 ± 1.2, values that highlight a batch with small deviations from the normal WHO values established for the sex and age of each child; in relation to the BMI z-score, 83% of the subjects were considered to be of a normal weight status, 13% underweight, 3% overweight, and 1% obese. There were no statistically significant differences in the BMI z-score between the genders (−0.8 ± 1.3 for females and 0.7 ± 01.2 for males, p > 0.05) (Table 1) (Figure 1).

Table 1.
Anthropological characteristics of the subjects in relation to the gender component.
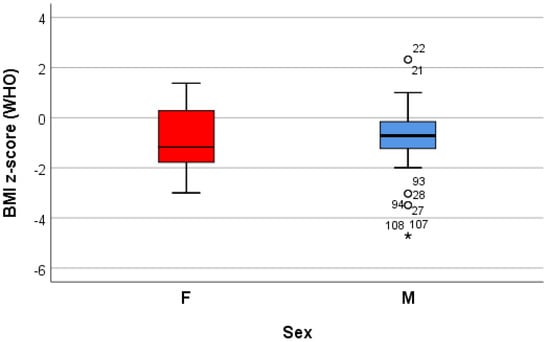
Figure 1.
“Box and whiskers” chart representing the BMI z-score (WHO), according to the gender of the patients.
- 2.
- Postural deformities
The examination of postural defects among students revealed the presence of scoliosis in 21% of the patients, kyphosis in 7.5%, lordosis in 1.5%, while 70% of the patients showed the association of at least two types of defects (Table 2).

Table 2.
The distribution of the patients in relation to the postural deformities recorded: singularly or with their associations.
For all of the postural defects except scoliosis, the results suggest an association between the postural disorder and the gender component, the cases being statistically significantly more frequent in boys than in girls (p < 0.05); only for kyphosis was there an association with the residence environment, the postural disorder being statistically significantly more frequent in urban areas (p < 0.05); the frequencies of the other postural deformities were double in the underweight patients compared to the normal weight ones (p < 0.05) (Table 3).

Table 3.
The associations of the postural deformities with the biological and demographic characteristics.
The combined effect of the children’s weight and height on the probability of developing a particular postural defect was assessed, based on the values of the standardized BMI score (BMI z-score) and the application of the logistic regression model. The odds ratio value (OR—“event odds ratio”) suggests how many times the chance of a given postural defect in a child increases (when OR > 1) or decreases (when OR < 1) when the BMI z-score increases by 1.
The data collected from 10 logistic regression models suggest that growing (increasing) the adjusted BMI z-score by one unit reduces the risk of dorsolumbar kyphosis and hemithorax unevenness. Increasing the adjusted BMI z-score by one unit significantly reduces (p < 0.05) the risk of developing scoliosis (p = 0.039), regardless of the localization; when referring to the localization, increasing the adjusted BMI z-score by one unit significantly reduces (p < 0.05) the risk of developing lumbar scoliosis (p = 0.020) and increases the risk of developing dorsal scoliosis (p = 0.018) (Table 4) (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4).

Table 4.
The influence of BMI on the development of postural disorders.
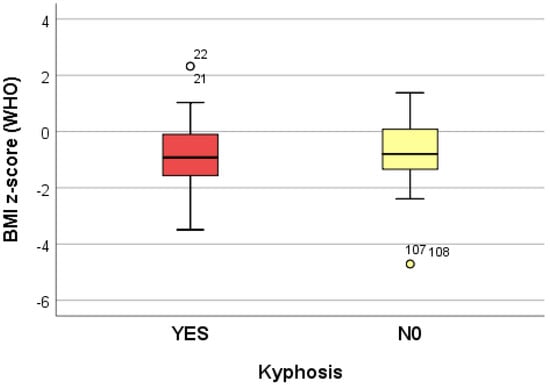
Figure 2.
“Box and whiskers” chart representing the BMI z-score (WHO), according to the presence of kyphosis.
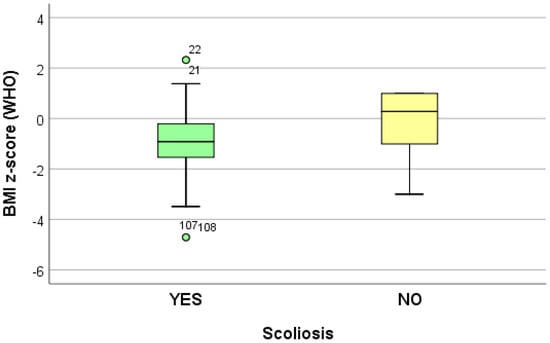
Figure 3.
“Box and whiskers” chart representing the BMI z-score (WHO), according to the presence of scoliosis.
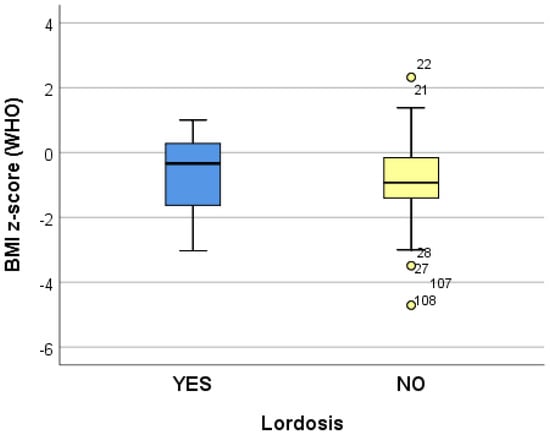
Figure 4.
“Box and whiskers” chart representing the BMI z-score (WHO), according to the presence of lordosis.
For all of the postural deformities, except lordosis, we found statistically significant differences (p < 0.05, X2 test) between the frequency of the postural deformities and the type of education; the highest significance of the education level was found for hemithorax unevenness and for other postural deformities (Table 5).

Table 5.
Distribution of postural deformities by educational level (number of patients).
The stratified analysis at the level of the associations of the postural deformities also highlighted the influence of the demographic characteristics on the postural defects. There were statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between the sub-batches, defined by the associations of the disorders (Table 6).

Table 6.
The biological characteristics of the patients in relation to the type of association of the postural deformities (including hemithorax unevenness).
We analyzed the factors that may pose a risk to children’s correct posture. These included carrying a backpack on one shoulder, the correct posture at the desk, the time allocated to classes, the time necessary for homework, and the time spent in front of electronic devices (phone, tablet), as well as the physical activity, leisure time, and eating habits of the children. We also looked for the presence of rickets sequelae, flat foot, or congenital club foot, as well as the presence of bone deformities in their parents.
Regarding the risk factors, we identified the presence of rickets sequelae in 70% of the patients, the presence of pectus excavatum in 43% of the patients, pectus carinatum in 27%, genu varum in 15%, flat foot in 12%, and the presence of bone deformities in the parents of 28% of the batch. Additionally, 90% of the children had an incorrect posture at the desk, while 42% incorrectly carried their backpack on one shoulder only (Table 7).

Table 7.
The distribution of risk factors in the global batch of postural deformities.
The analysis of the time spent daily in class versus on recreational activities highlights an average of 9 h allocated to classes and homework, 4 h in front of devices, and only 2 h playing (Table 8).

Table 8.
Time allocated to learning and recreational activities, global batch.
Almost a quarter of the patients (25%, 34 patients) were involved in sports, the most common being dancing (29%, 10 patients), sports involving hands (basketball, fencing, tennis, and volleyball) (29%, 10 patients), soccer (24%, 8 patients), and swimming (6%, 2 patients).
More than half of the investigated patients (69%) declared as their lifestyle an inadequate diet, represented by the predisposition for fast-food or irregular meals; the frequency differed statistically significantly (p = 0.000, Fischer’s Exact Test) in relation to the gender component, with boys being the predominant gender group for having an inappropriate diet (83%, 68/82 boys vs. 46%, 24/52 girls).
In terms of diet quality, we found associations between inadequate diet and postural disorders for kyphosis (p = 0.001, Fischer’s Exact Test), scoliosis (p = 0.001, Fischer’s Exact Test), hemithorax unevenness (p = 0.000, Fischer’s Exact Test) and other deformities (p = 0.001, Fischer’s Exact Test), as represented in Table 9.

Table 9.
The distribution of patients with deficient diets in relation to postural deformities and the risk of developing a postural deformity in the case of an inadequate diet.
- 3.
- The relationship between hand and back muscle strength and posture disorders
In half of the study population (68/134 patients), muscle strength was low (10%, 14/134 patients) or reduced (40%, 54/134 patients). The frequency was significantly (p = 0.005) higher in those with kyphosis (60/96 patients with kyphosis vs 8/32 patients without kyphosis) and those with other disorders (p = 0.000, 36/46 patients with other deformities vs. 32/88 patients without other deformities), as well as those with hemithorax unevenness (p = 0.001, 50/68 patients with hemithorax unevenness vs 18/66 patients without hemithorax unevenness). Statistically significant differences (p = 0.024) were also highlighted if the analysis was stratified at the level of the deformity associations (Table 10).

Table 10.
The associative distribution of patients with postural disorders in relation to muscle strength in the hands and back.
- 4.
- The relationship between diagnostic investigations and posture disorders
The stratified analysis at the level of the associations of the postural deformities and diagnostic procedures highlights the effect of vitamin deficiency in the occurrence of associated disorders (statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) for all of the assessments (vitamin D3, Ca, Mg, and alkaline phosphatase) (Table 11).

Table 11.
The statistics of the assessments of vitamin D3, Ca, Mg, and alkaline phosphatase in relation to the associations of the postural deformities.
In the global batch of patients with scoliosis, we identified significant (p < 0.05) direct, weak (r < 0.4) correlations between the Cobb angle and the demographic characteristics (age, weight, height, and BMI). If localization is taken into account, for patients with lumbar scoliosis we identified significant (p < 0.05) direct, medium (0.58 < r < 0.7) correlations between the Cobb angle and the demographic characteristics; for patients with lumbar scoliosis, we identified a significant (p < 0.05) direct, weak (r = 0.3) correlation between the Cobb angle and the weight status (BMI) (Table 12).

Table 12.
Testing the correlation between the Cobb angle and the anthropometric characteristics, scoliosis global batch and by scoliosis localization, respectively.
Testing the correlation between the value of the Cobb angle and the levels of vitamin D, serum calcium, and serum magnesium in the global scoliosis batch revealed statistically significant (p < 0.05) indirect, weak (p < 0.05) correlations between the Cobb angle and vitamin D3 (r = −0.433), Ca (r = −0.382), and Mg (r = −0.310); by localization, in the case of dorsal scoliosis, we identified significant (p < 0.05) indirect, weak-to-medium correlations between the Cobb angle and both Ca deficiency (r = −0.476) and leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (r = −0.361); in the case of dorsolumbar scoliosis, we identified significant (p < 0.05) indirect, weak-to-medium correlations between the Cobb angle and the levels of Ca (r = −0.478) and Mg (r = −0.439), as well as indirect, intense correlations with vitamin D3 (r = −0.730); we identified direct correlations (r = 0.475) with the ALP level.
In the global scoliosis group, we identified significant (p < 0.01) direct, weak correlations with class hours (r = 0.409) and with hours spent doing homework (r = 0.349); between the Cobb angle and the hours spent in front of the screen, the correlation was very weak (r = 0.218); between play hours and the Cobb angle value, we identified significant (p < 0.01), indirect, weak-to-medium (r = −0.472) correlations.
In the sub-batches of scoliosis localization, only in the case of dorsal scoliosis was a significant (p < 0.05) direct, weak correlation identified between the Cobb angle and the hours spent in front of devices (r = 0.359); in the case of dorsolumbar scoliosis, a significant (p < 0.05) direct, medium-to-intense correlation was identified between the Cobb angle and the hours spent learning or doing homework; an indirect, medium correlation was identified with the hours spent playing (r = −0.504) (Table 13).

Table 13.
Testing the correlation between the Cobb angle and the risk factors represented by the time allocated to various activities; sub-batches—the localization of scoliosis.
4. Discussion
Postural disorders have an increasing incidence among children, and studies are trying to identify the multiple risk factors involved in their occurrence. The prevention, early diagnosis, and treatment of postural defects, as well as the identification of the modifiable risk factors that may influence the disease and the establishment of appropriate strategies aimed at preventing them, are of great importance [].
There are certain periods of accelerated growth in a child’s life which are accompanied by postural changes and which require close parental supervision: early childhood and adolescence. Studies indicate that only 18–50% of children and adolescents have a correct body posture [,], with the majority of school-age children, especially primary and secondary school children, presenting posture disorders [].
In our study, the participants were patients aged 5–18 years; most of them were attending secondary school (35%), followed by primary school at 33.5%, but 5.9% were aged 5–6 years, which is in line with the data from previous studies, describing the occurrence of spinal deformities and postural disorders in children in their first year of school (6–7 years) [,].
The majority of the children in this study with posture disorders were male, as shown in the study conducted in 2023 by Anna Baranowska [], while Lei 2020 [] and Penha [] indicated a higher incidence in females, which was attributed to lower physical activity in girls compared to boys [,].
There are also studies on postural disorders in children that found no statistically significant differences between the parameters characterizing the posture of girls and boys [,].
Childhood obesity is a problem of global importance, with the WHO reporting an increase from 8% in 1990 to 20% in 2022. The overloading of the musculoskeletal system, as well as reduced physical activity, leads to the improper development of body posture patterns during the growth and development of children. Numerous studies have shown an increased incidence of postural disorders in overweight or obese children [,,,], but there are also studies that could not indicate an association between obesity and the occurrence of postural disorders [,].
In our research, based on the BMI classification (WHO z-score), the group of children examined was mostly in the normal weight range (83%), and no correlation between weight and postural disorders could be established.
The main postural defects found in the study were scoliosis in 86.5% of the patients, followed by kyphosis in 71%, lordosis in 28.4%, flat feet in 12%, and, very importantly, 70% of the children presented with more than two disorders in association.
In Anna Baranowska’s study, the main diagnosis was hyperlordosis (24.1%); scoliotic posture was present in one-third of the children studied, flat back in 18.4%, and the majority (75%) had more than one abnormality []. Lazić et al. determined a high incidence of scoliosis (67%) among the children and adolescents studied; hyperkyphosis was present in 27% of the children and hyperlordosis in 6% [], while Kolarová et al. diagnosed 65% of the children studied with a fallen foot arch, over 30% of the children with spinal curvature deformities in the sagittal plane, and 13% of the children with deformities in the frontal plane []. Dragić et al. determined an incidence of 83.9% of the children studied with some type of postural disorder in the sagittal plane [].
A large number of studies have been conducted on the impact of the weight of a school backpack on children [,], the correlation of its weight with gender or age, as well as the effect of asymmetrical carrying on one shoulder only [,].
For example, a study carried out by Spiteri et al. in schools in Malta showed that more than 70% of the students who were aged 8–13 years had a backpack exceeding the recommended backpack-weight-to-body-weight ratio of 10%, and a third of the children complained of back pain []. In a Polish study, although 60.2% of the students surveyed had a backpack weighing more than 10% of their body weight, no strong, statistically significant correlations were found between the weight of the school backpack and the incidence of postural defects [].
Carrying a backpack in an asymmetrical manner (on one shoulder) was found to negatively affect the spine, even if the weight of the backpack constituted 10% of the child’s weight, which was previously recommended as a safe shoulder load for a child’s shoulders [,].
Similarly, in our study, 42% of the children were carrying the backpack asymmetrically, on one shoulder, but, statistically, it was not possible to correlate asymmetrical carrying with the occurrence of posture disorders.
Another risk factor tracked in our study was poor posture at the home desk or school desk due to the use of non-ergonomic furniture, as was also shown in studies conducted in Poland, where 90% of children had an incorrect posture at the desk [].
The analysis of time spent in class versus on recreational activities in our study shows an average of 9 h allotted to classes and homework, 4 h in front of devices, and only 2 h for play. Most of the children sit at school desks that are not ergonomically adequate, thus having poor posture.
The list of risk factors associated with posture disorders that were assessed also included habits related to the use of mobile devices (watching TV, using computers, smartphones, and tablets), a common practice, especially among adolescents []. Thus, in 2018, approximately 95% of adolescents in the United States had access to smartphones, and, according to an international study, 44.4% of schoolchildren spend 4 h in front of a screen on days without school [,].
According to studies, the posture adopted for the use of a smartphone or a computer could cause defects related to the positioning of the shoulder blades in relation to each other and neck and shoulder discomfort, but this topic requires further investigation and new tools to assess the habits of mobile device use among children [,].
Nearly a quarter of the patients in our study [25%] engaged in a sports activity, the most common being dancing [29%], sports involving hands (basketball, fencing, tennis, and volleyball) [29%], soccer [24%], and swimming [6%].
In other studies, regular physical activity in school-aged children, at least three times a week, has been shown to help prevent postural abnormalities in the trunk, especially pilates, which can improve rib cage expansion and trunk flexibility []. Other sports, such as football and basketball, by improving neuromotor control, provide support to the trunk and pelvis, preventing spinal deformities, while rhythmic gymnastics and ballet are sports that increase the risk of spinal deformities [,].
Research conducted in Serbia over the last few decades has shown a linear decrease in the motor abilities of children [] with postural disorders, correlated with low levels of physical activity [,], which was also confirmed in our study, despite the different tests used.
More than half of the patients investigated in this study (69%) reported an inadequate diet as a lifestyle, represented by a predisposition for fast-food or irregular meals, which was also confirmed in Latalski’s study in 2013, in which 59.5% of patients with posture disorders had an unbalanced diet [].
Testing the correlation between the value of the Cobb angle and the levels of vitamin D, serum calcium, and serum magnesium showed a significant association, which was also confirmed in other preliminary studies that indicated an association between vitamin D and calcium deficiency and a significant increase in the Cobb angle [], as well as in other studies [,].
5. Conclusions
The majority of the children in our study showed an association of postural defects, predominantly the boys: they are sitting at school desks that are not ergonomically adequate, carrying their backpacks asymmetrically, spending more hours in front of electronic devices than doing physical activity, and have inadequate diets. Vitamin D, calcium, and magnesium deficiency also accelerates the progression of postural defects.
In conclusion, postural abnormalities in children have an increased incidence from an early age and are a result of negative lifestyle changes in recent years, both in children and their parents, represented by a sedentary lifestyle, a lack of physical activity, the excessive use of electronic devices, stress, and an inadequate diet.
Cohort studies are needed to identify the impact of environmental factors or lifestyle changes that cause the onset of postural disorders in children.
Education, awareness, the early identification of risk factors, and their removal, together with early diagnoses, are effective and imperative.
Limitations of Study
The limitations of this study are primarily related to the small number of participants and the cross-sectional nature of the study, based on self-reported data, which did not allow us to analyze the cause/effect associations of postural changes and lifestyle, but only the associations between the presence of musculoskeletal changes and the different risk factors through a multivariable analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.D. and I.R.M.; methodology, V.P. and R.P.; validation, S.-A.N. and A.N.D.; formal analysis, A.M.; investigation, D.M.; data curation, C.E.N.; writing—original draft preparation, V.P. and I.R.M.; writing—review and editing, D.D.; supervision, D.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The present study was supported by RIPLU TARGOVISTE S.R.L. (Targoviste, Romania), as a research grant of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova (grant no. 26/721/2/21.07.2023).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice in Research. The Ethics Committee of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova, Romania, granted the ethical approval for the study: 244/25 October 2023.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rusnák, R.; Kolarová, M.; Aštaryová, I.; Kutiš, P. Screening and Early Identification of Spinal Deformities and Posture in 311 Children: Results from 16 Districts in Slovakia. Rehabil. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 4758386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brzęk, A.; Dworrak, T.; Strauss, M.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Sabbah, I.; Dworrak, B.; Leischik, R. The weight of pupils’ schoolbags in early school age and its influence on body posture. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, L.; Lu, X.; Yan, B.; Huang, Y. Prevalence of Incorrect Posture among Children and Adolescents: Finding from a Large Population-Based Study in China. Iscience 2020, 23, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Banjevic, B. Analysis of postural disorders with preschool and school children at the regional level. J. Anthropol. Sport Phys. Educ. 2022, 6, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.-X.; Huang, C.-A.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Shi, Y.-F.; Chen, B.-D.; Zhang, H.-W.; Dai, Z.-Y.; Yu, X.-P.; Wang, X.-Y. Prevalence of the thoracic scoliosis in children and adolescent candidates for strabismus surgery: Results from a 1935-patient cross-sectional study in China. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minghelli, B.; Oliveira, R.; Nunes, C. Non-specific low back pain in adolescents from the south of Portugal: Prevalence and associated factors. J. Orthop. Sci. 2014, 19, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rosa, B.N.; Candotti, C.T.; Pivotto, L.R.; Noll, M.; Silva, M.G.; Vieira, A.; Loss, J.F. Back Pain and Body Posture Evaluation Instrument for Children and Adolescents (BackPEI-CA): Expansion, Content Validation, and Reliability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, J.J.; Graciosa, M.D.; de Medeiros, D.L.; Pacheco, S.C.; da Costa, L.M.; Ries, L.G. Influência da flexibilidade e sexonapostura de escolares [Influence of flexibility and gender on the posture of school children]. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2014, 32, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Voichyshyn, L.; Golod, N.; Marchuck, O.; Zastavna, O.; Chepurna, L.; Rybalko, P.; Khomenko, S.; Kuzmik, V.; Kolisnyk, S.; Babii, I. Physical Rehabilitation of Adolescents with Postural Disorders in the Sagittal Plane and its Relation to Neurophysiology. BRAIN Broad Res. Artif. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, M.; Yoshizawa, E.; Hayata, G.; Ohashi, S. Physical and psychological effects of postural educational intervention for students experienced school refusal. Curr. Psychol. 2023, 42, 3510–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonja-Medina, F.; Collazo-Diéguez, M.; Martínez-Romero, M.T.; Rodríguez-Ferrán, O.; Aparicio-Sarmiento, A.; Cejudo, A.; Andújar, P.; Sainz de Baranda, P. Classification System of the Sagittal Integral Morphotype in Children from the ISQUIOS Programme (Spain). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Penha, P.J.; João, S.M.; Casarotto, R.A.; Amino, C.J.; Penteado, D.C. Postural assessment of girls between 7 and 10 years of age. Clinics 2005, 60, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebo, B.G.; Henry, J.; Lafage, V.; Berjano, P. Sagittal deformities of the spine: Factors influencing the outcomes and complications. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24 (Suppl. S1), 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widhe, T. Spine: Posture, mobility and pain. A longitudinal study from childhood to adolescence. Eur. Spine J. 2001, 10, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marcu, I.R.; Dop, D.; Padureanu, V.; Niculescu, S.A.; Padureanu, R.; Niculescu, C.E.; Rogoveanu, O.C. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Etoricoxib Facilitates the Application of Individualized Exercise Programs in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis. Medicina 2020, 56, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- WHO Fact Sheet. Obesity and Overweight. 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/ (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Araújo, C.L.; Moreira, A.; Carvalho, G.S. Postural Education Programmes with School Children: A Scoping Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratenová, J.; Žejglicová, K.; Malý, M.; Filipová, V. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Poor Posture in School Children in the Czech Republic. J. Sch. Health 2007, 77, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafond, D.; Descarreaux, M.; Normand, M.C.; Harrison, D.E. Postural development in school children: A cross-sectional study. Chiropr. Osteopat. 2007, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Burdukiewicz, A.; Miałkowska, J.; Pietraszewska, J. Body build versus body posture of children and youth aged 7–12 years. Stand. Med. 2006, 3, 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- Brianezi, L.; Cajazeiro, D.C.; Maifrino, L.B.M. Prevalence of postural deviations in school of education and professional practice of physical education. Morphol. Sci. 2011, 28, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Baranowska, A.; Sierakowska, M.; Owczarczuk, A.; Olejnik, B.J.; Lankau, A.; Baranowski, P. An Analysis of the Risk Factors for Postural Defects among Early School-Aged Children. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Penha, P.J.; Penha, N.L.J.; De Carvalho, B.K.G.; Andrade, R.M.; Schmitt, A.C.B.; João, S.M.A. Posture alignment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Photogrammetry in scoliosis school screening. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2017, 40, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, O.; Mazet, C.; Mazet, D.; Hammes, A.; Schmitt, E. Age-dependency of posture parameters in children and adolescents. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 1607–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster, M.; Lee, A.J.; Burwell, R.G. Physical activities of patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) compared with a control group: Implications for etiology and possible prevention. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2006, 88-B (Suppl. II), 225. [Google Scholar]
- Drzał-Grabiec, J.; Truszczyńska, A.; Rykała, J.; Rachwał, M.; Snela, S.; Podgórska, J. Effect of asymmetrical backpack load on spinal curvature in school children. Work 2015, 51, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzeziński, M.; Czubek, Z.; Niedzielska, A.; Jankowski, M.; Kobus, T.; Ossowski, Z. Relationship between lower-extremity defects and body mass among polish children: A cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciałczyk-Paprocka, K.; Stawińska-Witoszyńska, B.; Kotwicki, T.; Sowińska, A.; Krzyżaniak, A.; Walkowiak, J.; Krzywińska-Wiewiorowska, M. Prevalence of incorrect body posture in children and adolescents with overweight and obesity. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2017, 176, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latalski, M.; Bylina, J.; Fatyga, M.; Repko, M.; Filipovic, M.; Jarosz, M.J.; Borowicz, K.B.; Matuszewski, Ł.; Trzpis, T. Risk factors of postural defects in children at school age. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2013, 20, 583–587. [Google Scholar]
- Gijon-Nogueron, G.; Martinez-Nova, A.; Alfageme-Garcia, P.; Montes-Alguacil, J.; Evans, A.M. International normative data for paediatric foot posture assessment: A cross-sectional investigation. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e023341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bubanj, S.; Đorđević, S.; Milenković, S.; Stanković, R.; Vidojević, M.; Đokić, M. Postural Disorders and Muscle Power in Primary School Children. Acta Fac. Medicae Naissensis 2021, 38, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarová, M.; Kutiš, P.; Rusnák, R.; Hrčková, Z.; Hudáková, Z.; Lysá, Ľ.; Luliak, M.; Babeľa, R. Analysis of body segments and postural state in school children. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2019, 40 (Suppl. S1), 17–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Genitrini, M.; Dotti, F.; Bianca, E.; Ferri, A. Impact of Backpacks on Ergonomics: Biomechanical and Physiological Effects: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Walicka-Cupryś, K.; Skalska-Izdebska, R.; Rachwał, M.; Truszczyńska, A. Influence of the Weight of a School Backpack on Spinal Curvature in the Sagittal Plane of Seven-Year-Old Children. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 817913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, M.H.; Yi, C.H.; Kwon, O.Y.; Cho, S.H.; Yoo, W.G. Changes in Neck Muscle Electromyography and Forward Head Posture of Children When Carrying Schoolbags. Ergonomics 2008, 51, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, M.; Orr, R.; Hing, W.; Milne, N.; Pope, R. The Impact of Backpack Loads on School Children: A Critical Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, K.; Busuttil, M.L.; Aquilina, S.; Gauci, D.; Camilleri, E.; Grech, V. Schoolbags and back pain in children between 8 and 13 years: A national study. Br. J. Pain 2017, 11, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzał-Grabiec, J.; Snela, S.; Rachwał, M.; Podgórska, J.; Rykała, J. Effects of Carrying a Backpack in an Asymmetrical Manner on the Asymmetries of the Trunk and Parameters Defining Lateral Flexion of the Spine. Hum. Factors 2015, 57, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrini, S.; Negrini, A. Postural Effects of Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Loads on the Spines of Schoolchildren. Scoliosis 2007, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozkowiak, M.; Żukowska, H. The significance of Good Chair as part of children’s school and home environment in the preventive treatment of body statistics distortions. J. Educ. Health Sport 2015, 5, 179–215. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Grote, L.; Kothgassner, O.D.; Felnhofer, A. Risk factors for problematic smartphone use in children and adolescents: A review of existing literature. Neuropsychiatrie 2019, 33, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Jiang, J. Teens, social media and technology 2018. Pew Res. Center 2018, 31, 1673–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Spina, G.; Bozzola, E.; Ferrara, P.; Zamperini, N.; Marino, F.; Caruso, C.; Antilici, L.; Villani, A. Children and Adolescent’s Perception of Media Device Use Consequences. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, S.Y.; De Chen, M.; Huang, Y.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, J.H. Association Between Smartphone Use and Musculoskeletal Discomfort in Adolescent Students. J. Community Health 2017, 42, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, E.; Thomée, S.; Grimby-Ekman, A.; Hagberg, M. Texting on mobile phones and musculoskeletal disorders in young adults: A five-year cohort study. Appl. Ergon. 2017, 58, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rrecaj-Malaj, S.; Beqaj, S.; Krasniqi, V.; Qorolli, M.; Tufekcievski, A. Outcome of 24 Weeks of Combined Schroth and Pilates Exercises on Cobb Angle, Angle of Trunk Rotation, Chest Expansion, Flexibility and Quality of Life in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2020, 26, e920449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Watanabe, K.; Michikawa, T.; Yonezawa, I.; Takaso, M.; Minami, S.; Soshi, S.; Tsuji, T.; Okada, E.; Abe, K.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Physical activities and lifestyle factors related to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2017, 99, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaturro, D.; Costantino, C.; Terrana, P.; Vitagliani, F.; Falco, V.; Cuntrera, D.; Sannasardo, C.E.; Vitale, F.; Letizia Mauro, G. Risk Factors, Lifestyle and Prevention among Adolescents with Idiopathic Juvenile Scoliosis: A Cross-Sectional Study in Eleven First-Grade Secondary Schools of Palermo Province, Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Andrašić, S.; Milić, Z.; Cvetković, M.; Ujsasi, D.; Orlic, D. Relations between biomechanical parameters and static power of arms in children with disturbed posture. Index Cover. 2017, 15, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Herdea, A.; Charkaoui, A.; Ulici, A. Prevalence of 25-OH-Vitamin D and Calcium Deficiency in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Med. Life 2020, 13, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, R.M.B.F.; Martins, D.E.; Wajchenberg, M.; Lazaretti, M.; Puertas, E.B.; Terreri, M.T.S.L.R.A.; Hayashi, L.F. Association between vitamin D levels and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Coluna/Columna 2014, 13, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevin, L. Effective therapeutic control of curve progression using calcium and vitamin D supplementation for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis—A randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial. Bone Abstr. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).