Artificial Intelligence in the Non-Invasive Detection of Melanoma
Abstract
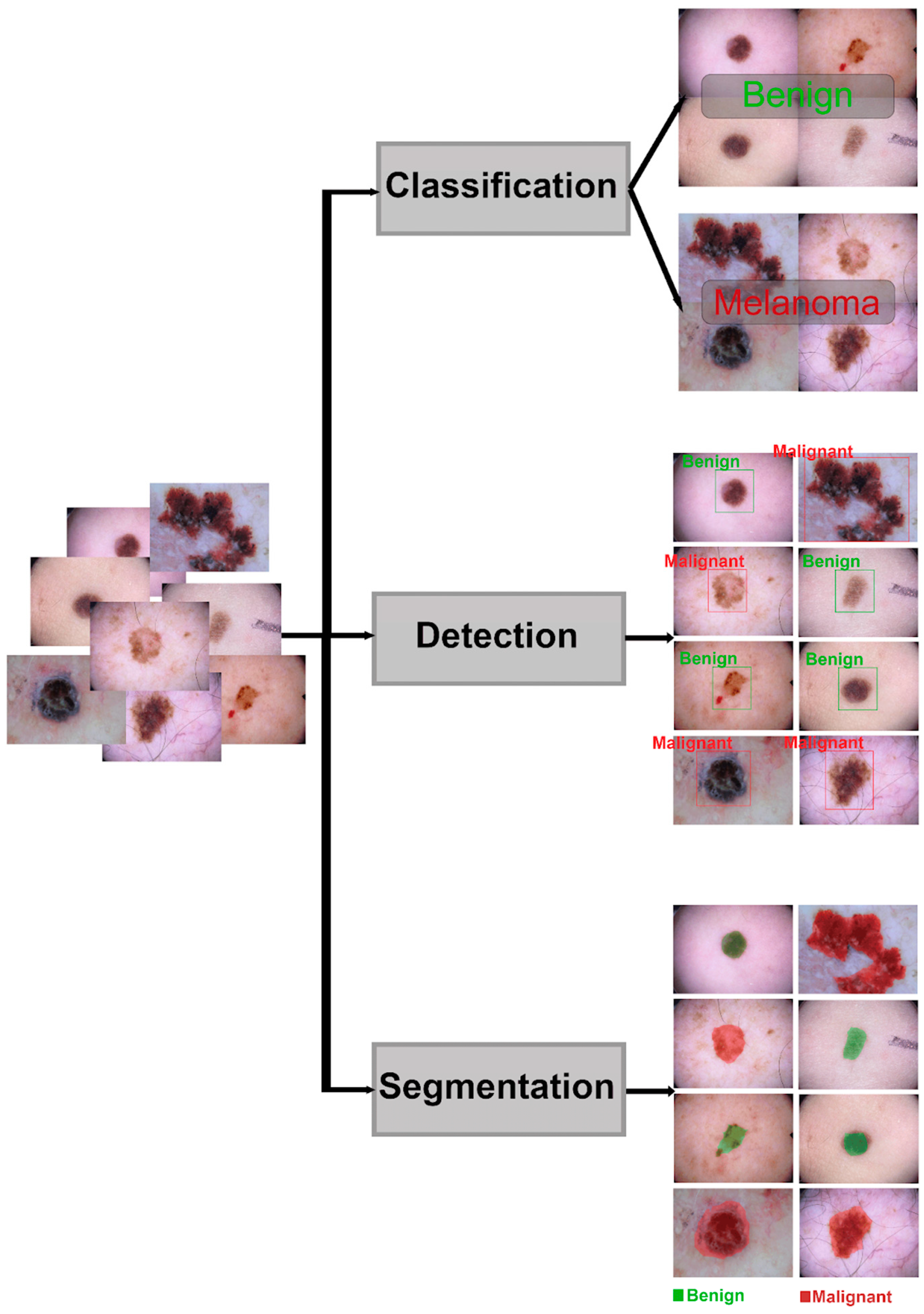
1. Introduction
1.1. Artificial Intelligence: Fundamental Principles
1.2. Evaluating Artificial Intelligence Algorithms
2. Datasets
2.1. ISIC Archive
2.2. HAM10000
2.3. PH2
2.4. DERMOFIT Image Library: Edinburgh Dataset
2.5. BCN20000
2.6. DermQuest
2.7. DermIS
2.8. Asan Dataset
2.9. MED-NODE
2.10. Fitzpatrick 17k
2.11. SCIN
2.12. SkinCAP
2.13. SLICE-3D Dataset
2.14. Diverse Dermatology Images
2.15. PAD-UFES-20
3. Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis of Melanoma
3.1. Utilization of Clinical Images
3.2. Utilization of Dermoscopic Images
3.2.1. Distinguishing Melanoma from Benign Lesions
| Publication | End-Point | Dataset | Algorithm | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masood et al. [51] | Classification (benign/melanoma) | 135 images (Clinical + dermoscopic) 107 for training, 14 for validation 14 for testing. Images were obtained from one clinic in France; the ethnicity and skin types were not specified. | Compared 3 ANN algorithms (RP, L-M, SCG) | SCG: Acc: 91.9% Sen: 92.6% Spe: 91.4% L-M: Acc: 91.1% Sen: 85.2% Spe: 95.1% RP: Acc: 88.1% Sen: 77.8% Spe: 95.1% |
| Aswin et al. [65] | Classification (Cancerous/Non-cancerous) | 30 dermoscopic images for training. 50 dermoscopic images for testing. No further information regarding the dataset was provided. | Hybrid Genetic Algorithm + ANN | Acc: 88% |
| Xie et al. [66] | Classification (MM/BN) | Dermoscopic images Xanthous race: 240 images (80 MM, 160 BN). Caucasian race: 360 images (120 MM, 240 BN). Images were obtained from a clinic in China. | Proposed: meta-ensemble model of multiple neural network ensembles Ensemble 1: single-hidden-layer BP nets with the same structures Ensemble 2: single-hidden-layer BP nets and fuzzy nets Ensemble 3: double-hidden-layer BP nets with different structures | Xanthous race: Sen: 95% Spe: 93.75% Acc: 94.17% Caucasian race: Sen: 83.33% Spe: 95% Acc: 91.11% |
| Marchetti et al. [52] | Classification (MM/BN) | ISBI 2016 challenge dataset [67]: MM: 248 images, BN: 1031 images, Train set: 900 images, Test set: 379 images, Reader study: 100 images (50 MM, 50 BN). | Five methods (unlearned and machine learning) were used to combine individual automated predictions into “fusion” algorithms | Top Fusion Algorithm: Greedy Fusion: Sen: 58% Spe: 92% AUC: 86% Dermatologists: Sen: 82% Spe: 59% AUC: 71% |
| Marchetti et al. [53] | Classification (MM/BN/SK) and (biopsy/observation) | ISIC archive [19]: 2750 dermoscopy images (521 (19%) MM, 1843 (67%) BN, and 386 (14%) SK). Training set: 2000 images, Validation: 150 images, Test set: 600 images. | ISBI 2017 Challenge top-ranked algorithm | Algorithm: Sen: 76% Spe: 85% AUC: 0.87 Dermatologists: Sen: 76.0% Spe: 72.6% AUC: 0.74 |
| Cueva et al. [68] | Classification (Cancerous/Non-cancerous) | PH2 database [23]: Training set: 30 images (10 MM, 10 common mole, 10 no-common mole). Test set: 201 images (80 common mole, 80 no-common mole, 41 MM). | ANN with backpropagation algorithm | After an analysis of 201 images in the algorithm developed a performance of 97.51% was obtained |
| Navarro et al. [69] | Segmentation and registration to evaluate lesion change | ISIC archive [19]: Training set: 2000 dermoscopic images. Validation: 150 dermoscopic images. Test set: 600 dermoscopic images. | Segmentation: LF-SLIC Registration: SP-SIFT | Acc: 0.96 for segmentation |
| Yu C. et al. [54] | Classification (melanoma/non-melanoma) | 725 images obtained from two clinics in South Korea. The ethnicity and skin types were not specified. (AM: 350 images, BN: 374 images). Group A: 175 images. AM, 187 images BN. Group B: 175 images. AM, 187 images BN. Training set: Group A images for training Group B. Group B images for training Group A. Test set: Group A images for Group A. Group B images for Group B. | CNN (VCG-16) | Group A: CNN: Sen: 92.57% Spe: 75.39% Acc: 83.51% Expert: Sen: 94.88% Spe: 68.72% Acc: 81.08% Non-expert: Sen: 41.71% Spe: 91.28% Acc: 67.84% Group B: CNN: Sen: 92.57% Spe: 68.16% Acc: 80.23% Expert: Sen: 98.29% Spe: 65.36% Acc: 81.64% Non-expert: Sen: 48.00% Spe: 77.10% Acc: 62.71% |
| Abbas et al. [55] | Classification (benign nevus/acral melanoma) | 724 images from Yonsei University, South Korea. The ethnicity and skin types were not specified [54] (350 acral melanoma, 374 benign nevi). 4344 images with data augmentation (2100 acral melanoma, 2244 benign nevi). | Compared three CNN algorithms (Seven-layered deep CNN, ResNet-18, AlexNet) | ResNet-18 Acc: 0.97 AUC: 0.97 AlexNet: Acc: 0.96 AUC: 0.96 Proposed ConvNet Acc: 0.91 AUC: 0.91 |
| Fink et al. [56] | Classification (Benign/Malignant) | Training set: >120,000, dermoscopic images and labels. Test set: 72 images (36 combined naevi, 36 melanomas). Images were obtained from three clinics in Germany; the skin types and ethnicity were not specified. | CNN (Moleanalyzer-Pro) based on a GoogleNet Inception_v4 architecture | CNN: Sen: 97.1% Spe: 78.8% Dermatologists: Sen: 90.6% Spe: 71.0% |
| Phillips et al. [70] | Classification (MM/dysplastic nevi/other) | Pretrained algorithm Training set (in study): 289 images (36 melanoma lesions; 67 nonmelanoma lesions, 186 control lesions). Test set: 1550 images Images were obtained from three clinics in Germany; the ethnicity and skin types were not specified. | SkinAnalytics (CNN) | The algorithm: İphone 6s image: AUC: 95.8% Spe: 78.1% Galaxy S6 image: AUC: 93.8% Spe: 75.6% DSLR image: AUC: 91.8% Spe: 45.5% Specialists: AUC: 77.8% Spe: 69.9% |
| Martin-Gonzalez et al. [71] | Classification (benign/ malignant skin lesion) | Pretrained with 37,688 images from ISIC archive [19] 2019 and 2020. Training set: 339 images (143 MM, 196 BN). Test set: 232 images (55 MM, 177 BN). Test set images were obtained from the clinic in Spain. The images used in the study were of light-skinned patients. | QuantusSKIN (CNN) | AUC: 0.813 Sen: 0.691 Spe: 0.802 Acc: 0.776 |
| Brinker et al. [57] | Classification (Melanoma/Nevi) | Training set: 12,378 dermoscopic images from the ISIC dataset [19]. Test set: 100 dermoscopic images (20 MM, 80 Nevi). | ResNet-50 (CNN) | Algorithm: Sen: 74.1% Spe: 86.5% Dermatologists: Sen: 74.1% Spe: 60% |
| Giulini et al. [58] | Classification (Melanoma/Nevi) | Over 28,000 dermoscopic images; the ethnicity and skin types of the training set were not specified. CNN test set: 2489 images (344 melanomas, 2155 nevi). Physician test set: 100 images (50 MM, 50 nevi). The test set consisted of images of patients with Fitzpatrick skin types 1–4. | Session 1: Physicians without CNN Session 2: Physicians with CNN | Physicians without CNN Sen: 56.31% Spe: 69.28% Physicians with CNN Sen: 67.88% Spe: 73.72% |
| Ding et al. [72] | Classification (Binary: melanoma/non-melanoma and multiclass: benign nevi, seborrheic keratosis or melanoma) | ISIC dataset [19]: Training set: 2000 images (374 MM, 254 SK, 1372 BN). Validation set: 150 images (30 MM, 42 SK, 78 BN). Test set: 600 images (117 MM, 90 SK, 393 BN). | Segmentation: U-Net Classification: Five CNNs (Inception-v3, ResNet-50, Densenet169, Inception-ResNet-v2, and Xception) with SE-block and the neural network for ensemble learning consisting of two local connected layers and a softmax layer | Binary: Inception-v3 Acc: 0.885 AUC: 0.883 ResNet-50 Acc: 0.88 AUC: 0.882 Densenet169 Acc: 0.893 AUC: 0.882 Inception-ResNet-v2 Acc: 0.89 AUC: 0.894 Xception Acc: 0.891 AUC: 0.896 Ensemble Acc:0.909 AUC: 0.911 Multiclass: Inception-v3 Acc: 0.792 AUC: 0.883 ResNet-50 Acc: 0.762 AUC: 0.864 Densenet169 Acc: 0.800 AUC: 0.881 Inception-ResNet-v2 Acc: 0.800 AUC: 0.873 Xception Acc: 0.810 AUC: 0.896 Ensemble Acc: 0.851 AUC: 0.913 |
| Yu L. et al. [73] | Segmentation and Classification (Benign/Malignant) | ISIC dataset [19]: Training set: 900 images. Test set: 350 images. | FCRN for skin lesion segmentation and very deep residual network for classification | Segmentation: Sen: 0.911 Spe: 0.957 Acc: 0.949 Classification with segmentation: Sen: 0.547 Spe: 0.931 Acc: 0.855 |
| Bisla et al. [74] | Classification (Nevus, SK, MM) | Training set: ISIC dataset [19]: 803 MM, 2107 nevus, 288 SK. PH2 dataset [23]: 40 MM, 80 Nevus Edinburgh dataset. [25]: 76 MM, 331 nevus, 257 SK. Test set: ISIC data sets 600 images (117 MM, 90 SK, and 393 nevus), | Segmentation: Modified U-Net (CNN) Augmentation: de-coupled DCGANs Classification:ResNet-50 | AUC: 0.915 Acc: 81.6% |
| Mahbod et al. [59] | Classification (MM/All, SK/All) | ISIC dataset [19]: Training: 2037 dermoscopic images (411 MM, 254 SK, 1372 BN). | Feature Extraction: Pretrained CNNs (AlexNet, ResNet-18 and VGG16) Classification: SVM | AUC: 90.69 |
| Bassel et al. [75] | Classification (Benign/Malignant) | ISIC dataset [19]: 1800 images of benign type and 1497 pictures of malignant cancer. Training set: 70% of images (1440 benign, 1197 malignant). Test set: 30% of images (360 benign, 300 malignant). | Model 1:Feature Extraction: ResNet50 Model 2:Feature Extraction: VCG-16 Model 3:Feature Extraction: Xception Classification: Stacked CV model (SVM+NN+RF+KNN) | ResNet Model: Acc: 81.6% AUC: 0.818 VCG-16 Model: Acc: 86.5% AUC: 0.843 Xception Model: Acc: 90.9% AUC: 0.917 |
| Ningrum et al. [60] | Classification (Melanoma/benign) | ISIC dataset [19]: 900 images. Training set: 720 images. Validation set: 180 images. Test set: 300 (93 malignant, 207 nonmalignant). | Classification: CNN model for images + ANN model for patient metadata | CNN Acc: 73.69 AUC: 82.4 CNN+ANN Acc: 92.34 AUC: 97.1 |
| Nambisan et al. [76] | Segmentation and classification (Melanoma/Benign) | ISIC dataset [19]: Segmentation task: 487 MM images. Classification task: 1000 images (500 MM, and 500 benign (100 images per class from the Actinic keratosis, Melanocytic nevus, Benign keratosis, Dermatofibroma, and Vascular lesion). | Segmentation (Classification dataset+Segmentation dataset (Irregular networks)) U-Net/U-Net++/MA-Net/PA-Net Handcrafted Feature Extraction Classification: Level 0 (without segmentation): DL classification model Level 1 (With segmentation and with level 0 model’s results): Conventional classification model | Conventional Ensemble Acc: 0.793 DL Ensemble Acc: 0.838 EfficientNet-B0 + Conventional Ensemble Acc: 0.862 |
| Collenne et al. [77] | Classification (Melanoma/Nevi) | ISIC dataset [19]: (6371 nevi and 1301 melanoma) Training set: 70% of images. Validation set: 10% of images. Test set: 20% of images. | Segmentation: U-Net Classification ANN (for asymmetry features + CNN (EfficientNet) | Handcrafted Model with asymmetry features (ANN): Acc: 79% AUC: 0.87 Sen: 90% Spe: 67% ANN+CNN: Sen: 0.92 Spe: 0.82 Acc: 0.87 AUC: 0.942 |
| Hekler et al. [61] | Classification (Melanoma/Nevi) | HAM10000 [22] and BCN20000 [26] datasets: 29,562 images (7794 melanoma and 21,768 nevi). 80% training, 20% validation Test set: SCP2 dataset, 293 melanoma and 363 melanocytic nevi from 617 patients. | ConvNeXT architecture 1. Classification using a single image 2. Classification using multiple real-world images 3. Classification using multiple artificially modified images | Single image approach: Acc: 0.905 ECE: 0.131 Multiview real-world approach: Acc: 0.930 ECE: 0.072 Multiview artificial approach: Acc: 0.929 ECE: 0.086 |
| Crawford et al. [62] | Classification (Excision/no excision) | Self-referred patients: The test set consisted of patient images, the majority of whom were of Scottish and Irish descent, mostly Fitzpatrick skin types 1, 2, and 3. | MoleAnalyzer Pro | AI Sen: 64.7% Spe: 75.76% PPV: 40.0% NPV: 89.6% Acc: 73.56% |
3.2.2. Distinguishing Melanoma from Other Skin Cancers
| Publication | End-Point | Dataset | Algorithm | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esteva et al. [78] | Classification Binary: Keratinocyte carcinoma/SK; melanoma/nevi 3-way: Benign/Malign/Non-neoplastic 9-way: Cutaneous lymphoma and lymphoid infiltrates/Benign dermal tumors, cysts, sinuses/Malignant dermal tumor/Benign epidermal tumors, hamartomas, milia, and growths/Malignant and premalignant epidermal tumors/Genodermatoses and supernumerary growths/Inflammatory conditions/Benign melanocytic lesions/Malignant Melanoma | ISIC [19] and Edinburgh dataset [25] and the Stanford Hospital: 129,450 clinical images, including 3374 dermoscopic images of 757 disease classes Training set: 127,463 images Test set: 1942 images | Google Inception v3 (CNN) | Binary classification (Algorithm AUC) Carcinoma AUC: 0.96 Melanoma AUC: 0.94 Melanoma (Dermoscopic images) AUC: 0.91 3-way classification: Dermatologist 1 Acc: 65.6% Dermatologist 2 Acc: 66.0% CNN Acc: 69.4 ± 0.8% CNN partitioning algorithm Acc: 72.1 ± 0.9% 9-way classification: Dermatologist 1 Acc: 53.3% Dermatologist 2 Acc: 55.0% CNN Acc: 48.9 ± 1.9% CNN partitioning algorithm Acc: 55.4 ± 1.7% |
| Rezvantalab et al. [79] | Classification (MM/Melanocytic Nevi/BCC/AKIEC/Benign keratosis/DF/Vascular lesion) | HAM10000 dataset [22]: 10,015 dermoscopic images (1113 MM, 6705 nevi, 514 BCC, 327 AK and intraepithelial carcinoma (AKIEC), 1099 benign keratosis, 115 DF, 142 vascular lesions) PH2 set [23]: 80 nevi, 40 MM Training set: 70% Validation set: 15% Test set: 15% | Compared CNNs for classification: Inception v3/InceptionResNet v2/ResNet 152/DenseNet 201 | AUC (Melanoma) Dermatologist AUC: 82.26 DenseNet 201 AUC: 93.80 ResNet 152 AUC: 94.40 Inception v3 AUC: 93.40 InceptionResNet v2 AUC: 93.20 AUC (BCC) Dermatologist AUC: 88.82 DenseNet 201 AUC: 99.30 ResNet 152 AUC: 99.10 Inception v3 AUC: 98.60 InceptionResNet v2 AUC: 98.60 |
| Maron et al. [80] | Classification 2-way: Benign/Malignant 5-way: AKIEC/BCC/MM/Nevi/BKL (benign keratosis, including seborrhoeic keratosis, solar lentigo and lichen planus like keratosis) | Training set: 11,444 images (ISIC Archive [19] and HAM10000 dataset [22]) Test set: 300 test images (60 for each of the five disease classes) (HAM10000 dataset) | CNN (ResNet50) | Two-way classification: CNN AUC: 0.928 CNN Spe: 91.3% Dermatologist Spe: 59.8% Five-way classification: CNN AUC: 0.960 CNN Spe: 89.2% Dermatologist Spe: 98.8% |
| Tschandl et al. [81] | Classification (Benign/Malignant) | Training set: 7895 dermoscopic and 5829 close-up images Test set: 2072 dermoscopic and close-up images | Combined convolutional neural network (cCNN) (InceptionResNetV2, InceptionV3, Xception, ResNet50) | cCNN: AUC: 0.695 Sen: 80.5% Spe: 53.5% Human Raters: AUC: 0.742 Sen: 77.6% Spe: 51.3% |
| Tschandl et al. [82] | Classification (7-way classification: intraepithelial carcinoma including AK and Bowen’s disease; BCC; benign keratinocytic lesions including solar lentigo, SK, and LPLK; dermatofibroma; melanoma; melanocytic nevi; and vascular lesions) | HAM10000 Dataset [22] Training set: 10,015 dermoscopic images Test set: 1195 images | Top 3 algorithms of the ISIC 2018 challenge [87] | Algorithms (mean): Sen: 81.9% Spe: 96.2% Human readers (mean): Sen: 67.8% Spe: 94.0% |
| Haenssle et al. [83] | Classification (Benign/Malignant) Management decision (treatment/ excision, no action, follow-up examination) | Pretrained CNN Test set: 100 images including pigmented/ non-pigmented and melanocytic/non-melanocytic skin lesions Dermatoscopic images were collected from several collaborating dermatologists and the ISIC archive [19]. The ethnicity and skin type of patients from whom images were obtained were not specified | Inception v4/Moleanalyzer Pro (CNN) | CNN Management Decision: Sen: 95.0% Spe: 76.7% Acc: 84.0% AUC: 0.918 CNN Diagnosis (Benign/Malignant) Sen: 95.0% Spe: 76.7% Acc: 84.0% Level 1 Management Decision: Dermatologist: Sen: 89.0% Spe: 80.7% Acc: 84.0% Level 1 Diagnosis (Benign/Malignant) Dermatologist: Sen: 83.8% Spe: 77.6% Acc: 80.1% Level 2 Management Decision: Dermatologist: Sen: 94.1% Spe: 80.4% Acc: 85.9% Level 2 Diagnosis (Benign/Malignant) Dermatologist: Sen: 90.6% Spe: 82.4% Acc: 85.7% |
| Hekler et al. [84] | Primary endpoint: Classification to 5 categories (MM/nevus/BCC/AK, Bowen’s disease or squamous cell carcinoma/seborrhoeic keratosis, lentigo solaris or lichen ruber planus) Secondary end-point: Binary classification (Benign/malignant) | HAM10000 Dataset [22] and ISIC dataset [19] Training set: 12,336 dermoscopic images (585 images of AK, Bowen, SCC, 910 images of BCC, 3101 images of seborrhoeic keratosis, lentigo solaris, lichen ruber planus, 4219 images of nevi, 3521 images of MM) | CNN (ResNet50) | Multiclass classification: Physician Acc: 42.94% CNN Acc: 81.59% Physician+CNN Acc: 82.95% Binary classification: Physician: Sen: 66% Spe: 62% CNN: Sen: 86.1% Spe: 89.2% Physician+CNN: Sen: 89% Spe: 84% |
| Xinrong Lu et al. [88] | Classification (normal, carcinoma, and melanoma) | HAM10000 dataset [22] Training set: 8012 images (%80) Test set: 2003 images (%20) | Proposed Xception (The ReLU activation function of the model was replaced with the swish activation function) compared with VGG16, InceptionV3, AlexNet and Xception | VGG16: Acc: 48.99 Sen: 53.7 InceptionV3: Acc: 52.99 Sen: 53.99 AlexNet: Acc: 75.99 Sen: 76.99 Xception: Acc: 92.90 Sen: 91.99 Proposed Xception: Acc: 100 Sen: 94.05 |
| Mengistu et al. [89] | Classification (BCC, SCC, MM) | DermQuest [27] and Dermnet [90] datasets 235 images (162 images for training and 73 images for testing) | Combined SOM and RBFNN and compared them with KNN, ANN, and naïve-Bayes | Proposed modelAcc: 93.15% KNNAcc: 71.23% ANNAcc: 63.01% Naïve-BayesAcc: 56.16% |
| Rashid et al. [91] | Classification (MM/Melanocytic Nevus/BCC/AKIEC/Benign Keratosis/DF/Vascular Lesion) | ISIC dataset [19] Training set: 8000 images Test set: 2000 images | GAN compared with CNN (DenseNet and ResNet-50) | GAN Acc: 0,861 DenseNet Acc: 0.815 ResNet-50 Acc: 0.792 |
| Alwakid et al. [92] | Classification (MM/BN/BCC/Vascular lesion/Benign keratosis/Actinic Carcinoma/DF) | HAM10000 dataset [22] 10,015 dermoscopic images Training set: 8029 images Validation set: 993 images Test set: 993 images | Inception-V3, InceptionResnet-V2 | Inception-V3: Acc: 0.897 Spe: 0.89 Sen: 0.90 InceptionResnet-V2: Acc: 0.913 Spe: 0.90 Sen: 0.91 |
| Felming-ham et al. [85] | Classification (Benign/Uncertain/Malignant) | Training set: 432,390 images from imaging and teledermatology reporting service (ethnicity and skin types were not specified) Version 1 CNN training set: 77.3% Benign and 22.7% malignant Version 2 CNN training set: 78.0% Benign and 22.0% malignant | Version 1: Plain Convolutional Model for pre-intervention period Version 2: Hierarchical deep learning architecture for postintervention period | CNN-sen: 95.8% CNN-spe: 71.5% Teledermatologist sen: 89.5% Teledermatologist-spe: 71.9% CNN-AUC: 0.837 Teledermatologist-AUC: 0.807 Initial resident management plan-AUC: 0.847 AI-assisted resident management plan-AUC: 0.879 Initial teledermatologist management plan-AUC: 0.821 |
| Barata et al. [86] | Classification (MM/BCC/AKIEC/BN/Benign keratinocytic lesions/DF/Vascular lesions) | Training set: HAM10000 dataset 10,015 dermoscopic images Test set: 1511 dermoscopic images; obtained from Austria, Australia, Turkey, New Zealand, Sweden, and Argentina The ethnicity and skin types were not specified | SL Model: ResNet34 Model RL Model: a deep-Q learning model based on a CNN and decides according to the reward system determined by medical experts | Supervised model: Sen (Melanoma): 61.4% Sen (BCC): 79.6% Acc: 77.8% Reinforcement Learning Model: Sen (Melanoma): 79.5% Sen (BCC): 87.1% Acc: 79.2% |
3.3. In Vivo Skin Imaging Devices
3.3.1. RCM
| Publication | End-Point | Dataset | Algorithm | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kose et al. [94] | Segmentation; detection of artifacts | 117 RCM mosaics; obtained from 7 clinics that collaborated internationally, the ethnicity and skin types of patients were not specified | MED-Net; an automated semantic segmentation method | Sensitivity: 82%, Specificity: 93% |
| Gerger et al. [95] | Classification; benign nevi vs. melanoma | 408 benign nevi and 449 melanoma images; obtained from one clinic in Austria, the ethnicity and skin types of patients were not specified | CART (Classification and Regression Trees) | Learning set: 97.31% of images correctly classified Training set: 81.03% of images correctly classified |
| Koller et al. [96] | Classification; benign nevi vs. melanoma | 4669 melanoma and 11,600 benign nevi RCM images; obtained from one clinic in Austria, the ethnicity and skin types of patients were not specified | CART (Classification and Regression Trees) | Learning set: 93.60% of the melanoma and 90.40% of the nevi images were correctly classified |
| Wodzinski et al. [97] | Classification; benign nevi vs. melanoma vs. BCC | 429 RCM mosaics; obtained through collaboration with two clinics from Italy and Poland, the ethnicity and skin types of patients were not specified | a CNN based on ResNet architecture | F1 score for melanoma in test set: 0.84 ± 0.03 |
| Kose et al. [98] | Segmentation; six distinct patterns (aspecific, non-lesion, artifact, ring, nested, meshwork) | 117 RCM mosaics; acquired at 4 different clinics in the US and a clinic in Italy, the ethnicity and skin types of patients were not specified | an automated semantic segmentation method, MED-Net | Pixel-wise mean sensitivity: 70 ± 11% Pixel-wise mean specificity: 95 ± 2%, respectively, with 0.71 ± 0.09 Dice coefficient over six classes. |
| D’Alonzo et al. [99] | Segmentation; “benign” and “aspecific (nonspecific)” regions | 157 RCM mosaics; obtained from 4 different clinics in the US and a clinic in Italy, the ethnicity and skin types of patients were not specified | Efficientnet, a deep neural network (DNN) | AUC of 0.969, and Dice coefficient of 0.778 |
| Mandal et al. [101] | Classification; Atypical intraepidermal melanocytic proliferation (AIMP) vs. Lentigo Maligna (LM) | 517 RCM stacks (389 LM and 148 AIMP) from 110 patients attended two clinics in Australia, the ethnicity and skin types of patients were not specified | DenseNet169, a CNN classifier | Accuracy: 0.80 F1 score for LM: 0.87 |
3.3.2. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and OCT-like Devices
4. Comparison of AI to Traditional Methods
5. Limitations
5.1. Datasets
5.1.1. Skin Type Diversity
5.1.2. Metadata
5.1.3. Combination of Different Modalities
5.1.4. Rare Subtypes
5.1.5. Diagnostic Method
5.1.6. Image Quality
5.2. Generalizability
5.3. Reliability
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Narayanan, D.L.; Saladi, R.N.; Fox, J.L. Ultraviolet radiation and skin cancer. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Society, A.C. What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer? 2023. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/what-is-melanoma.html (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Society, A.C. Key Statistics for Melanoma Skin Cancer. 2023. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Rastrelli, M.; Tropea, S.; Rossi, C.R.; Alaibac, M. Melanoma: Epidemiology, risk factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis and classification. In Vivo 2014, 28, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Henry, V.; Strong, E.; Sheriff, S.A.; Wanat, K.; Kasprzak, J.; Clark, M.; Shukla, M.; Zenga, J.; Stadler, M.; et al. Clinical Impact and Accuracy of Shave Biopsy for Initial Diagnosis of Cutaneous Melanoma. J. Surg. Res. 2023, 286, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Lee, A.; Ibrahimi, O.A.; Kim, N.; Bordeaux, J.; Chen, K.; Dinehart, S.; Goldberg, D.J.; Hanke, C.W.; Hruza, G.J.; et al. A multistep approach to improving biopsy site identification in dermatology: Physician, staff, and patient roles based on a Delphi consensus. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St John, J.; Walker, J.; Goldberg, D.; Maloney, M.E. Avoiding Medical Errors in Cutaneous Site Identification: A Best Practices Review. Dermatol. Surg. 2016, 42, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Levecq, O.; Azimani, H.; Siret, D.; Barut, A.; Suppa, M.; Del Marmol, V.; Malvehy, J.; Cinotti, E.; Rubegni, P.; et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography for high-resolution noninvasive imaging of skin tumors. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 106007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinotti, E.; Couzan, C.; Perrot, J.L.; Habougit, C.; Labeille, B.; Cambazard, F.; Moscarella, E.; Kyrgidis, A.; Argenziano, G.; Pellacani, G.; et al. In vivo confocal microscopic substrate of grey colour in melanosis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 2458–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, O.T.; Matin, R.N.; van der Schaar, M.; Prathivadi Bhayankaram, K.; Ranmuthu, C.K.I.; Islam, M.S.; Behiyat, D.; Boscott, R.; Calanzani, N.; Emery, J.; et al. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms for early detection of skin cancer in community and primary care settings: A systematic review. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e466–e476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.S.; An, H.G.; Oh, B.H.; Yang, S. Artificial Intelligence in Cutaneous Oncology. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogarty, D.T.; Su, J.C.; Phan, K.; Attia, M.; Hossny, M.; Nahavandi, S.; Lenane, P.; Moloney, F.J.; Yazdabadi, A. Artificial Intelligence in Dermatology-Where We Are and the Way to the Future: A Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Wang, J.V.; Motaparthi, K.; Lee, J.B. Artificial intelligence in dermatology for the clinician. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 39, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.P. The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, F.S. Receiver operating characteristic curve: Overview and practical use for clinicians. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 75, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. New Phytol. 1912, 11, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dildar, M.; Akram, S.; Irfan, M.; Khan, H.U.; Ramzan, M.; Mahmood, A.R.; Alsaiari, S.A.; Saeed, A.H.M.; Alraddadi, M.O.; Mahnashi, M.H. Skin cancer detection: A review using deep learning techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISIC Archive. Available online: https://challenge.isic-archive.com/data/ (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Rotemberg, V.; Kurtansky, N.; Betz-Stablein, B.; Caffery, L.; Chousakos, E.; Codella, N.; Combalia, M.; Dusza, S.; Guitera, P.; Gutman, D.; et al. A patient-centric dataset of images and metadata for identifying melanomas using clinical context. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtansky, N.R.; D’Alessandro, B.M.; Gillis, M.C.; Betz-Stablein, B.; Cerminara, S.E.; Garcia, R.; Girundi, M.A.; Goessinger, E.V.; Gottfrois, P.; Guitera, P.; et al. The SLICE-3D dataset: 400,000 skin lesion image crops extracted from 3D TBP for skin cancer detection. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschandl, P.; Rosendahl, C.; Kittler, H. The HAM10000 dataset, a large collection of multi-source dermatoscopic images of common pigmented skin lesions. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonca, T.; Ferreira, P.M.; Marques, J.S.; Marcal, A.R.; Rozeira, J. PH2—A dermoscopic image database for research and benchmarking. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2013, 2013, 5437–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, R.F.a.J. DERMOFIT Dataset. Available online: https://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/DERMOFIT/datasets.htm (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Ballerini, L.; Fisher, R.B.; Aldridge, B.; Rees, J. A color and texture based hierarchical K-NN approach to the classification of non-melanoma skin lesions. Color Med. Image Anal. 2013, 6, 63–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Pérez, C.; Combalia, M.; Podlipnik, S.; Codella, N.C.F.; Rotemberg, V.; Halpern, A.C.; Reiter, O.; Carrera, C.; Barreiro, A.; Helba, B.; et al. BCN20000: Dermoscopic Lesions in the Wild. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boer, A.; Nischal, K.C. www.derm101.com: A growing online resource for learning dermatology and dermatopathology. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2007, 73, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DermIS. Available online: https://www.dermis.net/dermisroot/en/home/index.htm (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Figshare. Asan and Hallym Dataset (Thumbnails); Figshare: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Kim, M.S.; Lim, W.; Park, G.H.; Park, I.; Chang, S.E. Classification of the Clinical Images for Benign and Malignant Cutaneous Tumors Using a Deep Learning Algorithm. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giotis, I.; Molders, N.; Land, S.; Biehl, M.; Jonkman, M.F.; Petkov, N. MED-NODE: A computer-assisted melanoma diagnosis system using non-dermoscopic images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 6578–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, M.; Harris, C.; Soenksen, L.; Lau, F.; Han, R.; Kim, A.; Koochek, A.; Badri, O. Evaluating deep neural networks trained on clinical images in dermatology with the fitzpatrick 17k dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1820–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Groh, M.; Harris, C.; Daneshjou, R.; Badri, O.; Koochek, A. Towards transparency in dermatology image datasets with skin tone annotations by experts, crowds, and an algorithm. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2022, 6, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKattash, J.A. DermaAmin. Available online: https://www.dermaamin.com/site/ (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Silva, S.F.d. Atlas dermatologico. Available online: https://atlasdermatologico.com.br (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Ward, A.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Lakshminarasimhan, S.; Carrick, A.; Campana, B.; Hartford, J.; Tiyasirichokchai, T.; Virmani, S.; Wong, R. Crowdsourcing Dermatology Images with Google Search Ads: Creating a Real-World Skin Condition Dataset. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.18545. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, W.; Afvari, S.; Han, Z.; Song, J.; Ji, Y.; He, X.; Gao, X. SkinCAP: A Multi-modal Dermatology Dataset Annotated with Rich Medical Captions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.18004. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshjou, R.; Vodrahalli, K.; Liang, W.; Novoa, R.A.; Jenkins, M.; Rotemberg, V.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Bailey, E.E.; Gevaert, O. Disparities in dermatology AI: Assessments using diverse clinical images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.08006. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, A.G.; Lima, G.R.; Salomao, A.S.; Krohling, B.; Biral, I.P.; de Angelo, G.G.; Alves Jr, F.C.; Esgario, J.G.; Simora, A.C.; Castro, P.B. PAD-UFES-20: A skin lesion dataset composed of patient data and clinical images collected from smartphones. Data Brief 2020, 32, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.F.; Sousa-Pinto, B.; Azevedo, L.F.; Barros, A.M.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J.; Haneke, E.; Correia, O. Clinical ABCDE rule for early melanoma detection. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2021, 31, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr-Esfahani, E.; Samavi, S.; Karimi, N.; Soroushmehr, S.M.R.; Jafari, M.H.; Ward, K.; Najarian, K. Melanoma detection by analysis of clinical images using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 1373–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, J.; Yolland, W.; Tschandl, P. Multimodal skin lesion classification using deep learning. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, P.R.; Mazboudi, P.; Reddy, A.J.; Farasat, V.P.; Guirgus, M.E.; Tak, N.; Min, M.; Arakji, G.H.; Patel, R. Leveraging machine learning for accurate detection and diagnosis of melanoma and nevi: An interdisciplinary study in dermatology. Cureus 2023, 15, e44120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorj, U.-O.; Lee, K.-K.; Choi, J.-Y.; Lee, M. The skin cancer classification using deep convolutional neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 9909–9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soenksen, L.R.; Kassis, T.; Conover, S.T.; Marti-Fuster, B.; Birkenfeld, J.S.; Tucker-Schwartz, J.; Naseem, A.; Stavert, R.R.; Kim, C.C.; Senna, M.M. Using deep learning for dermatologist-level detection of suspicious pigmented skin lesions from wide-field images. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabb3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomponiu, V.; Nejati, H.; Cheung, N.-M. Deepmole: Deep neural networks for skin mole lesion classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 2623–2627. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jain, A.; Eng, C.; Way, D.H.; Lee, K.; Bui, P.; Kanada, K.; de Oliveira Marinho, G.; Gallegos, J.; Gabriele, S. A deep learning system for differential diagnosis of skin diseases. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangers, T.; Reeder, S.; van der Vet, S.; Jhingoer, S.; Mooyaart, A.; Siegel, D.M.; Nijsten, T.; Wakkee, M. Validation of a market-approved artificial intelligence mobile health app for skin cancer screening: A prospective multicenter diagnostic accuracy study. Dermatology 2022, 238, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potluru, A.; Arora, A.; Arora, A.; Joiya, S.A. Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) for the Diagnosis of Melanoma Skin Lesions from Consumer-Grade Camera Photos. Cureus 2024, 16, e67559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, J.; Horimoto, K.; Sato, S.; Minowa, T.; Uhara, H. Dermoscopy of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, A.; Al-Jumaily, A.A.; Adnan, T. Development of automated diagnostic system for skin cancer: Performance analysis of neural network learning algorithms for classification. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning–ICANN 2014: 24th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Hamburg, Germany, 15–19 September 2014; pp. 837–844. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, M.A.; Codella, N.C.; Dusza, S.W.; Gutman, D.A.; Helba, B.; Kalloo, A.; Mishra, N.; Carrera, C.; Celebi, M.E.; DeFazio, J.L. Results of the 2016 international skin imaging collaboration isbi challenge: Comparison of the accuracy of computer algorithms to dermatologists for the diagnosis of melanoma from dermoscopic images. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.A.; Liopyris, K.; Dusza, S.W.; Codella, N.C.; Gutman, D.A.; Helba, B.; Kalloo, A.; Halpern, A.C.; Soyer, H.P.; Curiel-Lewandrowski, C. Computer algorithms show potential for improving dermatologists’ accuracy to diagnose cutaneous melanoma: Results of the International Skin Imaging Collaboration 2017. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yang, S.; Kim, W.; Jung, J.; Chung, K.-Y.; Lee, S.W.; Oh, B. Acral melanoma detection using a convolutional neural network for dermoscopy images. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193321. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, Q.; Ramzan, F.; Ghani, M.U. Acral melanoma detection using dermoscopic images and convolutional neural networks. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art. 2021, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, C.; Blum, A.; Buhl, T.; Mitteldorf, C.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; Deinlein, T.; Stolz, W.; Trennheuser, L.; Cussigh, C.; Deltgen, D. Diagnostic performance of a deep learning convolutional neural network in the differentiation of combined naevi and melanomas. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, T.J.; Hekler, A.; Enk, A.H.; Klode, J.; Hauschild, A.; Berking, C.; Schilling, B.; Haferkamp, S.; Schadendorf, D.; Holland-Letz, T. Deep learning outperformed 136 of 157 dermatologists in a head-to-head dermoscopic melanoma image classification task. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 113, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulini, M.; Goldust, M.; Grabbe, S.; Ludwigs, C.; Seliger, D.; Karagaiah, P.; Schepler, H.; Butsch, F.; Weidenthaler-Barth, B.; Rietz, S. Combining artificial intelligence and human expertise for more accurate dermoscopic melanoma diagnosis: A 2-session retrospective reader study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 90, 1266–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahbod, A.; Schaefer, G.; Wang, C.; Ecker, R.; Ellinge, I. Skin lesion classification using hybrid deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 1229–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Ningrum, D.N.A.; Yuan, S.-P.; Kung, W.-M.; Wu, C.-C.; Tzeng, I.-S.; Huang, C.-Y.; Li, J.Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-C. Deep learning classifier with patient’s metadata of dermoscopic images in malignant melanoma detection. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2021, 14, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hekler, A.; Maron, R.C.; Haggenmüller, S.; Schmitt, M.; Wies, C.; Utikal, J.S.; Meier, F.; Hobelsberger, S.; Gellrich, F.F.; Sergon, M. Using multiple real-world dermoscopic photographs of one lesion improves melanoma classification via deep learning. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 90, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, M.E.; Kamali, K.; Dorey, R.A.; MacIntyre, O.C.; Cleminson, K.; MacGillivary, M.L.; Green, P.J.; Langley, R.G.; Purdy, K.S.; DeCoste, R.C. Using artificial intelligence as a melanoma screening tool in self-referred patients. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2024, 28, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, T.; Hauser, K.; Hobelsberger, S.; Bucher, T.-C.; Garcia, C.N.; Wies, C.; Kittler, H.; Tschandl, P.; Navarrete-Dechent, C.; Podlipnik, S. Dermatologist-like explainable AI enhances trust and confidence in diagnosing melanoma. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, M.; Bissoto, A.; Santiago, C.; Barata, C. XAI for Skin Cancer Detection with Prototypes and Non-Expert Supervision. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01410. [Google Scholar]
- Aswin, R.; Jaleel, J.A.; Salim, S. Hybrid genetic algorithm—Artificial neural network classifier for skin cancer detection. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, Communication and Computational Technologies (ICCICCT), Kanyakumari District, India, 10–11 July 2014; pp. 1304–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, F.; Fan, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Meng, R.; Bovik, A. Melanoma Classification on Dermoscopy Images Using a Neural Network Ensemble Model. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, D.; Codella, N.C.; Celebi, E.; Helba, B.; Marchetti, M.; Mishra, N.; Halpern, A. Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: A challenge at the international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI) 2016, hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC). arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.01397. [Google Scholar]
- Cueva, W.F.; Muñoz, F.; Vásquez, G.; Delgado, G. Detection of skin cancer “Melanoma” through computer vision. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE XXIV International Conference on Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Computing (INTERCON), Cusco, Peru, 15–18 August 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, F.; Escudero-Vinolo, M.; Bescós, J. Accurate segmentation and registration of skin lesion images to evaluate lesion change. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 23, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.; Marsden, H.; Jaffe, W.; Matin, R.N.; Wali, G.N.; Greenhalgh, J.; McGrath, E.; James, R.; Ladoyanni, E.; Bewley, A. Assessment of accuracy of an artificial intelligence algorithm to detect melanoma in images of skin lesions. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1913436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gonzalez, M.; Azcarraga, C.; Martin-Gil, A.; Carpena-Torres, C.; Jaen, P. Efficacy of a deep learning convolutional neural network system for melanoma diagnosis in a hospital population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Song, J.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. Two-stage deep neural network via ensemble learning for melanoma classification. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 758495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, H.; Dou, Q.; Qin, J.; Heng, P.-A. Automated melanoma recognition in dermoscopy images via very deep residual networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 36, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisla, D.; Choromanska, A.; Berman, R.S.; Stein, J.A.; Polsky, D. Towards automated melanoma detection with deep learning: Data purification and augmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bassel, A.; Abdulkareem, A.B.; Alyasseri, Z.A.A.; Sani, N.S.; Mohammed, H.J. Automatic malignant and benign skin cancer classification using a hybrid deep learning approach. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, A.K.; Maurya, A.; Lama, N.; Phan, T.; Patel, G.; Miller, K.; Lama, B.; Hagerty, J.; Stanley, R.; Stoecker, W.V. Improving Automatic Melanoma Diagnosis Using Deep Learning-Based Segmentation of Irregular Networks. Cancers 2023, 15, 15041259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collenne, J.; Monnier, J.; Iguernaissi, R.; Nawaf, M.; Richard, M.A.; Grob, J.J.; Gaudy-Marqueste, C.; Dubuisson, S.; Merad, D. Fusion between an Algorithm Based on the Characterization of Melanocytic Lesions’ Asymmetry with an Ensemble of Convolutional Neural Networks for Melanoma Detection. J. Invest Dermatol. 2024, 144, 1600–1607.e1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezvantalab, A.; Safigholi, H.; Karimijeshni, S. Dermatologist level dermoscopy skin cancer classification using different deep learning convolutional neural networks algorithms. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.10348. [Google Scholar]
- Maron, R.C.; Weichenthal, M.; Utikal, J.S.; Hekler, A.; Berking, C.; Hauschild, A.; Enk, A.H.; Haferkamp, S.; Klode, J.; Schadendorf, D.; et al. Systematic outperformance of 112 dermatologists in multiclass skin cancer image classification by convolutional neural networks. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 119, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschandl, P.; Rosendahl, C.; Akay, B.N.; Argenziano, G.; Blum, A.; Braun, R.P.; Cabo, H.; Gourhant, J.Y.; Kreusch, J.; Lallas, A.; et al. Expert-Level Diagnosis of Nonpigmented Skin Cancer by Combined Convolutional Neural Networks. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschandl, P.; Codella, N.; Akay, B.N.; Argenziano, G.; Braun, R.P.; Cabo, H.; Gutman, D.; Halpern, A.; Helba, B.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; et al. Comparison of the accuracy of human readers versus machine-learning algorithms for pigmented skin lesion classification: An open, web-based, international, diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenssle, H.A.; Fink, C.; Toberer, F.; Winkler, J.; Stolz, W.; Deinlein, T.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; Lallas, A.; Emmert, S.; Buhl, T.; et al. Man against machine reloaded: Performance of a market-approved convolutional neural network in classifying a broad spectrum of skin lesions in comparison with 96 dermatologists working under less artificial conditions. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekler, A.; Utikal, J.S.; Enk, A.H.; Hauschild, A.; Weichenthal, M.; Maron, R.C.; Berking, C.; Haferkamp, S.; Klode, J.; Schadendorf, D.; et al. Superior skin cancer classification by the combination of human and artificial intelligence. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felmingham, C.; Pan, Y.; Kok, Y.; Kelly, J.; Gin, D.; Nguyen, J.; Goh, M.; Chamberlain, A.; Oakley, A.; Tucker, S.; et al. Improving skin cancer management with ARTificial intelligence: A pre-post intervention trial of an artificial intelligence system used as a diagnostic aid for skin cancer management in a real-world specialist dermatology setting. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 88, 1138–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, C.; Rotemberg, V.; Codella, N.C.F.; Tschandl, P.; Rinner, C.; Akay, B.N.; Apalla, Z.; Argenziano, G.; Halpern, A.; Lallas, A.; et al. A reinforcement learning model for AI-based decision support in skin cancer. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1941–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codella, N.; Rotemberg, V.; Tschandl, P.; Celebi, M.E.; Dusza, S.; Gutman, D.; Helba, B.; Kalloo, A.; Liopyris, K.; Marchetti, M. Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection 2018: A challenge hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (isic). arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.03368. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Firoozeh Abolhasani Zadeh, Y.A. Deep Learning-Based Classification for Melanoma Detection Using XceptionNet. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2196096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengistu, A.D.; Alemayehu, D.M. Computer vision for skin cancer diagnosis and recognition using RBF and SOM. International J. Image Process. (IJIP) 2015, 9, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- DermNet Image Dataset. Available online: https://dermnetnz.org/dermatology-image-dataset (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Rashid, H.; Tanveer, M.A.; Khan, H.A. Skin lesion classification using GAN based data augmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 41St Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 916–919. [Google Scholar]
- Alwakid, G.; Gouda, W.; Humayun, M.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. Diagnosing Melanomas in Dermoscopy Images Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atak, M.F.; Farabi, B.; Navarrete-Dechent, C.; Rubinstein, G.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Jain, M. Confocal microscopy for diagnosis and management of cutaneous malignancies: Clinical impacts and innovation. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, K.; Bozkurt, A.; Alessi-Fox, C.; Brooks, D.H.; Dy, J.G.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Gill, M. Utilizing machine learning for image quality assessment for reflectance confocal microscopy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerger, A.; Wiltgen, M.; Langsenlehner, U.; Richtig, E.; Horn, M.; Weger, W.; Ahlgrimm-Siess, V.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; Samonigg, H.; Smolle, J. Diagnostic image analysis of malignant melanoma in in vivo confocal laser-scanning microscopy: A preliminary study. Ski. Res. Technol. 2008, 14, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, S.; Wiltgen, M.; Ahlgrimm-Siess, V.; Weger, W.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; Richtig, E.; Smolle, J.; Gerger, A. In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy: Automated diagnostic image analysis of melanocytic skin tumours. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodzinski, M.; Skalski, A.; Witkowski, A.; Pellacani, G.; Ludzik, J. Convolutional neural network approach to classify skin lesions using reflectance confocal microscopy. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 4754–4757. [Google Scholar]
- Kose, K.; Bozkurt, A.; Alessi-Fox, C.; Gill, M.; Longo, C.; Pellacani, G.; Dy, J.G.; Brooks, D.H.; Rajadhyaksha, M. Segmentation of cellular patterns in confocal images of melanocytic lesions in vivo via a multiscale encoder-decoder network (MED-Net). Med. Image Anal. 2021, 67, 101841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alonzo, M.; Bozkurt, A.; Alessi-Fox, C.; Gill, M.; Brooks, D.H.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Kose, K.; Dy, J.G. Semantic segmentation of reflectance confocal microscopy mosaics of pigmented lesions using weak labels. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, S.; Valon, L.; Mancini, L.; Dray, N.; Caldarelli, P.; Gros, J.; Esposito, E.; Shorte, S.L.; Bally-Cuif, L.; Aulner, N. LocalZProjector and DeProj: A toolbox for local 2D projection and accurate morphometrics of large 3D microscopy images. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Priyam, S.; Chan, H.H.; Gouveia, B.M.; Guitera, P.; Song, Y.; Baker, M.A.B.; Vafaee, F. Computer-aided diagnosis of melanoma subtypes using reflectance confocal images. Cancers 2023, 15, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambichler, T.; Jaedicke, V.; Terras, S. Optical coherence tomography in dermatology: Technical and clinical aspects. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattler, E.; Kästle, R.; Welzel, J. Optical coherence tomography in dermatology. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 061224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, H.-Y.; Huang, S.-L.; Tjiu, J.-W.; Chen, H.H. Dermal epidermal junction detection for full-field optical coherence tomography data of human skin by deep learning. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 87, 101833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, F.H.; Mesica, A.; Gonzalez-Mercedes, M.; Deshmukh, T. Identification of Cancerous Skin Lesions Using Vibrational Optical Coherence Tomography (VOCT): Use of VOCT in Conjunction with Machine Learning to Diagnose Skin Cancer Remotely Using Telemedicine. Cancers 2022, 15, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Beirami, M.J.; Ebrahimpour, R.; Puyana, C.; Tsoukas, M.; Avanaki, K. Optical coherence tomography confirms non-malignant pigmented lesions in phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica using a support vector machine learning algorithm. Ski. Res. Technol. 2023, 29, e13377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.; Yi, J.-Y.; Hsu, T.-W.; Huang, S.-L. Integration of cellular-resolution optical coherence tomography and Raman spectroscopy for discrimination of skin cancer cells with machine learning. J. Biomed. Opt. 2023, 28, 096005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, M.P.; Sepúlveda, J.; Hidalgo, L.; Peirano, D.; Morel, M.; Uribe, P.; Rotemberg, V.; Briones, J.; Mery, D.; Navarrete-Dechent, C. A systematic review and meta-analysis of artificial intelligence versus clinicians for skin cancer diagnosis. NPJ Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, N.; Burke, T.; Courtney, J. Skin Type Diversity in Skin Lesion Datasets: A Review. Curr. Dermatol. Rep. 2024, 13, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshjou, R.; Smith, M.P.; Sun, M.D.; Rotemberg, V.; Zou, J. Lack of Transparency and Potential Bias in Artificial Intelligence Data Sets and Algorithms: A Scoping Review. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Khan, S.M.; Ji Xu, A.; Ibrahim, H.; Smith, L.; Caballero, J.; Zepeda, L.; de Blas Perez, C.; Denniston, A.K.; Liu, X.; et al. Characteristics of publicly available skin cancer image datasets: A systematic review. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e64–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Primiero, C.A.; Kulkarni, V.; Soyer, H.P.; Betz-Stablein, B. Artificial Intelligence for the Classification of Pigmented Skin Lesions in Populations with Skin of Color: A Systematic Review. Dermatology 2023, 239, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshjou, R.; Vodrahalli, K.; Novoa, R.A.; Jenkins, M.; Liang, W.; Rotemberg, V.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Bailey, E.E.; Gevaert, O.; et al. Disparities in dermatology AI performance on a diverse, curated clinical image set. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Soltan, A.; Trucco, E.; Matin, R.N. From data to diagnosis: Skin cancer image datasets for artificial intelligence. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 49, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinker, T.J.; Hekler, A.; Utikal, J.S.; Grabe, N.; Schadendorf, D.; Klode, J.; Berking, C.; Steeb, T.; Enk, A.H.; von Kalle, C. Skin Cancer Classification Using Convolutional Neural Networks: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2018, 20, e11936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.K.; Park, C.; Henao, R.; Kheterpal, M. Deep Learning in Dermatology: A Systematic Review of Current Approaches, Outcomes, and Limitations. JID Innov. 2023, 3, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, S.; Wen, D.; Ng, B.; Anand, R.; Matin, R.N.; Taghipour, K.; Esdaile, B. Identification of Incidental Skin Cancers Among Adults Referred to Dermatologists for Suspicious Skin Lesions. JAMA Netw. Open. 2020, 3, e2030107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, R.B.; Naysmith, L.; Ooi, E.T.; Murray, C.S.; Rees, J.L. The importance of a full clinical examination: Assessment of index lesions referred to a skin cancer clinic without a total body skin examination would miss one in three melanomas. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2013, 93, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha Roy, A.; Ren, J.; Azizi, S.; Loh, A.; Natarajan, V.; Mustafa, B.; Pawlowski, N.; Freyberg, J.; Liu, Y.; Beaver, Z.; et al. Does your dermatology classifier know what it doesn’t know? Detecting the long-tail of unseen conditions. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 75, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenssle, H.A.; Fink, C.; Schneiderbauer, R.; Toberer, F.; Buhl, T.; Blum, A.; Kalloo, A.; Hassen, A.B.H.; Thomas, L.; Enk, A.; et al. Man against machine: Diagnostic performance of a deep learning convolutional neural network for dermoscopic melanoma recognition in comparison to 58 dermatologists. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udrea, A.; Mitra, G.D.; Costea, D.; Noels, E.C.; Wakkee, M.; Siegel, D.M.; de Carvalho, T.M.; Nijsten, T.E.C. Accuracy of a smartphone application for triage of skin lesions based on machine learning algorithms. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, J.K.; Sies, K.; Fink, C.; Toberer, F.; Enk, A.; Deinlein, T.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; Thomas, L.; Lallas, A.; Blum, A.; et al. Melanoma recognition by a deep learning convolutional neural network-Performance in different melanoma subtypes and localisations. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 127, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrami, E.J.; Brown, A.C.; Salmon, P.J.M.; Leffell, D.J.; Ko, J.M.; Grant-Kels, J.M. Artificial intelligence in the detection of skin cancer. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekler, A.; Kather, J.N.; Krieghoff-Henning, E.; Utikal, J.S.; Meier, F.; Gellrich, F.F.; Upmeier Zu Belzen, J.; French, L.; Schlager, J.G.; Ghoreschi, K.; et al. Effects of Label Noise on Deep Learning-Based Skin Cancer Classification. Front Med. 2020, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, G.E.; Reicher, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Tse, D.; Shetty, S. Improving reference standards for validation of AI-based radiography. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshjou, R.; Barata, C.; Betz-Stablein, B.; Celebi, M.E.; Codella, N.; Combalia, M.; Guitera, P.; Gutman, D.; Halpern, A.; Helba, B.; et al. Checklist for Evaluation of Image-Based Artificial Intelligence Reports in Dermatology: CLEAR Derm Consensus Guidelines from the International Skin Imaging Collaboration Artificial Intelligence Working Group. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, M.; Muralidharan, V.; Rotemberg, V.; Novoa, R.A.; Chiou, A.S.; Sadée, C.Y.; Rapaport, B.; Yekrang, K.; Bitz, J.; Gevaert, O.; et al. Best Practices for Clinical Skin Image Acquisition in Translational Artificial Intelligence Research. J. Invest Dermatol. 2023, 143, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier-Hein, L.; Eisenmann, M.; Reinke, A.; Onogur, S.; Stankovic, M.; Scholz, P.; Arbel, T.; Bogunovic, H.; Bradley, A.P.; Carass, A.; et al. Why rankings of biomedical image analysis competitions should be interpreted with care. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, K.; Zaniolo, L.; Marques, O. Image quality issues in teledermatology: A comparative analysis of artificial intelligence solutions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.K.; Fink, C.; Toberer, F.; Enk, A.; Deinlein, T.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; Thomas, L.; Lallas, A.; Blum, A.; Stolz, W.; et al. Association Between Surgical Skin Markings in Dermoscopic Images and Diagnostic Performance of a Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Network for Melanoma Recognition. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, K.; Winkler, J.K.; Fink, C.; Bardehle, F.; Toberer, F.; Kommoss, F.K.F.; Buhl, T.; Enk, A.; Rosenberger, A.; Haenssle, H.A. Dark corner artefact and diagnostic performance of a market-approved neural network for skin cancer classification. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2021, 19, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, V.; Sinz, C.; Mittlböck, M.; Kittler, H.; Tschandl, P. Accuracy of computer-aided diagnosis of melanoma: A meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurowski, M.A.; Habas, P.A.; Zurada, J.M.; Lo, J.Y.; Baker, J.A.; Tourassi, G.D. Training neural network classifiers for medical decision making: The effects of imbalanced datasets on classification performance. Neural Netw. 2008, 21, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernbach, J.M.; Staartjes, V.E. Foundations of machine learning-based clinical prediction modeling: Part II—Generalization and overfitting. Mach. Learn. Clin. Neurosci. Found. Appl. 2022, 134, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fliorent, R.; Fardman, B.; Podwojniak, A.; Javaid, K.; Tan, I.J.; Ghani, H.; Truong, T.M.; Rao, B.; Heath, C. Artificial intelligence in dermatology: Advancements and challenges in skin of color. Int. J. Dermatol. 2024, 63, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, M.; Maki, A.; Mazurowski, M.A. A systematic study of the class imbalance problem in convolutional neural networks. Neural Netw. 2018, 106, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combalia, M.; Codella, N.; Rotemberg, V.; Carrera, C.; Dusza, S.; Gutman, D.; Helba, B.; Kittler, H.; Kurtansky, N.R.; Liopyris, K. Validation of artificial intelligence prediction models for skin cancer diagnosis using dermoscopy images: The 2019 International Skin Imaging Collaboration Grand Challenge. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e330–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Gadgil, S.U.; DeGrave, A.J.; Omiye, J.A.; Cai, Z.R.; Daneshjou, R.; Lee, S.I. Transparent medical image AI via an image-text foundation model grounded in medical literature. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Mahapatra, D.; Chandra, S.S.; Janda, M.; Soyer, P.; Ge, Z. Towards Trustable Skin Cancer Diagnosis via Rewriting Model’s Decision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 11568–11577. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, M.A.; Cowen, E.A.; Kurtansky, N.R.; Weber, J.; Dauscher, M.; DeFazio, J.; Deng, L.; Dusza, S.W.; Haliasos, H.; Halpern, A.C.; et al. Prospective validation of dermoscopy-based open-source artificial intelligence for melanoma diagnosis (PROVE-AI study). npj Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinlein, L.; Maron, R.C.; Hekler, A.; Haggenmüller, S.; Wies, C.; Utikal, J.S.; Meier, F.; Hobelsberger, S.; Gellrich, F.F.; Sergon, M.; et al. Prospective multicenter study using artificial intelligence to improve dermoscopic melanoma diagnosis in patient care. Commun. Med. 2024, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WG-19: Dermatology. Available online: https://www.dicomstandard.org/activity/wgs/wg-19 (accessed on 25 November 2024).
| Publication | End-Point | Dataset | Algorithm | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasr-Esfahani et al. [41] | Classification (benign/melanoma) | 170 clinical images that underwent data augmentation to generate 6120 images (80% training, 20% validation). Ethnicity was not specified. | CNN with 2 convolutional layers each followed by pooling layers along with a fully connected layer | Acc: 81% Spe: 80% Sen: 81% NPV: 86% PPV: 86% |
| Yap et al. [42] | Classification of melanoma from 5 different types of lesions | 2917 cases with each case containing patient metadata, macroscopic image and dermoscopic images with 5 classes (naevus, melanoma, BCC, SCC, and pigmented benign keratoses). Not specified where images were obtained from or ethnicity of images. | ResNet-50 with embedding networks | Macroscopic images alone AUC: 0.791 Macroscopic and dermoscopy AUC: 0.866 Macroscopic, dermoscopy and metadata AUC: 0.861 |
| Riazi Esfahani et al. [43] | Classification (malignant melanoma/benign nevi) | 793 images (437 malignant melanoma and 357 benign nevi). Ethnicity not specified. | CNN | Acc: 88.6% Spe: 88.6% Sen: 81.8% |
| Dorj et al. [44] | Classification of melanoma from 4 different skin cancers (actinic keratoses, BCC, SCC, melanoma) | 3753 images (2985 training and 758 testing) including 958 melanoma. Ethnicity not specified. | AlexNet with ECOC-SVM classifier | Acc: 0.942 Spe: 0.9074 Sen: 0.9783 |
| Soenksen et al. [45] | Classification across 6 different classes as well as distinguishing SPLs | 33,980 (including backgrounds, skin edges, bare skin sections, low priority NSPLs, medium priority NSPLs and SPLs) (60% training, 20% validation and 20% as testing). Ethnicity not specified. | DCNN with VGG16 Image Net pretrained network as transfer learning | Across all 6 classes AUCmicro: 0.97 Spemicro: 0.903 Senmicro: 0.899 For SPLs AUC: 0.935 |
| Pomponiu et al. [46] | Classification (melanoma/benign nevi) | 399 images (217 benign, 182 melanoma) from online image libraries. Ethnicity not specified. | CNN with a KNN classifier | Acc: 0.83 Spe: 0.95 Sen: 0.92 |
| Han et al. [30] | Melanoma detection from 12 different skin diseases | Training: 19,938 images from the Asan dataset [29], MED-NODE dataset [31], and atlas site images. Testing: 480 images from Asan and Edinburgh datasets [25]. Asan dataset was composed of mainly an Asian population and Edinburgh and MED-NODE were mainly composed of a Caucasian population. | ResNet152 | Asan AUC: 0.96 Spe: 0.904 Sen: 0.91 Edinburgh AUC: 0.88 Spe: 0.855 Sen: 0.807 |
| Liu et al. [47] | Primary: classification among 26 different skin conditions Secondary: classification among a full set of 419 different skin conditions | Training: 64,837 images with metadata. Validation set A: 14,833 images with metadata. Validation set B was used to compare to dermatologists: 3707 images with metadata. Training: 0.1% American Indian or Alaska Native, 11% Asian, 6.8% African American, 43.7% Hispanic, 1.4% Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, 34% White, 2.2% not specified. Validation A: 0.1% American Indian or Alaska Native, 12.6% Asian, 6.1% African American, 43.4% Hispanic, 1.6% Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, 31.3% White, 3.9% not specified Validation B: 0.9% American Indian or Alaska Native, 10.1% Asian, 6.3% African American, 42.5% Hispanic, 2% Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, 34.2% White, 4% not specified. | DLS with Inception-v4 modules and shallow module | Validation set A for 26 image classification: Acctop1: 0.71 Acctop3: 0.93 Sentop1: 0.58 Sentop3: 0.83 Validation set B for 26 image classification: Acctop1: 0.66 Acctop3: 0.9 Sentop1: 0.56 Sentop3: 0.64 Dermatologists: Acctop1: 0.63 Acctop3: 0.75 Sentop1: 0.51 Sentop3: 0.49 |
| Sangers et al. [48] | Classification (low/high risk) | 785 images (418 suspicious, 367 benign). Ethnicity not specified. | RD-174 | Overall app classification Sen: 0.869 Spe: 0.704 Classification for melanocytic lesions: Sen: 0.819 Spe: 0.733 |
| Polturu et al. [49] | Classification (non-melanoma/melanoma) | 206 images from DermIS [28] and Derm Quest [27] (87 nonmelanoma and 119 melanoma, 85% used for training and 15% used for testing). Ethnicity not specified. | AutoML was created using a no-code online service platform | Acc: 0.844 Sen: 0.833 Spe: 0.857 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
İsmail Mendi, B.; Kose, K.; Fleshner, L.; Adam, R.; Safai, B.; Farabi, B.; Atak, M.F. Artificial Intelligence in the Non-Invasive Detection of Melanoma. Life 2024, 14, 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14121602
İsmail Mendi B, Kose K, Fleshner L, Adam R, Safai B, Farabi B, Atak MF. Artificial Intelligence in the Non-Invasive Detection of Melanoma. Life. 2024; 14(12):1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14121602
Chicago/Turabian Styleİsmail Mendi, Banu, Kivanc Kose, Lauren Fleshner, Richard Adam, Bijan Safai, Banu Farabi, and Mehmet Fatih Atak. 2024. "Artificial Intelligence in the Non-Invasive Detection of Melanoma" Life 14, no. 12: 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14121602
APA Styleİsmail Mendi, B., Kose, K., Fleshner, L., Adam, R., Safai, B., Farabi, B., & Atak, M. F. (2024). Artificial Intelligence in the Non-Invasive Detection of Melanoma. Life, 14(12), 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14121602







