Assessing the Natural Source Zone Depletion of a Petroleum-Contaminated Clayey Soil Site in Southern China Combining Concentration Gradient Method and Metagenomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Soil Gas Measurement and Functional Gene Determination
2.2.1. Soil Gas Measurement
2.2.2. Functional Gene Determination
2.3. Assessment Method
2.4. Statistical Calculation
3. Results
3.1. Soil Gas Concentration Profile
3.2. Soil Gas Concentrate Gradient
3.3. Assessment of NSZD Rate
3.4. Functional Genes Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, P.; Lundegard, P.; Liu, Z. Source Zone Natural Attenuation at Petroleum Hydrocarbon Spill Sites-I: Site-Specific Assessment Approach. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. GWMR 2006, 26, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Wang, H.Q. Dynamic assessment of pollution risk of groundwater source area in Northern China. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITRC. LNAPL Site Management: LCSM Evolution, Decision Process, and Remedial Technologies; Interstate Technology & Regulatory Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Liang, F.; Meng, J.; Li, N. Effects of groundwater fluctuation on migration characteristics and representative elementary volume of entrapped LNAPL. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.R.; Walker, K.L.; Newell, C.J.; Askarani, K.K.; Li, Y.; McHugh, T.E. Natural Source Zone Depletion (NSZD) Insights from over 15 Years of Research and Measurements: A Multi-Site Study. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.W.; Davis, G.B.; DeVaull, G.E.; Garg, S.; Newell, C.J.; Rivett, M.O. Natural Source Zone Depletion (NSZD): From process understanding to effective implementation at LNAPL-impacted sites. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2022, 55, qjegh2021-166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Min, Z.; Caijuan, G.; Zhuo, N.; Yu, Z.; Jun, Q.; Wei, Z. Review on the Research Progress of Natural Source Zone Depletion in LNAPL Contaminated Sites. Rock Miner. Anal. 2022, 41, 704–716. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, S.; Newell, C.J.; Kulkarni, P.R.; King, D.C.; Adamson, D.T.; Renno, M.I.; Sale, T. Overview of Natural Source Zone Depletion: Processes, Controlling Factors, and Composition Change. Ground Water Monit. Remediat. 2017, 37, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, G.; Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Yang, T.; Huang, D.; Han, X.; Zhou, L. Microbial compositional and functional traits of BTEX and salinity co-contaminated shallow groundwater by produced water. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi Askarani, K. Thermal Monitoring of Natural Source Zone Depletion. Doctoral Dissertation, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.J.; Benede, E.; Beuthe, B.; Marti, M.; Lopez, A.S.; Koons, B.W.; Kirkman, A.J.; Barreales, L.A.; Grosjean, T.; Hjort, M. A comparison of three methods to assess natural source zone depletion at paved fuel retail sites. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2021, 54, 2689–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, M.K. Method Comparison for Analysis of LNAPL Natural Source Zone Depletion Using CO2 Fluxes. Doctoral Dissertation, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2015; pp. 1–145. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi Askarani, K.; Stockwell, E.B.; Piontek, K.R.; Sale, T.C. Thermal Monitoring of Natural Source Zone Depletion. Ground Water Monit. Remediat. 2018, 38, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarani, K.K.; Sale, T.C. Thermal estimation of natural source zone depletion rates without background correction. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.R.; Newell, C.J.; King, D.C.; Molofsky, L.J.; Garg, S. Application of Four Measurement Techniques to Understand Natural Source Zone Depletion Processes at an LNAPL Site. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2020, 40, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, G.; Sheng, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, H. Isotopes in groundwater (2H, 18O, 14C) revealed the climate and groundwater recharge in the Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, K.; Zimbron, J.; Sale, T.; Lyverse, M. Measurement of Natural Losses of LNAPL Using CO2 Traps. Ground Water 2015, 53, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ven, C.J.C.V.D.; Scully, K.H.; Frame, M.A.; Sihota, N.J.; Mayer, K.U. Impacts of water table fluctuations on actual and perceived natural source zone depletion rates. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 238, 103771. [Google Scholar]
- Ririe, G.; Sweeney, R. Rapid Approach to Evaluate NSZD at LNAPL Sites. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 8–12 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ririe, G.T.; Sweeney, R.E. Rapid Field Approach to Evaluating Natural Source Zone Depletion for a Range of Light Non-Aqueous Phase Liquid Sites. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2022, 42, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishgar, R.; Hettiaratchi, J.P.; Chu, A. Natural Source Zone Depletion (NSZD) Quantification Techniques: Innovations and Future Directions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; He, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.; Yin, M.; Ning, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhen, S. Application research of enhanced in-situ micro-ecological remediation of petroleum contaminated soil. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.L.; Zhou, C.H.; Fiore, S.; Yu, W.H. Interactions between microorganisms and clay minerals: New insights and broader applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 177, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugochukwu, U.C.; Jones, M.D.; Head, I.M.; Manning, D.A.C.; Fialips, C.I. Biodegradation and adsorption of crude oil hydrocarbons supported on “homoionic” montmorillonite clay minerals. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 87, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugochukwu, U.C.; Manning, D.A.C.; Fialips, C.I. Microbial degradation of crude oil hydrocarbons on organoclay minerals. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 144, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihota, N.; McAlexander, B.; Lyverse, M.; Mayer, K.U. Multi_year CO2 efflux measurements for assessing natural source zone depletion at a large hydrocarbon_impacted site. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 219, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRC CARE. Technical Measurement Guidance for LNAPL Natural Source Zone Depletion; CRC for Contamination Assessment and Remediation of the Environment: Newcastle, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Technical Guideline of Soil and Groundwater Self-Monitoring for Enterprises in Production; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Guo, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Zhang, M. Incorporating the Soil Gas Gradient Method and Functional Genes to Assess the Natural Source Zone Depletion at a Petroleum-Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Site of a Purification Plant in Northwest China. Life 2022, 13, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Cai, P.; Zhang, M. Metagenomic analysis revealed highly diverse carbon fixation microorganisms in a petroleum-hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, L.; Yu, S.; Ding, A.; Zuo, R.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Environmental stressors altered the groundwater microbiome and nitrogen cycling: A focus on influencing mechanisms and pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanish, L.F.; Sherwood, O.A.; Greg Lackey; Stephen Osborn; Robertson, C.E.; Harris, J.K.; Pace, N.; Ryan, J.N. Microbial and Biogeochemical Indicators of Methane in Groundwater Aquifers of the Denver Basin, Colorado. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, B.; Jia, H. Characterization of dissolved organic matter content, composition, and source during spring algal bloom in tributaries of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Meng, L.; Liu, F.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Mao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, H. Distribution, source investigation, and risk assessment of topsoil heavy metals in areas with intensive anthropogenic activities using the positive matrix factorization (PMF) model coupled with self-organizing map (SOM). Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6353–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, G.; Shi, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D. Cl, Br, B, Li, and noble gases isotopes to study the origin and evolution of deep groundwater in sedimentary basins: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1497–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundegard, P.D.; Johnson, P.C. Source Zone Natural Attenuation at Petroleum Hydrocarbon Spill Sites—II: Application to a Former Oil Field. Ground Water Monit. Remediat. 2006, 26, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millington, R.J.; Quirk, J.P. Permeability of porous solids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 1961, 57, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Kim, S.H.; Woo, H.; Choi, J.W.; Yun, S.-T.; Chung, J.; Lee, S. Groundwater-level fluctuation effects on petroleum hydrocarbons in vadose zones and their potential risks: Laboratory studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 463, 132837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunyan, X.; Qaria, M.A.; Qi, X.; Daochen, Z. The role of microorganisms in petroleum degradation: Current development and prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Fan, Y.; Chou, C.-W.; Yavari, S.; Williams, R.V.; Amster, I.J.; Brown, S.M.; Drake, I.J.; Duin, E.C.; Whitman, W.B.; et al. Expression of divergent methyl/alkyl coenzyme M reductases from uncultured archaea. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneron, A.; Bishop, A.; Alsop, E.B.; Hull, K.; Rhodes, I.; Hendricks, R.; Head, I.M.; Tsesmetzis, N. Microbial and Isotopic Evidence for Methane Cycling in Hydrocarbon-Containing Groundwater from the Pennsylvania Region. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, M.; Pan, N.; Wang, M. Effective gas diffusion coefficient in fibrous materials by mesoscopic modeling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 107, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- API. Quantification of Vapor Phase-related Natural Source Zone Depletion Processes; API: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Eichert, J.; McAlexander, B.; Lyverse, M.; Michalski, P.; Sihota, N. Spatial and Temporal Variation in Natural Source Zone Depletion Rates at a Former Oil Refinery. Vadose Zone J. VZJ 2017, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verginelli, I.; Baciocchi, R. Refinement of the gradient method for the estimation of natural source zone depletion at petroleum contaminated sites. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 241, 103807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Han, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, B. Recent Progress and Classification of Methanogens. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2014, 33, 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.-J.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Duan, C.-H.; Li, M. Genomic and transcriptomic insights into methanogenesis potential of novel methanogens from mangrove sediments. Microbiome 2020, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gan, Q.; Fan, C. Methyl-Coenzyme M Reductase and Its Post-translational Modifications. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 578356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.-P.; Du, J.; Köstlbacher, S.; Pjevac, P.; Orlić, S.; Sullivan, M.B. Viral potential to modulate microbial methane metabolism varies by habitat. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomina, M.; Skorochod, I. Microbial Interaction with Clay Minerals and Its Environmental and Biotechnological Implications. Minerals 2020, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.; Ekre, R.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Rittman, B.; Lundegard, P.; Hinchee, R. Assessment of the Natural Attenuation of NAPL Source Zones and Post-Treatment NAPL Source Zone Residuals; Arizona State University Tempe: Tampe, AZ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]

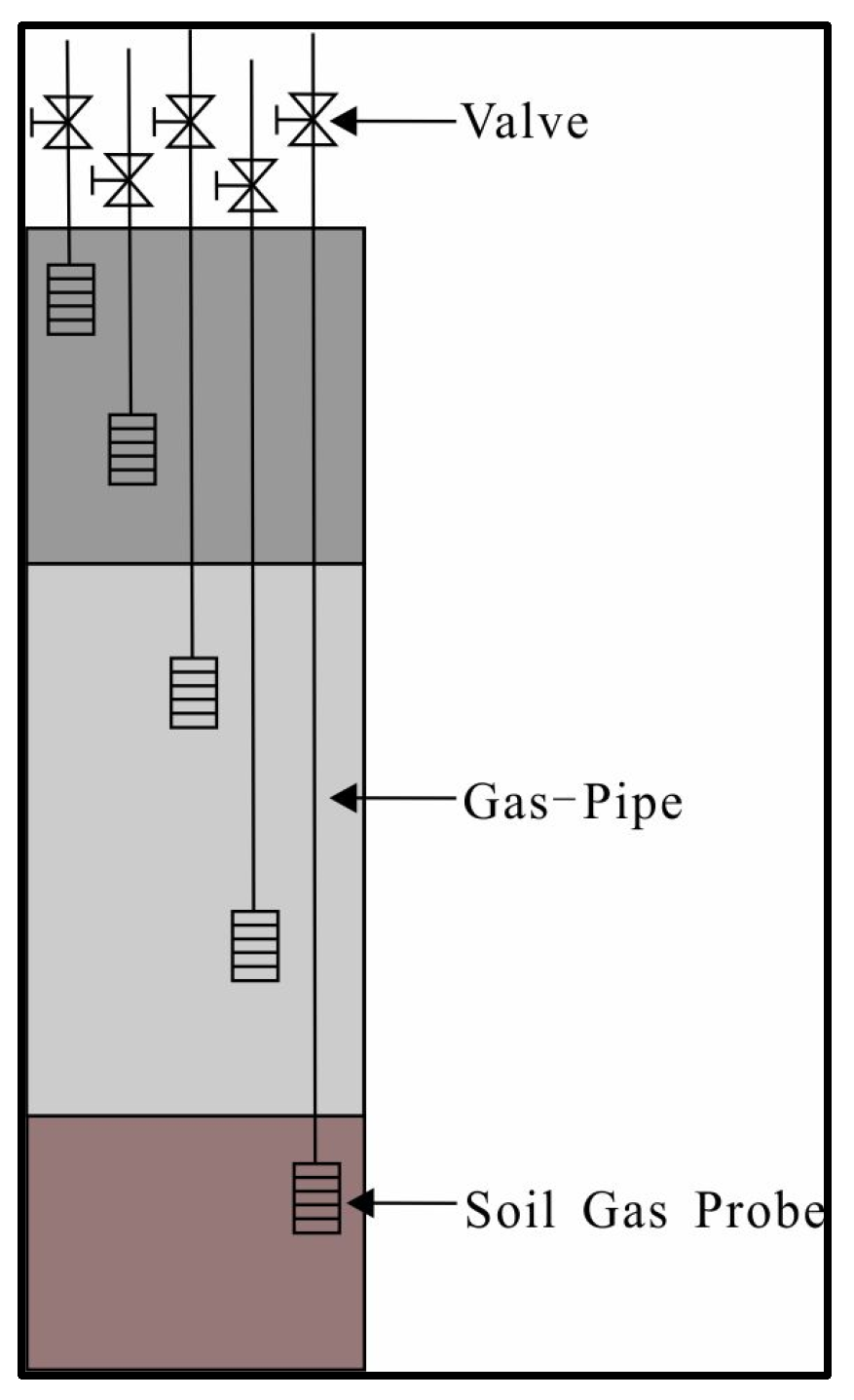
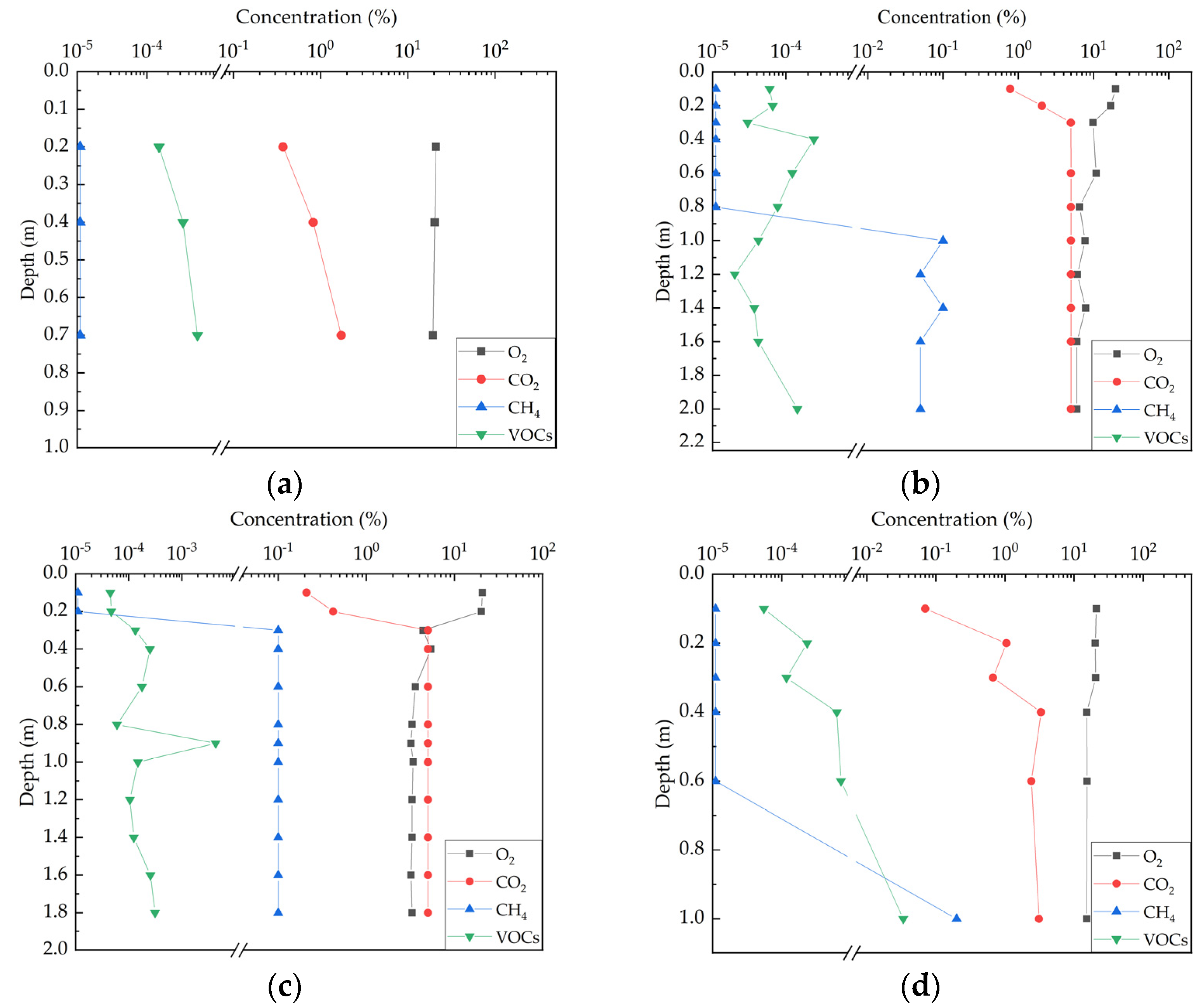
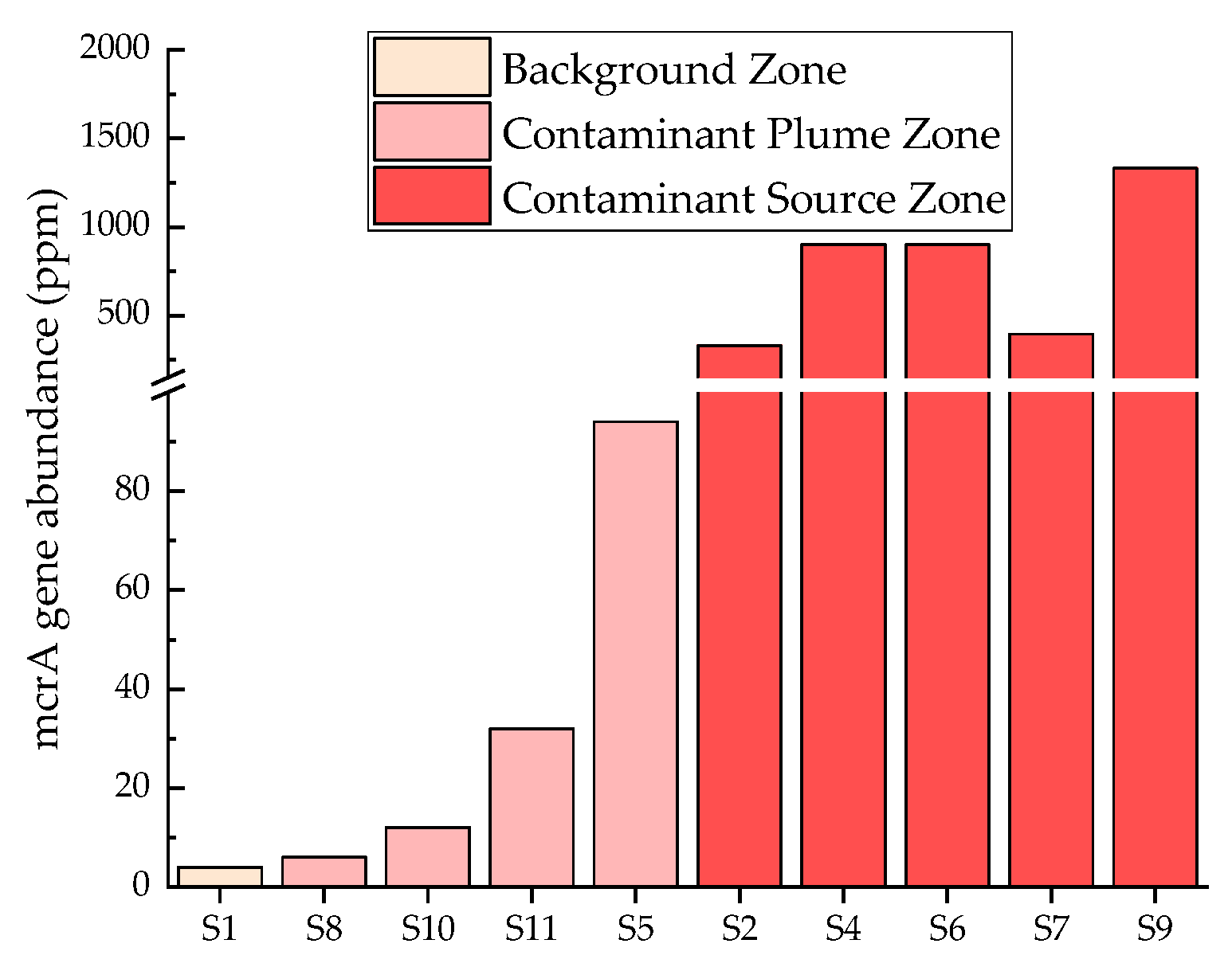
| Point | Depth (m) | O2 (kg/L/m) | CO2 (kg/L/m) | CH4 (kg/L/m) | VOCs (kg/L/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0–0.7 | −4.29 × 10−5 | 5.30 × 10−5 | 0 | 2.65 × 10−8 |
| S2 | 0–0.3 | −7.00 × 10−5 | 4.13 × 10−5 | 0 | 5.22 × 10−8 |
| S3 | 0–0.3 | −1.16 × 10−5 | 4.70 × 10−5 | 0.5 | 1.53 × 10−8 |
| S4 | 0–0.4 | −2.67 × 10−5 | 2.13 × 10−5 | 0 | 6.60 × 10−8 |
| Point | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated Rate (kg·m−2·a−1) | 0.04 | 0.71 | 1.19 | 0.27 |
| Correction for Calculated Rate (kg·m−2·a−1) | - | 0.67 | 1.15 | 0.23 |
| Calculated Rate Using CO2 Flux (kg·m−2·a−1) | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.17 |
| Correction for Calculated Rate Using CO2 Flux (kg·m−2·a−1) | - | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ning, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, F. Assessing the Natural Source Zone Depletion of a Petroleum-Contaminated Clayey Soil Site in Southern China Combining Concentration Gradient Method and Metagenomics. Life 2024, 14, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030337
Xu Z, Zhang M, Ning Z, He Z, Zhang F. Assessing the Natural Source Zone Depletion of a Petroleum-Contaminated Clayey Soil Site in Southern China Combining Concentration Gradient Method and Metagenomics. Life. 2024; 14(3):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030337
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhe, Min Zhang, Zhuo Ning, Ze He, and Fenge Zhang. 2024. "Assessing the Natural Source Zone Depletion of a Petroleum-Contaminated Clayey Soil Site in Southern China Combining Concentration Gradient Method and Metagenomics" Life 14, no. 3: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030337
APA StyleXu, Z., Zhang, M., Ning, Z., He, Z., & Zhang, F. (2024). Assessing the Natural Source Zone Depletion of a Petroleum-Contaminated Clayey Soil Site in Southern China Combining Concentration Gradient Method and Metagenomics. Life, 14(3), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030337






