Influence of Diet on Reproducible Corticosterone Levels in a Mouse Model of Maternal Separation with Early Weaning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
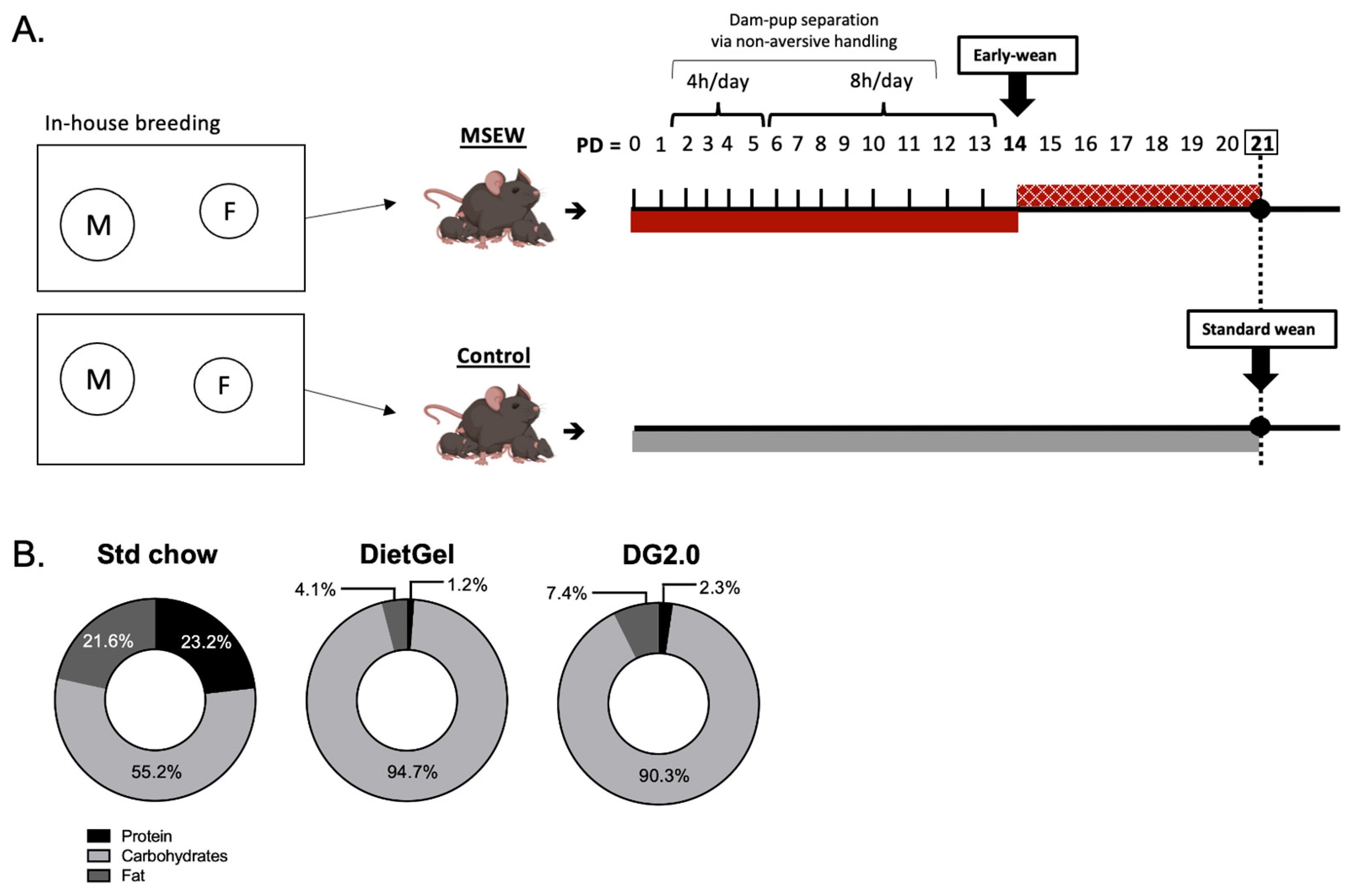
2.2. MSEW Protocol
2.3. Tissue Collection and Preparation
2.4. Corticosterone ELISA
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
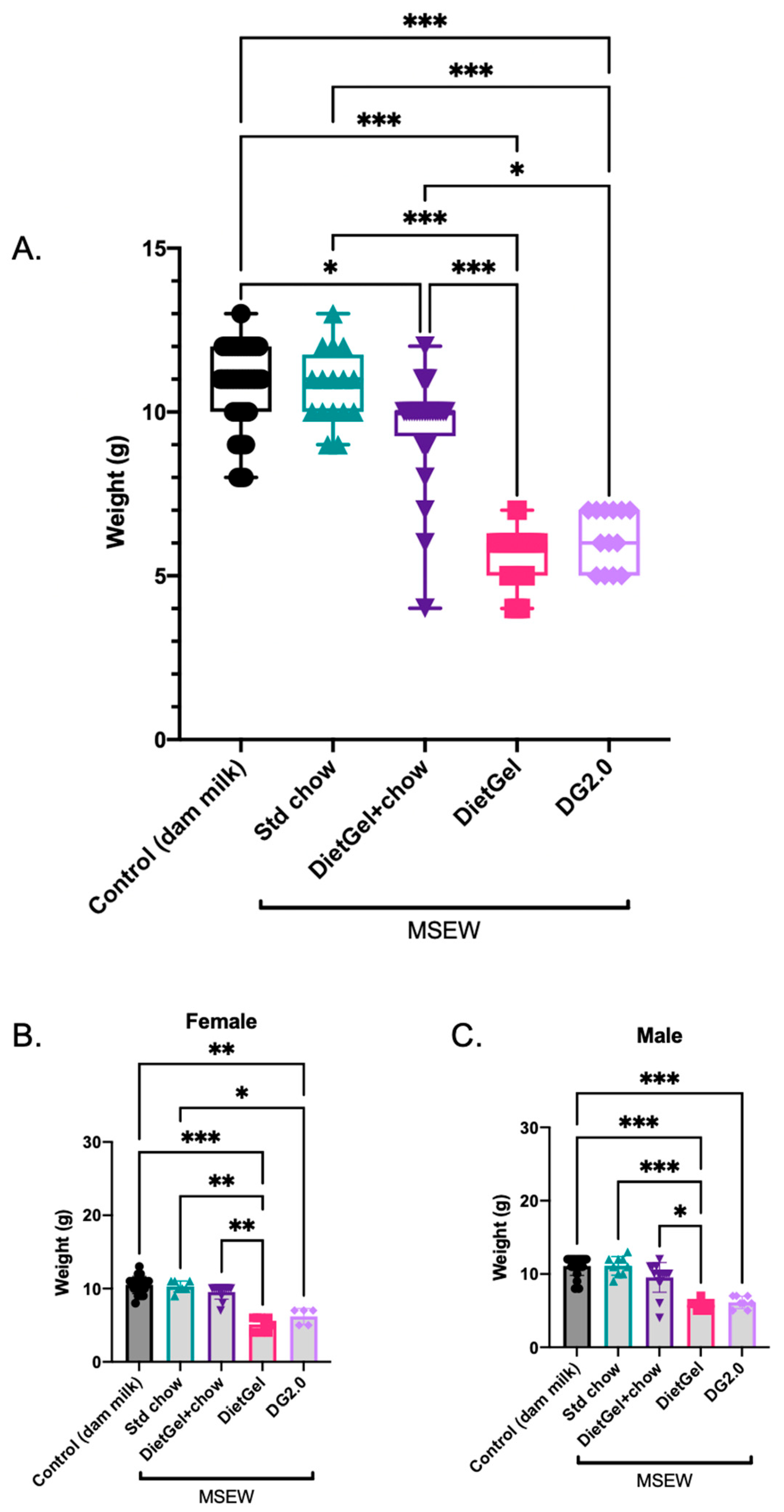
3.1. Variation in the Non-Milk Diet Alone Impacts Body Weight
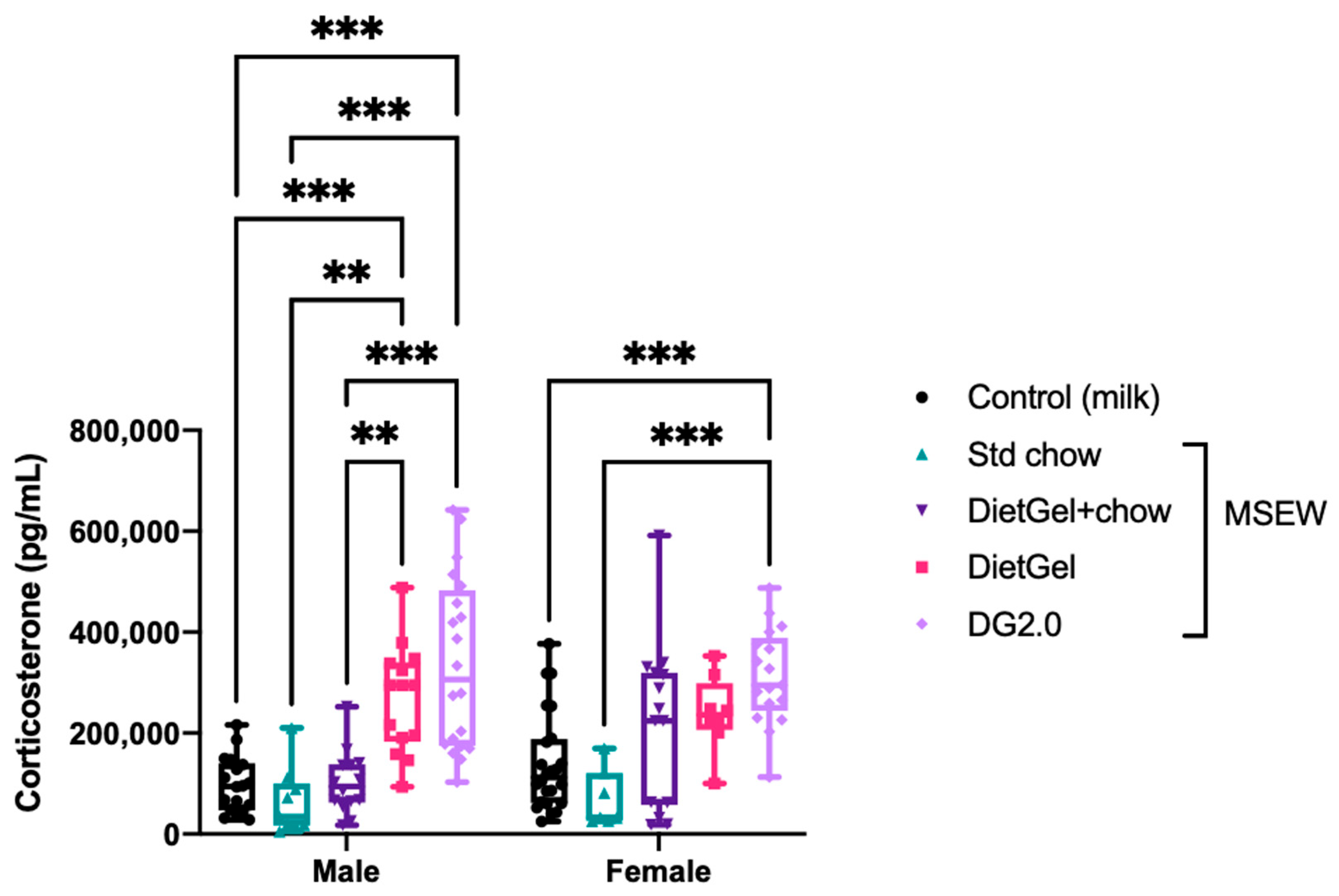
3.2. Select Non-Milk Diets Increased Circulating Corticosterone
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilbert, R.; Widom, C.S.; Browne, K.; Fergusson, D.; Webb, E.; Janson, S. Burden and consequences of child maltreatment in high-income countries. Lancet 2009, 373, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anda, R.F.; Felitti, V.J.; Bremner, J.D.; Walker, J.D.; Whitfield, C.; Perry, B.D.; Dube, S.R.; Giles, W.H. The enduring effects of abuse and related adverse experiences in childhood. A convergence of evidence from neurobiology and epidemiology. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 256, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felitti, V.J.; Anda, R.F.; Nordenberg, D.; Williamson, D.F.; Spitz, A.M.; Edwards, V.; Koss, M.P.; Marks, J.S. Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults. The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 1998, 14, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.M.; Hargrave, A.S.; Lisha, N.E.; Huang, A.J. Adverse Childhood Experiences and Aging-Associated Functional Impairment in a National Sample of Older Community-Dwelling Adults. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2023, 38, 3362–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, A.; Pariante, C.M.; Caspi, A.; Taylor, A.; Poulton, R. Childhood maltreatment predicts adult inflammation in a life-course study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegman, H.L.; Stetler, C. A meta-analytic review of the effects of childhood abuse on medical outcomes in adulthood. Psychosom. Med. 2009, 71, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkeila, J.; Vahtera, J.; Korkeila, K.; Kivimäki, M.; Sumanen, M.; Koskenvuo, K.; Koskenvuo, M. Childhood adversities as predictors of incident coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular disease. Heart 2010, 96, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, R.C.; Chang, Y.; Derby, C.A.; Bromberger, J.T.; Harlow, S.D.; Janssen, I.; Matthews, K.A. Abuse and subclinical cardiovascular disease among midlife women: The study of women’s health across the nation. Stroke 2014, 45, 2246–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, M.Y.; Barinas-Mitchell, E.; Maki, P.M.; Thurston, R.C. Childhood Maltreatment and Arterial Stiffness Among Midlife Women. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e026081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, J.; Chung, M.K.; Park, J.Y.; Shin, T.; Lee, K.J.; Lim, H.S.; Hwang, S.; Urtnasan, E.; Jo, Y.; et al. Childhood adversity and late-life depression: Moderated mediation model of stress and social support. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1183884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, D.S.; Galea, S. Life course epidemiology of trauma and related psychopathology in civilian populations. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2015, 17, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brew, B.K.; Lundholm, C.; Caffrey Osvald, E.; Chambers, G.; Öberg, S.; Fang, F.; Almqvist, C. Early-Life Adversity Due to Bereavement and Inflammatory Diseases in the Next Generation: A Population Study in Transgenerational Stress Exposure. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 191, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.G.; Ryu, V.; Kim, B.-T.; Kang, D.-W.; Jahng, J.W. Depressive behaviors and decreased expression of serotonin reuptake transporter in rats that experienced neonatal maternal separation. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 58, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targum, S.D.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Effect of Early Life Stress on Adult Psychiatric Disorders. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 16, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Danese, A.; Moffitt, T.E.; Pariante, C.M.; Ambler, A.; Poulton, R.; Caspi, A. Elevated inflammation levels in depressed adults with a history of childhood maltreatment. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2008, 65, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, A.; Moffitt, T.E.; Harrington, H.; Milne, B.J.; Polanczyk, G.; Pariante, C.M.; Poulton, R.; Caspi, A. Adverse childhood experiences and adult risk factors for age-related disease: Depression, inflammation, and clustering of metabolic risk markers. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2009, 163, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesuis, S.L.; Lucassen, P.J.; Krugers, H.J. Early life stress amplifies fear responses and hippocampal synaptic potentiation in the APPswe/PS1dE9 Alzheimer mouse model. Neuroscience 2021, 454, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschetter, K.E.; Callahan, L.B.; Flynn, S.A.; Rahman, S.; Beresford, T.P.; Ronan, P.J. Early life stress and susceptibility to addiction in adolescence. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2022, 161, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettway, Y.D.; Neder, T.H.; Ho, D.H.; Fox, B.M.; Burch, M.; Colson, J.; Liu, X.; Kellum, C.E.; Hyndman, K.A.; Pollock, J.S. Early life stress induces dysregulation of the heme pathway in adult mice. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón-Cortés, M. Sex differences in addiction-relevant behavioral outcomes in rodents following early life stress. Addict. Neurosci. 2023, 6, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanni, J.S.; Dieguez, H.H.; González Fleitas, M.F.; Canepa, E.; Berardino, B.; Repetto, E.M.; Villarreal, A.; Dorfman, D.; Rosenstein, R.E. Early life stress induces visual dysfunction and retinal structural alterations in adult mice. J. Neurochem. 2023, 165, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, R.Q.; Klocke, B.J.; Jennings, M.S.; Molina, P.A.; Hsu, J.S.; Kellum, C.E.; Alexander, K.L.; Lee, G.; Foote, J.B.; Lorenz, R.G.; et al. Early Life Stress in Mice Leads to Impaired Colonic Corticosterone Production and Prolonged Inflammation Following Induction of Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 29, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyrer-Jackson, J.M.; Overby, P.F.; Nagy, E.K.; Olive, M.F. Early Life Stress Promotes Heroin Seeking But Does Not Alter the Excitability of Insular Pyramidal Cells Targeting the Nucleus Accumbens. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 777826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apaydin, D.C.; Jaramillo, P.A.M.; Corradi, L.; Cosco, F.; Rathjen, F.G.; Kammertoens, T.; Filosa, A.; Sawamiphak, S. Early-Life Stress Regulates Cardiac Development through an IL-4-Glucocorticoid Signaling Balance. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Frick, J.M.; O’Neil, M.F.; Eller, O.C.; Morris, E.M.; Thyfault, J.P.; Christianson, J.A.; Lane, R.H. Early-life stress perturbs the epigenetics of Cd36 concurrent with adult onset of NAFLD in mice. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 94, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brix, L.M.; Monleon, D.; Collado, M.C.; Ederveen, T.H.A.; Toksöz, I.; Bordes, J.; van Doeselaar, L.; Engelhardt, C.; Mitra, S.; Narayan, S.; et al. Metabolic effects of early life stress and pre-pregnancy obesity are long lasting and sex specific in mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2023, 58, 2215–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterston, R.H.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Birney, E.; Rogers, J.; Abril, J.F.; Agarwal, P.; Agarwala, R.; Ainscough, R.; Alexandersson, M.; An, P.; et al. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature 2002, 420, 520–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaestri, C.; Pan, T.; Critz, M.; Ofray, D.; Gallo, M.; Bath, K.G. Type of early life adversity confers differential, sex-dependent effects on early maturational milestones in mice. Horm. Behav. 2020, 124, 104763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.D.; Bordner, K.A.; Elwafi, H.M.; Simen, A.A. Maternal separation with early weaning: A novel mouse model of early life neglect. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.; Gould, E. Early life stress in rodents: Animal models of illness or resilience? Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfitt, D.B.; Walton, J.R.; Corriveau, E.A.; Helmreich, D.L. Early life stress effects on adult stress-induced corticosterone secretion and anxiety-like behavior in the C57BL/6 mouse are not as robust as initially thought. Horm. Behav. 2007, 52, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlyle, B.C.; Duque, A.; Kitchen, R.R.; Bordner, K.A.; Coman, D.; Doolittle, E.; Papademetris, X.; Hyder, F.; Taylor, J.R.; Simen, A.A. Maternal separation with early weaning: A rodent model providing novel insights into neglect associated developmental deficits. Dev. Psychopathol. 2012, 24, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikusui, T.; Ichikawa, S.; Mori, Y. Maternal deprivation by early weaning increases corticosterone and decreases hippocampal BDNF and neurogenesis in mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Levine, J.L.S.; Avila-Quintero, V.; Bloch, M.; Kaffman, A. Systematic review and meta-analysis: Effects of maternal separation on anxiety-like behavior in rodents. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, M.; Wang, D.; Avila-Quintero, V.; Bloch, M.H.; Kaffman, A. Deficits in hippocampal-dependent memory across different rodent models of early life stress: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Ho, H.S.; Song, A.Y.; Low, J.; Je, H.S. Maternal Separation Does Not Produce a Significant Behavioral Change in Mice. Exp. Neurobiol. 2017, 26, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stupart, O.; Robbins, T.W.; Dalley, J.W. “The wrong tools for the right job”: A critical meta-analysis of traditional tests to assess behavioural impacts of maternal separation. Psychopharmacology 2023, 240, 2239–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolterink-Donselaar, I.G.; Meerding, J.M.; Fernandes, C. A method for gender determination in newborn dark pigmented mice. Lab. Anim. 2009, 38, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, K.; Hurst, J.L. Optimising reliability of mouse performance in behavioural testing: The major role of non-aversive handling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, K.; Hurst, J.L. Reducing mouse anxiety during handling: Effect of experience with handling tunnels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensini, F.; Inta, D.; Palme, R.; Brandwein, C.; Pfeiffer, N.; Riva, M.A.; Gass, P.; Mallien, A.S. The impact of handling technique and handling frequency on laboratory mouse welfare is sex-specific. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, J.M.; Dwyer, D.M.; Flecknell, P.A.; Leach, M.C.; Rowe, C. Handling method alters the hedonic value of reward in laboratory mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.L.; West, R.S. Taming anxiety in laboratory mice. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 825–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Figueiredo, H.F.; Ostrander, M.M.; Choi, D.C.; Engeland, W.C.; Herman, J.P. Chronic stress induces adrenal hyperplasia and hypertrophy in a subregion-specific manner. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291, E965–E973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpierre, C.; Fantin, R.; Barboza-Solis, C.; Lepage, B.; Darnaudéry, M.; Kelly-Irving, M. The early life nutritional environment and early life stress as potential pathways towards the metabolic syndrome in mid-life? A lifecourse analysis using the 1958 British Birth cohort. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncker, H.G.; van Keulen, B.J.; Finken, M.J.J.; de Rooij, S.R.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Korosi, A. The Potential Role of Nutrition in Modulating the Long-Term Consequences of Early-Life Stress. Nestlé Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2021, 96, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Kruskal-Wallis Test (Multiple Comparisons) | |
|---|---|
| (A) Combined sexes | |
| p value | <0.001 |
| Exact or approximate p value? | Approximate |
| p value summary | *** |
| Do the medians vary signif. (p < 0.05) | Yes |
| Number of groups | 5 |
| Kruskal-Wallis statistic | 82.58 |
| (B) Females | |
| p value | <0.001 |
| Exact or approximate p value? | Approximate |
| p value summary | *** |
| Do the medians vary signif. (p < 0.05) | Yes |
| Number of groups | 5 |
| Kruskal-Wallis statistic | 35.38 |
| (C) Males | |
| p value | <0.001 |
| Exact or approximate p value? | Approximate |
| p value summary | *** |
| Do the medians vary signif. (p < 0.05) | Yes |
| Number of groups | 5 |
| Kruskal-Wallis statistic | 46.98 |
| ANOVA Table | F (DFn, DFd) | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction | F (4, 136) = 1.874 | p = 0.12 |
| Sex | F (1, 136) = 1.095 | p = 0.30 |
| Treatment | F (4, 136) = 25.38 | p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choe, J.Y.; Donkor, M.; Thorpe, R.J., Jr.; Allen, M.S.; Phillips, N.R.; Jones, H.P. Influence of Diet on Reproducible Corticosterone Levels in a Mouse Model of Maternal Separation with Early Weaning. Life 2024, 14, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070880
Choe JY, Donkor M, Thorpe RJ Jr., Allen MS, Phillips NR, Jones HP. Influence of Diet on Reproducible Corticosterone Levels in a Mouse Model of Maternal Separation with Early Weaning. Life. 2024; 14(7):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070880
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoe, Jamie Y., Michael Donkor, Roland J. Thorpe, Jr., Michael S. Allen, Nicole R. Phillips, and Harlan P. Jones. 2024. "Influence of Diet on Reproducible Corticosterone Levels in a Mouse Model of Maternal Separation with Early Weaning" Life 14, no. 7: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070880
APA StyleChoe, J. Y., Donkor, M., Thorpe, R. J., Jr., Allen, M. S., Phillips, N. R., & Jones, H. P. (2024). Influence of Diet on Reproducible Corticosterone Levels in a Mouse Model of Maternal Separation with Early Weaning. Life, 14(7), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070880







