Associations of Serum Cystatin C, DNAm Cystatin C, Renal Function, and Mortality in U.S. Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
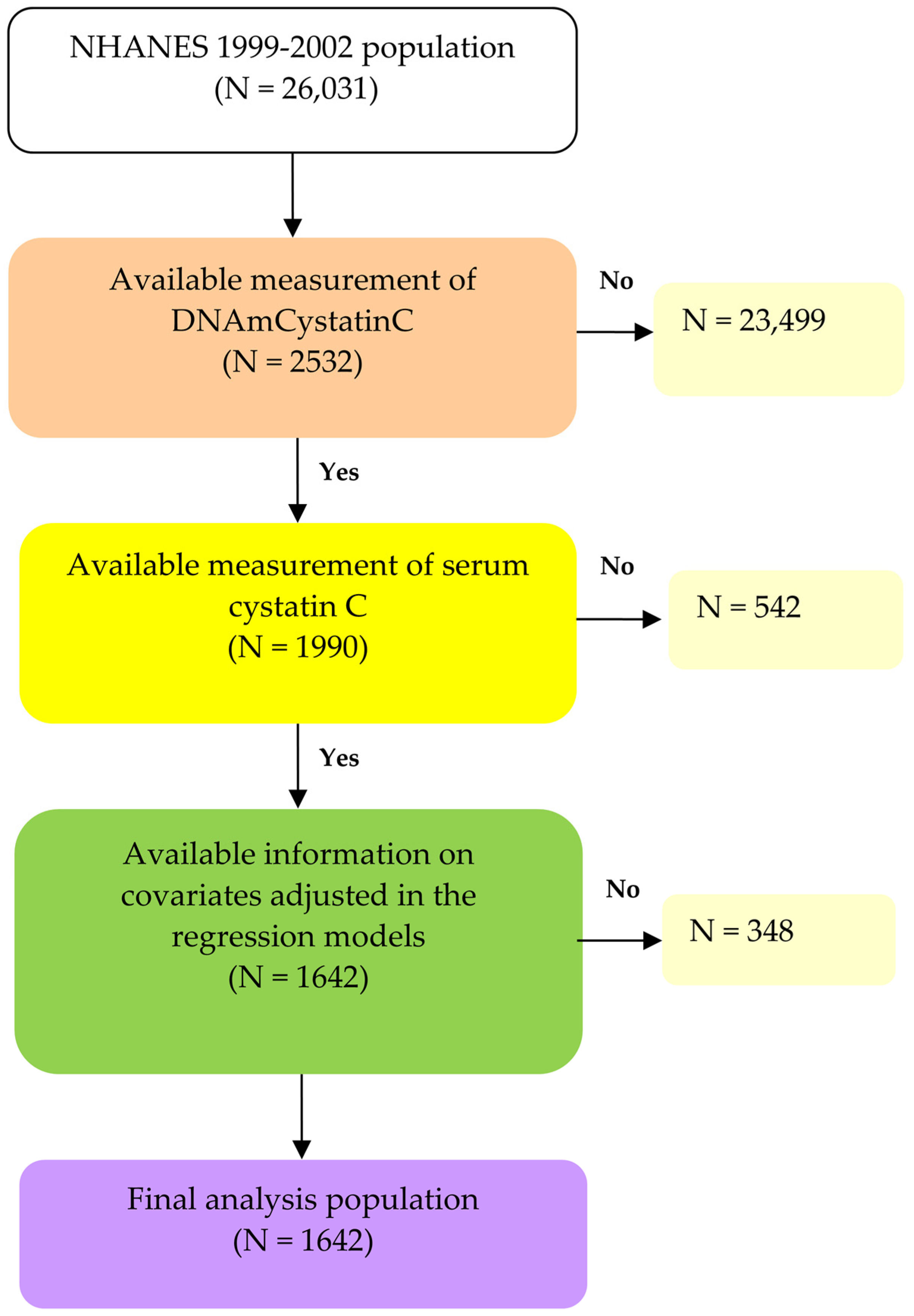
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Measurement of DNAmCystatinC
2.3. Measurement of Serum Cystatin C
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CHD | Coronary heart disease |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DNAmCystatinC | DNA methylation-predicted cystatin C |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| eGFRcr-cys | Estimated glomerular filtration rate calculated using both creatinine and cystatin C |
| ETS | Exposed to secondhand smoke |
| HR | Hazard ratios |
| Ln | Natural logarithm |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| NCHS | National Center for Health Statistics |
| NHANES | National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
| OR | Odds ratios |
References
- Wong, G.; Bernier-Jean, A.; Rovin, B.H.; Ronco, P. Time for Action: Recognising chronic kidney disease as a major non-communicable disease driver of premature mortality. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 1144–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, C.; Secondulfo, C.; Bilancio, G.; Visco, V.; Virtuoso, N.; Migliarino, S.; Ciccarelli, M.; Di Pietro, P.; La Mura, L.; Damato, A.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease with Mineral Bone Disorder and Vascular Calcification: An Overview. Life 2024, 14, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowski, J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Böhm, M.; Marx, N. Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease. Circulation 2021, 143, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, J.; Remuzzi, G.; Saran, R.; Williams, D.E.; Ríos-Burrows, N.; Powe, N.R.; Brück, K.; Wanner, C.; Stel, V.S.; Venuthurupalli, S.K.; et al. Taming the chronic kidney disease epidemic: A global view of surveillance efforts. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, N.; Schaeffner, E. New biomarkers for estimating glomerular filtration rate. J. Lab. Precis. Med. 2018, 3, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehlé, T.; Delanaye, P. Which is the best glomerular filtration marker: Creatinine, cystatin C or both? Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 54, e14278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onopiuk, A.; Tokarzewicz, A.; Gorodkiewicz, E. Cystatin C: A kidney function biomarker. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2015, 68, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Inker, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Tighiouart, H.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Feldman, H.I.; Greene, T.; Kusek, J.W.; Manzi, J.; Van Lente, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; et al. Estimating glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine and cystatin C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, X. Cystatin C is a disease-associated protein subject to multiple regulation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Yang, C.; Hua, R.; Xie, W.; Zhang, L. Association of Cystatin C Kidney Function Measures With Long-term Deficit-Accumulation Frailty Trajectories and Physical Function Decline. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2234208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.K.; Lin, J.-W.; Caffrey, J.L.; Chang, M.-H.; Hwang, J.-J.; Lin, Y.-S. Cystatin C and long-term mortality among subjects with normal creatinine-based estimated glomerular filtration rates: NHANES III (Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Dai, W. Serum Cystatin C and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Ethnic Chinese Patients With Normal Renal Function. Lab. Med. 2016, 47, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, C.; Bacalini, M.G.; Sazzini, M.; Pirazzini, C.; Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Luiselli, D. The epigenetic side of human adaptation: Hypotheses, evidences and theories. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2015, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, D. Expanding Role of Epigenetics in Human Health and Disease. Explor. Res. Hypothesis Med. 2024, 9, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, Y.; Bejaoui, Y.; El Hajj, N. DNA Methylation Biomarkers in Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillary, R.F.; Stevenson, A.J.; McCartney, D.L.; Campbell, A.; Walker, R.M.; Howard, D.M.; Ritchie, C.W.; Horvath, S.; Hayward, C.; McIntosh, A.M.; et al. Epigenetic measures of ageing predict the prevalence and incidence of leading causes of death and disease burden. Clin. Epigenet. 2020, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matías-García, P.R.; Ward-Caviness, C.K.; Raffield, L.M.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wilson, R.; Gào, X.; Nano, J.; Bostom, A.; Colicino, E.; et al. DNAm-based signatures of accelerated aging and mortality in blood are associated with low renal function. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanifuji, T.; Okazaki, S.; Otsuka, I.; Mouri, K.; Horai, T.; Shindo, R.; Shirai, T.; Hishimoto, A. Epigenetic clock analysis reveals increased plasma cystatin C levels based on DNA methylation in major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 322, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. NHANES 1999–2000. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/continuousnhanes/default.aspx?BeginYear=1999 (accessed on 5 October 2024).
- CDC. NHANES 1999–2002 DNA Methylation Array and Epigenetic Biomarkers. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/DNAm/Default.aspx (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- CDC. 2001–2002 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies: Cystatin C (Surplus). Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Data/Nhanes/Public/2001/DataFiles/SSCYST_B.htm (accessed on 5 October 2024).
- Lindsay, R.P.; Tsoh, J.Y.; Sung, H.Y.; Max, W. Secondhand smoke exposure and serum cotinine levels among current smokers in the USA. Tob. Control 2016, 25, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NKF. CKD-EPI Creatinine-Cystatin Equation (2021). Available online: https://www.kidney.org/ckd-epi-creatinine-cystatin-equation-2021 (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- Yan, M.T.; Chao, C.T.; Lin, S.H. Chronic Kidney Disease: Strategies to Retard Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: 2001–2002 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies: Medical Conditions. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Data/Nhanes/Public/2001/DataFiles/MCQ_B.htm (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- NCHS. NCHS Data Linkage: 2019 Public-Use Linked Mortality Files. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data-linkage/mortality-public.htm (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- CDC. Analytic and Reporting Guidelines: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/tutorials/Weighting.aspx (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- Tanto, C.; Bawazier, L.A.; Marbun, M.B.H.; Rizka, A.; Renaldi, K. Cystatin C as Predictor of Long-Term Mortality in Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2022, 4, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Hang, D.; Fu, Z. Associations of serum cystatin C concentrations with total mortality and mortality of 12 site-specific cancers. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1209349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.T.; Quach, A.; Wilson, J.G.; Reiner, A.P.; Aviv, A.; Raj, K.; Hou, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Li, Y.; Stewart, J.D.; et al. DNA methylation GrimAge strongly predicts lifespan and healthspan. Aging 2019, 11, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oblak, L.; van der Zaag, J.; Higgins-Chen, A.T.; Levine, M.E.; Boks, M.P. A systematic review of biological, social and environmental factors associated with epigenetic clock acceleration. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 69, 101348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mons, U.; Holleczek, B.; Saum, K.U.; Brenner, H. Epigenetic age acceleration predicts cancer, cardiovascular, and all-cause mortality in a German case cohort. Clin. Epigenet. 2016, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetker, N.S.; Pankow, J.S.; Bressler, J.; Morrison, A.C.; Boerwinkle, E. Prospective Study of Epigenetic Age Acceleration and Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes in the ARIC Study (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities). Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2018, 11, e001937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Joyce, B.T.; Colicino, E.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Dai, Q.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Kibbe, W.; Gao, T.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Blood Epigenetic Age may Predict Cancer Incidence and Mortality. EBioMedicine 2016, 5, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresovich, J.K.; Xu, Z.; O’Brien, K.M.; Weinberg, C.R.; Sandler, D.P.; Taylor, J.A. Epigenetic mortality predictors and incidence of breast cancer. Aging 2019, 11, 11975–11987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, T.; Nguyen, S.; Colicino, E.; Ochoa-Rosales, C.; Hill, W.D.; Brody, J.A.; Soerensen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Baldassari, A.R.; Elhadad, M.A.; et al. Integrative analysis of clinical and epigenetic biomarkers of mortality. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Schöttker, B.; Florath, I.; Stock, C.; Butterbach, K.; Holleczek, B.; Mons, U.; Brenner, H. Smoking-Associated DNA Methylation Biomarkers and Their Predictive Value for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 124, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Sotgiu, E.; Assaretti, S.; Baralla, A.; Mangoni, A.A.; Satta, A.; Carru, C. Cholesterol lowering treatment restores blood global DNA methylation in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2017, 27, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B.; Rysz-Górzyńska, M.; Gluba-Brzózka, A. Are Alterations in DNA Methylation Related to CKD Development? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| N | Serum Cystatin C (mg/L) | p-Value | DNAmCystatinC (Kilobase Pair) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 1642 | 1.008 (1.003) | 623.576 (1.001) | ||
| Sex | 0.151 | 0.025 | |||
| Men | 836 | 1.018 (1.010) | 625.531 (1.002) | ||
| Women | 806 | 0.997 (1.010) | 621.554 (1.002) | ||
| Age (in years) | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| 50–65 | 583 | 0.919 (1.011) | 594.870 (1.002) | ||
| ≥65 | 1059 | 1.060 (1.009) | 639.966 (1.001) | ||
| Ethnicity | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| Mexican-American | 482 | 0.956 (1.014) | 624.704 (1.002) | ||
| Other Hispanic | 88 | 0.993 (1.023) | 617.930 (1.006) | ||
| Non-Hispanic white | 669 | 1.047 (1.010) | 627.799 (1.002) | ||
| Non-Hispanic black | 352 | 1.019 (1.018) | 616.392 (1.003) | ||
| Other ethnicity | 51 | 0.946 (1.037) | 617.401 (1.009) | ||
| Family poverty–income ratio | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| <1 | 294 | 1.046 (1.019) | 628.626 (1.003) | ||
| 1–3 | 778 | 1.025 (1.011) | 628.720 (1.002) | ||
| >3 | 570 | 0.965 (1.011) | 614.062 (1.002) | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 0.064 | <0.001 | |||
| <25 | 441 | 0.987 (1.014) | 629.762 (1.003) | ||
| 25–30 | 653 | 1.003 (1.012) | 623.989 (1.002) | ||
| >30 | 548 | 1.030 (1.012) | 618.154 (1.002) | ||
| Smoking status | 0.032 | 0.004 | |||
| Non-smoker | 1026 | 0.993 (1.009) | 625.323 (1.002) | ||
| ETS | 334 | 1.039 (1.018) | 623.468 (1.003) | ||
| Current smoker | 282 | 1.023 (1.018) | 617.388 (1.003) | ||
| Alcohol consumption (drinks/year) | 0.012 | 0.001 | |||
| <12 | 650 | 1.030 (1.015) | 627.205 (1.002) | ||
| ≥12 | 992 | 0.993 (1.015) | 621.209 (1.002) | ||
| Hypertension | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| No | 568 | 0.935 (1.009) | 616.044 (1.002) | ||
| Yes | 1074 | 1.049 (1.010) | 627.597 (1.002) | ||
| Diabetes Mellitus | <0.001 | 0.345 | |||
| No | 1223 | 0.992 (1.008) | 623.084 (1.002) | ||
| Yes | 419 | 1.053 (1.017) | 625.014 (1.003) | ||
| Hypercholesterolemia | 0.892 | 0.454 | |||
| No | 1040 | 1.008 (1.010) | 624.083 (1.001) | ||
| Yes | 602 | 1.006 (1.011) | 622.700 (1.002) | ||
| History of CVD | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| No | 1292 | 0.974 (1.007) | 620.713 (1.002) | ||
| Yes | 350 | 1.140 (1.019) | 634.261 (1.003) | ||
| History of cancer | 0.036 | <0.001 | |||
| No | 1396 | 1.001 (1.008) | 621.751 (1.001) | ||
| Yes | 246 | 1.045 (1.016) | 634.036 (1.004) |
| DNAmCystatinC (Kilobase Pair) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adjusted β (SE) | p-Value | |
| eGFRcr-cys (mL/min/1.73 m2) | ||
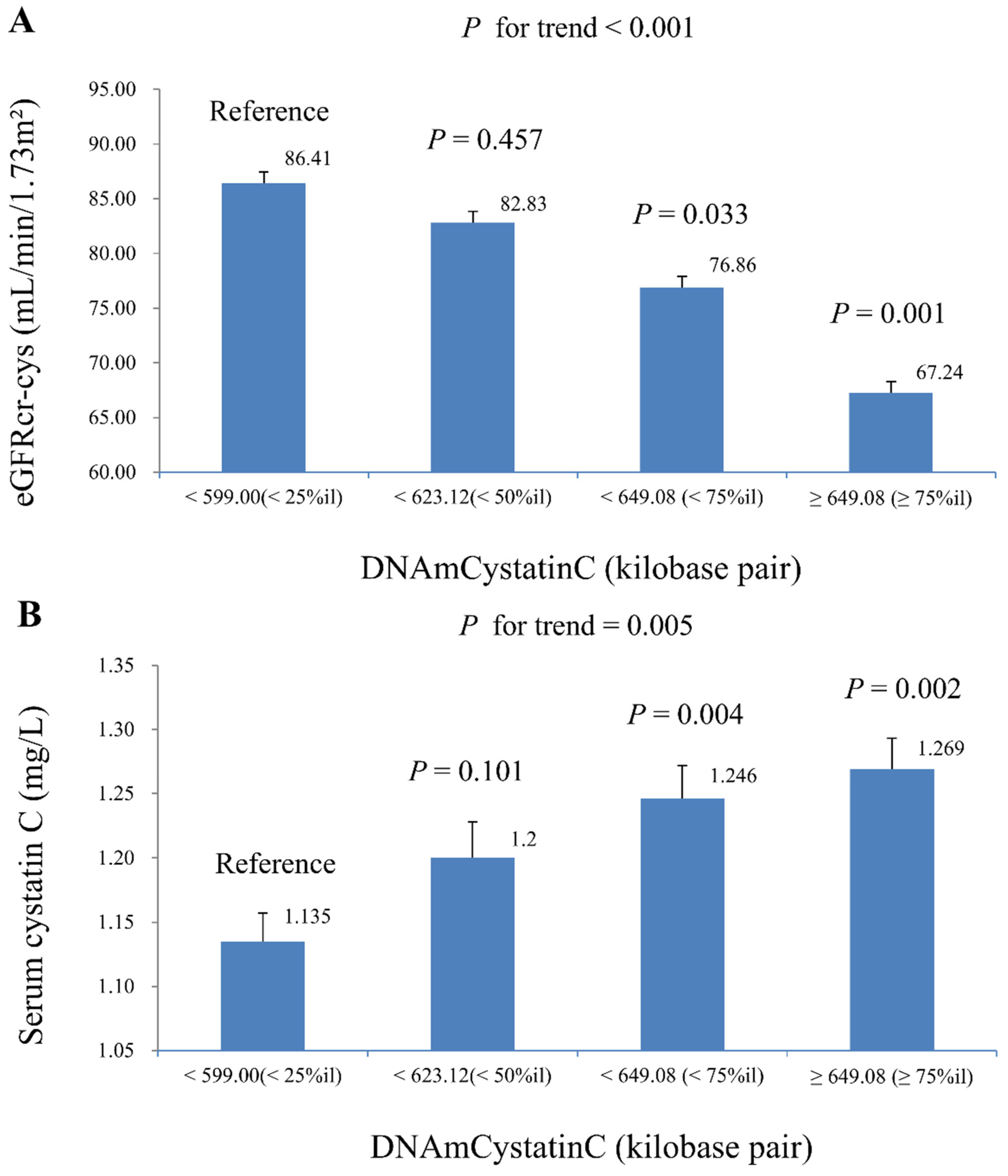
| Model 1 | −1.306 (0.534) | 0.021 |
| Model 2 | −1.123 (0.449) | 0.018 |
| Serum cystatin C (mg/L) | ||
| Model 1 | 1.134 (0.399) | 0.008 |
| Model 2 | 0.993 (0.334) | 0.006 |
| Model 3 | 0.773 (0.267) | 0.007 |
| Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Ln-eGFRcr-cys (mL/min/1.73 m2) | ||||
| All-cause mortality | 0.48 (0.38–0.60) | <0.001 | ||
| Cardiovascular mortality * | 0.57 (0.37–0.86) | 0.009 | ||
| Cancer-related mortality | 0.80 (0.36–1.75) | 0.559 | ||
| Serum cystatin C (mg/L) | ||||
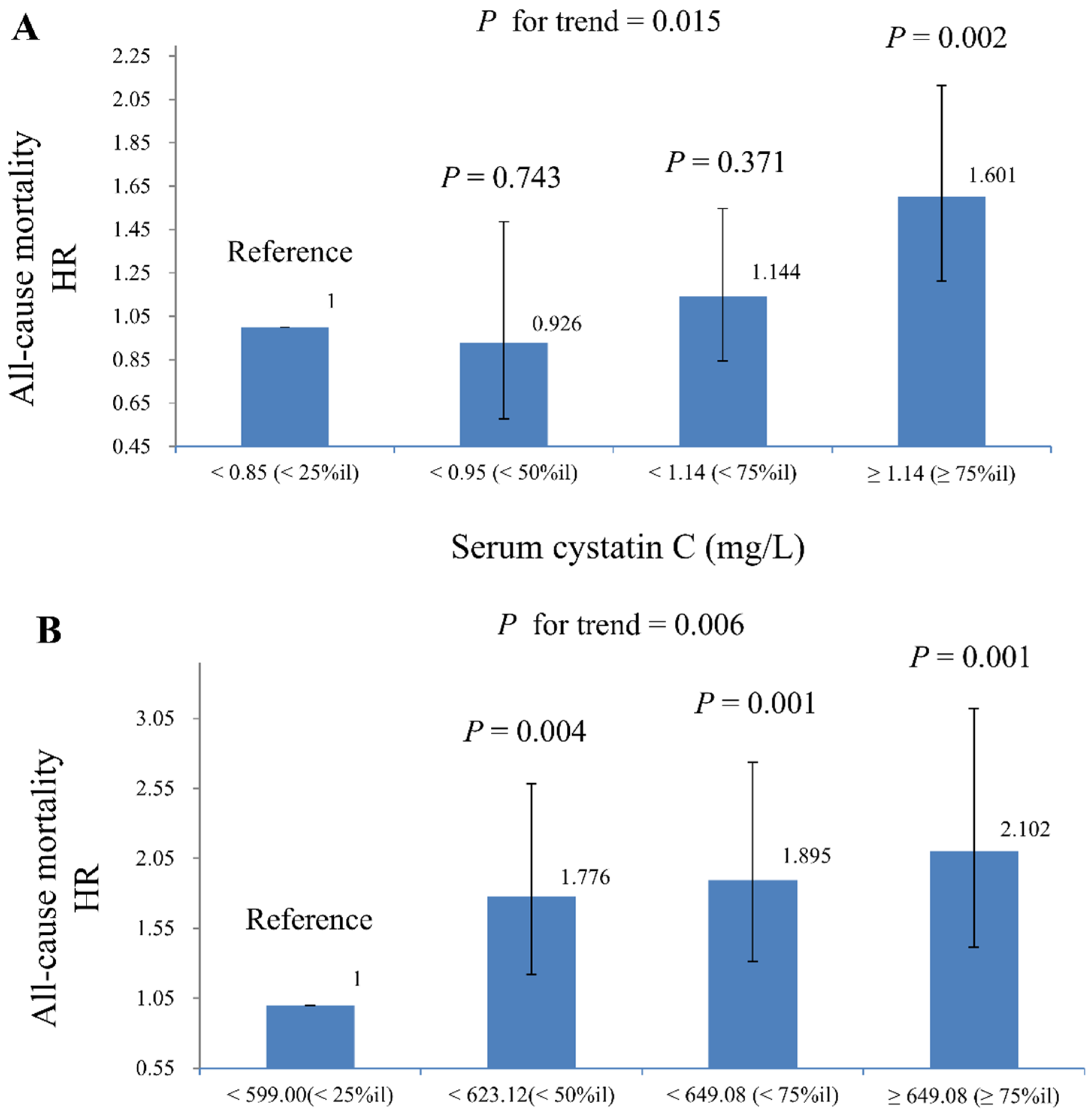
| All-cause mortality | 3.04 (2.20–4.18) | <0.001 | 2.87 (1.938–4.26) | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular mortality * | 2.53 (1.50–4.26) | 0.001 | 3.04 (1.34–6.88) | 0.010 |
| Cancer-related mortality | 1.60 (0.64–3.99) | 0.305 | 1.01 (0.28–3.65) | 0.991 |
| DNAmCystatinC (kilobase pair) | ||||
| All-cause mortality | 238.82 (11.02–5174.95) | 0.001 | 135.86 (5.51–3349.69) | 0.004 |
| Cardiovascular mortality * | 40.70 (0.08–21,934.33) | 0.238 | 28.53 (0.05–14,967.83) | 0.283 |
| Cancer-related mortality | 25.69 (0.03–19,764.14) | 0.326 | 15.26 (0.02–10,671.01) | 0.402 |
| DNAmCystatinC (Kilobase Pair) | Unweighted Number/ Population Size | All-Cause Mortality | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | p for Interaction | ||
| Gender | 0.661 | |||
| Men | 836/19,240,990 | 1.07 (1.01–1.15) | 0.033 | |
| Women | 806/23,851,402 | 2.11 (1.04–4.26) | 0.018 | |
| Age, years | 0.681 | |||
| 50–64 | 583/16,069,197 | 1.84 (1.10–3.09) | 0.010 | |
| ≥65 | 1.059/27,023,195 | 1.58 (0.99–2.54) | 0.059 | |
| Ethnicity | 0.644 | |||
| Non-Hispanic white | 669/34,366,802 | 1.80 (1.01–3.20) | 0.047 | |
| Other | 973/8,725,590 | 1.07 (1.02–1.12) | 0.008 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.303 | |||
| <30 | 1094/29,164,479 | 1.76 (1.06–2.91) | 0.010 | |
| ≥30 | 548/13,927,913 | 1.26 (0.99–1.61) | 0.075 | |
| Smoking status | 0.848 | |||
| Active smoker and ETS | 616/15,995,657 | 1.62 (1.02–2.58) | 0.043 | |
| Non-smoker | 1026/27,096,734 | 1.45 (0.99–1.90) | 0.081 | |
| Alcohol consumption (drinks/year) | 0.056 | |||
| <12 | 650/16,198,402 | 1.04 (0.65–1.71) | 0.785 | |
| ≥12 | 992/26,893,989 | 1.86 (1.27–2.73) | <0.001 | |
| CKD | 0.002 | |||
| No | 1374/36,086,885 | 1.77 (1.19–2.64) | <0.001 | |
| Yes | 268/7,005,507 | 0.96 (0.71–1.29) | 0.530 | |
| All-Cause Mortality | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Cystatin C (mg/L) | DNAmCystatinC (Kilobase Pair) | Unweighted Number/Population Size | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | p for Trend | p for Interaction |
| ≤0.950 (50%ile) | ≤623.124 (50%ile) | 511/14,524,136 | 1 | Reference | <0.001 | 0.078 |
| >623.124 (50%ile) | 274/5,165,348 | 1.31 (0.92–1.86) | 0.219 | |||
| >0.950 (50%ile) | ≤623.124 (50%ile) | 310/9,500,488 | 1.64 (1.22–2.20) | 0.002 | ||
| >623.124 (50%ile) | 547/13,092,392 | 1.85 (1.37–2.50) | <0.001 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, Y.-W.; Huang, W.-C.; Wang, C.; Lin, C.-Y. Associations of Serum Cystatin C, DNAm Cystatin C, Renal Function, and Mortality in U.S. Adults. Life 2025, 15, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010013
Fang Y-W, Huang W-C, Wang C, Lin C-Y. Associations of Serum Cystatin C, DNAm Cystatin C, Renal Function, and Mortality in U.S. Adults. Life. 2025; 15(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Yu-Wei, Wei-Chung Huang, Chikang Wang, and Chien-Yu Lin. 2025. "Associations of Serum Cystatin C, DNAm Cystatin C, Renal Function, and Mortality in U.S. Adults" Life 15, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010013
APA StyleFang, Y.-W., Huang, W.-C., Wang, C., & Lin, C.-Y. (2025). Associations of Serum Cystatin C, DNAm Cystatin C, Renal Function, and Mortality in U.S. Adults. Life, 15(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010013







