Health Impacts of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
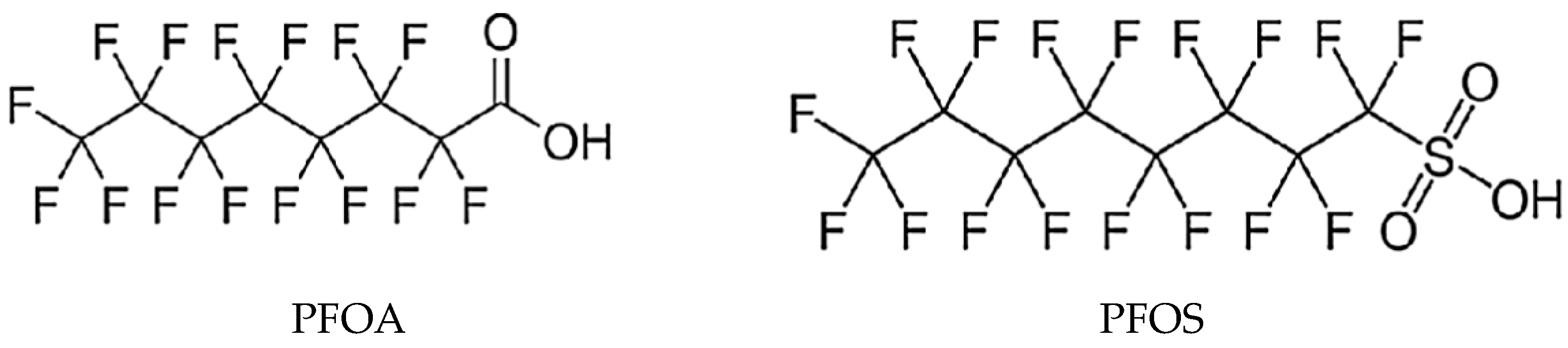
2. Properties of PFASs
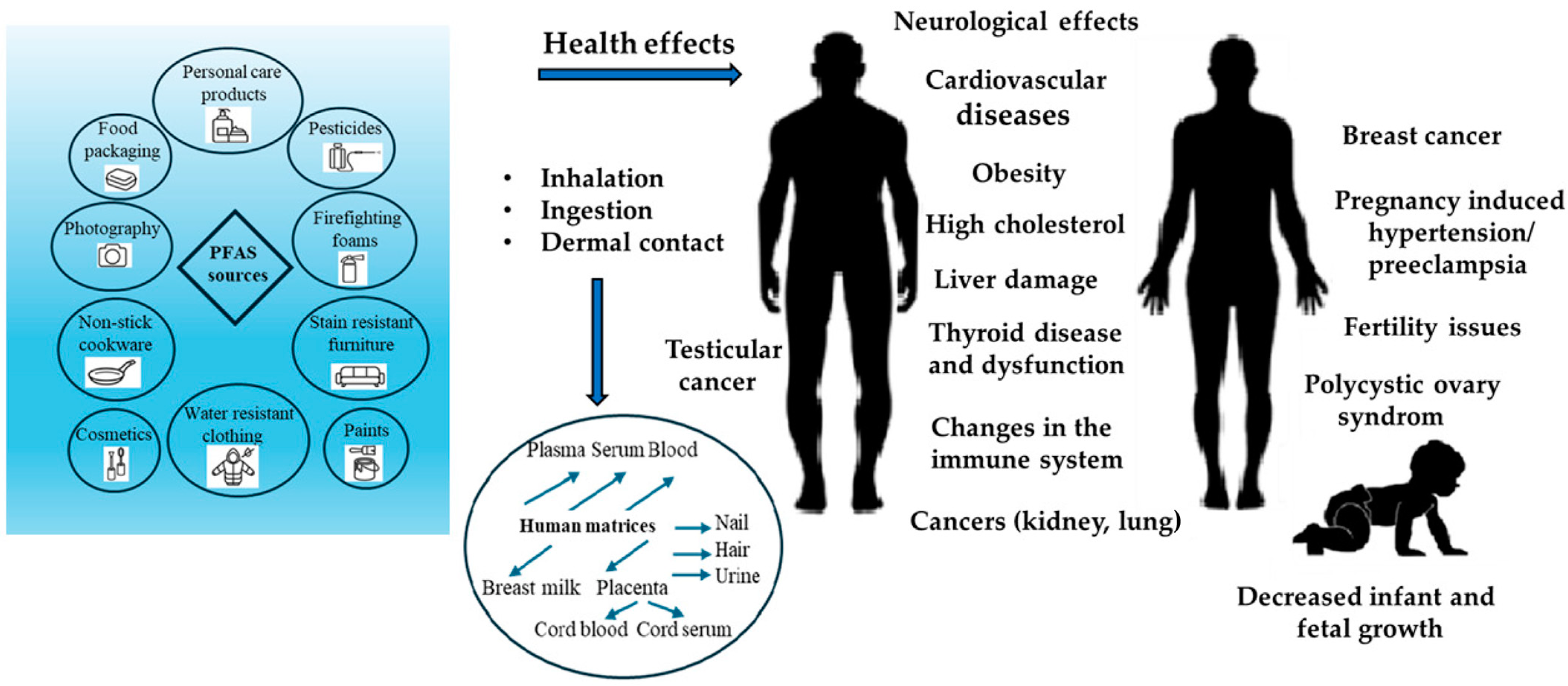
3. Sources of PFAS Exposure
Removal of PFASs
4. Analytical Techniques
5. Human Matrices
5.1. Hair
5.2. Placenta
5.3. Breast Milk
6. Health Effects
6.1. Lipid Metabolism
6.2. Diabetes Mellitus
6.3. Disorders in Women
6.4. Thyroid Hormones
6.5. Liver Disorders
6.5.1. General Liver Toxicity
6.5.2. Dyslipidemia, Steatosis, and Steatohepatitis
6.5.3. Hepatocarcinogenesis
6.6. Hypertension
6.7. Cancer
6.8. Obesity
6.9. Autism
6.10. Respiratory Diseases
6.11. Kidney Diseases
6.12. Cardiovascular Diseases
6.13. Bone Metabolism
6.14. Neurodevelopment in Child
6.15. Cerebral Palsy
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Sidek, L.M.; Zakaria, M.P.; Al-Garadi, M.A.; Suratman, S. Environmental occurrence and assessment of organic pollutants in surface sediments of South Peninsular Malaysia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Ohoro, C.R.; Adeniji, A.O.; Okoh, A.I.; Okoh, O.O. Spatial monitoring and health risk assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in environmental matrices from an industrialized impacted canal in South Africa. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 3409. [Google Scholar]
- Ohoro, C.R.; Adeniji, A.O.; Semerjian, L.; Okoh, A.I.; Okoh, O.O. Occurrence and risk assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface water and sediment of Nahoon River Estuary. Molecules 2022, 27, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EU. Directive 2006/122/EC of the European parliament and of the council of 12. Off. J. Eur. Union L 2006, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. 2009. Decision SC-4/17. Listing of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid, Its Salts and Perfluorooctane Sulfonyl Fluoride. UNEP-POPS-COP.4-SC-4-17. Conference of the Parties to the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants, Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: http://chm.pops.int/TheConvention/ConferenceoftheParties/ReportsandDecisions/tabid/208/Default.aspx (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- UNEP. 2019. Decision SC-9/12. Listing of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA), Its Salts and PFOA-Related Compounds. UNEP-POPS-COP.9-SC-9-12. Conference of the Parties to the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants, Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: http://chm.pops.int/TheConvention/ConferenceoftheParties/Meetings/COP9/tabid/7521/ItemId/7235/Default.aspx (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- UNEP. 2022. Decision SC-10/13. Perfluorohexane Sulfonic Acid (PFHxS), its Salts and PFHxS-Related Compounds. United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), ed. SC-10/13. Conference of the Parties to the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants, Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: http://chm.pops.int/TheConvention/ThePOPs/TheNewPOPs/tabid/2511/Default.aspx (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513. [Google Scholar]
- Buck, R.C.; Korzeniowski, S.H.; Laganis, E.; Adamsky, F. Identification and classification of commercially relevant per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 1045. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann, R.; Letcher, R.J. The universe of fluorinated polymers and polymeric substances and potential environmental impacts and concerns. Curr. Opin. Green. Sustain. Chem. 2023, 41, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teaf, C.M.; Garber, M.M.; Covert, D.J.; Tuovila, B.J. Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA): Environmental Sources, Chemistry, Toxicology, and Potential Risks. Soil. Sediment. Contam. 2019, 28, 258–273. [Google Scholar]
- Ateia, M.; Maroli, A.; Tharayil, N.; Karanfil, T. The overlooked short- and ultrashort-chain poly- and perfluorinated substances: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 866–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, M.; Huo, X.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Y.; Jin, F.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J. Association of emerging and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113691. [Google Scholar]
- Heydebreck, F.; Tang, J.; Xie, Z.; Ebinghaus, R. Alternative and Legacy Perfluoroalkyl Substances: Differences between European and Chinese River/Estuary Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fromme, H.; Wöckner, M.; Roscher, E.; Völkel, W. ADONA and perfluoroalkylated substances in plasma samples of German blood donors living in South Germany. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, P. A review of sources, multimedia distribution and health risks of novel fluorinated alternatives. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Vestergren, R.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C.; Liang, Y.; Cai, Y. Human Exposure and Elimination Kinetics of Chlorinated Polyfluoroalkyl Ether Sulfonic Acids (Cl-PFESAs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; He, J.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and alternatives (short-chain analogues, F-53B, GenX and FC-98) in residential soils of China: Present implications of replacing legacy PFASs. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105419. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Fluorinated alternatives to long-chain perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs), perfluoroalkane sulfonic acids (PFSAs) and their potential precursors. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 242. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, A.D.; Armitage, J.M.; Bruton, T.A.; Dassuncao, C.; Heiger-Bernays, W.; Hu, X.C.; Kärrman, A.; Kelly, B.; Ng, C.; Robuck, A.; et al. PFAS Exposure Pathways for Humans and Wildlife: A Synthesis of Current Knowledge and Key Gaps in Understanding. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 631. [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca, N.M.; Minucci, J.M.; Mullikin, A.; Slover, R.; Hubal, E.A.C. Human exposure pathways to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from indoor media: A systematic review. Environ. Int. 2022, 162, 107149. [Google Scholar]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Kewalramani, J.A.; Li, B.; Marsh, R.W. A Review of the Applications, Environmental Release, and Remediation Technologies of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, A.; Sadmani, A.H.M.A.; Reinhart, D.; Chang, N.B.; Goel, R. Per and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) as a contaminant of emerging concern in surface water: A transboundary review of their occurrences and toxicity effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126361. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, S.C.E.; Wanninayake, D.; Chen, D.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Li, Q. Physicochemical properties and interactions of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)—Challenges and opportunities in sensing and remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 5, 166764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliano, E.; Sgroi, M.; Falciglia, P.P.; Vagliasindi, F.G.A.; Roccaro, P. Removal of poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water by adsorption: Role of PFAS chain length, effect of organic matter and challenges in adsorbent regeneration. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, E.R.; Wang, Y.; Huo, J.; Li, A. Properties and fate and transport of persistent and mobile polar organic water pollutants: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, M.; Gong, T.; Zan, R.; Wang, W. Transport behavior difference and transport model of long- and short-chain per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in underground environmental media: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnowska, A.; Mudlaff, M.; Gorb, L.; Bulawska, N.; Zdybel, S.; Bakker, M.; Peijnenburg, W.; Puzyn, T. Expanding the applicability domain of QSPRs for predicting water solubility and vapor pressure of PFAS. Chemosphere 2023, 340, 139965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Occurrence of legacy and emerging poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances in water: A case study in Tianjin (China). Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokranov, A.K.; LeBlanc, D.R.; Pickard, H.M.; Ruyle, B.J.; Barber, L.B.; Hull, R.B.; Sunderland, E.M.; Vecitis, C.D. Surface-water/groundwater boundaries affect seasonal PFAS concentrations and PFAA precursor transformations. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2021, 23, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohoro, C.R.; Amaku, J.F.; Conradie, J.; Olisah, C.; Akpomie, K.G.; Malloum, A.; Akpotu, S.O.; Adegoke, K.A.; Okeke, E.S.; Omotola, E.O. Effect of physicochemical parameters on the occurrence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in aquatic environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 208, 117040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (pfass) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ.Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, A.R.; Klos, K.S.; Greene, C.W.; Huset, C.A.; Barry, K.M.; Goeden, H.M. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in powdered infant formula: Potential exposures and health risks. J. Environ. Expo. Assess. 2024, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaKind, J.S.; Naiman, J.; Verner, M.-A.; Léveque, L.; Fenton, S. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in breast milk and infant formula: A global issue. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Dane, J.; Kanel, S.R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Cawdrey, R.W.; Ambade, B.; Struckhoff, G.C.; Wilkin, R. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and wastewater: A critical review of their global occurrence and distribution. Sci.Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance toxicity and human health review: Current state of knowledge and strategies for informing future research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nannaware, N.; Mayilswamy, N.; Kandasubramanian, B. PFAS: Exploration of neurotoxicity and environmental impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 12815. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Namazkar, S.; Ragnarsdottir, O.; Josefsson, A.; Branzell, F.; Abel, S.; Abdallah, M.A.-E.; Harrad, S.; Benskin, J.P. Characterization and dermal bioaccessibility of residual- and listed PFAS ingredients in cosmetic products. Environ. Sci. 2024, 26, 259. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.F.; Peldszus, S.; Anderson, W.B. Behaviour and fate of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2014, 50, 318. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Ishaq, Z.; He, C.; Banks, A.P.W.; Braunig, J.; Thai, P.K.; Jayarathne, A.; Mueller, J.F.; Wang, X. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in floor dust from different indoor environments in Australia: Levels, variation, and human exposure risks. Chemosphere 2024, 366, 143372. [Google Scholar]
- Mamsen, L.S.; Jönsson, B.A.G.; Lindh, C.H.; Olesen, R.H.; Larsen, A.; Ernst, E.; Kelsey, T.W.; Andersen, C.Y. Concentration of perfluorinated compounds and cotinine in human foetal organs, placenta, and maternal plasma. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596–597, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Q.; Huang, H.; Tang, P.; Liang, J.; Chen, J.; Mu, C.; Pan, D.; Lv, F.; Zhou, L.; Long, J.; et al. Associations of prenatal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and fetal sex hormones in the Guangxi Zhuang Birth Cohort Study: Greater effect of long-chain PFAS. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 272, 116054. [Google Scholar]
- Høyer, B.B.; Bondea, J.P.; Tøttenborga, S.S.; Ramlau-Hansend, S.H.; Lindhe, C.; Pedersenf, H.S.; Toft, G. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances during pregnancy and child behaviour at 5 to 9 years of age. Horm. Behav. 2018, 101, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Lu, H.; Ma, B.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C.; Ying, C.; et al. Exposure to elevated per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in early pregnancy is related to increased risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A nested casecontrol study in Shanghai, China. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharal, B.; Ruchitha, C.; Kumar, P.; Pandey, R.; Rachamalla, M.; Niyogi, S.; Naidu, R.; Kaundal, R.K. Neurotoxicity of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Evidence and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 176941. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Varma, R.S.; Nadagouda, M.N. Remediation and mineralization processes for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148987. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Mezgebe, B.; Hejase, C.A.; Sahle-Demessie, E.; Nadagouda, M.N. Photodegradation and photocatalysis of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A review of recent progress. Next Mater. 2024, 2, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, K.H.; Seo, J.I.; Kim, S.M.; Shiea, J.; Yoo, H.H. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): Trends in mass spectrometric analysis for human biomonitoring and exposure patterns from recent global cohort studies. Environ. Int. 2024, 194, 109117. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, R.; Zhou, Y.; Nyberg, E.; Namazkar, S.; Yongning, W.; Xiao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Bergman, Å.; Benskin, J.P. Emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in human milk from Sweden and China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, D.; Yan, H. Advancements in detection techniques for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: A comprehensive review. .Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 176, 117754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, G.; Cafagna, S.; Polledri, E.; Mercadante, R.; Fustinoni, S. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the quantitation of 30 legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in human plasma, including HFPO-DA, DONA, and cC6O4. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1259–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Bangma, J.; Barry, K.M.; Fisher, C.M.; Genualdi, S.; Guillette, T.C.; Huset, C.A.; McCord, J.; Ng, B.; Place, B.J.; Reiner, J.L.; et al. PFAS ghosts: How to identify, evaluate, and exorcise new and existing analytical interference. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Panuwet, P.; Hunter, R.E.; D’Souza, P.E.; Chen, X.; Radford, S.A.; Cohen, J.R.; Marder, M.E.; Kartavenka, K.; Ryan, P.B.; Boyd Barr, D. Biological Matrix Effects in Quantitative Tandem Mass Spectrometry-Based Analytical Methods: Advancing Biomonitoring. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 46, 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. On-line solid phase extraction–ultra high performance liquid chromatography–quadrupole/Orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry determination of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in human serum. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1212, 123484. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, S.; Tan, R.; Guo, J.; Qi, X.; Chang, X.; et al. Associations of perfluoroalkyl substances with adipocytokines in umbilical cord serum: A mixtures approach. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Yuen, C.N.T.; Lin, H.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lam, P.K.S. Tracing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the aquatic environment: Target analysis and beyond. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 169, 11735. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, R.; Hu, F.; Liu, R.; Ruan, T.; Jiang, G. Simultaneous qualitative and quantitative analysis of fluoroalkyl sulfonates in riverine water by liquid chromatography coupled with Orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 2016, 1435, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.; Aro, R.; Wang, T.; Yeung, L.W.Y. Towards a Comprehensive Analytical Workflow for the Chemical Characterisation of Organofluorine in Consumer Products and Environmental Samples. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 115423. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yu, N.; Wang, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Pan, B.; Yu, H.; Wei, S. Comprehensive Exposure Studies of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the General Population: Target, Nontarget Screening, and Toxicity Prediction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14617. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, H.; Harada, K.H.; Kasuga, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Onuma, H.; Nishimura, H.; Kusama, R.; Yokoyama, K.; Zhu, J.; Harada Sassa, M.; et al. Serum perfluoroalkyl substances and breast breastrisk in Japanese women: A case-control study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 800, 149316. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, H.; Harada, K.H.; Kasuga, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Onuma, H.; Nishimura, H.; Kusama, R.; Yokoyama, K.; Zhu, J.; Harada Sassa, M.; et al. Association between serum concentrations of perfluoroalkyl substances and global DNA methylation levels in peripheral blood leukocytes of Japanese women: A crosssectional study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 159923. [Google Scholar]
- Dhiman, S.; Ansari, N.G. A review on extraction, analytical and rapid detection techniques of Per/Poly fluoro alkyl substances in different matrices. Microchem. J. 2024, 196, 109667. [Google Scholar]
- Di Giorgi, A.; Maida, N.L.; Taoussi, O.; Pichini, S.; Busardó, F.P.B.; Tini, A.; Di Trana, A. Analysis of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in conventional and unconventional matrices: Clinical outcomes. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar]
- Olomukoro, A.A.; Emmons, R.V.; Godage, N.H.; Cudjoe, E.; Gionfriddo, E. Ion exchange solid phase microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography/laminar flow tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of perfluoroalkyl substances in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1651, 462335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Macheka, L.R.; Olowoyo, J.O.; Mugivhisa, L.L.; Abafe, O.A. Determination and assessment of human dietary intake of per and polyfluoroalkyl substances in retail dairy milk and infant formula from South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142697. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, N.I.; Becanova, J.; Lohmann, R. A sensitive method for the detection of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in dairy milk. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1235. [Google Scholar]
- Timshina, A.S.; Robey, N.M.; Oldnettle, A.; Barron, S.; Mehdi, Q.; Cerlanek, A.; Townsend, T.G.; Bowden, J.A. Investigating the sources and fate of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in food waste compost. Waste Manag. 2024, 180, 125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drage, D.S.; Sharkey, M.; Berresheim, H.; Coggins, M.; Harrad, S. Rapid determination of selected PFAS in textiles entering the waste stream. Toxics 2023, 11, 11010055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miralles, P.; Beser, M.I.; Sanchís, Y.; Yusá, V.; Coscollá, C. Determination of 21 per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances in paper- and cardboard-based food contact materials by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 1559. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, Y.; Liang, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Hou, X.; Dong, H.; Wang, L. Fluorine and nitrogen functionalized magnetic graphene as a novel adsorbent for extraction of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances from water and functional beverages followed by HPLC-Orbitrap HRMS determination. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138103. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, A.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Cao, X. New deep eutectic solvent based superparamagnetic nanofluid for determination of perfluoroalkyl substances in edible oils. Talanta 2021, 228, 122214. [Google Scholar]
- Androulakakis, N.; Alygizakis, G.; Gkotsis, M.C.; Nika, V.; Nikolopoulou, E.; Bizani, E.; Chadwick, E.; Cincinelli, A.; Claßen, D.; Danielsson, S.; et al. Determination of 56 per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in top predators and their prey from Northern Europe by LC-MS/MS. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131775. [Google Scholar]
- Megson, D.; Bruce-Vanderpuije, P.; Idowu, I.G.; Ekpe, O.D.; Sandau, C.D. A systematic review for non-targeted analysis of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 960, 178240. [Google Scholar]
- Comito, R.; Porru, E.; Violante, F.S. Analytical methods employed in the identification and quantification of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in human matrices—A scoping review. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Liu, X.; Xie, X.; Zhou, X.; Pan, Y.; Dai, J. Exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in early pregnancy, risk of gestational diabetes mellitus, potential pathways, and influencing factors in pregnant women: A nested case-control study. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 326, 121504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Tang, B.; Nie, S.; Zhao, N.; He, L.; Cui, J.; Mao, W.; Jin, H. Distribution of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances and their precursors in human blood. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Román, A.; Abilleira, E.; Irizar, A.; Santa-Marina, L.; Gonzalez-Gay, B.; Etxebarria, N. Optimization for the analysis of 42 per- and polyfluorinated substances in human plasma: A high-throughput method for epidemiological studies. J. Chromatogr. A. 2023, 1712, 464481. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Duan, L.; Dong, B.; Dong, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Yang, L.; Shi, H. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in cord serum of newborns and their potential factors. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137525. [Google Scholar]
- Rokoff, L.B.; Wallenborn, J.T.; Harris, M.H.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Criswell, R.; Romano, M.E.; Young, J.G.; Calafati, A.M.; Oken, E.; Sagiv, S.K.; et al. Plasma concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in pregnancy and breastfeeding duration in Project Viva. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-Y.; Qiao, J.-C.; Gui, S.-Y.; Xu, K.-X.; Dzhambov, A.M.; Zhang, X.-J. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116064. [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Lyu, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Occurrences of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in human milk in China: Results of the third National Human Milk Survey (2017–2020). J. Hazard. Mat. 2023, 443, 130163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, M.; Harmouche-Karaki, M.; Matta, J.; Mahfouz, Y.; Salameh, P.; Younes, H.; Helou, K.; Finan, R.; Abi-Tayeh, G.; Meslimani, M.; et al. Maternal Serum, Cord and Human Milk Levels of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Association with Predictors and Effect on Newborn Anthropometry. Toxics 2023, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Gao, J.; He, M. Association between serum per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances levels and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125233. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, K.; Motoki, N.; Inaba, Y.; Toubou, H.; Shibazaki, T.; Nakayama, S.F.; Kamijima, M.; Tsukahara, T.; Nomiyama, T. Maternal Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Offspring Chromosomal Abnormalities: The Japan Environment and Children’s Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2024, 132, 97004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, N.; Ding, L. Associations between serum per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances as mixtures and lipid levels: A cross-sectional study in Jinan. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partington, J.M.; Marchiandi, J.; Szabo, D.; Gooley, A.; Kouremenos, K.; Smith, F.; Clarke, B.O. Validating blood microsampling for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances quantification in whole blood. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1713, 464522. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, M.E.; Gallagher, L.G.; Price, G.; Crawford, K.A.; Criswell, R.; Baker, E.; Botelho, J.C.; Calafat, A.M.; Karagas, M.R. Plasma per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance mixtures during pregnancy and duration of breastfeeding in the New Hampshire birth cohort study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2024, 258, 114359. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Tian, Z. Associations between per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances exposure and thyroid hormone levels in the elderly. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gui, J.G.; Howe, C.G.; Emond, J.A.; Criswell, R.L.; Gallagher, L.G.; Huset, C.A.; Peterson, L.A.; Botelho, J.C.; Calafat, A.M.; et al. Association of diet with per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in plasma and human milk in the New Hampshire Birth Cohort Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 933, 173157. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.-Y.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Sun, X.-F.; Feng, J.J.; Mai, L.; Wu, C.-C.; Huang, G.-L.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.-W.; Liu, L.-Y. The effect of per and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) exposure on gestational diabetes mellitus and its subclinical risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis protocol. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108719. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yan, P.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Tian, M.; Huang, Q.; Yan, J.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Profiles and transplacental transfer of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in maternal and umbilical cord blood: A birth cohort study in Zhoushan, Zhejiang Province, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133501. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, Q.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Hua, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Zheng, R. A novel high-throughput quantitative method for the determination of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances in human plasma based on UHPLC-Q/Orbitrap HRMS coupled with isotope internal standard. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136138. [Google Scholar]
- Belay, M.H.; Robotti, E.; Ghignone, A.; Fabbris, A.; Brandi, J.; Cecconi, D.; Masini, M.A.; Dondero, F.; Marengo, E. Sensitive and accurate determination of 32 PFAS in human serum using online SPE-UHPLC-HRMS. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 485, 136780. [Google Scholar]
- Eick, S.M.; Sehgal, N.; Salamova, A.; Fiedler, N.; Hood, R.B.; Yakimavets, V.; Promkam, N.; Prapamontol, T.; Suttiwan, P.; Sittiwang, S.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in paired serum and breastmilk samples among pregnant farmworkers in Thailand. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2025, 264, 114509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camdzic, D.; Dickman, R.A.; Joyce, A.S.; Wallace, J.S.; Ferguson, P.L.; Aga, D.S. Quantitation of Total PFAS Including Trifluoroacetic Acid with Fluorine NuclearMagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 5484–5488. [Google Scholar]
- Camdzic, D.; Dickman, R.A.; Aga, D.S. Total and class-specific analysis of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in environmental samples using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2021, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.U.; Crimi, M.; Andreescu, S. Current and emerging analytical techniques for the determination of PFAS in environmental samples. Tren. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 37, e00198. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, A.; Jacobs, G.; Vanermen, G.; Covaci, A.; Voorspoels, S. New approach for assessing human perfluoroalkyl exposure via hair. Talanta 2015, 144, 574. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Li, M.; Tang, B.; Luo, W.; Ma, Y.; Ren, M.; Yu, Y.; Luo, X.; Mai, B. Levels, spatial distribution, and impact factors of heavy metals in the hair of metropolitan residents in China and human health implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10578. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, E.M.; Dereumeaux, C.; Guldner, L.; Briand, O.; Vandentorren, S.; Oleko, A.; Zaros, C.; Appenzeller, B.M.R. Hair versus urine for the biomonitoring of pesticide exposure: Results from a pilot cohort study on pregnant women. Environ. Int. 2021, 152, 106481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yan, X.; Tang, B.; Luo, W.; Chen, S.; Luo, X.; Zheng, J.; Mai, B.; Yu, Y. Human hair as a noninvasive matrix to assess exposure to micro-organic contaminants: State of the art review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164341. [Google Scholar]
- Appenzeller, B.M.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Hair analysis for biomonitoring of environmental and occupational exposure to organic pollutants: State of the art, critical review and future needs. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 210, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Vestergren, R.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, Y.; Cai, Y. Using hair, nail and urine samples for human exposure assessment of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Lyu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Occurence of perfluoroalkyl substances in matched human serum, urine, hair and nail. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Y.; Lalwani, D.; Kwok, K.Y.; Yamazaki, E.; Taniyasu, S.; Kumar, N.J.I.; Lam, P.K.S.; Yamashita, N. Assessing exposure to legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances via hair—The first nationwide survey in India. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, J.; Lefeuvre, S.; Guihenneuc, J.; Cambien, G.; Dupuis, A.; Venisse, N. Analytical methods and biomonitoring results in hair for the assessment of exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals: A literature review. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.-F.; Hsu, J.-Y.; Hsiao, P.-Z.; Chou, T.-C.; Liao, P.-C. Hair specimens in exposome-health research: Opportunities, challenges, and app lications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 178, 117825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, E.; Fais, P.; Cecchetto, G.; Montisci, M.; Viel, G.; Pascali, J.P. Determination of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in human hair by liquid chromatography-high accurate mass spectrometry (LC-QTOF). J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1172, 122651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karzi, V.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Vakonaki, E.; Alegakis, T.; Katsikantami, I.; Sifakis, S.; Rizos, A.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Biomonitoring of bisphenol A, triclosan and perfluorooctanoic acid in hair samples of children and adults. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 110 Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Exposure assessment to parabens, bisphenol A and perfluoroalkyl compounds in children, women and men by hair analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, T.; Cui, Q.; Buka, S.L.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.; Xia, W.; Yeung, L.W.; Li, Y.; et al. Novel Chlorinated polyfluorinated ether sulfonates and legacy per-/polyfluoroalkyl substances: Placental transfer and relationship with serum albumin and glomerular filtration rate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Zhuang, T.; Liu, X.; Fu, J.; Zhang, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, A.; Liang, Y.; Song, M.; et al. Prenatal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and association between the placental transfer efficiencies and dissociation constant of serum proteins-PFAS complexes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, B.E.; Fenton, S.E. Early life exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and latent health outcomes: A review including the placenta as a target tissue and possible driver of peri- and postnatal effects. Toxicology 2020, 443, 152565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yin, S.; Kelly, B.C.; Liu, W. Chlorinated Polyfluoroalkyl Ether Sulfonic Acids in Matched Maternal, Cord, and Placenta Samples: A Study of Transplacental Transfer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, W.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, R.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C.; Yao, Q.; Yuan, T.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Efficiency of maternal-fetal transfer of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lib, A.; Buchananb, S.; Liu, W. Exposure characteristics for congeners, isomers, and enantiomers of perfluoroalkyl substances in mothers and infants. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Shao, L.-X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, S.-W.; Wang, X.; Lu, G.-L.; Wang, X.; Jin, J.-H. Target analysis and suspect screening of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in paired samples of maternal serum, umbilical cord serum, and placenta near fluorochemical plants in Fuxin, China. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Breastfeeding. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/breastfeeding#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- LaKind, J.S.; Verner, M.A.; Rogers, R.D.; Goeden, H.; Naiman, D.Q.; Marchitti, S.A.; Lehmann, G.M.; Hines, E.P.; Fenton, S.E. Current breast milk PFAS levels in the United States and Canada: After all this time, why don’t we know more? Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 25002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawn, D.F.K.; Dufresne, G.; Clément, G.; Fraser, W.D.; Arbuckle, T.E. Perfluorinated alkyl substances in Canadian human milk as part of the Maternal- Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals (MIREC) study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, L.; Siljander, H.; Duberg, D.; Honkanen, J.; Virtanen, S.M.; Orešič, M.; Knip, M.; Hyöyläinen, T. Exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances associates with an altered lipid composition of breast milk. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.M.; Ashley-Martin, J.; Liang, C.L.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Borghese, M.M.; Buckley, J.P.; Cecil, K.M.; Chen, A.; Dodds, L.; et al. Personal care product use and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in pregnant and lactating people in the Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals study. Environ. Int. 2024, 193, 109094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonato, M.; Corrá, F.; Bellio, M.; Guidolin, L.; Tallandini, L.; Irato, P.; Santovito, G. PFAS Environmental Pollution and Antioxidant Responses: An Overview of the Impact on Human Field. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojkumar, Y.; Pilli, S.; Rao, P.V.; Tyagi, R.D. Sources, occurrence and toxic effects of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2023, 97, 107174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, H.W.; Lim, Y.H.; Bae, S.; Kho, Y.; Hong, Y.C.; Shin, C.H.; Yang, S.W. The serum concentrations of perfluoroalkyl compounds were inversely associated with growth parameters in 2-year old children. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 226. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, M.H.; Oken, E.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Bellinger, D.C.; Webster, T.F.; White, R.F.; Sagiv, S.K. Prenatal and childhood exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and child cognition. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, C.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Li, Z.; Ren, A. Prenatal exposure to poly/perfluoroalkyl substances and risk for congenital heart disease in offspring. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134008. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Yu, K.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L. Association between prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances and respiratory tract infections in preschool children. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110156. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Dong, H.; Li, J. Reproductive toxicity of PFOA, PFOS and their substitutes: A review based on epidemiological and toxicological evidence. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118485. [Google Scholar]
- Wee, S.Y.; Aris, A.Z. Environmental impacts, exposure pathways, and health effects of PFOA and PFOS. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115663. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control. 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/index.html (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Perfluoroalkyls. 2021. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp200.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Ho, S.H.; Soh, S.X.H.; Wang, M.X.; Ong, J.; Seah, A.; Wong, Y.; Fang, Z.; Sima, S.; Lim, J.T. Perfluoroalkyl substances and lipid concentrations in the blood: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158036. [Google Scholar]
- Gardener, H.; Sun, Q.; Grandjean, P. PFAS concentration during pregnancy in relation to cardiometabolic health and birth outcomes. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110287. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Du, H.; Fang, H.; Han, M.; Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Yi, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Serum perfluoroalkyl substances in relation to lipid metabolism in Chinese pregnant women. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 128566. [Google Scholar]
- Zuanna, T.D.; Savitz, D.A.; Barbieri, G.; Pitter, G.; Jeddi, M.Z.; Daprá, F.; Fabricio, A.S.C.; Russo, F.; Fletcher, T.; Canova, C. The association between perfluoroalkyl substances and lipid profile in exposed pregnant women in the Veneto region, Italy. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 209, 111805. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Sun, H.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.; Lub, Y.; Han, L.; Chenc, L. Serum concentrations of per-/polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of type 2 diabetes: A case-control study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhoua, Q.; Ding, J.; Yin, S.; Shang, X.; Tian, Y. Exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances as a risk factor for gestational diabetes mellitus through interference with glucose homeostasis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Kim, S.-H. Associations between serum perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl concentrations and diabetes mellitus in the Korean general population: Insights from the Korean National Environmental Health Survey 2018–2020. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2024, 259, 114385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.P.; Harvey, A.J.; Finger, B.J.; Tarulli, G.A. Endocrine disrupting chemicals: Impacts on human fertility and fecundity during the peri-conception period. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110694. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Hong, X.; Zhao, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, B. The effects of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances on female fertility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Yin, S.; Li, F.; Xu, C. In utero exposure to per-/polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs): Preeclampsia in pregnancy and low birth weight for neonates. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137490. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, M.; Eatman, J.A.; Dunlop, A.L.; Barr, D.B.; Kannan, K.; Corwin, E.K.; Ryan, P.B.; Panuwet, P.; Yakimavets, V.; Taibl, K.R.; et al. Prenatal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and associations with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in the Atlanta African American Maternal-Child cohort. Chemosphere 2024, 357, 142052. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Martin, L.; Mustieles, V.; Ghaly, M.; Archer, M.; Sun, Y.; Torres, N.; Coburn-Sanderson, A.; Souter, I.; Petrozza, J.C.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances exposure is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome risk among women attending a fertility clinic. Hum. Reprod. 2024, 39, deae108.923. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, W.; Qiu, W.; Ao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J. Environmental Exposure to Emerging Alternatives of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in Women Diagnosed with Infertility: A Mixture Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 057001. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.; Feng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xiao, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, K. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Their Potential Effects on Female Reproductive Diseases. Toxics 2024, 12, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wu, Y.; Tao, G.; Xu, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, M.; Gu, T.; Xiong, J.; Xiao, S.; Wei, X.; et al. Association between PFAS exposure and thyroid health: A systematic review and meta-analysis for adolescents, pregnant women, adults and toxicological evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 175958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeaux, L.M.; Doherty, B.T.; Gallagher, L.G.; Zoeller, R.T.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Calafat, A.M.; Karagas, M.R.; Yolton, K.; Cheng, A.; Lanphearh, B.P.; et al. Maternal serum perfluoroalkyl substance mixtures and thyroid hormone concentrations in maternal and cord sera: The HOME Study. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, P.; Sheng, J.; Lou, X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, L.; Xiang, J.; Cheng, P.; Xu, D.; et al. Associations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and alternatives with subclinical hypothyroidism in children: A cross-sectional study in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177809. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Espinosa, M.J.; Mondal, D.; Armstrong, B.; Bloom, M.S.; Fletcher, T. Thyroid function and perfluoroalkyl acids in children living near a chemical plant. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 12, 1036. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, V.; Leonardi, G.; Genser, B.; Lopez-Espinosa, M.J.; Frisbee, S.J.; Karlsson, L.; Ducatman, A.M.; Fletcher, T. Serum perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) concentrations and liver function biomarkers in a population. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 655. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Wang, Z.; Miao, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Yuan, W. Prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances and thyroid hormone concentrations in cord plasma in a Chinese birth cohort. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Qu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Ji, S.; Chang, X.; Zhao, F.; Lv, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Associations between serum per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and thyroid hormones in Chinese adults: A nationally representative cross-sectional study. Environ. Int. 2024, 184, 108459. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wen, L.L.; Lin, L.Y.; Wen, T.W.; Lien, G.W.; Hsu, S.H.; Chien, K.L.; Liao, C.C.; Sung, F.C.; Chen, P.C.; et al. The associations between serum perfluorinated chemicals and thyroid function in adolescents and young adults. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 637. [Google Scholar]
- Freire, C.; Vela-Soria, F.; Castiello, F.; Salamanca-Fernandez, E.; Quesada-Jimenez, R.; Lopez-Alados, M.C.; Fernandez, M.F.; Olea, N. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and association with thyroid hormones in adolescent males. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2023, 252, 114219. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.C.; Johns, L.E.; Meeker, J.D. Serum biomarkers of exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances in relation to serum testosterone and measures of thyroid function among adults and adolescents from NHANES 2011–2012. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.-N.; Wang, X.-C.; Su, L.-Q.; Ji, S.-S.; Gu, W.; Barrett, H.; Dong, X.-J.; Zhu, H.-J.; Hou, S.-S.; Li, Z.-H.; et al. The association between per-/polyfluoroalkyl substances in serum and thyroid function parameters: A cross-sectional study on teenagers living near a Chinese fluorochemical industrial plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lin, Y.; Qin, L.; Zeng, X.; Jiang, H.; Liang, Y.; Wen, S.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Li, C.; et al. Serum metabolome associated with novel and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances exposure and thyroid cancer risk: A multi-module integrated analysis based on machine learning. Environ. Int. 2025, 195, 109203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maerten, A.; Callewaert, E.; Sanz-Serrano, J.; Devisscher, L.; Vinken, M. Effects of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances on the liver: Human-relevant mechanisms of toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 17671. [Google Scholar]
- Omoike, O.E.; Pack, R.P.; Mamudu, H.M.; Liu, Y.; Strasser, S.; Zheng, S.; Okoro, J.; Wang, L. Association between per and polyfluoroalkyl substances and markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110361. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, R.; McConnell, R.; Conti, D.; Grazuleviciene, R.; Slama, R.; Thomsen, C.; Wright, J.; Vos, M.; Vrijheid, M.; Chatzi, L. Prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances and child liver injury. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 3, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.J.; Cui, X.X.; Tan, Y.W.; Dong, P.X.; Ou, Y.Q.; Li, Q.Q.; Chu, C.; Wu, L.Y.; Liang, L.X.; Qin, S.J.; et al. Per- and perfluoroalkyl substances alternatives, mixtures and liver function in adults: A community-based population study in China. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107179. [Google Scholar]
- Nian, M.; Li, Q.-Q.; Bloom, M.; Qian, Z.; Syberg, K.M.; Vaughn, M.G.; Wang, S.-Q.; Wei, Q.; Zeeshan, M.; Gurram, N.; et al. Liver function biomarkers disorder is associated with exposure to perfluoroalkyl acids in adults: Isomers of C8 Health Project in China. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Palazzolo, S.; Caligiuri, I.; Sfriso, A.A.; Mauceri, M.; Rotondo, R.; Campagnol, D.; Canzonieri, V.; Rizzolio, F. Early warnings by liver organoids on short- and long-chain PFAS toxicity. Toxics 2022, 10, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Su, W.; Li, H.; Li, L.; An, Z.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Guo, H.; et al. Association of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances with hepatic steatosis and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease among patients with acute coronary syndrome. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115473. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Ling, X.; He, S.; Cui, H.; Yang, Z.; An, H.; Wang, L.; Zou, P.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; et al. PPARα/ACOX1 as a novel target for hepatic lipid metabolism disorders induced by per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: An integrated approach. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108138. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Ouyang, T.; Liu, H.; Cao, L.; Chen, W. Perfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) exposure and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the elderly: Results from NHANES 2003–2014. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 64342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; McConnell, R.; Catherine, C.; Xu, S.; Walker, D.I.; Stratakis, N.; Jones, D.P.; Miller, G.W.; Peng, C.; Conti, D.V.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver in children: An untargeted metabolomics approach. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- 169Dai, C.; Peng, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, F.; Lin, N. Distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in blood, serum, and urine of patients with liver cancer and associations with liver function biomarkers. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 139, 418. [Google Scholar]
- Erinc, A.; Davis, M.B.; Padmanabhan, V.; Langen, E.; Goodrich, J.M. Considering environmental exposures to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) as risk factors for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ji, H.; Liang, H.; Yuan, W.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Niu, J.; Shi, H.; Wen, S.; Miao, M. Associations of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances with gestational hypertension and blood pressure during pregnancy: A cohort study. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114284. [Google Scholar]
- Preston, E.V.; Hivert, M.-F.; Fleisch, A.F.; Calafat, A.M.; Sagiv, S.K.; Perng, W.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Chavarro, J.E.; Oken, E.; Zota, A.R.; et al. Early-pregnancy plasma per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) concentrations and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in the Project Viva cohort. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahm, S.; Bonde, J.P.; Chiu, W.A.; Hoppin, J.; Kanno, J.; Abdallah, M.; Blystone, C.R.; Calkins, M.M.; Dong, G.H.; Dorman, D.C.; et al. Carcinogenicity of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 2, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Report on the 2016 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) International Decontamination Research and Development Conference. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations/regulations (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Zheng, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Zheng, S.; Sun, B. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and cancer: Detection methodologies, epidemiological insights, potential carcinogenic mechanisms, and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176158. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, N.; Dai, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, D. Occurrence and distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in human livers with cancer. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111775. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, J.; Barry, K.H.; Huang, W.-Y.; Sampson, J.N.; Hofmann, J.N.; Silverman, D.T.; Calafat, A.M.; Botelho, J.C.; Kato, K.; Purdue, M.P.; et al. A prospective nested case-control study of serum concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and aggressive prostate cancer risk. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Shi, J.; Gao, X.; He, L.; Huang, H.; Zhao, G.; Wu, G.; Yu, T.; An, Q.; Mai, L.; et al. Associations of exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances mixture with the numbers of lymph nodes in colorectal cancer patients. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dou, Q.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Yin, C.; Ma, L.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances exposure and the risk of breast cancer: A nested case-control study in Jinchang Cohort. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119909. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tateo, V.; Thompson, Z.J.; Gilbert, S.M.; Cortessis, V.K.; Daneshmand, S.; Masterson, T.A.; Feldman, D.R.; Pierorazio, P.M.; Prakash, G.; Heidenreich, A.; et al. Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Testicular Cancer: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. 2025, 87, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-N.; Hu, Y.-H.; Xu, T.-T.; Luan, Y.-L.; Zeng, L.-X.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Guo, Y. Exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in lung cancer patients and their associations with clinical health indicators. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 350, 123995. [Google Scholar]
- Hanvoravongchai, J.; Laochindawat, M.; Kimura, Y.; Mise, N.; Ichihara, S. Clinical, histological, molecular, and toxicokinetic renal outcomes of per-/polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2024, 368, 143745. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Hu, Y.; Niu, Q.; Yan, Y. Associations between co-exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and metabolic diseases: The mediating roles of inflammation and oxidative stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176187. [Google Scholar]
- Averina, M.; Brox, J.; Huber, S.; Furberg, A.-S. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and dyslipidemia, hypertension and obesity in adolescents. The Fit Futures study. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110740. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, S.D.; Yao, P.; Vaughn, M.G.; Qian, Z. PFAS exposure and overweight/obesity among children in a nationally representative sample. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128852. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, Z.; Ritz, B.; von Ehrenstein, O.S.; Bech, B.H.; Nohr, E.A.; Fei, C.; Bossi, R.; Henriksen, T.B.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C.; Olsen, J. Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and childhood autism in association with prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances: A nested case-control study in the Danish National Birth Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyall, K.; Yau, V.M.; Hansen, R.; Kharrazi, M.; Yoshida, C.K.; Calafat, A.M.; Windham, G.; Croen, L.A. Prenatal Maternal Serum Concentrations of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Association with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Intellectual Disability. Environ. Health Persp. 2018, 126, 017001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Ghisari, M.; Kjeldsen, L.; Wielsøe, M.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, B.; Mortensen, E.L.; Abdallah, M.W.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C. Autism spectrum disorders, endocrine disrupting compounds, and heavy metals in amniotic fluid: A case-control study. Mol. Autism 2019, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skogheim, T.S.; Weyde, K.V.F.; Aase, H.; Engel, S.M.; Sur’en, P.; Øie, M.G.; Biele, G.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Haug, L.S.; et al. Prenatal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and associations with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder in children. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111692. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Bennett, D.H.; Calafat, A.M.; Tancredi, D.; Roa, D.L.; Schmidt, R.J.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Shin, H.-M. Prenatal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in association with autism spectrum disorder in the MARBLES study. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhou, R.; Yang, C.; Huang, Q.; Cheng, S. Impact of polyfluoroalkyl chemicals and volatile organic compounds exposure on lung function of American adults. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, A.; Faridi, S.; Sly, P.D.; Stone, L.; Kennedy, L.P.; Mahabee-Gittens, E.M. Asthma and decreased lung function in children exposed to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): An updated meta-analysis unveiling research gaps. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119827. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, Y.-P.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, M.-H.; Tsai, M.-S.; Hsieh, W.-S.; Chen, P.-C. Intrauterine exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances may harm children’s lung function development. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110178. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.-X.; Dong, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qian, Z.; Geiger, S.D.; Bingheim, E.; Tang, X.; Wu, Y.; Lv, J.; et al. Joint effects of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance alternatives and heavy metals on renal health: A community-based population study in China. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115057. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Duan, Z.; He, W.; Chen, T.; Tang, H.; Du, S.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Iijima, Y.; et al. Kidney function decline mediates the adverse effects of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on uric acid levels and hyperuricemia risk. J. Hazard. Mat. 2024, 471, 134312. [Google Scholar]
- Dunder, L.; Salihovic, S.; Varotsis, G.; Lind, P.M.; Elmståhl, S.; Lind, L. Plasma levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and cardiovascular disease—Results from two independent population-based cohorts and a meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2023, 181, 108250. [Google Scholar]
- Dunder, L.; Salihovic, S.; Lind, P.M.; Elmståhl, S.; Lind, L. Plasma levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are associated with altered levels of proteins previously linked to inflammation, metabolism and cardiovascular disease. Environ. Int. 2023, 177, 107979. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, J.P.; Zhou, J.; Marquess, K.M.; Lanphear, B.P.; Cecil, K.M.; Chen, A.; Sears, C.G.; Xu, Y.; Yolton, K.; Kalkwarf, H.J.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and bone mineral content in early adolescence: Modification by diet and physical activity. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, O.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, J.; et al. Associations of prenatal PFAS exposure and early childhood neurodevelopment: Evidence from the Shanghai Maternal-Child Pairs Cohort. Environ. Int. 2023, 173, 107850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, C.V.; Till, C.; Green, R.; El-Sabbagh, J.; Arbuckle, T.Y.; Hornung, R.; Lanphear, B.; Seguin, J.R.; Booij, L.; Fisher, M.; et al. Prenatal exposure to legacy PFAS and neurodevelopment in preschool-aged Canadian children: The MIREC cohort. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2023, 98, 107181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilhelmsson, A.; Rylander, L.; Jöud, A.; Lindh, C.H.; Mattsson, K.; Liew, Z.; Guo, P.; Ritz, B.; Källén, K.; Thacher, J.D. Exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in early pregnancy and risk of cerebral palsy in children. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, Z.; Ritz, B.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C.; Henriksen, T.B.; Nohr, E.A.; Bech, B.H.; Fei, C.; Bossi, R.; von Ehrenstein, O.S.; Streja, E.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances and the Risk of Congenital Cerebral Palsy in Children. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 180, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Analyte | Pretreatment | Analytical Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal serum | PFOS, PFOA | Extraction with ACN Sonication, centrifugation Next extraction with ACN | LC-MS/MS ESI- | [75] |
| Blood | PFOS, PFOA | Extraction with ACN Sonication, centrifugation Next extraction with ACN Purification on ENVI-Carb cartridge | UPLC-MS/MS ESI- | [76] |
| Human plasma | 42 PFASs | Captiva EMR-Lipid (1 mL, 96-well plate, 40 mg sorbent mass) | LC-q-Orbitrap ESI- | [77] |
| Cord serum | 19 PFASs | ACN Off-line SPE (Oasis WAX) | UHPLC-MS/MS ESI- | [78] |
| Plasma | PFOA, PFOS PFHxS, PFNA, PFDA, EtFOSAA, MeFOSAA | On-line SPE (Polaris C18 HD 10 mm × 2 mm) | HPLC-MS/MS | [79] |
| Cerebrospinal fluid | 26 PFASs | LLE with ethyl acetate | UPLC-MS/MS ESI- | [80] |
| Breast milk | 30 PFASs | Off-line SPE (Oasis WAX 6 mL/150 mg) | UPLC-MS/MS ESI- | [81] |
| Maternal, cord serum, breast milk | PFHpA, PFOA, PFHxS, PFOS, PFNA, and PFDA | On-line SPE (HyperSep C8-SE (7 μm)) | HPLC-MS/MS ESI- | [82] |
| Serum | PFOA, PFNA, PFCA | Sonication with 0.5 M TBAS and NaHCO3/Na2CO3 (pH = 10) Shaking with MTBE | UPLC-MS/MS ESI- | [83] |
| Maternal, cord blood | PFDA, PFDS PFHxS, PFNA, PFOA, PFOS, PFTrDA, PFUnA | On-line SPE (Oasis WAX 2.1 × 20 mm, 30 μm) | LC-MS/MS ESI- | [84] |
| Human serum | 18 PFASs | QuEChERS | UHPLC-Orbitrap MS ESI- | [85] |
| Whole blood | 75 PFASs | Filter-assisted precipitation, 1 mL SPE filter cartridge with two filter frits; MeOH, ACN, IPA | LC-MS/MS ESI- | [86] |
| Plasma | PFHxS, PFOA, PFNA, PFOS, PFDA | On-line SPE (HySphere C8-SE, 7 µM) | HPLC-MS/MS ESI- | [87] |
| Plasma | 14 PFASs | Off-line SPE (Oasis®Wax, 150 mg, 6 mL, 30 μm) | HPLC-MS/MS ESI- | [88] |
| Plasma, human milk | PFOA, PFOS, PFNA, PFDA, PFHxS PFHpA, PFHpS, PFHxA | On-line SPE (HySphere C8-SE, 7 μM) On-line SPE (Oasis WAX 30 µm, 10 mm × 1 mm) | HPLC-MS/MS | [89] |
| Plasma | 17 PFASs | 0.5 mol.L−1 tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate + 0.25 mol.L−1 NaHCO3/Na2CO3 + MTBE | LC-MS/MS ESI- | [90] |
| Cord blood | 24 PFASs | TBA + Na2CO3 + MTBE | LC-MS/MS ESI- | [91] |
| Plasma | 56 PFASs | ACN Off-line SPE (Anavo® HMR–Lipid SPE) | UHPLC-Q/Orbitrap HRMS | [92] |
| Serum | 32 PFASs | On-line SPE (Strata-X- AW 20 × 2.0 mm, 25 μm) | UHPLC-Orbitrap HRMS | [93] |
| Serum, breast milk | PFOS, PFOA, PFNA, PFHpA, PFHxS, PFDA, PFUnDA, PFDoDA | On-line SPE (Strata RP, 2.1 × 20 mm) | UPLC-MS/MS ESI- | [94] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mišľanová, C.; Valachovičová, M. Health Impacts of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): A Comprehensive Review. Life 2025, 15, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040573
Mišľanová C, Valachovičová M. Health Impacts of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): A Comprehensive Review. Life. 2025; 15(4):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040573
Chicago/Turabian StyleMišľanová, Csilla, and Martina Valachovičová. 2025. "Health Impacts of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): A Comprehensive Review" Life 15, no. 4: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040573
APA StyleMišľanová, C., & Valachovičová, M. (2025). Health Impacts of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): A Comprehensive Review. Life, 15(4), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040573







