Space Radiation: The Number One Risk to Astronaut Health beyond Low Earth Orbit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
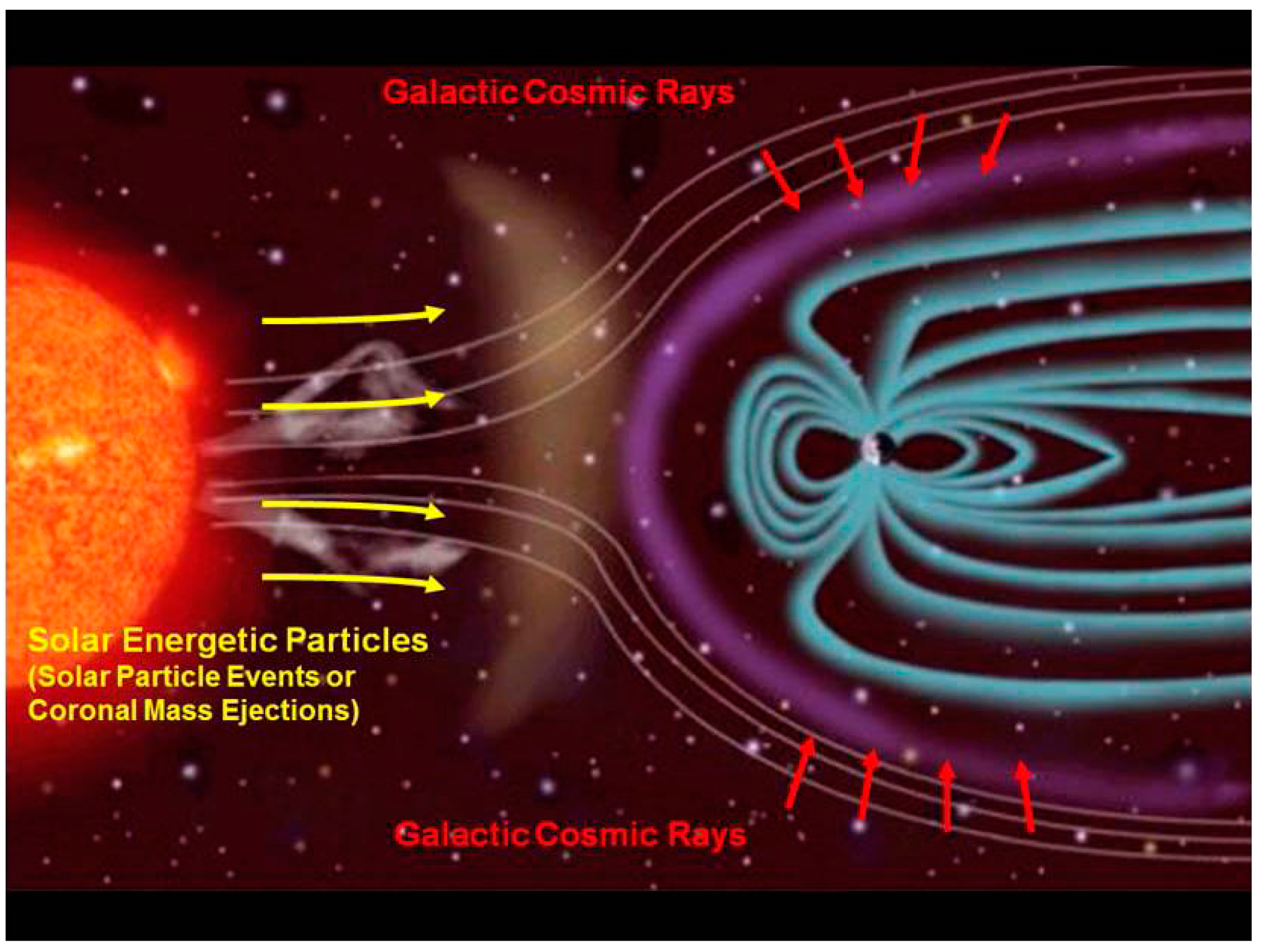
2. The Pernicious Interplanetary Space Radiation Environment
2.1. Galactic Cosmic Radiation

2.2. SPE Radiation

2.3. Intravehicular Radiation
3. Biomedical Consequences of Exposure to Space Radiation

3.1. Degenerative Tissue Effects from Radiation Exposure

3.2. Radiation Carcinogenesis
| Age in Years | Dose Limit-Male Astronauts (Average Life-Loss Per Death in Years) | Dose Limit-Female Astronauts (Average Life-Loss Per Death in Years) |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 520 mSv (15.7) | 370 mSv (15.9) |
| 30 | 620 mSv (15.4) | 470 mSv (15.7) |
| 35 | 720 mSv (15.0) | 550 mSv (15.3) |
| 40 | 800 mSv (14.2) | 620 mSv (14.7) |
| 45 | 950 mSv (13.5) | 750 mSv (14.0) |
| 50 | 1150 mSv (12.5) | 920 mSv (13.2) |
| 55 | 1470 mSv (11.5) | 1120 mSv (12.2) |
3.3. Acute and Late CNS Effects from Radiation Exposure
3.4. Radiation Syndromes Due to SPEs

4. Synergistic Effects and Individual Susceptibility
5. Research Considerations
5.1. Simulating the Space Radiation Environment
5.2. Selection of Appropriate Animal Models
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simpson, J.A. Elemental and isotopic composition of the galactic cosmic rays. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 1983, 33, 323–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP). Information Needed to Make Radiation Protection Recommendations for Space Missions Beyond Low-Earth Orbit; NCRP: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Committee on the Evaluation of Radiation Shielding for Space Exploration; Aeronautics and Space Engineering Board; Division on Engineering and Physical Sciences; National Research Council. Managing Space Radiation Risk in the New Era of Space Exploration; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cucinotta, F.A.; Durante, M. Evidence Report: Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis; National Aeronautical and Space Agency: Houston, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cucinotta, F.A.; Wang, H.; Huff, J.L. Evidence Report: Risk of Acute or Late Central Nervous System Effects from Radiation Exposure; National Aeronautical and Space Agency: Houston, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Huff, J.L.; Casey, R.; Kim, M.H.; Cucinotta, F.A. Evidence Report: Risk of Acute Radiation Syndromes Due to Solar Particle Events; National Aeronautical and Space Agency: Houston, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huff, J.L.; Cucinotta, F.A. Evidence Report: Risk of Degenerative Tissue or other Health Effects from Radiation Exposure; National Aeronautical and Space Agency: Houston, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cucinotta, F.A.; Kim, M.H.; Ren, L. Evaluating shielding effectiveness for reducing space radiation cancer risks. Radiat. Meas. 2006, 41, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Badwar, G.D.; O’Neill, P.M. Long-term modulation of galactic cosmic radiation and its model for space exploration. Adv. Space Res. 1994, 14, 749–757. [Google Scholar]
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP). Radiation Protection Guidance for Activities in Low-Earth Orbit; NCRP: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin, C.; Hassler, D.M.; Cucinotta, F.A.; Ehresmann, B.; Wimmer-Schweigruber, R.F.; Brinza, D.E.; Kang, S.; Weigle, G.; Bottcher, S.; Bohm, E.; et al. Measurements of energetic particle radiation in transit to mars on the mars science laboratory. Science 2013, 340, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Cucinotta, F.A.; Nikjoo, H.; Goodhead, D.T. The effects of delta rays on the number of particle-track traversals per cell in laboratory and space exposures. Radiat. Res. 1998, 150, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP). Guidance on Radiation Received in Space Activities; NCRP: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, L.W.; Cucinotta, F.A.; Wilson, J.W.; Bagga, R. Estimates of hze particle contributions to spe radiation exposures on interplanetary missions. Adv. Space Res. 1994, 14, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; George, K.A.; Cucinotta, F.A. Evaluation of skin cancer risks from lunar and mars missions. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 37, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longnecker, D.E.; Manning, F.J.; Worth, M.H., Jr. Review of Nasa’s Longitudinal Study of Astronaut Health; National Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, S.C.; McGale, P.; Taylor, C.W.; Peto, R. Long-term mortality from heart disease and lung cancer after radiotherapy for early breast cancer: Prospective cohort study of about 300,000 women in us seer cancer registries. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Kusunoki, Y.; Hakoda, M.; Morishita, Y.; Kubo, Y.; Maki, M.; Kasagi, F.; Kodama, K.; Macphee, D.G.; Kyoizumi, S. Radiation dose-dependent increases in inflammatory response markers in a-bomb survivors. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2003, 79, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Yamada, M.; Kasagi, F.; Shimizu, Y.; Shigematsu, I. Profiles of non-cancer diseases in atomic bomb survivors. World Health Stat. Q. 1996, 49, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Preston, D.L.; Shimizu, Y.; Pierce, D.A.; Suyama, A.; Mabuchi, K. Studies of mortality of atomic bomb survivors. Report 13: Solid cancer and noncancer disease mortality: 1950–1997. Radiat. Res. 2003, 160, 381–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, E.J. Early and late mammalian responses to heavy charged particles. Adv. Space Res. 1986, 6, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadesus, G.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Stellwagen, H.M.; Smith, M.A.; Rabin, B.M.; Joseph, J.A. Hippocampal neurogenesis and psa-ncam expression following exposure to 56fe particles mimics that seen during aging in rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2005, 40, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Tribble, D.L.; Barcellos-Hoff, M.H.; Chu, B.M.; Gong, E.L. Ionizing radiation accelerates aortic lesion formation in fat-fed mice via sod-inhibitable processes. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Schulte, B.A.; LaRue, A.C.; Ogawa, M.; Zhou, D. Total body irradiation selectively induces murine hematopoietic stem cell senescence. Blood 2006, 107, 358–366. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, V.V.; Ainsworth, E.J. Late effects of heavy charged particles on the fine structure of the mouse coronary artery. Radiat. Res. 1982, 91, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, T.K.; Hopewell, J.W. Effects of single doses of radiation on cardiac function in the rat. Radiother. Oncol. 1985, 3, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP). Potential Impact of Individual Genetic Susceptibility and Previous Radiation Exposure on Radiation Risk for Astronauts; NCRP: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Maalouf, M.; Durante, M.; Foray, N. Biological effects of space radiation on human cells: History, advances and outcomes. J. Radiat. Res. 2011, 52, 126–146. [Google Scholar]
- Cucinotta, F.A.; Kim, M.H.; Willingham, V.; George, K.A. Physical and biological organ dosimetry analysis for international space station astronauts. Radiat. Res. 2008, 170, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Health Effects of Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation: Beir V; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Shavers, M.R.; Zapp, N.; Barber, R.E.; Wilson, J.W.; Qualls, G.; Toupes, L.; Ramsey, S.; Vinci, V.; Smith, G.; Cucinotta, F.A. Implementation of alara radiation protection on the iss through polyethylene shielding augmentation of the service module crew quarters. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 34, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, P.B.; Billica, R.D.; Johnson, G.S.; Wear, M.L.; Pool, S.L. Risk of cancer mortality among the longitudinal study of astronaut health (lsah) participants. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1998, 69, 142–144. [Google Scholar]
- Hamm, P.B.; Nicogossian, A.E.; Pool, S.L.; Wear, M.L.; Billica, R.D. Design and current status of the longitudinal study of astronaut health. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2000, 71, 564–570. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, L.E.; Pepper, L.J.; Hamm, P.B.; Gilbert, S.L. Longitudinal study of astronaut health: Mortality in the years 1959–1991. Radiat. Res. 1993, 133, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnken, R.; Barratt, M.; Walker, S. Presentation to the Institute of Medicine-Ethics Principles and Guidelines for Health Standards for Long Duration and Exploration Spaceflights; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van Baalen, M.; National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center, Houston, TX, USA. Personal communication, 2014.
- Durante, M.; Snigiryova, G.; Akaeva, E.; Bogomazova, A.; Druzhinin, S.; Fedorenko, B.; Greco, O.; Novitskaya, N.; Rubanovich, A.; Shevchenko, V.; et al. Chromosome aberration dosimetry in cosmonauts after single or multiple space flights. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2003, 103, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, K.A.; Durante, M.; Wu, H.; Willingham, V.; Badwar, G.D.; Cucinotta, F.A. Chromosome aberrations in the blood lymphocytes of astronauts after space flight. Radiat. Res. 2001, 156, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, K.A.; Durante, M.; Willingham, V.; Cucinotta, F.A. Chromosome aberrations of clonal origin are present in astronauts’ blood lymphocytes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2004, 104, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, M.; Durante, M.; Johannes, C.; Pieper, R.; Obe, G. Space radiation does not induce a significant increase of intrachromosomal exchanges in astronauts’ lymphocytes. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2005, 44, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Aeronautics and Space Agency (NASA). Nasa space flight humans system standard, volume 1: Crew health. In Space-Permissible Exposure Limit (SPEL) for Space Flight Radiation Exposure Standard; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, R.W.; Haser, J.K. Neurocognitive effects of treatment for childhood cancer. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2006, 12, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.R.; Chen, G.T.; Blakely, E.A. Current considerations in heavy charged-particle radiotherapy: A clinical research trial of the university of california lawrence berkeley laboratory, northern california oncology group, and radiation therapy oncology group. Radiat. Res. Suppl. 1985, 8, S263–S271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrikant, J.I.; Lyman, J.T.; Frankel, K.A. Heavy charged-particle bragg peak radiosurgery for intracranial vascular disorders. Radiat. Res. Suppl. 1985, 8, S244–S258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keime-Guibert, F.; Napolitano, M.; Delattre, J.Y. Neurological complications of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. J. Neurol. 1998, 245, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellberg, R.N.; Hanamura, T.; Davis, K.R.; Lyons, S.L.; Adams, R.D. Bragg-peak proton-beam therapy for arteriovenous malformations of the brain. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 309, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.P.; Fabrikant, J.I.; Frankel, K.A.; Phillips, M.H.; Lyman, J.T. Stereotactic heavy-charged-particle bragg peak radiosurgery for the treatment of intracranial arteriovenous malformations in childhood and adolescence. Neurosurgery 1989, 24, 841–852. [Google Scholar]
- Schultheiss, T.E.; Kun, L.E.; Ang, K.K.; Stephens, L.C. Radiation response of the central nervous system. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 31, 1093–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, G.K.; Fabrikant, J.I.; Marks, M.P.; Levy, R.P.; Frankel, K.A.; Phillips, M.H.; Shuer, L.M.; Silverberg, G.D. Stereotactic heavy-charged-particle bragg-peak radiation for intracranial arteriovenous malformations. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suit, H.; Goitein, M.; Munzenrider, J.; Verhey, L.; Blitzer, P.; Gragoudas, E.; Koehler, A.M.; Urie, M.; Gentry, R.; Shipley, W.; et al. Evaluation of the clinical applicability of proton beams in definitive fractionated radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1982, 8, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofilon, P.J.; Fike, J.R. The radioresponse of the central nervous system: A dynamic process. Radiat. Res. 2000, 153, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Hze-Particle Effects in Manned Spaceflight; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Radiation Hazards to Crews of Interplanetary Missions:Biological Issues and Research Strategies; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, P. Stochastics of hze-induced microlesions. Adv. Space Res. 1989, 9, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britten, R.A.; Davis, L.K.; Johnson, A.M.; Keeney, S.; Siegel, A.; Sanford, L.D.; Singletary, S.J.; Lonart, G. Low (20 cGy) doses of 1 GeV/u 56Fe-particle radiation lead to a persistent reduction in the spatial learning ability of rats. Radiat. Res. 2012, 177, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonart, G.; Parris, B.; Johnson, A.M.; Miles, S.; Sanford, L.D.; Singletary, S.J.; Britten, R.A. Executive function in rats is impaired by low (20 cGy) doses of 1 GeV/u 56Fe particles. Radiat. Res. 2012, 178, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabin, B.M.; Joseph, J.A.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Heavy particle irradiation, neurochemistry and behavior: Thresholds, dose-response curves and recovery of function. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 33, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, S.P.; Bischoff-Grethe, A.; Dinges, D.F.; Ayalon, L.; Mednick, S.C.; Meloy, M.J. The neural basis of the psychomotor vigilance task. Sleep 2005, 28, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Dinges, D.F. Sleep deprivation and vigilant attention. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2008, 1129, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.M.; Roma, P.G.; Brady, J.V.; Hienz, R.D. Neurobehavioral effects of space radiation on choice impulsivity. In Proceedings of the 18th Biannual Meeting of the International Academy of Astronautics’ Humans in Space Symposium, Houston, TX, USA, 11–15 April 2011.
- Hienz, R.D.; Davis, C.M.; Weed, M.R.; Guida, P.M.; Gooden, V.L.; Brady, J.V.; Roma, P.G. Neurobehavioral effects of space radiation on psychomotor vigilance and reaction time tests. In Proceedings of the 18th Biannual Meeting of the International Academy of Astronautics’ Humans in Space Symposium, Houston, TX, USA, 11–15 April 2011.
- Parsons, J.L.; Townsend, L.W. Interplanetary crew dose rates for the august 1972 solar particle event. Radiat. Res. 2000, 153, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Sanzari, J.K.; Diffenderfer, E.S.; Yee, S.S.; Seykora, J.T.; Maks, C.; Ware, J.H.; Litt, H.I.; Reetz, J.A.; McDonough, J.; et al. Acute biological effects of simulating the whole-body radiation dose distribution from a solar particle event using a porcine model. Radiat. Res. 2011, 176, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanzari, J.K.; Wan, X.S.; Wroe, A.J.; Rightnar, S.; Cengel, K.A.; Diffenderfer, E.S.; Krigsfeld, G.S.; Gridley, D.S.; Kennedy, A.R. Acute hematological effects of solar particle event proton radiation in the porcine model. Radiat. Res. 2013, 180, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanzari, J.K.; Romero-Weaver, A.L.; James, G.; Krigsfeld, G.S.; Lin, L.; Diffenderfer, E.S.; Kennedy, A.R. Leukocyte activity is altered in a ground based murine model of microgravity and proton radiation exposure. PLoS One 2013, 8, e71757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Holmes, V.; Ni, H.; Sanzari, J.K.; Kennedy, A.R.; Weissman, D. Hindlimb suspension and spe-like radiation impairs clearance of bacterial infections. PLoS One 2014, 9, e85665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.L. Characterization of radiation-induced emesis in the ferret. Radiat. Res. 1988, 114, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanzari, J.K.; Wan, X.S.; Krigsfeld, G.S.; King, G.L.; Miller, A.; Mick, R.; Gridley, D.S.; Wroe, A.J.; Rightnar, S.; Dolney, D.; et al. Effects of solar particle event proton radiation on parameters related to ferret emesis. Radiat. Res. 2013, 180, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Weaver, A.L.; Wan, X.S.; Diffenderfer, E.S.; Lin, L.; Kennedy, A.R. Effect of SPE-like proton or photon radiation on the kinetics of mouse peripheral blood cells and radiation biological effectiveness determinations. Astrobiology 2014, 13, 570–577. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, A.R. Biological effects of space radiation and development of effective countermeasures. Life Sci. Space Res. 2014, 1, 10–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, J.M.; Blevins, N.A.; Meling, D.D.; Peterlin, M.B.; Gridley, D.S.; Cengel, K.A.; Freund, G.G. The biobehavioral and neuroimmune impact of low-dose ionizing radiation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- York, J.M.; McDaniel, A.W.; Blevins, N.A.; Gullet, R.R.; Allison, S.O.; Cengel, K.A.; Freund, G.G. Individually ventilated cages cause chronic low-grade hypoxia impacting mice hematologically and behaviorally. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 951–958. [Google Scholar]
- Maks, C.J.; Wan, X.S.; Ware, J.H.; Romero-Weaver, A.L.; Sanzari, J.K.; Wilson, J.M.; Rightnar, S.; Wroe, A.J.; Koss, P.; Gridley, D.S.; et al. Analysis of white blood cell counts in mice after gamma- or proton-radiation exposure. Radiat. Res. 2011, 176, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanzari, J.K.; Wambi, C.; Lewis-Wambi, J.S.; Kennedy, A.R. Antioxidant dietary supplementation in mice exposed to proton radiation attenuates expression of programmed cell death-associated genes. Radiat. Res. 2011, 175, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Krigsfeld, G.S.; Sanzari, J.K.; Wagner, E.S.; Mick, R.; Kennedy, A.R. Comparison of hindlimb unloading and partial weight suspension models for spaceflight-type condition induced effects on white blood cells. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCarlo, A.L.; Poncz, M.; Cassatt, D.R.; Shah, J.R.; Czarniecki, C.W.; Maidment, B.W. Medical countermeasures for platelet regeneration after radiation exposure. Report of a workshop and guided discussion sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Bethesda, MD, March 22–23, 2010. Radiat. Res. 2011, 176, e0001–e0015. [Google Scholar]
- National Space Biomedical Research Institute. National Space Biomedical Research Institute Request for Applications Nsbri-Rfa-13–02 to Establish A Center for Space Radiation Research (Csrr); National Space Biomedical Research Institute: Houston, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Blakely, E.A.; Lauriston, S. Taylor lecture on radiation protection and measurements: What makes particle radiation so effective? Health Phys. 2012, 103, 508–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, A.D.; Gondre-Lewis, T.; McBride, W.; Miller, L.; Pellmar, T.C.; Rockwell, S. Animal models for radiation injury, protection and therapy. Radiat. Res. 2005, 164, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackam, D.G.; Redelmeier, D.A. Translation of research evidence from animals to humans. JAMA 2006, 296, 1731–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Perel, P.; Roberts, I.; Sena, E.; Wheble, P.; Briscoe, C.; Sandercock, P.; Macleod, M.; Mignini, L.E.; Jayaram, P.; Khan, K.S. Comparison of treatment effects between animal experiments and clinical trials: Systematic review. BMJ 2007, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackam, D.G. Translating animal research into clinical benefit. BMJ 2007, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.M.; Roma, P.G.; Armour, E.; Gooden, V.L.; Brady, J.V.; Weed, M.R.; Heinz, R.D. Effects of x-ray radiation on complex visual discrimination learning and social recognition memory in rats. PLoS One 2014, 9, e104393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chancellor, J.C.; Scott, G.B.I.; Sutton, J.P. Space Radiation: The Number One Risk to Astronaut Health beyond Low Earth Orbit. Life 2014, 4, 491-510. https://doi.org/10.3390/life4030491
Chancellor JC, Scott GBI, Sutton JP. Space Radiation: The Number One Risk to Astronaut Health beyond Low Earth Orbit. Life. 2014; 4(3):491-510. https://doi.org/10.3390/life4030491
Chicago/Turabian StyleChancellor, Jeffery C., Graham B. I. Scott, and Jeffrey P. Sutton. 2014. "Space Radiation: The Number One Risk to Astronaut Health beyond Low Earth Orbit" Life 4, no. 3: 491-510. https://doi.org/10.3390/life4030491
APA StyleChancellor, J. C., Scott, G. B. I., & Sutton, J. P. (2014). Space Radiation: The Number One Risk to Astronaut Health beyond Low Earth Orbit. Life, 4(3), 491-510. https://doi.org/10.3390/life4030491




