Metagenomic Analysis of Microbial Community Compositions and Cold-Responsive Stress Genes in Selected Antarctic Lacustrine and Soil Ecosystems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Reads Processing Using Bioinformatics Tools
2.4. Filtering Cold-Induced and Cold-Associated General Stress-Responsive Proteins Using R Code
2.5. Comparison of the Taxonomic Distribution and the Filtered Protein Sequences Using Bioinformatics Tools
3. Results
3.1. Total Sequence Reads
3.2. Taxonomic Distribution and Abundance
3.3. Comparative Analyses of Functional Profiles
3.4. Cold-Induced Proteins in the Water Metagenomes
3.5. Cold-Induced Proteins in the Combined Soil and Lake Sediment Metagenomes
3.6. Cold-Associated General Stress-Responsive Proteins in the Water Metagenomes
3.7. Cold-Associated General Stress-Responsive Proteins in the Combined Soil and Lake Sediment Metagenomes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knoll, A.H. Life on a Young Planet: The First Three Billion Years of Evolution on Earth; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780691165530. [Google Scholar]
- Whitman, W.B.; Coleman, D.C.; Wiebe, W.J. Prokaryotes: The unseen majority. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6578–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothschild, L.J.; Mancinelli, R.L. Life in extreme environments. Nature 2001, 409, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampelotto, P.H. Extremophiles and extreme environments. Life 2013, 3, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häggblom, M.; Margesin, R. Microbial life in cold ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 53, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laybourn-Parry, J. No place too cold. Science 2009, 324, 1521–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onofri, S.; Selbmann, L.; De Hoog, G.; Grube, M.; Barreca, D.; Ruisi, S.; Zucconi, L. Evolution and adaptation of fungi at boundaries of life. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 40, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, N.; Cameron, R.E.; Hubbard, J.S. Microbiology of the dry valleys of Antarctica. Science 1972, 176, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, D.A. Cryptic microbial communities in Antarctic deserts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19749–19750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, M.; Greening, C.; Vanwonterghem, I.; Carere, C.R.; Bay, S.K.; Steen, J.A.; Montgomery, K.; Lines, T.; Beardall, J.; van Dorst, J. Atmospheric trace gases support primary production in Antarctic desert surface soil. Nature 2017, 552, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatina, A.; Medvedeva, S.; Shmakov, S.; Logacheva, M.D.; Krylenkov, V.; Severinov, K. Metagenomic analysis of bacterial communities of Antarctic surface snow. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Montenegro, M.A.; Ballesteros, G.I.; Castro-Nallar, E.; Meneses, C.; Torres-Díaz, C.; Gallardo-Cerda, J. Metagenomic exploration of soils microbial communities associated to Antarctic vascular plants. PeerJ Preprints 2018, 6, e26508v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommers, P.; Darcy, J.L.; Gendron, E.M.; Stanish, L.F.; Bagshaw, E.A.; Porazinska, D.L.; Schmidt, S.K. Diversity patterns of microbial eukaryotes mirror those of bacteria in Antarctic cryoconite holes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 94, fix167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytgat, B.; Verleyen, E.; Obbels, D.; Peeters, K.; De Wever, A.; D’hondt, S.; De Meyer, T.; Van Criekinge, W.; Vyverman, W.; Willems, A. Bacterial diversity assessment in Antarctic terrestrial and aquatic microbial mats: A comparison between bidirectional pyrosequencing and cultivation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilkins, D.; Yau, S.; Williams, T.J.; Allen, M.A.; Brown, M.V.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Lauro, F.M.; Cavicchioli, R. Key microbial drivers in antarctic aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 303–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanueva, A.; Tuffin, M.; Cary, C.; Cowan, D.A. Molecular adaptations to psychrophily: The impact of ‘omic’technologies. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.; Hakim, J.A.; Bej, A.K. Metagenomic analysis of microbial cold stress proteins in polar lacustrine ecosystems. In Stress and Environmental Regulation of Gene Expression and Adaptation in Bacteria; De Bruijn, F., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 837–844. ISBN 9781119004813. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, H.; Hakim, J.A.; Fisher, P.R.; Grueneberg, A.; Andersen, D.T.; Bej, A.K. Distribution of cold adaptation proteins in microbial mats in Lake Joyce, Antarctica: Analysis of metagenomic data by using two bioinformatics tools. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 120, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribelli, P.M.; López, N.I. Reporting key features in cold-adapted bacteria. Life 2018, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, S.; Cavicchioli, R. Microbial communities in Antarctic lakes: Entirely new perspectives from metagenomics and metaproteomics. Microbiol. Aust. 2011, 32, 157–159. [Google Scholar]
- Varin, T.; Lovejoy, C.; Jungblut, A.D.; Vincent, W.F.; Corbeil, J. Metagenomic analysis of stress genes in microbial mat communities from Antarctica and the High Arctic. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priscu, J.C.; Wolf, C.F.; Takacs, C.D.; Fritsen, C.H.; Laybourn-Parry, J.; Roberts, E.C.; Sattler, B.; Lyons, W.B. Carbon transformations in a perennially ice-covered Antarctic lake. Bioscience 1999, 49, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laybourn-Parry, J.; Wadham, J.L. Antarctic Lakes; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; ISBN 9780199670505. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, J.S.; Vick-Majors, T.J.; Morgan-Kiss, R.; Takacs-Vesbach, C.; Ducklow, H.W.; Priscu, J.C. Microbial community dynamics in two polar extremes: The lakes of the McMurdo Dry Valleys and the West Antarctic Peninsula marine ecosystem. Bioscience 2016, 66, 829–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, D.; Doran, P.; Bolshiyanov, D.; Rice, J.; Galchenko, V.; Cherych, N.; Wharton, R.; McKay, C.; Meyer, M.; Garshnek, V. A preliminary comparison of two perennially ice-covered lakes in Antarctica: Analogs of past martian lacustrine environments. Adv. Space Res. 1995, 15, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, R.A.; Simmons, G.M.; McKay, C.P. Perennially ice-covered Lake Hoare, Antarctica: Physical environment, biology and sedimentation. Hydrobiologia 1989, 172, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spigel, R.H.; Priscu, J.C. Physical Limnology of the McMurdo Dry Valleys Lakes. In Ecosystem Dynamics in a Polar Desert: The McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica; Priscu, J.C., Ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; Volume 72, pp. 157–187. ISBN 9780875908991. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, M.; Kim, M.; Takacs-Vesbach, C.; Lee, J.; Hong, S.G.; Kim, S.J.; Priscu, J.C.; Kim, O.S. Niche specialization of bacteria in permanently ice-covered lakes of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2258–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, H.; McKay, C.; Andersen, D. Modeling circulation and seasonal fluctuations in perennially ice-covered and ice-walled Lake Untersee, Antarctica. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1139–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, D.; Sumner, D.; Hawes, I.; Webster-Brown, J.; McKay, C. Discovery of large conical stromatolites in Lake Untersee, Antarctica. Geobiology 2011, 9, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wand, U.; Schwarz, G.; Brüggemann, E.; Bräuer, K. Evidence for physical and chemical stratification in Lake Untersee (central Dronning Maud Land, East Antarctica). Antarct. Sci. 1997, 9, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wand, U.; Perlt, J. Glacial boulders ‘floating’ on the ice cover of Lake Untersee, East Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 1999, 11, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, U.; Samarkin, V.A.; Nitzsche, H.-M.; Hubberten, H.-W. Biogeochemistry of methane in the permanently ice-covered Lake Untersee, central Dronning Maud Land, East Antarctica. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1180–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, D. Antarctic Inland Waters: Scientific Diving in the Perennially Ice-Covered Lakes of the McMurdo Dry Valleys and Bunger Hills. In Proceedings of the International Polar Diving Workshop, Svalbard, 2007; Lang, M.A., Sayer, M.D.J., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, E.M.; Wilkening, J.; Wilke, A.; Antonopoulos, D.; Meyer, F. Using the Metagenomics RAST server (MG-RAST) for analyzing shotgun metagenomes. Cold Spring Harbor Protoc. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; D’Souza, M.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A. The metagenomics RAST server—A public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, H.; Mojib, N.; Hakim, J.A.; Hawes, I.; Tanabe, Y.; Andersen, D.T.; Bej, A.K. Microbial communities and their predicted metabolic functions in growth laminae of a unique large conical mat from Lake Untersee, East Antarctica. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungblut, A.D.; Hawes, I. Using Captain Scott's discovery specimens to unlock the past: Has Antarctic cyanobacterial diversity changed over the last 100 years? Proc. R. Soc. B 2017, 284, 20170833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausubel, F.M.; Brent, R.; Kingston, R.E.; Moore, D.D.; Smith, J.G.; Sideman, J.G.; Struhl, K. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; John Wiley & Sons: Media, PA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, C.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Williams, T.J.; Lauro, F.M.; Raftery, M.; Gibson, J.A.; Andrews-Pfannkoch, C.; Lewis, M.; Hoffman, J.M.; Thomas, T. Metaproteogenomic analysis of a dominant green sulfur bacterium from Ace Lake, Antarctica. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1002–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauro, F.M.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Yau, S.; Brown, M.V.; Ng, C.; Wilkins, D.; Raftery, M.J.; Gibson, J.A.; Andrews-Pfannkoch, C.; Lewis, M. An integrative study of a meromictic lake ecosystem in Antarctica. ISME J. 2011, 5, 879–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.J.; Wilkins, D.; Long, E.; Evans, F.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Raftery, M.J.; Cavicchioli, R. The role of planktonic Flavobacteria in processing algal organic matter in coastal East Antarctica revealed using metagenomics and metaproteomics. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Goethem, M.W.; Pierneef, R.; Bezuidt, O.K.; Van De Peer, Y.; Cowan, D.A.; Makhalanyane, T.P. A reservoir of ‘historical’ antibiotic resistance genes in remote pristine Antarctic soils. Microbiome 2018, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fierer, N.; Leff, J.W.; Adams, B.J.; Nielsen, U.N.; Bates, S.T.; Lauber, C.L.; Owens, S.; Gilbert, J.A.; Wall, D.H.; Caporaso, J.G. Cross-biome metagenomic analyses of soil microbial communities and their functional attributes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21390–21395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joshi, N.; Fass, J. Sickle: A Sliding-Window, Adaptive, Quality-Based Trimming Tool for Fastq Files, Version 1.33, Software. 2011. Available online: https://github.com/najoshi/sickle (accessed on 10 July 2018).
- Andrews, S. Fastqc: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data, Version 0.11.7, Software. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 10 July 2018).
- Peng, Y.; Leung, H.C.; Yiu, S.-M.; Chin, F.Y. IDBA-UD: A de novo assembler for single-cell and metagenomic sequencing data with highly uneven depth. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. Quast: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overbeek, R.; Begley, T.; Butler, R.M.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Chuang, H.-Y.; Cohoon, M.; de Crécy-Lagard, V.; Diaz, N.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R. The subsystems approach to genome annotation and its use in the project to annotate 1000 genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5691–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluman, A.G. Elementary Statistics: A Step by Step Approach, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780073271606. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. Stamp: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Primer v5 (Plymouth Routines in Multivariate Ecological Research): User Manual/Tutorial; Primer-E: Plymouth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, J.; Wish, M. Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences: Multidimensional Scaling; Sage: Beverly Hills, CA, USA, 1978; Volume 11, ISBN 9780803909403. [Google Scholar]
- Dawyndt, P.; De Meyer, H.; De Baets, B. The complete linkage clustering algorithm revisited. Soft Comput. 2005, 9, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, C.J. Ecological Methodology; Benjamin/Cummings: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1999; Volume 620, ISBN 9780321021731. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.A., III; Callister, S.J.; Moore, R.J.; Baker, E.S.; Jansson, J.K. The past, present and future of microbiome analyses. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöling, S.; Cowan, D.A. Metagenomics: Microbial community genomes revealed. In Psychrophiles: From Biodiversity to Biotechnology; Margesin, R., Schinner, F., Marx, J.C., Gerday, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 313–332. ISBN 9783540743347. [Google Scholar]
- Fuks, G.; Elgart, M.; Amir, A.; Zeisel, A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Soen, Y.; Shental, N. Combining 16S rRNA gene variable regions enables high-resolution microbial community profiling. Microbiome 2018, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mackelprang, R.; Burkert, A.; Haw, M.; Mahendrarajah, T.; Conaway, C.H.; Douglas, T.A.; Waldrop, M.P. Microbial survival strategies in ancient permafrost: Insights from metagenomics. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, C.M.; Bowman, J.P.; Guezennec, J. Effects of incubation temperature on growth and production of exopolysaccharides by an Antarctic sea ice bacterium grown in batch culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3519–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maayer, P.; Anderson, D.; Cary, C.; Cowan, D.A. Some like it cold: Understanding the survival strategies of psychrophiles. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Kim, G.; Jung, Y.-J.; Choe, C.-D.; Yim, J.H.; Lee, H.K.; Hong, S.G. Polar and Alpine Microbial Collection (PAMC): A culture collection dedicated to polar and alpine microorganisms. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaji, S. Bacterial biodiversity, cold adaptation and biotechnological importance of bacteria occurring in Antarctica. Proc. Ind. Natl. Sci. Acad. USA 2017, 83, 327–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, D.A.; Newsham, K.; Thorne, M.; Calvo-Bado, L.; Krsek, M.; Laskaris, P.; Hodson, A.; Wellington, E.M. Metagenomic analysis of a southern maritime Antarctic soil. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöling, S.; Cowan, D.A. High 16S rDNA bacterial diversity in glacial meltwater lake sediment, Bratina Island, Antarctica. Extremophiles 2003, 7, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawid, W. Biology and global distribution of myxobacteria in soils. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 403–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bárria, C.; Malecki, M.; Arraiano, C.M. Bacterial adaptation to cold. Microbiology 2013, 159, 2437–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mojib, N.; Andersen, D.T.; Bej, A.K. Structure and function of a cold shock domain fold protein, CspD, in Janthinobacterium sp. Ant5-2 from East Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 319, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.G.; Krah, R.; Tafuri, S.R.; Wolffe, A.P. DNA gyrase, CS7.4, and the cold shock response in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 5798–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severinov, K. RNA polymerase structure–function: Insights into points of transcriptional regulation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2000, 3, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, K.B.; Storey, J.M. Protein Adaptations and Signal Transduction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 2, ISBN 9780444507594. [Google Scholar]
- Chintalapati, S.; Kiran, M.; Shivaji, S. Role of membrane lipid fatty acids in cold adaptation. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004, 50, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hunger, K.; Beckering, C.L.; Wiegeshoff, F.; Graumann, P.L.; Marahiel, M.A. Cold-induced putative DEAD box RNA helicases CshA and CshB are essential for cold adaptation and interact with cold shock protein B in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaji, S.; Prakash, J.S. How do bacteria sense and respond to low temperature? Arch. Microbiol. 2010, 192, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.H.; Marahiel, M.A. Coping with the cold: The cold shock response in the Gram-positive soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2002, 357, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.K.; Roy, I. Effect of trehalose on protein structure. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandror, O.; DeLeon, A.; Goldberg, A.L. Trehalose synthesis is induced upon exposure of Escherichia coli to cold and is essential for viability at low temperatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9727–9732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phadtare, S. Recent developments in bacterial cold-shock response. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2004, 6, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, A.S.; Crowe, J.H.; Crowe, L.M. Effects of three stabilizing agents-proline, betaine, and trehalose-on membrane phospholipids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1986, 245, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.H.; Marahiel, M.A. Bacterial cold shock responses. Sci. Prog. 2003, 86, 9–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dersch, P.; Kneip, S.; Bremer, E. The nucleoid-associated DNA-binding protein H-NS is required for the efficient adaptation of Escherichia coli K-12 to a cold environment. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1994, 245, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorman, C.J. H-NS-like nucleoid-associated proteins, mobile genetic elements and horizontal gene transfer in bacteria. Plasmid 2014, 75, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- La Teana, A.; Brandi, A.; Falconi, M.; Spurio, R.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C. Identification of a cold shock transcriptional enhancer of the Escherichia coli gene encoding nucleoid protein H-NS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10907–10911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White-Ziegler, C.A.; Davis, T.R. Genome-wide identification of H-NS-controlled, temperature-regulated genes in Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, T.; Kataoka, K.; Ogata, Y.; Inoue, R.I.; Sekimizu, K. Increase in negative supercoiling of plasmid DNA in Escherichia coli exposed to cold shock. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 23, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, C.; Wiezer, A.; Strittmatter, A.W.; Daniel, R. Phylogenetic diversity and metabolic potential revealed in a glacier ice metagenome. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7519–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Médigue, C.; Krin, E.; Pascal, G.; Barbe, V.; Bernsel, A.; Bertin, P.N.; Cheung, F.; Cruveiller, S.; D’Amico, S.; Duilio, A. Coping with cold: The genome of the versatile marine Antarctica bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalluge, J.J.; Hamamoto, T.; Horikoshi, K.; Morita, R.Y.; Stetter, K.O.; McCloskey, J.A. Posttranscriptional modification of tRNA in psychrophilic bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 1918–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucciarelli, S.; Devaraj, R.R.; Mancini, A.; Ballarini, P.; Castelli, M.; Schrallhammer, M.; Petroni, G.; Miceli, C. Microbial consortium associated with the Antarctic marine ciliate Euplotes focardii: An investigation from genomic sequences. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
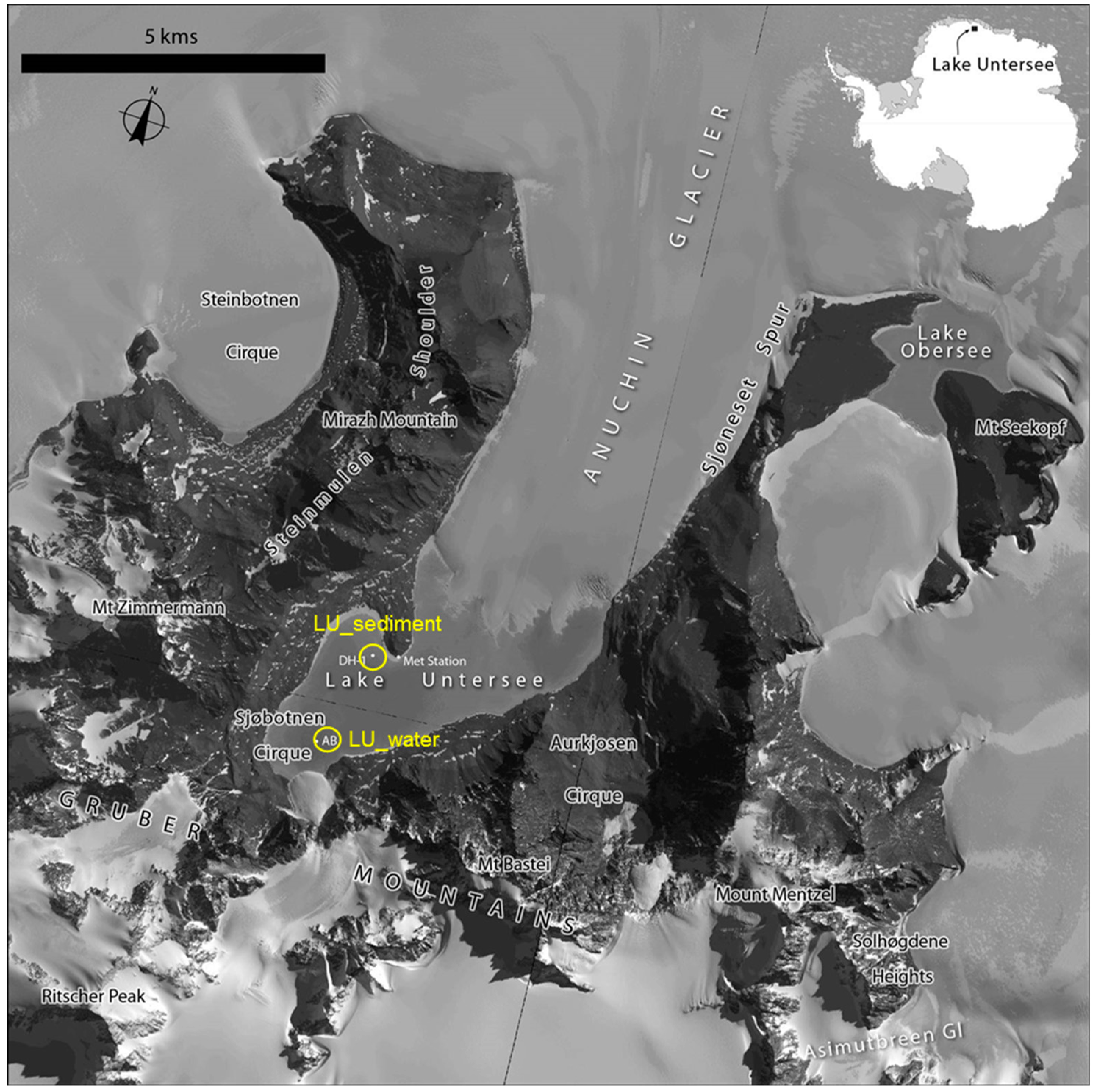




| Samples | Location | Sample Type | Total Annotated Sequence Reads | MG-RAST ID | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lake Untersee | 71.35609° S 13.4268° E | Freshwater | 96,838 | This study | This study |
| Ace Lake | 68.47° S 78.18° E | Saline water (originally freshwater) | 114,319 | mgm4443684.3 | [40,41] |
| Newcomb Bay Lake | 66.27° S 110.53° E | Marine habitat water | 80,924 | mgm4443686.3 | [42] |
| Lake Untersee | 71.34197° S 13.45458° E | Sediment | 119,907 | This study | This study |
| Mount Seuss | 77.02° S 161.85° E | Soil | 91,656 | mgm4667023.3 | [43] |
| McMurdo Dry Valleys | 77.63° S 162.88° E 1 | Soil | 27,582 | mgm4575389.3 | [44] |
| 77.73° S 162.31° E 2 | Soil | 25,064 | mgm4575387.3 | ||
| 77.60° S 163.25° E 3 | Soil | 18,398 | mgm4575388.3 | ||
| 77.53° S 161.70° E 4 | Soil | 24,184 | mgm4575390.3 |
| Number of Genes Found in Each Antarctic Metagenome | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein or SEED subsystem name | Lake Untersee water | Ace Lake water | Newcomb Bay water | Lake Untersee sediment | Mount Seuss soil | McMurdo Dry Valleys soil |
| Cold-Induced Proteins | ||||||
| Pyruvate metabolism | ||||||
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component, AceE | 65 | 255 | 96 | 70 | 26 | 111 |
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component alpha subunit | 13 | 12 | 50 | 33 | 39 | 35 |
| Cold stress proteins | ||||||
| CspA | 49 | 21 | 40 | 31 | 11 | 33 |
| CspB | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 0 |
| CspC | 8 | 26 | 9 | 8 | 11 | 8 |
| CspD | 7 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 1 |
| CspE | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 12 | 5 |
| CspG | 15 | 15 | 29 | 18 | 11 | 12 |
| Antifreeze protein | 3 | 3 | 15 | 6 | 1 | 10 |
| Di- and oligosaccharides | ||||||
| Trehalose synthase | 14 | 58 | 0 | 24 | 62 | 156 |
| Protein biosynthesis | ||||||
| Translation initiation factor 1 | 38 | 49 | 23 | 36 | 31 | 46 |
| Translation initiation factor 2 | 80 | 160 | 193 | 106 | 108 | 114 |
| Translation initiation factor 3 | 23 | 68 | 29 | 33 | 33 | 39 |
| Ribosome-binding factor A, RbfA | 11 | 26 | 35 | 17 | 3 | 14 |
| Clustering-based subsystems | ||||||
| Transcription termination protein NusA | 65 | 81 | 103 | 65 | 36 | 84 |
| DNA metabolism | ||||||
| DNA-binding protein H-NS | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| DNA-binding protein HU | 12 | 76 | 32 | 12 | 76 | 6 |
| DNA-binding protein HU-alpha | 4 | 23 | 1 | 7 | 23 | 3 |
| DNA replication | ||||||
| DNA gyrase subunit A | 133 | 149 | 158 | 163 | 155 | 152 |
| RecA protein | 117 | 132 | 125 | 83 | 164 | 73 |
| Chromosomal replication initiator protein DnaA | 80 | 139 | 102 | 84 | 283 | 102 |
| Nucleosides and nucleotides | ||||||
| Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) | 33 | 47 | 75 | 24 | 63 | 42 |
| Protein folding | ||||||
| Chaperone protein DnaJ | 58 | 100 | 100 | 69 | 70 | 91 |
| Chaperone protein DnaK | 189 | 160 | 182 | 158 | 183 | 179 |
| RNA metabolism | ||||||
| Cold-shock DEAD-box protein A (CSDA) | 27 | 31 | 84 | 40 | 58 | 70 |
| Unsaturated fatty acids | ||||||
| Fatty acid desaturase | 22 | 33 | 34 | 66 | 114 | 65 |
| Cold-Associated General Stress-Responsive Proteins | ||||||
| Amino acids and derivatives | ||||||
| Glycine biosynthesis | 42 | 40 | 16 | 69 | 34 | 28 |
| Glutamate biosynthesis | 83 | 214 | 119 | 75 | 199 | 123 |
| Bacterial cell division | ||||||
| Cell division trigger factor | 9 | 52 | 68 | 31 | 15 | 27 |
| Osmotic stress | ||||||
| Choline and betaine uptake, betaine biosynthesis | 21 | 287 | 204 | 35 | 176 | 31 |
| Cell wall and capsule (Capsular and extracellular polysaccharides) | ||||||
| Exopolysaccharide biosynthesis | 85 | 42 | 44 | 104 | 102 | 131 |
| DNA replication | ||||||
| DNA gyrase subunit B | 150 | 178 | 160 | 115 | 286 | 149 |
| Protein folding | ||||||
| Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | 18 | 18 | 3 | 31 | 224 | 5 |
| RNA metabolism | ||||||
| Chaperone protein HscB | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| tRNA dihydrouridine synthase A | 1 | 3 | 9 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| tRNA dihydrouridine synthase B | 40 | 28 | 60 | 63 | 43 | 32 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koo, H.; Hakim, J.A.; Morrow, C.D.; Crowley, M.R.; Andersen, D.T.; Bej, A.K. Metagenomic Analysis of Microbial Community Compositions and Cold-Responsive Stress Genes in Selected Antarctic Lacustrine and Soil Ecosystems. Life 2018, 8, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/life8030029
Koo H, Hakim JA, Morrow CD, Crowley MR, Andersen DT, Bej AK. Metagenomic Analysis of Microbial Community Compositions and Cold-Responsive Stress Genes in Selected Antarctic Lacustrine and Soil Ecosystems. Life. 2018; 8(3):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/life8030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoo, Hyunmin, Joseph A. Hakim, Casey D. Morrow, Michael R. Crowley, Dale T. Andersen, and Asim K. Bej. 2018. "Metagenomic Analysis of Microbial Community Compositions and Cold-Responsive Stress Genes in Selected Antarctic Lacustrine and Soil Ecosystems" Life 8, no. 3: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/life8030029
APA StyleKoo, H., Hakim, J. A., Morrow, C. D., Crowley, M. R., Andersen, D. T., & Bej, A. K. (2018). Metagenomic Analysis of Microbial Community Compositions and Cold-Responsive Stress Genes in Selected Antarctic Lacustrine and Soil Ecosystems. Life, 8(3), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/life8030029






