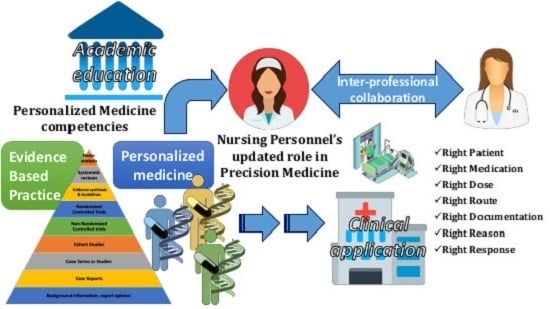
Nursing Personnel in the Era of Personalized Healthcare in Clinical Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
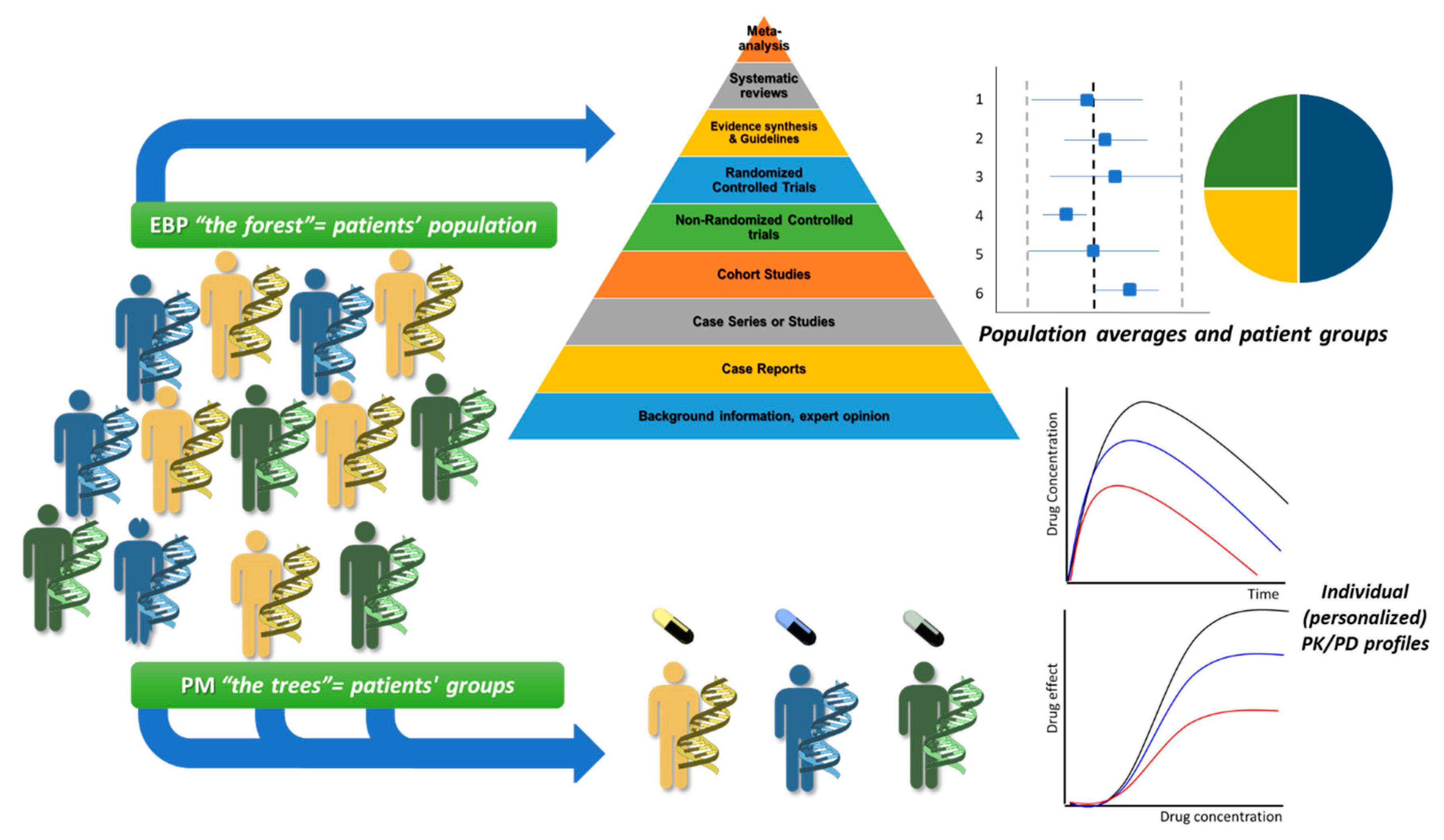
1.1. Clinical Pharmacology, Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM), Special Population Groups, and Pharmacogenetics/Pharmacogenomics
1.2. Personalized Nursing Care: What Does the New Nursing Role Entail for the Goals of Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) and PM?
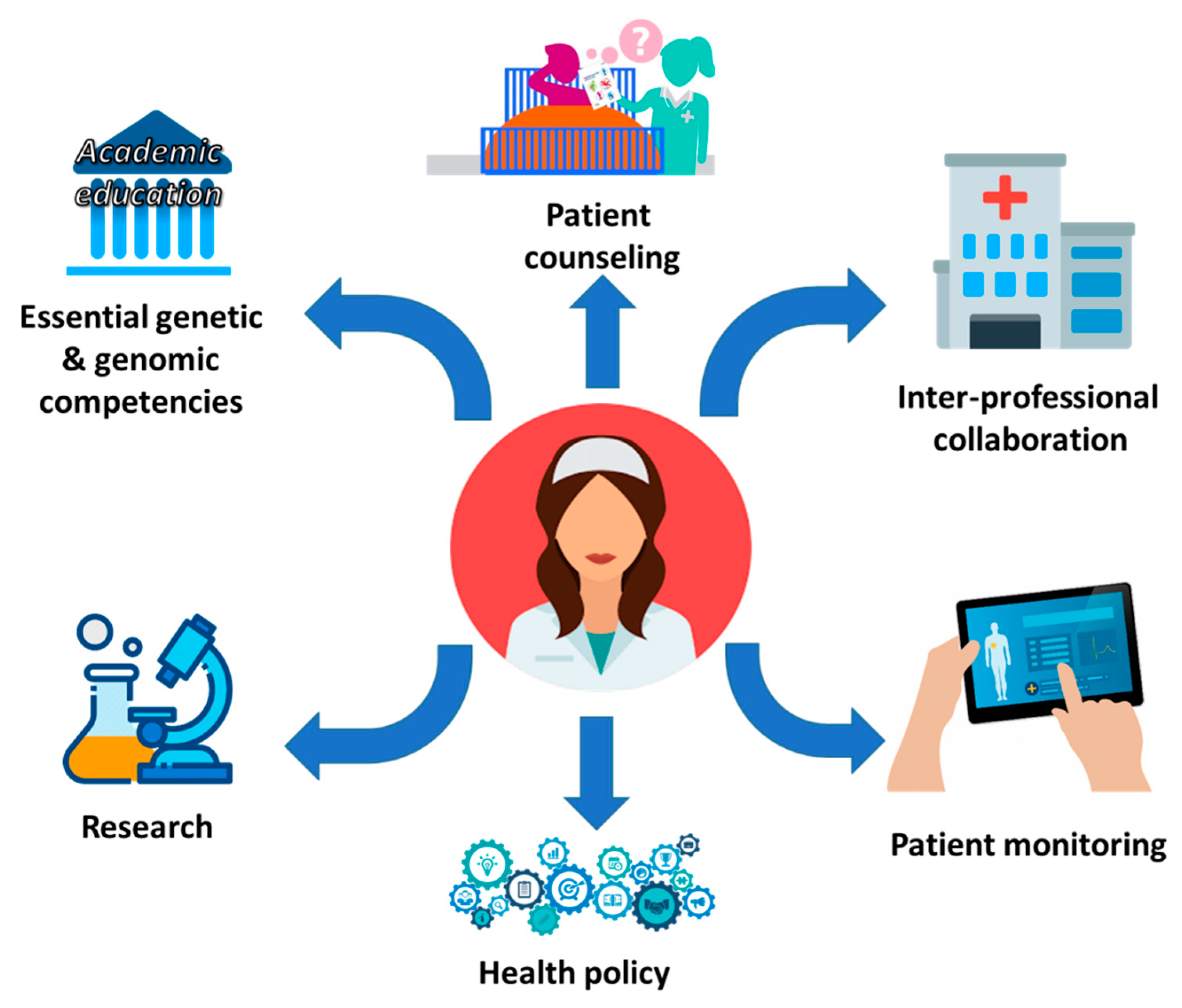
1.3. Milestones for NP toward the Requirements of A Modern Healthcare System
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayes, D.F.; Markus, H.S.; Leslie, R.D.; Topol, E.J. Personalized medicine: Risk prediction, targeted therapies, and mobile health technology. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, E.A. The Precision Medicine Initiative. JAMA 2015, 313, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzel, J.N.; Blazer, K.R.; Macdonald, D.J.; Culver, J.O.; Offit, K. Genetics, genomics, and cancer risk assessment: State of the Art and Future Directions in the Era of Personalized Medicine. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 327–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, G.R.; Sinkunas, V.; Liguori, G.R.; Auler-Júnior, J.O.C. Precision Medicine: Changing the way we think about healthcare. Clinics 2018, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulciani, S.; di Lonardo, A.; Fagnani, C.; Taruscio, D. P4 Medicine versus Hippocrates. Ann. Dell’Istit. Super. Sanità 2017, 53, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg, G.S.; Phillips, K.A. Precision Medicine: From Science to Value. Heal. Aff. 2018, 37, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmesgern, E.; Benediktsson, I.; Norstedt, I. Personalized Medicine in Europe. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 10, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Correia, R.; Ferreira, D.; Bacelar-Silva, G.M.; Vieira-Marques, P.; Maranhão, P. Personalised medicine challenges: Quality of data. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2018, 6, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorderstrasse, A.A.; Hammer, M.J.; Dungan, J.L. Nursing Implications of Personalized and Precision Medicine. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2014, 30, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koning, P.; Keirns, J. Clinical pharmacology, biomarkers, and personalized medicine: Education please. Biomark. Med. 2009, 3, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitezić, D.; Božina, N.; Mršić-Pelčić, J.; Turk, V.E.; Francetić, I. Personalized Medicine in Clinical Pharmacology. In Personalized Medicine in Healthcare Systems; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 265–278. [Google Scholar]
- Aronson, J.K. What do clinical pharmacologists do? A questionnaire survey of senior UK clinical pharmacologists. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 73, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.H.; Henry, D.; Gray, J.; Day, R.; Bochner, F.; Ferro, A.; Pirmohamed, M.; Mörike, K.; Schwab, M. Achieving the World Health Organization’s vision for clinical pharmacology. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 81, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grissinger, M. The Five Rights: A Destination Without a Map. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 542. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, A.S. Best practice in therapeutic drug monitoring. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 46, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.; Liu, Y. The nine rights of medication administration: An overview. Br. J. Nurs. 2010, 19, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sime, F.B.; Roberts, M.S.; Roberts, J.A. Optimization of dosing regimens and dosing in special populations. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, J.; Carvalho, B.; Shafer, S.L.; Flood, P. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Drugs Commonly Used in Pregnancy and Parturition. Anesthesia Analg. 2016, 122, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelet, R.; van Bocxlaer, J.; Vermeulen, A. PBPK in Preterm and Term Neonates: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23, 5943–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pariente, G.; Leibson, T.; Carls, A.; Adams-Webber, T.; Ito, S.; Koren, G. Pregnancy-Associated Changes in Pharmacokinetics: A Systematic Review. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeeck, R.K. Pharmacokinetics and dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic dysfunction. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 64, 1147–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeeck, R.K.; Musuamba, F.T. Pharmacokinetics and dosage adjustment in patients with renal dysfunction. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascorbi, I.; Tyndale, R.F. Progress in Pharmacogenomics: Bridging the Gap from Research to Practice. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 95, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalow, W. Pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics: Origin, status, and the hope for personalized medicine. Pharmacogenom. J. 2006, 6, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizirianakis, I.S. Improving pharmacotherapy outcomes by pharmacogenomics: From expectation to reality? Pharmacogenomics 2005, 6, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizirianakis, I.S.; Vizirianakis, I.S. Clinical Translation of Genotyping and Haplotyping Data. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2007, 46, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Pharmacogenetics of cytochrome P450 and its applications in drug therapy: The past, present and future. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancova, P.; Anzenbacher, P.; Anzenbacherova, E. Phase II drug metabolizing enzymes. Biomed. Pap. 2010, 154, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.K.; Brockmoller, J.; Broly, F.; Eichelbaum, M.; Evans, W.E.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Huang, J.-D.; Idle, J.R.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Ishizaki, T.; et al. Nomenclature for human CYP2D6 alleles. Pharmacogenetics 1996, 6, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.-F.; Liu, J.-P.; Chowbay, B. Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 enzymes and its clinical impact. Drug Metab. Rev. 2009, 41, 89–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, M.; Schaeffeler, E. Warfarin pharmacogenetics meets clinical use. Blood 2011, 118, 2938–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, R.; Conte, F.; Fiscon, G.; Pecce, V.; Sponziello, M.; Durante, C.; Farina, L.; Filetti, S.; Paci, P.; Verrienti, A. BRAFV600E-mutant cancers display a variety of networks by SWIM analysis: Prediction of vemurafenib clinical response. Endocrine 2019, 64, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.Z.; Raut, C.P. Targeted therapy and personalized medicine in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Drug resistance, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 5123–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, U.A.; Zanger, U.M.; Schwab, M. Omics and Drug Response. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 475–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, F.S.; Das, K.; Wang, J.; Vakil, H.; Kuo, J.Z.; Blackwell, W.-L.B.; Lim, S.W.; O Goodarzi, M.; Bernstein, K.; I Rotter, J.; et al. Personalized medicine and pharmacogenetic biomarkers: Progress in molecular oncology testing. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 12, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popat, S.; Yap, T.A. Toward precision medicine with next-generation EGFR inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. Pharmacogenom. Pers. Med. 2014, 7, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljalil, K.; Pan, X.; Pansari, A.; Jamei, M.; Johnson, T.N. Preterm Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model. Part II: Applications of the Model to Predict Drug Pharmacokinetics in the Preterm Population. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 59, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallmann, A.; Solodenko, J.; Ince, I.; Eissing, T. Applied Concepts in PBPK Modeling: How to Extend an Open Systems Pharmacology Model to the Special Population of Pregnant Women. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2018, 7, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, M. Recent Advances in Development and Application of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Models: A Transition from Academic Curiosity to Regulatory Acceptance. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 2, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnisch, L.; Shepard, T.; Pons, G.; Della-Pasqua, O.E. Modeling and simulation as a tool to bridge efficacy and safety data in special populations. CPT: Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2013, 2, e28-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, I.E.; Jones, N.S.; Musib, L. Pediatric Dose Selection and Utility of PBPK in Determining Dose. AAPS J. 2018, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanakis, M.; Marias, K. In silico evaluation of gadofosveset pharmacokinetics in different population groups using the Simcyp® simulator platform. Silico Pharmacol. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bhattaram, V.A.; Booth, B.P.; Ramchandani, R.P.; Beasley, B.N.; Wang, Y.; Tandon, V.; Duan, J.Z.; Baweja, R.K.; Marroum, P.J.; Uppoor, R.S.; et al. Impact of pharmacometrics on drug approval and labeling decisions: A survey of 42 new drug applications. AAPS J. 2005, 7, E503–E512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krekels, E.H.J.; van Hasselt, J.G.C.; Anker, J.N.V.D.; Allegaert, K.; Tibboel, D.; Knibbe, C.A.J. Evidence-based drug treatment for special patient populations through model-based approaches. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, S22–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, N.; Gallo, L.; Busse, J.W. Evidence-based medicine and precision medicine: Complementary approaches to clinical decision-making. Precis. Clin. Med. 2018, 1, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Sturmberg, J.P.; Lukersmith, S.; Madden, R.H.; Torkfar, G.; Colagiuri, R.; Salvador-Carulla, L. Evidence-based medicine: Is it a bridge too far? Heal. Res. Policy Syst. 2015, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masic, I.; Miokovic, M.; Muhamedagic, B. Evidence Based Medicine—New Approaches and Challenges. Acta Inform. Med. 2008, 16, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.C. Types of studies and research design. Ind. J. Anaesth. 2016, 60, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, M.H.; Asi, N.; Alsawas, M.; Alahdab, F. New evidence pyramid. Evid. Based Med. 2016, 21, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, J.S.; Lew, D. Reconciling evidence-based medicine and precision medicine in the era of big data: Challenges and opportunities. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, R.L.; Duan, N.; Braslow, J. Evidence-Based Medicine, Heterogeneity of Treatment Effects, and the Trouble with Averages. Milbank Q. 2004, 82, 661–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brænd, A.M.; Straand, J.; Klovning, A. Clinical drug trials in general practice: How well are external validity issues reported? BMC Fam. Pr. 2017, 18, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, M.; Dionne, J.; Pinho, G.; Gignac, J.; Almirall, J.; Lapointe, L. Randomized Controlled Trials: Do They Have External Validity for Patients with Multiple Comorbidities? Ann. Fam. Med. 2006, 4, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britten, N.; Pope, C.; Halford, S.; Richeldi, L. What if we made stratified medicine work for patients? Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Erikainen, S.; Chan, S. Contested futures: Envisioning “Personalized,” “Stratified,” and “Precision” medicine. New Genet. Soc. 2019, 38, 308–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonergan, M.; Senn, S.; McNamee, C.; Daly, A.K.; Sutton, R.; Hattersley, A.T.; Pearson, E.; Pirmohamed, M. Defining drug response for stratified medicine. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusheim, M.R.; Berndt, E.R. The clinical benefits, ethics, and economics of stratified medicine and companion diagnostics. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, D.; Valencia, A. Big data analytics for personalized medicine. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 58, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulsen, T.; Jamuar, S.S.; Moody, A.R.; Karnes, J.H.; Varga, O.; Hedensted, S.; Spreafico, R.; Hafler, D.A.; McKinney, E.F. From Big Data to Precision Medicine. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandori, C.; Kemp, C.J. Personalized Cancer Models for Target Discovery, and Precision Medicine. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrotin, Y.; Sanchez, C.; Cornet, A.; van de Put, J.; Douette, P.; Gharbi, M. Soluble biomarkers development in osteoarthritis: From discovery to personalized medicine. Biomarkers 2016, 20, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.M. Towards a More Personalized Treatment of Dyslipidemias to Prevent Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizinga, T.W.J. Personalized medicine in rheumatoid arthritis: Is the glass half full or half empty? J. Intern. Med. 2015, 277, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovich, A.; Kendrick, J. Personalized Management of Bone and Mineral Disorders and Precision Medicine in End-Stage Kidney Disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinberger, J.W.; Pollin, T.I. Personalized medicine in diabetes mellitus: Current opportunities and prospects. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2015, 1346, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streja, E.; Streja, D.A.; SooHoo, M.; Kleine, C.-E.; Hsiung, J.-T.; Park, C.; Moradi, H. Precision Medicine and Personalized Management of Lipoprotein and Lipid Disorders in Chronic and End-Stage Kidney Disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Völzke, H.; Schmidt, C.O.; Baumeister, S.E.; Ittermann, T.; Fung, G.; Krafczyk-Korth, J.; Hoffmann, W.; Schwab, M.; Zu Schwabedissen, H.E.M.; Dörr, M.; et al. Personalized cardiovascular medicine: Concepts and methodological considerations. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2013, 10, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kim, J.; Spiegel, J.; Ferguson, S.M. Developing products for personalized medicine: NIH Research Tools Policy applications. Pers. Med. 2004, 1, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizirianakis, I.S.; Mystridis, G.A.; Avgoustakis, K.; Fatouros, D.; Spanakis, M. Enabling personalized cancer medicine decisions: The challenging pharmacological approach of PBPK models for nanomedicine and pharmacogenomics (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1891–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Servellen, G.; Sarna, L.; Nyamathi, A.; Padilla, G.; Brecht, M.L.; Jablonski, K.J. Emotional distress in women with symptomatic HIV disease. Issues Ment. Heal. Nurs. 1998, 19, 173–188. [Google Scholar]
- Cornally, N.; McCarthy, G. Help-seeking behaviour: A concept analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Pr. 2011, 17, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.F. Personalized Medicine: Been There, Done That, Always Needs Work! Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 1251–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Personalized medicine and patient modelling. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2014, 9, 213–219. [CrossRef]
- McNeil, B.J.; Elfrink, V.L.; Pierce, S.T. Preparing student nurses, faculty, and clinicians for 21st century informatics practice: Findings from a national survey of nursing education programs in the United States. Stud. Heal. Technol. Inf. 2004, 107, 903–907. [Google Scholar]
- Nagle, L.M. Everything I know about informatics, I did not learn in nursing school. Nurs. Leadersh. 2007, 20, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiba, D.J. NURSING 2.0: Should we as educators be crafting the next generation of nursing practice? Nurs. Educ. Perspect. 2009, 30, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stacey, D.; de Grasse, C.; Johnston, L. Addressing the Support Needs of Women at High Risk for Breast Cancer: Evidence-Based Care by Advanced Practice Nurses. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 2002, 29, E77–E84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizon, D.S.; Politi, M.C.; Back, A.L. The Power of Words: Discussing Decision Making and Prognosis. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2013, 33, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.J. A Concept Analysis of Personalized Health Care in Nursing. Nurs. Forum 2015, 51, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.R.; Kurnat-Thoma, E.; Starkweather, A.; Henderson, W.A.; Cashion, A.K.; Williams, J.K.; Katapodi, M.C.; Reuter-Rice, K.; Hickey, K.T.; de Mendoza, V.B.; et al. Precision health: A nursing perspective. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2019, 7, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martha, S.R.; Auld, J.P.; Hash, J.B.; Hong, H. Precision Health in Aging and Nursing Practice. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 2020, 46, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patelarou, A.E.; Kyriakoulis, K.G.; Stamou, A.; Laliotis, A.; Sifaki-Pistolla, D.; Matalliotakis, M.; Prokopakis, E.; Patelarou, E. Approaches to teach evidence-based practice among health professionals: An overview of the existing evidence. Adv. Med Educ. Pr. 2017, 8, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prows, C.A.; Glass, M.; Nicol, M.J.; Skirton, H.; Williams, J.K. Genomics in Nursing Education. J. Nurs. Sch. 2005, 37, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.K.; Prows, C.A.; Conley, Y.P.; Eggert, J.; Kirk, M.; Nichols, F. Strategies to Prepare Faculty to Integrate Genomics into Nursing Education Programs. J. Nurs. Sch. 2011, 43, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackett, D.L.; Rosenberg, W.M.C.; Gray, J.A.M.; Haynes, R.B.; Richardson, W.S. Evidence based medicine: What it is and what it is not. BMJ 1996, 312, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genetics/Genomics competencies for RNs and nurses with graduate degrees. Nurs. Manag. 2019, 50, 1–3. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, K.E.; Tinley, S.; Seibert, D. Development of the Essential Genetic and Genomic Competencies for Nurses with Graduate Degrees. Annu. Rev. Nurs. Res. 2011, 29, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, K.T.; Katapodi, M.C.; Coleman, B.; Reuter-Rice, K.; Starkweather, A. Improving Utilization of the Family History in the Electronic Health Record. J. Nurs. Sch. 2016, 49, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, B.M.; Dere, W.; Schiffman, J.D. Family Health History. JAMA 2015, 313, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patelarou, A.; Dafermos, V.; Brokalaki, H.; Melas, C.D.; Koukia, E. The evidence-based practice readiness survey. Int. J. Evid. Based Heal. 2015, 13, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, B.M. The Evidence-Based Practice Mentor: A Promising Strategy for Implementing and Sustaining EBP in Healthcare Systems. Worldv. Evid. Based Nurs. 2007, 4, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patelarou, A.E.; Laliotis, A.; Brokalaki, H.; Petrakis, J.; Dafermos, V.; Koukia, E. Readiness for and predictors of evidence base practice in Greek healthcare settings. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2017, 35, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfantou, D.F.; Laliotis, A.; Patelarou, A.E.; Pistolla, D.S.; Matalliotakis, M.; Patelarou, E. Importance of Leadership Style towards Quality of Care Measures in Healthcare Settings: A Systematic Review. Healtcare 2017, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyszczyk, P.; Acevedo, A.; Davidoff, E.; Timmins, L.M.; Berrios, I.M.; Patel, M.; White, C.; Lowe, C.; Sherba, J.J.; Hartmanshenn, C.; et al. The growing role of precision and personalized medicine for cancer treatment. Technology 2018, 6, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, C.P.; Hentschel, B.; Szucs, T.D.; Leo, C. FDA and EMA Approvals of New Breast Cancer Drugs—A Comparative Regulatory Analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, S.; Ghersi, D. Building towards precision medicine: Empowering medical professionals for the next revolution. BMC Med Genom. 2016, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Terminology (/Synonyms) | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Personalized/stratified/precision & medicine/pharmacotherapy/healthcare | The use of an individual’s genetic and epigenetic information to tailor drug therapy or preventive care. It aims to stratify patients into similar cohorts with medical interventions to be customized based on individual/cohort characteristics. |
| Personal genomic profile | Sequencing, analysis, and interpretation of the genome for an individual (patient or citizen). It includes techniques for single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis, partial, or full-genome sequencing. It is used to analyze trait expression, disease risk assessment, and ancestry. |
| Biomarker | A biological characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator or normal or pathological processes or used as response to a therapeutic intervention. |
| Genetic testing | Detection of specific alleles, mutations, genotypes, or karyotypes that are associated with heritable traits, diseases, or predispositions to disease for the individual or their descendants. |
| Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) | Genome screens of unrelated individuals and appropriately matched controls or parent–affected child trios to establish whether any genetic variant, i.e., any SNP is associated with a trait |
| Genomics | The full genetic complement of an organism that is sequenced, assembled, and analyzed regarding its structure and function. |
| Genomic analysis/profiling | Recognition, measurement, or comparison of genomic features (i.e., DNA sequences, gene expression or regulation, and functional element annotation) at a genomic scale. |
| Metabolomics | Systematic identification and quantification of the small-molecule metabolic products (the metabolome) of a biological system (cell, tissue, organ, biological fluid, or organism) at a specific point in time. |
| Molecular diagnosis | Identification of genomic variants to enable detection, diagnosis, subclassification, prognosis, and monitoring response to therapy. |
| Proteomics | Study of proteome or the techniques used to determine the entire set of proteins for an organism or a system. |
| Transcriptomics | The screening or analysis of the complete set of RNA (coding and non-coding) that is produced by the genome (from one or more cells) under specific circumstances using high-throughput methods. |
| Pharmacogenomics | The study of how genetic variation influences responses to drugs. |
| Pharmacogenetics | How an individual can benefit from specific drugs due to inter-subject genetic variation that affects their response to drugs/pharmaceuticals and other xenobiotics, both therapeutically and in terms of adverse effects. |
| Pharmacometrics | Implementation of model-based approaches of biology, physiology, pharmacology, and disease that aim to describe and quantify interactions among drugs (or other chemicals) and patients such as therapeutic response or adverse effects. |
| Single-nucleotide polymorphism | A DNA sequence variation occurring when a single nucleotide in the genome (or other shared sequence) differs between members of a species or paired chromosomes in an individual. |
| Title | Link | Description | Target Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Public Health Genomics | https://www.cdc.gov/genomics/; https://www.cdc.gov/genomics/translation/GAPPNet/index.htm/ | General Genetic/Genomic Resources/innovative public health genomics programs | Health Professionals, Scientists, Public |
| International Society of Nurses in Genetics | https://www.isong.org/page-1325075 | Webinars, annual conference | Nurses |
| National Human Genome Research Institute | https://www.genome.gov/ | Educational resources, research training, professional development programs | Health Professionals, Scientists, Public |
| Global Alliance for Genomics and Health | https://www.ga4gh.org/ | Education resources, toolkit | Health Professionals, Scientists, Public |
| Global Genetics and Genomics Community | https://www.genomicscases.net/en/ | Educational resources | Health Professionals, Scientists, Public |
| Genetics Education Program for Nurses (GEPN), Cincinnati Children’s | https://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/education/clinical/nursing/genetics | Free modules, audio-slide content | Nurses |
| Health Education England-Genomics Education Programme | https://www.genomicseducation.hee.nhs.uk/education/?swoof=1&product_cat=online-courses | Educational resources and online courses, Master’s degree | Health Professionals, Scientists |
| phgFoundation (Public Health Genomics Foundation), University of Cambridge | https://www.phgfoundation.org/ | Bespoke training, training placements, internship opportunities | Public, post-graduate students, trainees and visiting scholars |
| The European Society of Human Genetics (ESHG) | https://www.eshg.org/index.php?id=education | Courses, events, glossary, clinical genomics guide app, quiz app | Health Professionals, academics, students, teachers |
| Genetics/Genomics Competency Center | https://genomicseducation.net/competency | Educational material, resources, competencies maps | Health Professionals |
| Center Genetics Education Canada–Knowledge Organization | https://geneticseducation.ca/ | Educational resources, seminars, public resource, events | Health Professionals, Public |
| Australian Genomics Health Alliance | https://www.melbournebioinformatics.org.au/project/austgenomics/ | Workshops | Health Professionals, students, academics |
| Centre for Genetics Education (CGE) | https://gardn.org.au/support-groups/directory/#!biz/id/594b367907ac801805955111 | Online training modules, fact sheets, patient’s booklets, and pamphlets | Health Professionals, public |
| The Jackson Laboratory | https://www.jax.org/personalized-medicine/precision-medicine-and-you/genetics-vs-genomics | Online learning courses, training programs | Health Professionals, students, teachers, researchers |
| Genomic Applications in Practice and Prevention Network (GAPPNet™) | https://www.cdc.gov/genomics/translation/GAPPNet/index.htm/ | General Genetic information, Fact sheets | Health Professionals |
| Genetics/Genomics Competency Center for Education (G2C2) | https://www.genomicseducation.net/ | Online genomics educational materials | Health Professionals |
| National Library of Medicine: Genetics Home Reference | https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/ | Online material on basic genetics | Health Professionals, public |
| Omics Nursing Science & Education Network (ONSEN)—[National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), National Cancer Institute (NCI), and National Institute of Nursing Research (NINR)] | https://omicsnursingnetwork.net/ | Mentorship opportunities, pre- and/or post-doctoral training positions, research collaboration | Nurses |
| National Institute of Nursing Research -Summer Genetics Institute (SGI) | https://www.ninr.nih.gov/training/trainingopportunitiesintramural/summergeneticsinstitute | Summer course, lectures, and hands-on laboratory training | Nurses, academics, students |
| National Human Genome Research Institute: Talking Glossary | https://www.genome.gov/10002134/1999-release-talking-glossary | Online genetics glossary, text, audio and visual materials | Health Professionals, students, public |
| U.S. Surgeon General’s: My Family Health Portrait | https://phgkb.cdc.gov/FHH/html/index.html | Family History Resources | Public |
| National Cancer Institute: Cancer Genetics Risk Assessment and Counseling | https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/genetics/risk-assessment-pdq | Genetic Education and Counseling | Health Professionals |
| Omics Nursing Science and Education Network (ONSEN) | https://omicsnursingnetwork.net/ | Leveled knowledge matrix, list of mentors and list of pre- and post-doctoral training positions | Nurses, trainees, investigators, mentors |
| Beijing Genomics Institute | https://en.genomics.cn/ | Youth science programs, videos, conference, events | Health Professionals, students, teachers, researchers |
| Genetic Database Kanehisa Laboratory in Kyoto University | https://www.genome.jp/en/about_dbget.html | Bioinformatics tools | Health Professionals, students, teachers, researchers |
| EuroGentest | http://www.eurogentest.org/index.php?id=894 | Online courses, lessons, information on genetics | Public, Health professionals |
| Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory—DNA from the beginning | http://www.dnaftb.org/ | Educational programs, courses | Public, students |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spanakis, M.; Patelarou, A.E.; Patelarou, E. Nursing Personnel in the Era of Personalized Healthcare in Clinical Practice. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030056
Spanakis M, Patelarou AE, Patelarou E. Nursing Personnel in the Era of Personalized Healthcare in Clinical Practice. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2020; 10(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpanakis, Marios, Athina E. Patelarou, and Evridiki Patelarou. 2020. "Nursing Personnel in the Era of Personalized Healthcare in Clinical Practice" Journal of Personalized Medicine 10, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030056
APA StyleSpanakis, M., Patelarou, A. E., & Patelarou, E. (2020). Nursing Personnel in the Era of Personalized Healthcare in Clinical Practice. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030056