Semantic Priming in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Subjects: Effect of Different Time of Presentation of Word-Pairs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Neuropsychological Examination
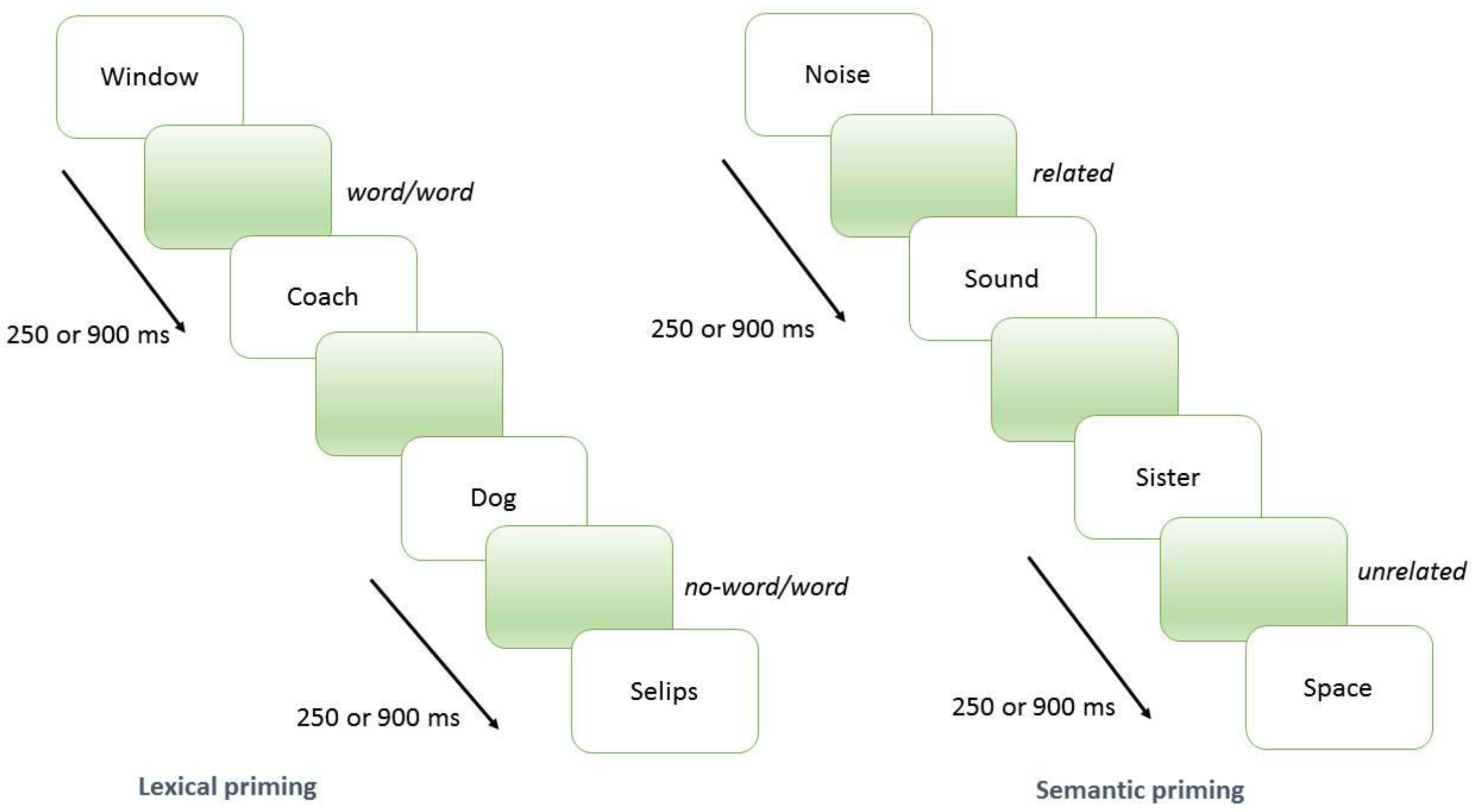
2.2. Lexical and Semantic Priming Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Lexicality Effect
3.1.1. Priming Effect at SOA 250 ms
3.1.2. Priming Effect at 900 ms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. List of Items
| TARGET WORD | RELATED PRIME | UNRELATED PRIME |
| vinegar | Salad | Hawk |
| student | Schoolchildren | Peacock |
| aerial | Cable | Walnut |
| banana | Gorilla | Die |
| mouth | Tongue | Species |
| orange | Peel | Sign |
| Dog | Peace | Owner |
| song | Voice | Point |
| horse | Animal | Example |
| colour | Red | Need |
| deluge | Thunder | Ram |
| dragon | fairy tales | Lip |
| grass | Lawn | People |
| summer | Sun | Land |
| river | Water | Game |
| giraffe | Height | Accent |
| Trip | Coach | Gasp |
| Ant | Bug | Candle |
| winter | Snow | Number |
| lake | Fish | Time |
| snail | Shell | Wax |
| mum | Sun | News |
| Sea | Island | Year |
| pencil | Case | Diamond |
| mule | Stable | Witch |
| nose | Face | Day |
| Ship | Voat | Arm |
| grandchild | Family | Answer |
| gandfather | Father | Bottom |
| track | Trace | Fear |
| vegetable garden | Vegetable | Loft |
| package | Courier | Bundle |
| planet | Heart | Minute |
| Rain | Weather | Type |
| spider | Venom | Steam |
| noise | Sound | Begin |
| classroom | School | Cold |
| seed | Grain | Injury |
| sister | Brother | Space |
| sauce | Tomato | Sheet |
| nest | Hibernation | Paint |
| roof | House | Name |
| cough | Sickness | Can |
| trumpet | Brass | Mill |
| coach | Binary | Steak |
| wind | Air | Part |
| worm | Maggot | Elf |
| volcano | Eruption | Reflex |
| Paw | Claw | Door |
| mosquito | Sting | Chest |
References
- Taylor, K.I.; Probst, A. Anatomic localization of the transentorhinal region of the perirhinal cortex. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejanin, A.; Schonhaut, D.R.; La Joie, R.; Kramer, J.H.; Baker, S.L.; Sosa, N.; Ayakta, N.; Cantwell, A.; Janabi, M.; Lauriola, M.; et al. Tau pathology and neurodegeneration contribute to cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2017, 140, 3286–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, A.; Fedio, P. Word production and comprehension in Alzheimer’s disease: The breakdown of semantic knowledge. Brain Lang. 1983, 19, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, F.J.; Collins, C.; Corkin, S.; Rosen, T.J. Equivalent forms of the Boston Naming Test. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1986, 8, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, J.R.; Salmon, D.P.; Butters, N. Semantic memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease: Failure of access or degraded knowledge? Neuropsychologia 1992, 30, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, B.A.; Dronkers, N.F.; Koss, E.; Delis, D.C.; Friedland, R.P. Retrieval from semantic memory in Alzheimer-type dementia. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1986, 8, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tröster, A.I.; Salmon, D.P.; McCullough, D.; Butters, N. A comparison of the category fluency deficits associated with Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s disease. Brain Lang. 1989, 37, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayles, K.A.; Tomoeda, C.K.; Trosset, M.W. Naming and categorical knowledge in Alzheimer’s disease: The process of semantic memory deterioration. Brain Lang. 1990, 39, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, J.R.; Patterson, K. Is semantic memory consistently impaired early in the course of Alzheimer’s disease? Neuroanatomical and diagnostic implications. Neuropsychologia 1995, 33, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsch, A.U.; Bondi, M.W.; Butters, N.; Salmon, D.P.; Katzman, R.; Thal, L.J. Comparisons of verbal fluency tasks in the detection of dementia of the Alzheimer type. Arch. Neurol. 1992, 49, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutter-Upham, K.E.; Saykin, A.J.; Rabin, L.A.; Roth, R.M.; Wishart, H.A.; Pare, N.; Flashman, L.A. Verbal fluency performance in amnestic MCI and older adults with cognitive complaints. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2008, 23, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adlam, A.L.; Bozeat, S.; Arnold, R.; Watson, P.; Hodges, J.R. Semantic knowledge in mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer’s disease. Cortex 2006, 42, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.J.; Rich, J.B.; Troyer, A.K. Verbal fluency patterns in amnestic mild cognitive impairment are characteristic of Alzheimer’s type dementia. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2006, 12, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amieva, H.; Letenneur, L.; Dartigues, J.F.; Rouch-Leroyer, I.; Sourgen, C.; D’Alchee-Biree, F.; Dib, M.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Orgogozo, J.M.; Fabrigoule, C. Annual rate and predictors of conversion to dementia in subjects presenting mild cognitive impairment criteria defined according to a population-based study. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2004, 18, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, S.; Brambati, S.M.; Ansado, J.; Barbeau, E.J.; Felician, O.; Didic, M.; Lacombe, J.; Goldstein, R.; Chayer, C.; Kergoat, M.J. The cognitive and neural expression of semantic memory impairment in mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, H.E.H.; Rayner, K.; Chumbley, J.I. Comparing naming, lexical decision, and eye fixation times: Word frequency effects and individual differences. Mem. Cognit. 1998, 26, 1270–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juhasz, B.J. Age-of-acquisition effects in word and picture identification. Psychol. Bull. 2005, 131, 684–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.J.; Jane Fitch, F.; Ellis, A.W. Age of acquisition affects object recognition and naming in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2006, 28, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrard, P.; Maloney, L.M.; Hodges, J.R.; Patterson, K. The effects of very early Alzheimer’s disease on the characteristics of writing by a renowned author. Brain J. Neurol. 2005, 128, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes-McKay, K.E.; Ellis, A.W.; Shanks, M.F.; Venneri, A. The age of acquisition of words produced in a semantic fluency task can reliably differentiate normal from pathological age related cognitive decline. Neuropsychologia 2005, 43, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, K.M.; Zimmerman, M.E.; Sanders, A.E. Differential impacts of age of acquisition on letter and semantic fluency in Alzheimer’s disease patients and healthy older adults. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2011, 64, 2383–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venneri, A.; McGeown, W.J.; Hietanen, H.M.; Guerrini, C.; Ellis, A.W.; Shanks, M.F. The anatomical bases of semantic retrieval deficits in early Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, M.G.; Marra, C.; Spinelli, P.; Caprara, A.; Scaricamazza, E.; Castelli, D.; Canulli, S.; Gainotti, G.; Quaranta, D. Typicality of words produced on a semantic fluency task in amnesic mild cognitive impairment: Linguistic analysis and risk of conversion to dementia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 42, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venneri, A.; Jahn-Carta, C.; de Marco, M.; Quaranta, D.; Marra, C. Diagnostic and prognostic role of semantic processing in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Biomark. Med. 2018, 12, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duong, A.; Whitehead, V.; Hanratty, K.; Chertkow, H. The nature of lexico-semantic processing deficits in mild cognitive impairment. Neuropsychologia 2006, 44, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.S.; Moss, M.B.; Tanzi, R.; Jones, K. Preclinical prediction of AD using neuropsychological tests. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2001, 7, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.; Ratcliff, G.; Belle, S.H.; Cauley, J.A.; DeKosky, S.T.; Ganguli, M. Patterns of cognitive decline in presymptomatic Alzheimer disease: A prospective community study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2001, 58, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodges, J.R.; Patterson, K.; Graham, N.; Dawson, K. Naming and knowing in dementia of Alzheimer’s type. Brain Lang. 1996, 54, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Watson, P.; Hodges, J.R. The nature and staging of attention dysfunction in early (minimal and mild) Alzheimer’s disease: Relationship to episodic and semantic memory impairment. Neuropsychologia 2000, 38, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, A.; Hodges, J.R. Initial letter and semantic category fluency in Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and progressive supranuclear palsy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quaranta, D.; Piccininni, C.; Caprara, A.; Malandrino, A.; Gainotti, G.; Marra, C. Semantic Relations in a Categorical Verbal Fluency Test: An Exploratory Investigation in Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, A.M.; Loftus, E.F. A spreading-activation theory of semantic processing. Psychol. Rev. 1975, 82, 407–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, J.H. Semantic priming and retrieval from lexical memory: Roles of inhibitionless spreading activation and limited-capacity attention. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1977, 106, 226–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, P.; Holbrook, J.P. Semantic memory and priming. In Handbook of Psychology; Healy, A.F., Proctor, R.W., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Plaut, D.C.; Booth, J.R. Individual and developmental differences in semantic priming: Empirical and computational support for a single-mechanism account of lexical processing. Psychol. Rev. 2000, 107, 786–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foster, P.S.; Drago, V.; Yung, R.C.; Pearson, J.; Stringer, K.; Giovannetti, T.; Libon, D.; Heilman, K.M. Differential lexical and semantic spreading activation in Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Demen. 2013, 28, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.E.; Chenery, H.J.; Ingram, J.C. Semantic priming in Alzheimer’s dementia: Evidence for dissociation of automatic and attentional processes. Brain Lang. 2001, 76, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveri, M.C.; Monteleone, D.; Burani, C.; Tabossi, P. Automatic semantic facilitation in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1996, 18, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, D.P.; Butters, N.; Chan, A.S. The deterioration of semantic memory in Alzheimer’s disease. Can. J. Exp. Psychol. Rev. Can. Psychol. Exp. 1999, 53, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, R.; Carlesimo, G.A.; Zannino, G.D.; Mauri, M.; Muolo, B.; Pettenati, C.; Caltagirone, C. Intentional and automatic measures of specific-category effect in the semantic impairment of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia 2003, 41, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, B.A.; Shenaut, G.K.; Jagust, W.J.; Stillman, R.C. Automatic semantic priming with various category relations in Alzheimer’s disease and normal aging. Psychol. Aging 1991, 6, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertkow, H.; Bub, D.; Bergman, H.; Bruemmer, A.; Merling, A.; Rothfleisch, J. Increased semantic priming in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1994, 16, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertkow, H.; Bub, D.; Seidenberg, M. Priming and semantic memory loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Lang. 1989, 36, 420–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebes, R.D.; Brady, C.B.; Huff, F.J. Automatic and attentional mechanisms of semantic priming in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1989, 11, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balota, D.A.; Watson, J.M.; Duchek, J.M.; Ferraro, F.R. Cross-modal semantic and homograph priming in healthy young, healthy old, and in Alzheimer’s disease individuals. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 1999, 5, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffard, B.; Desgranges, B.; Nore-Mary, F.; Lalevée, C.; de la Sayette, V.; Pasquier, F.; Eustache, F. The nature of semantic memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease: New insights from hyperpriming effects. Brain J. Neurol. 2001, 124, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perri, R.; Zannino, G.D.; Caltagirone, C.; Carlesimo, G.A. Semantic priming for coordinate distant concepts in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.L.; Friedman, R.B. The underlying mechanisms of semantic memory loss in Alzheimer’s disease and semantic dementia. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glosser, G.; Friedman, R.B.; Grugan, P.K.; Lee, J.H.; Grossman, M. Lexical semantic and associative priming in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychology 1998, 12, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffard, B.; Desgranges, B.; Nore-Mary, F.; Lalevée, C.; Beaunieux, H.; de la Sayette, V.; Pasquier, F.; Eustache, F. The dynamic time course of semantic memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease: Clues from hyperpriming and hypopriming effects. Brain J. Neurol. 2002, 125, 2044–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulatti, C.; Calia, C.; De Caro, M.F.; Della Sala, S. The cumulative semantic interference effect in normal and pathological ageing. Neuropsychologia 2014, 65, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winblad, B.; Palmer, K.; Kivipelto, M.; Jelic, V.; Fratiglioni, L.; Wahlund, L.O.; Nordberg, A.; Backman, L.; Albert, M.; Almkvist, O.; et al. Mild cognitive impairment--beyond controversies, towards a consensus: Report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlesimo, G.A.; Caltagirone, C.; Gainotti, G.; Fadda, L.; Gallassi, R.; Lorusso, S.; Marfia, G.; Marra, C.; Nocentini, U.; Parnetti, L. The mental deterioration battery: Normative data, diagnostic reliability and qualitative analyses of cognitive impairment. Eur. Neurol. 1996, 36, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarra, P.; Vezzadini, G.; Dieci, F.; Zonato, F.; Venneri, A. Una versione abbreviata del test di Stroop: Dati normativi nella popolazione italiana. Nuova Riv. Neurol. 2002, 12, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Marra, C.; Gainotti, G.; Scaricamazza, E.; Piccininni, C.; Ferraccioli, M.; Quaranta, D. The Multiple Features Target Cancellation (MFTC): An attentional visual conjunction search test. Normative values for the Italian population. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, M.; Costa, A.; Caltagirone, C.; Carlesimo, G.A. Forward and backward span for verbal and visuo-spatial data: Standardization and normative data from an Italian adult population. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, D.; Caprara, A.; Piccininni, C.; Vita, M.G.; Gainotti, G.; Marra, C. Standardization, Clinical Validation, and Typicality Norms of a New Test Assessing Semantic Verbal Fluency. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. Off. J. Natl. Acad. Neuropsychol. 2016, 31, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balota, D.A.; Chumbley, J.I. Are lexical decisions a good measure of lexical access? The role of word frequency in the neglected decision stage. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1984, 10, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HS | MCI | Non Converters-MCI | Converters-MCI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOA 250 ms | ||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | P | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p | |
| Words | 813.37 | 248.266 | 1046.15 | 375.320 | <0.001 | 1052.94 | 366.878 | 1036.24 | 387.545 | n.s. |
| No words | 1205.38 | 483.902 | 1573.38 | 471.991 | <0.001 | 1547.61 | 480.800 | 1610.85 | 456.888 | n.s. |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| SOA 900 ms | ||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | P | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p | |
| Words | 808.15 | 247.161 | 1002.23 | 331.279 | <0.001 | 996.86 | 323.493 | 1010.02 | 342.552 | n.s. |
| No words | 1177.64 | 460.944 | 1543.75 | 462.437 | <0.001 | 1519.25 | 468.131 | 1579.34 | 452.266 | n.s. |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| HS | MCI | No Converters-MCI | Converters-MCI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOA 250 ms | ||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Related words | 778.27 | 187.428 | 944.01 | 248.428 | 969.00 | 229.787 | 923.58 | 261.521 |
| Unrelated words | 814.46 | 212.969 | 985.38 | 253.232 | 1029.33 | 246.156 | 949.46 | 253.915 |
| p | 0.015 | 0.003 | 0.038 | 0.321 | ||||
| Cohen’s d | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.10 | ||||
| SOA 900 ms | ||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Related words | 776.68 | 214.317 | 922.60 | 234.317 | 930.11 | 220.048 | 913.64 | 250.716 |
| Unrelated words | 806.21 | 204.353 | 962.37 | 242.047 | 982.23 | 244.109 | 938.63 | 238.152 |
| p | 0.071 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.745 | ||||
| Cohen’s d | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.10 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guglielmi, V.; Quaranta, D.; Mega, I.; Costantini, E.M.; Carrarini, C.; Innocenti, A.; Marra, C. Semantic Priming in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Subjects: Effect of Different Time of Presentation of Word-Pairs. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030057
Guglielmi V, Quaranta D, Mega I, Costantini EM, Carrarini C, Innocenti A, Marra C. Semantic Priming in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Subjects: Effect of Different Time of Presentation of Word-Pairs. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2020; 10(3):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030057
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuglielmi, Valeria, Davide Quaranta, Ilaria Mega, Emanuele Maria Costantini, Claudia Carrarini, Alice Innocenti, and Camillo Marra. 2020. "Semantic Priming in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Subjects: Effect of Different Time of Presentation of Word-Pairs" Journal of Personalized Medicine 10, no. 3: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030057
APA StyleGuglielmi, V., Quaranta, D., Mega, I., Costantini, E. M., Carrarini, C., Innocenti, A., & Marra, C. (2020). Semantic Priming in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Subjects: Effect of Different Time of Presentation of Word-Pairs. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(3), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030057





