An Ex Vivo and In Silico Study Providing Insights into the Interplay of Circulating miRNAs Level, Platelet Reactivity and Thrombin Generation: Looking beyond Traditional Pharmacogenetics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Blood Collection
2.3. Platelet Function Evaluation
2.4. Selection of Candidate miRNAs
2.5. Plasma miRNA Extraction and Analysis
2.6. Plasma Sample Quality Control
2.7. Gene Ontology and Pathway Analysis
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Sample Quality Controls
3.2. miRNA Reference Panel for the Normalization Procedure
3.3. Correlation between miRNA Level and Platelet Aggregation
3.4. Correlation between miRNA Level and In Vivo Thrombin-Generation Markers
3.5. Gene Ontology Analysis
4. Discussion
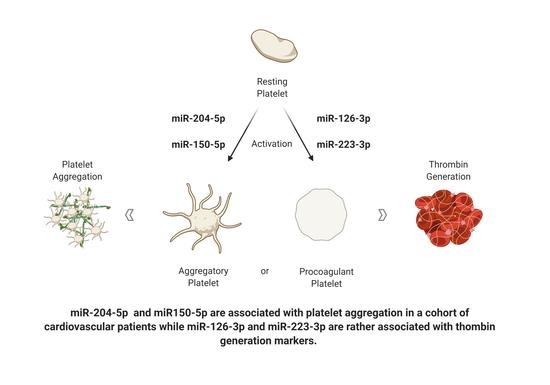
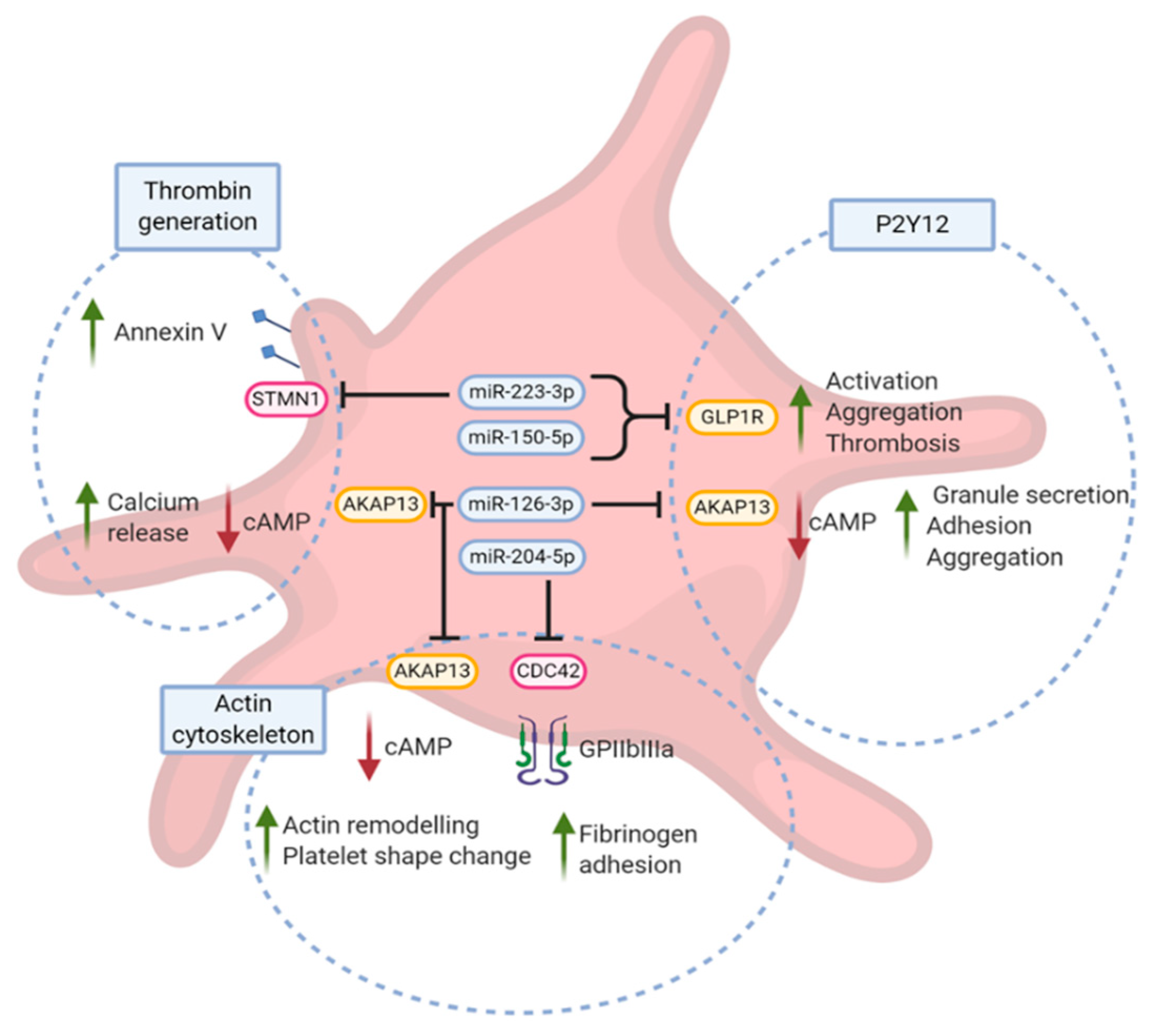
4.1. Association of Candidate miRNA with Platelet Aggregation
4.2. Association of Candidate miRNAs and In Vivo Thrombin Generation Markers
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghoshal, K.; Bhattacharyya, M. Overview of Platelet Physiology: Its Hemostatic and Nonhemostatic Role in Disease Pathogenesis. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 781857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willoughby, S.; Holmes, A.; Loscalzo, J. Platelets and cardiovascular disease. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2002, 1, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badimon, L.; Padró, T.; Vilahur, G. Atherosclerosis, platelets and thrombosis in acute ischaemic heart disease. Eur. Hear. J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2012, 1, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P.; Nesbitt, W.S.; Westein, E. Dynamics of platelet thrombus formation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7 (Suppl. 1), 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberio, L.; Ravanat, C.; Hechler, B.; Mangin, P.H.; Lanza, F.; Gachet, C. Delayed-onset of procoagulant signalling revealed by kinetic analysis of COAT platelet formation. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bray, P.F.; Mathias, R.A.; Faraday, N.; Yanek, L.R.; Fallin, M.D.; Herrera-Galeano, J.E.; Wilson, A.F.; Becker, L.C.; Becker, D.M. Heritability of platelet function in families with premature coronary artery disease. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.S.; Bergmeijer, T.O.; Gong, L.; Reny, J.; Lewis, J.P.; Mitchell, B.D.; Alexopoulos, D.; Aradi, D.; Altman, R.B.; Bliden, K.; et al. Genomewide Association Study of Platelet Reactivity and Cardiovascular Response in Patients Treated with Clopidogrel: A Study by the International Clopidogrel Pharmacogenomics Consortium. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 108, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurtz, M.; Kristensen, S.D.; Hvas, A.-M.; Grove, E.L. Pharmacogenetics of the Antiplatelet Effect of Aspirin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 5294–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, P.; Plante, I.; Ouellet, D.L.; Perron, M.P.; Rousseau, G.; Provost, P. Existence of a microRNA pathway in anucleate platelets. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stakos, D.A.; Gatsiou, A.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Tselepis, A.D.; Stellos, K. Platelet microRNAs: From platelet biology to possible disease biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Platelets 2013, 24, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaioni, C.; Gustapane, M.; Cialdella, P.; Della Bona, R.; Biasucci, L.M. Microparticles and microRNAs: New players in the complex field of coagulation. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2013, 8, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondal, T.; Nielsen, S.J.; Baker, A.; Andreasen, D.; Mouritzen, P.; Teilum, M.W.; Dahlsveen, I.K. Assessing sample and miRNA profile quality in serum and plasma or other biofluids. Methods 2013, 59, S1–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, T.L.; Mayr, M.; Hackl, M. microRNAs as Promising Biomarkers of Platelet Activity in Antiplatelet Therapy Monitoring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voora, D.; Ginsburg, G.S.; Åkerblom, A. Platelet RNA as a novel biomarker for the response to antiplatelet therapy. Futur. Cardiol. 2014, 10, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtlscherer, S.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Circulating MicroRNAs. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zapilko, V.; Fish, R.J.; Garcia, A.; Reny, J.-L.; Dunoyer-Geindre, S.; Lecompte, T.; Neerman-Arbez, M.; Fontana, P. MicroRNA-126 is a regulator of platelet-supported thrombin generation. Platelets 2020, 31, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Dunoyer-Geindre, S.; Fish, R.J.; Neerman-Arbez, M.; Reny, J.-L.; Fontana, P. Methods to Investigate miRNA Function: Focus on Platelet Reactivity. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 121, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojkovic, S.; Nossent, A.Y.; Haller, P.; Jäger, B.; Vargas, K.G.; Wojta, J.; Huber, K. MicroRNAs as Regulators and Biomarkers of Platelet Function and Activity in Coronary Artery Disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reny, J.-L.; Berdagué, P.; Poncet, A.; Barazer, I.; Nolli, S.; Fabbro-Peray, P.; Schved, J.-F.; Bounameaux, H.; Mach, F.; de Moerloose, P.; et al. Antiplatelet Drug Response Status Does Not Predict Recurrent Ischemic Events in Stable Cardiovascular Patients. Circulation 2012, 125, 3201–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontana, P.; Berdagué, P.; Castelli, C.; Nolli, S.; Barazer, I.; Fabbro-Peray, P.; Schved, J.-F.; Bounameaux, H.; Mach, F.; De Moerloose, P.; et al. Clinical predictors of dual aspirin and clopidogrel poor responsiveness in stable cardiovascular patients from the ADRIE study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, L.M.; Edelstein, L.C.; Nagalla, S.; Woodley, A.B.; Chen, E.S.; Kong, X.; Ma, L.; Fortina, P.; Kunapuli, S.; Holinstat, M.; et al. Human platelet microRNA-mRNA networks associated with age and gender revealed by integrated plateletomics. Blood 2014, 123, e37–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zufferey, A.; Ibberson, M.; Reny, J.-L.; Nolli, S.; Schvartz, D.; Docquier, M.; Xenarios, I.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Fontana, P. New molecular insights into modulation of platelet reactivity in aspirin-treated patients using a network-based approach. Qual. Life Res. 2016, 135, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Zeng, X.; Cheng, B.; Ma, X.; Yuan, H.; Nie, X.; Gong, M.; Zhang, H. Platelets in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients with High Platelet Reactivity after Dual Antiplatelet Therapy Exhibit Upregulation of miR-204-5p. Ann. Clin Lab. Sci. 2019, 49, 619–631. [Google Scholar]
- Kroh, E.M.; Parkin, R.K.; Mitchell, P.S.; Tewari, M. Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods 2010, 50, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zalewski, K.; Misiek, M.; Kowalik, A.; Bakuła-Zalewska, E.; Kopczyński, J.; Zielińska, A.; Bidziński, M.; Radziszewski, J.; Góźdź, S.; Kowalewska, M. Normalizers for microRNA quantification in plasma of patients with vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia lesions and vulvar carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317717140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, Q.; Tang, G.; Shen, X.; Lv, K.; Wu, Y.; Bi, J. Different Normalization Strategies Might Cause Inconsistent Variation in Circulating microRNAs in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mompeón, A.; Ortega-Paz, L.; Vidal-Gómez, X.; Costa, T.J.; Pérez-Cremades, D.; Garcia-Blas, S.; Brugaletta, S.; Sanchis, J.; Sabate, M.; Novella, S.; et al. Disparate miRNA expression in serum and plasma of patients with acute myocardial infarction: A systematic and paired comparative analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, M.G.M.; Halliani, A.; Moerland, P.D.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Creemers, E.E.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.-J. Normalization panels for the reliable quantification of circulating microRNAs by RT-qPCR. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 3853–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Lin, F.-C.; Chen, S.-J.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chung, W.-J.; Cheng, C.-I. Optimized Collection Protocol for Plasma MicroRNA Measurement in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2901938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- St-Pierre, J.; Grégoire, J.-C.; Vaillancourt, C. A simple method to assess group difference in RT-qPCR reference gene selection using GeNorm: The case of the placental sex. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ancrenaz, V.; Daali, Y.; Fontana, P.; Besson, M.; Samer, C.; Dayer, P.; Desmeules, J. Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms and Drug—Drug Interactions on Clopidogrel and Prasugrel Response Variability. Curr. Drug Metab. 2010, 11, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, N.; Skroblin, P.; Barwari, T.; Huntley, R.P.; Lu, R.; Joshi, A.; Lovering, R.C.; Mayr, M. MicroRNA Biomarkers and Platelet Reactivity. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frelinger, A.L.; Furman, M.I.; Linden, M.D.; Li, Y.; Fox, M.L.; Barnard, M.R.; Michelson, A.D. Residual Arachidonic Acid–Induced Platelet Activation via an Adenosine Diphosphate–Dependent but Cyclooxygenase-1– and Cyclooxygenase-2–Independent Pathway. Circulation 2006, 113, 2888–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zufferey, A.; Reny, J.-L.; Combescure, C.; De Moerloose, P.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Fontana, P. Platelet reactivity is a stable and global phenomenon in aspirin-treated cardiovascular patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 106, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barale, C.; Buracco, S.; Cavalot, F.; Frascaroli, C.; Guerrasio, A.; Russo, I. Glucagon-like peptide 1-related peptides increase nitric oxide effects to reduce platelet activation. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahal, H. GLP-1R, a Novel Receptor in Platelets; and the Use of Liraglutide in the Treatment of Obesity in Women with PCOS. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Hull, Hull, UK, The University of York, York, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Steven, S.; Jurk, K.; Kopp, M.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Mikhed, Y.; Schwierczek, K.; Roohani, S.; Kashani, F.; Oelze, M.; Klein, T.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signalling reduces microvascular thrombosis, nitro-oxidative stress and platelet activation in endotoxaemic mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 174, 1620–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sternkopf, M.; Nagy, M.; Baaten, C.C.; Kuijpers, M.J.; Tullemans, B.M.; Wirth, J.; Theelen, W.; Mastenbroek, T.G.; Lehrke, M.; Winnerling, B.; et al. Native, Intact Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Is a Natural Suppressor of Thrombus Growth Under Physiological Flow Conditions. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, e65–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron-Vendrig, A.; Reheman, A.; Siraj, M.A.; Xu, X.R.; Wang, Y.; Lei, X.; Afroze, T.; Shikatani, E.; El-Mounayri, O.; Noyan, H.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Activation Attenuates Platelet Aggregation and Thrombosis. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaudewitz, D.; Skroblin, P.; Bender, L.H.; Barwari, T.; Willeit, P.; Pechlaner, R.; Sunderland, N.P.; Willeit, K.; Morton, A.C.; Armstrong, P.C.; et al. Association of MicroRNAs and YRNAs With Platelet Function. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Dunoyer-Geindre, S.; Zapilko, V.; Nolli, S.; Reny, J.-L.; Fontana, P. Functional Validation of microRNA-126-3p as a Platelet Reactivity Regulator Using Human Haematopoietic Stem Cells. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raslan, Z.; Aburima, A.; Naseem, K.M. The Spatiotemporal Regulation of cAMP Signaling in Blood Platelets—Old Friends and New Players. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Colman, R.W. Thrombin regulates intracellular cyclic AMP concentration in human platelets through phosphorylation/activation of phosphodiesterase 3A. Blood 2007, 110, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smolenski, A.P. Novel roles of cAMP/cGMP-dependent signaling in platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Deng, X.; Wu, M.; Zhang, G.; Huang, J. Down-regulation of miRNA-204 by LMP-1 enhances CDC42 activity and facilitates invasion of EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, A.; Dunoyer-Geindre, S.; Nolli, S.; Reny, J.L.; Fontana, P. Impact of miR-204 on Human Platelets; Oral Communication; ISTH: Melbourne, BC, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, H.H.; Heemskerk, J.W.M.; Levi, M.; Reitsma, P.H. New Fundamentals in Hemostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 327–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, W.; Tong, J.H.M.; Chan, A.W.H.; Lung, R.W.M.; Chau, S.L.; Wong, Q.W.L.; Wong, N.; Yu, J.; Cheng, A.S.L.; To, K.F. Stathmin1 Plays Oncogenic Role and Is a Target of MicroRNA-223 in Gastric Cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, H.-B.; Hao, C.J.; Cui, Y.; Han, X.-C.; Hu, Y.; Li, F.-F.; Xia, H.-F.; Ma, X. MiR-101 Is Involved in Human Breast Carcinogenesis by Targeting Stathmin1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, S.; Wurtzel, J.G.; Chen, X.; Ma, P.; Goldfinger, L.E. High-efficiency unassisted transfection of platelets with naked double-stranded miRNAs modulates signal-activated translation and platelet function. Platelets 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.-J.; Lei, H.-P.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.-Y.; Deng, C.-Y.; Sheng, W.-S.; Fu, Y.-H.; Li, X.-H.; Lin, Y.-B.; Han, Y.-L.; et al. Plasma miR-142 predicts major adverse cardiovascular events as an intermediate biomarker of dual antiplatelet therapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Willeit, P.; Zampetaki, A.; Dudek, K.; Kaudewitz, D.; King, A.; Kirkby, N.S.; Crosby-Nwaobi, R.; Prokopi, M.; Drozdov, I.; Langley, S.R.; et al. Circulating MicroRNAs as Novel Biomarkers for Platelet Activation. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

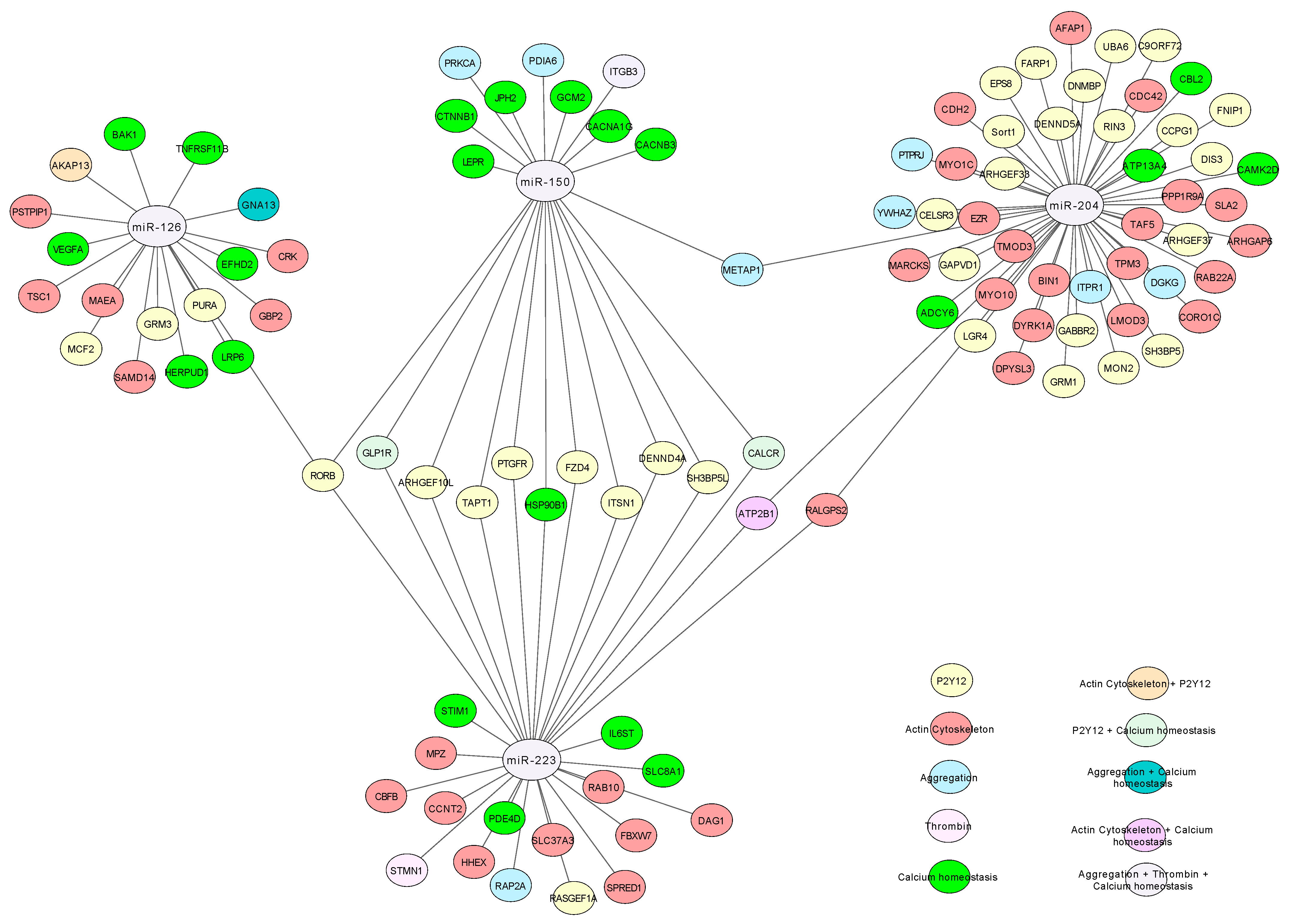
| Pathways | GO Terms |
|---|---|
| Aggregation | Platelet aggregation |
| Platelet activation | |
| Regulation of platelet aggregation | |
| P2Y12 | G protein-coupled adenosine receptor activity |
| ADP receptor activity | |
| G protein-coupled receptor activity | |
| Guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity | |
| G protein-coupled purinergic nucleotide receptor activity) | |
| Thrombin generation | Thrombin-activated receptor activity |
| Thrombin-activated receptor signalling pathway | |
| Fibrinogen binding | |
| Blood coagulation common pathway | |
| Actin cytoskeleton | Actin cytoskeleton |
| Calcium homeostasis | Vacuolar calcium ion homeostasis Golgi calcium ion homeostasis |
| Cellular calcium ion homeostasis | |
| Mitochondrial calcium ion homeostasis | |
| Mitochondrial, calcium ion homeostasis | |
| Endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis | |
| Smooth endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis | |
| Regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration | |
| Circadian regulation of calcium ion oscillation | |
| Bone remodeling |
| miRNA | geNorm M Value |
|---|---|
| miR-106-5p | 1.018 |
| miR-93 | 0.926 |
| miR-484 | 0.874 |
| miR-16 | 0.760 |
| Agonists | miR-126-3p | miR-204-5p | miR-150-5p | miR-223-3p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rho | p-Value | Rho | p-Value | Rho | p-Value | Rho | p-Value | |
| AA | 0.210 | 0.004 | 0.183 | 0.029 | 0.079 | 0.282 | 0.058 | 0.431 |
| ADP 5 | 0.074 | 0.321 | 0.184 | 0.028 | 0.132 | 0.071 | 0.015 | 0.837 |
| ADP 20 | 0.148 | 0.046 | 0.158 | 0.06 | 0.257 | <0.001 | 0.166 | 0.023 |
| Collagen | 0.144 | 0.053 | 0.279 | 0.001 | 0.260 | <0.001 | 0.178 | 0.014 |
| F1+2 | 0.329 * | <0.001 * | 0.173 | 0.040 | 0.124 * | 0.092 * | 0.224 | 0.002 |
| TAT | 0.182 * | 0.014 * | 0.115 | 0.174 | 0.046 * | 0.533 * | 0.281 | <0.001 |
| NS | <0.2 | 0.2–0.3 | >0.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, A.; Dunoyer-Geindre, S.; Nolli, S.; Reny, J.-L.; Fontana, P. An Ex Vivo and In Silico Study Providing Insights into the Interplay of Circulating miRNAs Level, Platelet Reactivity and Thrombin Generation: Looking beyond Traditional Pharmacogenetics. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11050323
Garcia A, Dunoyer-Geindre S, Nolli S, Reny J-L, Fontana P. An Ex Vivo and In Silico Study Providing Insights into the Interplay of Circulating miRNAs Level, Platelet Reactivity and Thrombin Generation: Looking beyond Traditional Pharmacogenetics. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(5):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11050323
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Alix, Sylvie Dunoyer-Geindre, Séverine Nolli, Jean-Luc Reny, and Pierre Fontana. 2021. "An Ex Vivo and In Silico Study Providing Insights into the Interplay of Circulating miRNAs Level, Platelet Reactivity and Thrombin Generation: Looking beyond Traditional Pharmacogenetics" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 5: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11050323
APA StyleGarcia, A., Dunoyer-Geindre, S., Nolli, S., Reny, J.-L., & Fontana, P. (2021). An Ex Vivo and In Silico Study Providing Insights into the Interplay of Circulating miRNAs Level, Platelet Reactivity and Thrombin Generation: Looking beyond Traditional Pharmacogenetics. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(5), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11050323