Non-Syndromic Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Mild Mutations in COL1A2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Subject Enrollment
2.2. Genomic DNA Isolation
2.3. Candidate Gene Sequencing of the DSPP Gene
2.4. Whole-Exome Sequencing
2.5. Haplotype Construction
3. Results
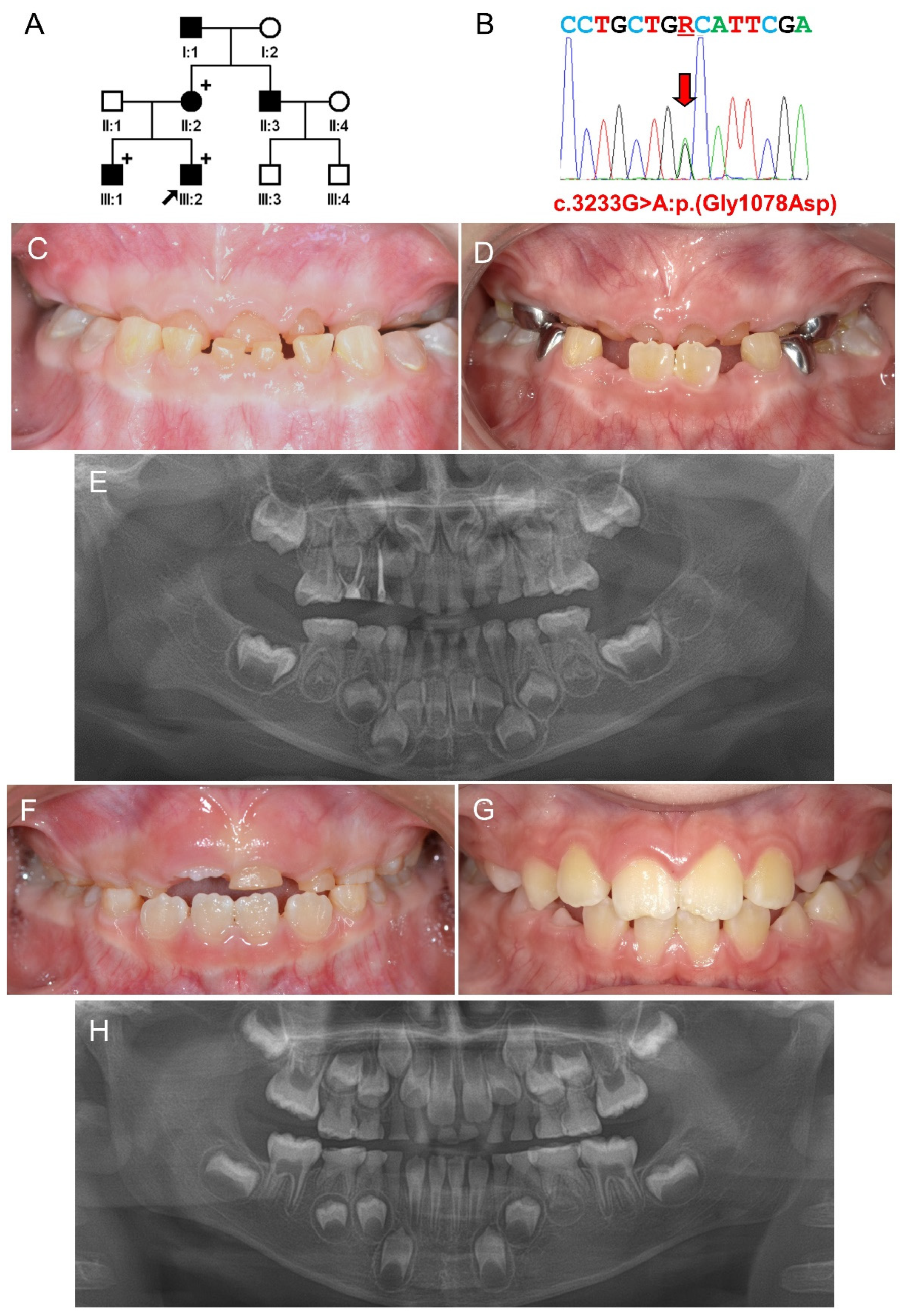
3.1. Family 1
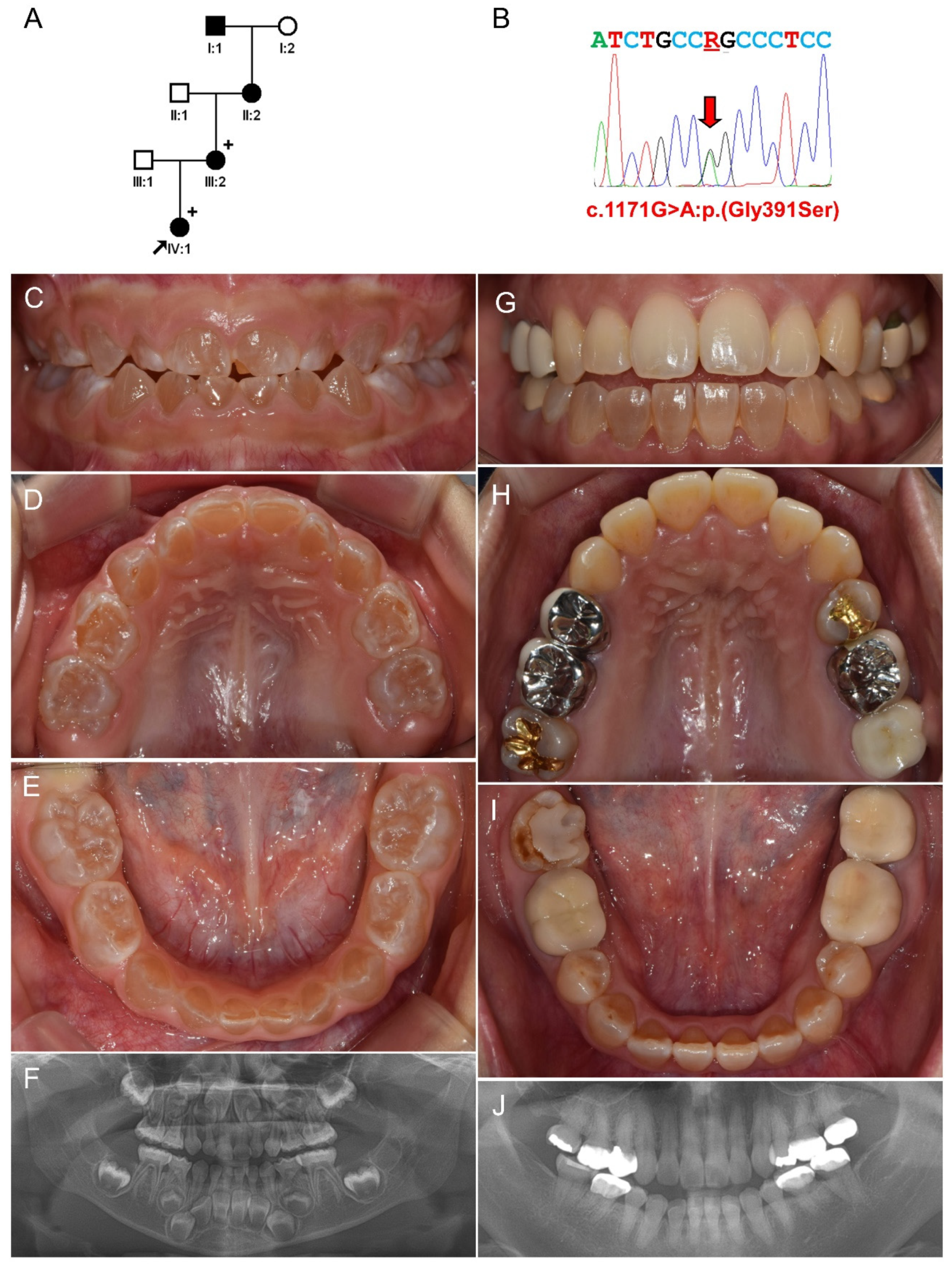
3.2. Family 2
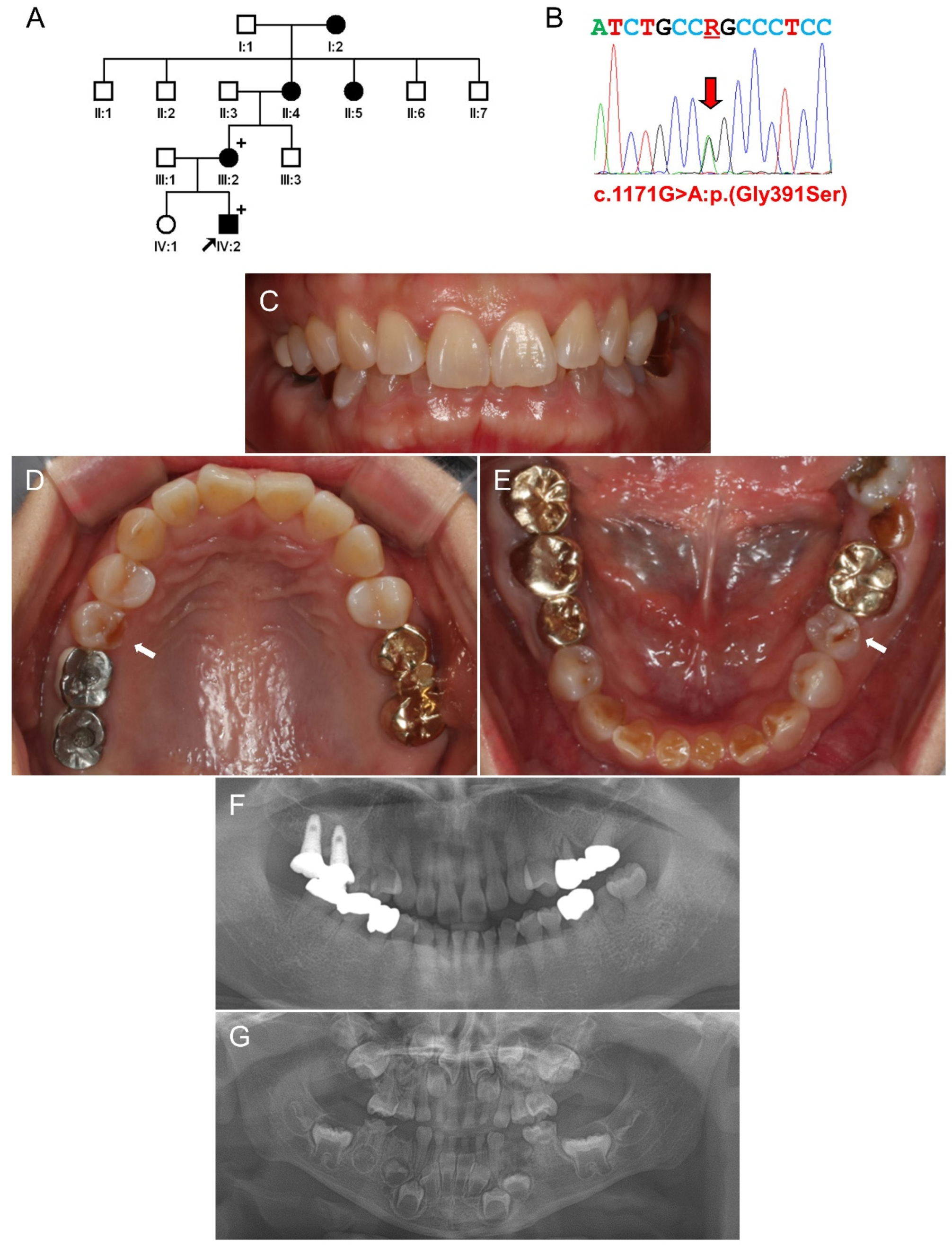
3.3. Family 3
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nanci, A. Ten Cate’s Oral Histology, 8th ed.; Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, M.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Young, M.; Boskey, A. Dentin structure composition and mineralization. Front. Biosci. 2011, E3, 711–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Song, M.; Kim, E.; Shon, W.; Chugal, N.; Bogen, G.; Lin, L.; Kim, R.; Park, N.-H.; Kang, M. Pulp-dentin Regeneration: Current State and Future Prospects. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, E.D.; Bixler, D.; el-Kafrawy, A.M. A proposed classification for heritable human dentine defects with a description of a new entity. Arch. Oral Biol. 1973, 18, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, M.J.; McDonnell, S.T.; Mackie, I.; Dixon, M.J. Hereditary dentine disorders: Dentinogenesis imperfecta and dentine dysplasia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2008, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, C.; Gao, S.; Qiu, C.; Liu, P.; Wu, G.; Qiang, B.; Lo, W.H.; Shen, Y. DSPP mutation in dentinogenesis imperfecta Shields type II. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Yu, C.; Chou, X.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Y.; Bu, L.; Fu, G.; Qian, M.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; et al. Dentinogenesis imperfecta 1 with or without progressive hearing loss is associated with distinct mutations in DSPP. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Hu, J.C.-C.; Lee, J.-I.; Moon, S.-K.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jang, K.-T.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, C.-C.; Hahn, S.-H.; Simmer, J.P. Mutational hot spot in the DSPP gene causing dentinogenesis imperfecta type II. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 116, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKnight, D.A.; Hart, P.S.; Hart, T.C.; Hartsfield, J.K.; Wilson, A.; Wright, J.T.; Fisher, L.W. A comprehensive analysis of normal variation and disease-causing mutations in the humanDSPPgene. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajpar, M.H.; Koch, M.J.; Davies, R.M.; Mellody, K.T.; Kielty, C.M.; Dixon, M.J. Mutation of the signal peptide region of the bicistronic gene DSPP affects translocation to the endoplasmic reticulum and results in defective dentine biomineralization. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-W.; Simmer, J.P. Hereditary Dentin Defects. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Nam, S.-H.; Jang, K.-T.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, C.-C.; Hahn, S.-H.; Hu, J.C.-C.; Simmer, J.P. A novel splice acceptor mutation in the DSPP gene causing dentinogenesis imperfecta type II. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 115, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.-E.; Kang, H.-Y.; Lee, S.-K.; Yoo, S.-H.; Lee, J.-C.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Nam, K.H.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, J.-C. Novel dentin phosphoprotein frameshift mutations in dentinogenesis imperfecta type II. Clin. Genet. 2011, 79, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kang, J.; Seymen, F.; Koruyucu, M.; Zhang, H.; Kasimoglu, Y.; Bayram, M.; Tuna-Ince, E.; Bayrak, S.; Tuloglu, N.; et al. Alteration of Exon Definition Causes Amelogenesis Imperfecta. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Der Auwera, G.A.; Carneiro, M.O.; Hartl, C.; Poplin, R.; Del Angel, G.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Jordan, T.; Shakir, K.; Roazen, D.; Thibault, J.; et al. From FastQ Data to High-Confidence Variant Calls: The Genome Analysis Toolkit Best Practices Pipeline. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 43, 11.10.1–11.10.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillence, D.O.; Senn, A.; Danks, D.M. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Med. Genet. 1979, 16, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marini, J.C.; Forlino, A.; Bächinger, H.P.; Bishop, N.J.; Byers, P.H.; De Paepe, A.; Fassier, F.; Fratzl-Zelman, N.; Kozloff, K.M.; Krakow, D.; et al. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, F.; Lalic, L.; Roughley, P.; Glorieux, F.H. Genotype–phenotype correlations in nonlethal osteogenesis imperfecta caused by mutations in the helical domain of collagen type I. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, J.C.; Forlino, A.; Cabral, W.A.; Barnes, A.M.; Antonio, J.D.S.; Milgrom, S.; Hyland, J.C.; Körkkö, J.; Prockop, D.J.; De Paepe, A.; et al. Consortium for osteogenesis imperfecta mutations in the helical domain of type I collagen: Regions rich in lethal mutations align with collagen binding sites for integrins and proteoglycans. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, K.; Åström, E.; Rubin, C.-J.; Grigelioniene, G.; Malmgren, B.; Ljunggren, Ö.; Kindmark, A. Genetic epidemiology, prevalence, and genotype–phenotype correlations in the Swedish population with osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.-K.; Chan, H.-C.; Makovey, I.; Simmer, J.P.; Hu, J.C.-C. Novel PAX9 and COL1A2 Missense Mutations Causing Tooth Agenesis and OI/DGI without Skeletal Abnormalities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kantaputra, P.N.; Chinadet, W.; Intachai, W.; Ngamphiw, C.; Cairns, J.R.K.; Tongsima, S. Isolated dentinogenesis imperfecta with glass-like enamel caused by COL1A2 mutation. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2018, 176, 2919–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Viswanathan, V.K. Osteogenesis Imperfecta. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2021; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, A.; Tournis, S.; Kämpe, A.; Ain, N.U.; Taylan, F.; Doulgeraki, A.; Mäkitie, O. Autosomal Recessive Osteogenesis Imperfecta Caused by a Novel Homozygous COL1A2 Mutation. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 103, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Udomchaiprasertkul, W.; Kuptanon, C.; Porntaveetus, T.; Shotelersuk, V. A family with homozygous and heterozygous p.Gly337Ser mutations in COL1A2. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Hyun, H.-K.; Lee, J.-C.; Lee, Z.H.; Kim, J.-W. Non-Syndromic Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Mild Mutations in COL1A2. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060526
Lee Y, Kim YJ, Hyun H-K, Lee J-C, Lee ZH, Kim J-W. Non-Syndromic Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Mild Mutations in COL1A2. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(6):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060526
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yejin, Youn Jung Kim, Hong-Keun Hyun, Jae-Cheoun Lee, Zang Hee Lee, and Jung-Wook Kim. 2021. "Non-Syndromic Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Mild Mutations in COL1A2" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 6: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060526
APA StyleLee, Y., Kim, Y. J., Hyun, H.-K., Lee, J.-C., Lee, Z. H., & Kim, J.-W. (2021). Non-Syndromic Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Mild Mutations in COL1A2. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(6), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060526






