Prediction of Probable Major Depressive Disorder in the Taiwan Biobank: An Integrated Machine Learning and Genome-Wide Analysis Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Genotyping Data and Quality Controls
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Key eQTL SNPs
2.5. An Integrated Machine Learning and Genome-Wide Analysis Approach
2.6. Machine Learning Algorithms for Benchmarking
2.7. Evaluation of the Predictive Performance
3. Results
3.1. The Study Cohort in the Taiwan Biobank
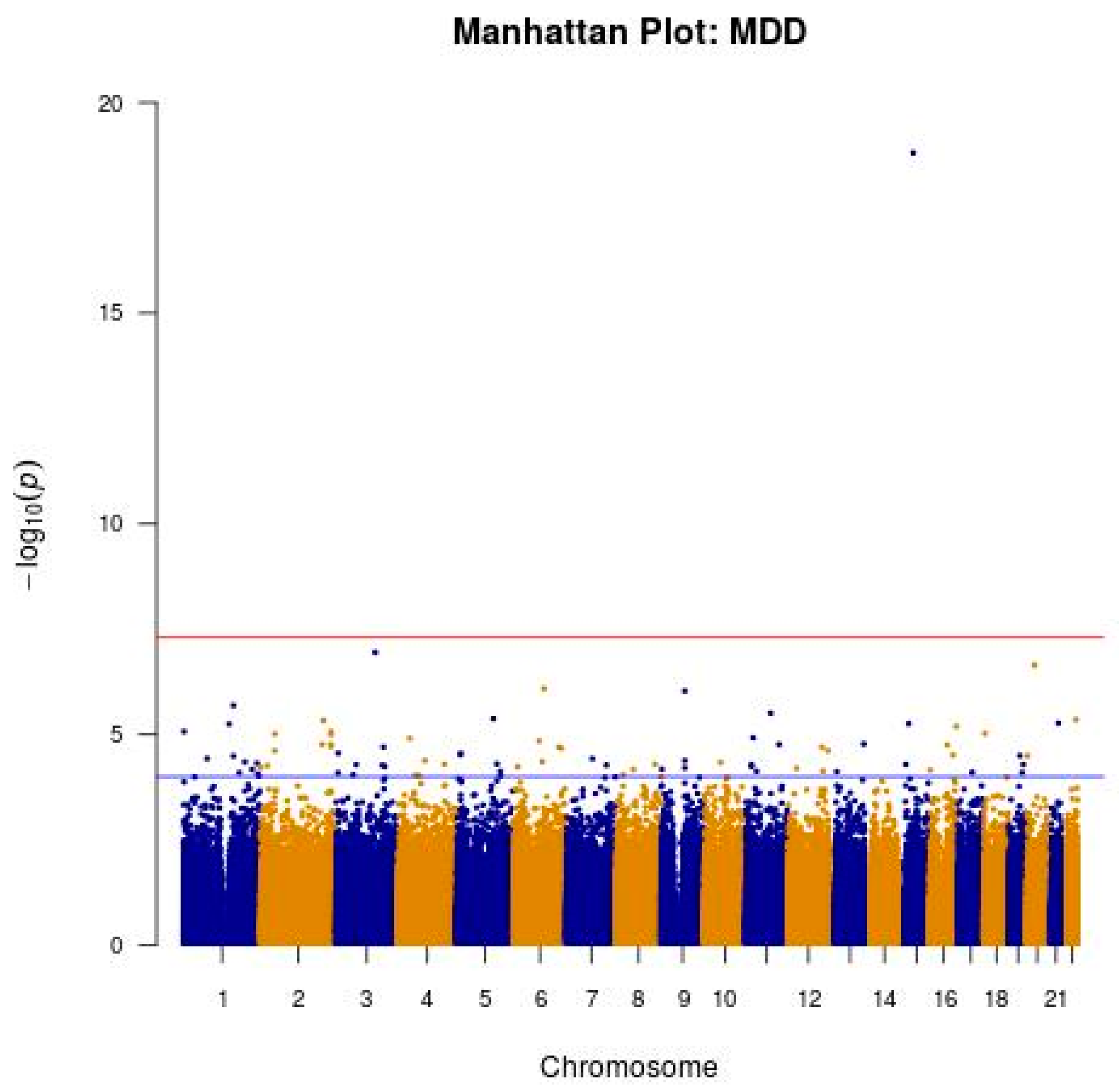
3.2. GWAS of Probable MDD in the Taiwanese Population
3.3. Key eQTL SNPs for Probable MDD Identified in the Taiwanese Population
3.4. Prediction of Probable MDD with a Random Undersampling Technique
3.5. Prediction of Probable MDD with a Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, E.; Lin, C.-H.; Lane, H.-Y. Precision psychiatry applications with pharmacogenomics: Artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bzdok, D.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Machine Learning for Precision Psychiatry: Opportunities and Challenges. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gandal, M.J.; Leppa, V.; Won, H.; Parikshak, N.N.; Geschwind, D.H. The road to precision psychiatry: Translating genetics into disease mechanisms. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, E.; Kuo, P.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yu, Y.W.-Y.; Yang, A.C.; Tsai, S.-J. A deep learning approach for predicting antidepressant response in major depression using clinical and genetic biomarkers. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, E.; Kuo, P.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yu, Y.W.-Y.; Yang, A.C.; Tsai, S.-J. Prediction of antidepressant treatment response and remission using an ensemble machine learning framework. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Lin, C.-H.; Lane, H.-Y. Applying a bagging ensemble machine learning approach to predict functional outcome of schizophrenia with clinical symptoms and cognitive functions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.; Lin, C.-H.; Hung, C.-C.; Lane, H.-Y. An ensemble approach to predict schizophrenia using protein data in the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) and tryptophan catabolic pathways. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Lane, H.-Y. Machine learning and systems genomics approaches for multi-omics data. Biomark. Res. 2017, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iniesta, R.; Stahl, D.; McGuffin, P. Machine learning, statistical learning and the future of biological research in psychiatry. Psychol. Med. 2016, 46, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dwyer, D.B.; Falkai, P.; Koutsouleris, N. Machine Learning Approaches for Clinical Psychology and Psychiatry. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2018, 14, 91–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; van Loo, H.M.; Wardenaar, K.J.; Bossarte, R.M.; Brenner, L.A.; Cai, T.; Ebert, D.D.; Hwang, I.; Li, J.; de Jonge, P. Testing a machine-learning algorithm to predict the persistence and severity of major depressive disorder from baseline self-reports. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemesure, M.D.; Heinz, M.V.; Huang, R.; Jacobson, N.C. Predictive modeling of depression and anxiety using electronic health records and a novel machine learning approach with artificial intelligence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, B.; Fiori, L.M.; Turecki, G.; Trakadis, Y.J. Machine learning analysis of blood microRNA data in major depression: A case-control study for biomarker discovery. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 23, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciobanu, L.G.; Sachdev, P.S.; Trollor, J.N.; Reppermund, S.; Thalamuthu, A.; Mather, K.A.; Cohen-Woods, S.; Stacey, D.; Toben, C.; Schubert, K.O. Downregulated transferrin receptor in the blood predicts recurrent MDD in the elderly cohort: A fuzzy forests approach. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 267, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hankey, J.; Cao, B.; Chokka, P. Screening for major depressive disorder in a tertiary mental health centre using EarlyDetect: A machine learning-based pilot study. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 2021, 3, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arloth, J.; Eraslan, G.; Andlauer, T.F.; Martins, J.; Iurato, S.; Kühnel, B.; Waldenberger, M.; Frank, J.; Gold, R.; Hemmer, B. DeepWAS: Multivariate genotype-phenotype associations by directly integrating regulatory information using deep learning. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ripke, S.; Wray, N.R.; Lewis, C.M.; Hamilton, S.P.; Weissman, M.M.; Breen, G.; Byrne, E.M.; Blackwood, D.H.; Boomsma, D.I.; Cichon, S. A mega-analysis of genome-wide association studies for major depressive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 497. [Google Scholar]
- Wray, N.R.; Ripke, S.; Mattheisen, M.; Trzaskowski, M.; Byrne, E.M.; Abdellaoui, A.; Adams, M.J.; Agerbo, E.; Air, T.M.; Andlauer, T.M. Genome-wide association analyses identify 44 risk variants and refine the genetic architecture of major depression. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Clarke, T.-K.; Hafferty, J.D.; Gibson, J.; Shirali, M.; Coleman, J.R.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Ward, J.; Wigmore, E.M. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Han, G.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y.; Ge, T.; Yang, W.; Cui, R.; Xu, S.; Li, B. Gender differences in depression: Evidence from genetics. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 562316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, A.; Almli, L.; Smith, A.; Lori, A.; Leveille, J.; Ressler, K.J.; Jovanovic, T.; Bradley, B. A genome-wide association study of emotion dysregulation: Evidence for interleukin 2 receptor alpha. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 83, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Shi, C.; Zhang, K.; Xu, Q. The gender-specific association of EHD3 polymorphisms with major depressive disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 567, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galar, M.; Fernandez, A.; Barrenechea, E.; Bustince, H.; Herrera, F. A review on ensembles for the class imbalance problem: Bagging-, boosting-, and hybrid-based approaches. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C 2011, 42, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Kuo, P.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yang, A.; Tsai, S.-J. Association and interaction effects of interleukin-12 related genes and physical activity on cognitive aging in old adults in the Taiwanese population. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B.; Löwe, B. An ultra-brief screening scale for anxiety and depression: The PHQ–4. Psychosomatics 2009, 50, 613–621. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, E.; Kuo, P.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Yang, A.C.; Kao, C.F.; Tsai, S.J. Association and interaction of APOA5, BUD13, CETP, LIPA and health-related behavior with metabolic syndrome in a Taiwanese population. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, E.; Kuo, P.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Yang, A.C.; Tsai, S.J. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway-associated genes SMAD2 and TGFBR2 are implicated in metabolic syndrome in a Taiwanese population. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.H.; Yang, J.H.; Chiang, C.W.K.; Hsiung, C.N.; Wu, P.E.; Chang, L.C.; Chu, H.W.; Chang, J.; Song, I.W.; Yang, S.L.; et al. Population structure of Han Chinese in the modern Taiwanese population based on 10,000 participants in the Taiwan Biobank project. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 5321–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.-J.; Tsai, S.-J.; Kuo, P.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yang, A.C.; Lin, E.; Lan, T.-H. An association study in the Taiwan Biobank reveals RORA as a novel locus for sleep duration in the Taiwanese Population. Sleep Med. 2020, 73, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, L.D.; Kellis, M. HaploReg v4: Systematic mining of putative causal variants, cell types, regulators and target genes for human complex traits and disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D877–D881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers: Francisco, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, E.; Mukherjee, S.; Kannan, S. A deep adversarial variational autoencoder model for dimensionality reduction in single-cell RNA sequencing analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Cessie, S.; Van Houwelingen, J.C. Ridge estimators in logistic regression. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C 1992, 41, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, E.; Hwang, Y. A support vector machine approach to assess drug efficacy of interferon-alpha and ribavirin combination therapy. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2008, 12, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.-C.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Lin, E. A comparison of classification methods for predicting Chronic Fatigue Syndrome based on genetic data. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linden, A. Measuring diagnostic and predictive accuracy in disease management: An introduction to receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2006, 12, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buniello, A.; MacArthur, J.A.L.; Cerezo, M.; Harris, L.W.; Hayhurst, J.; Malangone, C.; McMahon, A.; Morales, J.; Mountjoy, E.; Sollis, E. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog of published genome-wide association studies, targeted arrays and summary statistics 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1005–D1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Consortium, G. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) pilot analysis: Multitissue gene regulation in humans. Science 2015, 348, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, L.S.; Adams, M.J.; Arnau-Soler, A.; Clarke, T.-K.; Howard, D.M.; Zeng, Y.; Davies, G.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Fernandez-Pujals, A.M.; Gibson, J. Genome-wide meta-analyses of stratified depression in Generation Scotland and UK Biobank. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boden, J.M.; Fergusson, D.M. Alcohol and depression. Addiction 2011, 106, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, R.K.; Weiss, R.D. Alcohol use disorder and depressive disorders. Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev. 2019, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, L.Y.; Keene, D.R.; Renard, M.; De Backer, J. FBN1: The disease-causing gene for Marfan syndrome and other genetic disorders. Gene 2016, 591, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurovic, S.; Gustafsson, O.; Mattingsdal, M.; Athanasiu, L.; Bjella, T.; Tesli, M.; Agartz, I.; Lorentzen, S.; Melle, I.; Morken, G. A genome-wide association study of bipolar disorder in Norwegian individuals, followed by replication in Icelandic sample. J. Affect. Disord. 2010, 126, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, G.; Ji, W.; Feng, G.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Zeng, Z. Common variants in the BCL9 gene conferring risk of schizophrenia. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nivard, M.; Mbarek, H.; Hottenga, J.; Smit, J.; Jansen, R.; Penninx, B.; Middeldorp, C.; Boomsma, D. Further confirmation of the association between anxiety and CTNND2: Replication in humans. Genes Brain Behav. 2014, 13, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, E.C.; Wiste, A.; Radmanesh, F.; Almli, L.M.; Gogarten, S.M.; Sofer, T.; Faul, J.D.; Kardia, S.L.; Smith, J.A.; Weir, D.R. Genome-wide association study (GWAS) and genome-wide by environment interaction study (GWEIS) of depressive symptoms in African American and Hispanic/Latina women. Depress. Anxiety 2016, 33, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartova, L.; Dold, M.; Fugger, G.; Kautzky, A.; Mitschek, M.M.M.; Weidenauer, A.; Handschuh, P.A.; Frey, R.; Mandelli, L.; Zohar, J. The Role of Relationship Status in Major Depressive Disorder-Results of the European Group for the Study of Resistant Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 286, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferis, B.J.; Nazareth, I.; Marston, L.; Moreno-Kustner, B.; Bellón, J.Á.; Svab, I.; Rotar, D.; Geerlings, M.I.; Xavier, M.; Goncalves-Pereira, M. Associations between unemployment and major depressive disorder: Evidence from an international, prospective study (the predict cohort). Soc. Sci. Med. 2011, 73, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakulinen, C.; Böckerman, P.; Pulkki-Råback, L.; Virtanen, M.; Elovainio, M. Employment and earnings trajectories before and after sickness absence due to major depressive disorder: A nationwide case–control study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2021, 78, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasco, J.A.; Williams, L.J.; Jacka, F.N.; Ng, F.; Henry, M.J.; Nicholson, G.C.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Berk, M. Tobacco smoking as a risk factor for major depressive disorder: Population-based study. Br. J. Psychiatry 2008, 193, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, A.H.; Pilver, C.E.; Desai, R.A.; Mazure, C.M.; McKee, S.A. The relationship of major depressive disorder and gender to changes in smoking for current and former smokers: Longitudinal evaluation in the US population. Addiction 2012, 107, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murcia, M.; Chastang, J.-F.; Niedhammer, I. Educational inequalities in major depressive and generalized anxiety disorders: Results from the French national SIP study. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2015, 50, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barger, S.D.; Messerli-Bürgy, N.; Barth, J. Social relationship correlates of major depressive disorder and depressive symptoms in Switzerland: Nationally representative cross sectional study. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaakxs, R.; Comijs, H.C.; Lamers, F.; Kok, R.M.; Beekman, A.T.; Penninx, B.W. Associations between age and the course of major depressive disorder: A 2-year longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C. Epidemiology of women and depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2003, 74, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkowska, G.; Stockmeier, C.A. Astrocyte pathology in major depressive disorder: Insights from human postmortem brain tissue. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagy, C.; Suderman, M.; Yang, J.; Szyf, M.; Mechawar, N.; Ernst, C.; Turecki, G. Astrocytic abnormalities and global DNA methylation patterns in depression and suicide. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Verwer, R.W.; Lucassen, P.J.; Huitinga, I.; Swaab, D.F. Prefrontal cortex alterations in glia gene expression in schizophrenia with and without suicide. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 121, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, A.; Saeedi, M.; Maghsoudi, A.; Shalbaf, A. Major depressive disorder diagnosis based on effective connectivity in EEG signals: A convolutional neural network and long short-term memory approach. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2021, 15, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.S.-T.; Lee, C.-S.; Gunnell, D.; Lee, W.-C.; Cheng, A.T.-A. Changing trends in the prevalence of common mental disorders in Taiwan: A 20-year repeated cross-sectional survey. Lancet 2013, 381, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyes, K.M.; Gary, D.; O’Malley, P.M.; Hamilton, A.; Schulenberg, J. Recent increases in depressive symptoms among US adolescents: Trends from 1991 to 2018. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2019, 54, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyes, K.M.; Nicholson, R.; Kinley, J.; Raposo, S.; Stein, M.B.; Goldner, E.M.; Sareen, J. Age, period, and cohort effects in psychological distress in the United States and Canada. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, E.; Lin, C.-H.; Lane, H.-Y. Relevant applications of generative adversarial networks in drug design and discovery: Molecular de novo design, dimensionality reduction, and de novo peptide and protein design. Molecules 2020, 25, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.; Lin, C.-H.; Lane, H.-Y. Machine Learning and Deep Learning for the Pharmacogenomics of Antidepressant Treatments. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]

| Characteristic | Overall | Probable MDD | Control | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of subjects, n | 9828 | 2457 | 7371 | |
| Mean age ± SD, years | 51.2 ± 10.4 | 51.7 ± 10.0 | 51.0 ± 10.5 | 0.009 |
| Male (%) | 25.2% | 19.8% | 26.8% | <0.001 |
| Education 1, n (seven categories) | 12/7/619/835/ 3133/4402/811 | 3/2/149/247/ 857/1022/174 | 9/5/470/588 2276/3380/637 | <0.001 |
| Married, n | 7006 | 1486 | 5520 | <0.001 |
| Lived alone, n | 943 | 348 | 595 | <0.001 |
| Currently employed, n | 4719 | 252 | 4467 | <0.001 |
| Current alcohol drinker, n | 433 | 106 | 327 | 0.798 |
| Ever-smoker, n | 2312 | 701 | 1611 | <0.001 |
| Any physical activity, n | 4413 | 1081 | 3332 | 0.297 |
| CHR | Gene | SNP | A1 | A2 | Region | MAF | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LINC00624-BCL9 | rs11240075 | T | C | intergenic | 0.247 | 1.68 | (1.34–2.10) | 5.60 × 10−6 |
| 1 | TOMM40L, MIR5187 | rs3813628 | A | C | 5′-UTR | 0.465 | 0.77 | (0.69–0.86) | 2.04 × 10−6 |
| 1 | NR1I3 | rs2307424 | G | A | synonymous | 0.476 | 0.80 | (0.72–0.89) | 3.26 × 10−5 |
| 1 | CEP350-QSOX1 | rs12040314 | G | A | intergenic | 0.247 | 0.83 | (0.76–0.91) | 8.03 × 10−5 |
| 3 | LOC105377123 | rs1443524 | G | A | intronic | 0.326 | 1.39 | (1.18–1.63) | 5.18 × 10−5 |
| 5 | CTNND2-RNU6-679P | rs12516830 | T | C | intergenic | 0.250 | 0.82 | (0.75–0.90) | 2.79 × 10−5 |
| 5 | FBN2 | rs11241959 | G | A | intronic | 0.180 | 0.82 | (0.74–0.90) | 4.94 × 10−5 |
| 6 | MCUR1 | rs3734669 | T | G | 3′-UTR | 0.453 | 0.80 | (0.72–0.89) | 5.87 × 10−5 |
| 8 | BIN3 | rs6558174 | A | G | intronic | 0.270 | 1.48 | (1.22–1.81) | 9.11 × 10−5 |
| 12 | RPH3A | rs4767012 | G | A | intronic | 0.275 | 0.72 | (0.61–0.85) | 7.34 × 10−5 |
| 13 | CYCSP33-PARP4 | rs9511242 | A | G | intergenic | 0.349 | 0.83 | (0.75–0.91) | 7.61 × 10−5 |
| 13 | RAB20-NAXD | rs9559849 | A | G | intergenic | 0.470 | 1.29 | (1.15–1.44) | 1.68 × 10−5 |
| 15 | PWRN1 | rs7403037 | G | T | intronic | 0.160 | 0.56 | (0.43–0.74) | 5.13 × 10−5 |
| 16 | METRN | rs66649828 | A | G | intronic | 0.405 | 1.21 | (1.10–1.33) | 6.98 × 10−5 |
| 16 | LOC101928474 | rs7188498 | A | G | intronic | 0.183 | 0.60 | (0.48–0.75) | 6.40 × 10−6 |
| 19 | EEF1A1P7-LINC01531 | rs12978607 | A | C | intergenic | 0.490 | 1.24 | (1.12–1.38) | 3.19 × 10−5 |
| 19 | PTGIR | rs11083840 | G | T | intronic | 0.416 | 0.79 | (0.70–0.88) | 5.12 × 10−5 |
| Algorithm | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic ridge regression | 0.8242 ± 0.0176 | 0.7618 ± 0.0177 | 0.7618 ± 0.0177 |
| SVM | 0.7576 ± 0.0185 | 0.7576 ± 0.0185 | 0.7576 ± 0.0185 |
| C4.5 decision tree | 0.7586 ± 0.0203 | 0.7571 ± 0.0187 | 0.7571 ± 0.0187 |
| LogitBoost | 0.8246 ± 0.0176 | 0.7619 ± 0.0171 | 0.7619 ± 0.0171 |
| Random forests | 0.8179 ± 0.0185 | 0.7588 ± 0.0186 | 0.7588 ± 0.0186 |
| Algorithm | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic ridge regression | 0.8557 ± 0.0100 | 0.7772 ± 0.0126 | 0.7674 ± 0.0146 |
| SVM | 0.7681 ± 0.0061 | 0.7592 ± 0.0082 | 0.7771 ± 0.0060 |
| C4.5 decision tree | 0.8370 ± 0.0110 | 0.7845 ± 0.0104 | 0.7636 ± 0.0124 |
| LogitBoost | 0.8559 ± 0.0100 | 0.7778 ± 0.0127 | 0.7688 ± 0.0145 |
| Random forests | 0.8905 ± 0.0088 | 0.8072 ± 0.0102 | 0.7860 ± 0.0124 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, E.; Kuo, P.-H.; Lin, W.-Y.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yang, A.C.; Tsai, S.-J. Prediction of Probable Major Depressive Disorder in the Taiwan Biobank: An Integrated Machine Learning and Genome-Wide Analysis Approach. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070597
Lin E, Kuo P-H, Lin W-Y, Liu Y-L, Yang AC, Tsai S-J. Prediction of Probable Major Depressive Disorder in the Taiwan Biobank: An Integrated Machine Learning and Genome-Wide Analysis Approach. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(7):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070597
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Eugene, Po-Hsiu Kuo, Wan-Yu Lin, Yu-Li Liu, Albert C. Yang, and Shih-Jen Tsai. 2021. "Prediction of Probable Major Depressive Disorder in the Taiwan Biobank: An Integrated Machine Learning and Genome-Wide Analysis Approach" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 7: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070597
APA StyleLin, E., Kuo, P.-H., Lin, W.-Y., Liu, Y.-L., Yang, A. C., & Tsai, S.-J. (2021). Prediction of Probable Major Depressive Disorder in the Taiwan Biobank: An Integrated Machine Learning and Genome-Wide Analysis Approach. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(7), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070597







